Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1327results about "Water acting propulsive elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
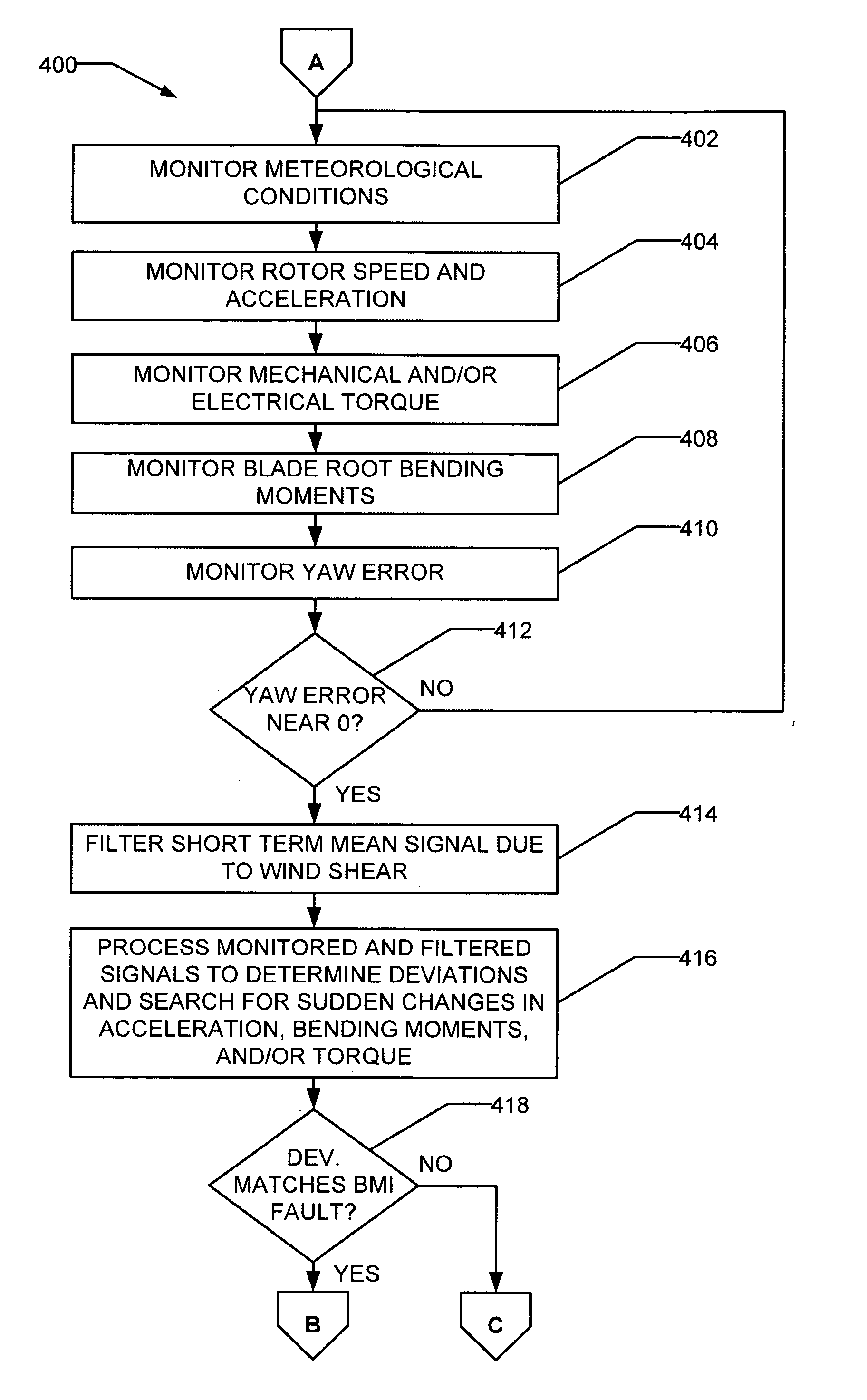
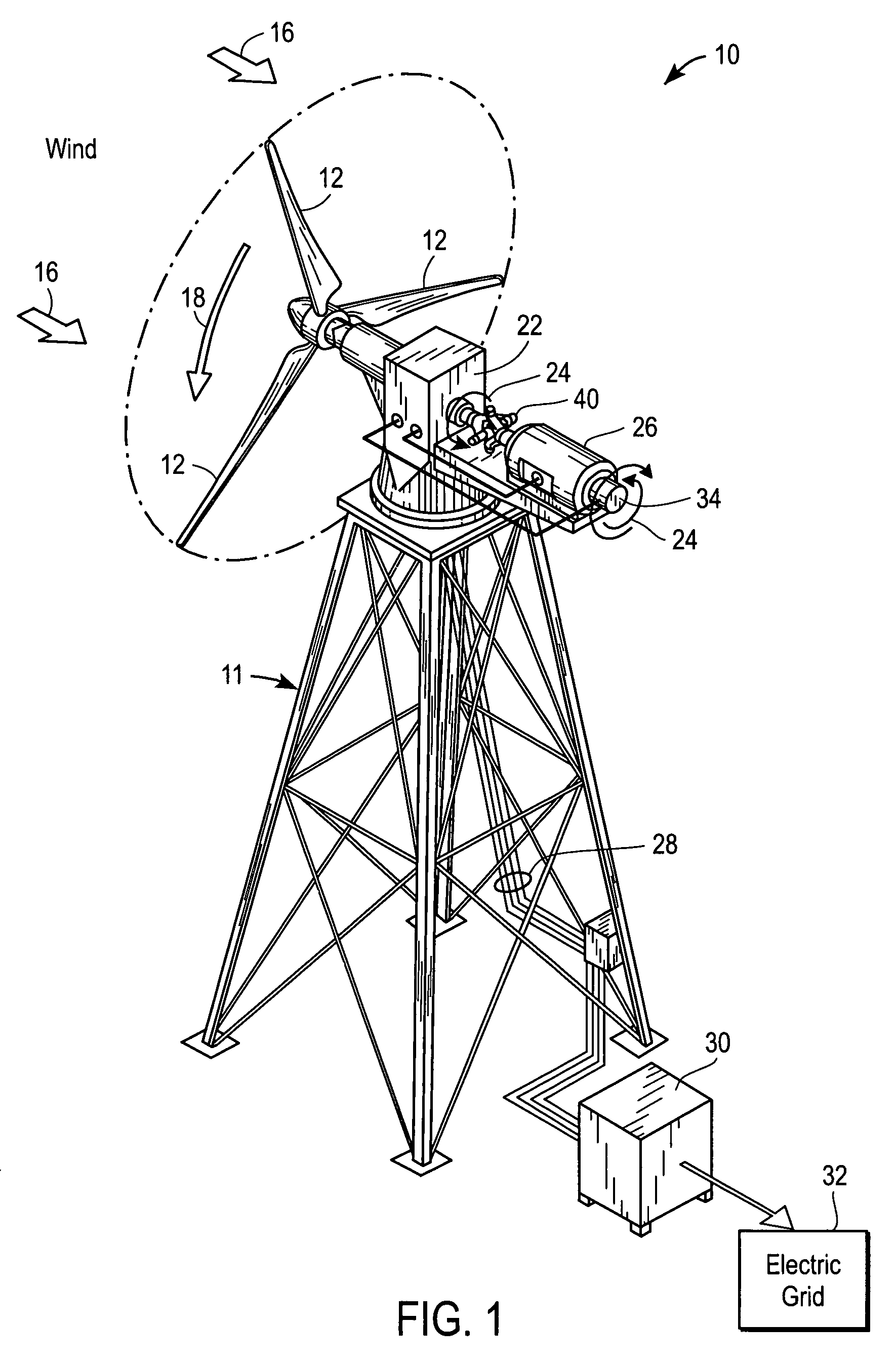
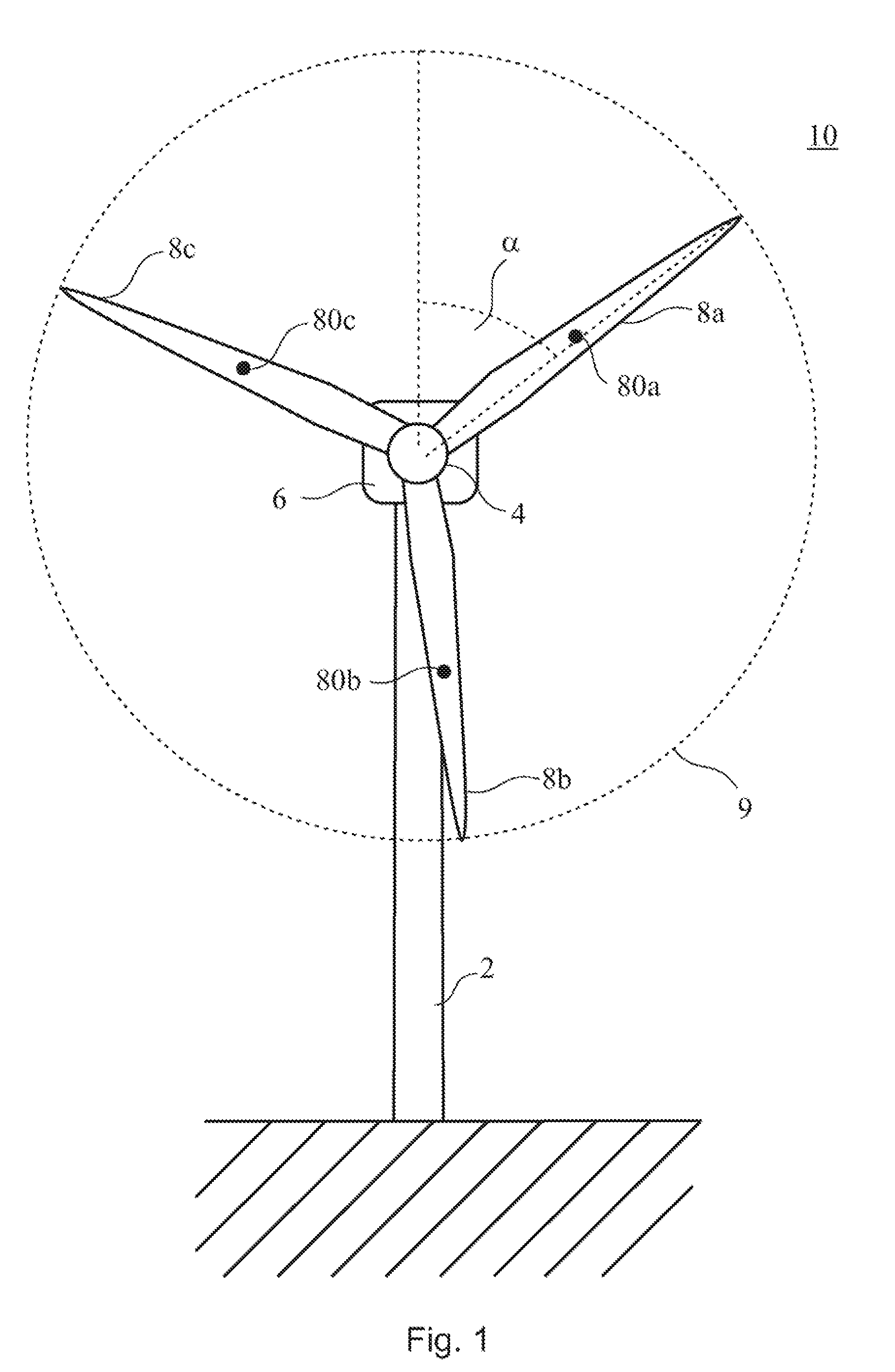
Methods and apparatus for rotor blade ice detection
ActiveUS20050276696A1Reduced lifting capabilityDiminished aerodynamic rotor blade performancePropellersWind motor controlIcing conditionsEngineering
A method for detecting ice on a wind turbine having a rotor and one or more rotor blades each having blade roots includes monitoring meteorological conditions relating to icing conditions and monitoring one or more physical characteristics of the wind turbine in operation that vary in accordance with at least one of the mass of the one or more rotor blades or a mass imbalance between the rotor blades. The method also includes using the one or more monitored physical characteristics to determine whether a blade mass anomaly exists, determining whether the monitored meteorological conditions are consistent with blade icing; and signaling an icing-related blade mass anomaly when a blade mass anomaly is determined to exist and the monitored meteorological conditions are determined to be consistent with icing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
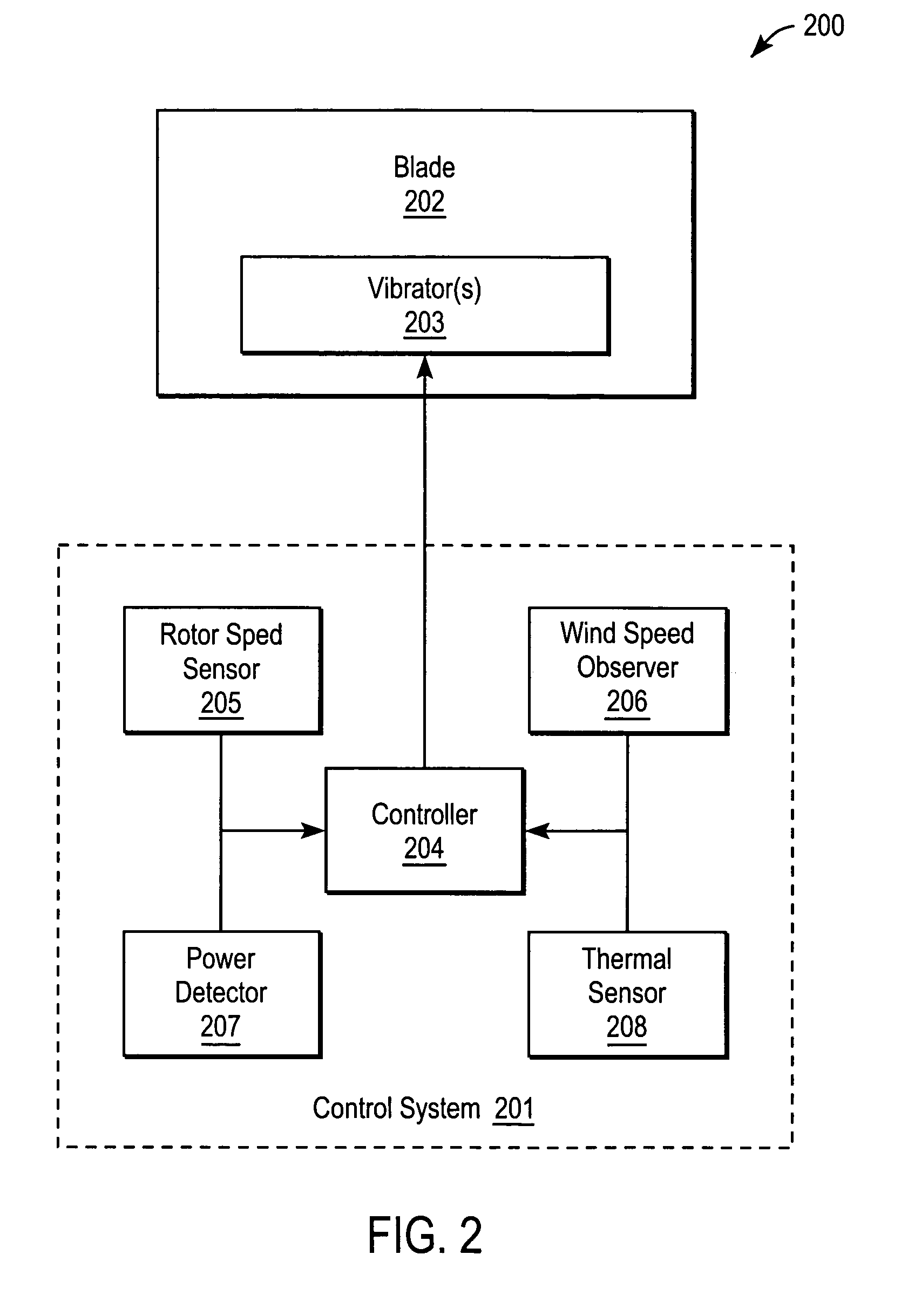
Deicing device for wind turbine blades
Methods and Apparatuses for deicing a wind turbine blade are described herein. In one embodiment, an exemplary process includes detecting an icy condition on a wind turbine blade and causing at least a portion of the wind turbine blade to vibrate, causing the ice built up on the wind turbine blade to break off.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
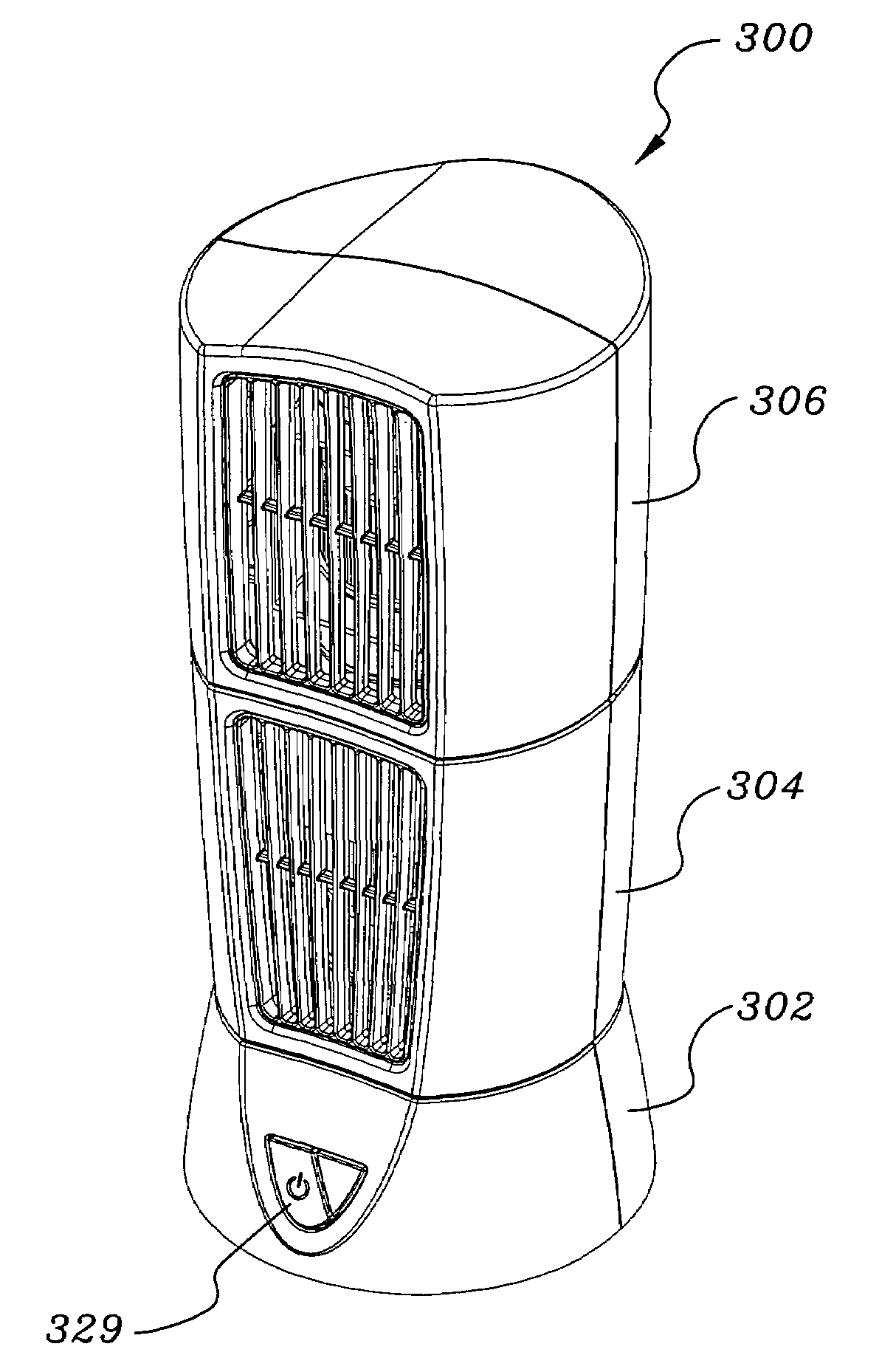
Multi-directional air circulating fan
Owner:LASKO OPERATION HLDG LLC
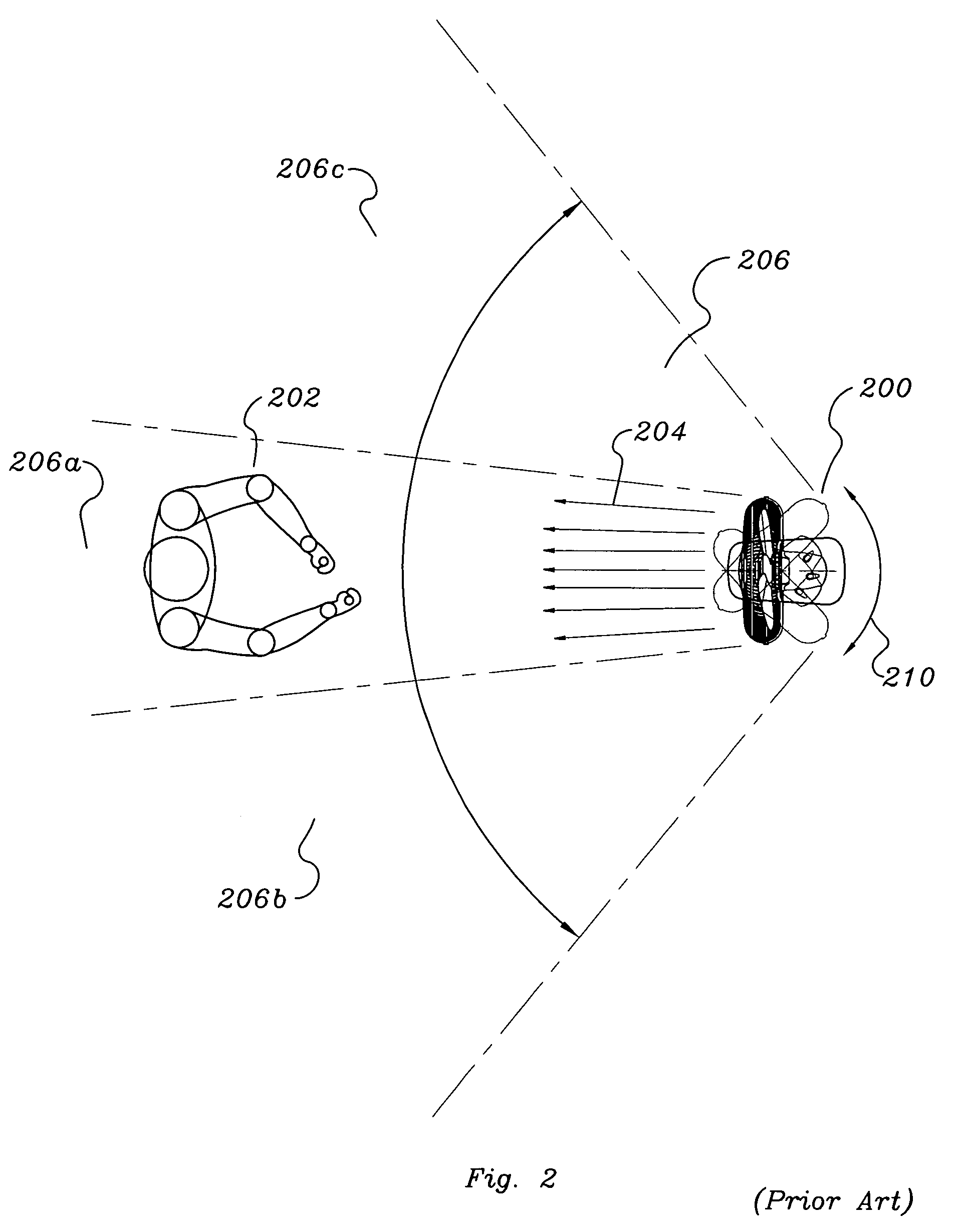
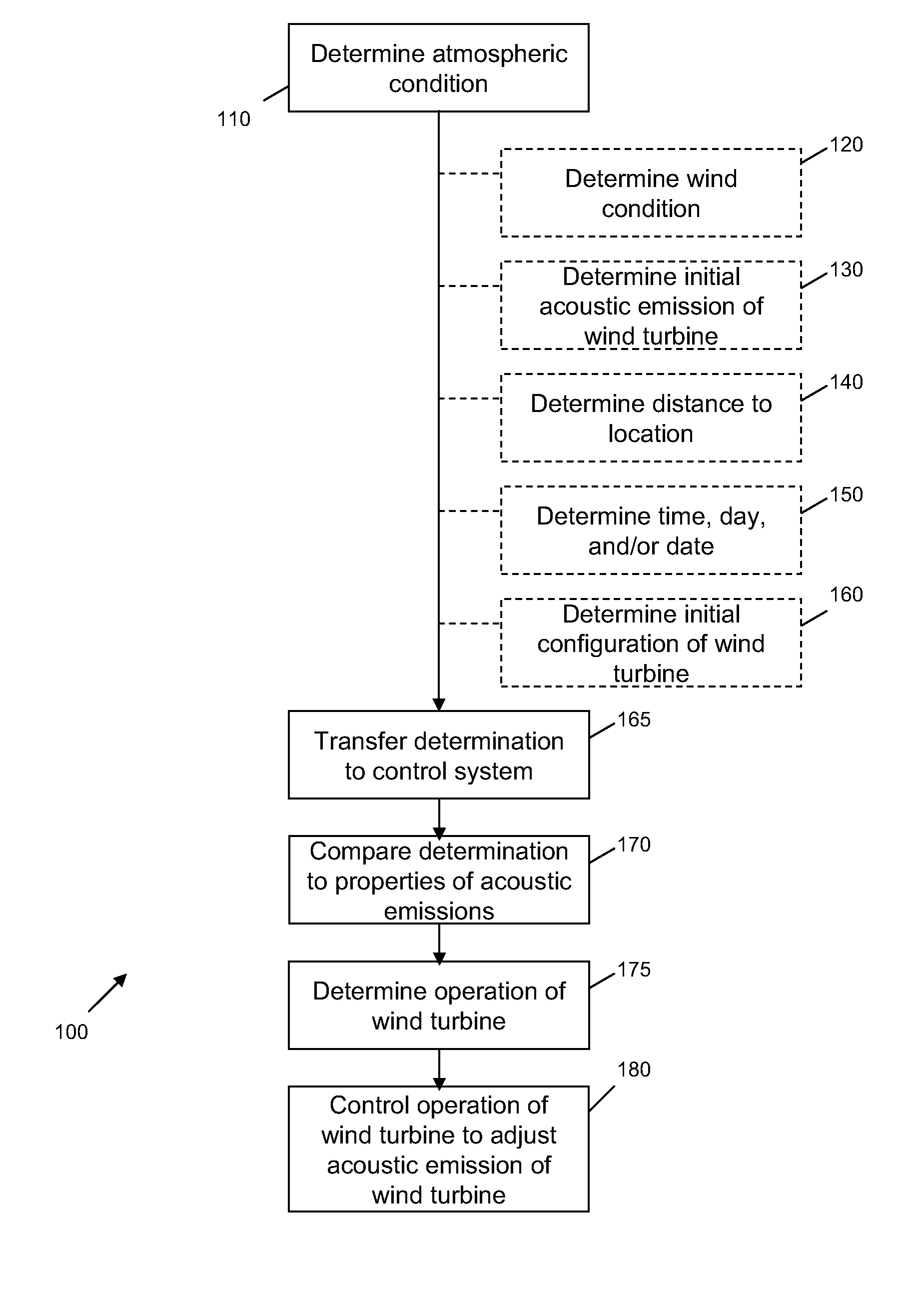
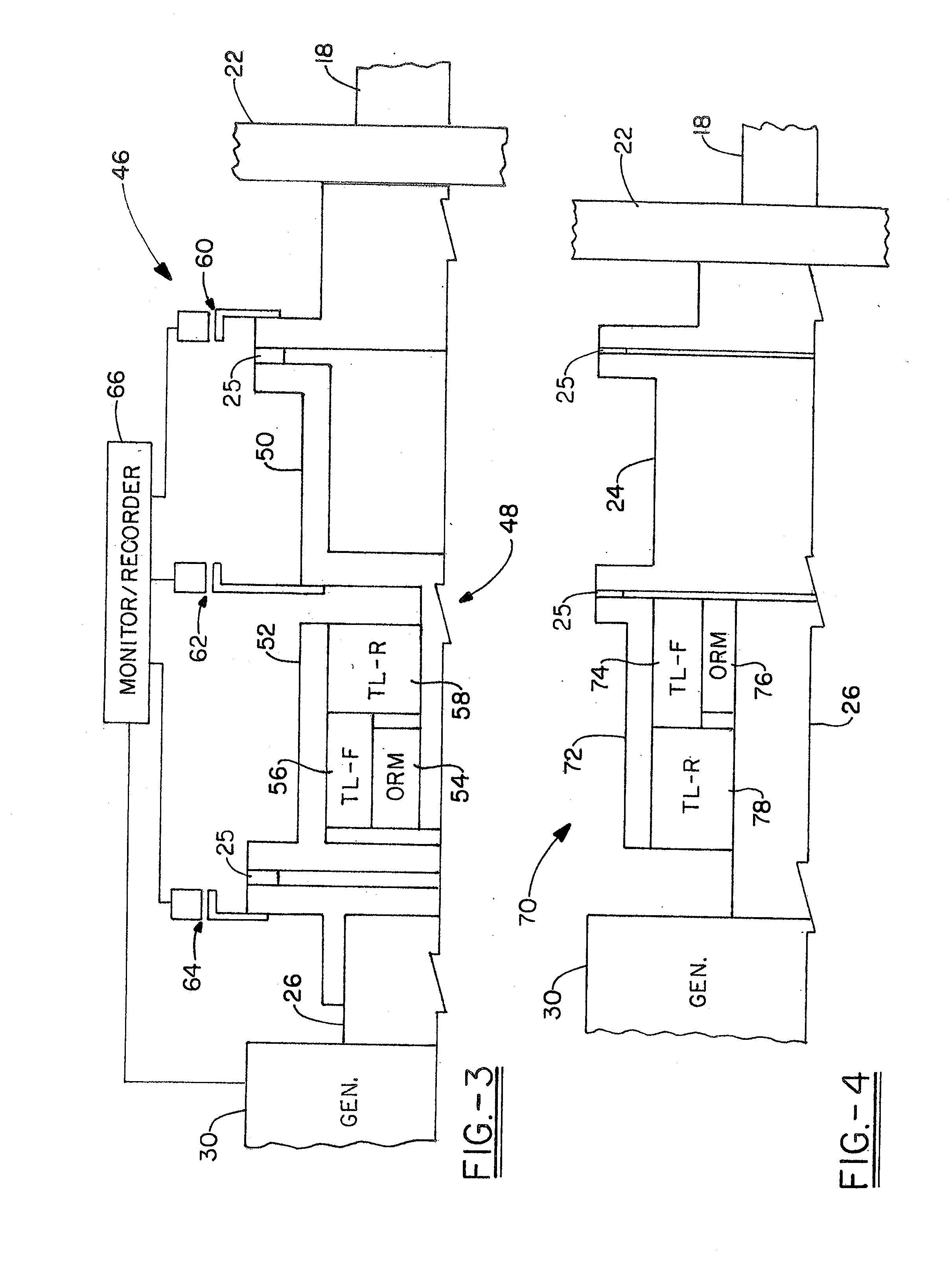
Method and apparatus for controlling acoustic emissions of a wind turbine
A method and an apparatus for monitoring an acoustic emission of a wind turbine that includes a rotor blade. The apparatus includes at least one sensor operatively coupled to the wind turbine. The sensor is configured to detect an atmospheric condition. A control system is communicatively coupled to the sensor, and configured to control operation of the wind turbine to adjust the acoustic emission of the wind turbine based on the atmospheric condition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
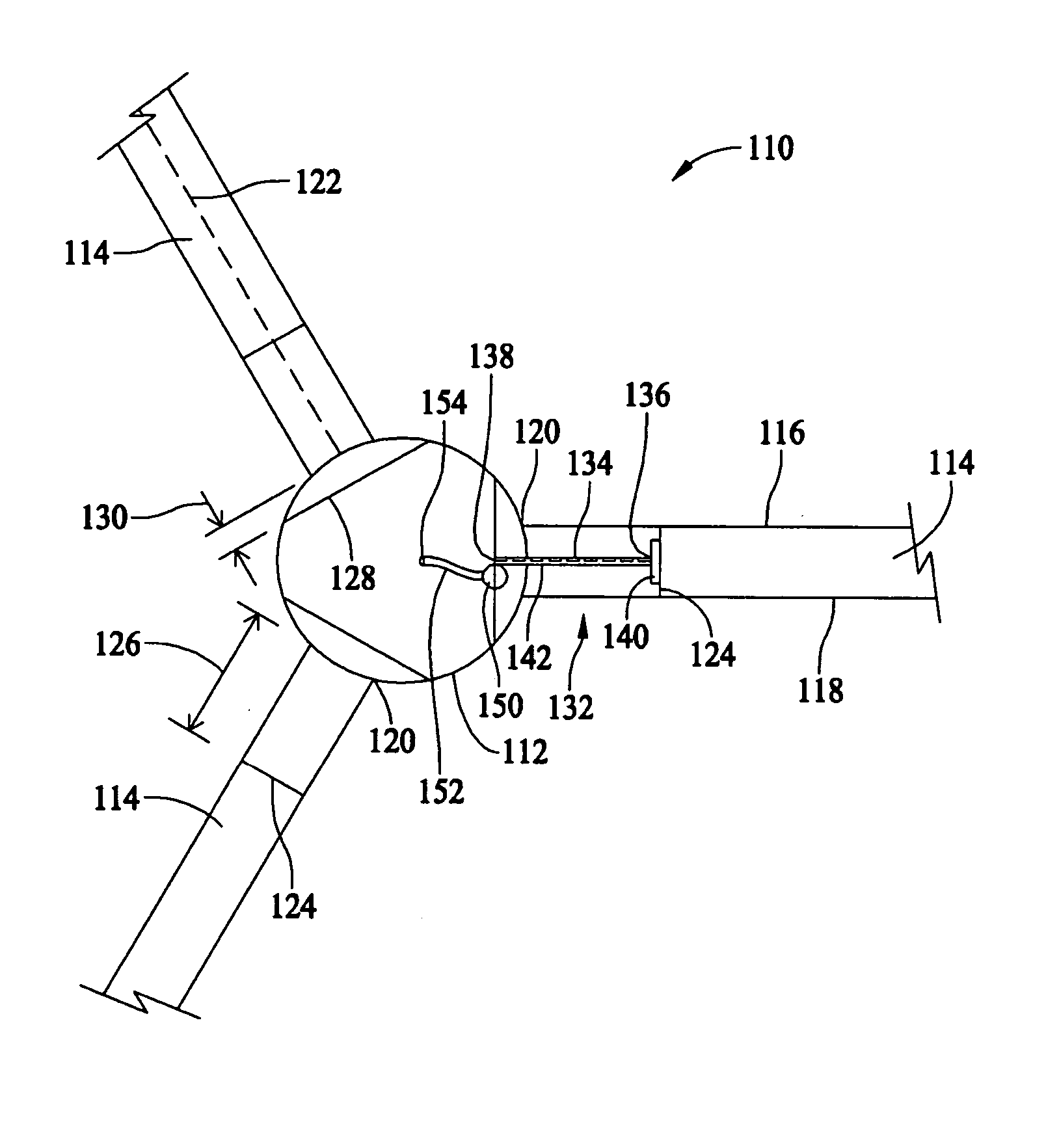
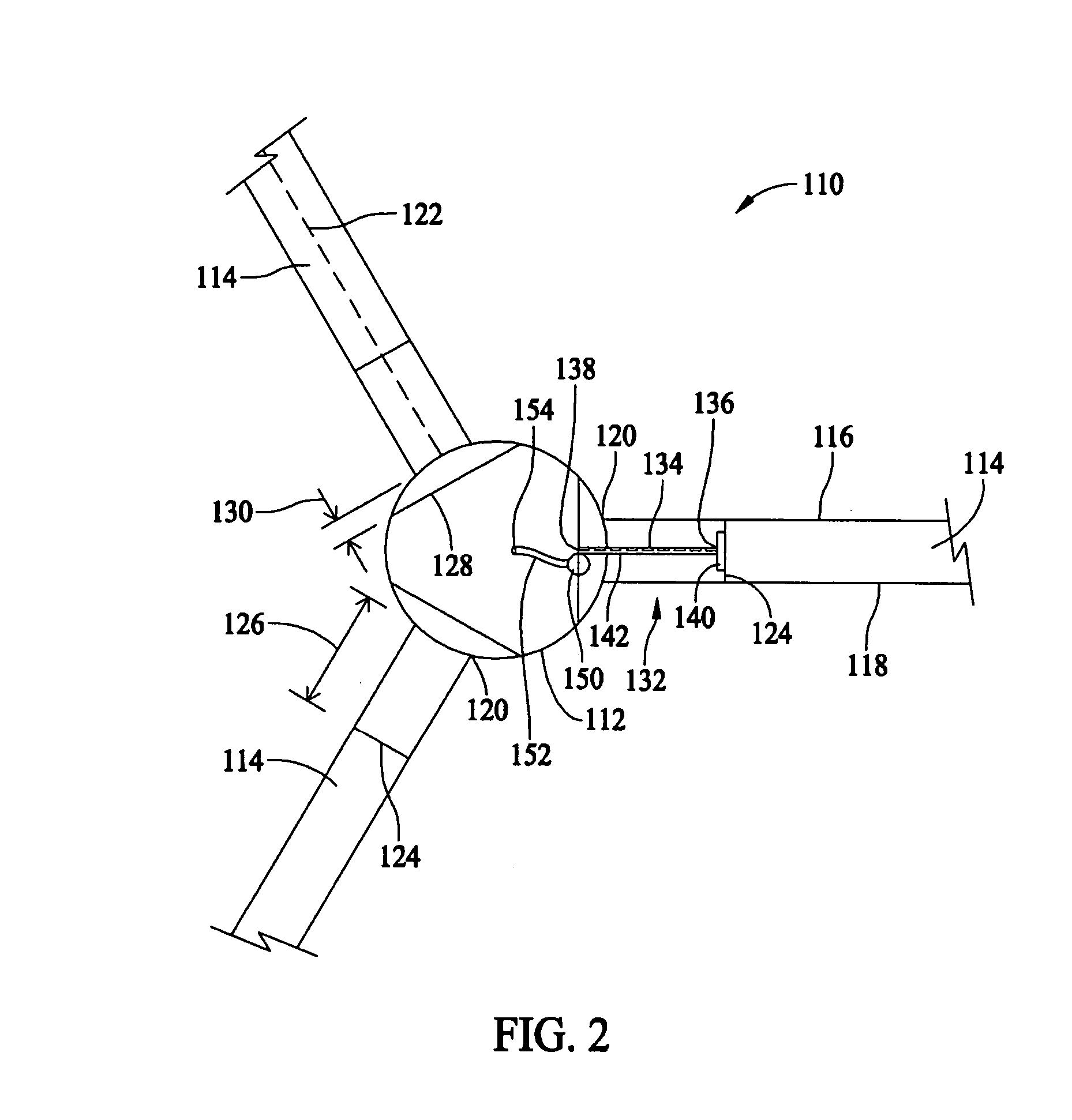
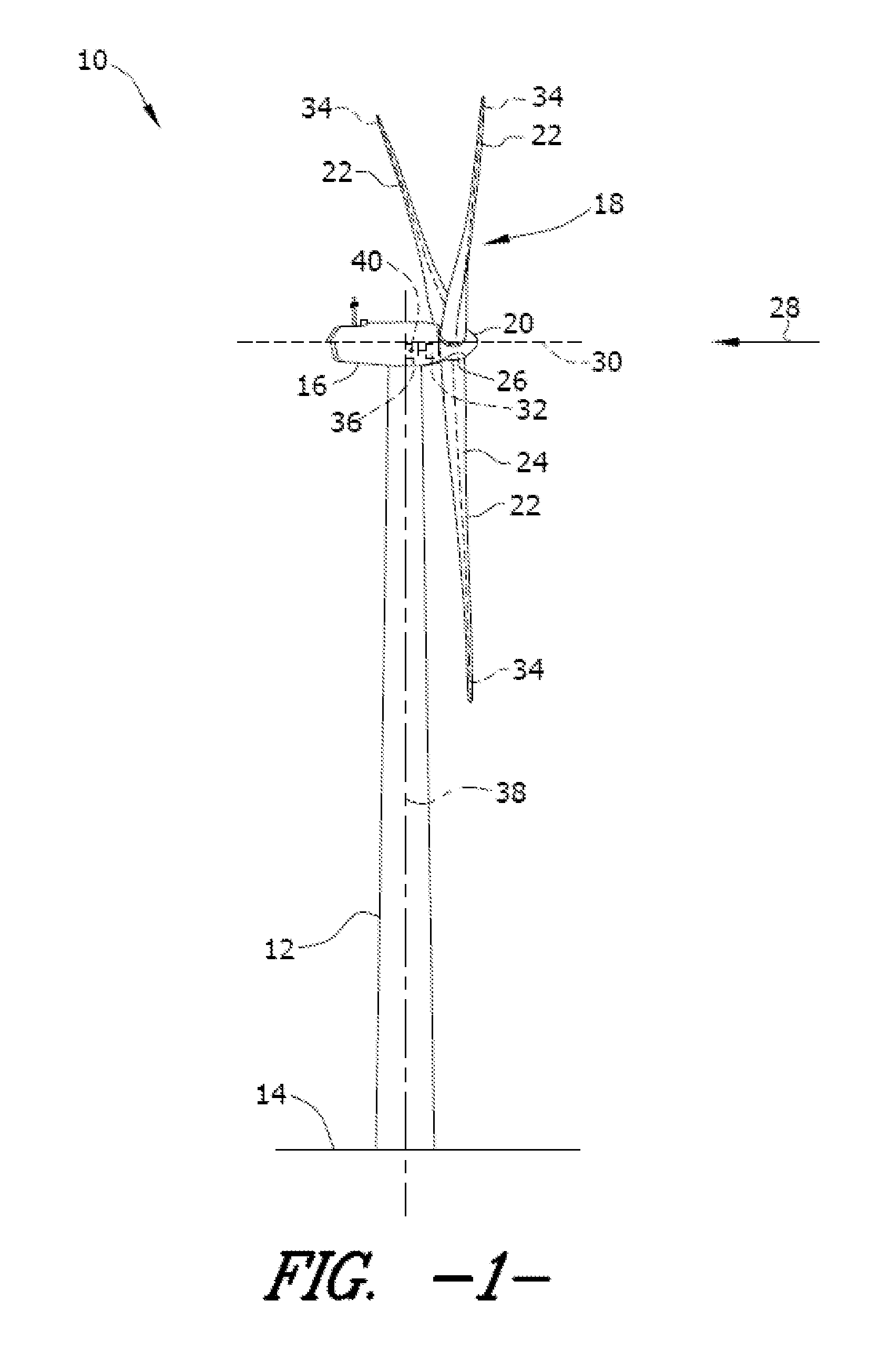
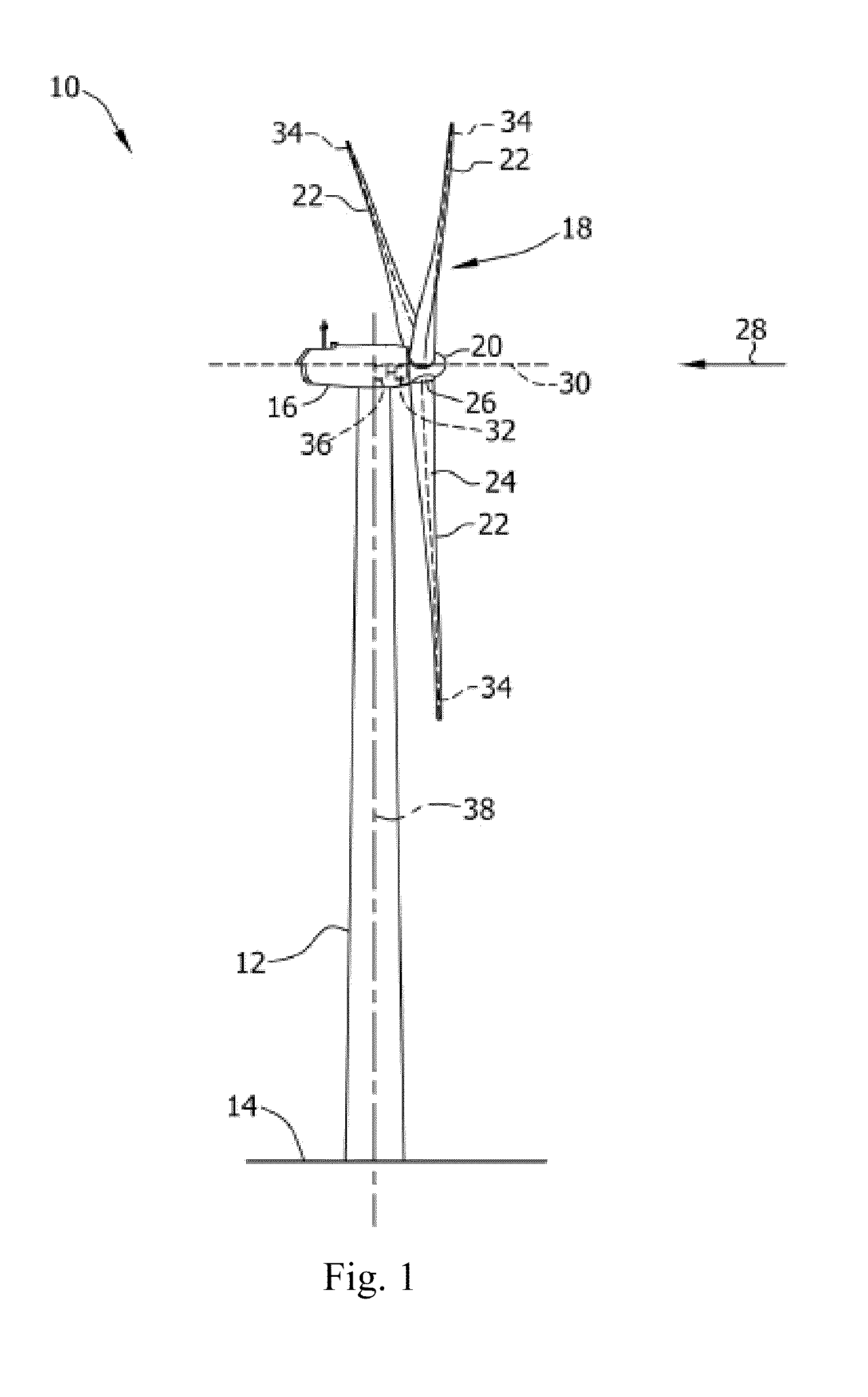
Methods and apparatus for measuring wind turbine blade deflection
A method for determining rotor blade deflection, wherein a rotor blade is coupled to a hub, includes coupling a first end of a beam to the rotor blade, positioning a second end of the beam adjacent the hub, measuring the deflection of the beam using at least one sensor, and determining the deflection of the blade based on the deflection of the beam.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Blade extension for rotor blade in wind turbine
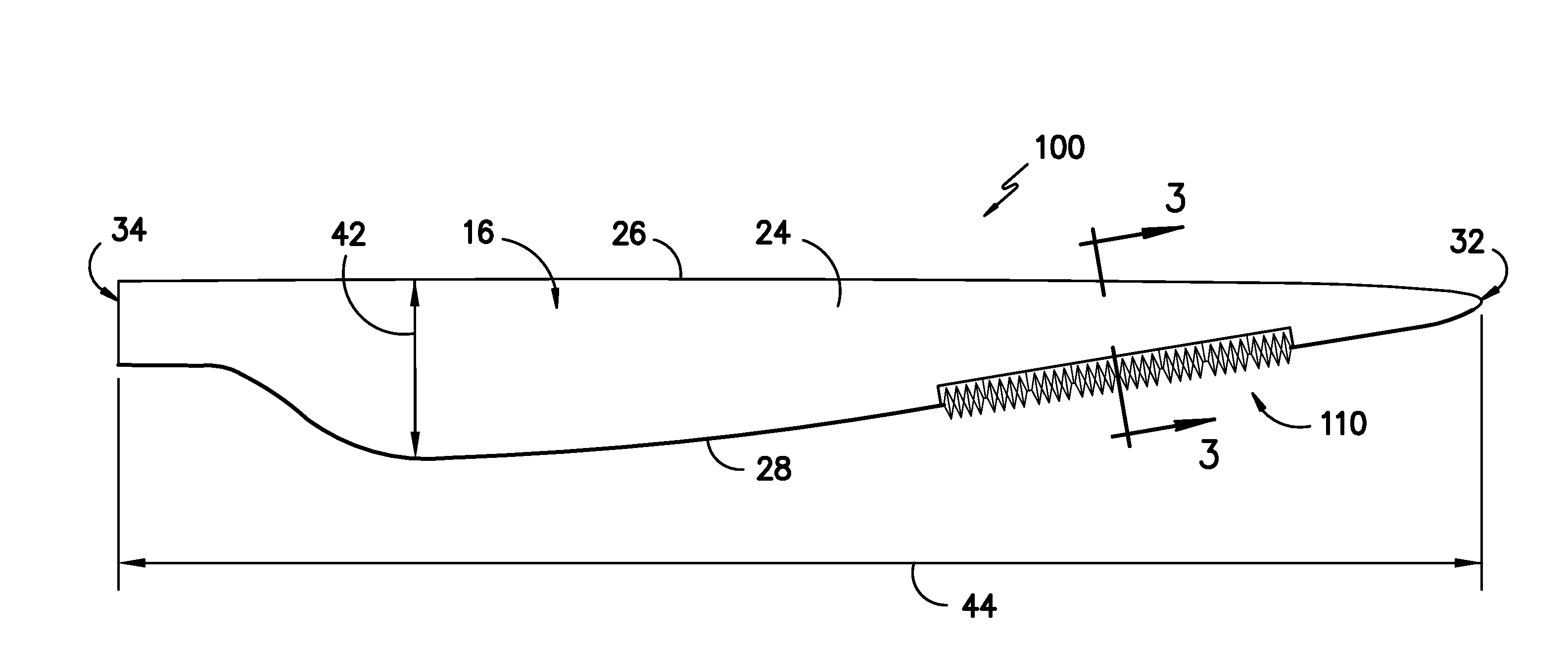
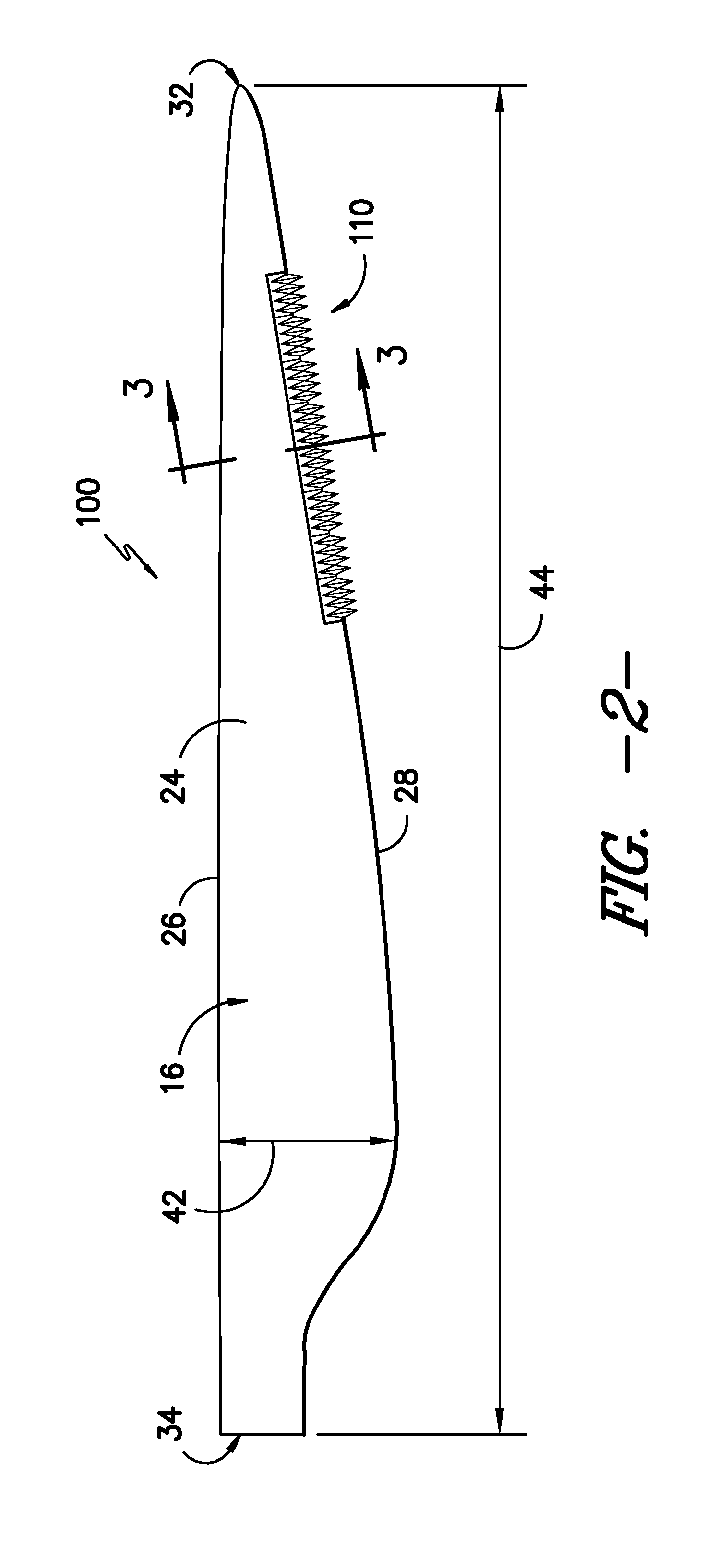
A rotor blade assembly is disclosed. The rotor blade assembly includes a rotor blade and a blade extension. The rotor blade has a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root. The rotor blade further has an aerodynamic profile. The blade extension is mounted to the rotor blade. The blade extension includes a cutaway mounting portion for mounting the blade extension to the rotor blade such that the blade extension is generally flush with at least one of the pressure side or the suction side of the rotor blade. The cutaway mounting portion defines a notch configured to locate the blade extension relative to the rotor blade.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
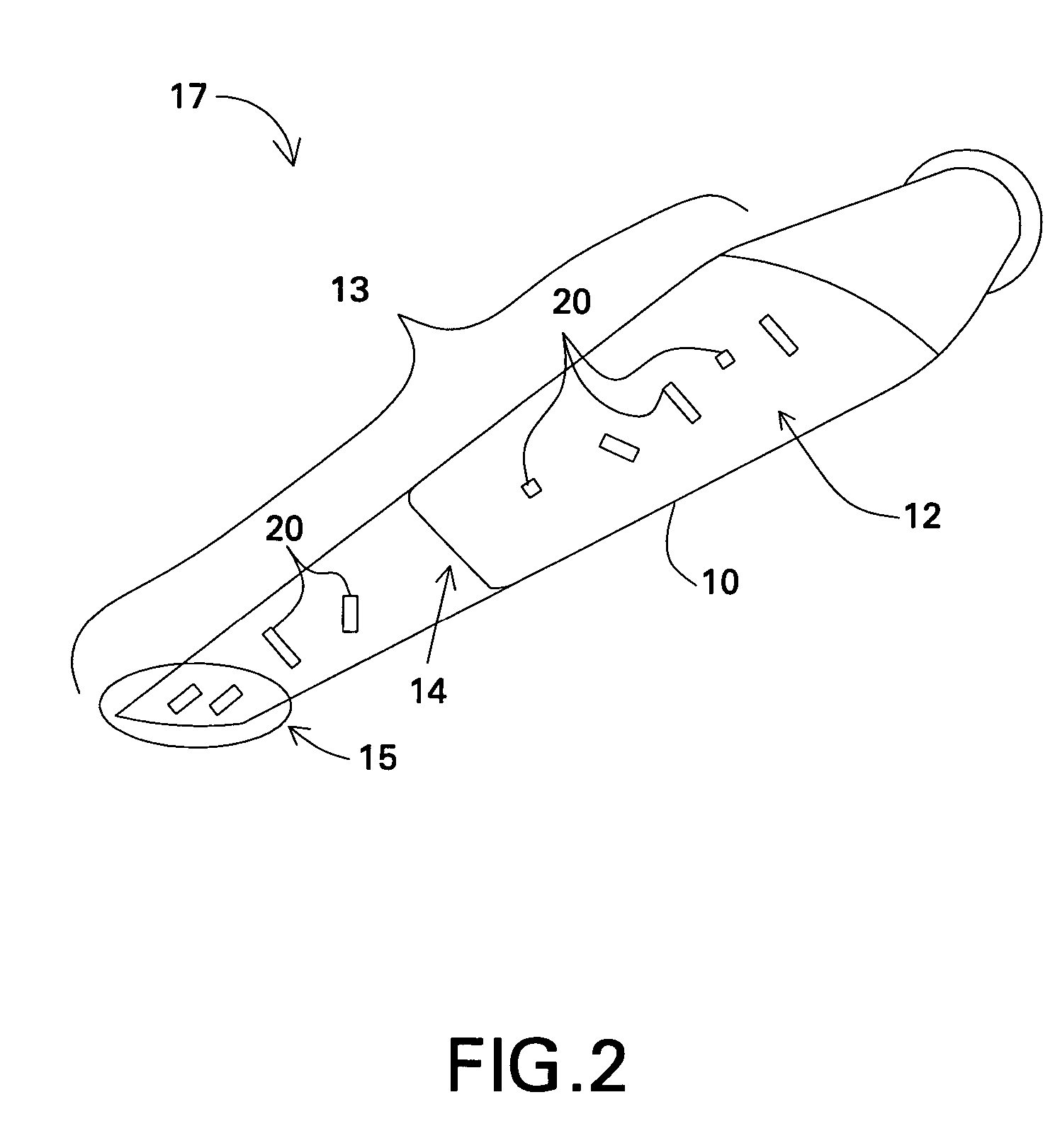
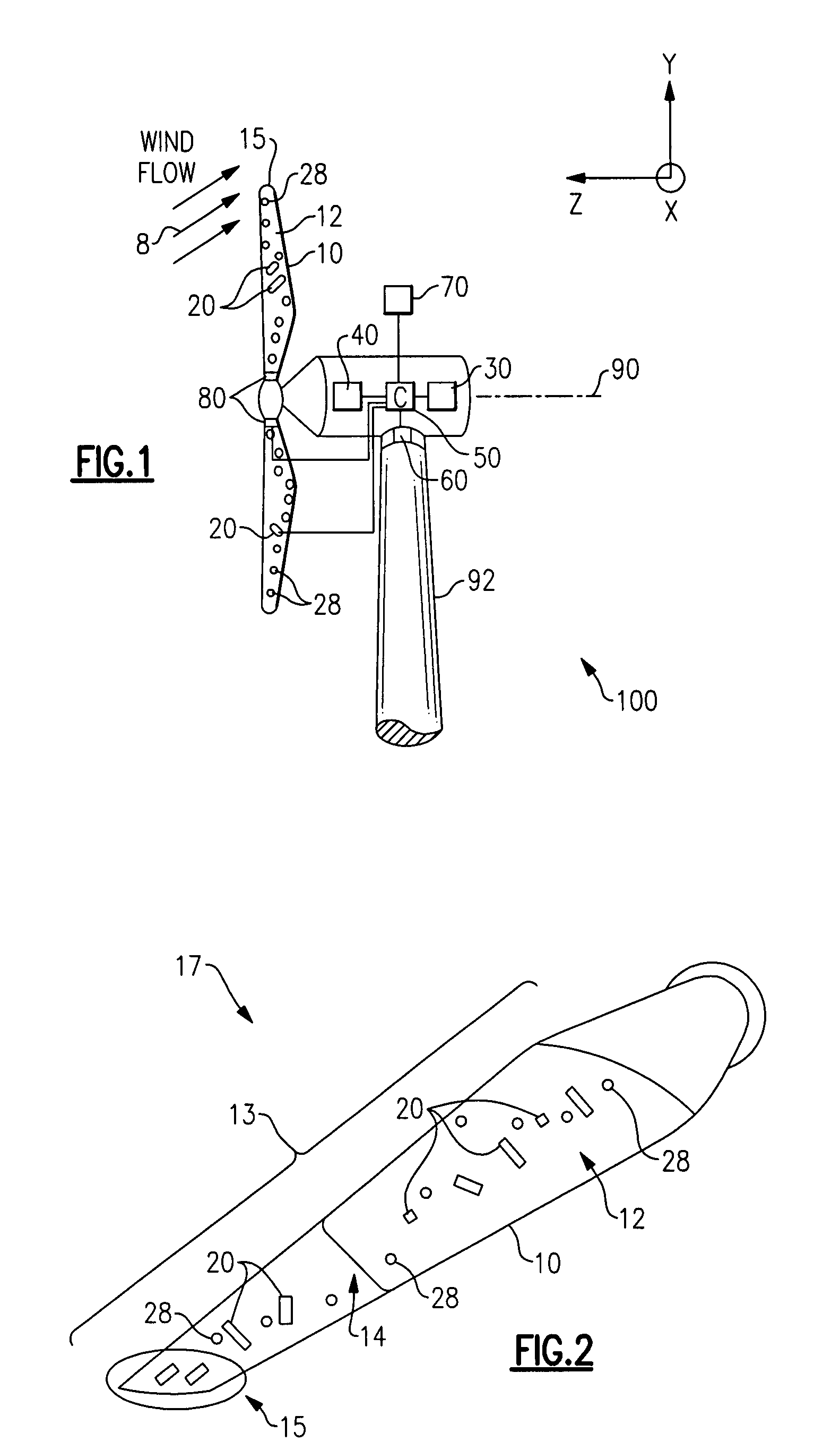
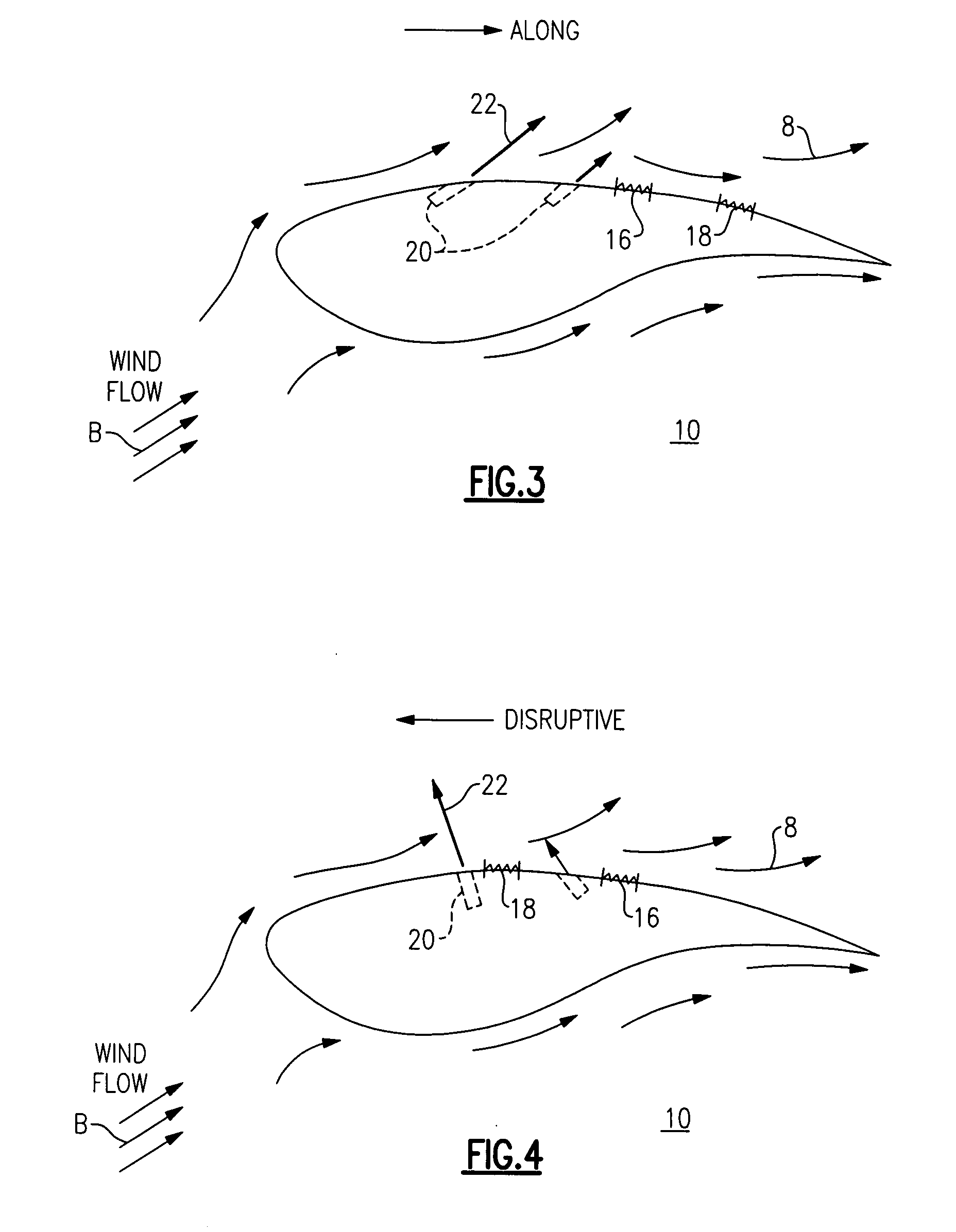
Active flow modifications on wind turbine blades
ActiveUS7387491B2Reduce system loadImprove performancePropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeEngineering
A wind turbine blade is situated on a wind turbine and includes a side and a tip. The blade is configured to rotate about an axis upon an impact of a wind flow on the blade. An active flow modification device is disposed on the blade. The active flow modification device is configured to receive active flow instructions and to modify the wind flow proximate to the blade. The resulting wind turbine blade uses these active flow modifications to achieve reduced loads, reduced aerodynamic losses, reduced noise, enhanced energy capture, or combinations thereof.
Owner:LM WIND POWER US TECH APS
Power loss reduction in turbulent wind for a wind turbine using localized sensing and control
InactiveUS20080317598A1Reduce impactMinimize the differencePropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeAngle of attack
A wind turbine blade assembly includes at least one local load sensor disposed on and / or within a surface of the wind turbine blade and at least one active flow modification device disposed on and / or within a surface of the wind turbine blade and configured to alter the aerodynamics of the wind turbine blade in response to real time local load sensor measurements such that a difference between a current angle of attack and an optimum angle of attack on the wind turbine blade is substantially minimized.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
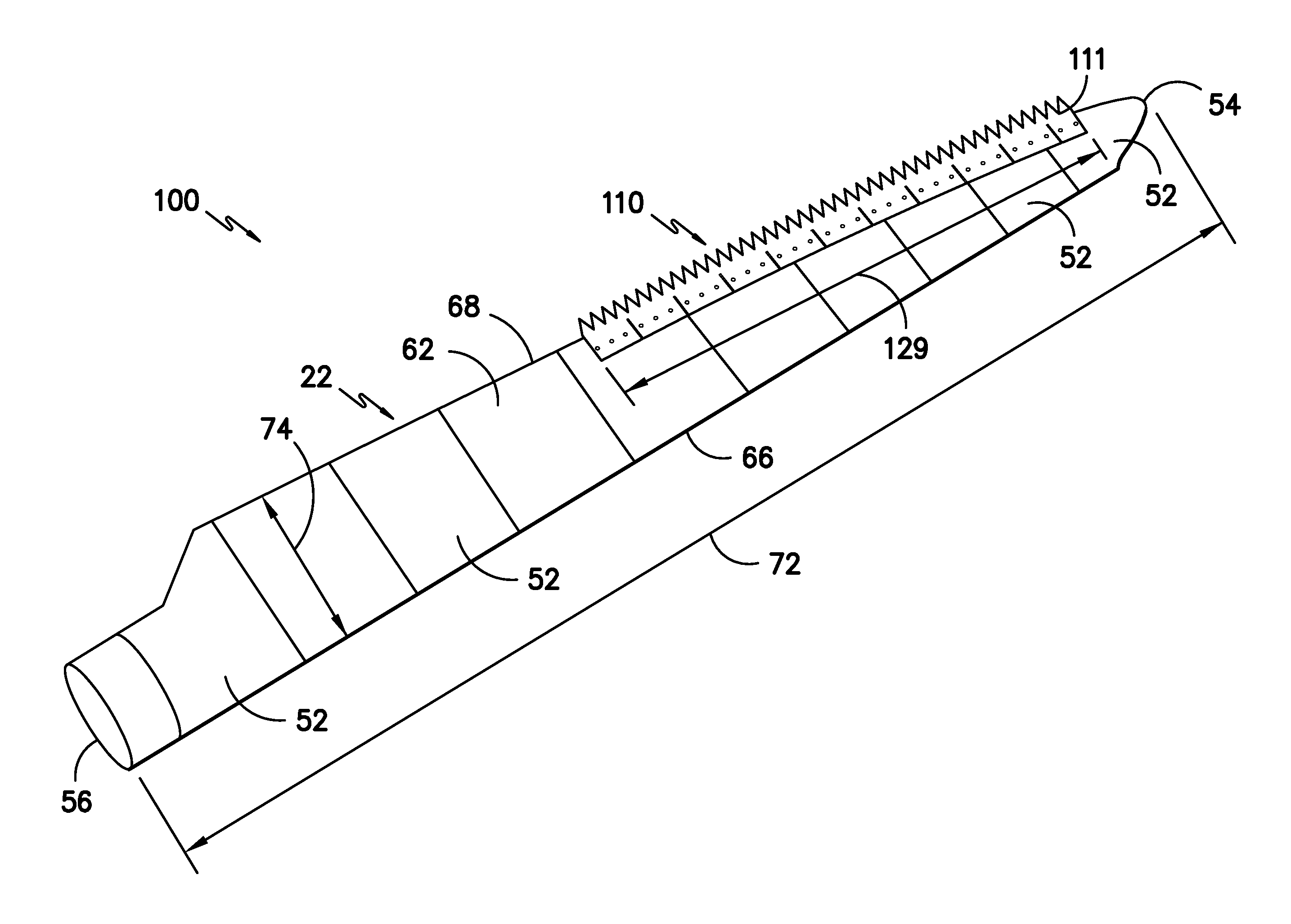
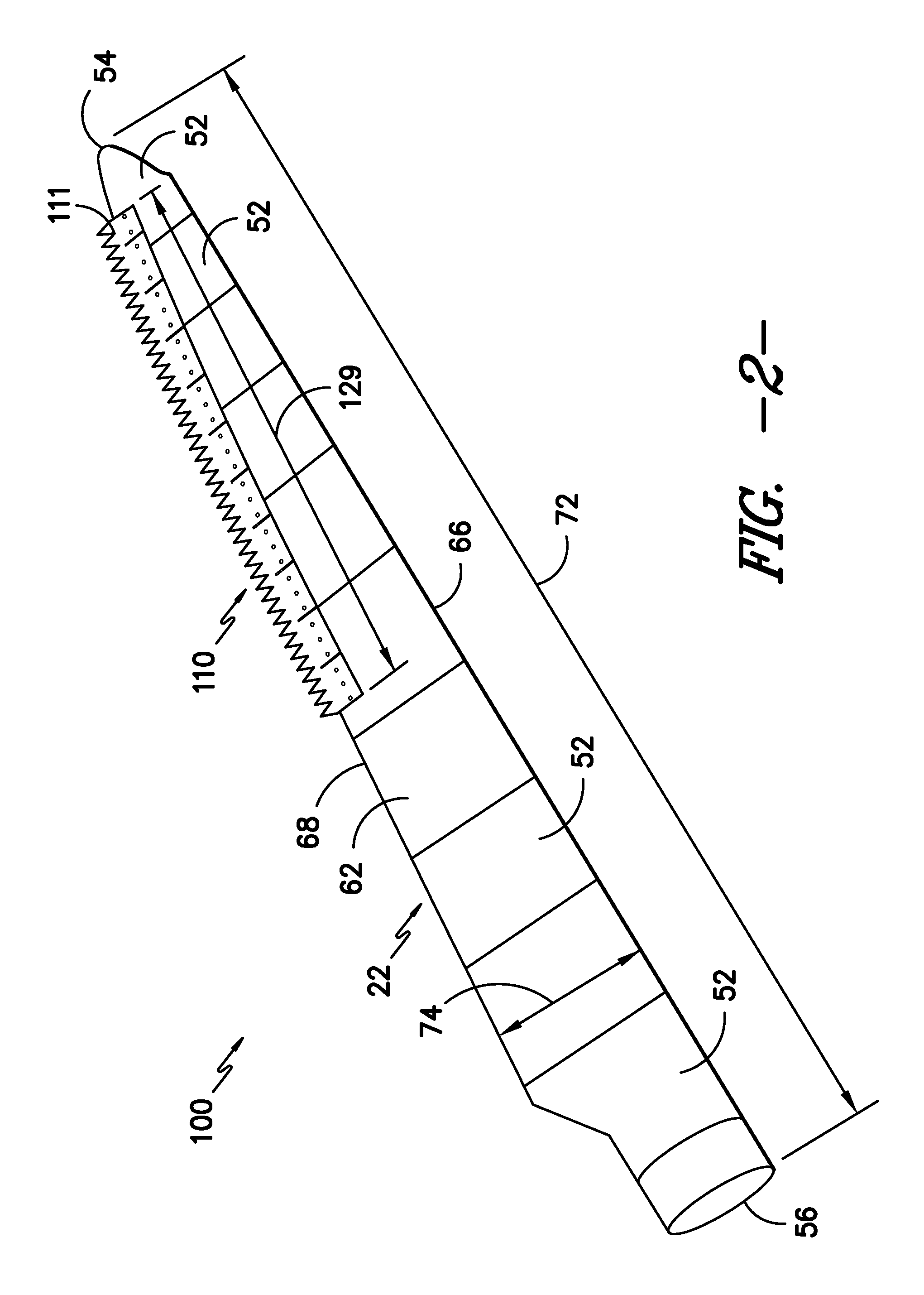
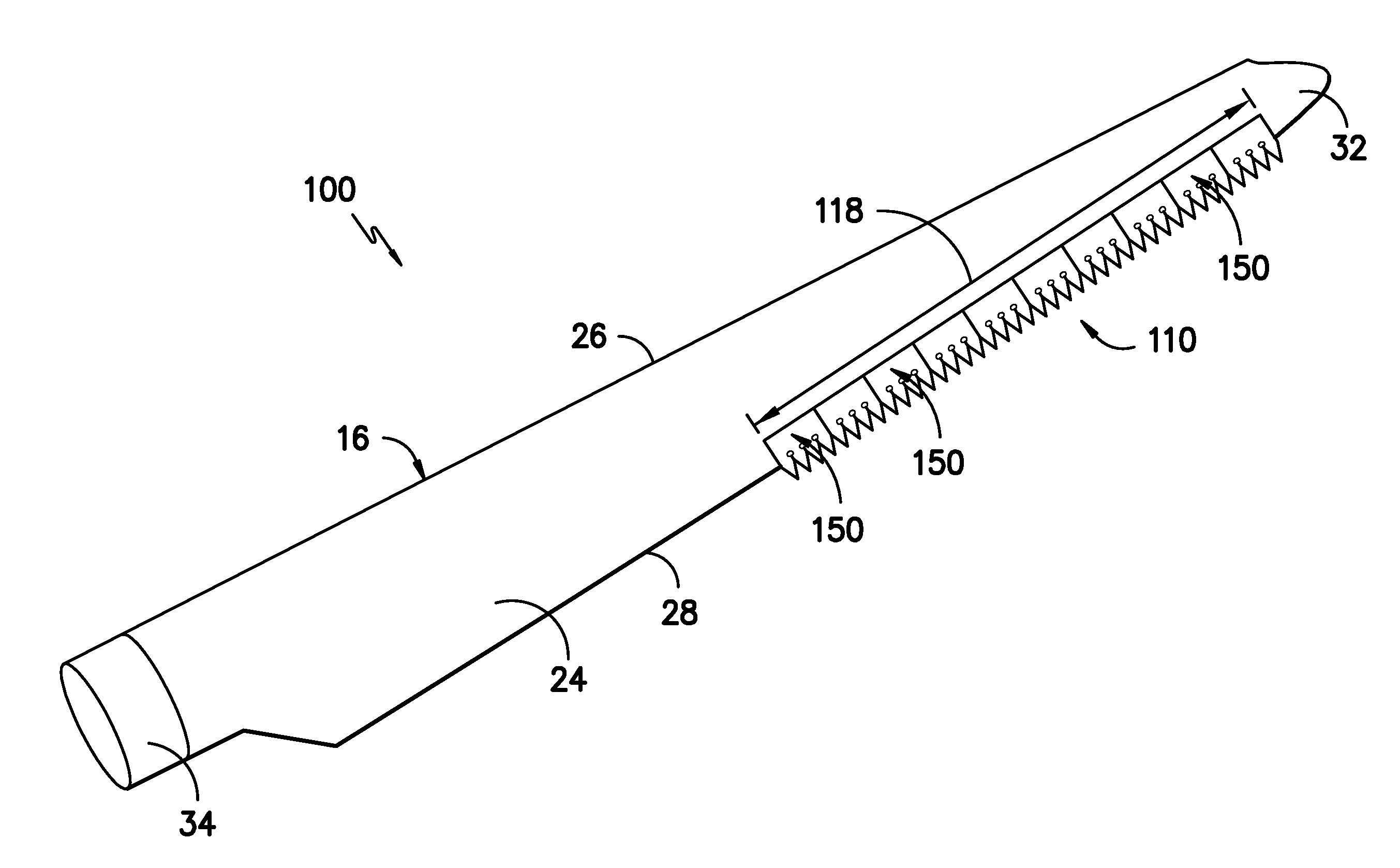
Noise reducer for rotor blade in wind turbine
A rotor blade assembly and a method for reducing the noise of a rotor blade for a wind turbine are disclosed. The rotor blade has surfaces defining a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root. The rotor blade assembly further includes a noise reducer configured on a surface of the rotor blade, the noise reducer including a plurality of noise reduction features. Each of the plurality of noise reduction features includes a first surface and a second surface. The first surface includes a first portion mounted to one of the pressure side or the suction side and a second portion configured to interact with wind flowing past the other of the pressure side or the suction side. The second surface interrupts an aerodynamic contour of the one of the pressure side or the suction side.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
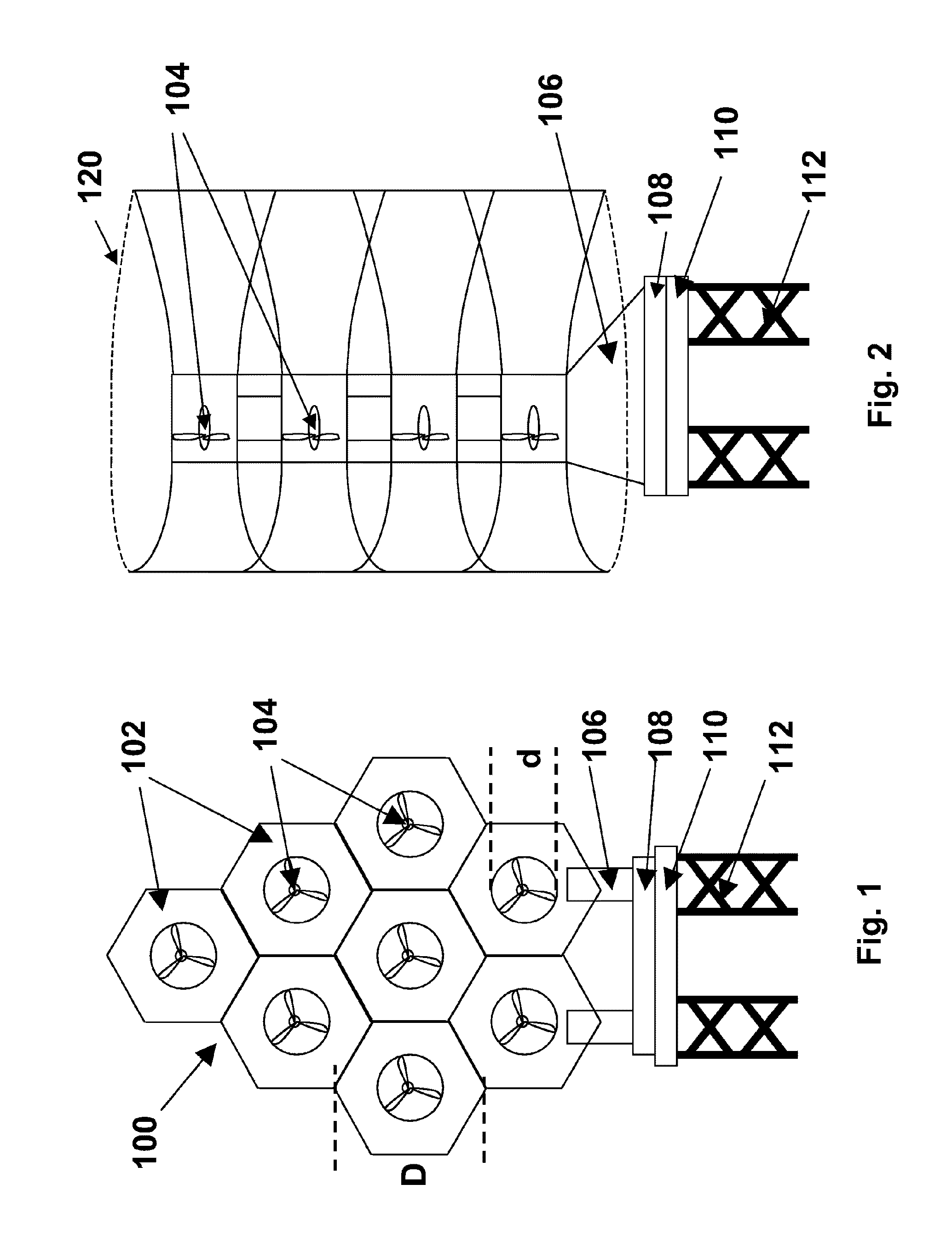
Power generation assemblies and apparatus
InactiveUS20100219645A1Increase hydrodynamic massExtended maintenance periodWind motor assemblyWind motor supports/mountsQuadrilateralTension-leg platform
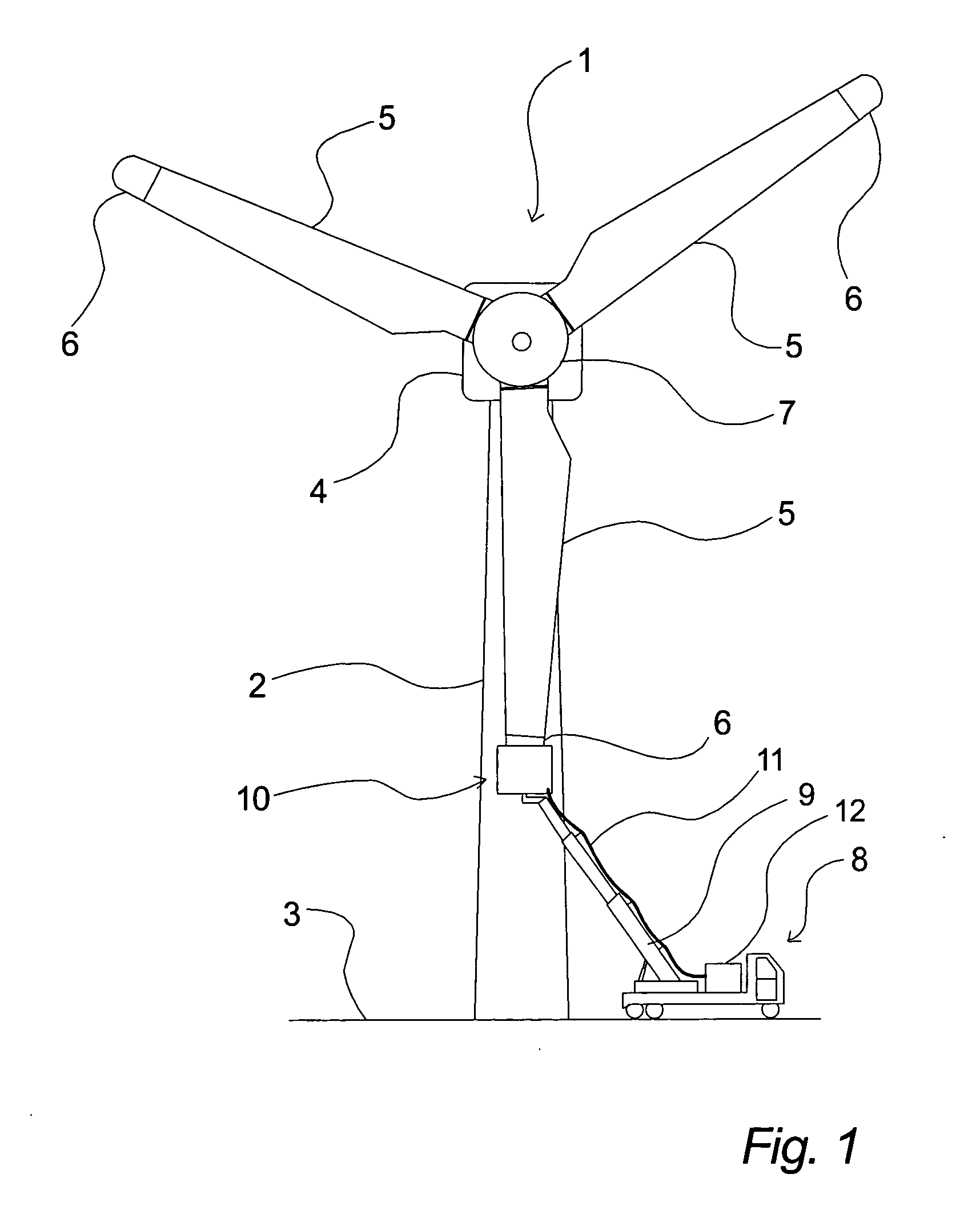
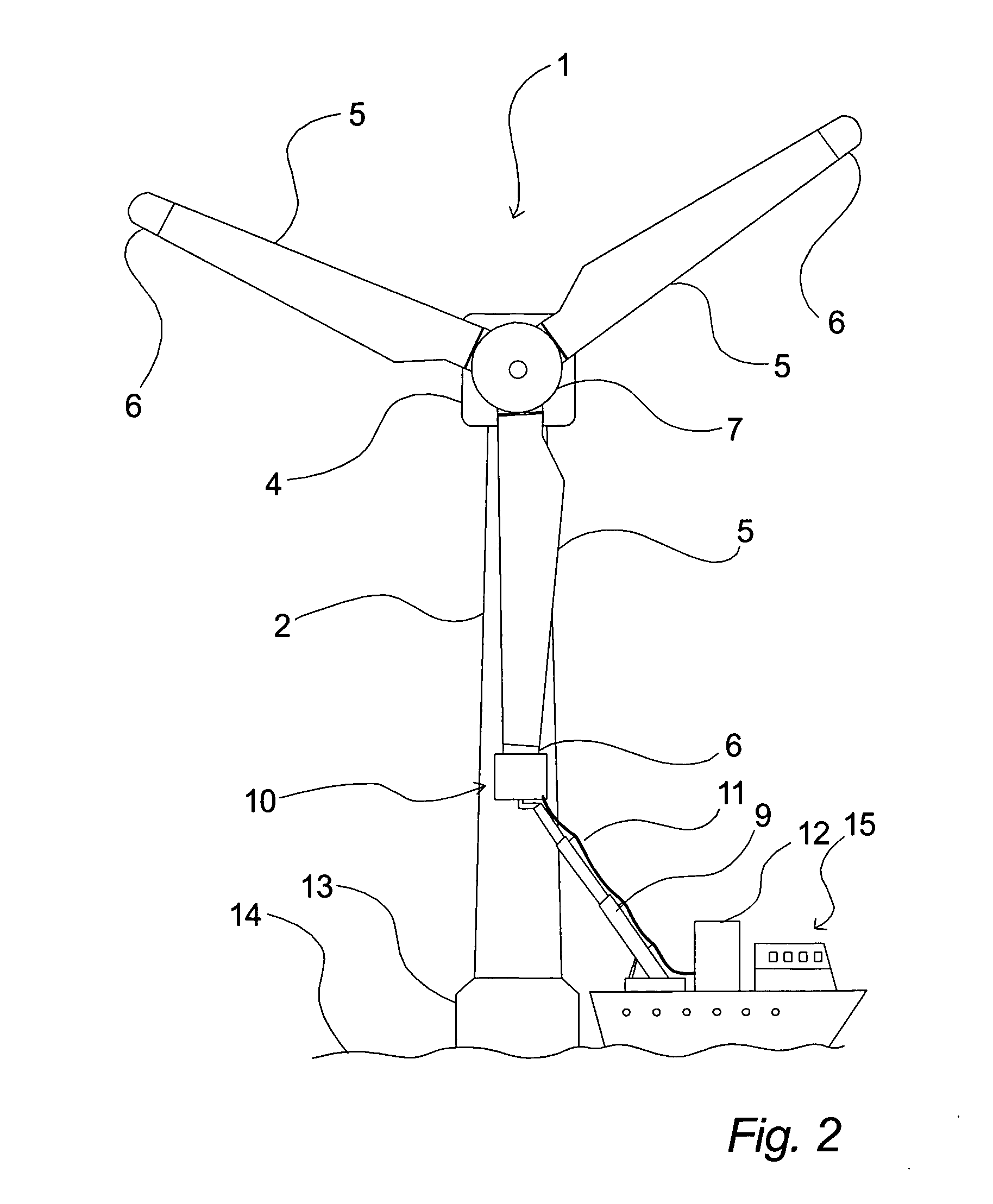
A floating power generation assembly has at least three floating units (3400) provided with power generation means (3402, 3404) and floating in a body of water. At least one of the three floating units (3400) is a tension leg platform. The assembly also comprises first anchors secured to a surface beneath the water, and first cables (3414, 3416) connecting the buoyant body (3400) to the first anchors. Second anchors are secured to the underwater surface and connected by second cables (3412) to the floating units (3400). The floating units (3400) are arranged substantially at the vertices of at least one triangle or quadrilateral.
Owner:YAMAMOTO SHIGEYUKI +1
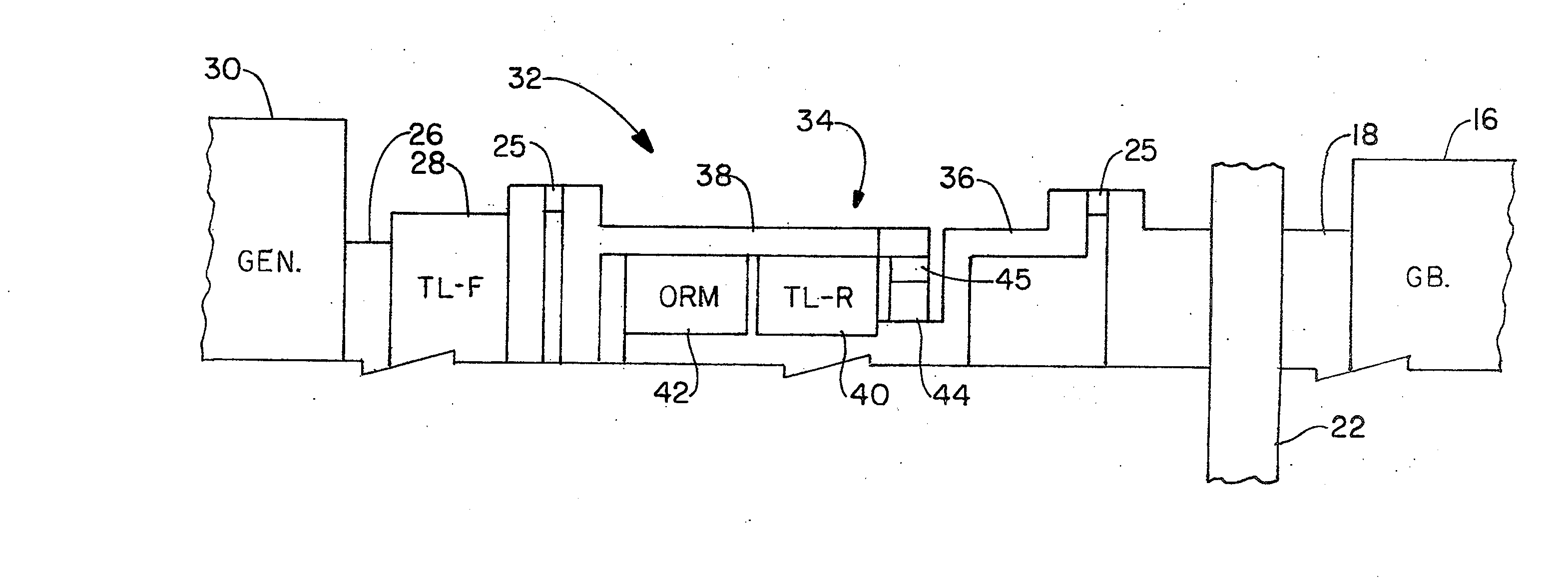
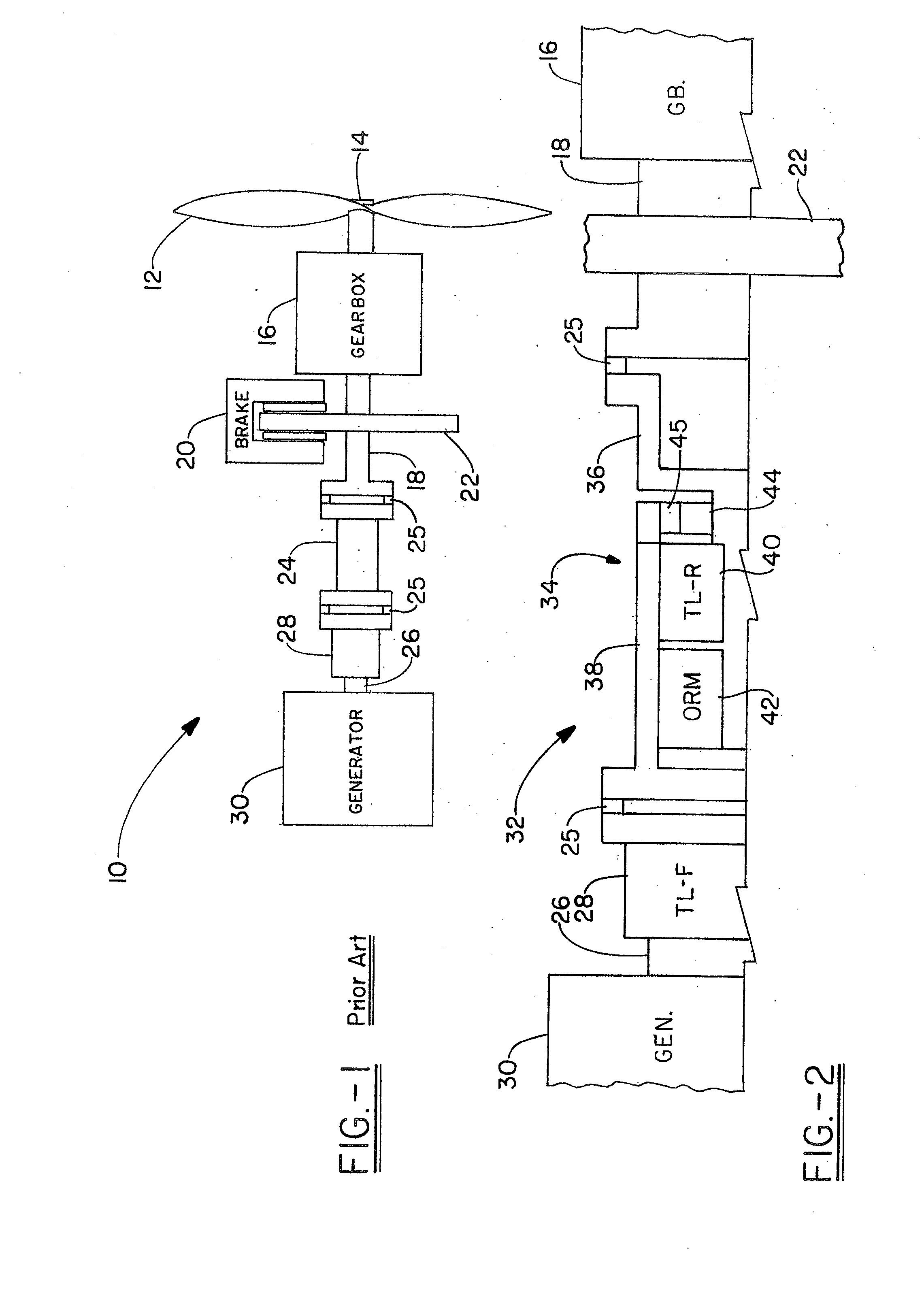
Wind turbine torque limiting clutch system
ActiveUS20120201679A1Improve operationIncreased durabilityPropellersPump componentsCoupling systemInterconnection
An asymmetric torque limiting coupling system for use on wind turbines, in which a forward torque limiting clutch and a reverse torque limiting clutch are provided in paired relation, with the reverse torque limiting clutch having a characteristic slip torque that is significantly less than that of the forward torque limiting clutch. In a specific embodiment disclosed, an asymmetric torque limiter interconnects a wind turbine with a generator shaft. The coupling includes an input housing and an output hub, with an overrunning mechanism interposed between the two. A first torque limiting mechanism is provided in series interconnection with the overrunning mechanism between the input housing and hub, while a second torque limiting mechanism is provided in parallel interconnection with the overrunning mechanism between the input housing and output hub.
Owner:PT TECH LLC
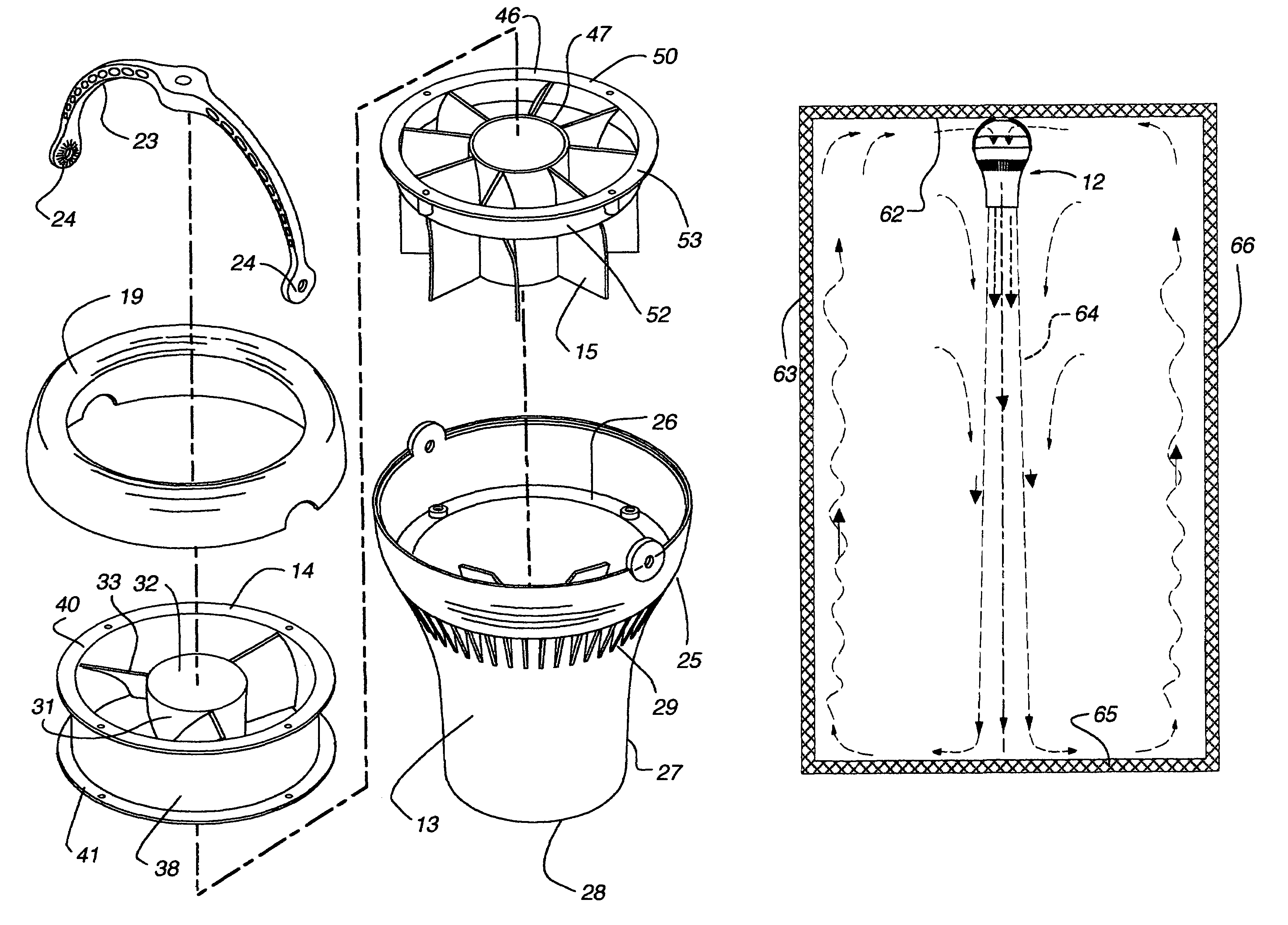
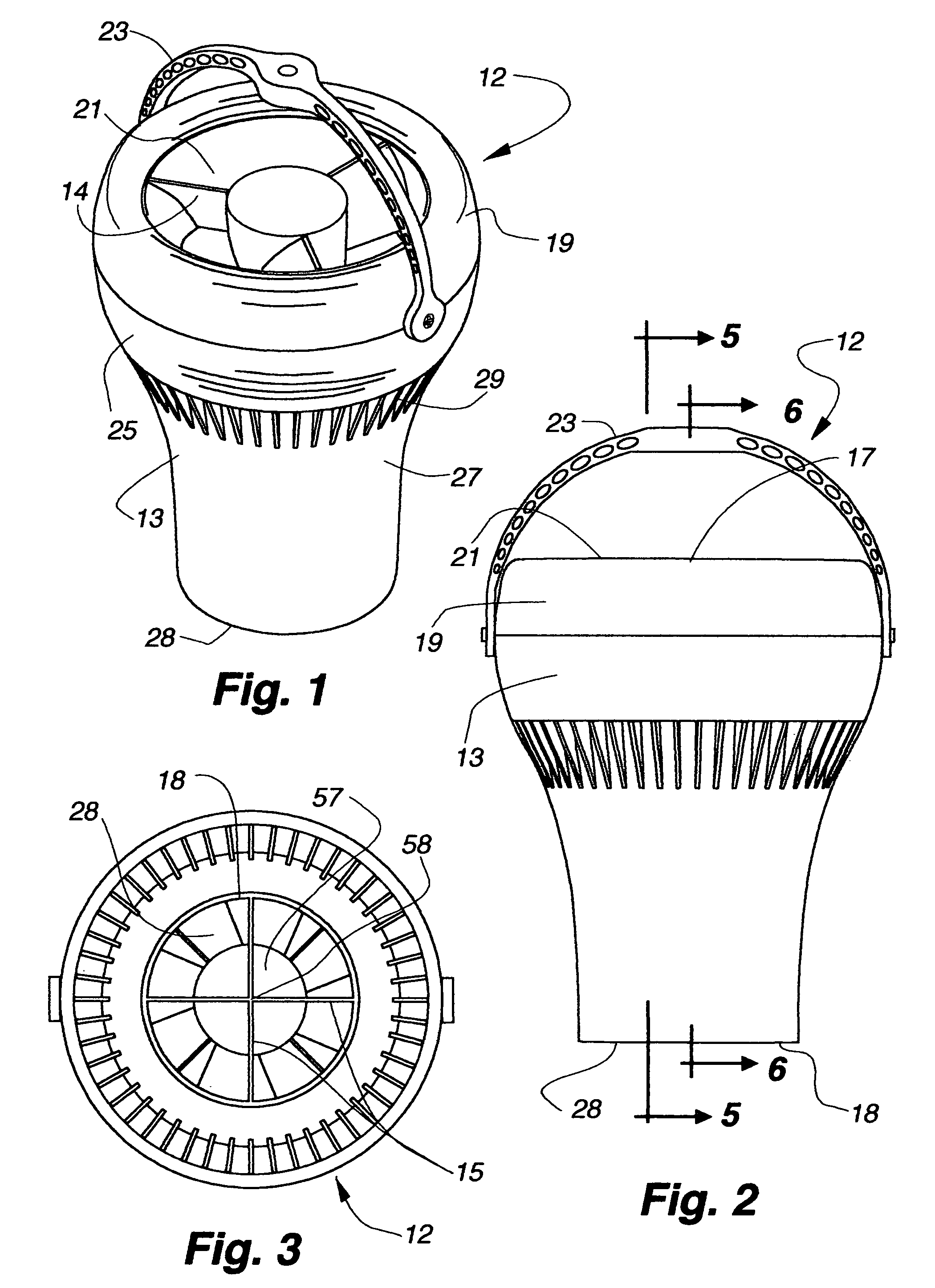
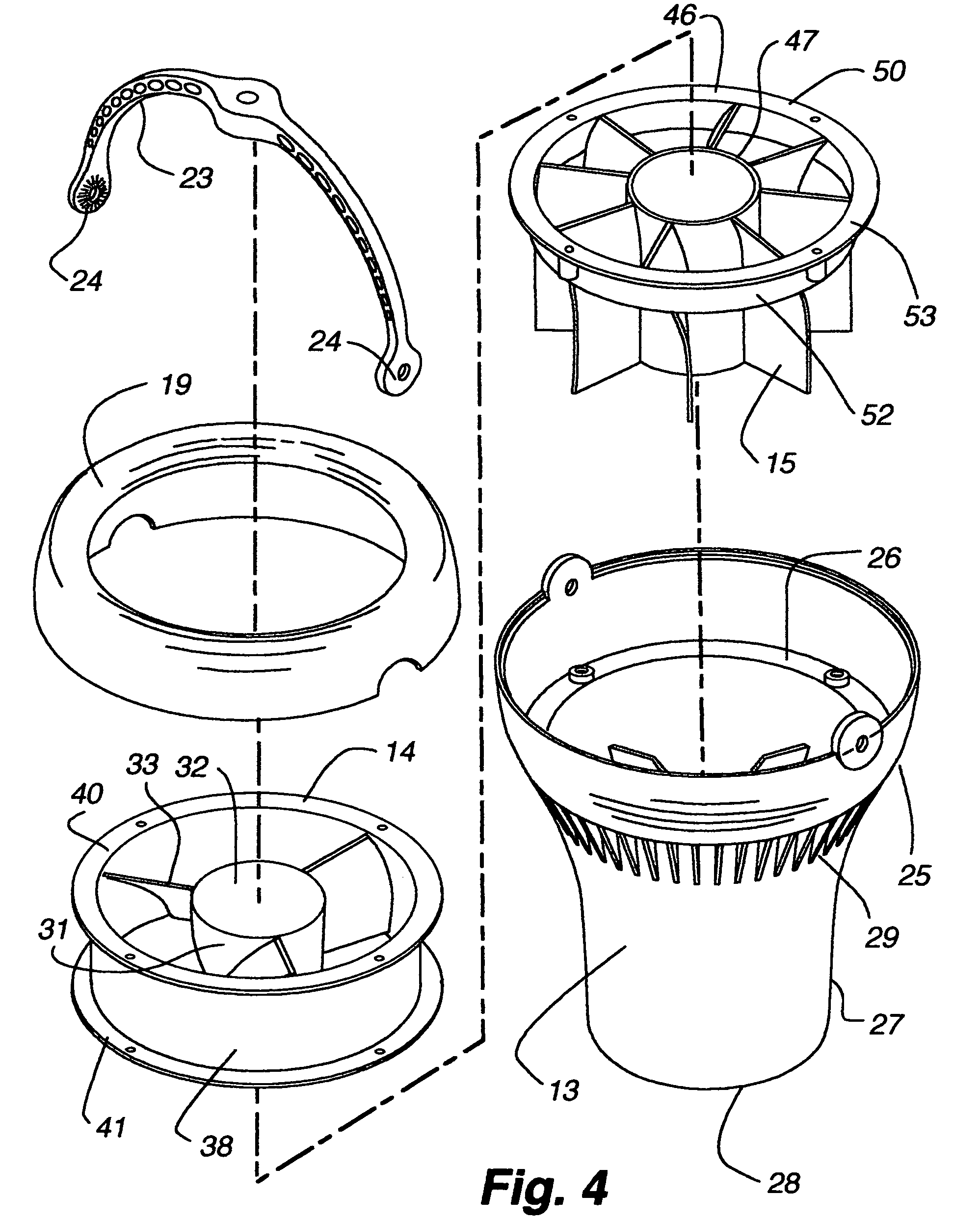
Columnar air moving devices, systems and methods
Air moving device includes a housing, an impeller in the housing for generating a downward air flow, and vanes in the housing in close proximity to and a selected distance below the impeller to straighten the air flow. The device produces an air flow that substantially remains in a column over a substantial distance. The method includes producing an air flow that substantially remains in a column over a substantial distance and directing the air flow from the ceiling towards the floor to provide temperature destratification of the air in an enclosed space. The method also includes directing warm air from the ceiling to the floor and storing heat in the floor, apparatus on the floor and ground under the floor. The stored heat is released when the ceiling is cooler than the floor.
Owner:AIRIUS IP HLDG
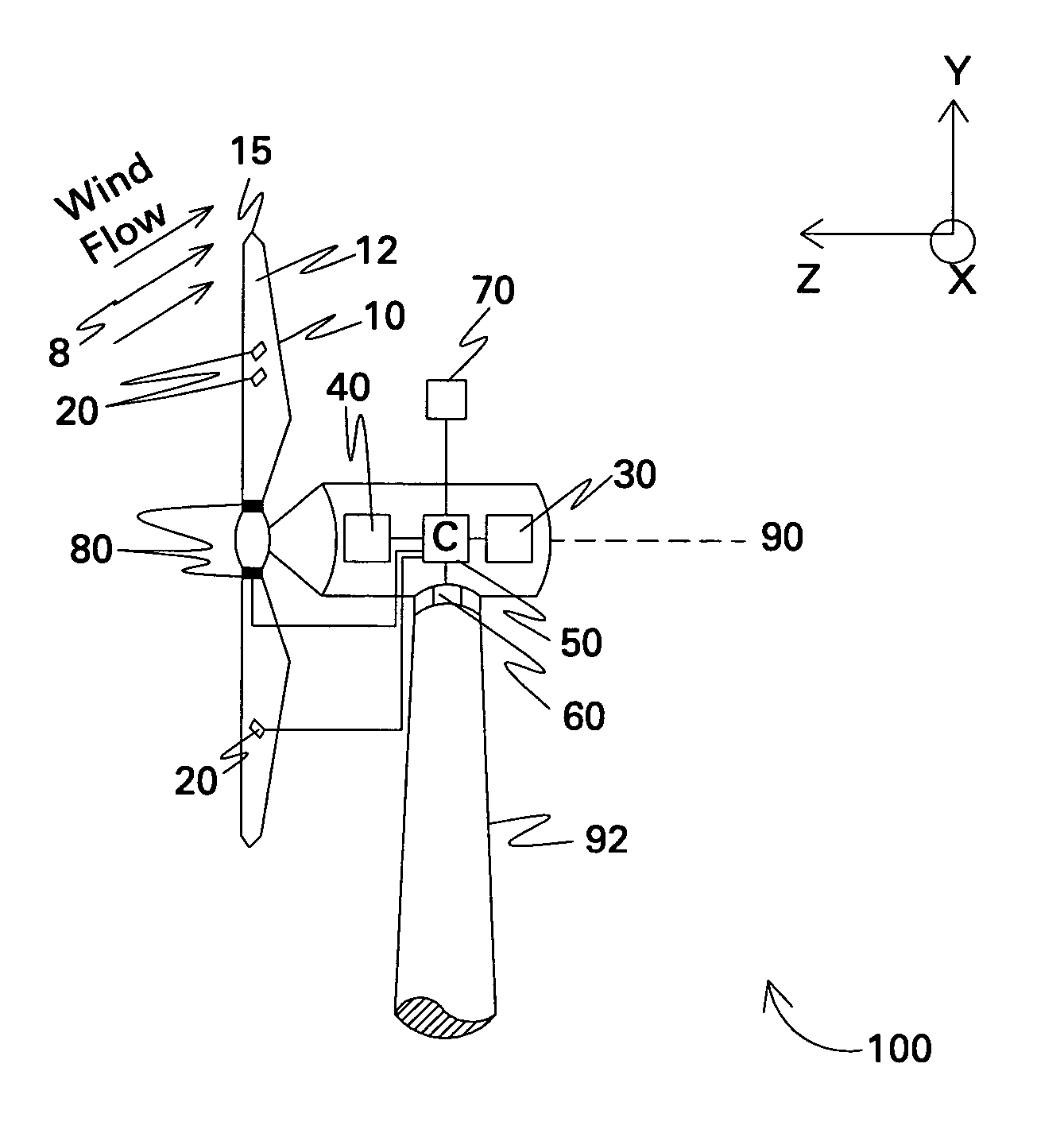
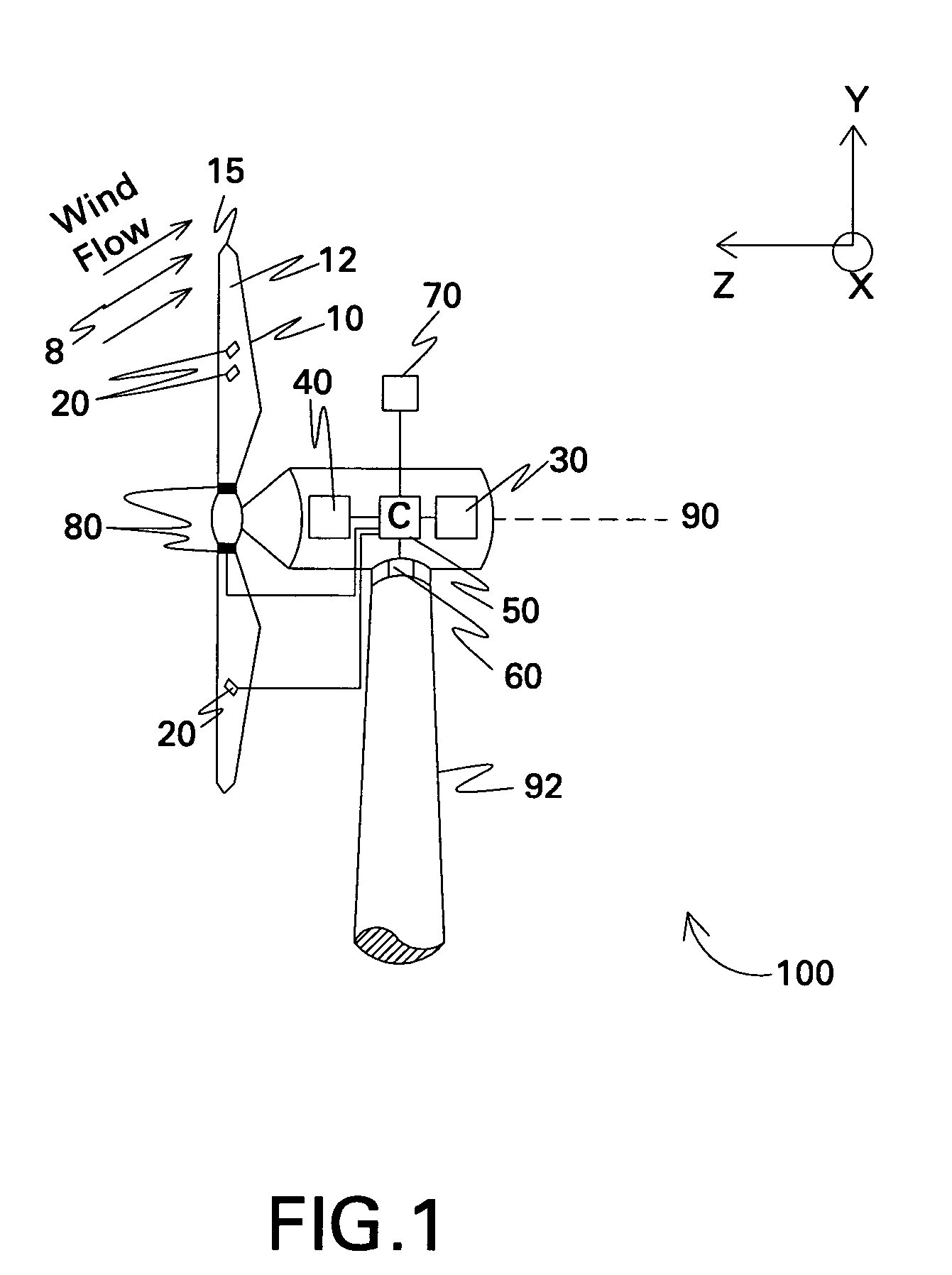
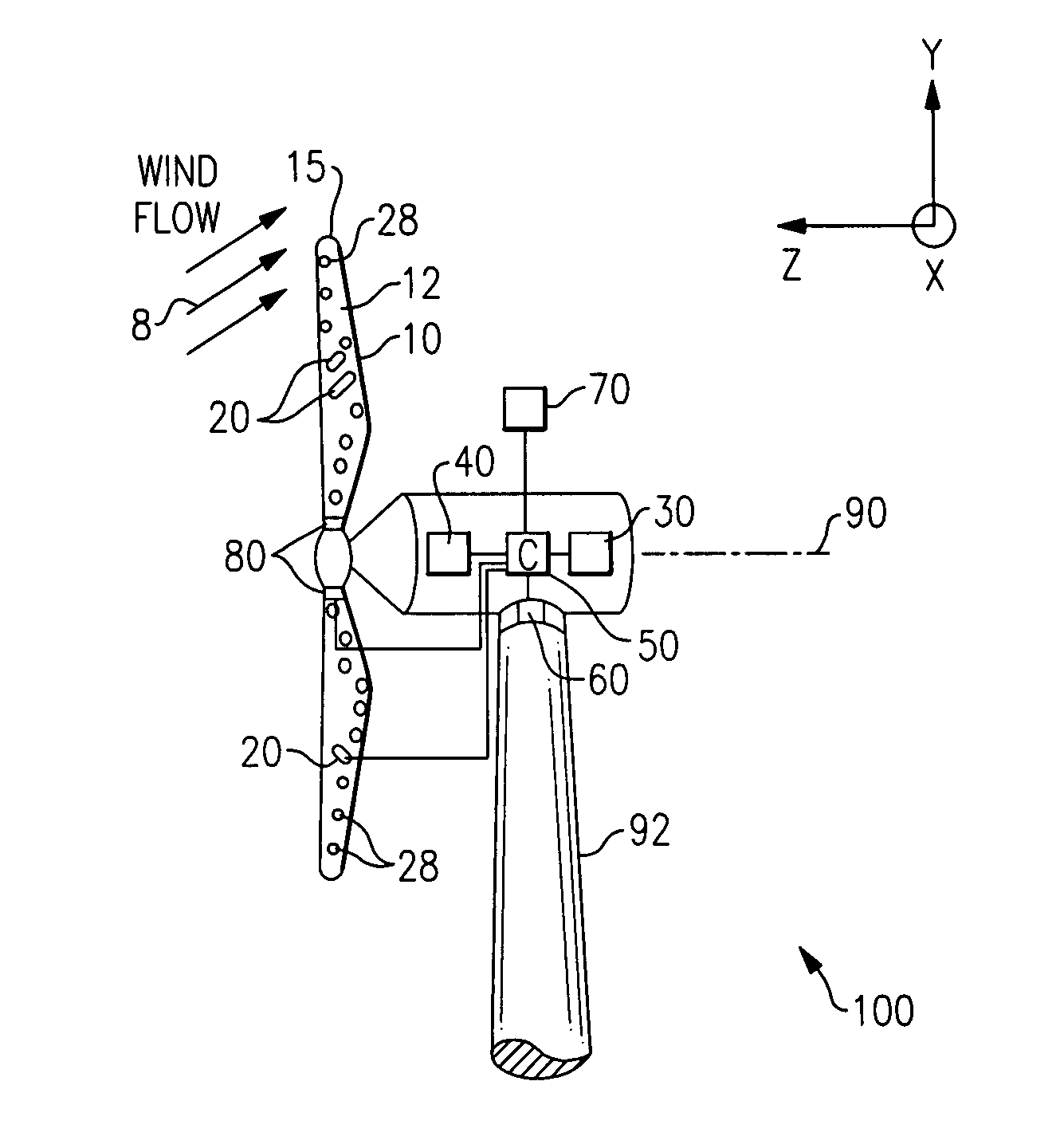
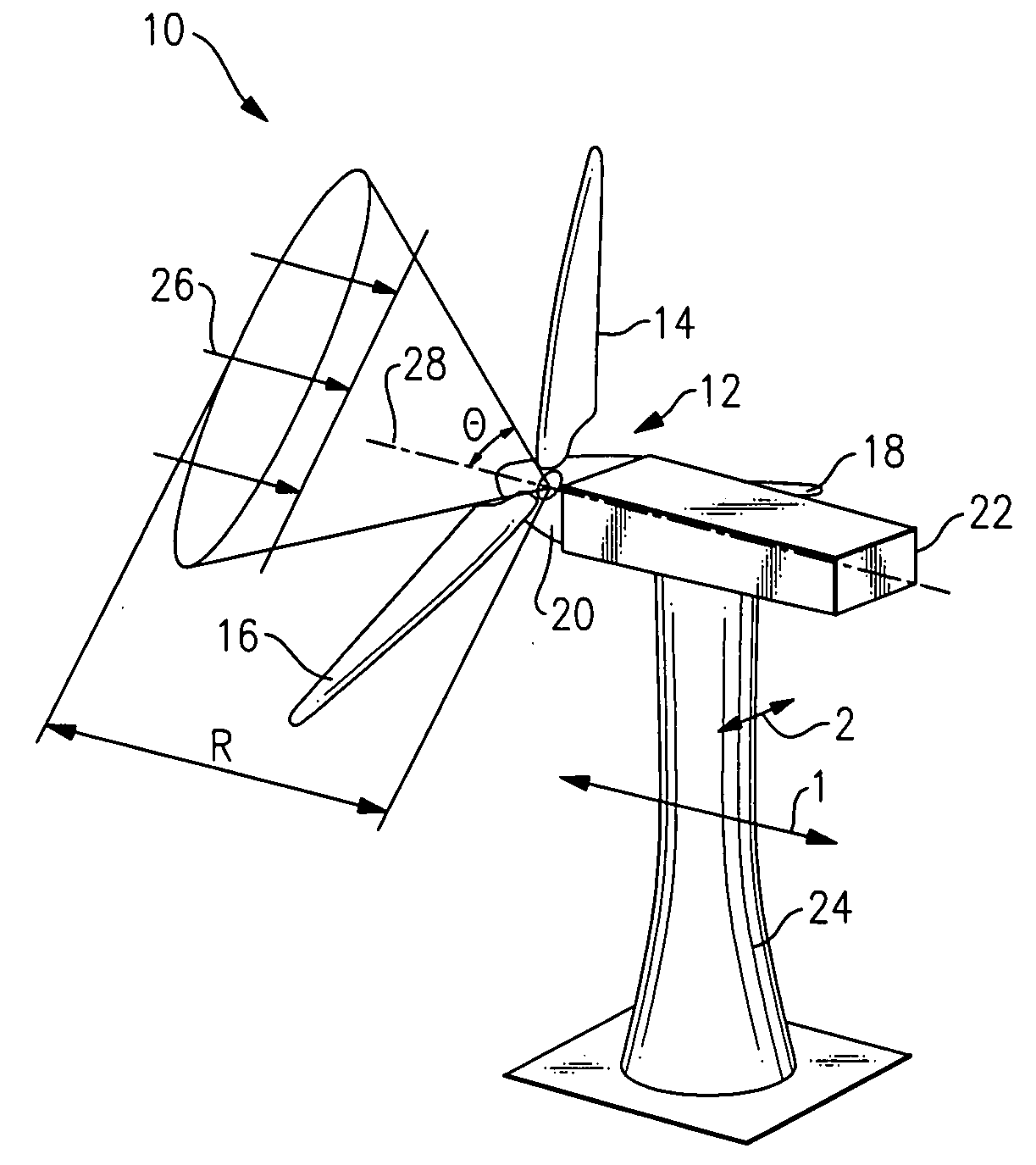
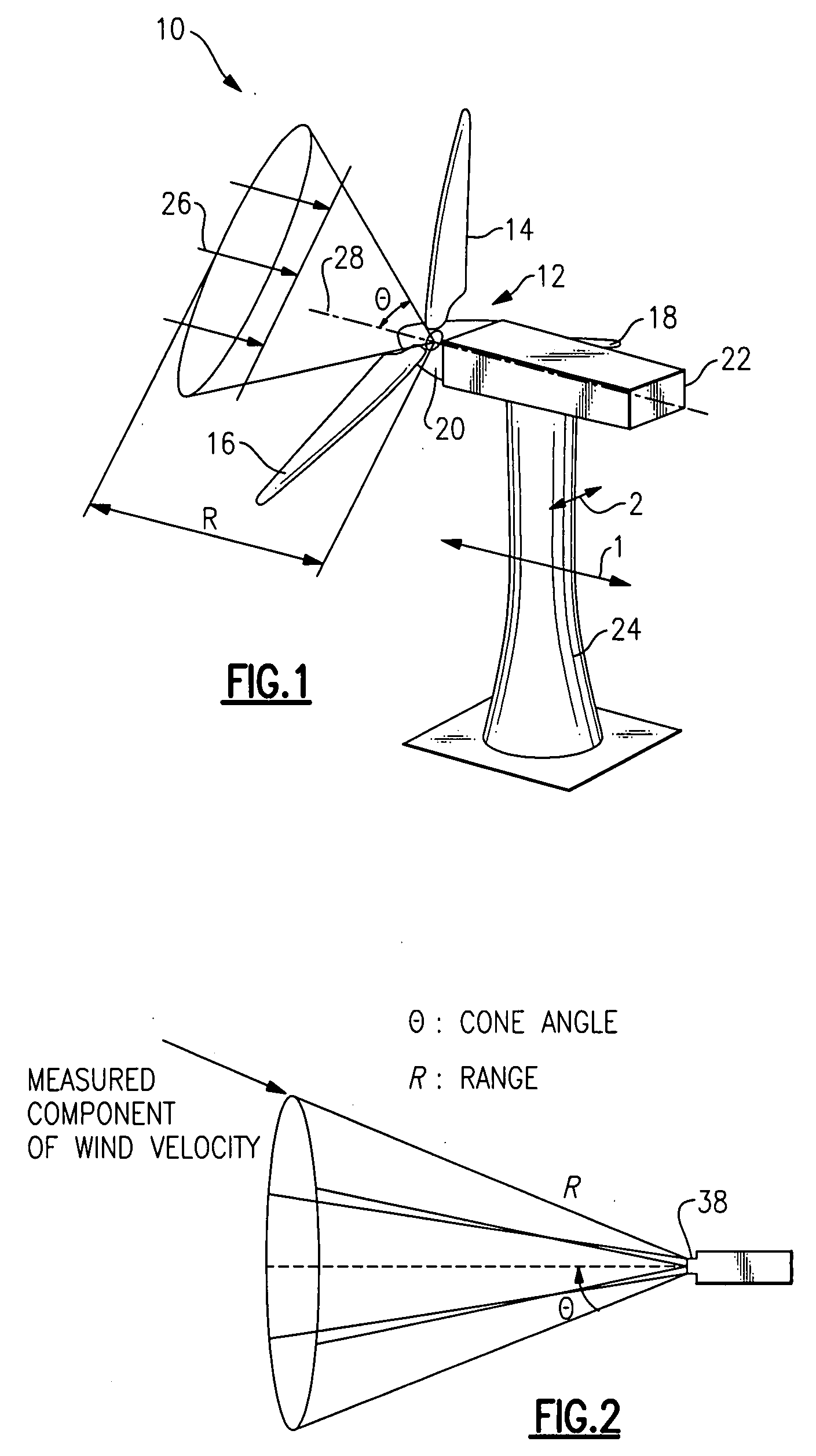
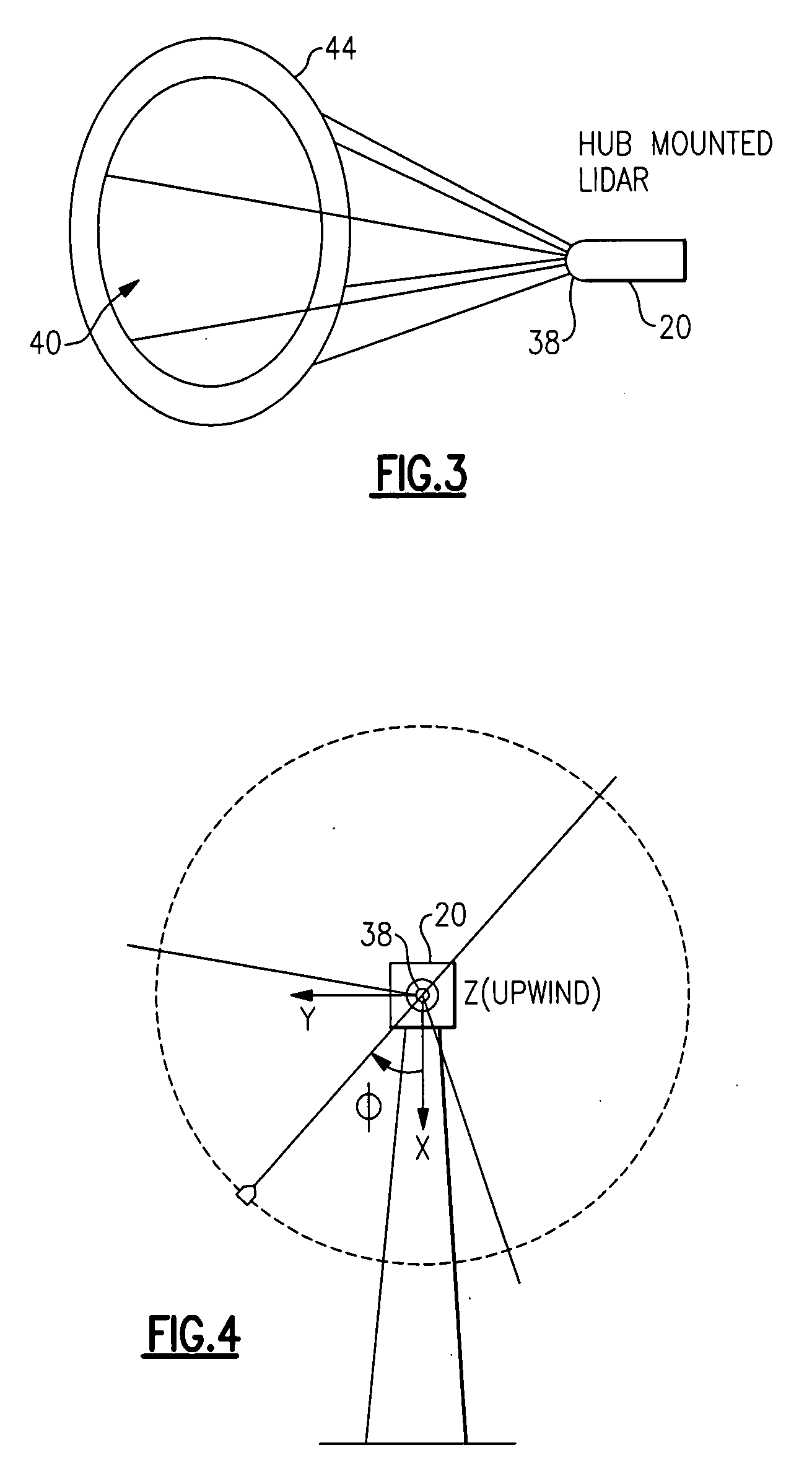
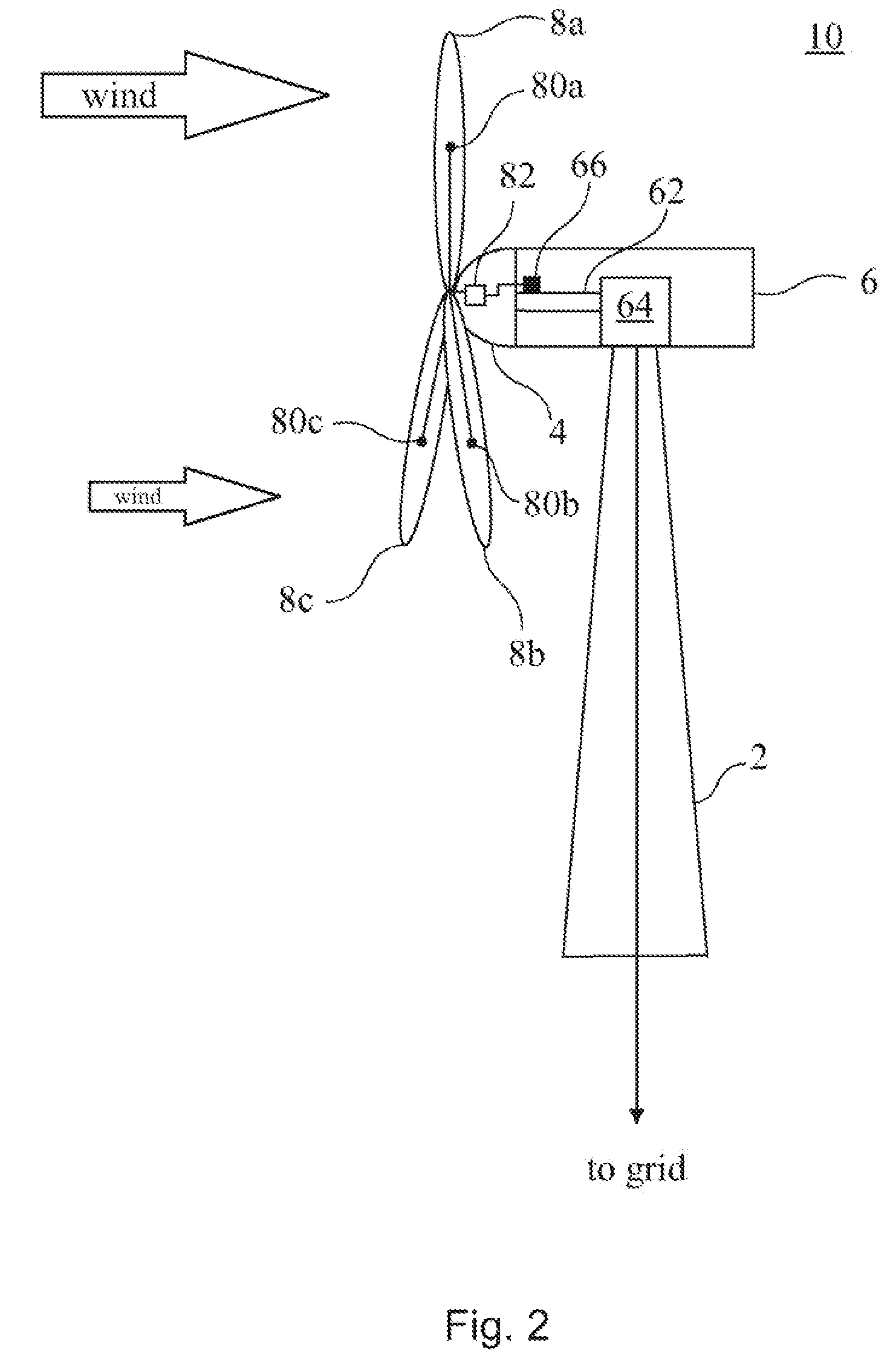
Method and apparatus to determine the wind speed and direction experienced by a wind turbine
ActiveUS20070086893A1Low costSimple and robust and low cost apparatusPropellersWind motor controlNacelleEngineering
An apparatus and a method used to determine the speed and direction of the wind experienced by a wind turbine are provided. The apparatus comprises at least one sensor fixed to the rotor of the wind turbine, an angular sensor to measure the angular position of the rotor of the wind turbine, and a circuit which converts the relationship between the output of the at least one sensor and the output of the angular sensor into the speed and direction of the wind experienced by the wind turbine. According to the invention, the sensing apparatus can measure the wind speed and direction in three dimensions. In addition, mounting the sensors directly to the rotor of the wind turbine results in a very simple and robust installation. Mounting the sensors directly to the rotor also eliminates the turbulence from the rotor and the nacelle of the wind turbine from affecting the sensors.
Owner:ROMO WIND AG
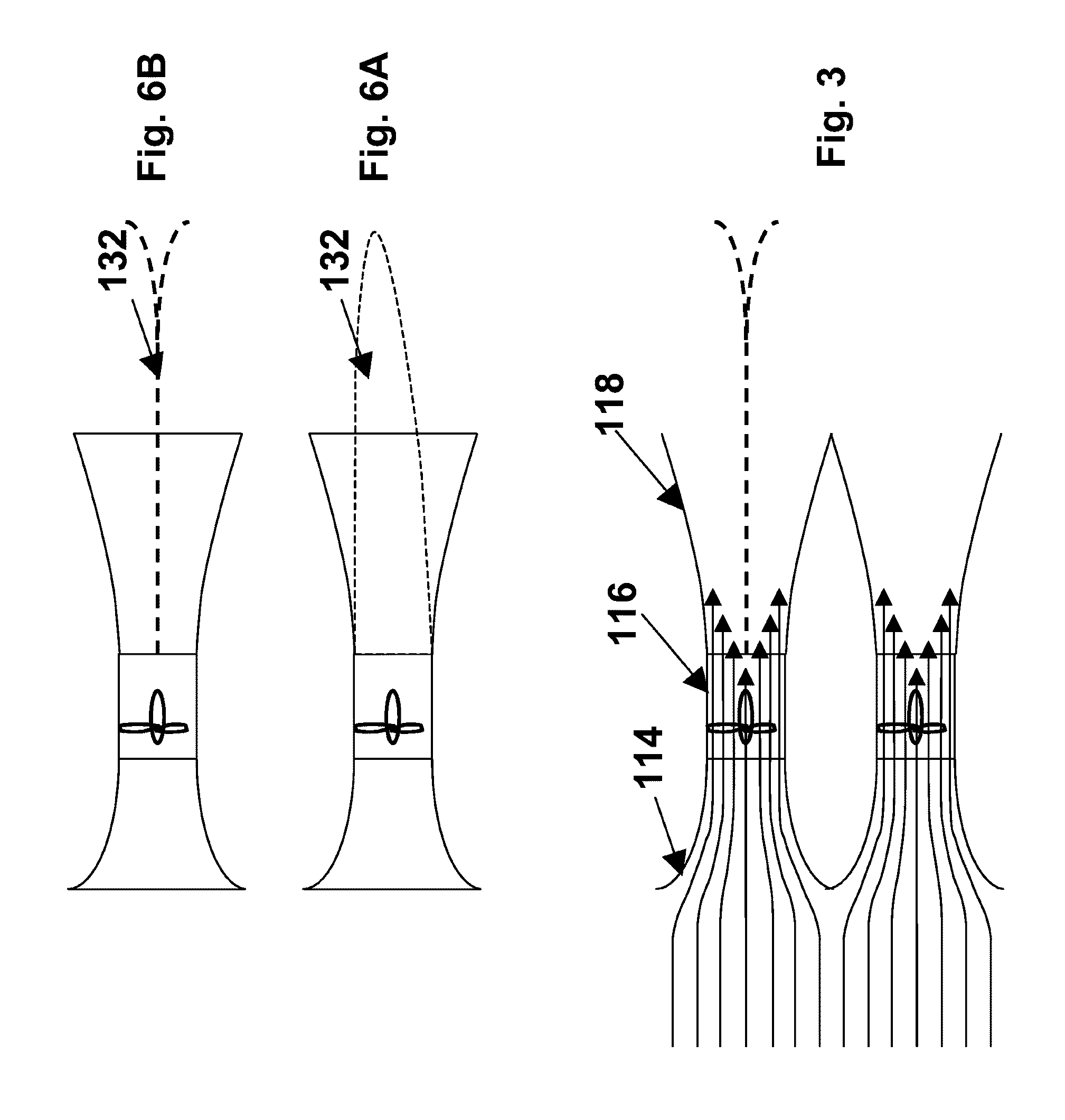
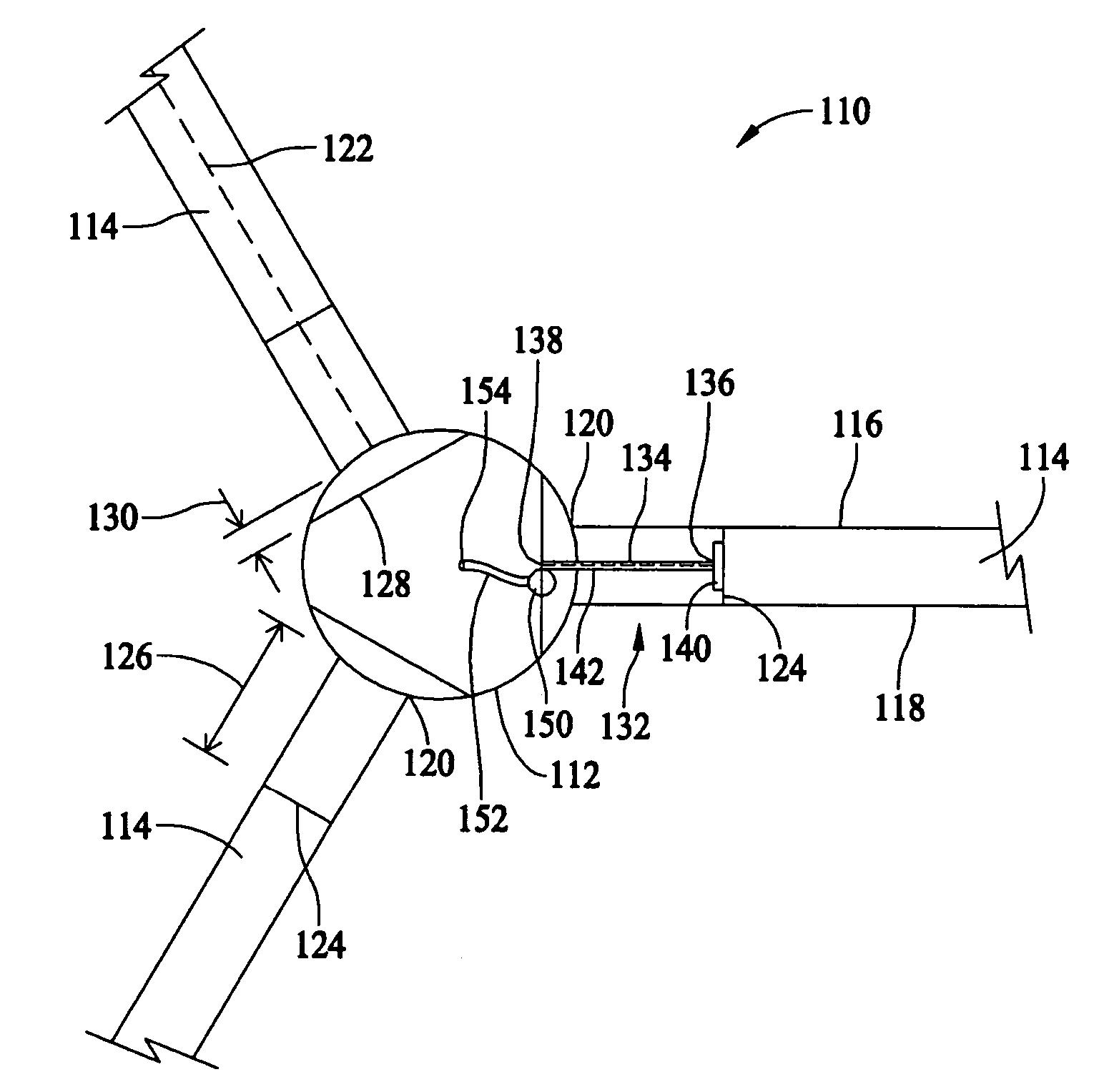
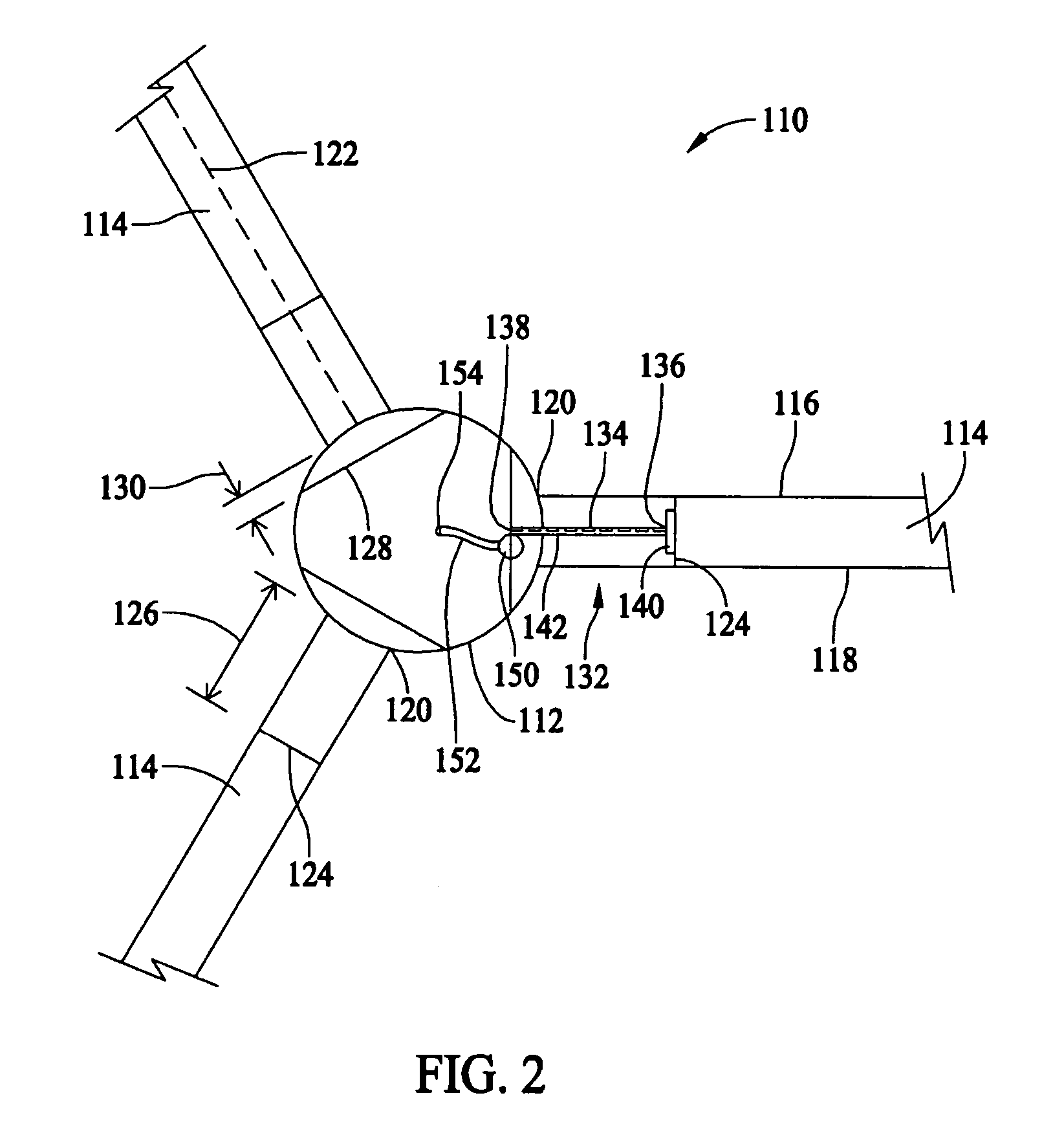
Lightning protection system for a wind turbine
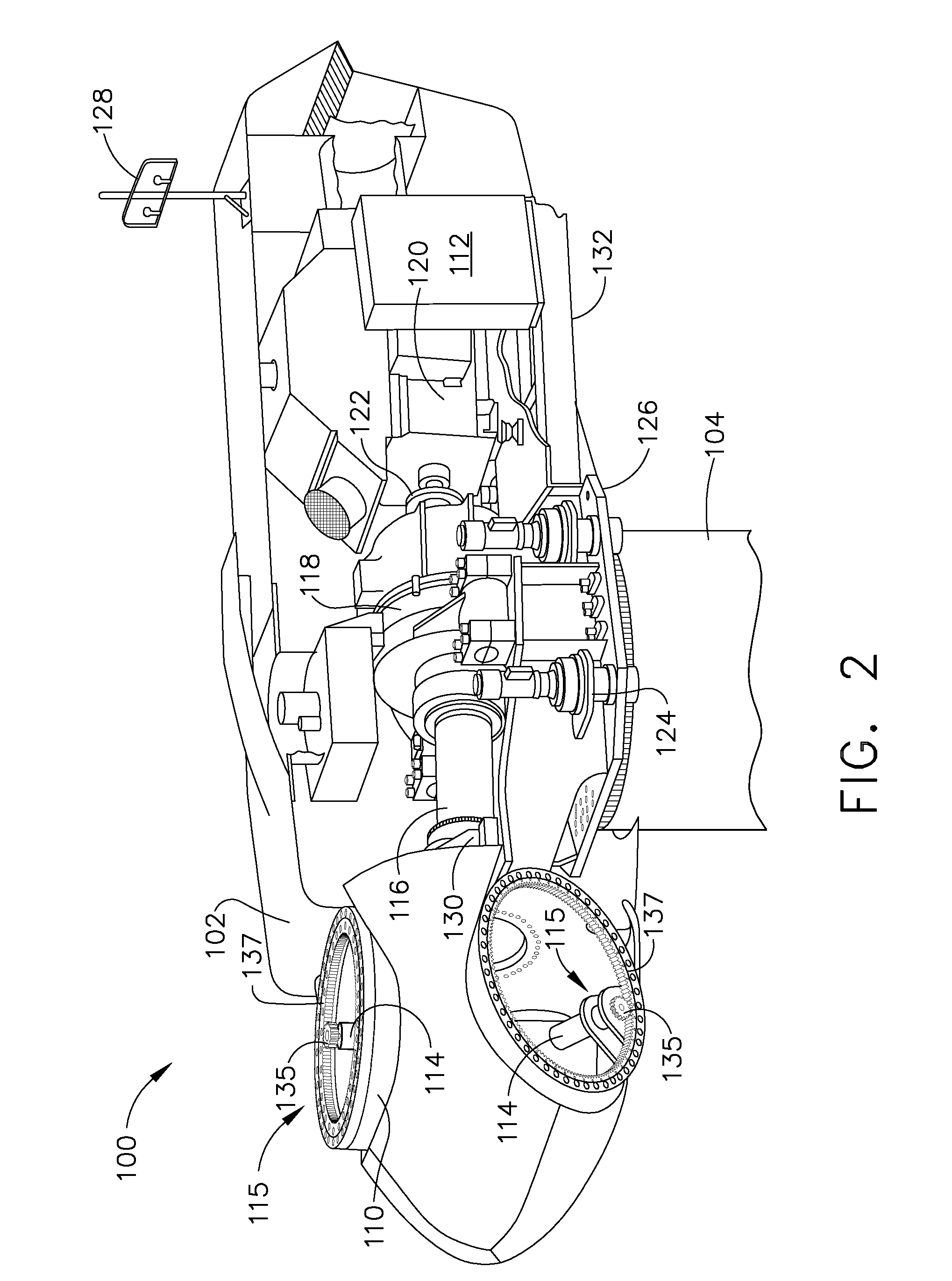
In a wind turbine (104, 500, 704) having a plurality of blades (132, 404, 516, 744) and a blade rotor hub (120, 712), a lightning protection system (100, 504, 700) for conducting lightning strikes to any one of the blades and the region surrounding the blade hub along a path around the blade hub and critical components of the wind turbine, such as the generator (112, 716), gearbox (708) and main turbine bearings (176, 724).
Owner:WEG ELECTRIC CORP
System and method for loads reduction in a horizontal-axis wind turbine using upwind information
A system and method provide a proactive mechanism to control pitching of the blades of a wind turbine to compensate for rotor imbalance during normal operation by pitching the blades individually or asymmetrically, based on turbulent wind gust measurements in front of the rotor, determined before it reaches the rotor blades.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for treatment of a rotor blade on a windmill
ActiveUS20050042102A1High degree of automationLow costPropellersPretreated surfacesMechanical engineeringWindmill
Method and apparatus for treatment of a surface of a rotor blade of a windmill, the apparatus being placed in such a manner to be moveable in relation to the surface of a rotor blade, and the apparatus being caused to move depending on a form of treatment determined by means for treatment mounted on, in or next to the apparatus. In this manner, various forms of treatment of a rotor blade may be carried out such as for instance washing, finishing, sealing, etc.
Owner:PP ENERGY APS
Wind turbine blade deflection control system
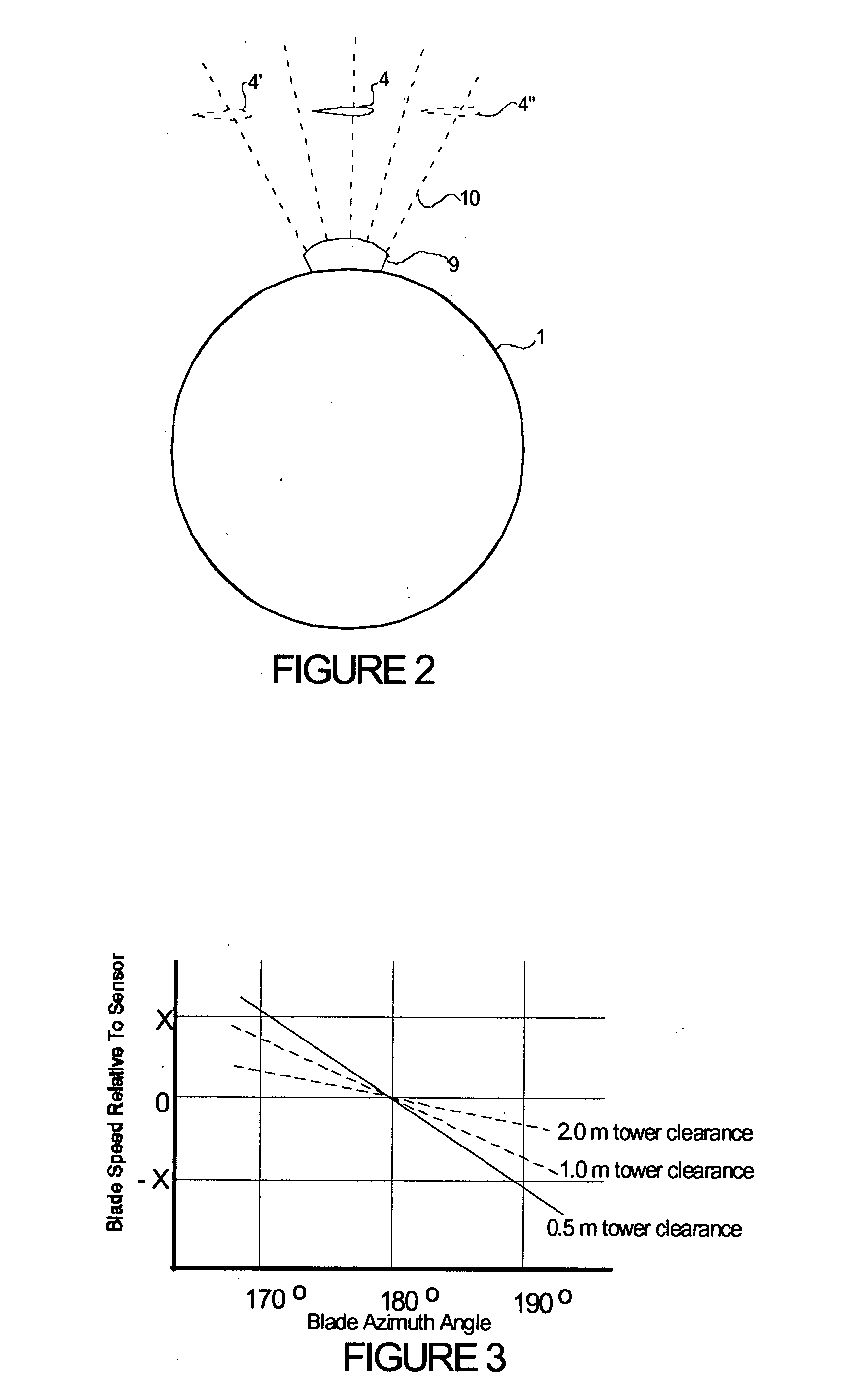
A wind turbine with a sensor that measures the out-of-plane deflection of the blades and a controller that uses the signal from the sensor to determine the risk of a tower strike. The controller takes any necessary action to prevent a tower strike when it determines that the risk of a strike is high. The sensor can include strain gages or accelerometers mounted on the blades or it can include a fixed sensor mounted on the side of the tower to measure tower clearance as the blade passes by. The control action taken can include pitching blades, yawing the nacelle, or stopping the turbine. The controller is preferably a fuzzy logic controller.
Owner:BOSCHE JOHN VANDEN
Turbine seal plate locking system
A seal plate assembly is provided in a rotor disc for a turbine engine. The seal plate assembly includes a radially extending flange on the disc and an annular groove defined between a radial surface on the flange and a face of the disc. An annular outer surface extends axially in facing relationship to an annular inner surface of the groove. A plate structure is supported between the inner and outer surfaces, and a lock structure is provided for holding the plate structure in place. The lock structure includes an axial leg that is adapted to be located between an inner edge of the plate structure and the inner surface of the groove, and the lock structure further includes a radial leg that is adapted to be located between the radial surface on the flange and an outwardly facing surface of the plate structure.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Active damping of wind turbine blades
A wind turbine blade, includes a sensor, arranged upstream from a trailing edge of the blade for measuring an airflow characteristic near a surface of the blade; and an actuator, arranged downstream from the sensor, for adjusting the airflow in response to the measured characteristic.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
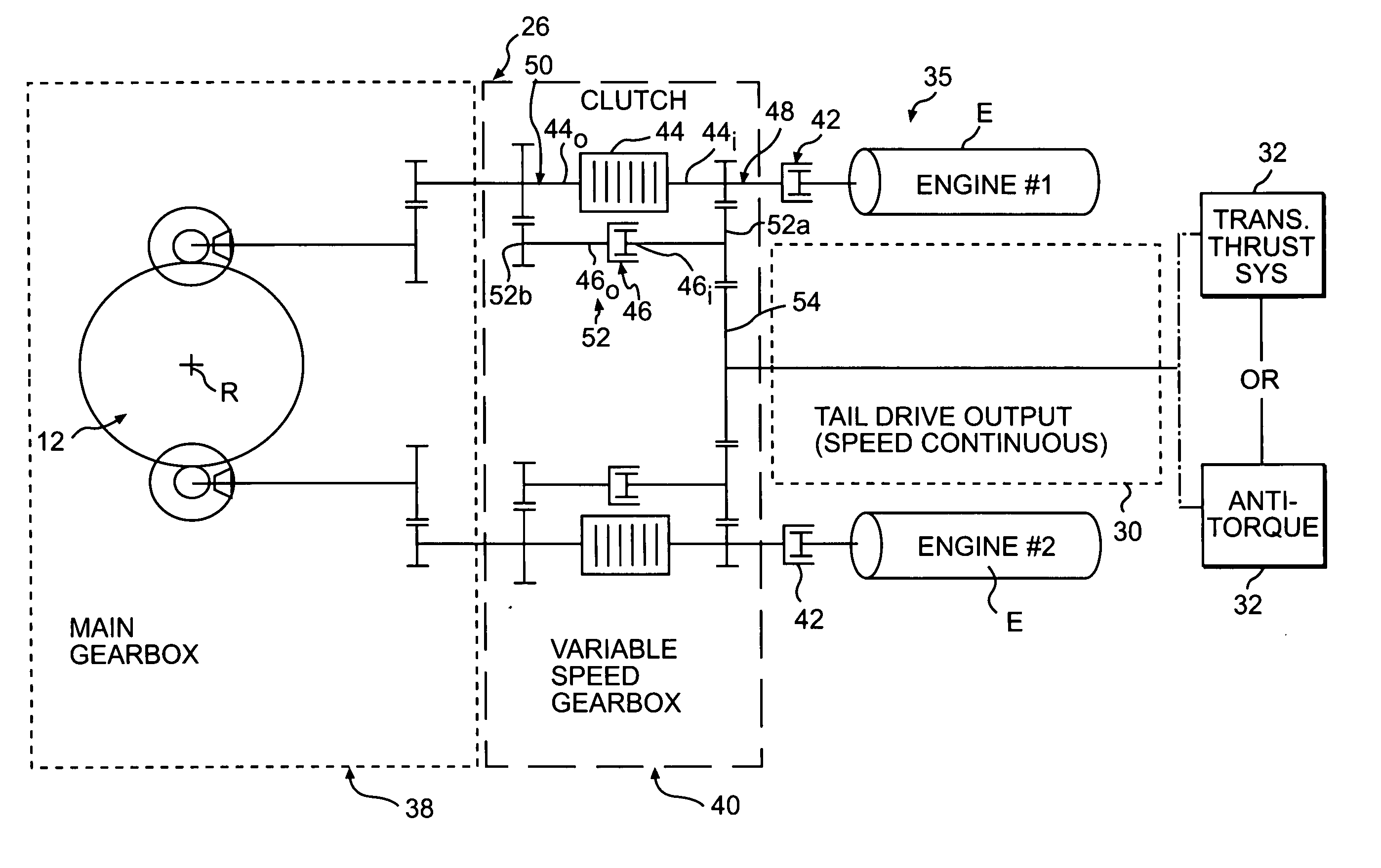
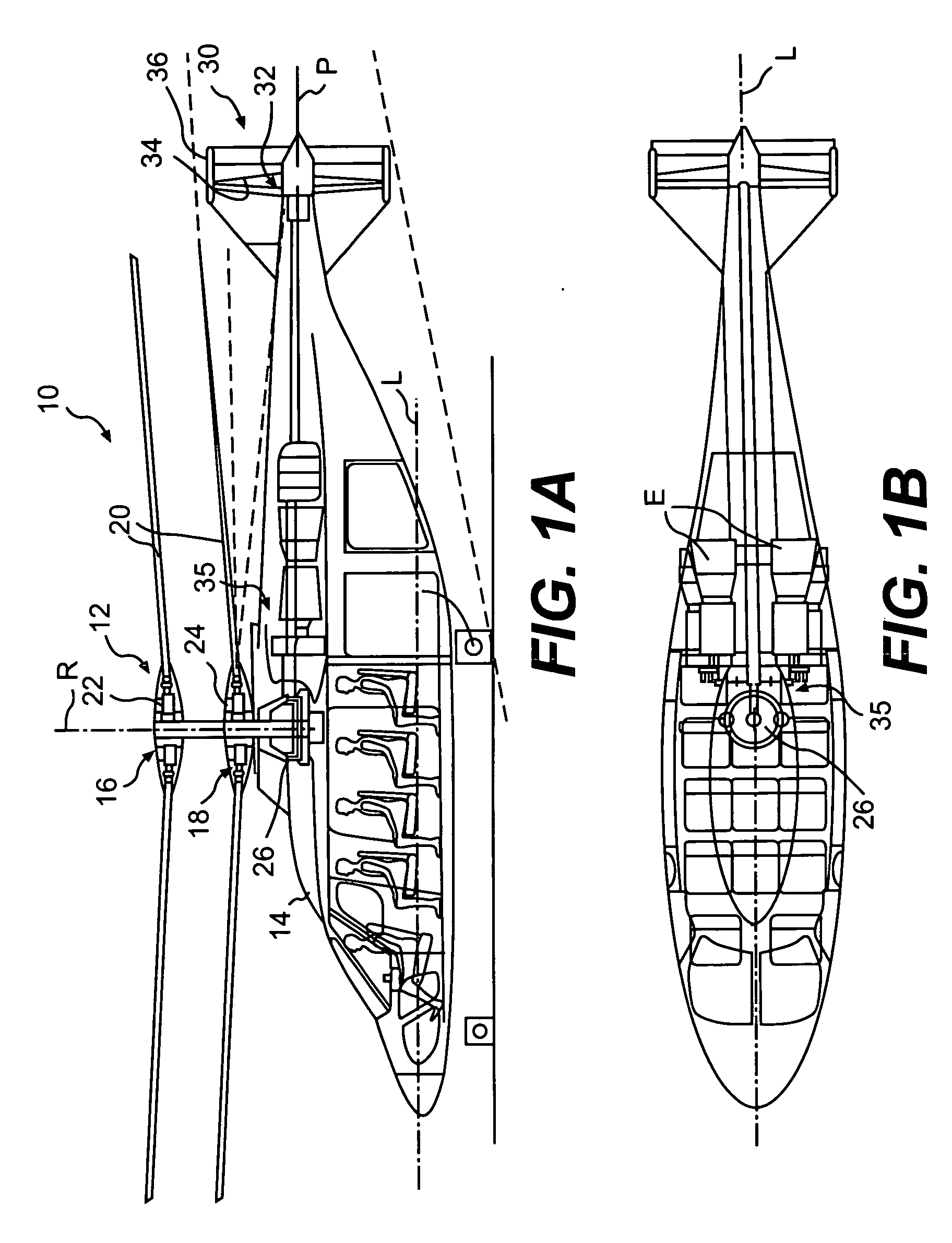
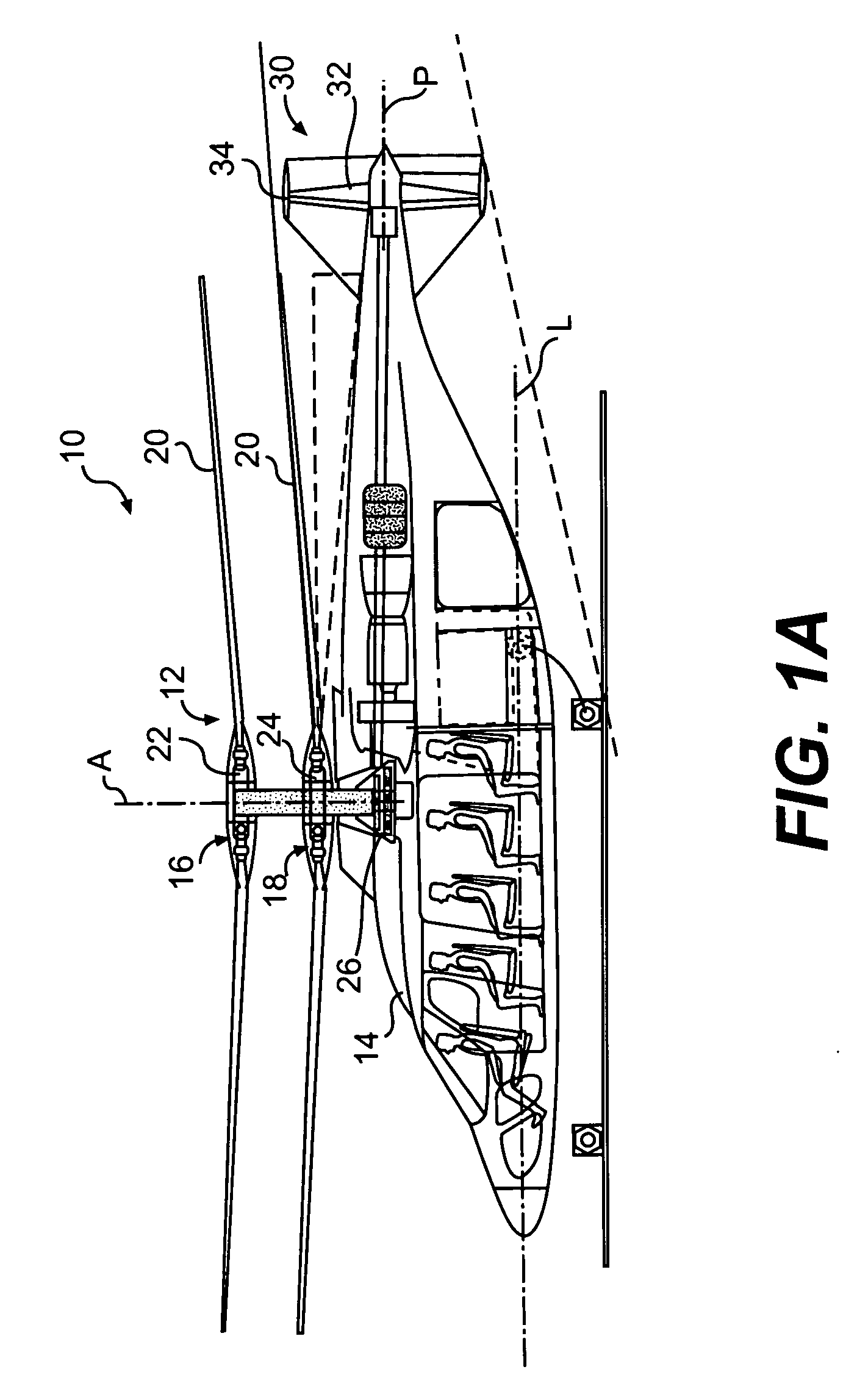
Variable speed transmission for a rotary wing aircraft
ActiveUS20060269414A1Maximize aircraft performanceFacilitates different flight spectrumPropellersPump componentsFreewheelGear wheel
A transmission gearbox for a rotary-wing aircraft includes a main gearbox and a variable speed gearbox in meshing engagement with the main rotor gearbox. The variable speed gearbox permits at least two different RPMs for the main rotor system without disengaging the engine(s) or changing engine RPMs. The variable speed gearbox includes a clutch, preferably a multi-plate clutch, and a freewheel unit for each engine. A gear path drives the main gearbox in a “high rotor speed mode” when the clutch is engaged to drive the main rotor system at high rotor rpm for hover flight profile. A reduced gear path drives the main gearbox in a “low rotor speed mode” when the clutch is disengaged and power is transferred through the freewheel unit, to drive the main rotor system at lower rotor rpm for high speed flight. The variable speed gearbox may be configured for a tail drive system that operates at a continuous speed, a tail drive system that changes speed with the main rotor shaft or for no tail drive system.
Owner:ACRESSO SOFTWARE +1
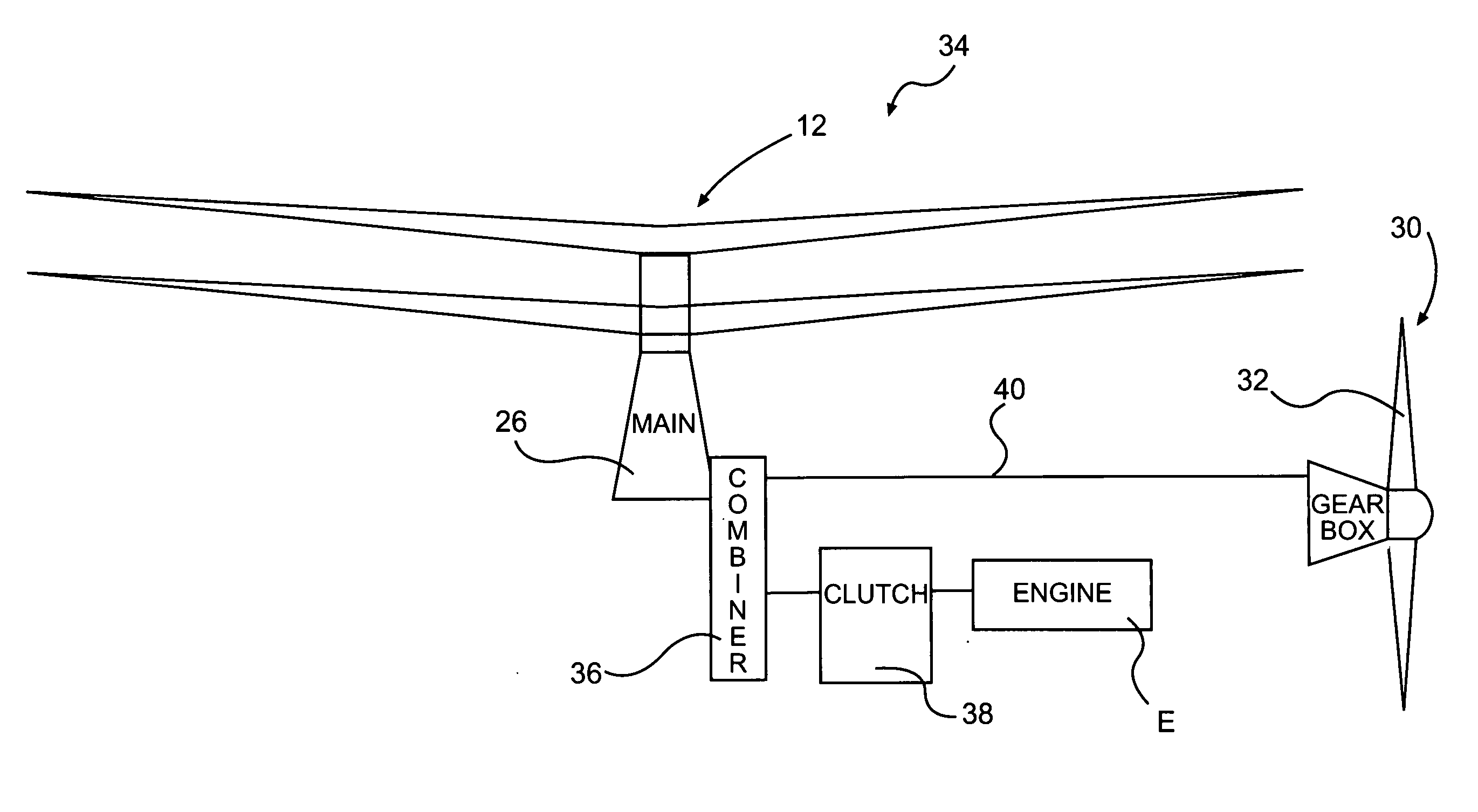
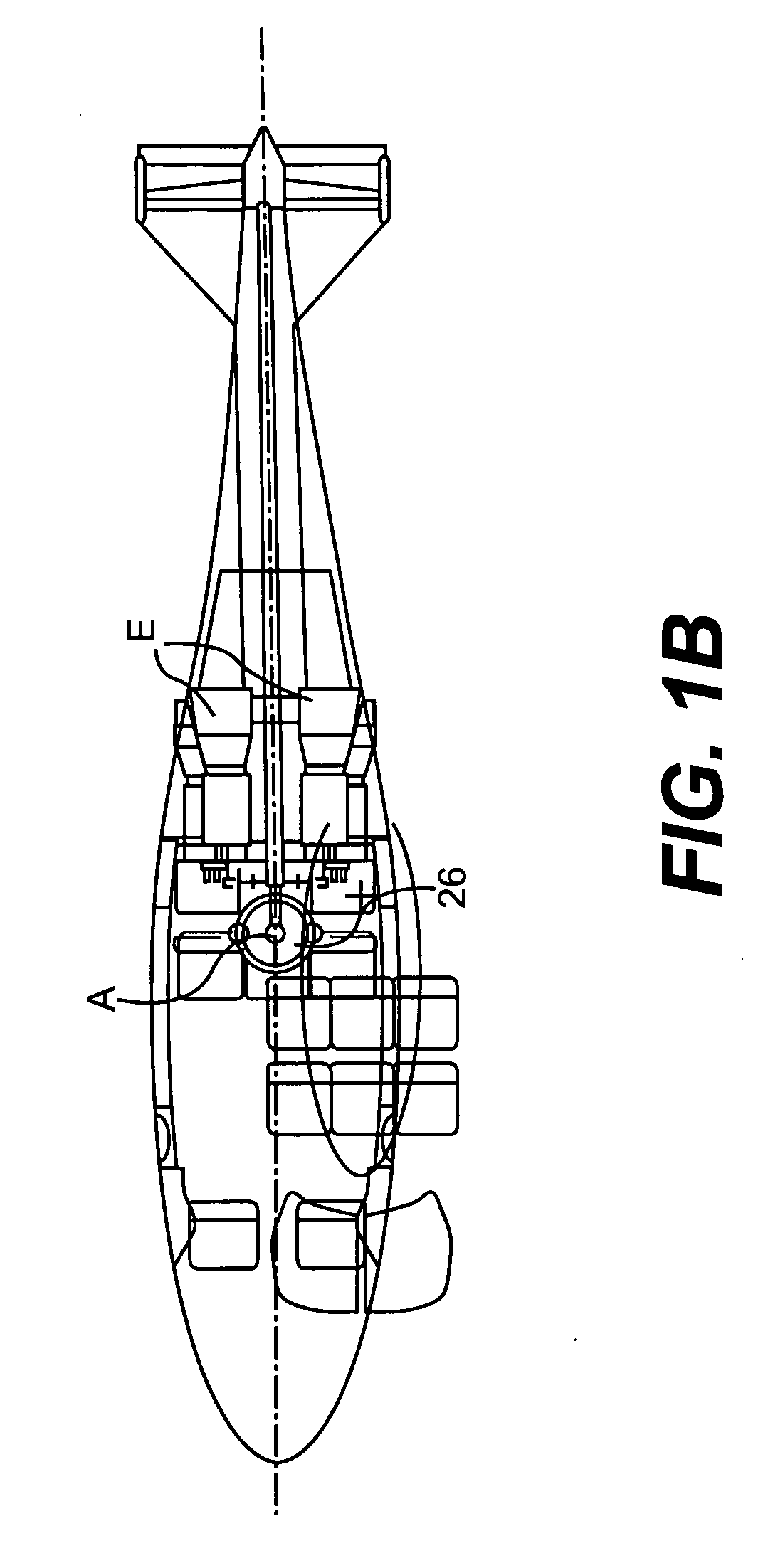
Rotor drive and control system for a high speed rotary wing aircraft
ActiveUS20060269413A1Vibration minimizationNegative liftPropellersPump componentsControl systemFlight vehicle
A drive system for a high speed rotary-wing aircraft includes a combiner gearbox in meshing engagement with a main gearbox. The combiner gearbox is driven by one or more engines such that a main rotor system and a translational thrust system are driven thereby. The engine drives the combiner gearbox and thus the main gearbox through an overrunning clutch. The drive system permits the main rotor system RPM to be controlled by offloading power to the translational thrust system during a high speed flight profile.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Methods and apparatus for reducing peak wind turbine loads
ActiveUS20060002791A1Reduce peak loadReduce the possibilityPropellersWind motor controlTurbinePeak load
A method for reducing peak loads of wind turbines in a changing wind environment includes measuring or estimating an instantaneous wind speed and direction at the wind turbine and determining a yaw error of the wind turbine relative to the measured instantaneous wind direction. The method further includes comparing the yaw error to a yaw error trigger that has different values at different wind speeds and shutting down the wind turbine when the yaw error exceeds the yaw error trigger corresponding to the measured or estimated instantaneous wind speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine, wind turbine controller and method for controlling a wind turbine
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
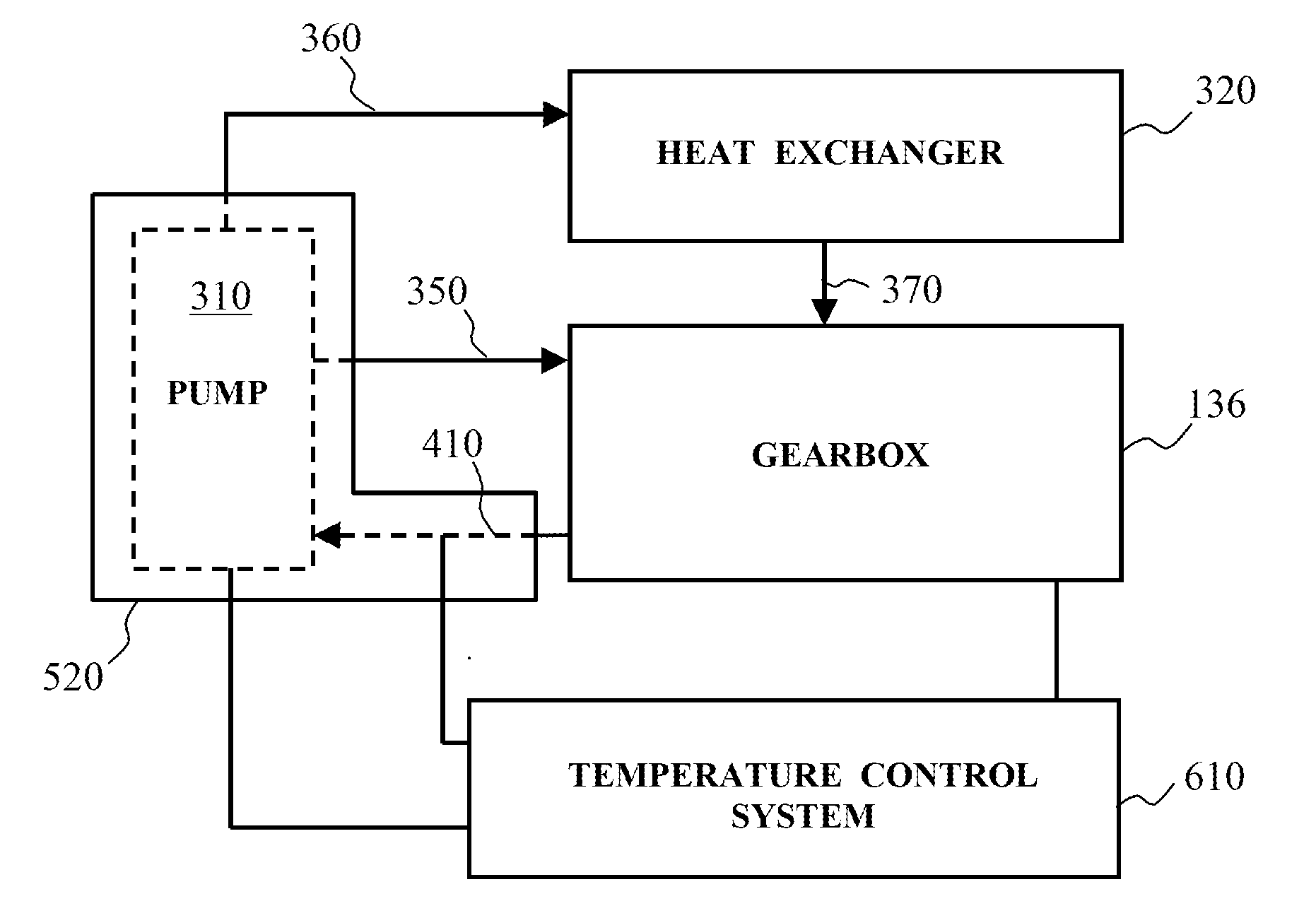
Lubrication heating system and wind turbine incorporating same
A wind turbine is provided having a gearbox containing a lubrication medium, a pump for circulating the lubrication medium. and a gearbox lubrication suction pipe for transporting the lubrication medium from the gearbox to the pump. A heater is in thermal connection to, at least a portion of, the gearbox lubrication suction pipe. This heater is used to heat the lubrication medium contained within the gearbox lubrication suction pipe to a temperature where damage to the pump is avoided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Noise reducer for rotor blade in wind turbine
A rotor blade assembly for a wind turbine is disclosed. The rotor blade assembly includes a rotor blade having a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root, the rotor blade further defining a pitch axis. The rotor blade assembly further includes a noise reducer mounted to the rotor blade. The noise reducer includes a base plate defining a base line, a plurality of noise reduction features extending from the base line, and a plurality of apertures defined in the base plate. Each aperture is positioned on an opposite side of the base line from the plurality of noise reduction features such that the aperture is fully defined in the base plate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Independent sensing system for wind turbines
InactiveUS20090232635A1Preventing and eliminating propagationPermit flexibilityPropellersWind motor controlTurbineWind force
A wireless sensing device for use in a wind turbine having a sensor capable of measuring one or more parameters for wind turbine operation. The sensing device also include a transmission device capable of wirelessly transmitting one or more signals corresponding to the one or more measured parameters to a controller. An independent power source is included to power the transmission device and the sensor. A method for system for operating and monitoring wind turbine operation are also disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for pressure adaptive morphing structure
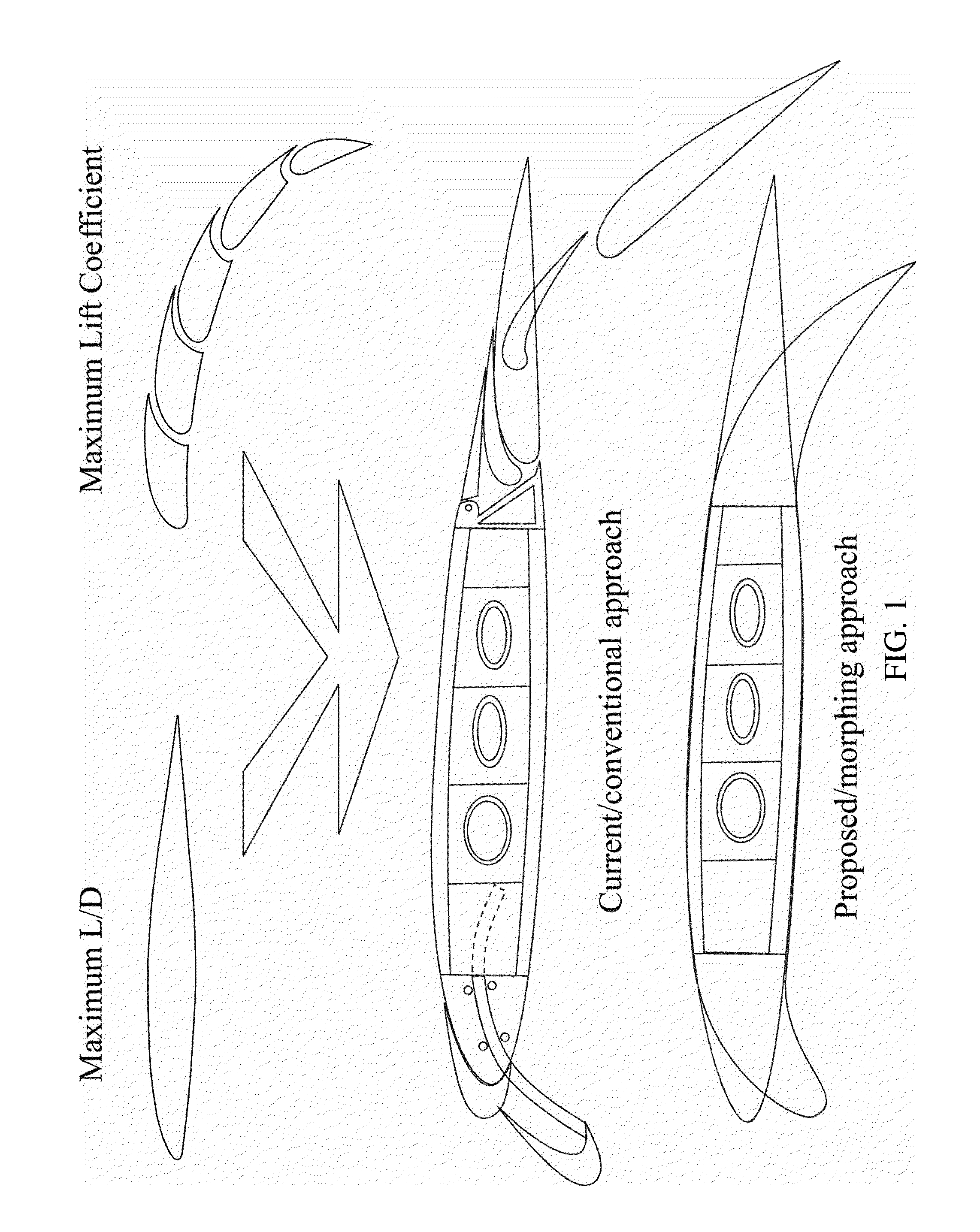
ActiveUS20110038727A1Altered stiffnessMaximize efficiencyPropellersAircraft stabilisationMorphingDifferential pressure
A method and apparatus for a novel adaptive aerostructure is presented that relies on certified aerospace materials and can therefore be applied in conventional passenger aircraft. This structure consists of a honeycomb material which cells extend over a significant length perpendicular to the plane of the cells. Each of the cells contains an inelastic pouch (or bladder) that forms a circular tube when the cell forms a perfect hexagon. By changing the cell differential pressure (CDP) the stiffness of the honeycomb can be altered. Using an external force or the elastic force within the honeycomb material, the honeycomb can be deformed such that the cells deviate from their perfect-hexagonal shape. It can be shown that by increasing the CDP, the structure eventually returns to a perfect hexagon. By doing so, a fully embedded pneumatic actuator is created that can perform work and substitute conventional low-bandwidth flight control actuators. It is shown that two approaches can be taken to regulate the stiffness of this embedded actuator.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
System and method for monitoring and controlling wind turbine blade deflection
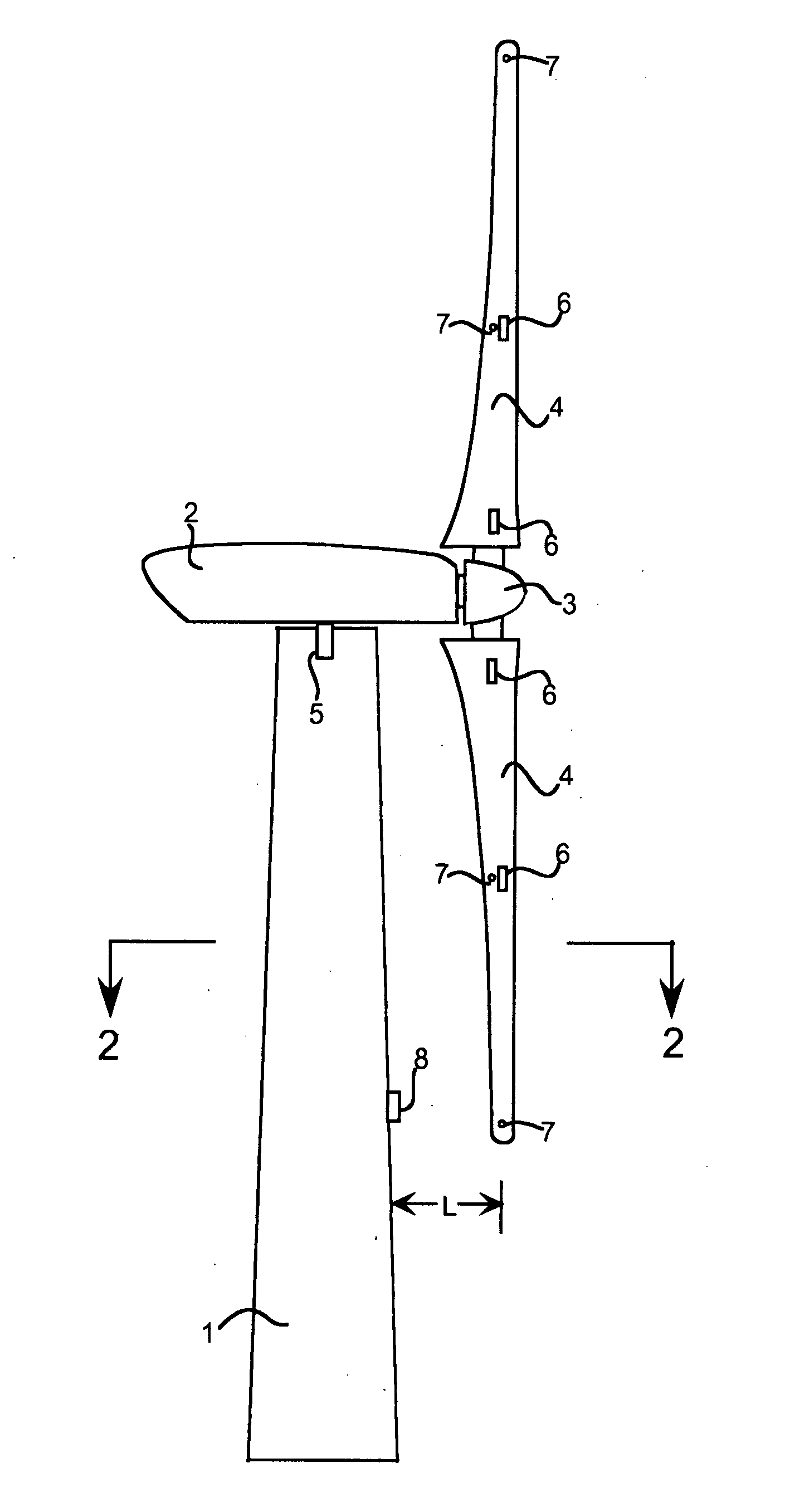
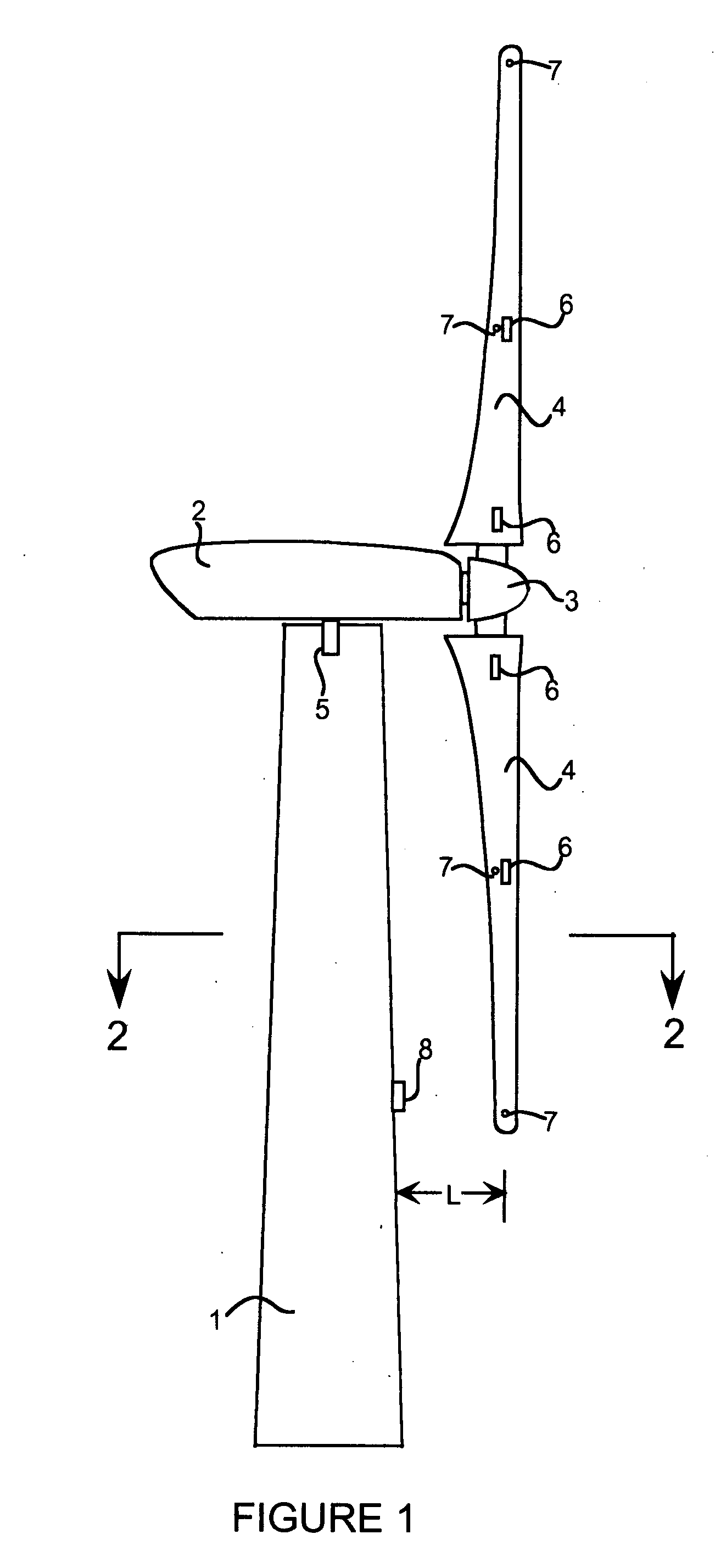
A system is disclosed for monitoring and controlling the deflection of turbine blades of a wind turbine. The system includes a passive position detecting apparatus and a controller. The passive position detecting apparatus may be configured to acquire and transmit data relating directly to a position of at least one of the turbine blades. The controller may be configured to receive the data from the passive position detecting apparatus and compare such data to a known position reference to determine turbine blade deflection.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for measuring wind turbine blade deflection
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
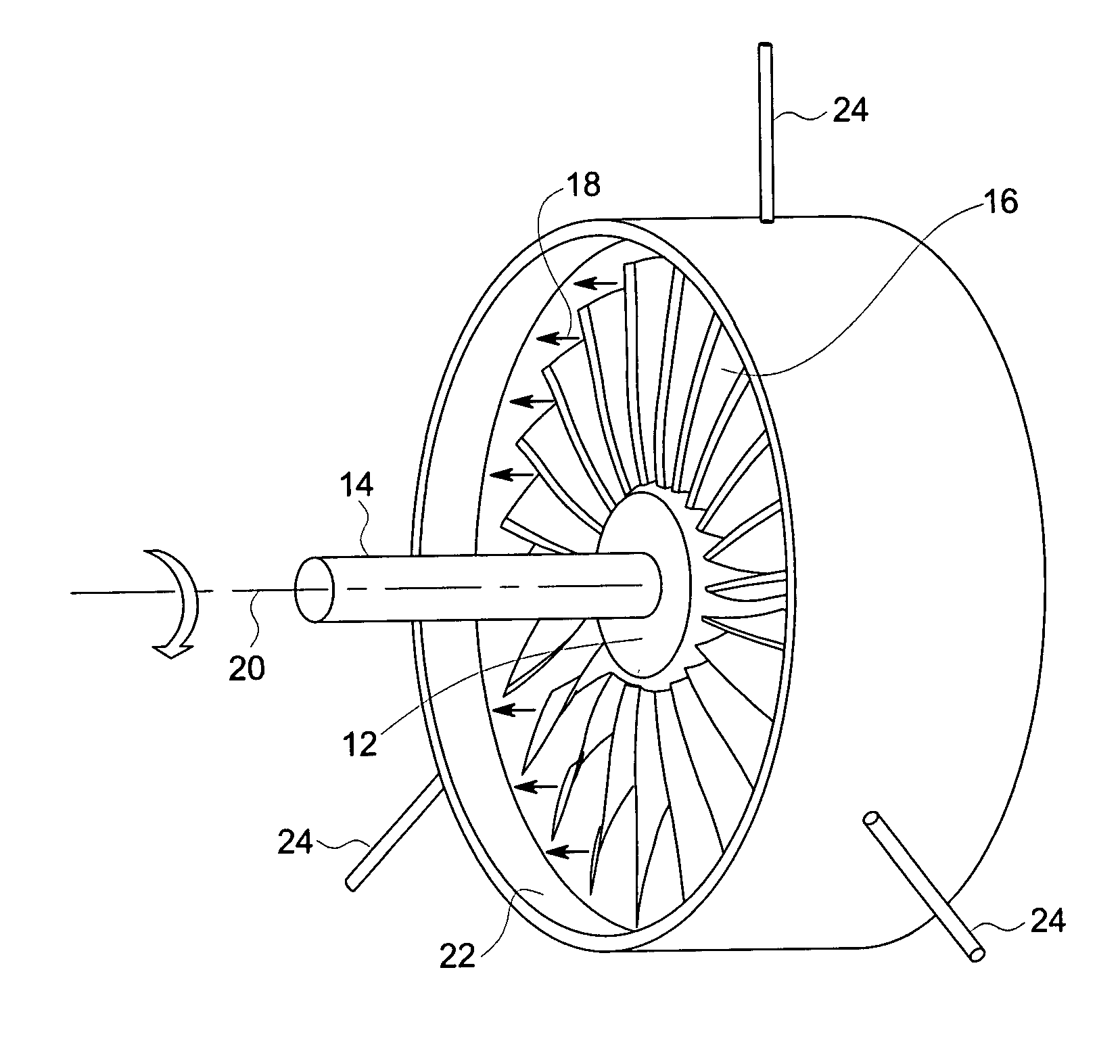
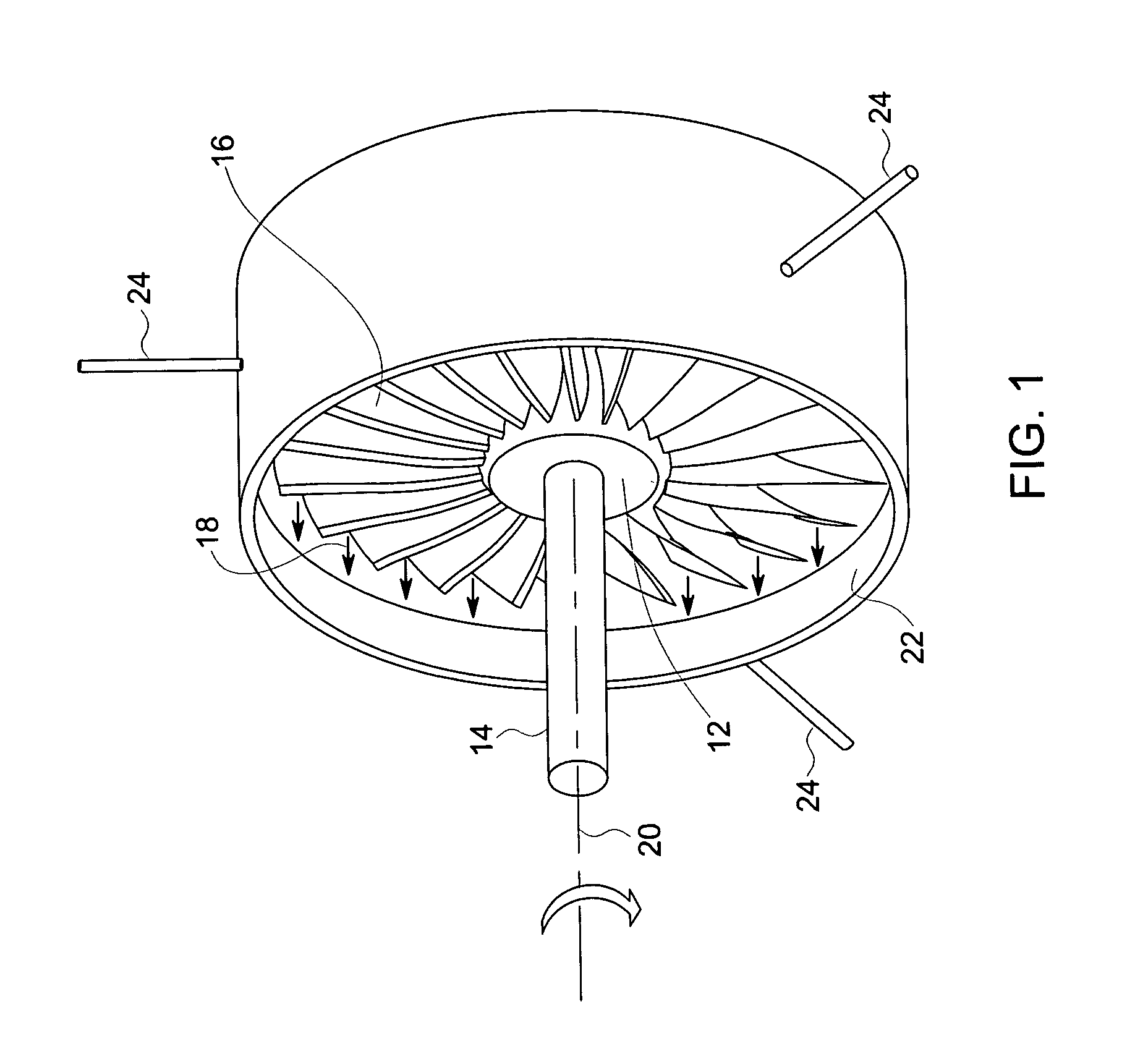
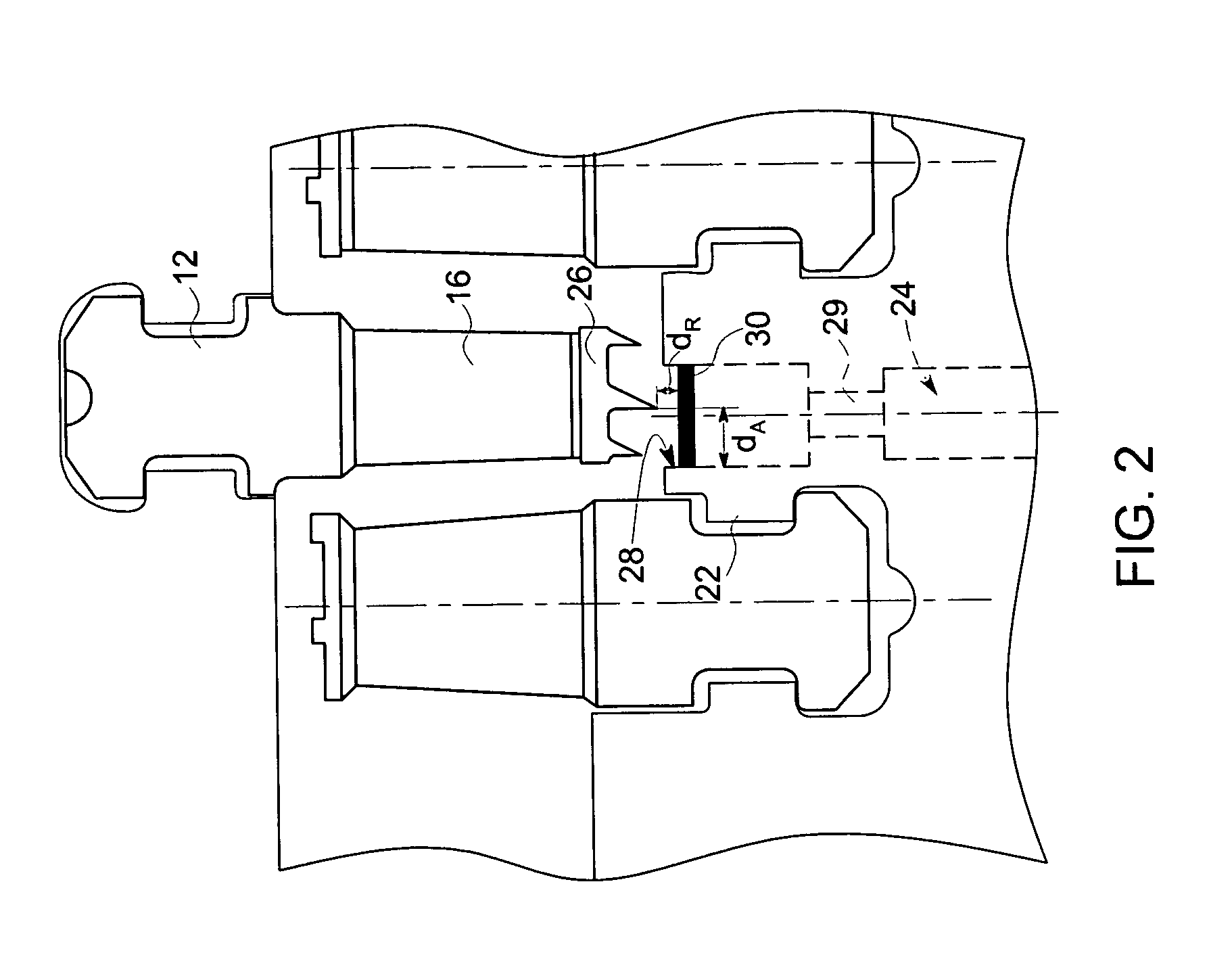
Displacement sensor system and method of operation
A clearance sensing system for a rotating machine includes a plurality of sensor probes disposed within a stationary shroud of the rotating machine. Each of the plurality of sensor probes is adapted to measure a parameter indicative of an axial and a radial displacement of a rotating component within the shroud and to produce a signal that corresponds to the parameter. In certain embodiments, this parameter may include a capacitance between the rotating component and the sensor probe. The clearance sensing system further includes a circuit that receives the signal from each of the plurality of sensor probes and determines (a) the axial displacement of the rotating component within the shroud and (b) a radial displacement of the rotating component relative to the shroud.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com