Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
175 results about "Providing presence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
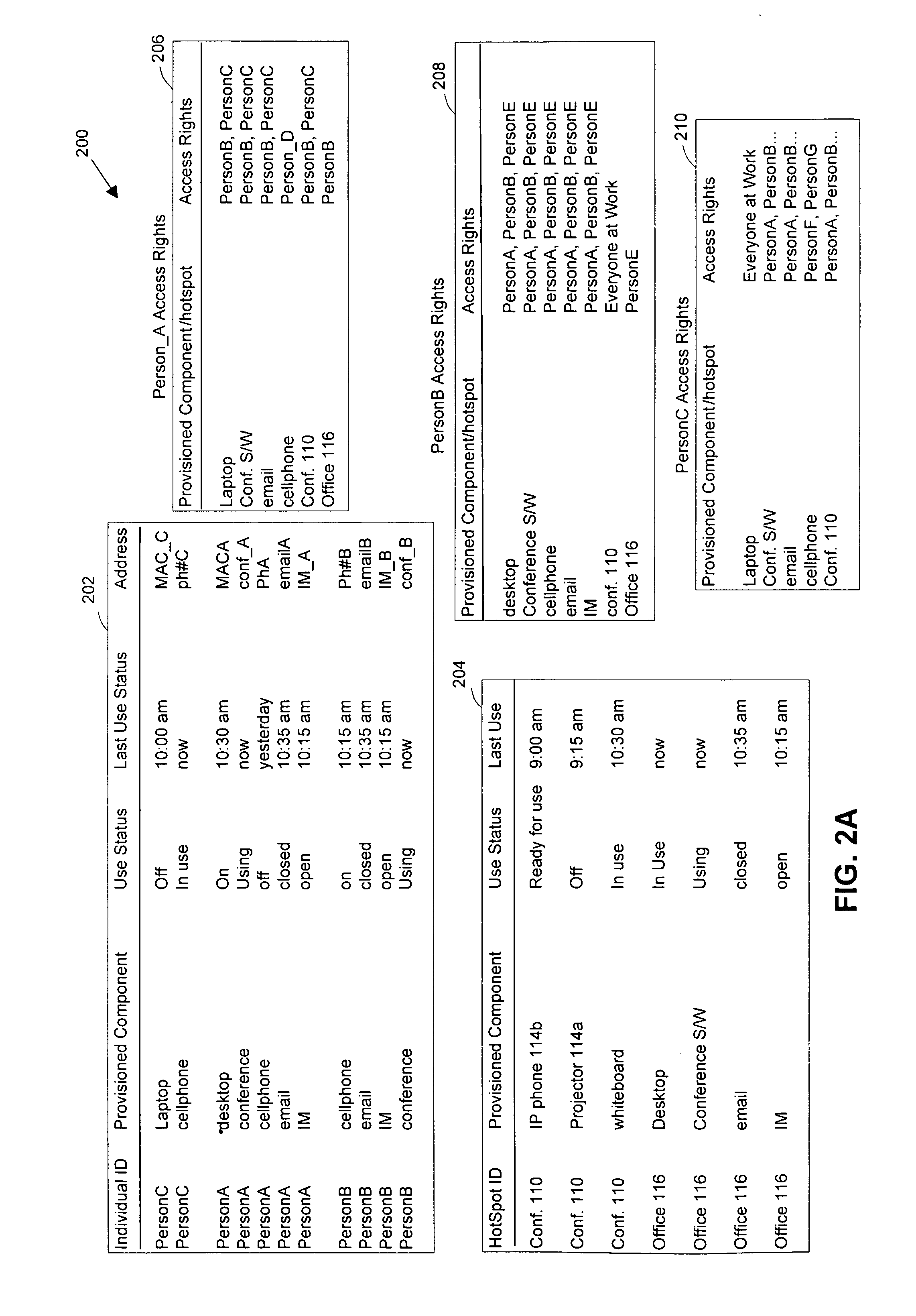
Method and system for rating patents and other intangible assets
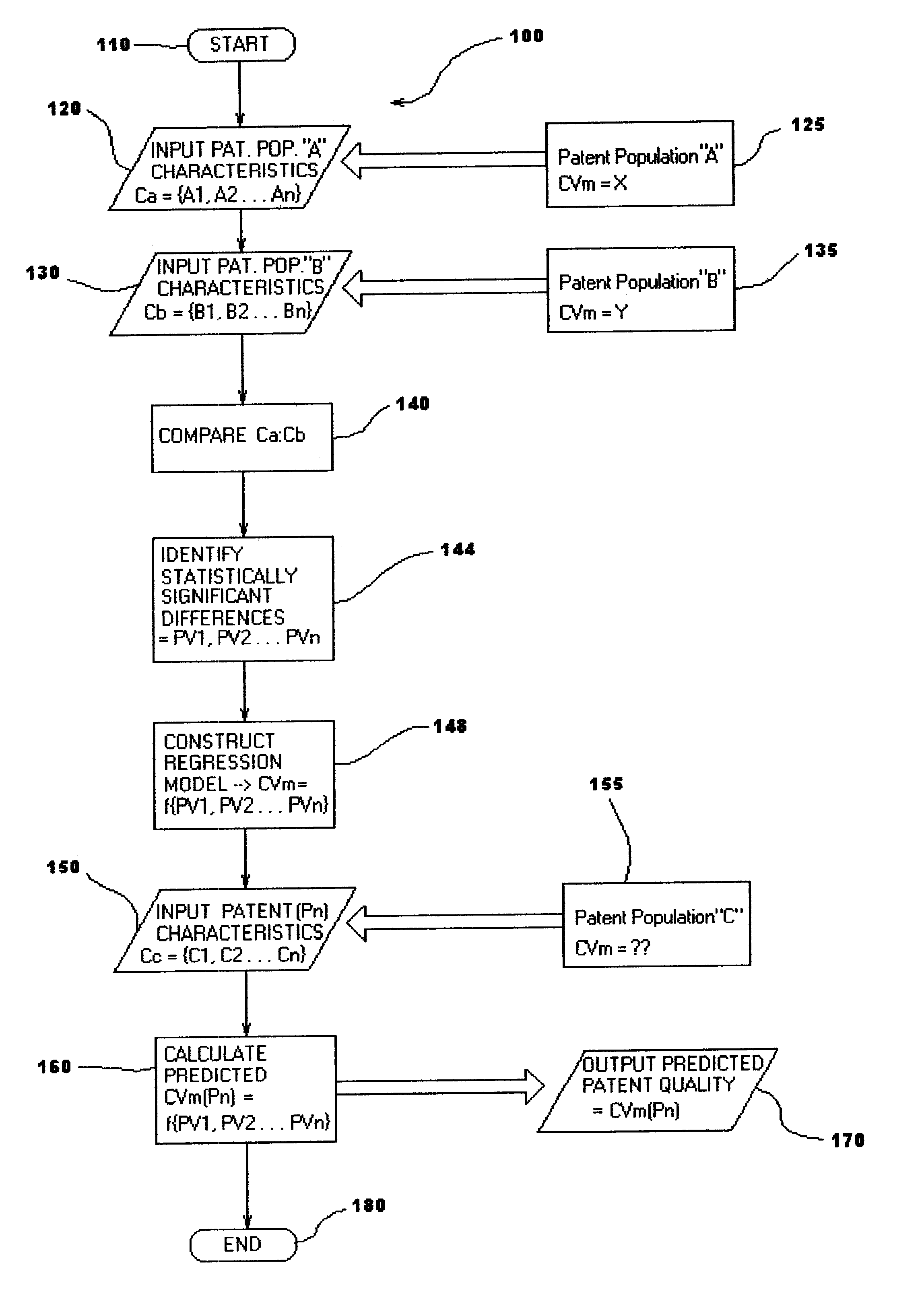
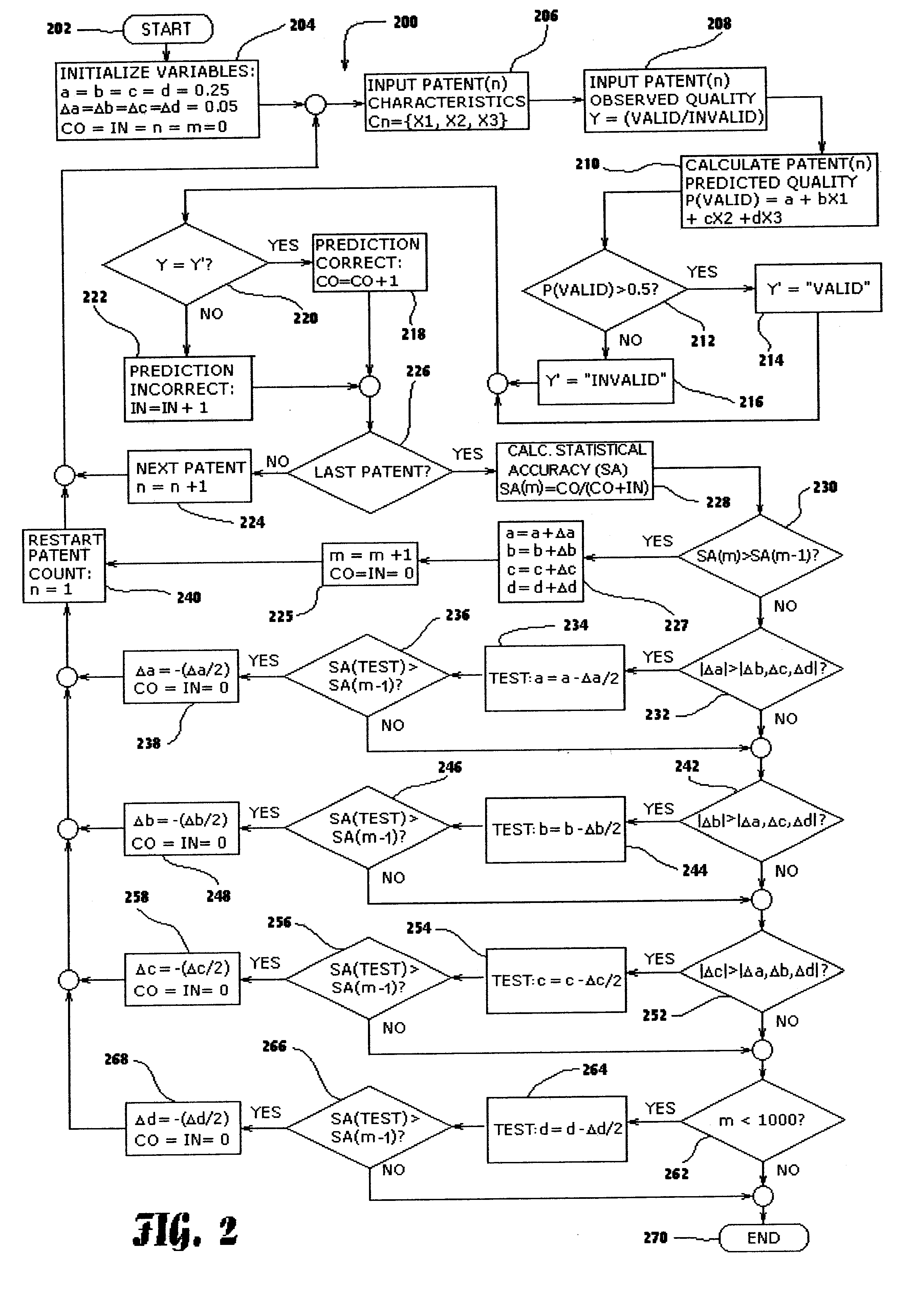
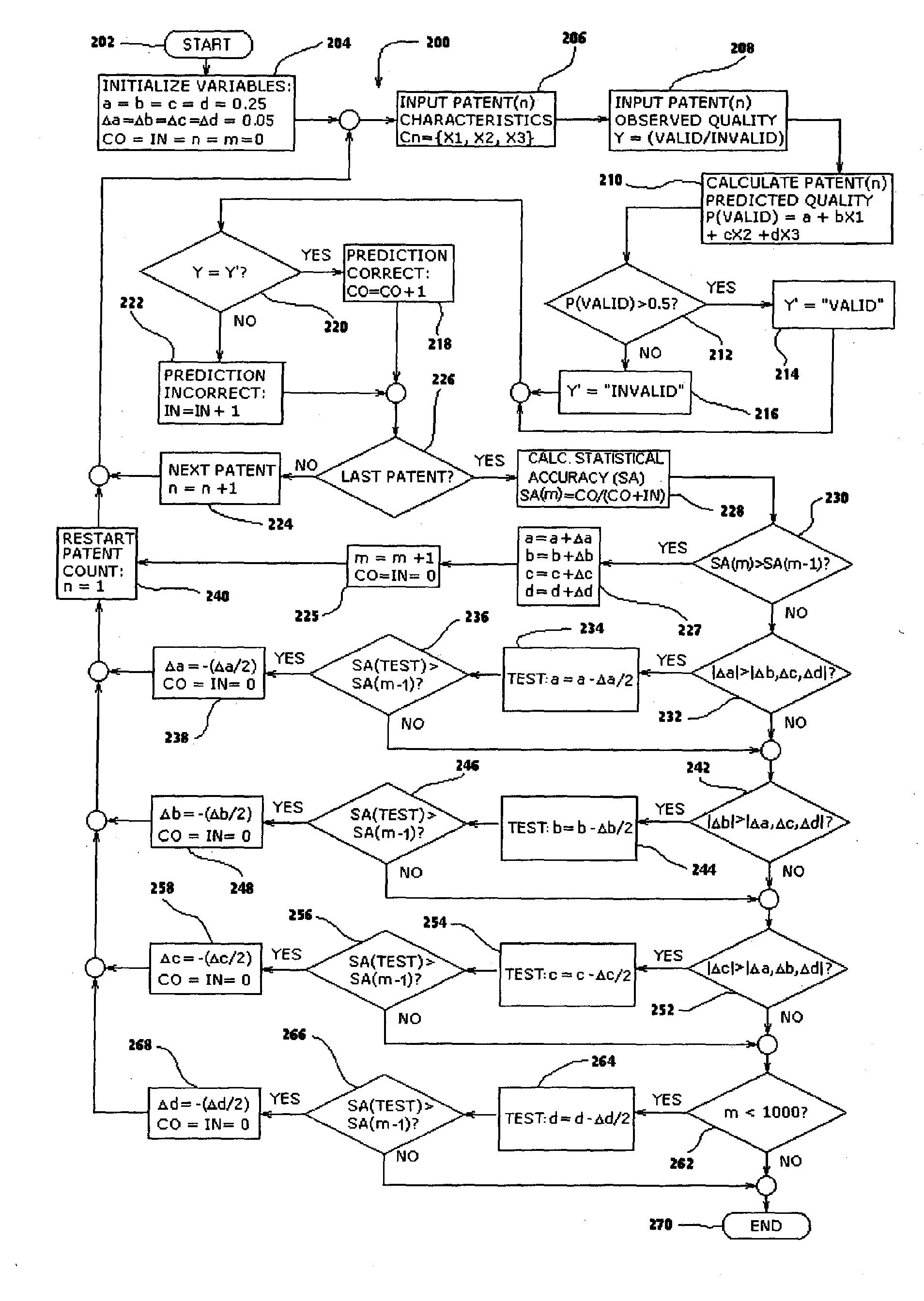
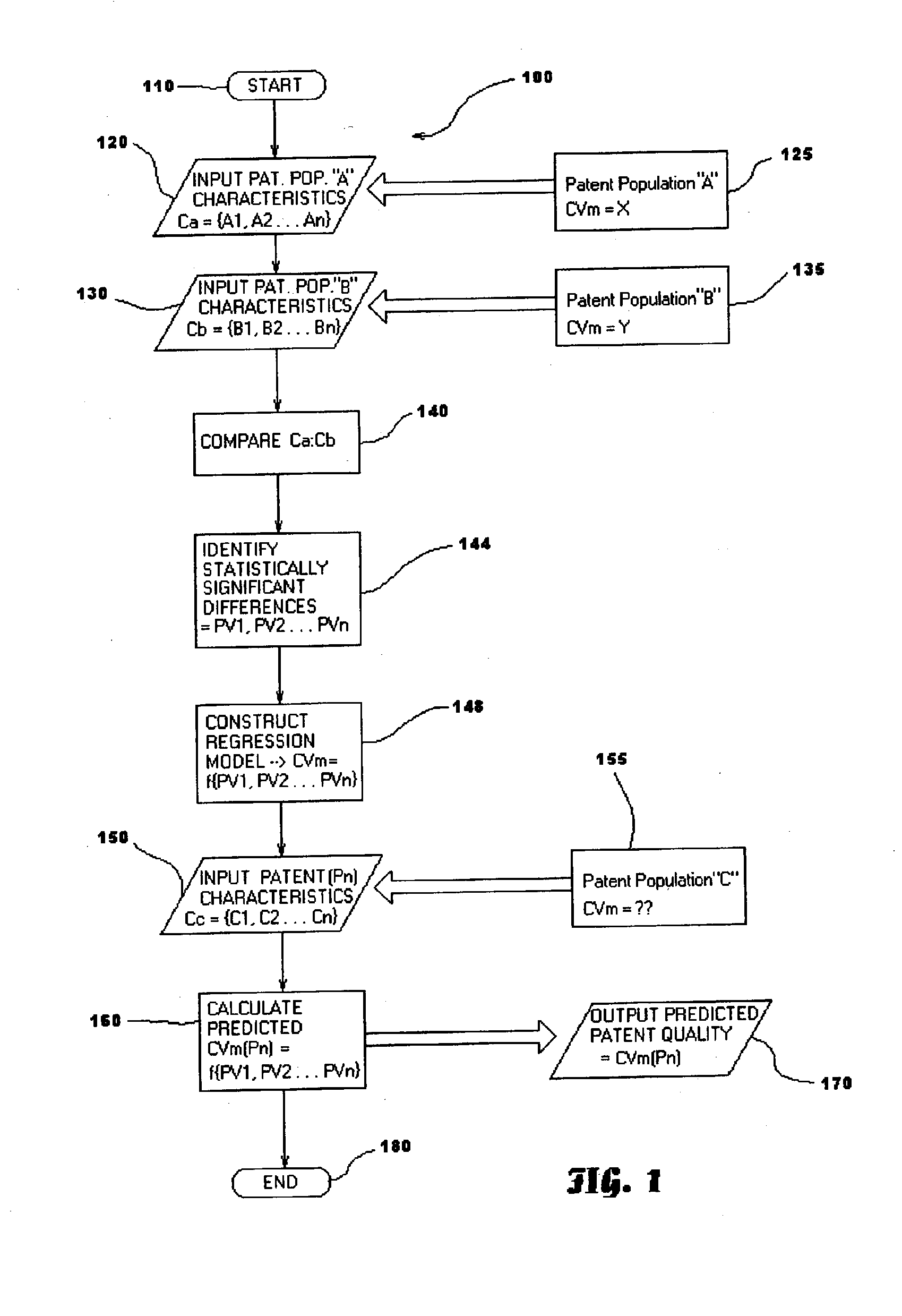
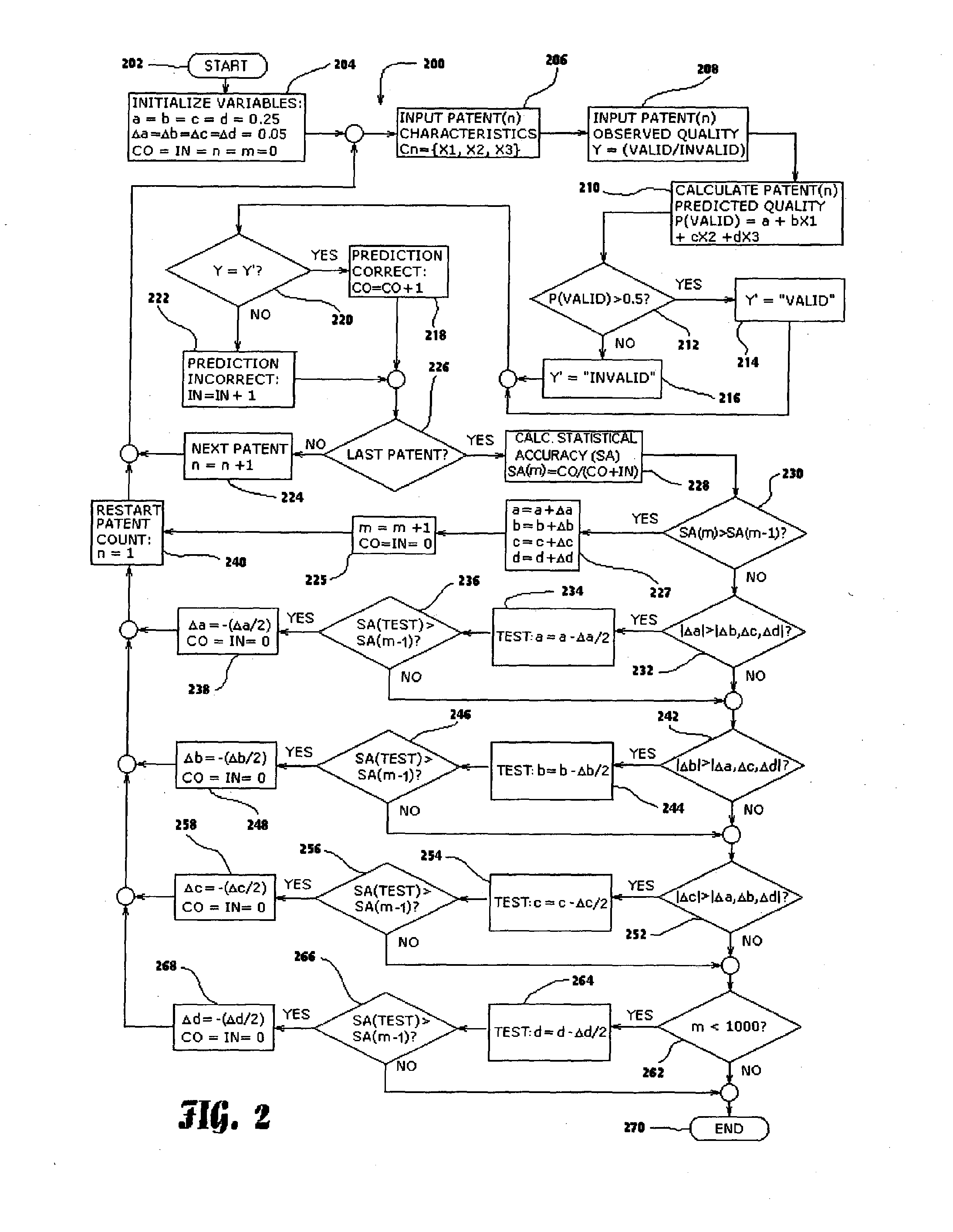
A statistical patent rating method and system is provided for independently assessing the relative breadth ("B"), defensibility ("D") and commercial relevance ("R") of individual patent assets and other intangible intellectual property assets. The invention provides new and valuable information that can be used by patent valuation experts, investment advisors, economists and others to help guide future patent investment decisions, licensing programs, patent appraisals, tax valuations, transfer pricing, economic forecasting and planning, and even mediation and / or settlement of patent litigation lawsuits. In one embodiment the invention provides a statistically-based patent rating method and system whereby relative ratings or rankings are generated using a database of patent information by identifying and comparing various characteristics of each individual patent to a statistically determined distribution of the same characteristics within a given patent population. For example, a first population of patents having a known relatively high intrinsic value or quality (e.g. successfully litigated patents) is compared to a second population of patents having a known relatively low intrinsic value or quality (e.g. unsuccessfully litigated patents). Based on a statistical comparison of the two populations, certain characteristics are identified as being more prevalent or more pronounced in one population group or the other to a statistically significant degree. Multiple such statistical comparisons are used to construct and optimize a computer model or computer algorithm that can then be used to predict and / or provide statistically-accurate probabilities of a desired value or quality being present or a future event occurring, given the identified characteristics of an individual patent or group of patents.
Owner:PATENTRATINGS
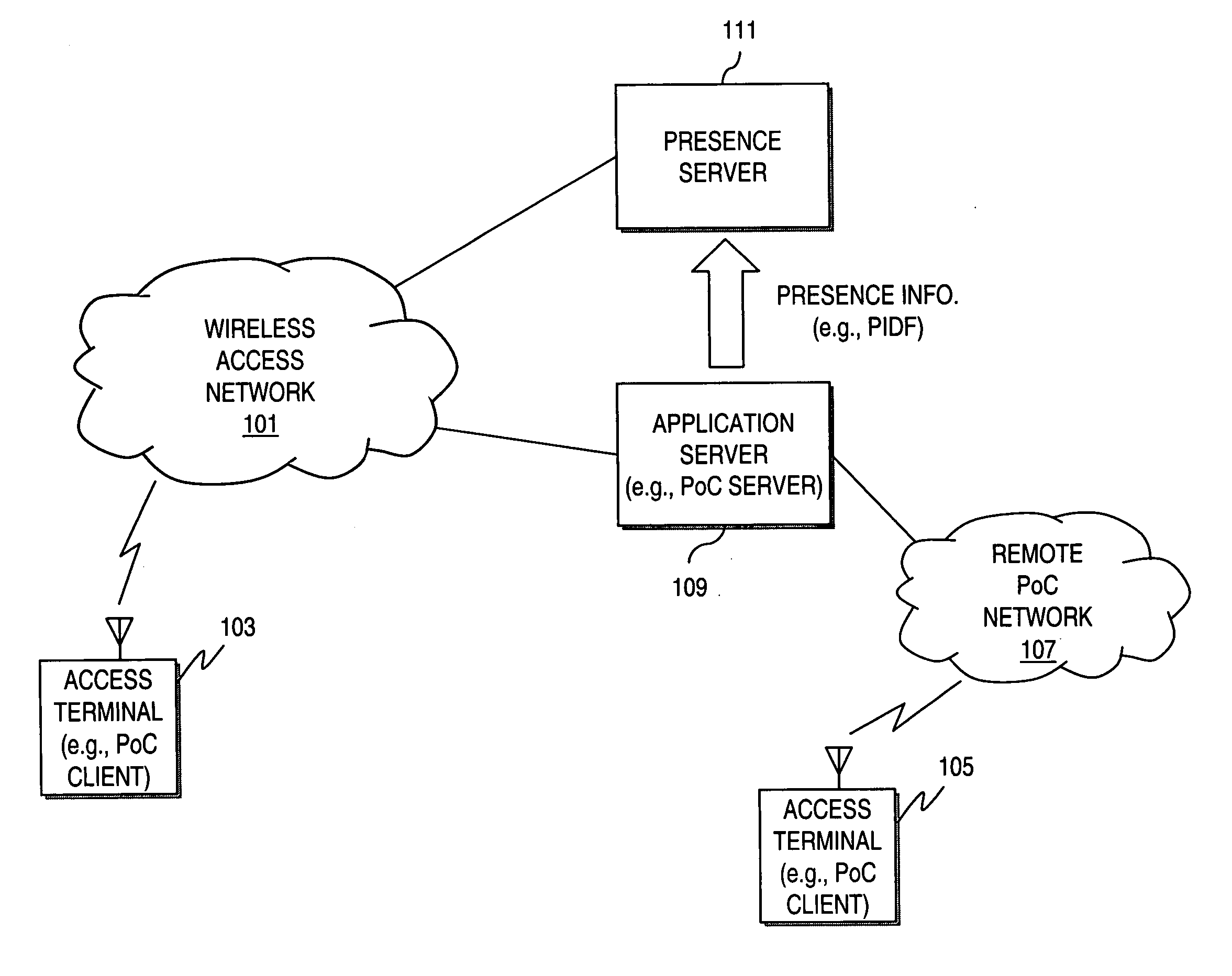
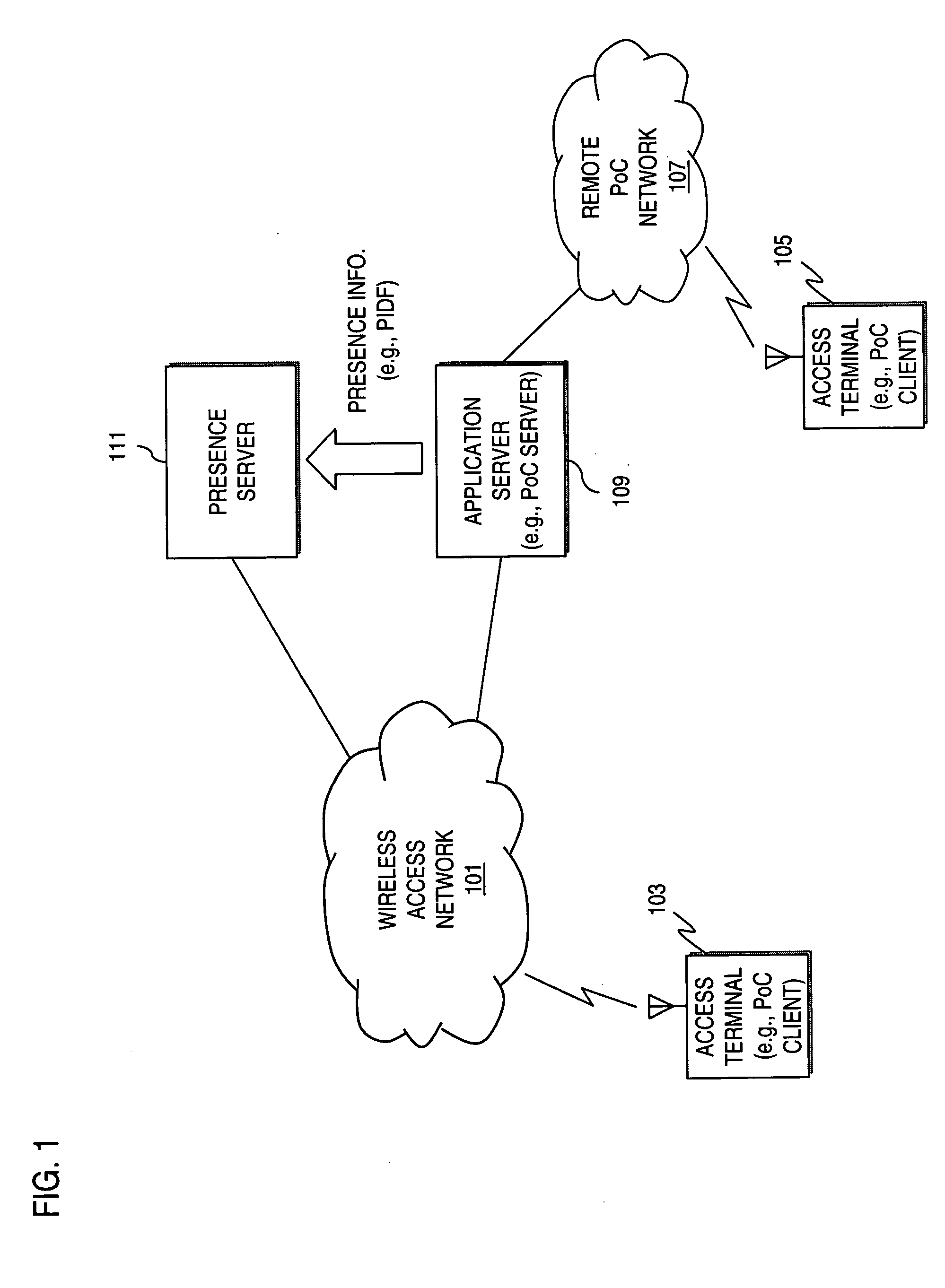
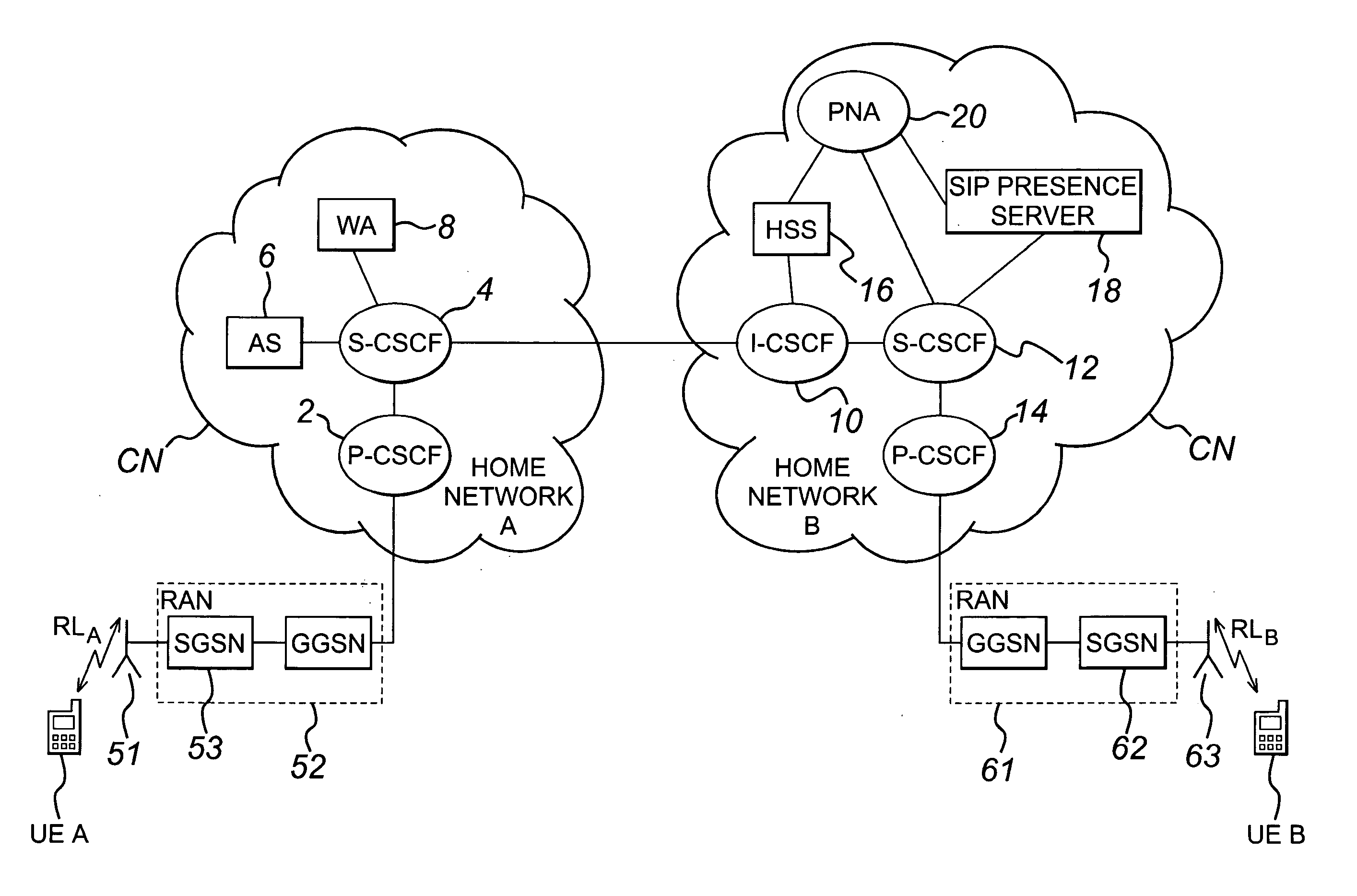
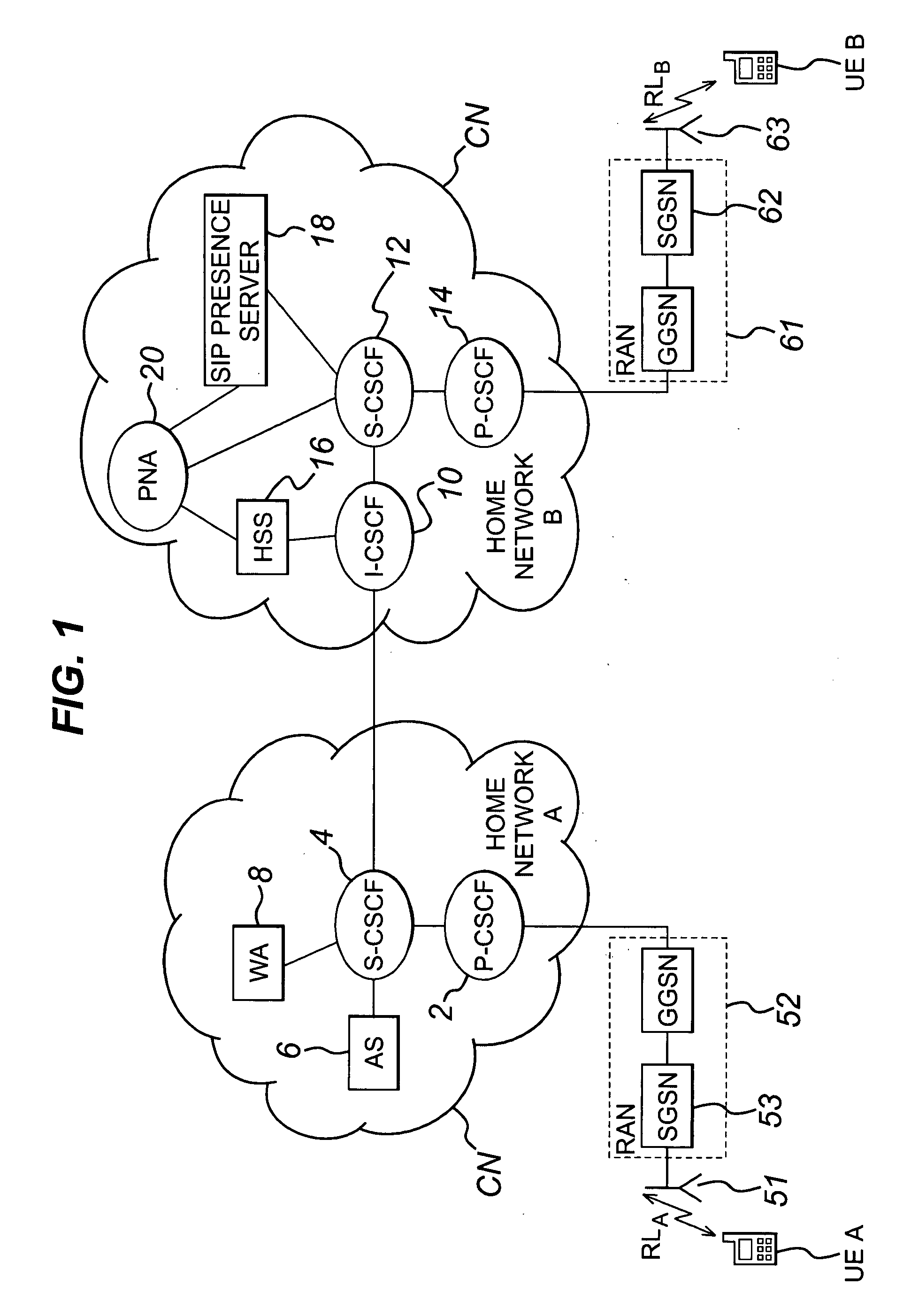
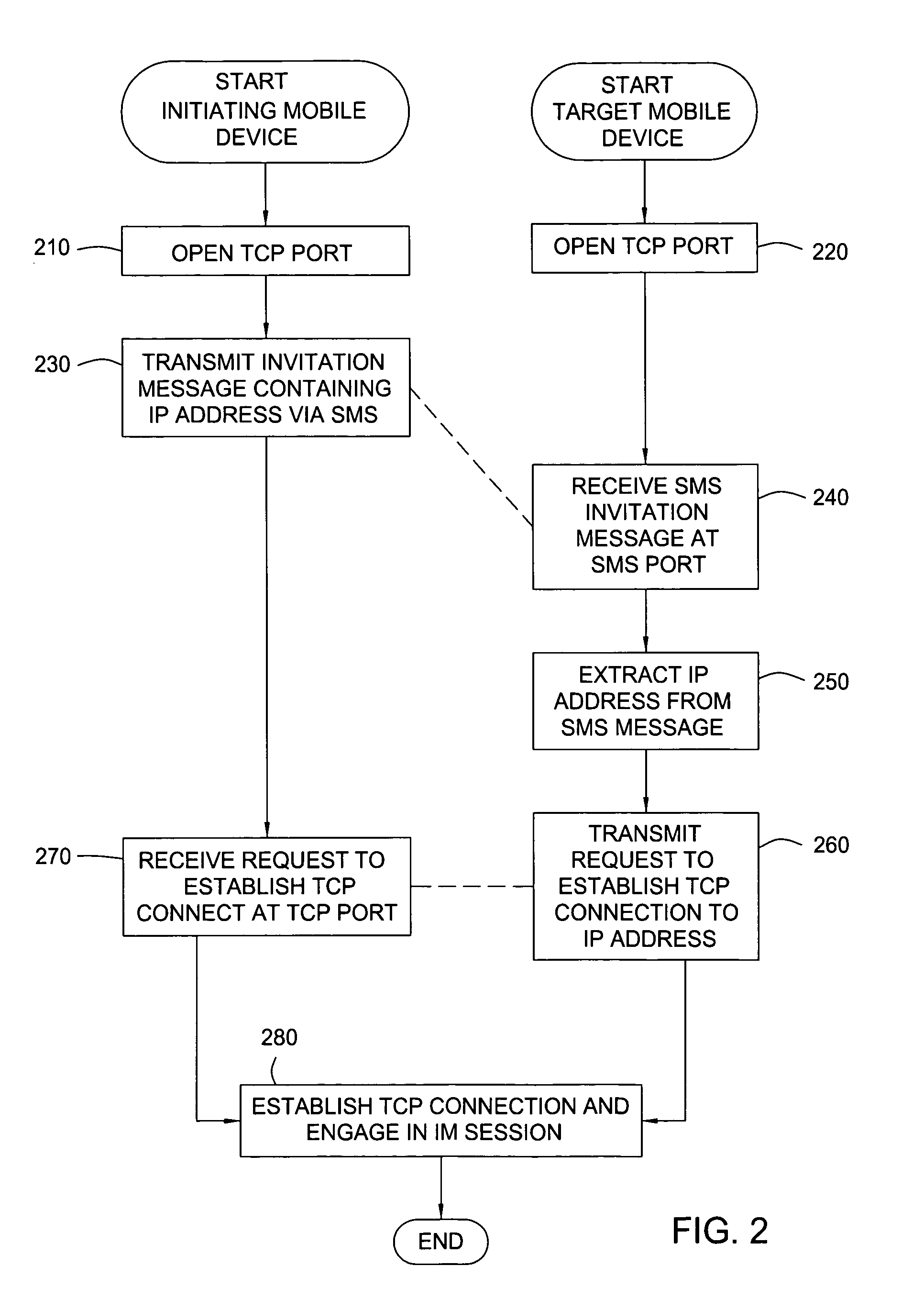
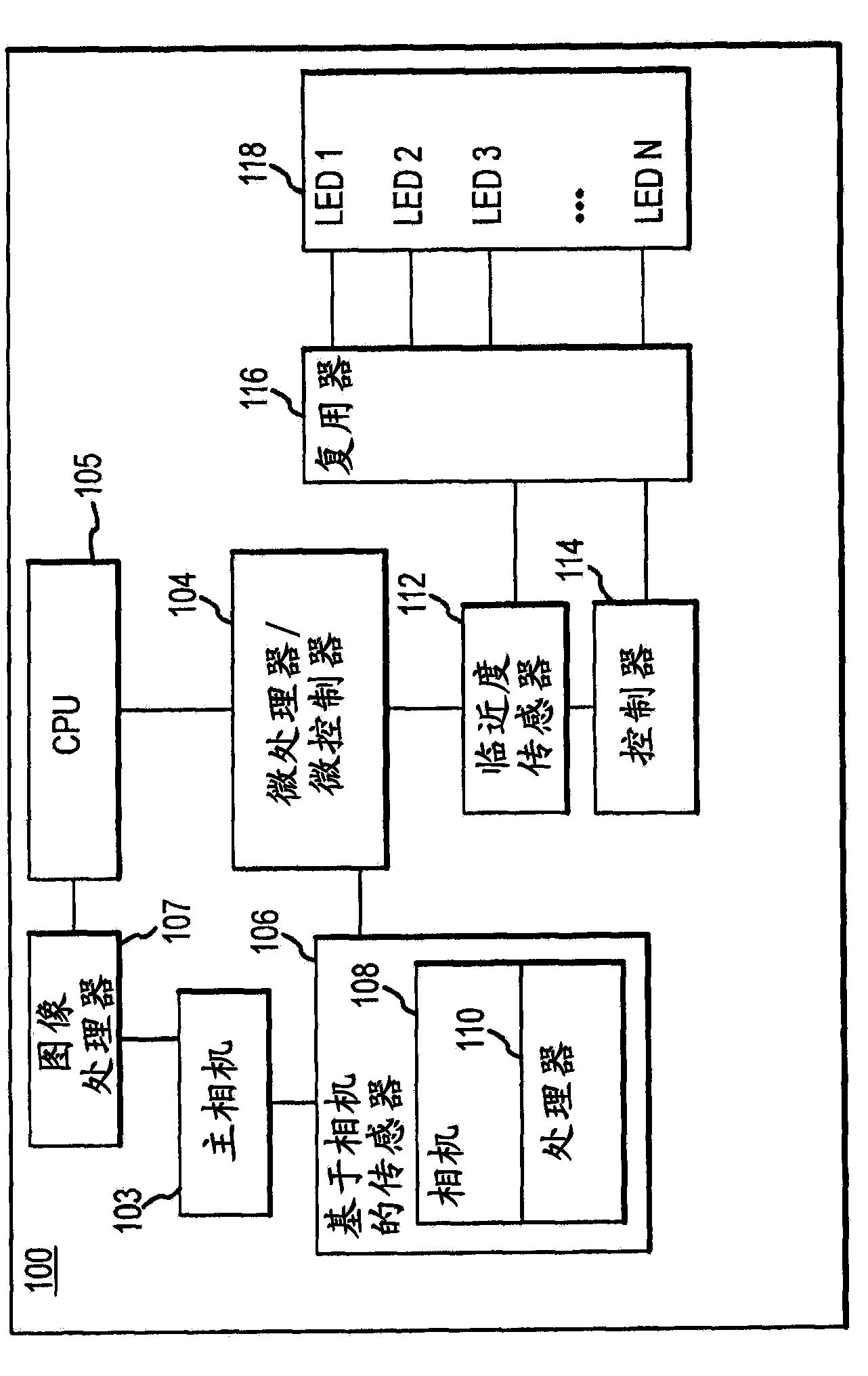
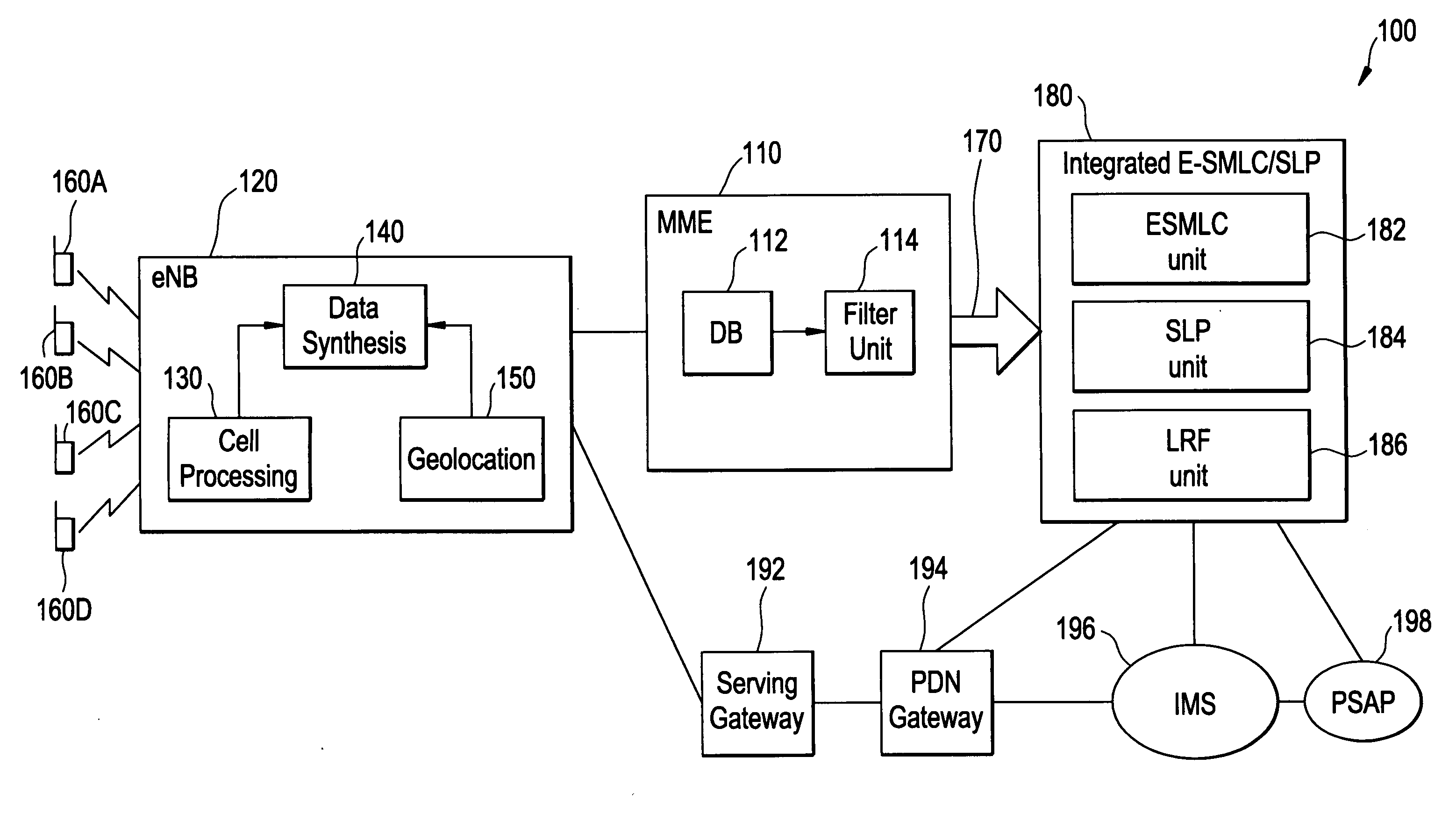
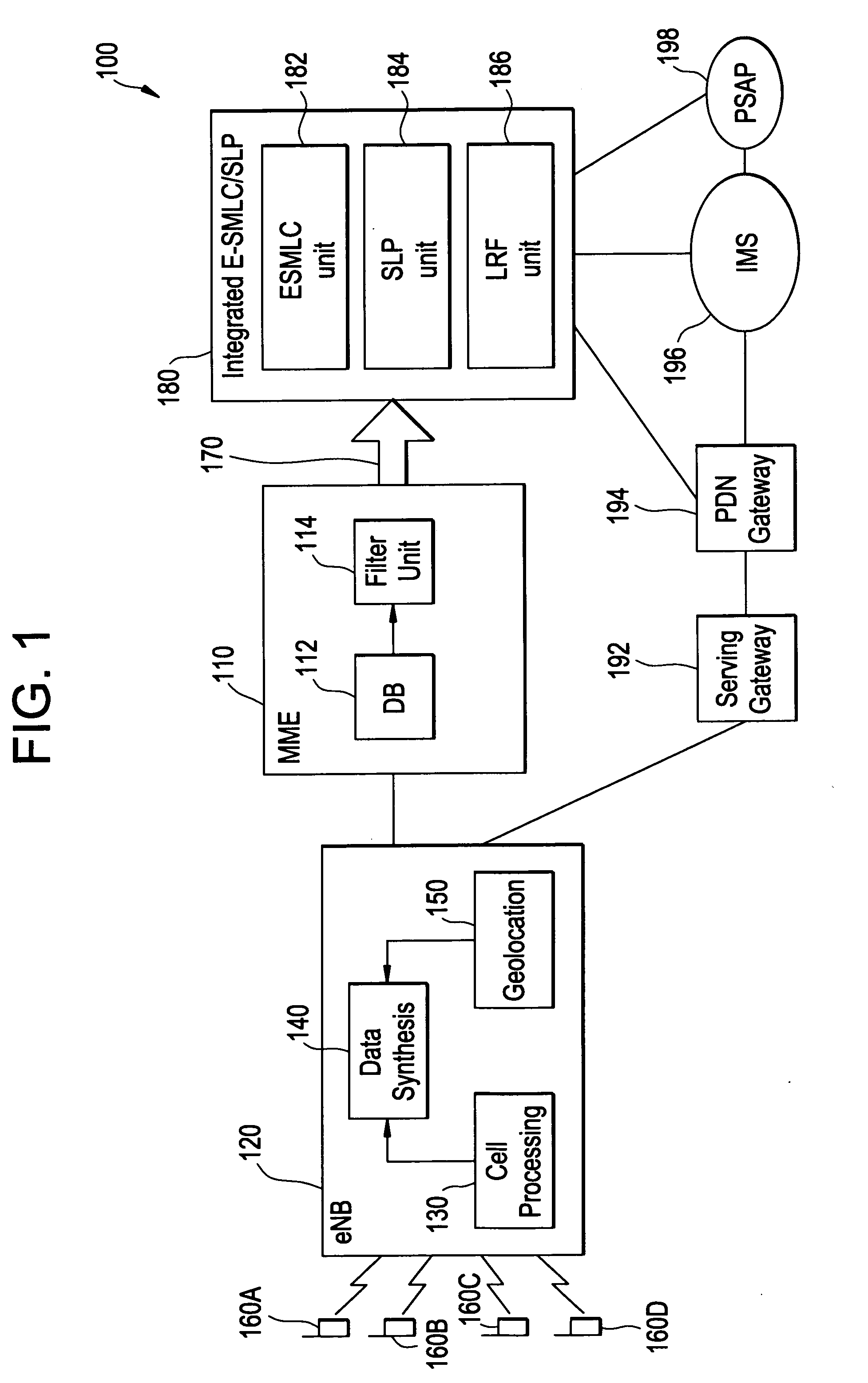
Method and apparatus for providing presence information
InactiveUS20070233859A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksTemporal informationState of art
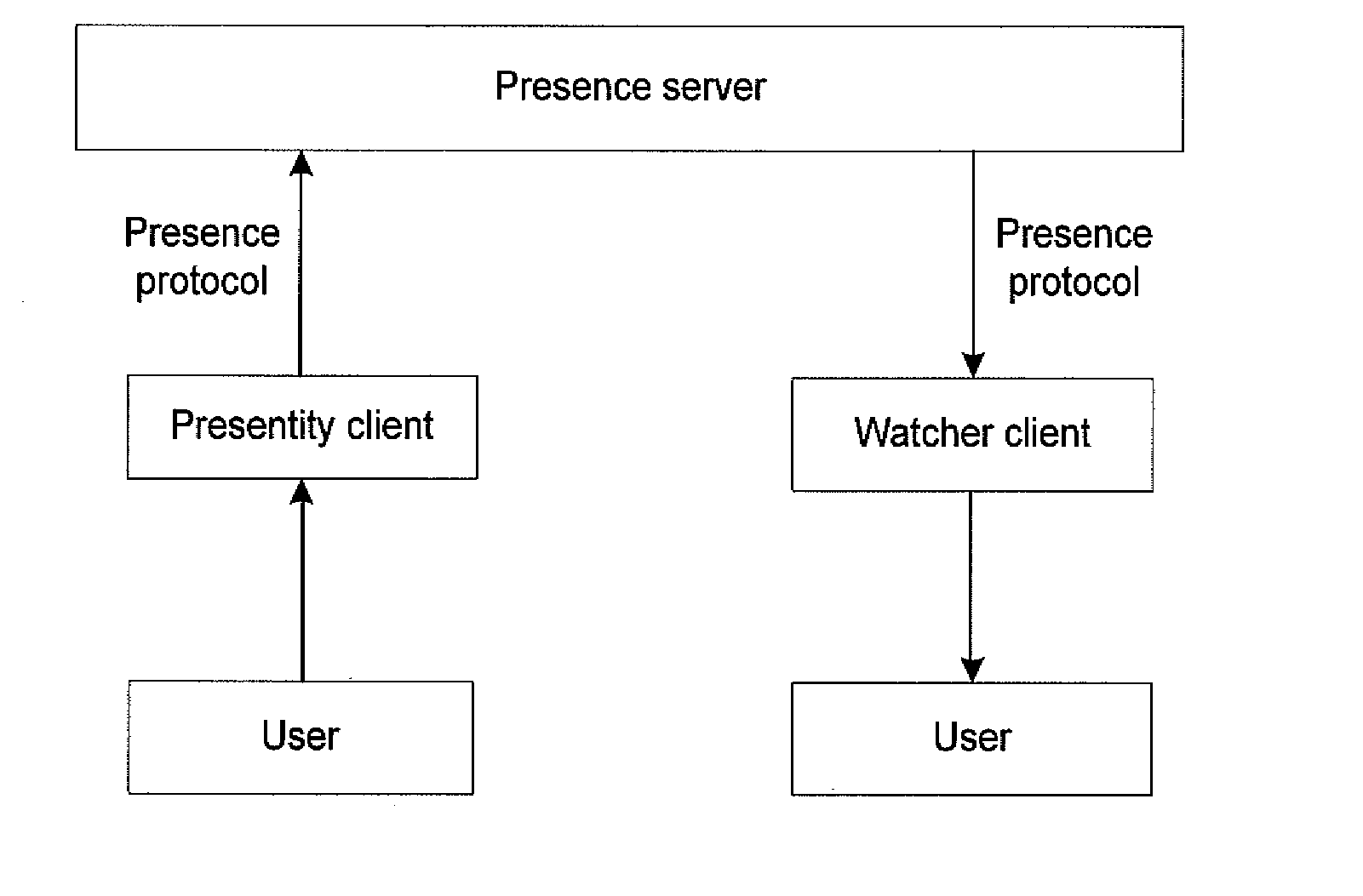
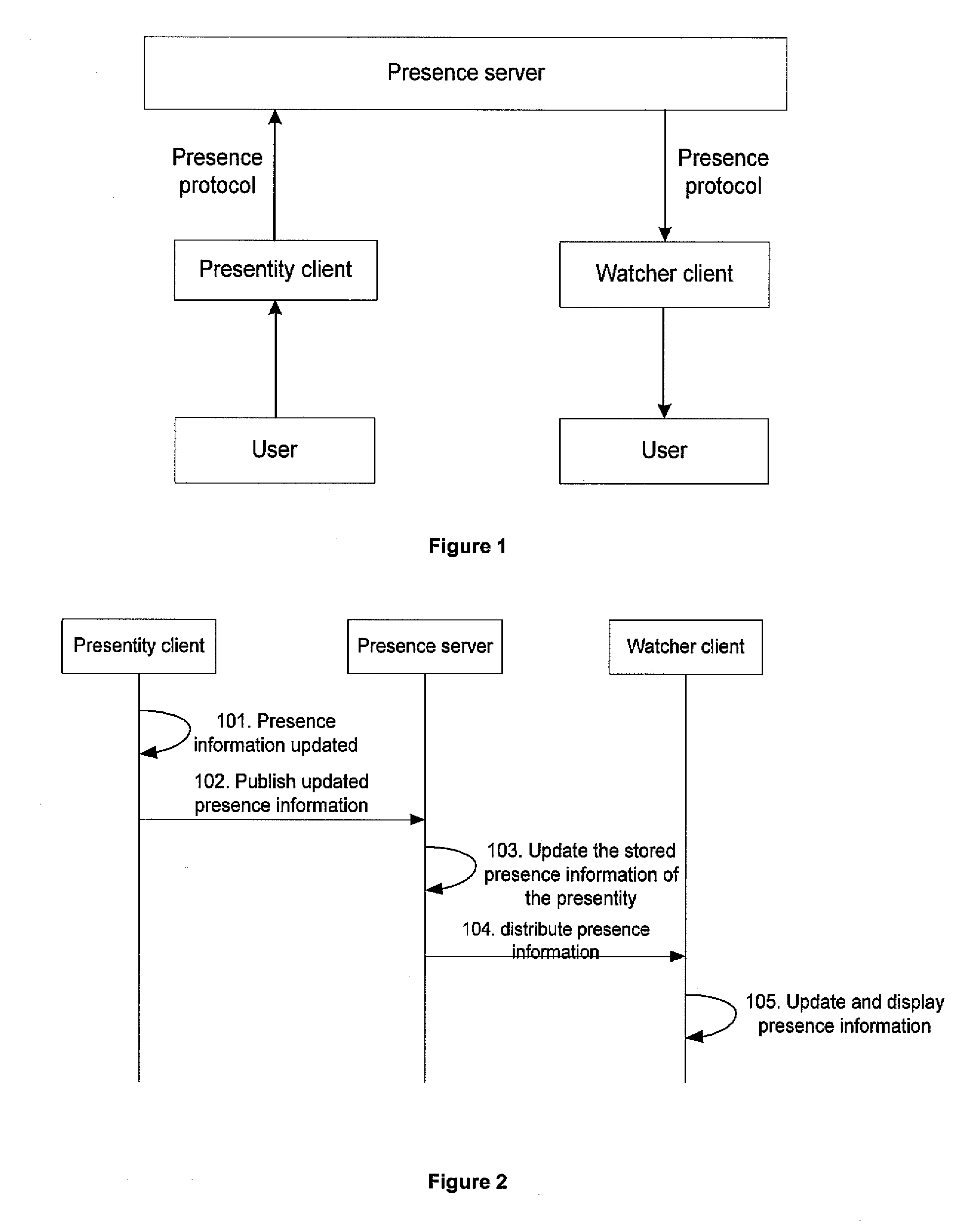
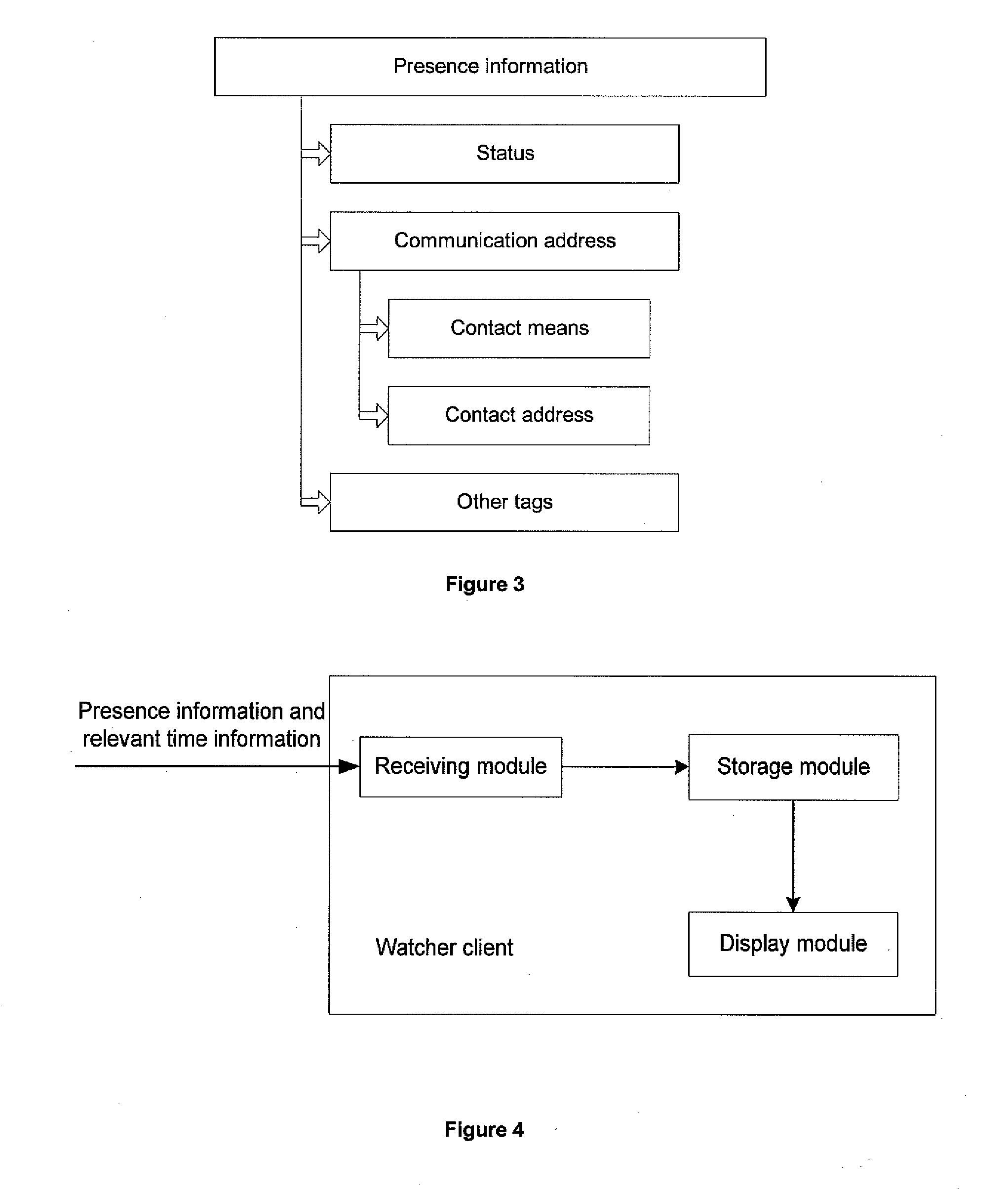
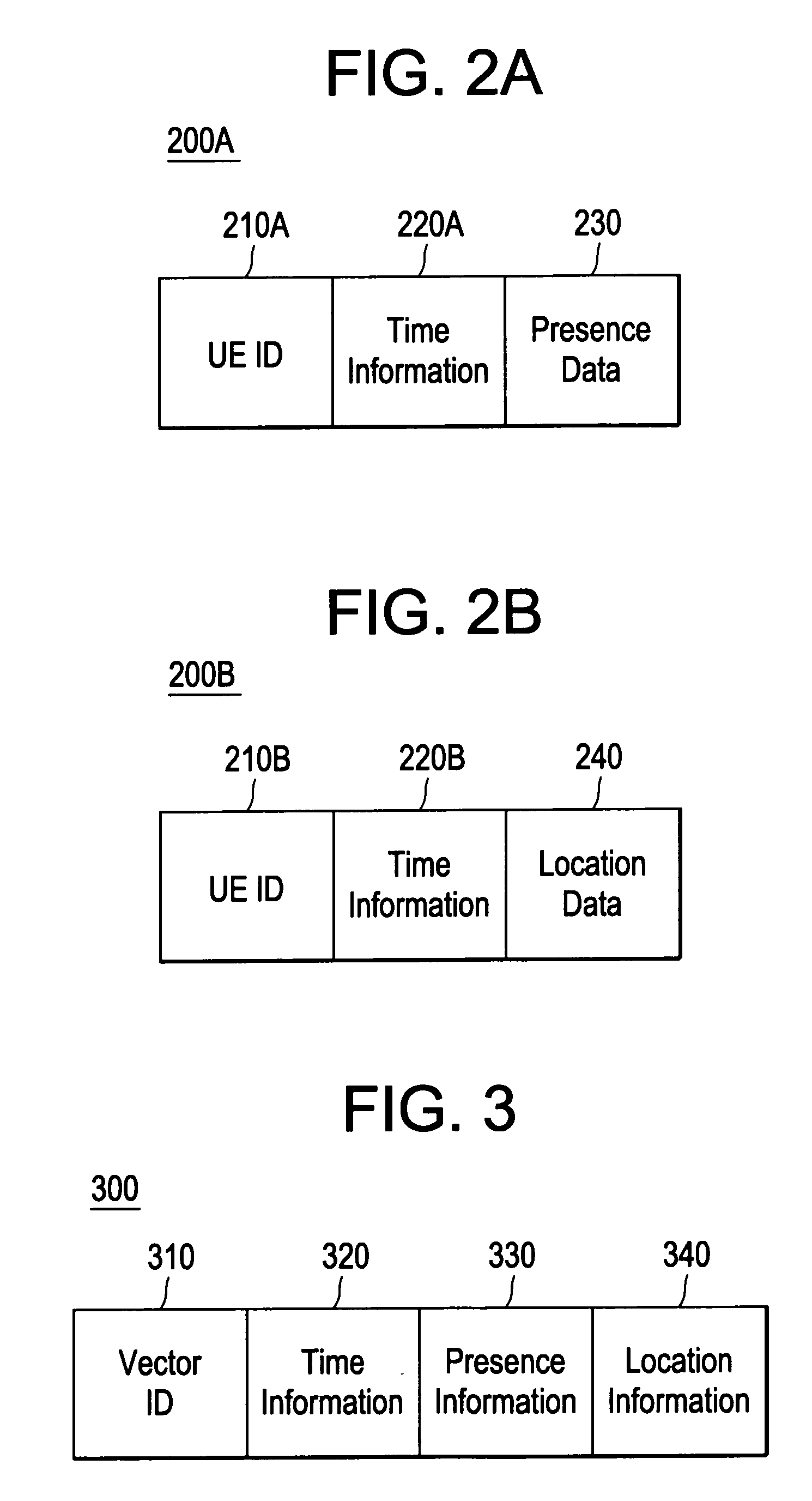
The present invention discloses a method for providing presence information, a watcher, a presence server, a presence system and a presentity. It enables the provisioning of history and future presence information, while the prior arts can provide only presence information corresponding to the current time. The method provided by the present invention includes: setting time elements of presence information; recording relevant time information of presence information in the time elements; providing the watcher with presence information together with relevant time information.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
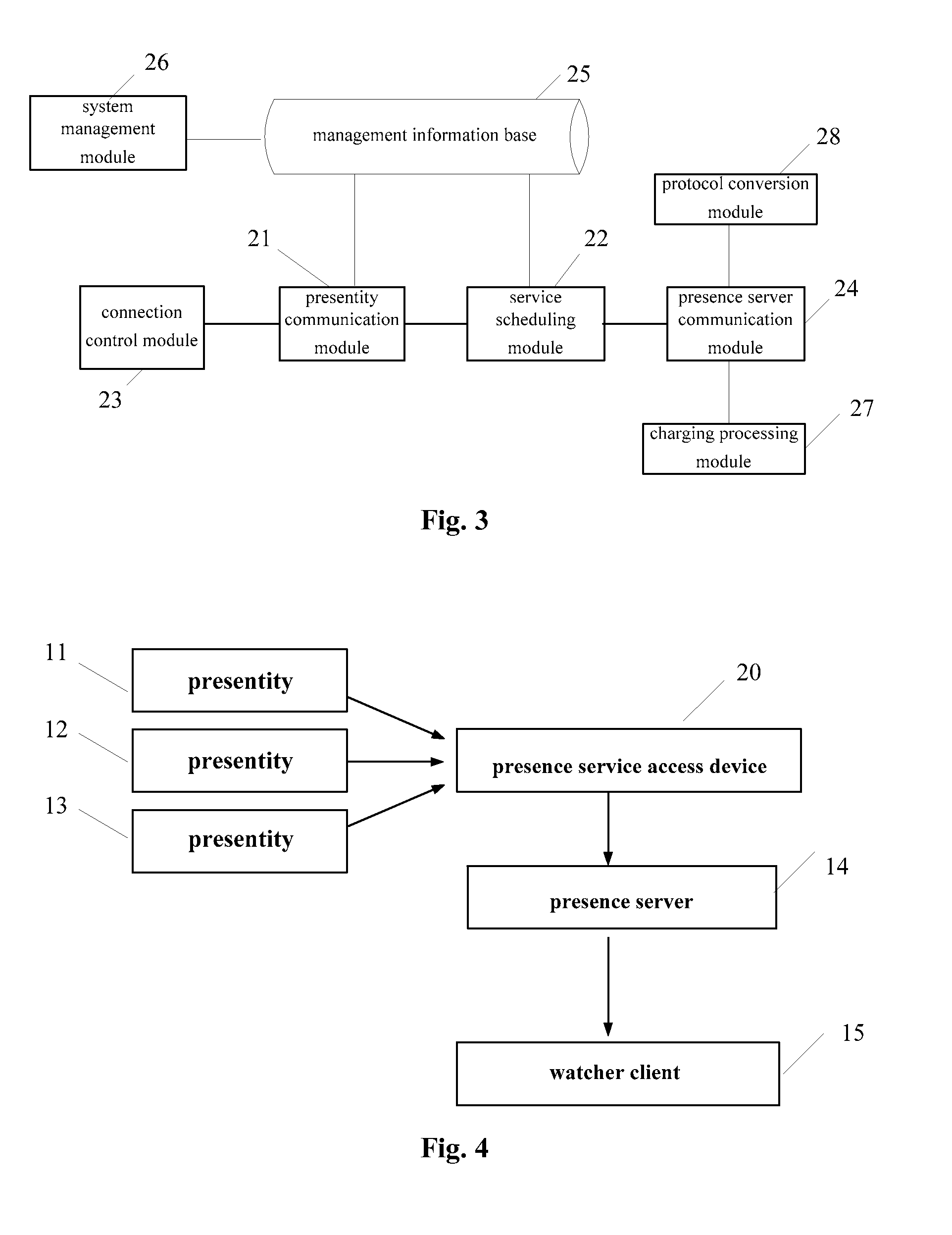
Presence service access device, presence service system and method for publishing and acquiring presence information
ActiveUS20080313329A1Reduce loadImprove efficiencyDigital computer detailsOffice automationPresence serviceProviding presence
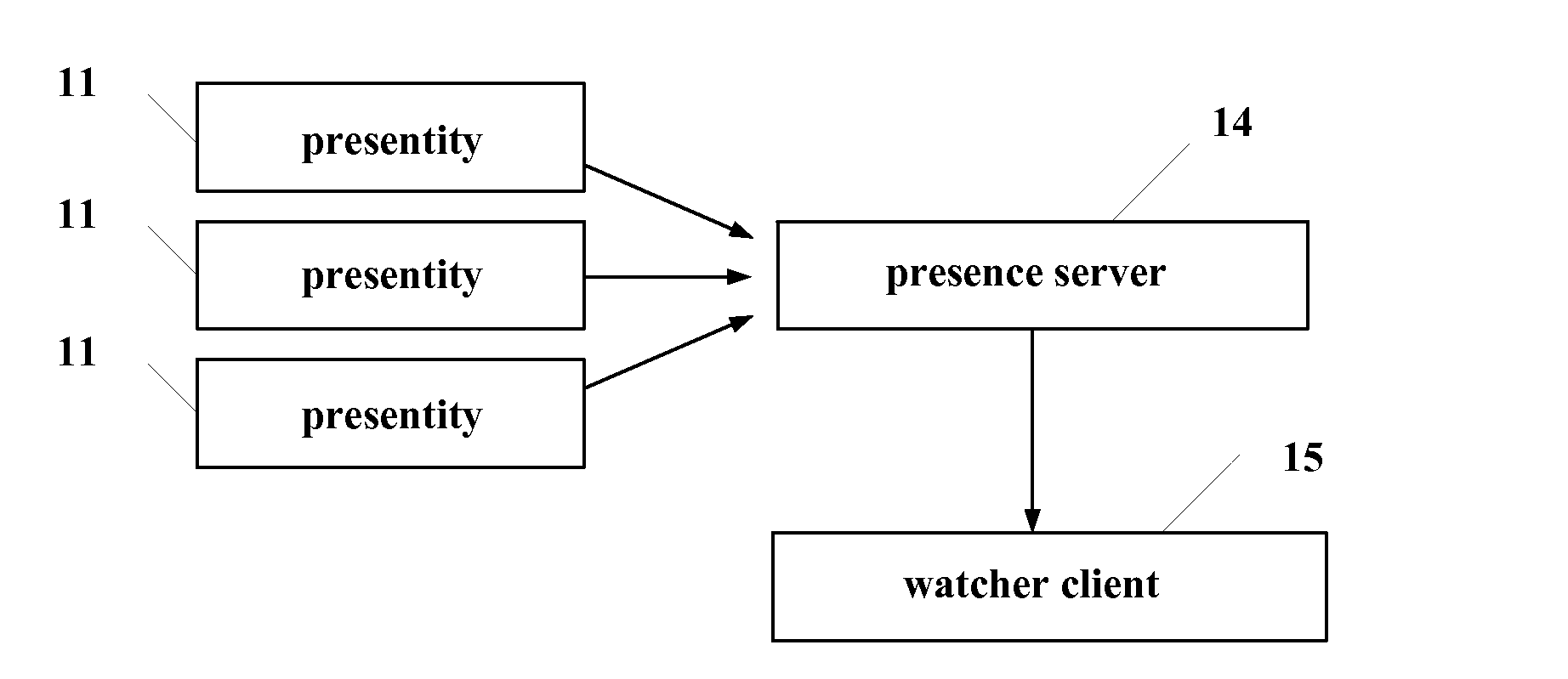
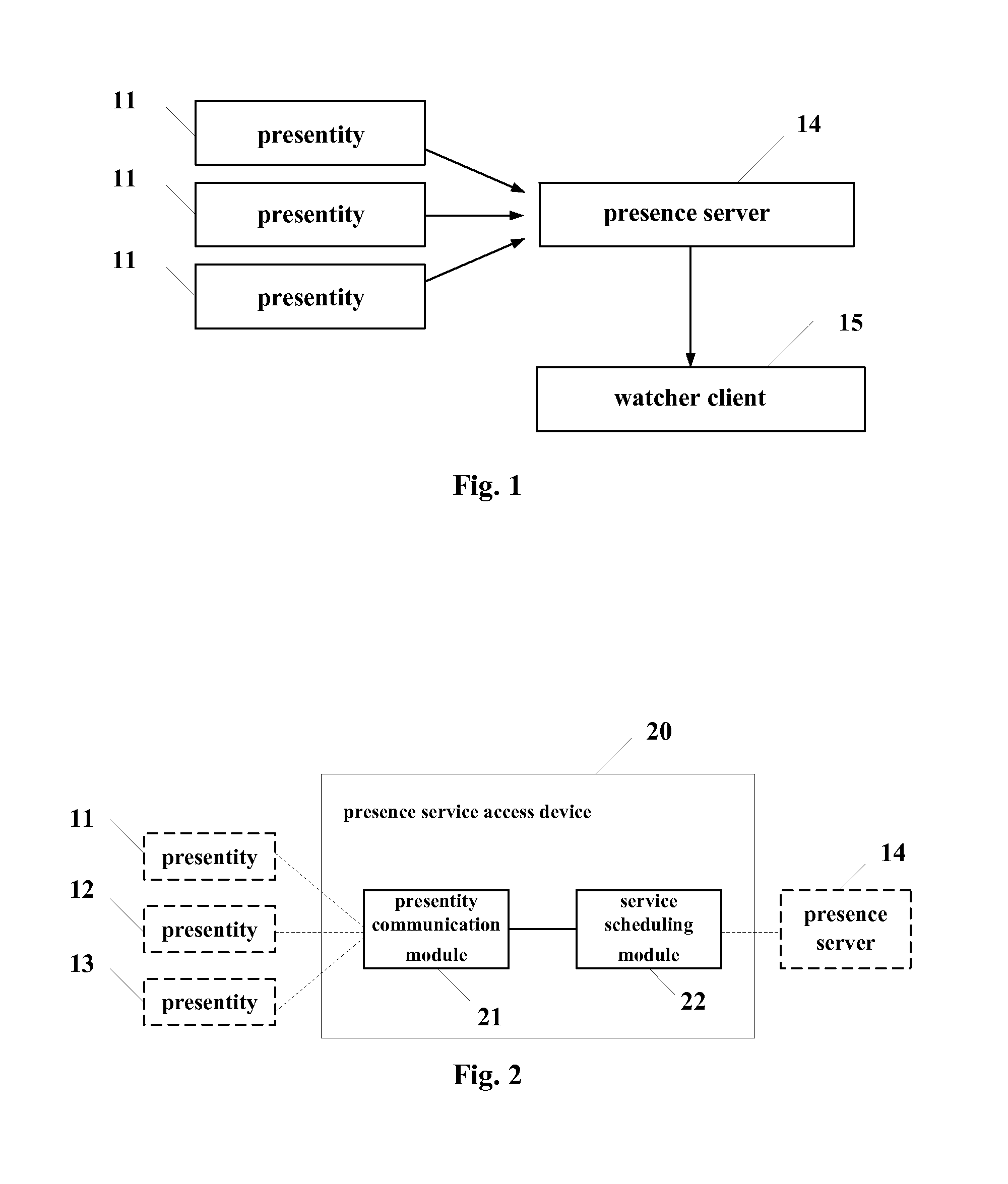
A presence service access device is disclosed for a presentity to publish presence information and transmit said information to the presence server, the device comprising a presentity communication module and a service scheduling control module. Further disclosed is a presence service system using the presence service access device, comprising a presentity, a presence service access device, a presence server, and a watcher client. Also disclosed is a method of publishing and acquiring presence information comprising steps of: 1. a presentity which publishes presence information; 2. the presence service access device which receives the presence information published by the presentity and forwards the same to a presence server; and 3. the presence server which distributes the presence information to corresponding watcher client. According to the present invention, various presentities provide presence information to watcher clients by connecting presence servers through a presence service access device.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
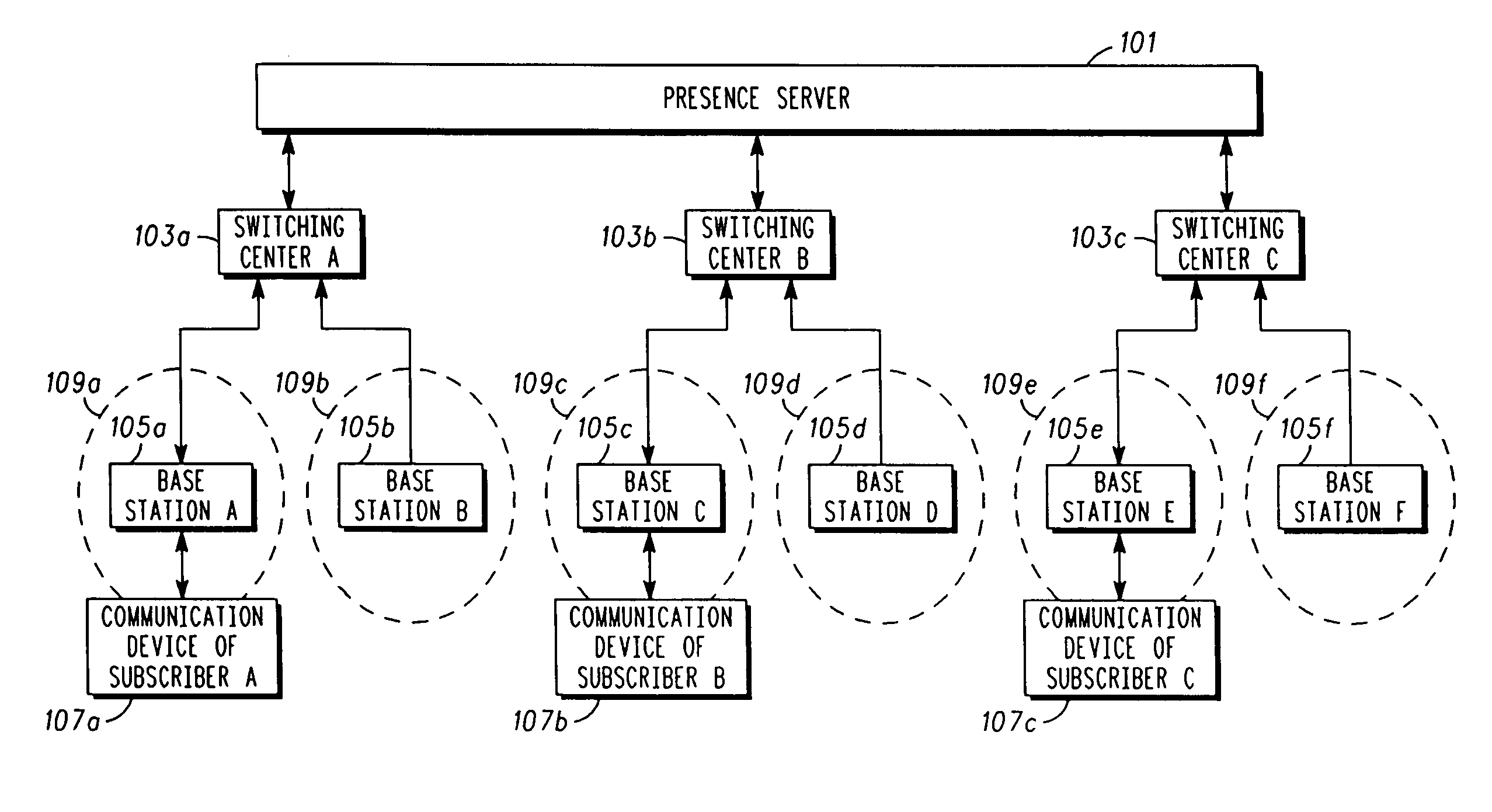
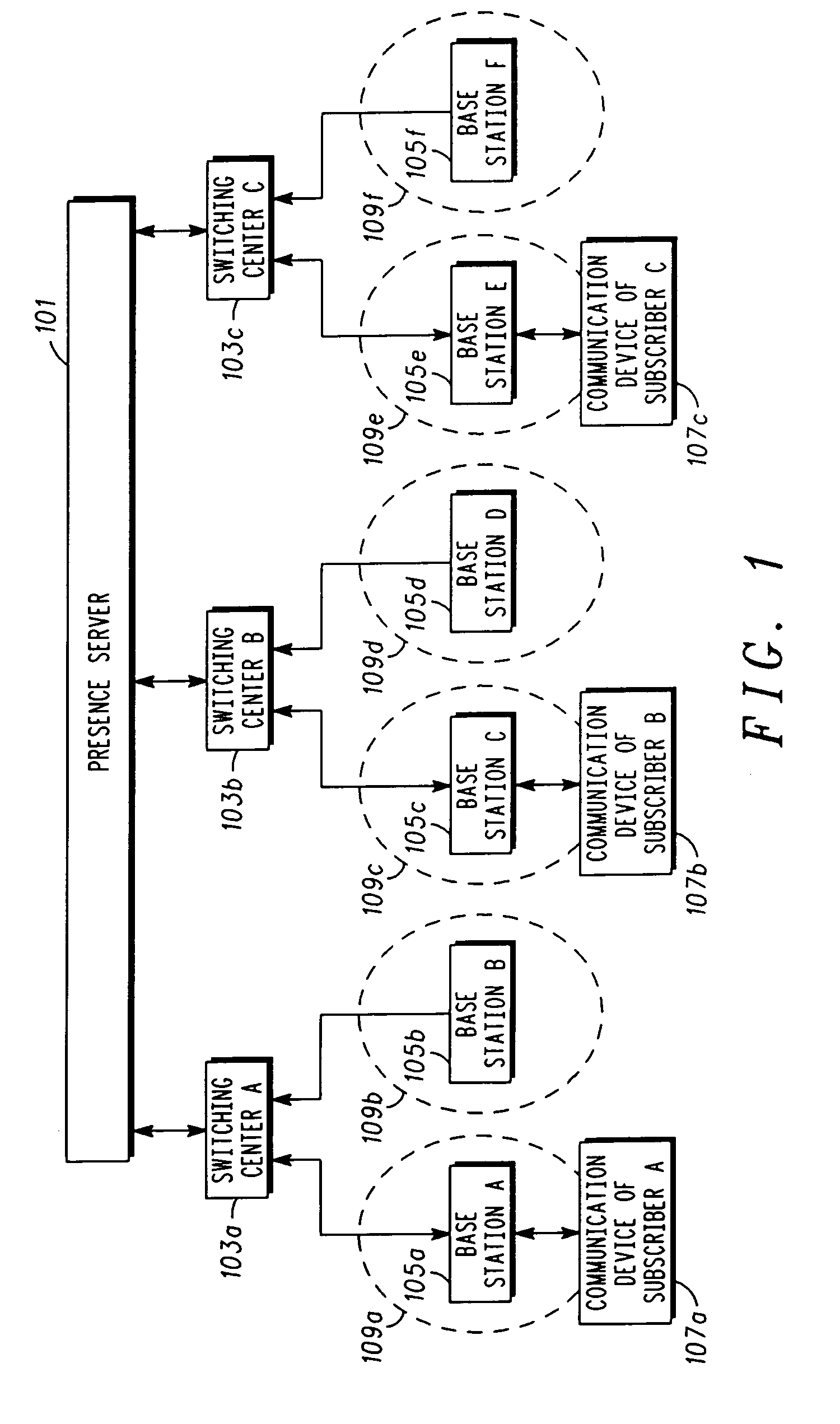
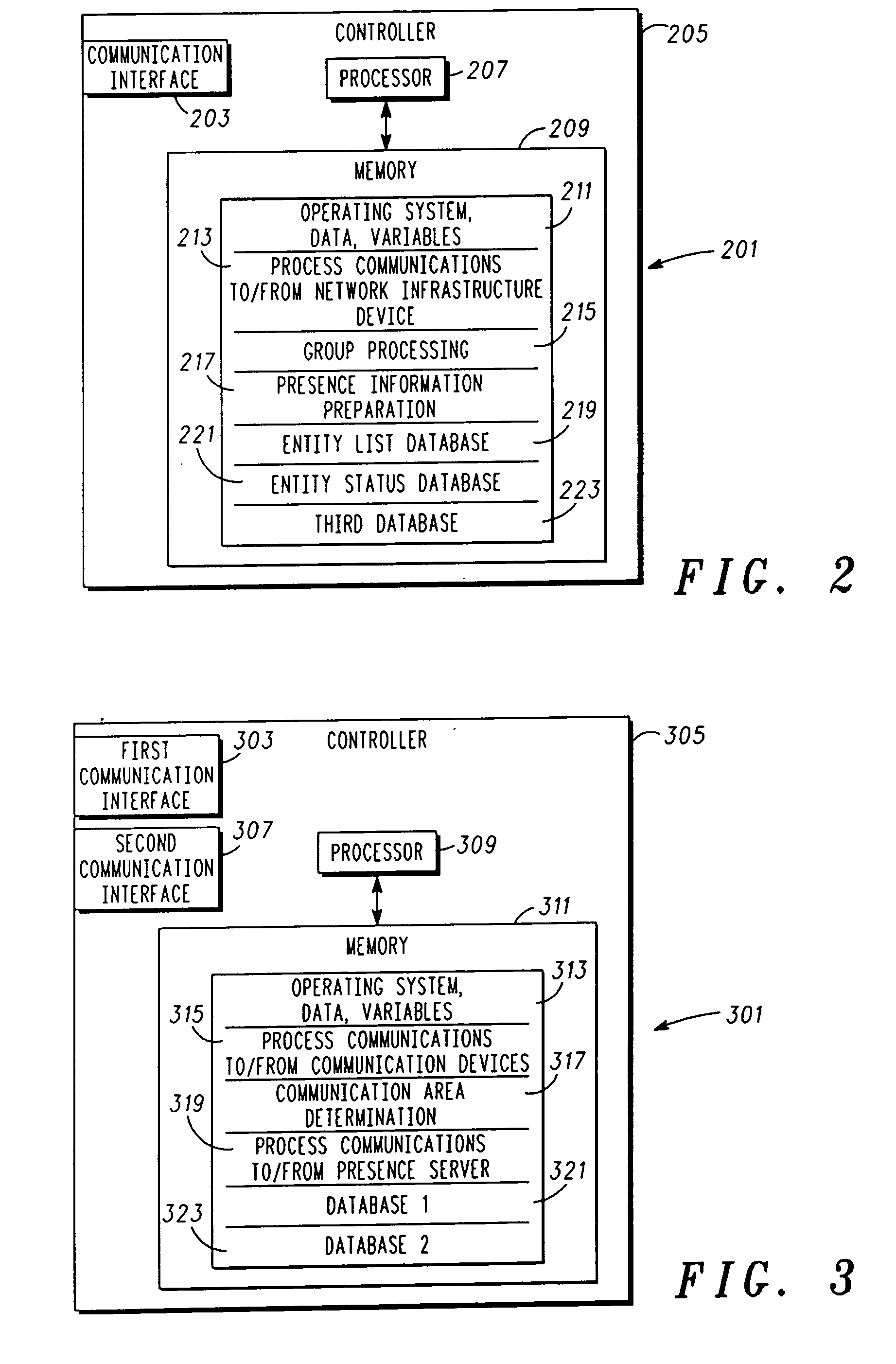
Providing presence information in a communication network
ActiveUS20060119882A1Broadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexCommunication unitProviding presence
A server (101) designates and assigns each of a plurality of communication devices to at least one of a plurality of groups. The server (101) prepares a communication having presence information corresponding to a status of the communication devices in the group; determines network infrastructure device(s) serving the group; and transmits, at a pre-determined time, the communication to the network infrastructure device(s). A network infrastructure device (103a-c, 105a-f) receives the communication and transmits, as a common channel signal during the pre-determined time, a signal with the presence information. A communication unit (107a, 107b, 107c) receives an indication of the pre-determined time; transmits, at an interval proximate to the pre-determined time, a signal indicating the communication device's status; and receives, at the pre-determined time, the signal with the presence information.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
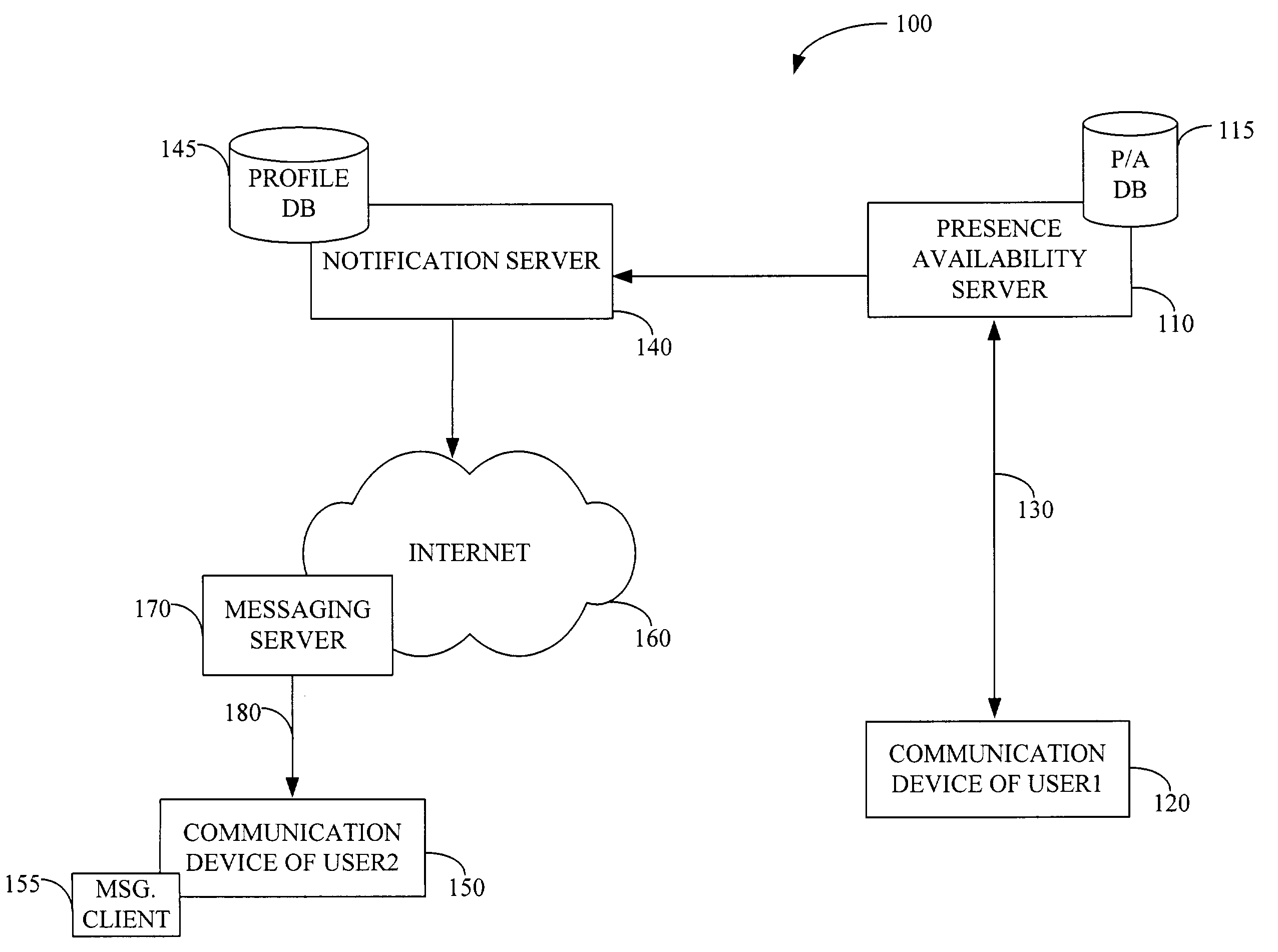
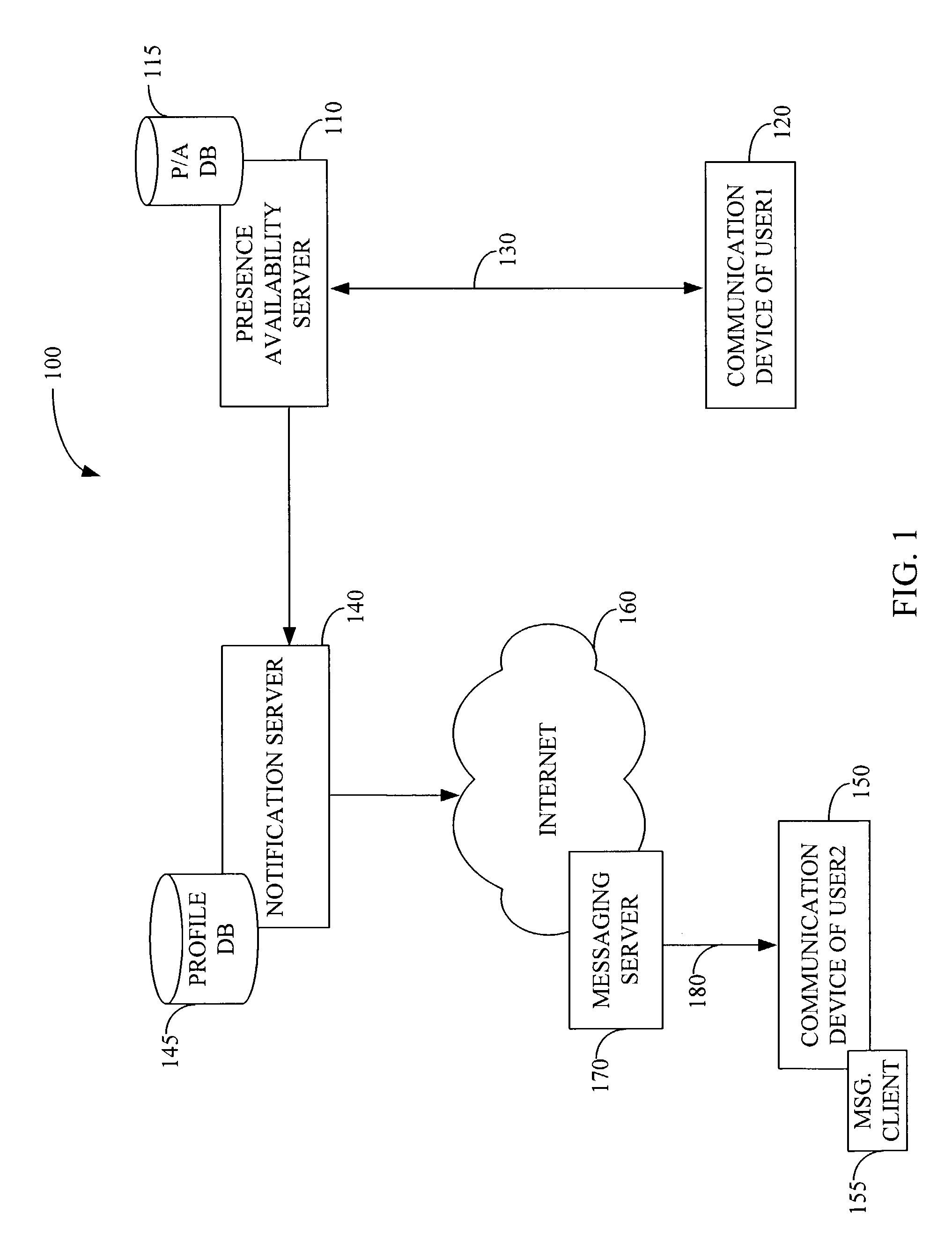
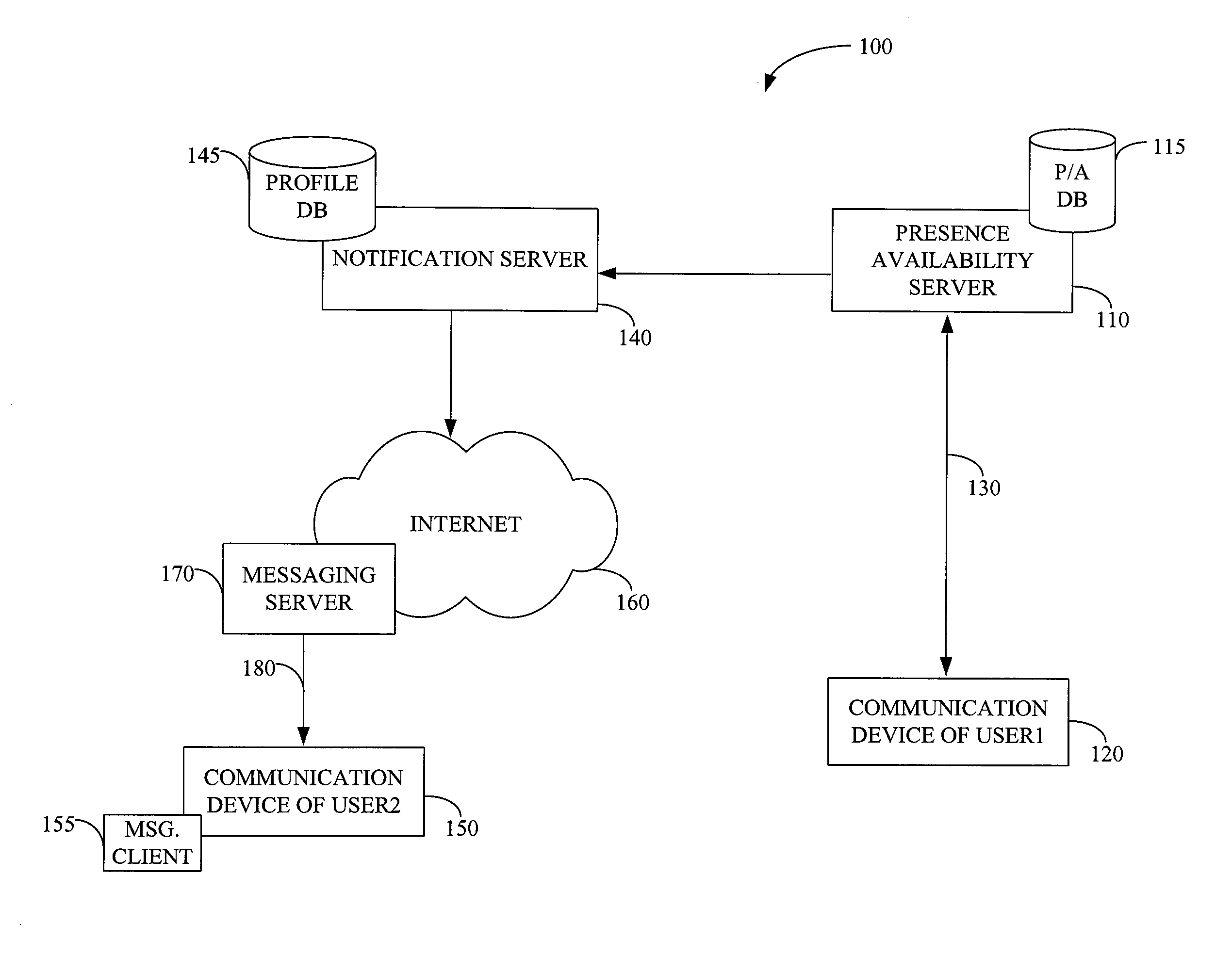
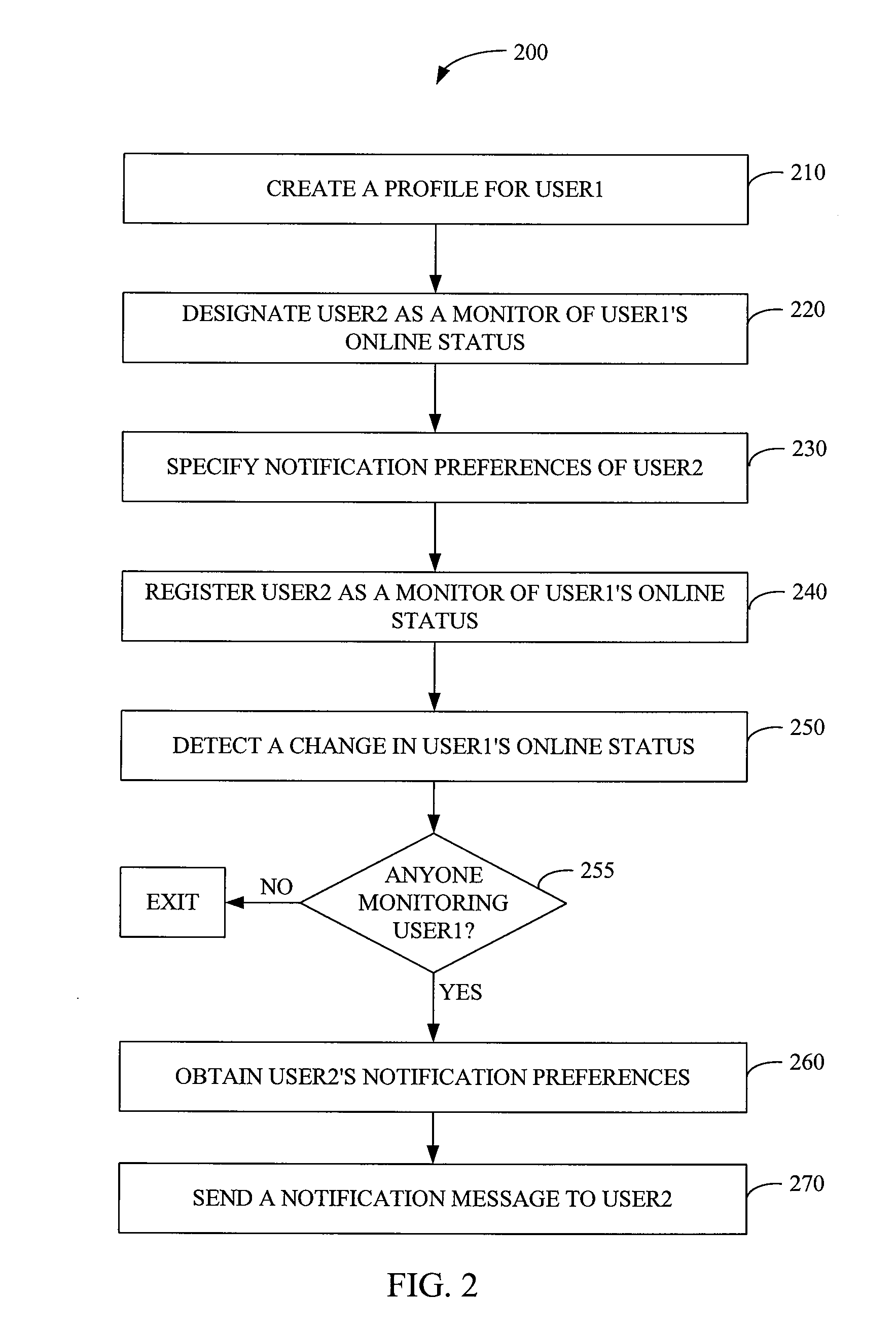
Real-time notification of presence availability changes
InactiveUS7395329B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksProviding presenceCommunication device
Preferred embodiments of the present invention provide a system and method for providing presence and availability status information of a first user to a second user. The system includes a presence availability server for storing presence and availability status information of the first user. The presence availability server is configured to detect a change in the presence and availability status of the first user. The presence availability server also informs a notification server of a change in the presence and availability status of the first user. The notification server sends a notification message to a communication device of the second user. The notification message contains current presence and availability status information of the first user. Other systems and methods are also provided.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
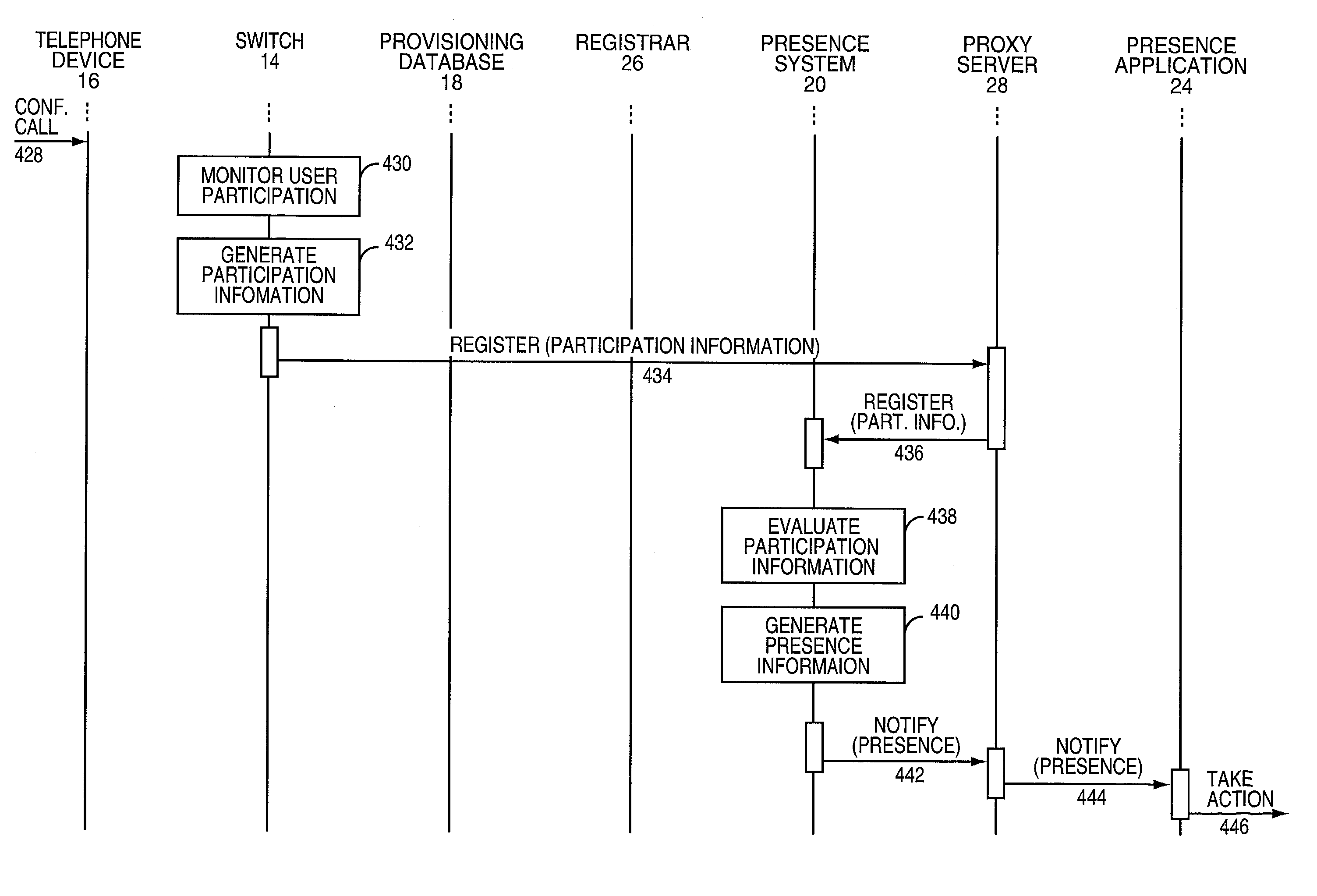
Presence information based on media activity
InactiveUS7139797B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionProviding presenceUser involvement
The present invention provides presence information to a subscriber indicative of the availability of a user who is already actively participating in a communication session. A presence system receives and processes participation information, which bears on the degree in which the user is participating in the communication session, and generates the presence information based on defined processing rules. The resultant presence information may indicate whether the user can be interrupted to accept other communications while engaged in the communication session. If the user can be interrupted, the presence information may also identify the most appropriate methods to contact the user during the communication session.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
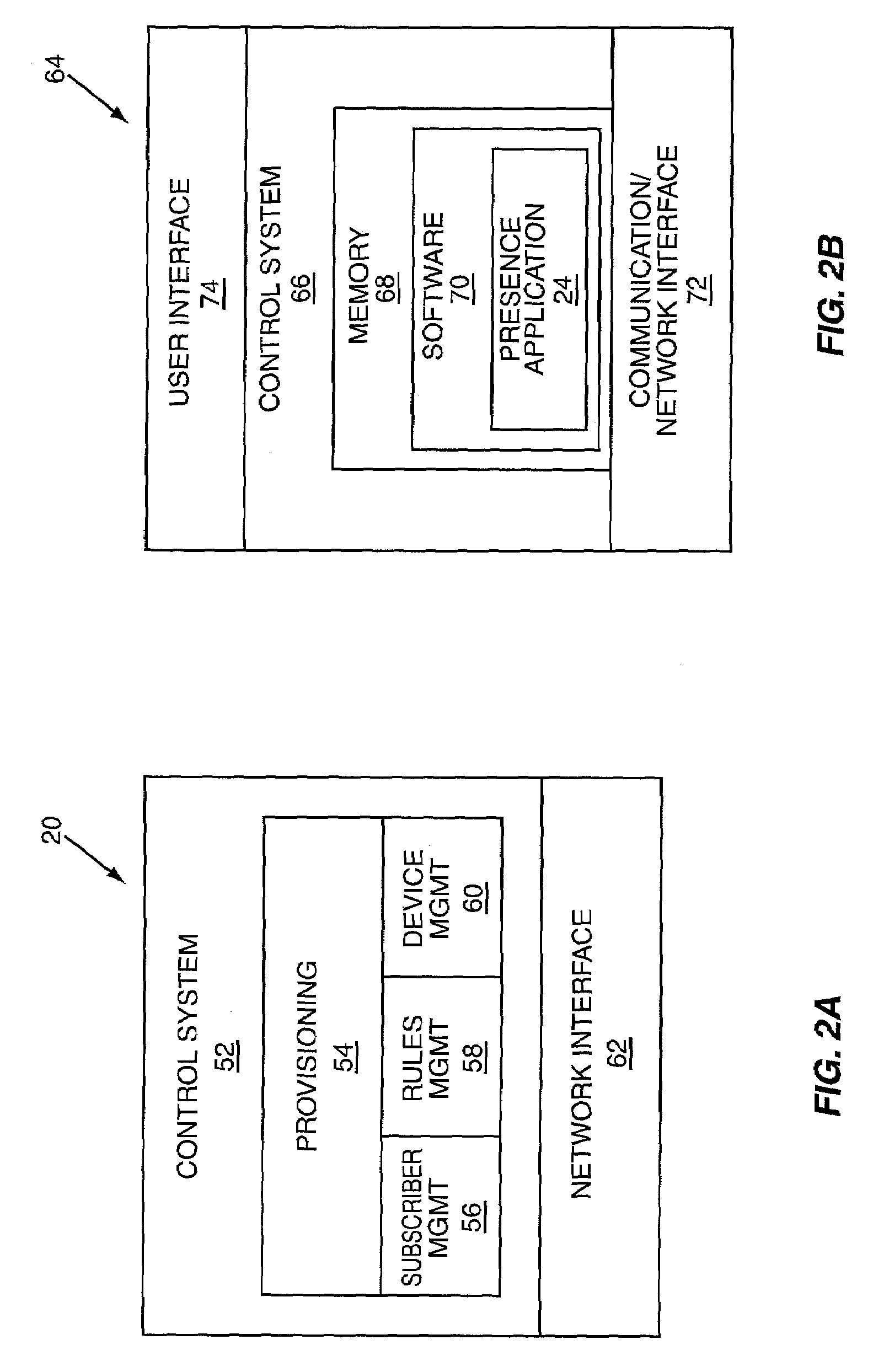
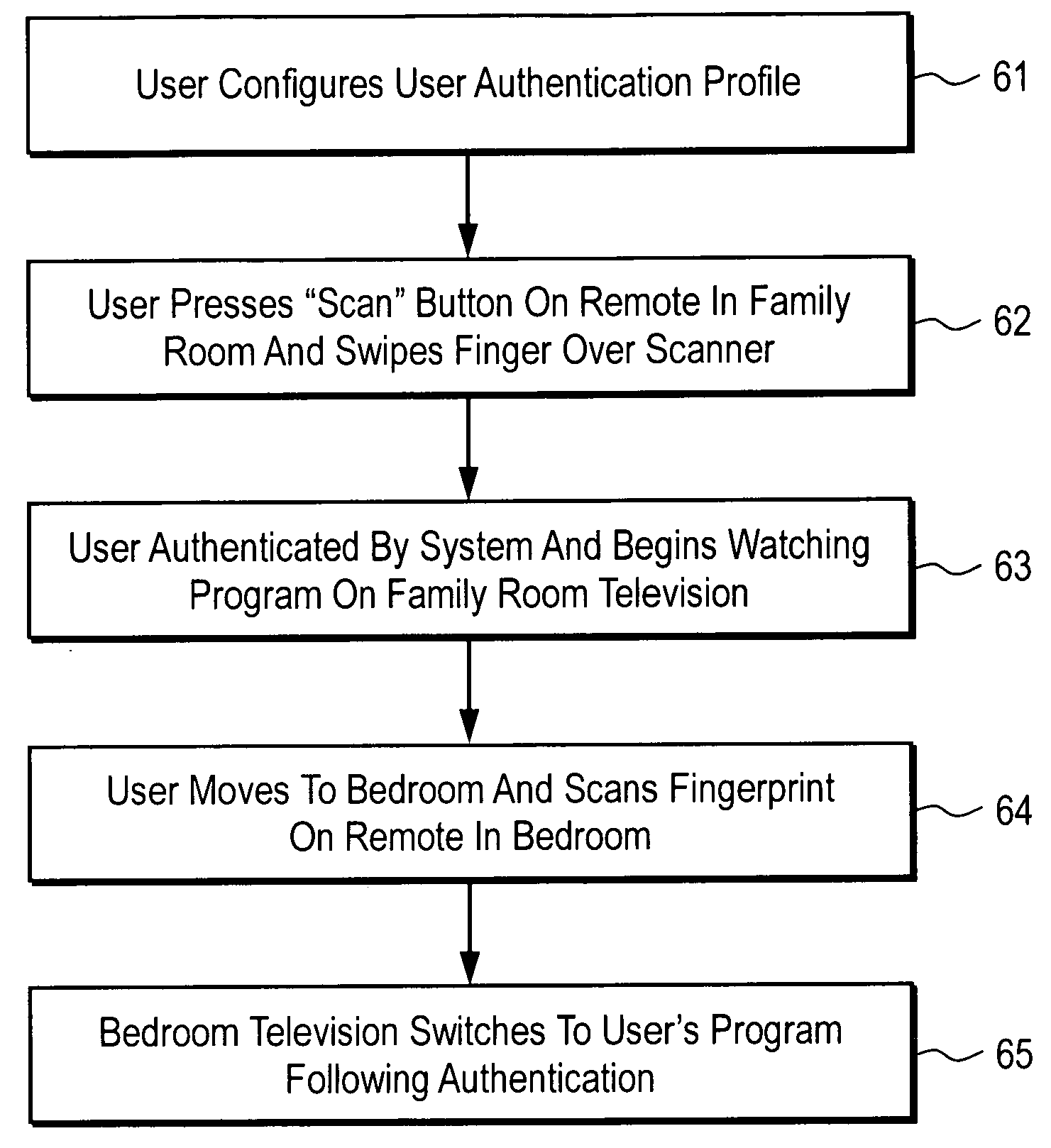
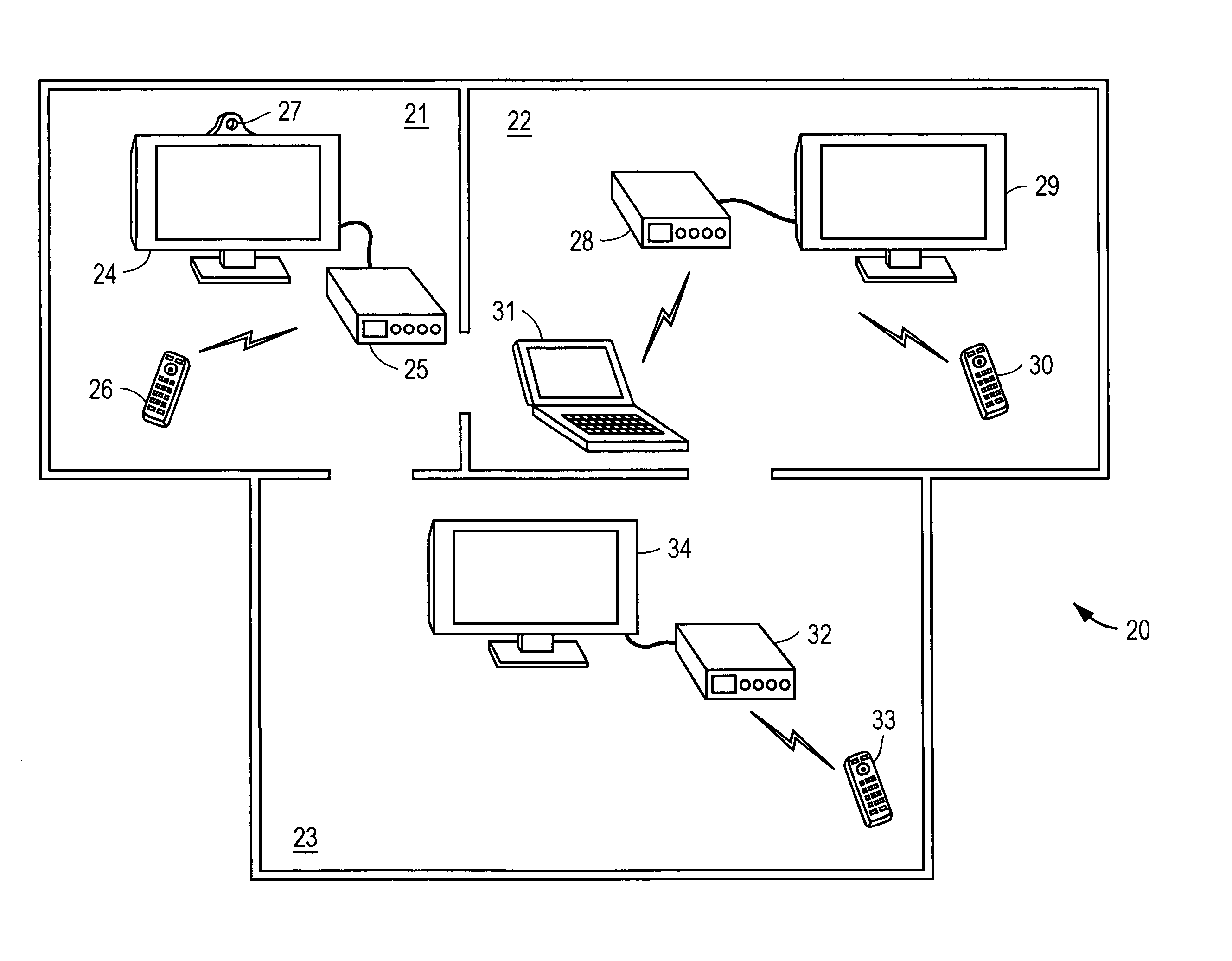
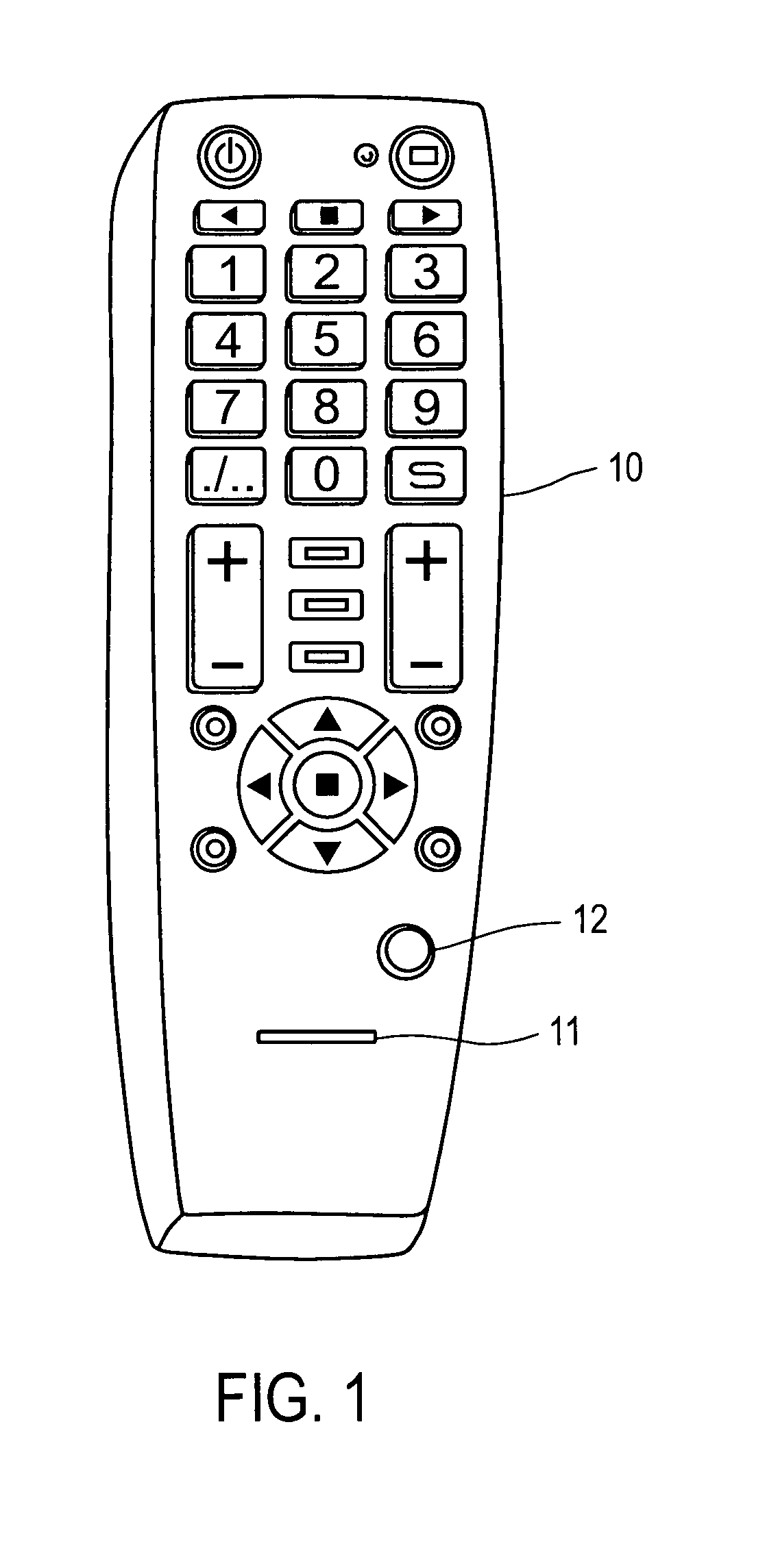
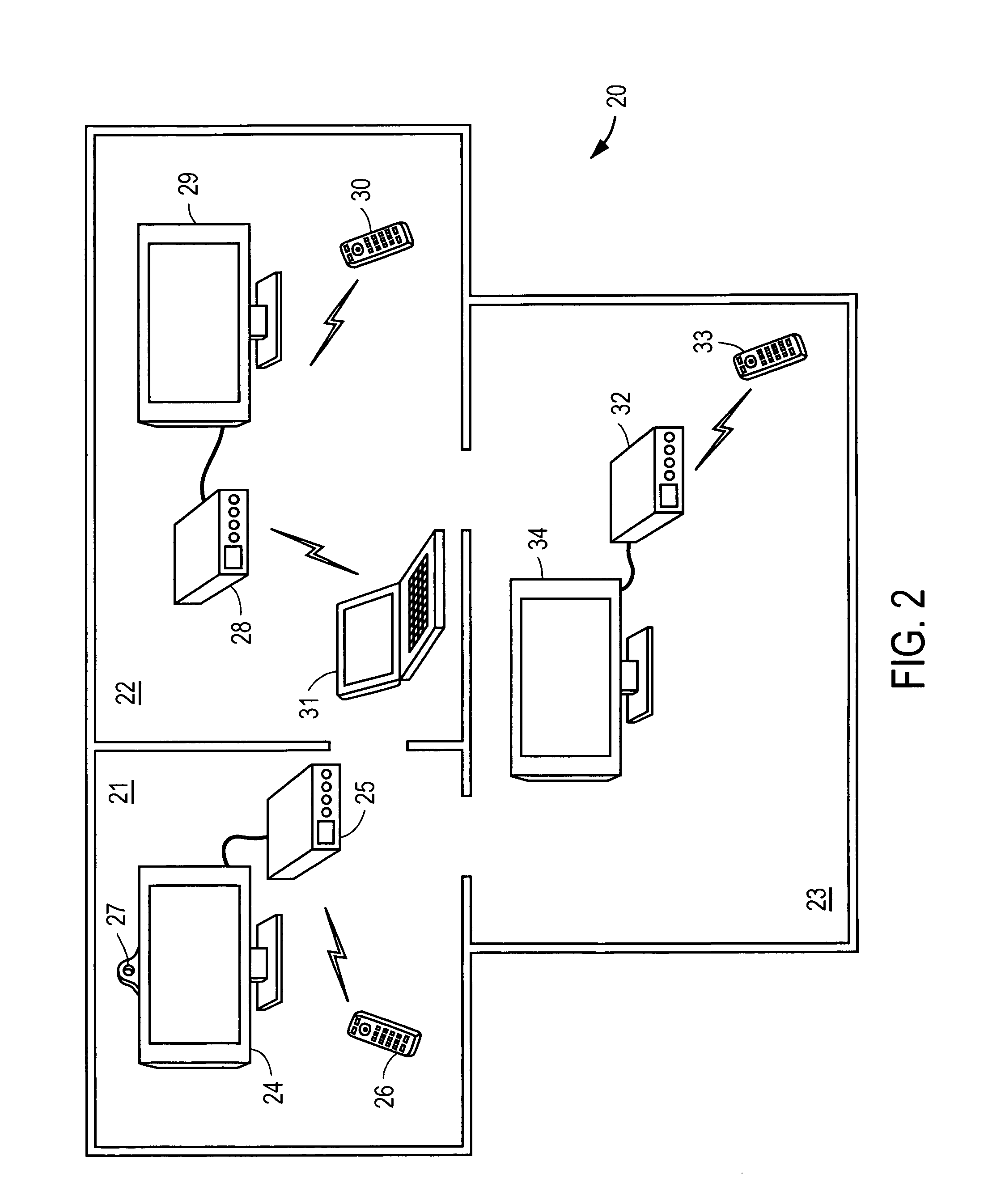
Home entertainment system providing presence and mobility via remote control authentication
InactiveUS20090146779A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsBiometric dataRemote control
An apparatus in one embodiment is operable to receive, from a remote control device associated with a video display device, biometric input of a user. Responsive to a match of the biometric input with stored biometric data of the user, the user is authenticated. The remote control device and / or the video display device are then configured based on user settings associated with the stored biometric data of the user. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
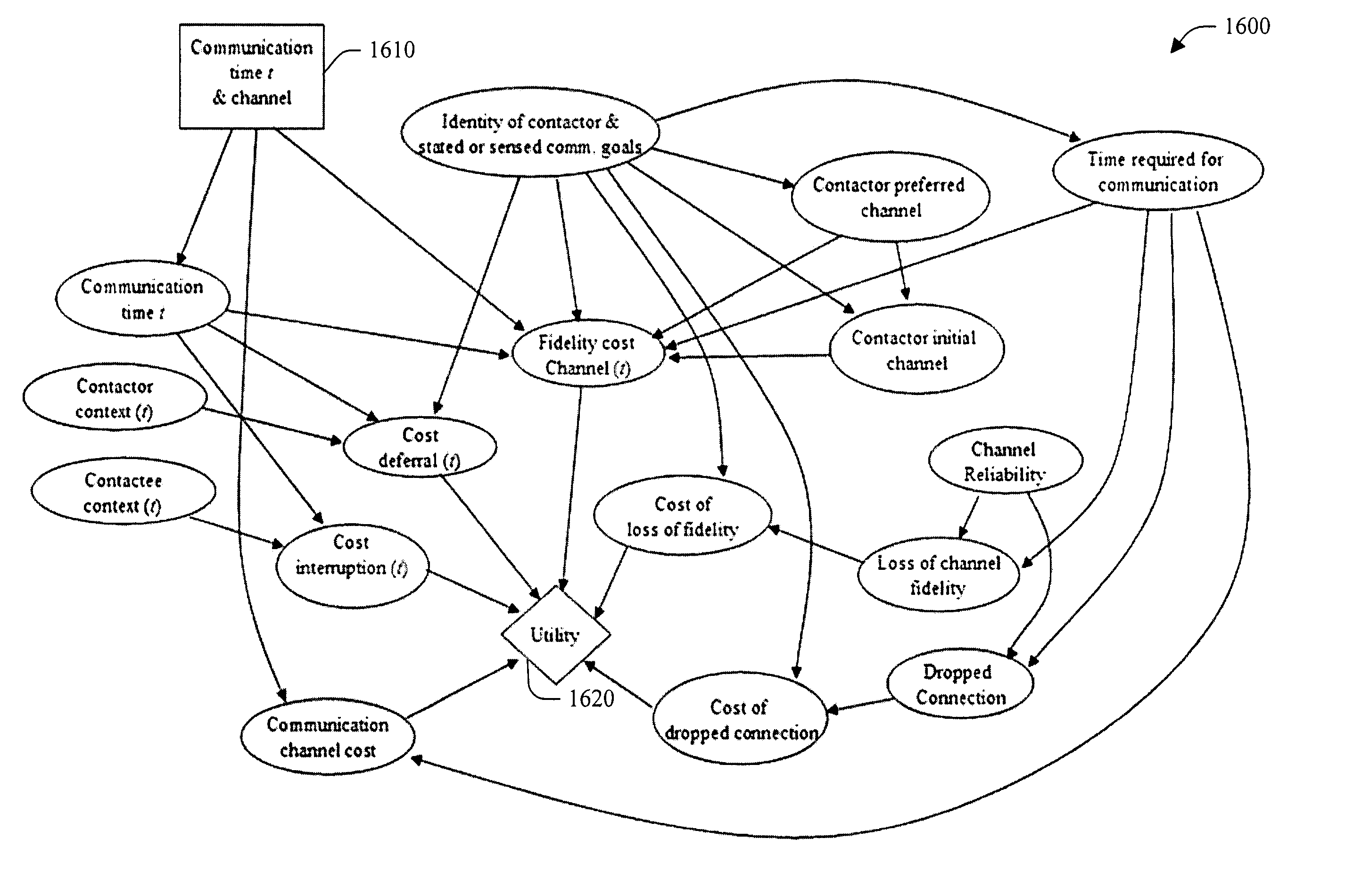
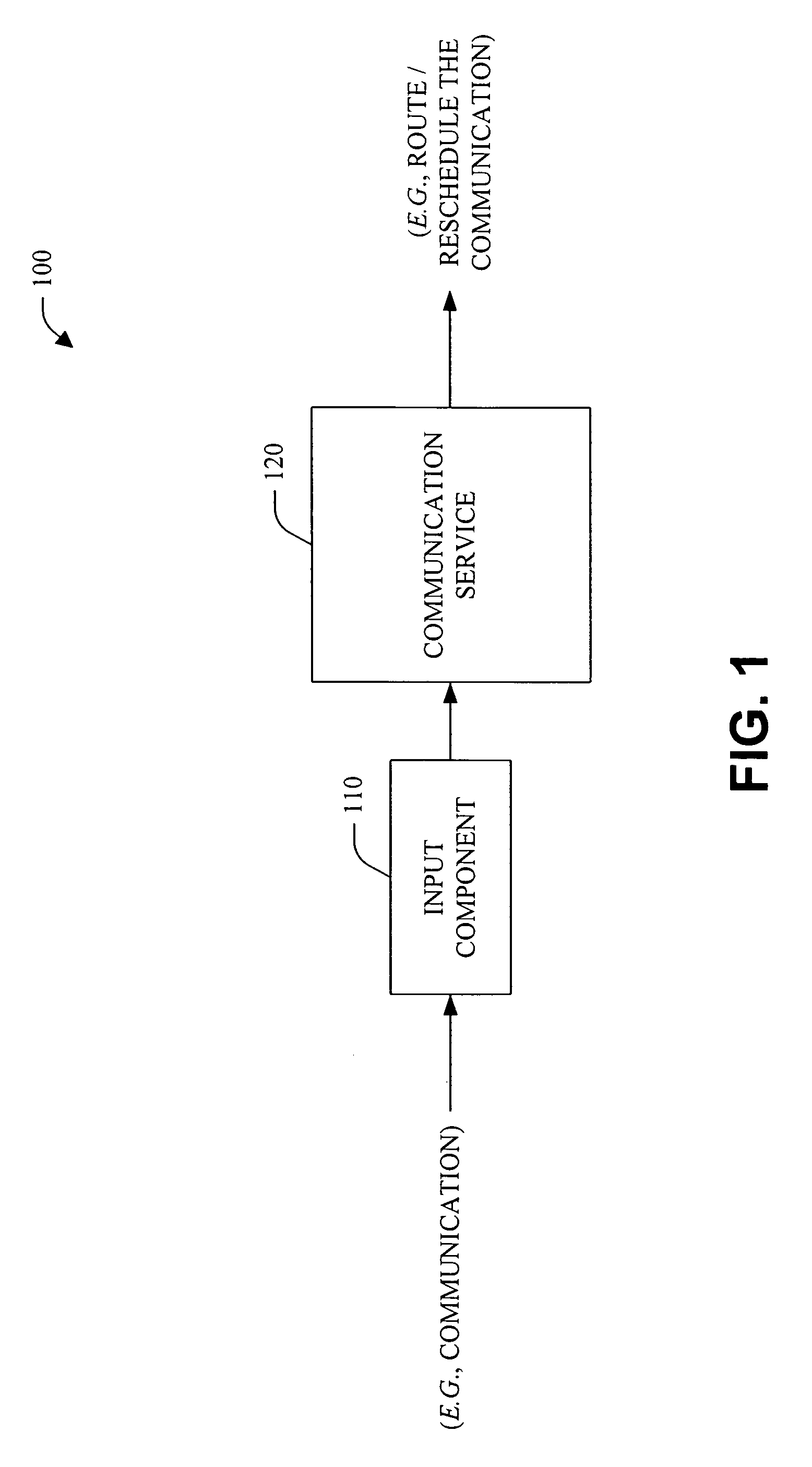
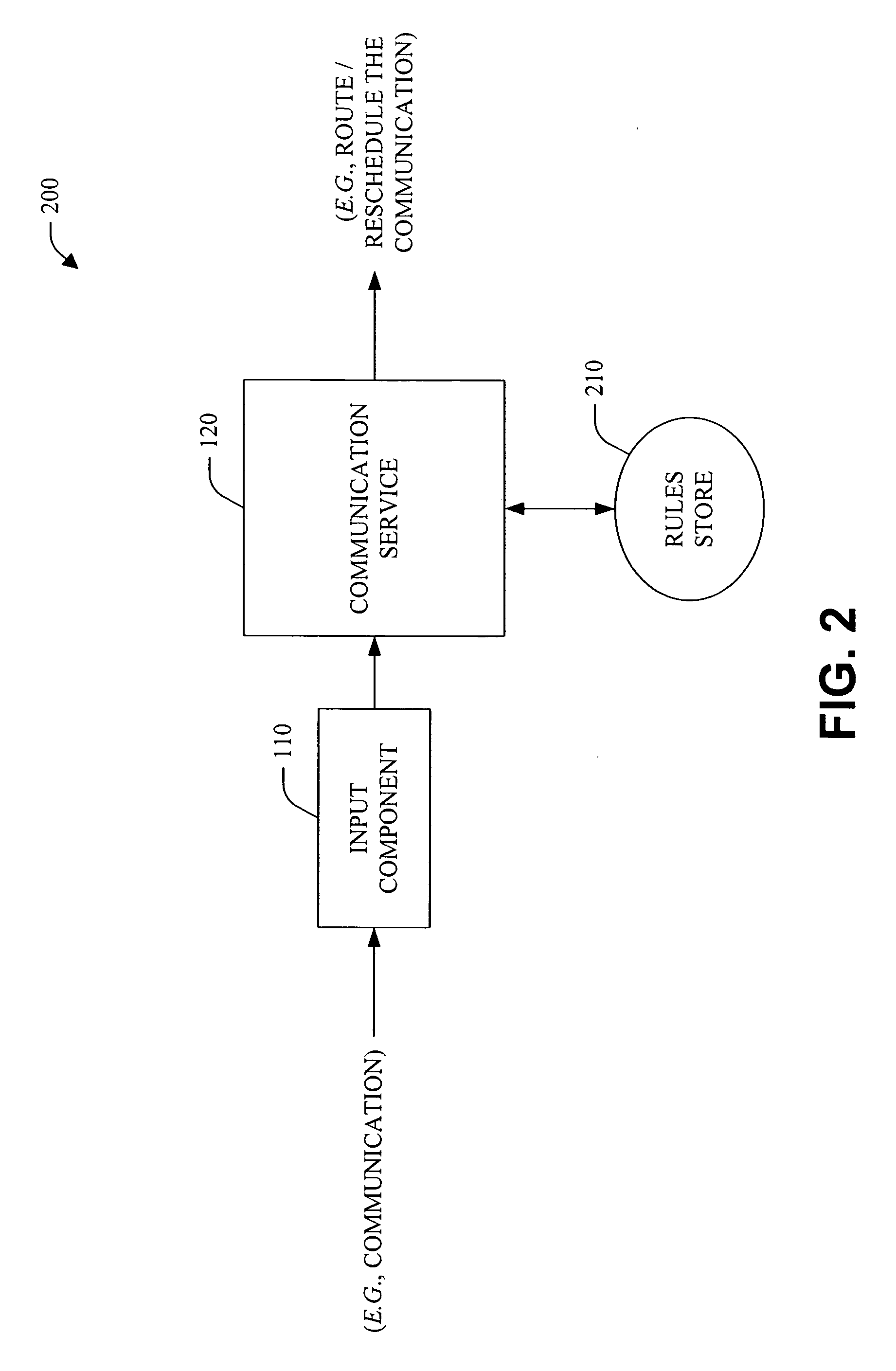
Designs, interfaces, and policies for systems that enhance communication and minimize disruption by encoding preferences and situations
InactiveUS20050084082A1Enhance interpersonal communicationValue maximizationSpecial service for subscribersDigital computer detailsCost benefitStatus changed
The present invention relates to utilizing identity and context-sensitive decision-making for handling communications, including, channel selection, routing, and rescheduling operations. The systems and methods provide a service that allows users to assess preferences regarding real-time call handling and performs dynamic decision-making about the best timing and channel for interpersonal communication. This service can be based on various cost-benefit analyses (e.g., basic and extended) that consider cost of interruption and preferences of contactors and contactees to guide communications, and / or on decision-making under uncertainty. Statistical models that are learned from data are joined with user preferences to generate expected costs of interruption for office activity and over time, based on a user's activities, locations, calendar information and preference assessments. In addition, statistical forecasting provides presence and availability predictions. The foregoing can provide an enhanced interpersonal communication system that can maximize the value and minimize the cost of communication among people.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and Method for Providing Presence
ActiveUS20110085654A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsSession Initiation ProtocolProviding presence
A system that incorporates teachings of the present disclosure may include, for example, a server having a controller to receive presence information from each presence source of a plurality of presence sources, wherein the presence information is associated with a user, receive a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) which identifies the user, wherein identification information associated with the user from each presence source is mapped to the SIP URI, select at least a portion of the received presence information to be utilized in determining a presence status of the user, determine the presence status of the user based on the selected presence information, and transmit the presence status and the SIP URI to a computing device operably coupled to an Internet Protocol Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) network. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
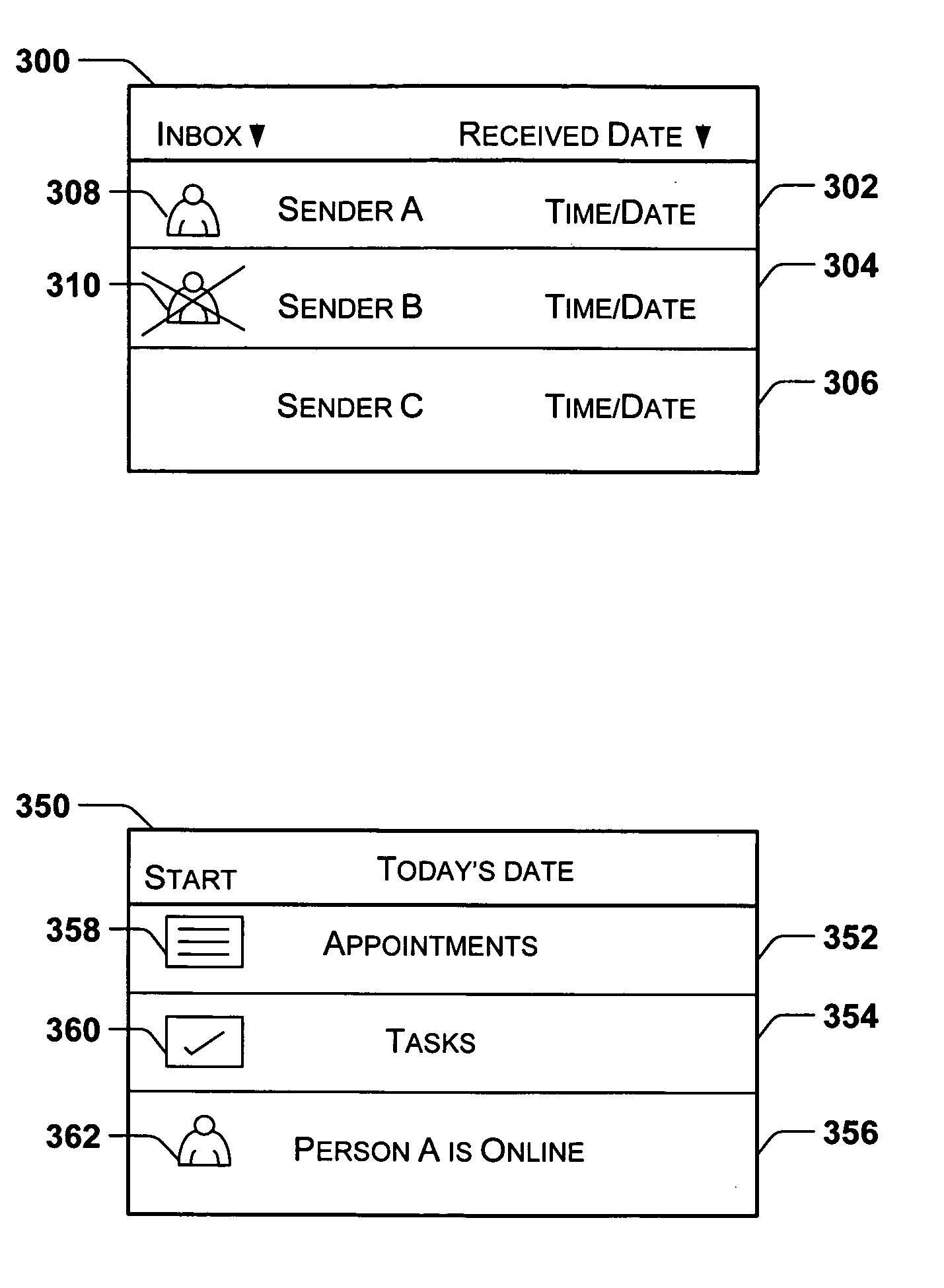
System and method for automatic selection of an instant messenger client
InactiveUS20060047747A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksProviding presenceClient-side
Automatic selection of an instant messenger (IM) client is made in response to a request to initiate a communication activity with a selected contact, such as an IM chat session. The IM client is selected according to which IM client is providing presence information related to the contact. The IM client is also selected according to which IM client is capable of handling the requested communication activity. An IM client may be selected if it can handle the requested communication activity irrespective of whether the contact is online with the IM client.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System, apparatus, and method for providing presence boosted message service reports
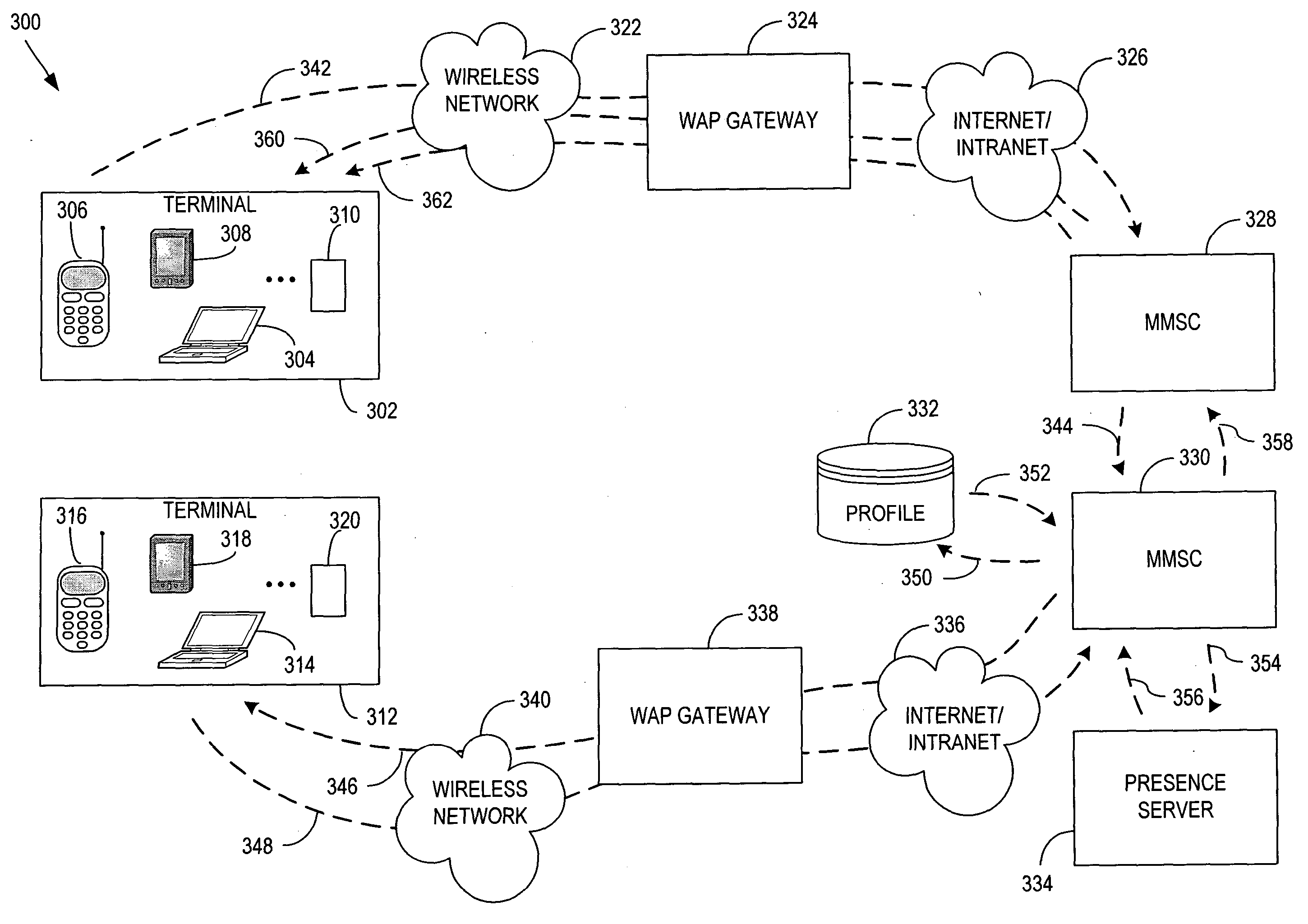
InactiveUS20050033852A1Facilitate communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingConfigfsProviding presence
A system, apparatus, and method is provided for automatically providing presence information using existing messaging services. Backward messaging such as read reports and delivery reports automatically include presence information from presence server (334) according to user preferences contained within profile database (332). The presence information may be disseminated through any messaging service, such as the Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) and is also supported by Session Initiated Protocol (SIP) signalling.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Method and apparatus for delivering an electronic mail message with an indication of the presence of the sender
InactiveUS20050071428A1Improve productivityGood choiceDigital data processing detailsSpecial service for subscribersProviding presenceClient-side
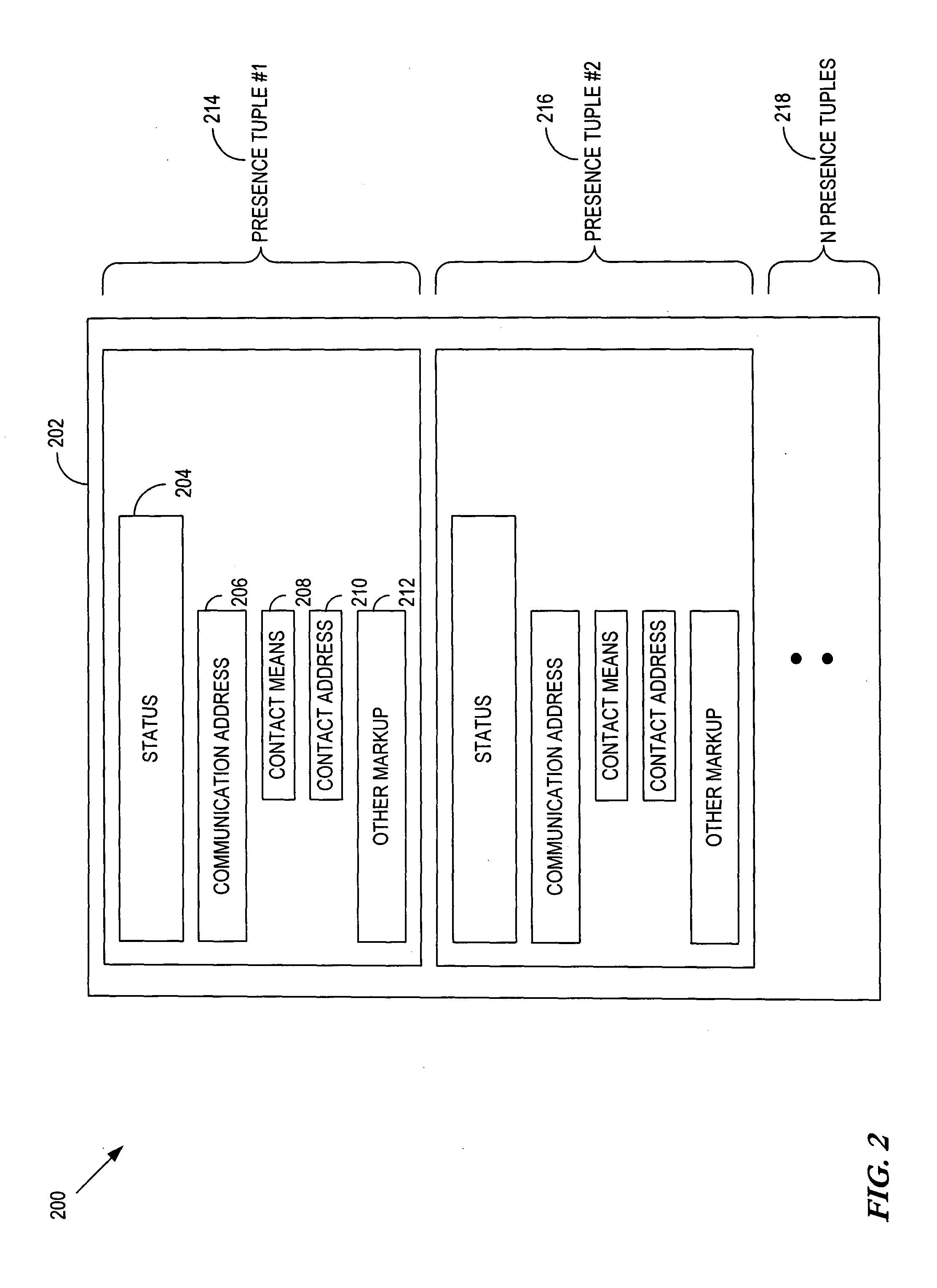
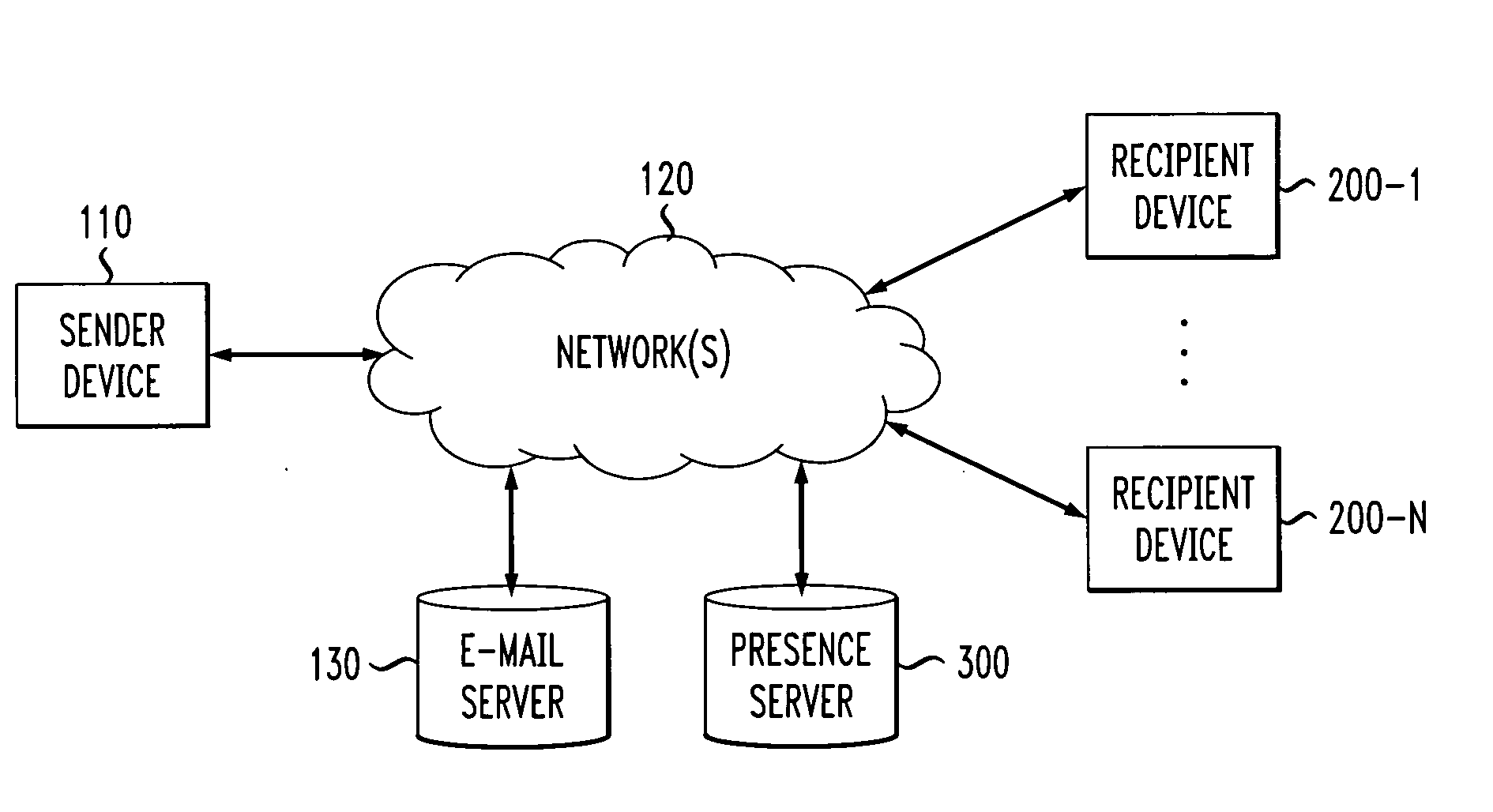
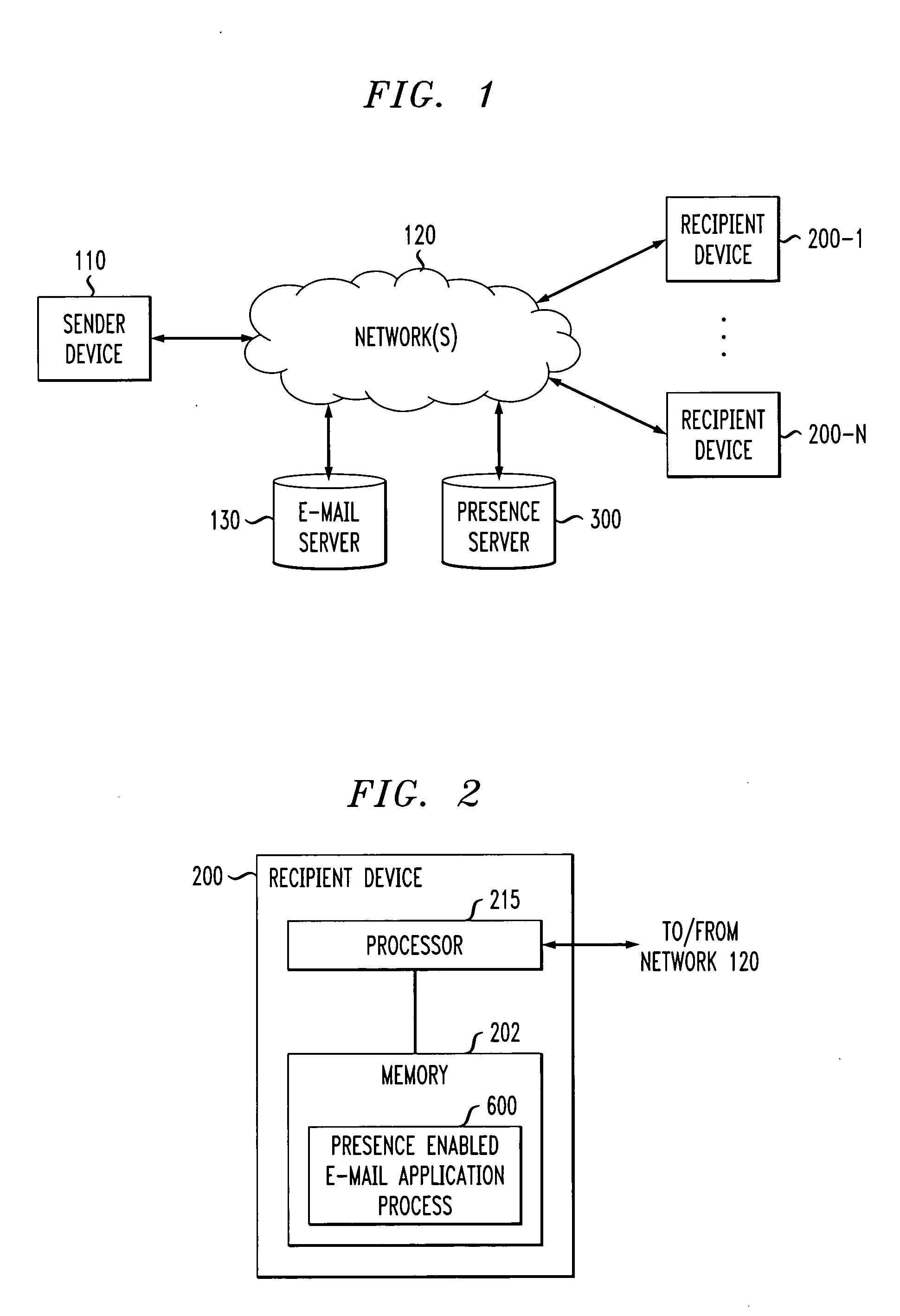
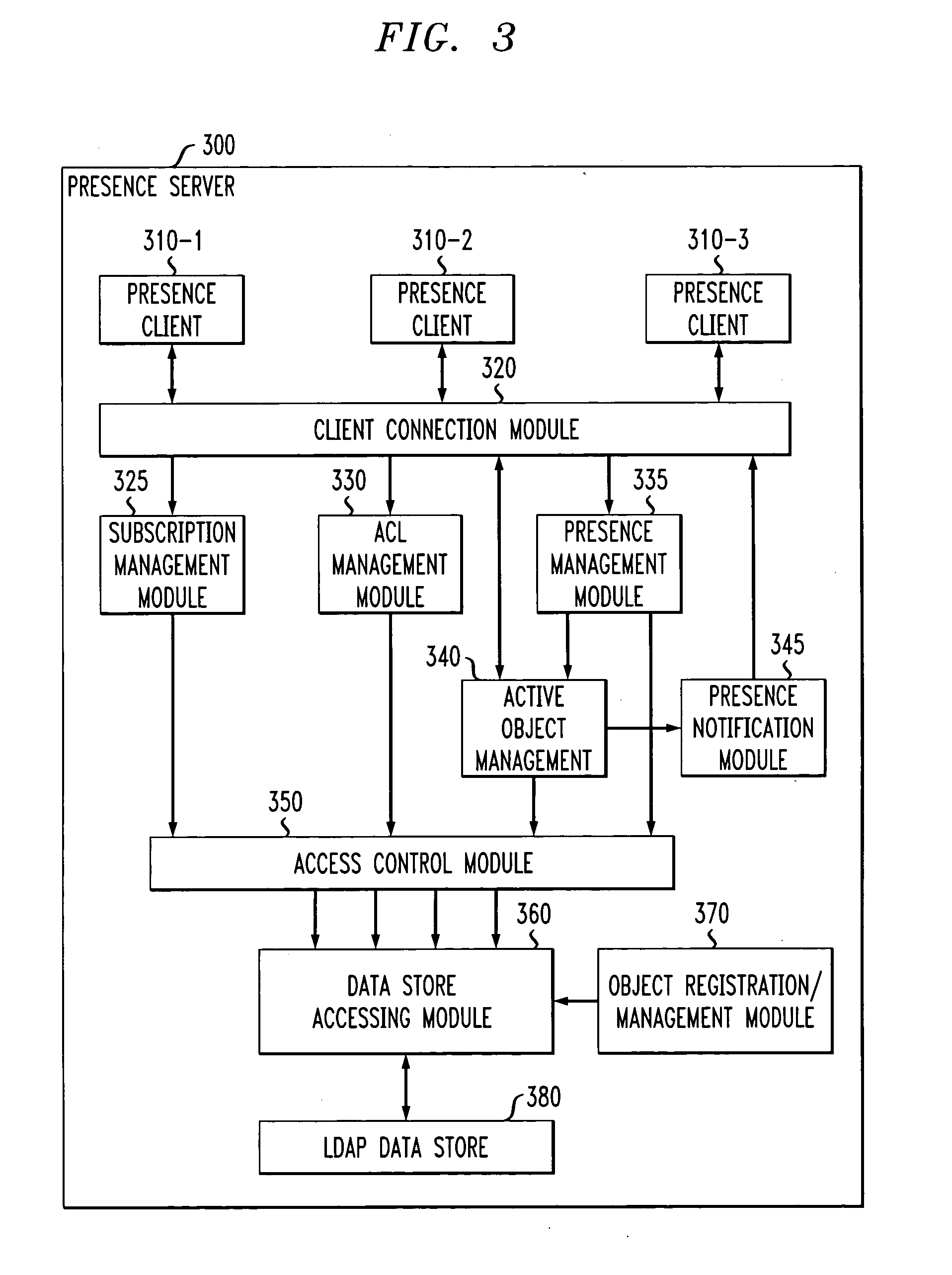
A method and apparatus are disclosed for delivering electronic mail messages to one or more intended recipients with an indication of the presence of the sender. A message recipient can automatically respond to a text-based email message using a non-textual form of communication The presence server can provide presence information across domains so that a user in one domain can automatically obtain presence information and respond to a user in another domain. A client-side presence enabled email application process (i) retrieves email messages from an email server of a user, (ii) queries a presence server to determine the presence of the sender of each retrieved email message, and (iii) presents the retrieved email message(s) to the recipient with an indication of the presence of the sender. In addition, the disclosed presence enabled email application process allows the message recipient to automatically respond, for example, by an email, instant message or telephone call to a device where the sender is believed to be present.
Owner:AVAYA INC
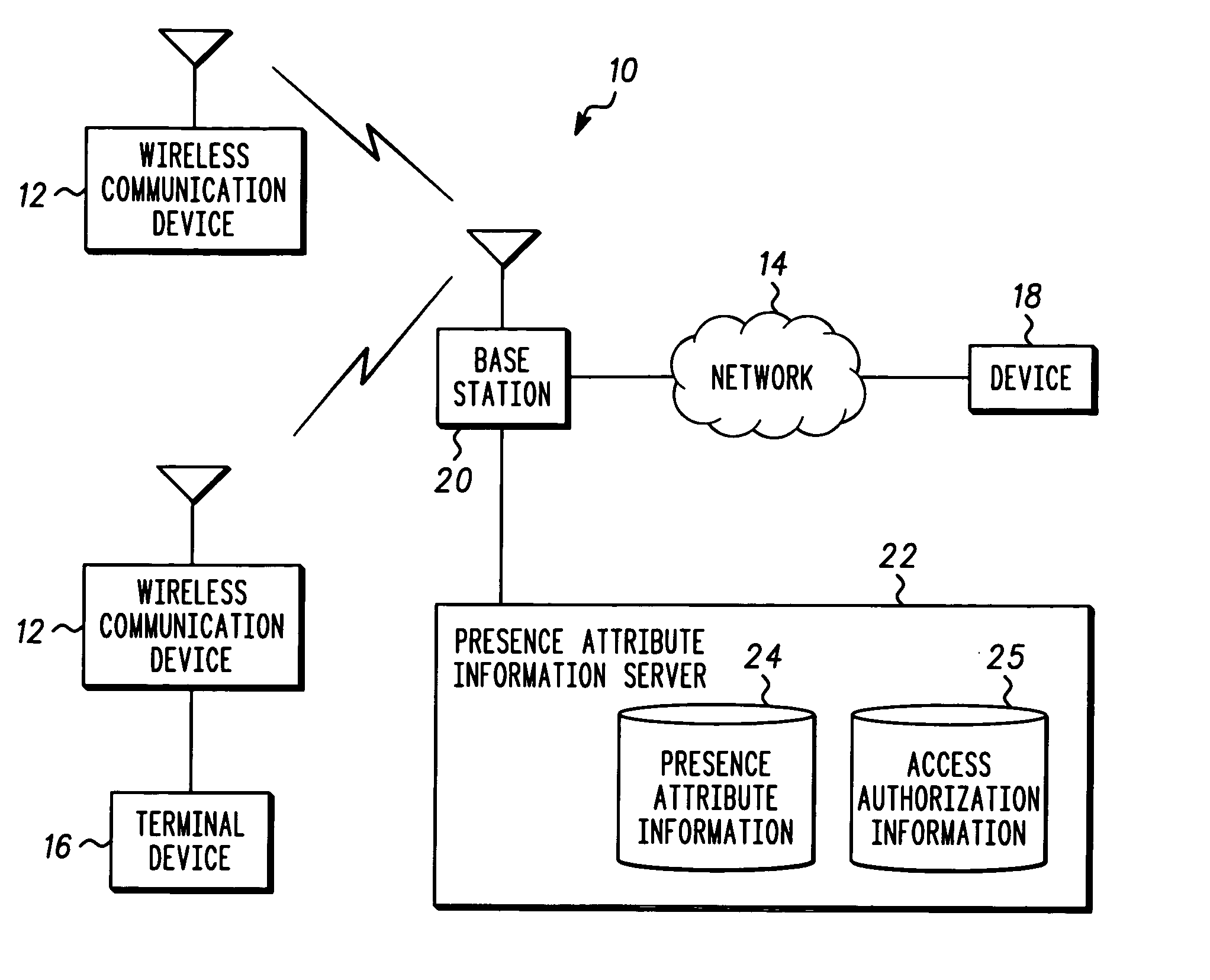
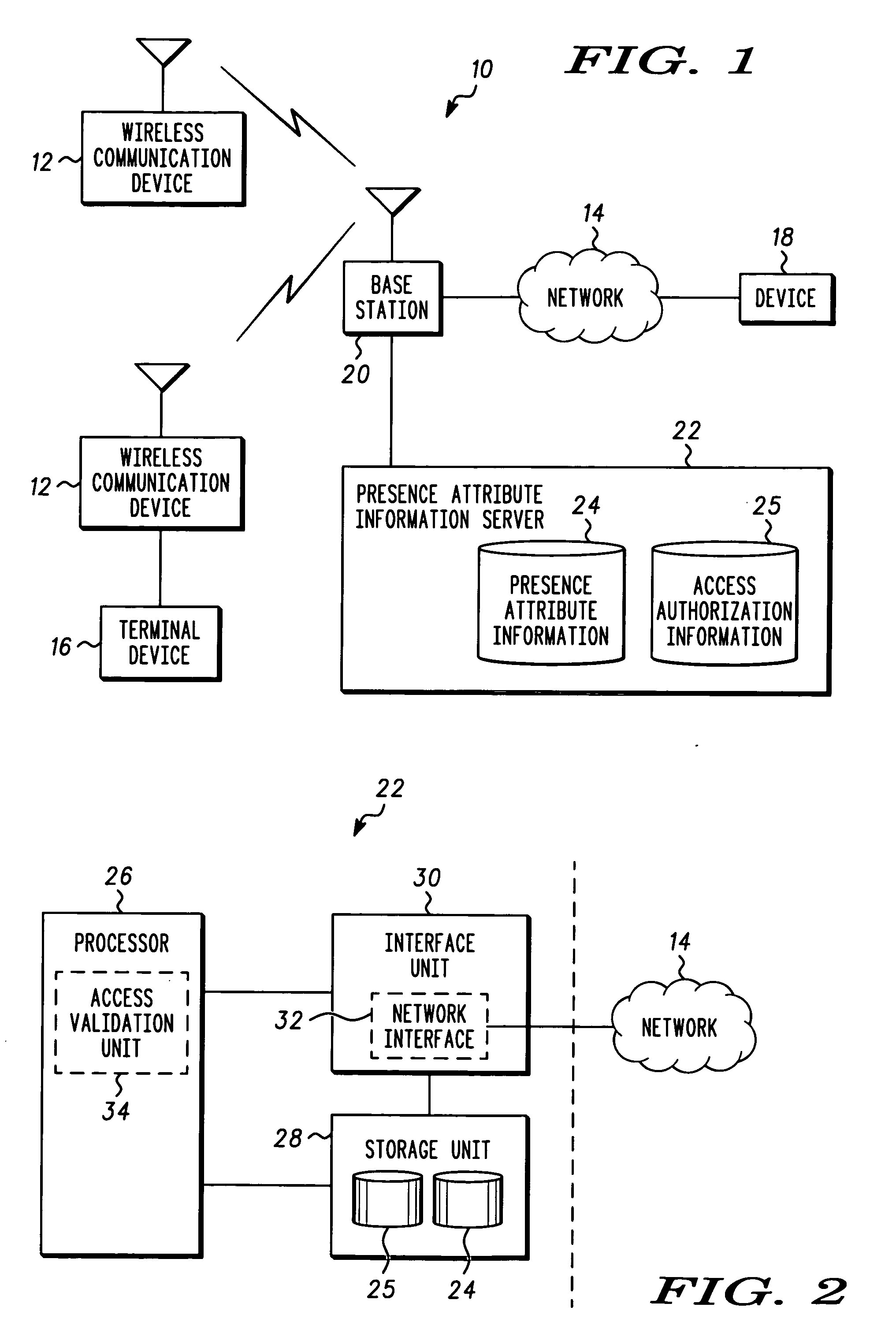
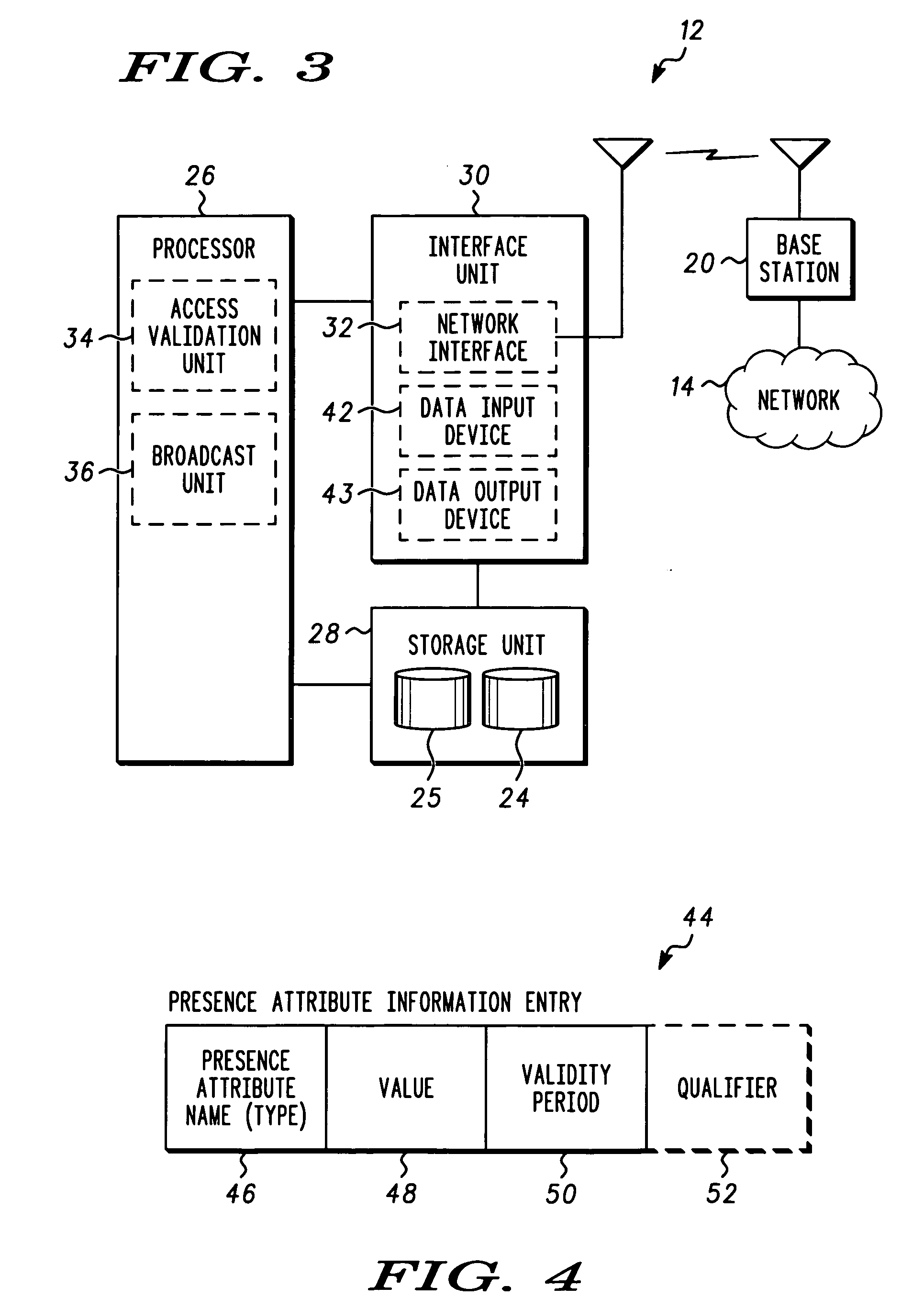
Method and system for managing access to presence attribute information
ActiveUS20050144333A1Data processing applicationsUser identity/authority verificationProviding presenceApplication software
A presence attribute information server and manager application, and corresponding method is provided for managing access to presence attribute information. In addition to the presence attribute information entries, access authorization entries associated with at least some of the presence attribute information entries are provided which define conditions in which access to the presence attribute information is authorized. Generally, the defined conditions can include temporal and / or spatial requirements associated with either the user requesting the presence attribute information or the person / item associated with the presence attribute information, for purposes of establishing authorization to access the presence attribute information.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for providing presence information in support of wireless communication services
ActiveUS20070010275A1Effectively determining presenceConnection managementBroadcast service distributionProviding presenceTelecommunications
Owner:INVT SPE LLC
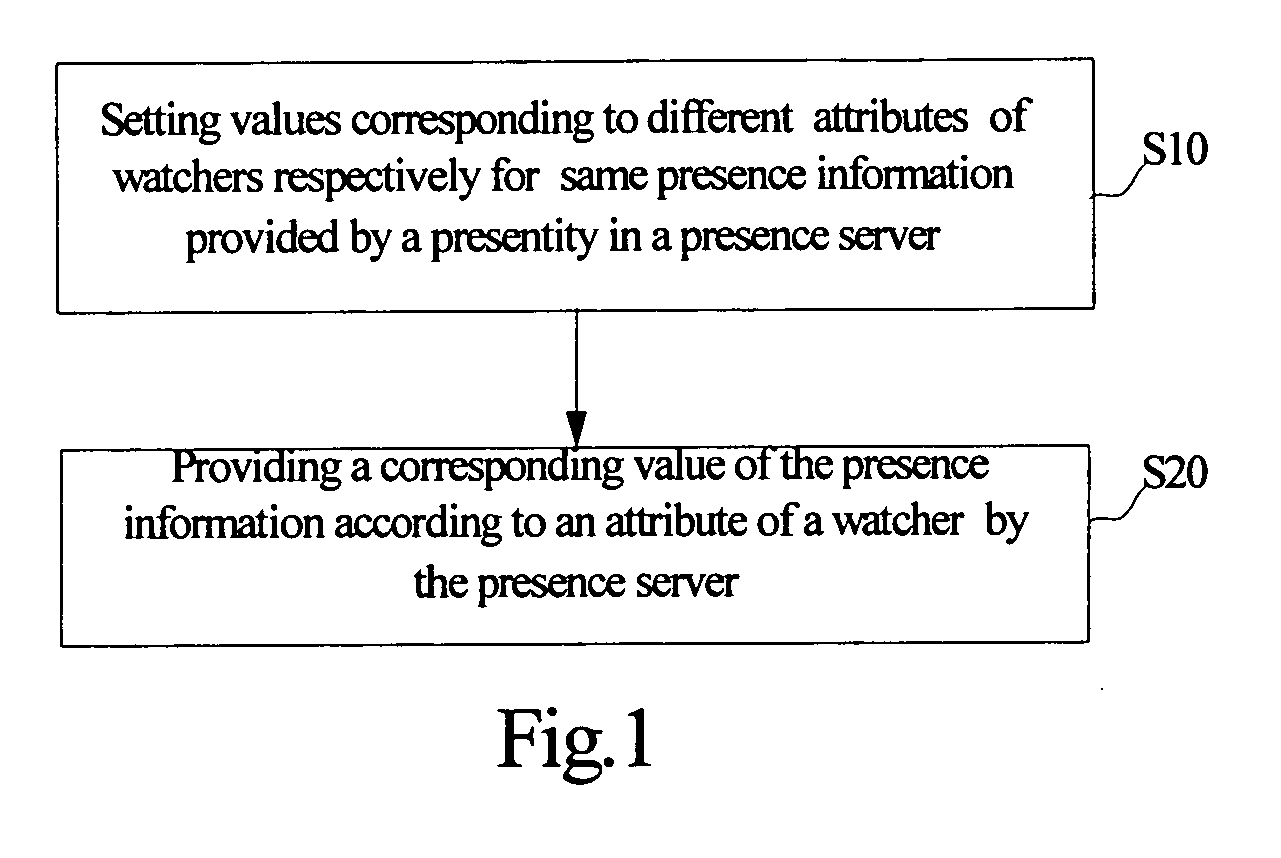
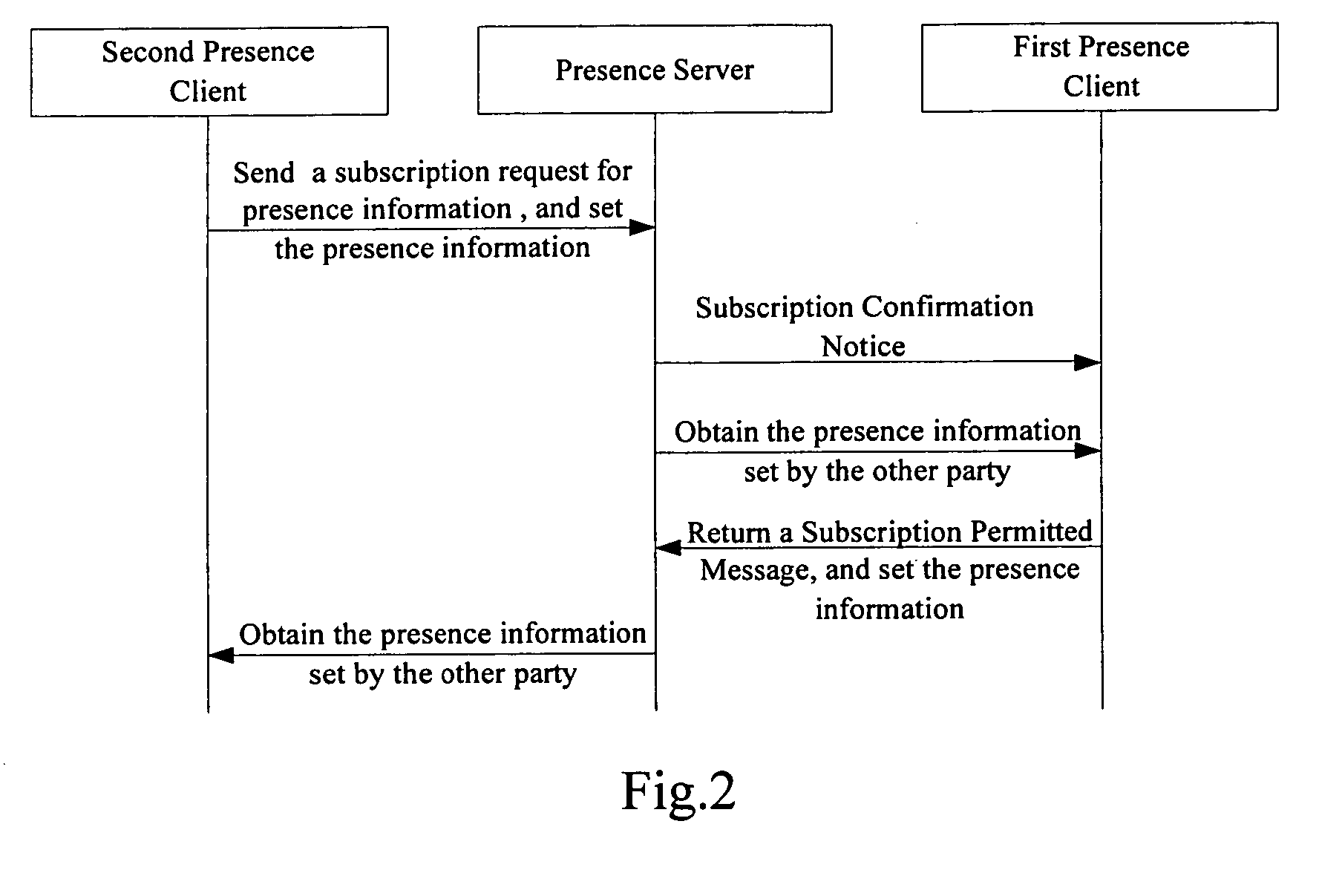
Method and system for providing presence information, the presence server thereof
InactiveUS20080114776A1Data switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsProviding presence
A method for providing presence information is applied to a presence system, that includes a presentity, a presence server and at least one watcher. The method includes that in the presence server setting separately the value corresponding to the watcher's attributes for the same presence information provided by the presentity. The presence server provides the corresponding value of the presence information according to the watcher's attributes. Accordingly, there is also a system for providing presence information and the presence server thereof. The invention can provide the corresponding value of the presence information according to the different watchers.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
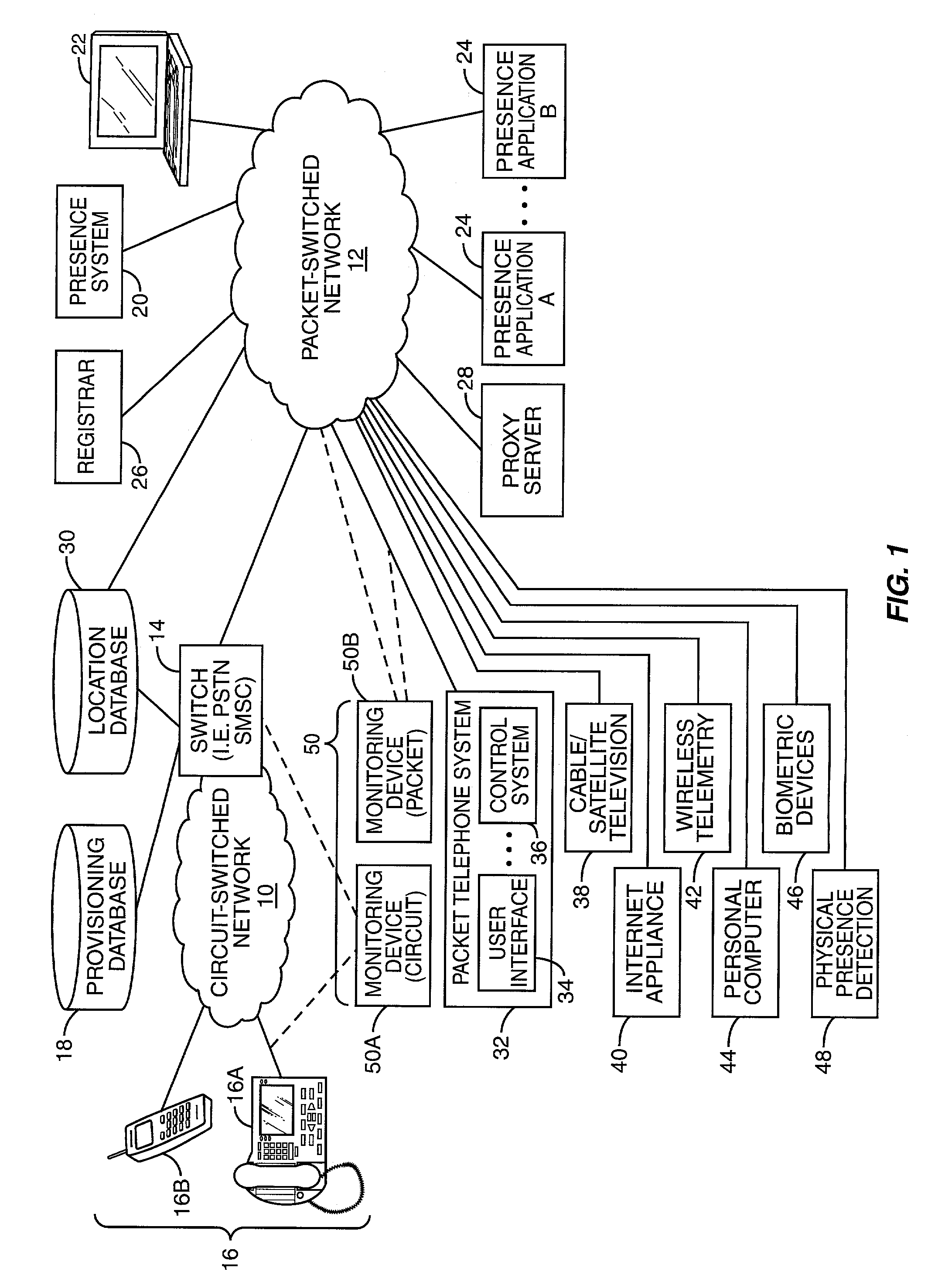
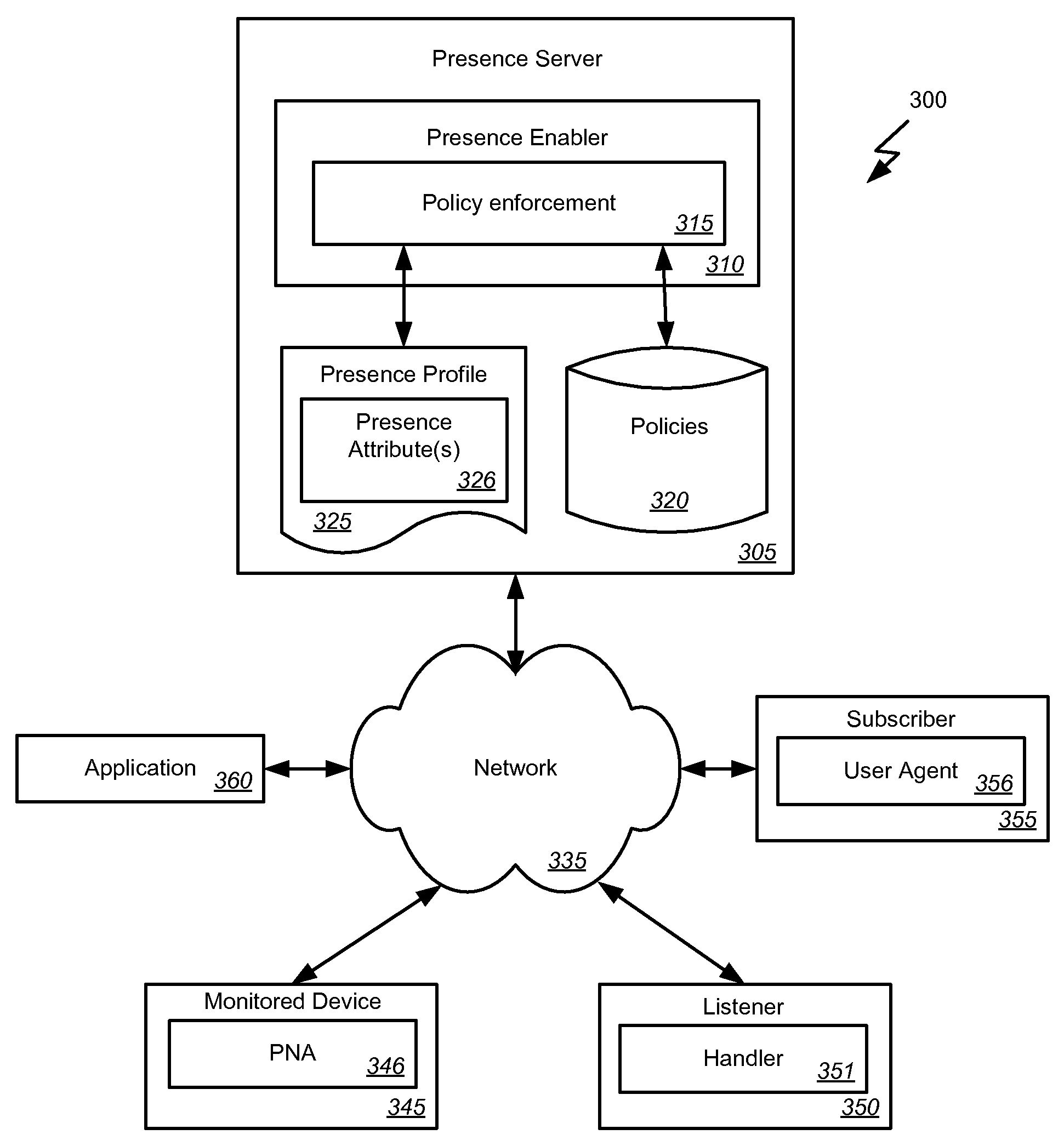
Presence-based event driven architecture
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for using a presence-based network to monitor systems, devices, or agents. According to one embodiment, monitoring a system can comprise receiving a publication of one or more presence attributes from a presence network agent. The presence attributes can comprise at least one attribute indicating information other than presence information. A presence profile associated with the presence network agent can be updated based on the received presence attributes. One or more of the presence attributes of the presence profile associated with the presence network agent can be provided to a listener. For example, providing presence attributes to the listener can comprise providing a notification of a change in the at least one presence attribute. Additionally or alternatively, a request can be received from the listener for one or more presence attributes and the presence attribute can be provided in response to the request.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
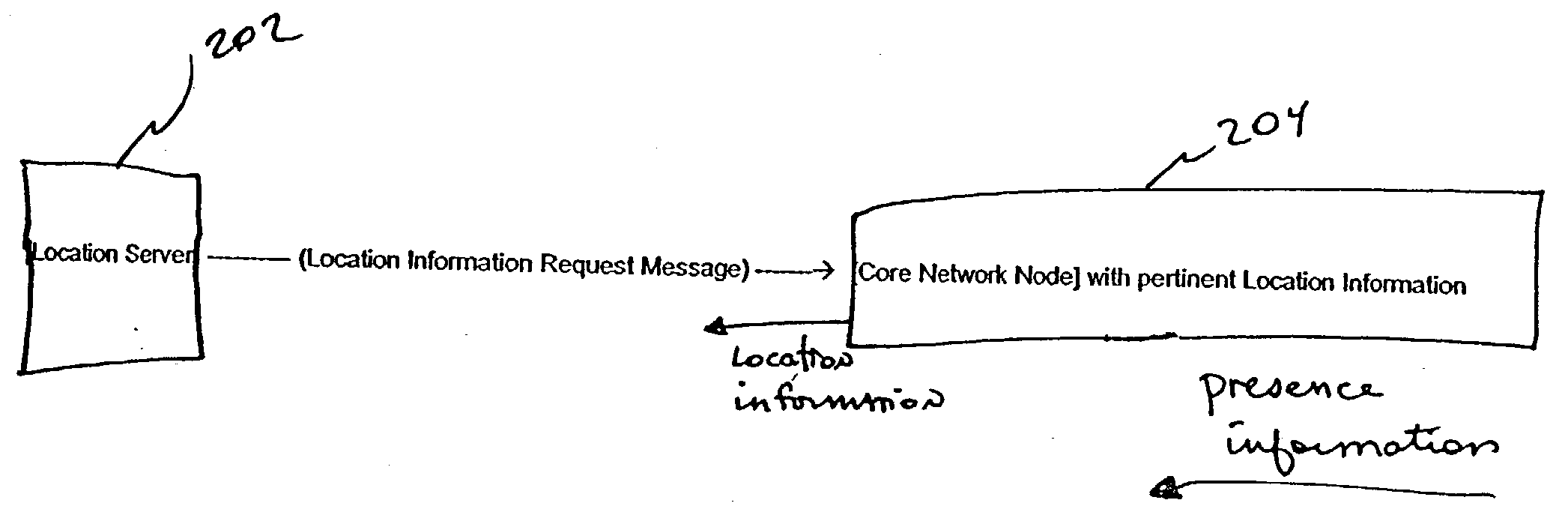
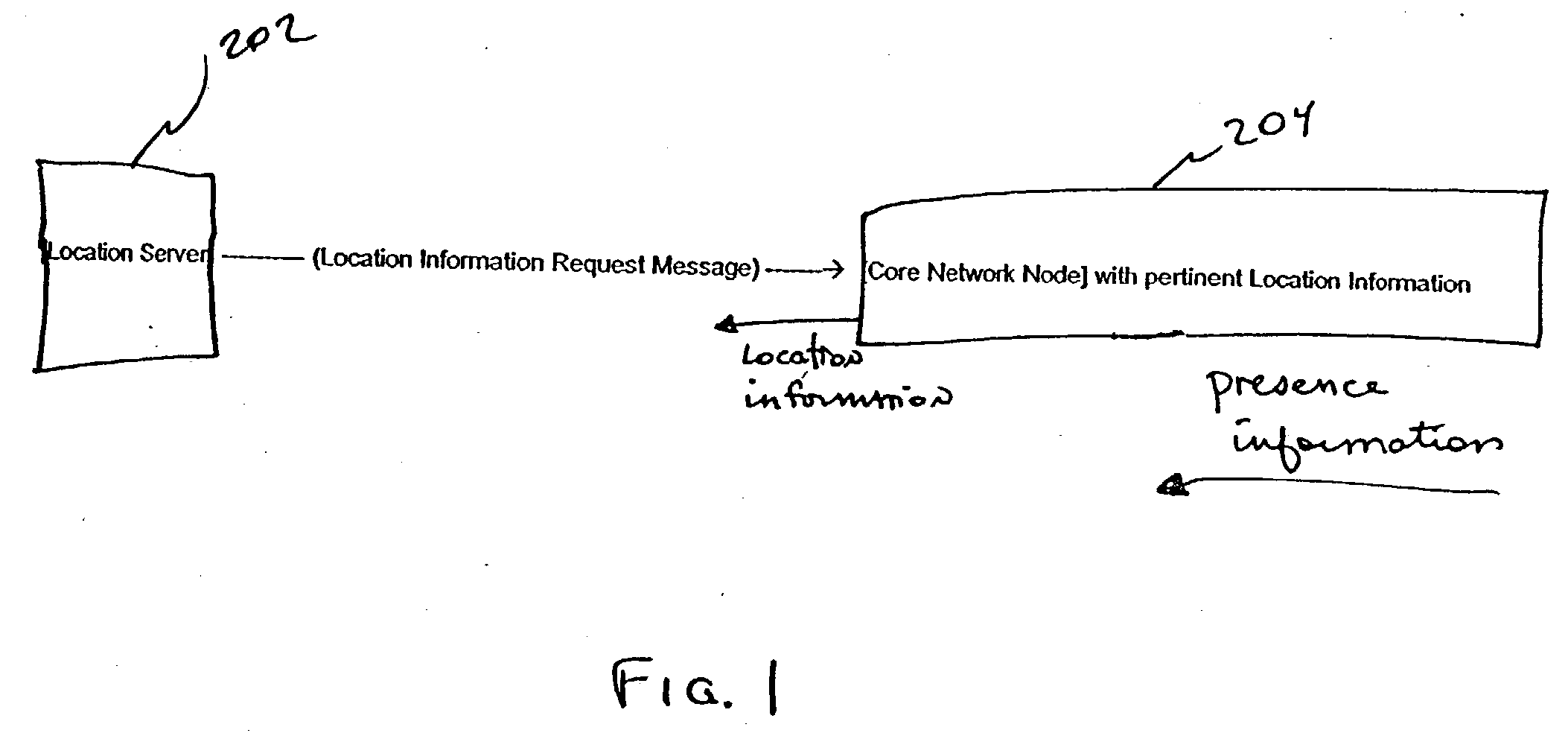
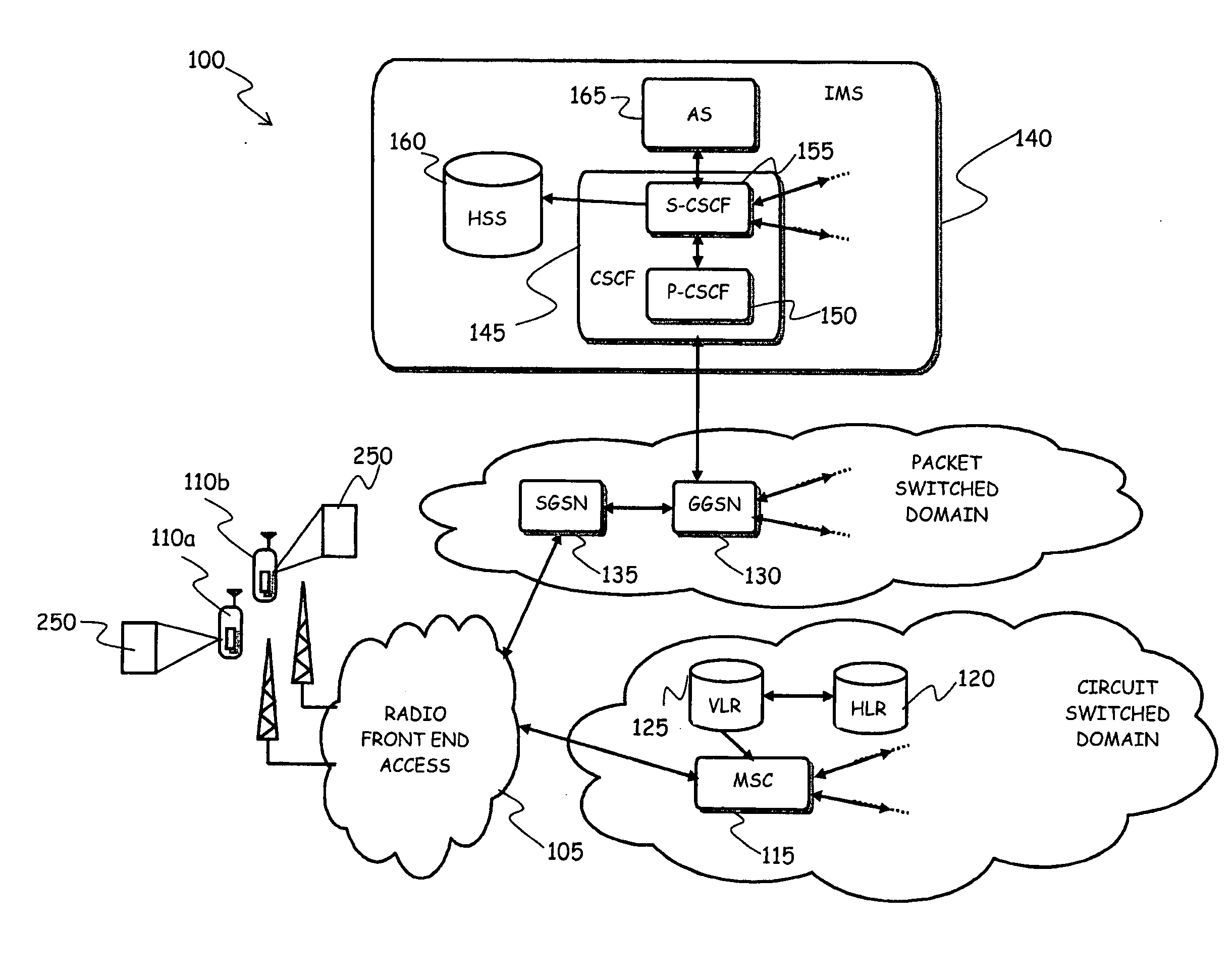
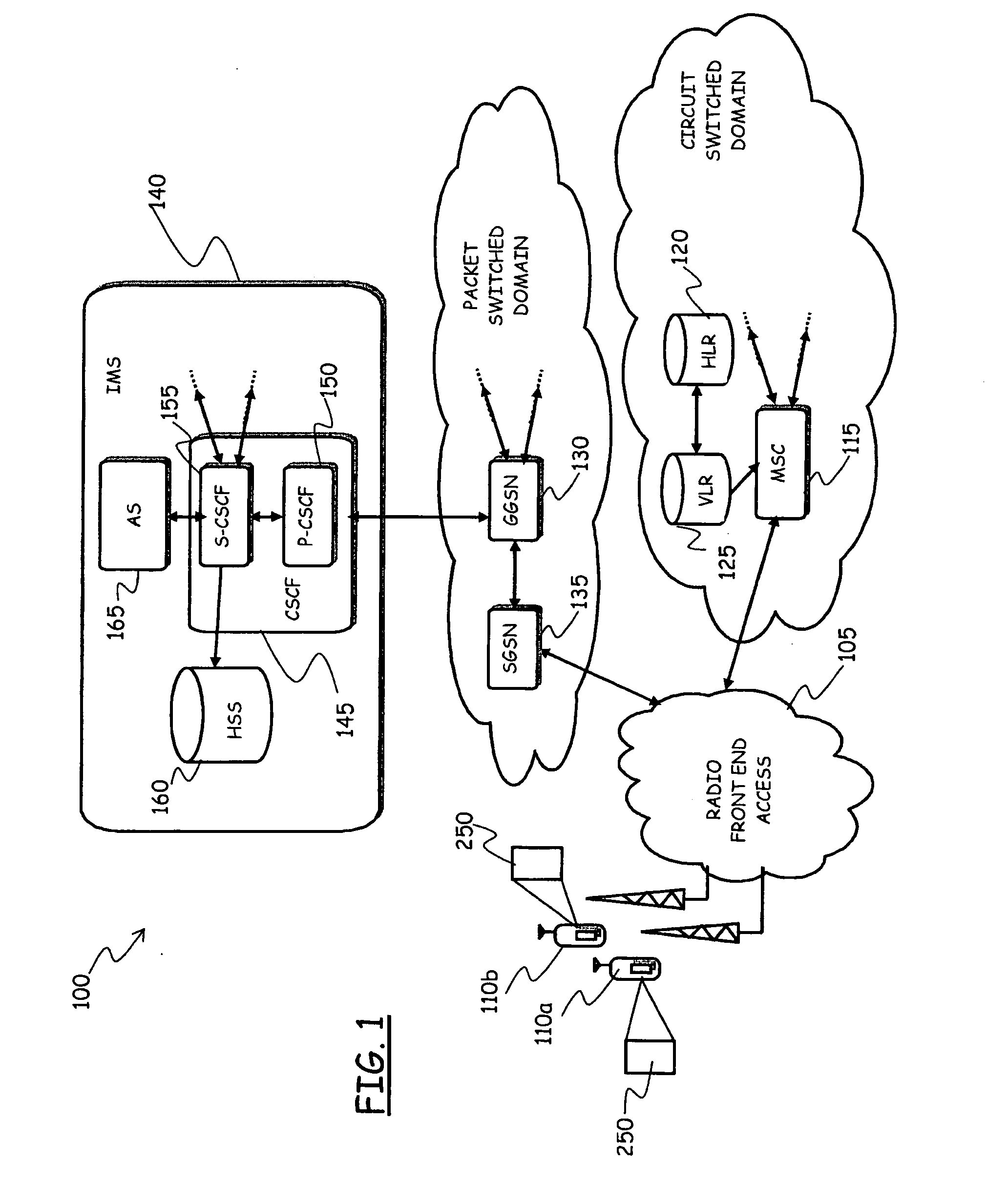
Location derived presence information
InactiveUS20040203922A1Highly available and scalable distributedMinimizing over-lapping integrationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesPresence serviceProviding presence
The number of messages required in networks where both location and presence services are deployed may be reduced, by retrieving presence data from messages otherwise intended to provide only location information. Thus, information determined in a location service scheme is utilized to provide a presence service as well. A location server requests mobile subscriber (MS) information from a Core Network (CN) Node (i.e. HLR, MSC, etc.) that can be used in determining the Location of the MS. A single message aggregates retrieval of information for two services, specifically, for both location and presence.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Presence services in a wireless communications network
InactiveUS20060148477A1Wireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPresence serviceProviding presence
A method of providing presence services in a mobile communications network, the method comprising: receiving a presence update message from a first user of a mobile device, said presence update message including a device activity presence attribute indicating activity of the mobile device; and transmitting the device activity presence attribute to a second user, which is arranged to display information representing the device activity.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
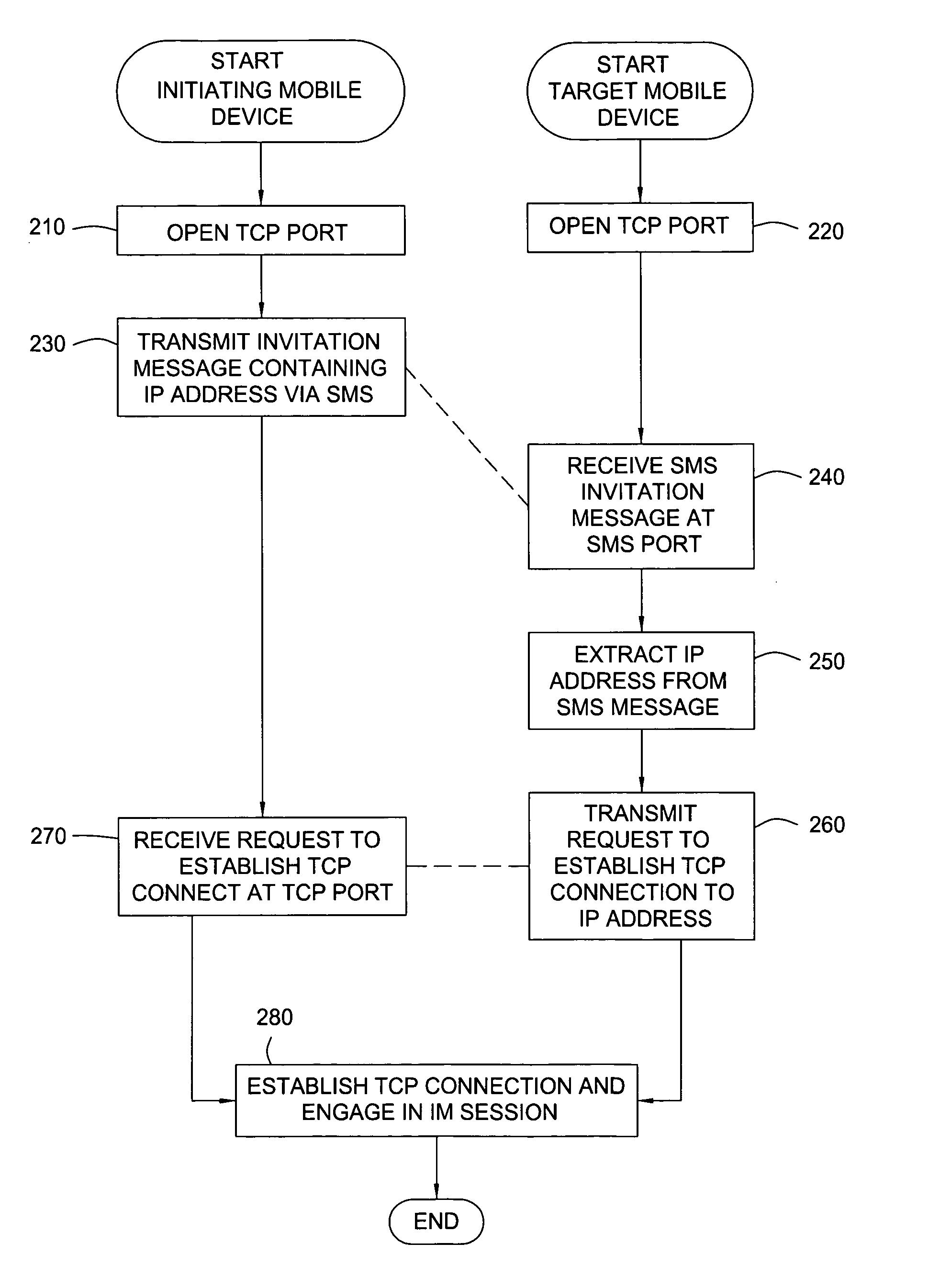
Peer-to-peer mobile instant messaging method and device
ActiveUS20050220134A1Firmly connectedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationProviding presenceNetwork data
A technique is provided for establishing peer-to-peer session-based instant messaging between mobile devices without the need for using an instant messaging registration or log-in server to provide presence information. Session-based instant messaging communications between mobile devices are established by transmitting necessary address information through page-based messaging services that utilize the underlying digital mobile network databases and services to resolve the identification and location of the mobile devices.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Home entertainment system providing presence and mobility via remote control authentication
InactiveUS8299889B2Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsBiometric dataProviding presence
An apparatus in one embodiment is operable to receive, from a remote control device associated with a video display device, biometric input of a user. Responsive to a match of the biometric input with stored biometric data of the user, the user is authenticated. The remote control device and / or the video display device are then configured based on user settings associated with the stored biometric data of the user. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Communication terminal, terminal switching system, and terminal switching method
ActiveUS20090055537A1Special service for subscribersMultiple digital computer combinationsTelecommunicationsProviding presence
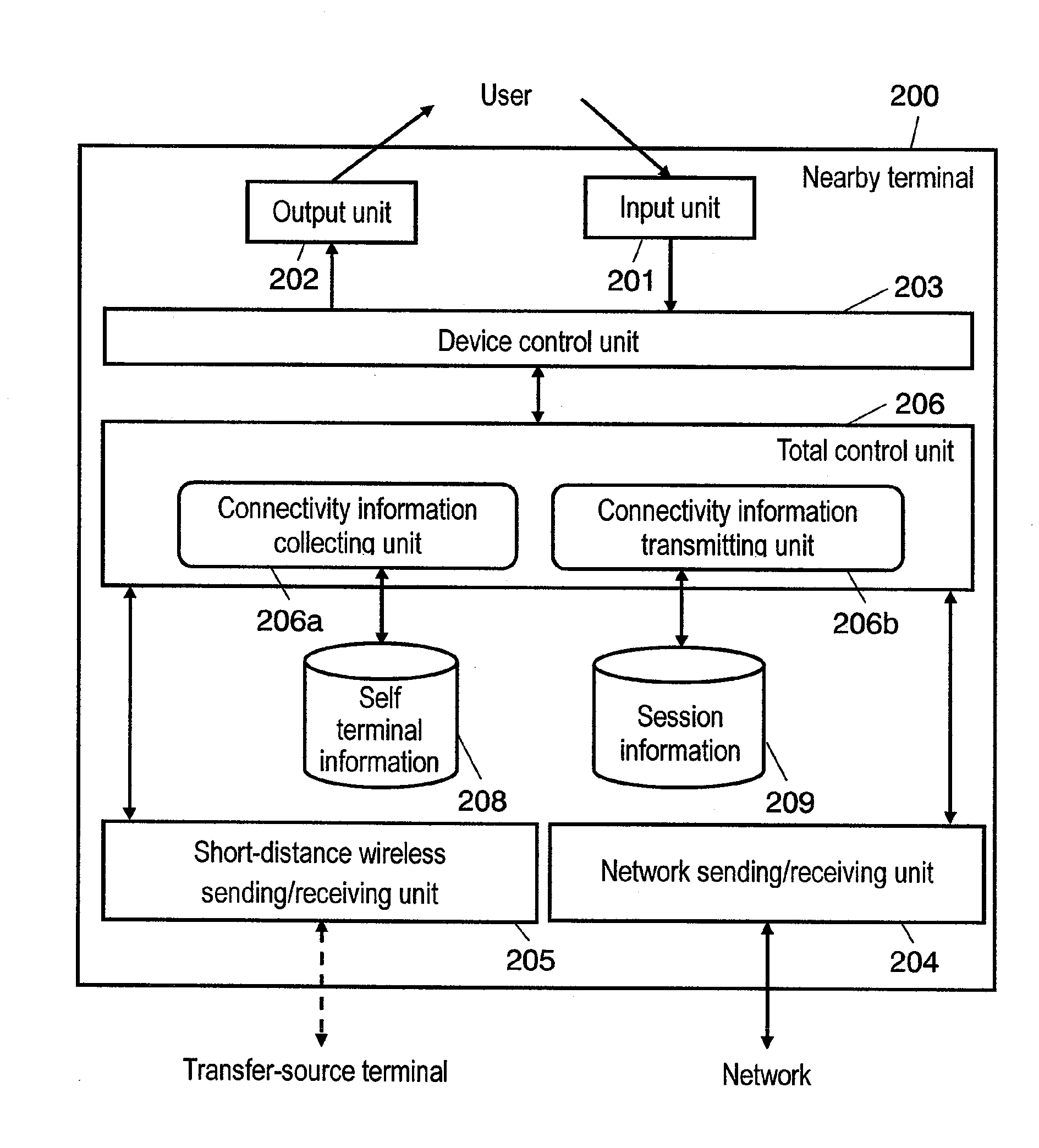
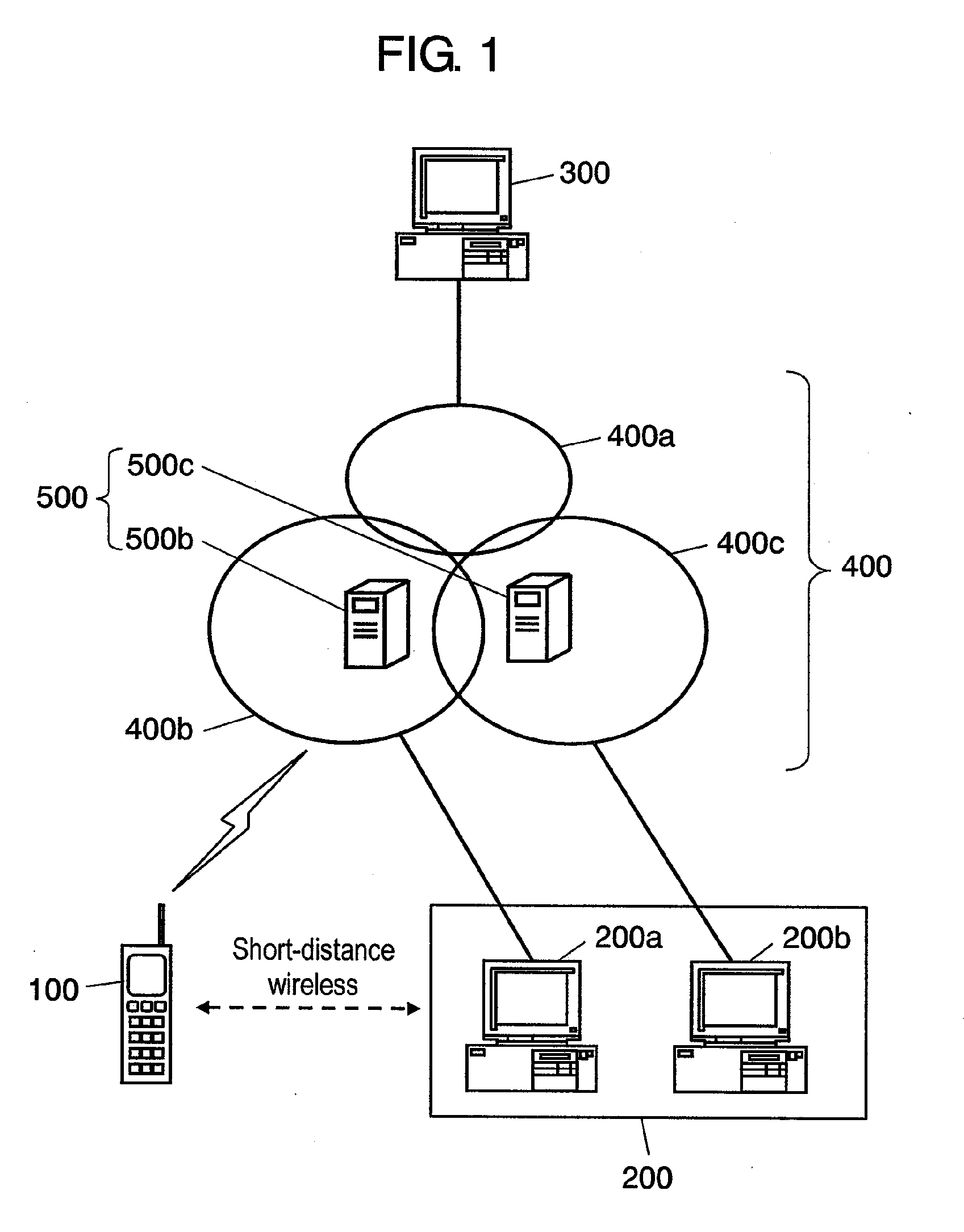
A transfer-source terminal, a communication-destination terminal, and a nearby terminal existing in the neighborhood of transfer-source terminal are provided. The nearby terminal collects connectivity information for monitoring connectivity after terminal switching by performing a communication process with the communication-destination terminal, and transmits the connectivity information collected to the transfer-source terminal. The transfer-source terminal receives connectivity information from the nearby terminal by a connectivity information receiving unit, determines a transfer-destination terminal from among the nearby terminals according to connectivity information by a transfer-destination terminal determinating unit, and transfers a communication session with a communication-destination terminal to the transfer-destination terminal determined, by a session transferring unit.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
RFID for available resources not connected to the network
ActiveUS20070036318A1Improve conferencingSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsProviding presence
Disclosed are apparatus and techniques for providing presence and location information from available media resources to participants in a media conference so that the participants can use then use such available resources in the conferencing interaction. When participating in such rich media conferences with presence and location capabilities, apparatus and techniques are provided for determining the device(s) being used and their capabilities and determining available resources presently connected to a network that is available to the participants and presenting such presence information to the conference participants. Additionally, apparatus and techniques are provided for obtaining presence and location knowledge of potential resources that are accessible but not connected to the network or shutdown and presenting such information to the participants. Thus, the participants can obtain presence and location information regarding accessible resources, including off-line or shutdown resources, and then use such information to enhance the conference in a number of ways.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Real-Time Notification of Presence Changes
InactiveUS20080244026A1Special service for subscribersMultiple digital computer combinationsProviding presenceCommunication device
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
Presence sensing
InactiveCN103534664APower supply for data processingEnergy efficient computingProviding presenceSimulation
Owner:APPLE INC
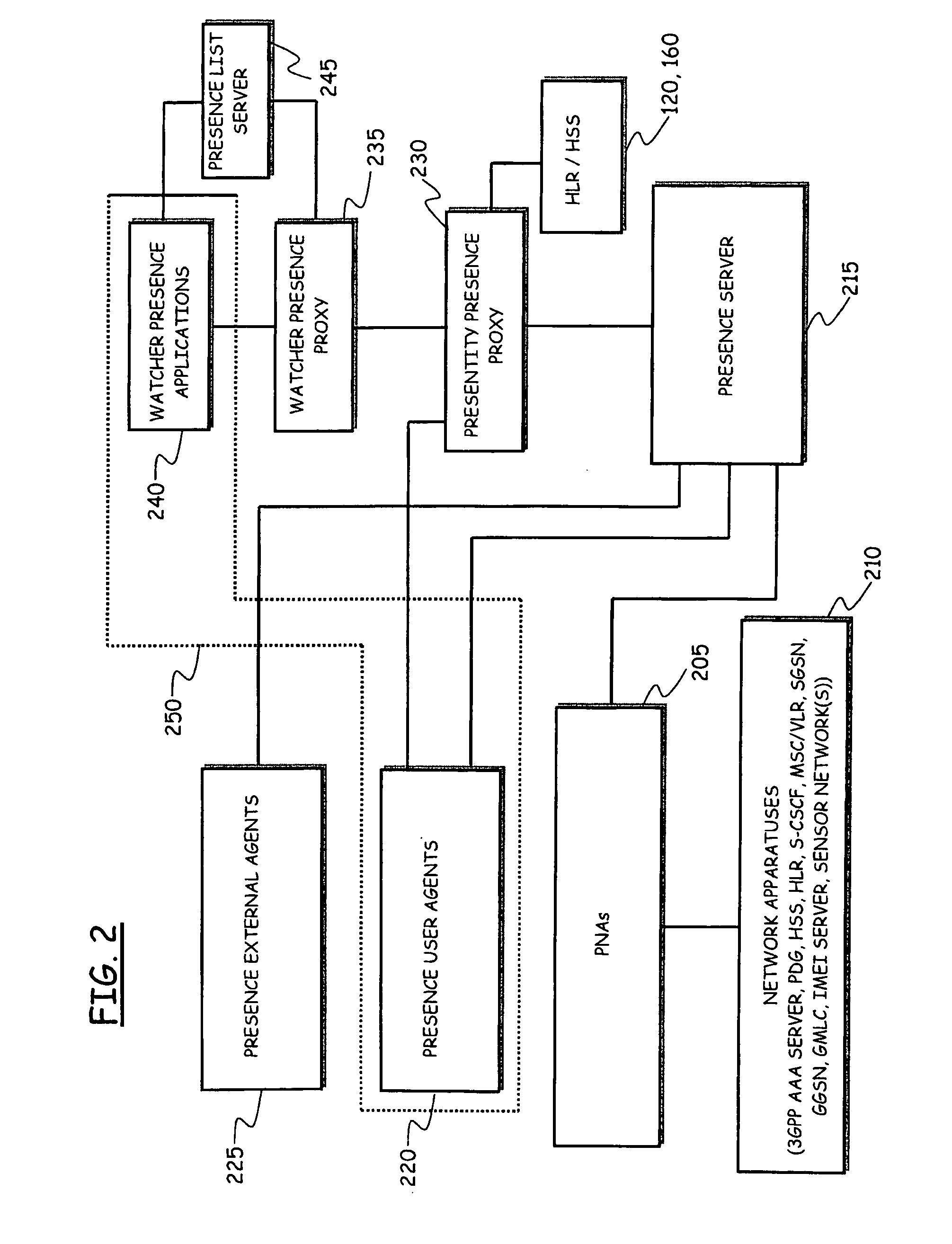
Method and System for Providing Presence Information
ActiveUS20090275314A1Reduce loadReduce data volumeSpecial service for subscribersData switching networksTelecommunications networkProviding presence
A method for providing presence information associated with a first user of a telecommunications network, includes collecting from at least one network apparatus user-related data adapted to build the presence information; and publishing the collected user-related data. The publishing includes arranging the collected user-related data in the presence information and making it available to at least a second user. The collecting of the user-related data from the network apparatus is conditioned to the receipt from the second user of a request for providing the presence information for the first user.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Method for providing presence and location information of mobiles in a wireless network
InactiveUS20110013528A1Easy to identifyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProviding presenceMobile device
In one embodiment, the method includes collecting, at the base station, presence information for each of the plurality of mobile devices, respectively. Location information is collected at the base station for each of the plurality of mobile devices, respectively. Integrated information is generated at the base station for each of the plurality of mobile devices, respectively, based on the collected presence and location information.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
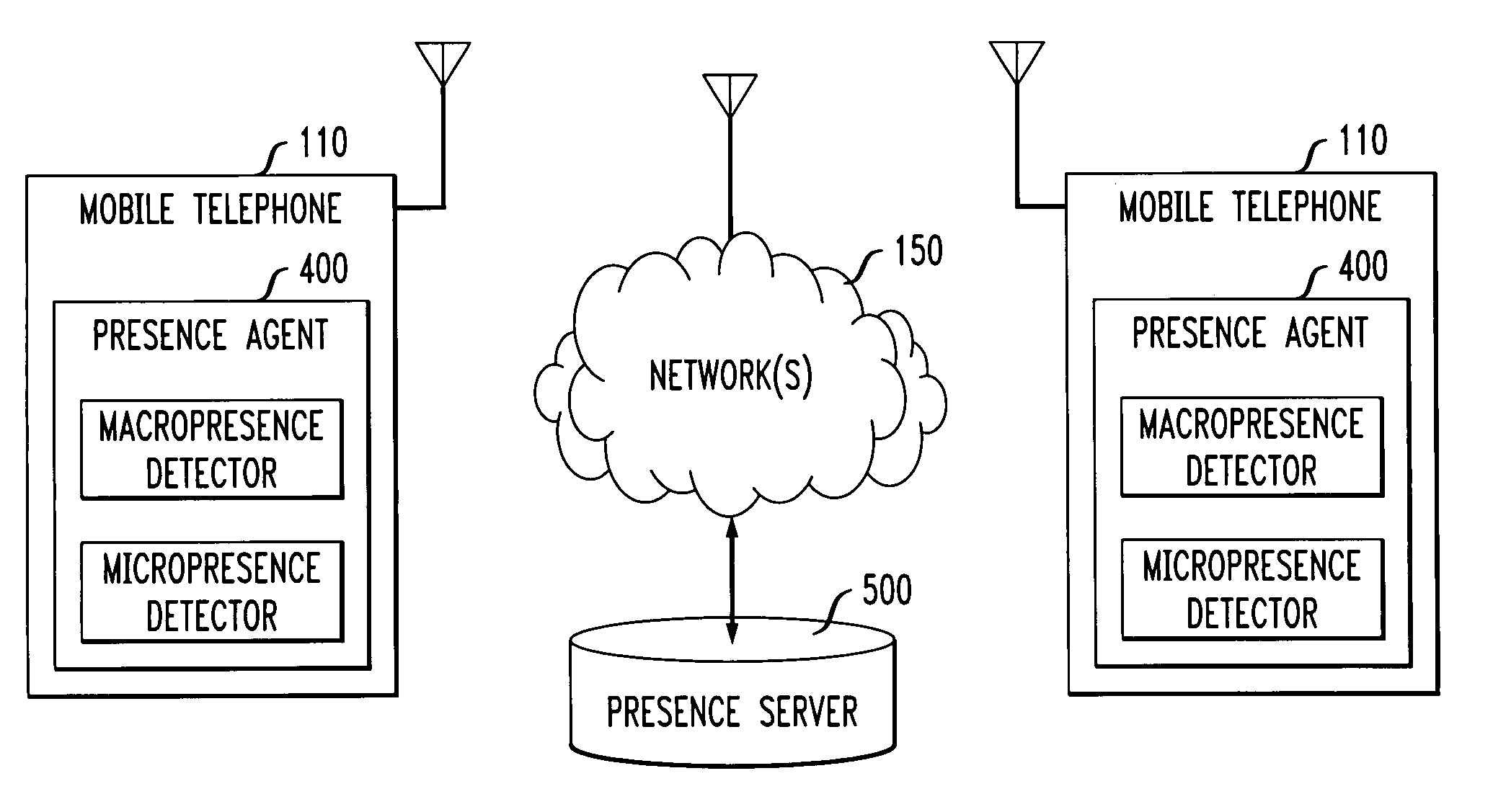
Methods and apparatus for determining a presence of a user
ActiveUS20060117050A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsProviding presenceMultimedia
Owner:AVAYA INC
System and method for providing presence age information in a unified communication system
A telecommunications system includes a network; a plurality of client devices operably coupled to said network, said plurality of client devices adapted to set one or more time contact parameters for buddies on a contact list; and a presence server including a timer, and adapted to maintain a timing of time contacts for selected contacts responsive to said parameters.
Owner:UNIFY INC
Method and system for rating patents and other intangible assets
A statistical patent rating method and system is provided for independently assessing the relative breadth (“B”), defensibility (“D”) and commercial relevance (“R”) of individual patent assets and other intangible intellectual property assets. The invention provides new and valuable information that can be used by patent valuation experts, investment advisors, economists and others to help guide future patent investment decisions, licensing programs, patent appraisals, tax valuations, transfer pricing, economic forecasting and planning, and even mediation and / or settlement of patent litigation lawsuits. In one embodiment the invention provides a statistically-based patent rating method and system whereby relative ratings or rankings are generated using a database of patent information by identifying and comparing various characteristics of each individual patent to a statistically determined distribution of the same characteristics within a given patent population. For example, a first population of patents having a known relatively high intrinsic value or quality (e.g. successfully litigated patents) is compared to a second population of patents having a known relatively low intrinsic value or quality (e.g. unsuccessfully litigated patents). Based on a statistical comparison of the two populations, certain characteristics are identified as being more prevalent or more pronounced in one population group or the other to a statistically significant degree. Multiple such statistical comparisons are used to construct and optimize a computer model or computer algorithm that can then be used to predict and / or provide statistically-accurate probabilities of a desired value or quality being present or a future event occurring, given the identified characteristics of an individual patent or group of patents.
Owner:PATENTRATINGS
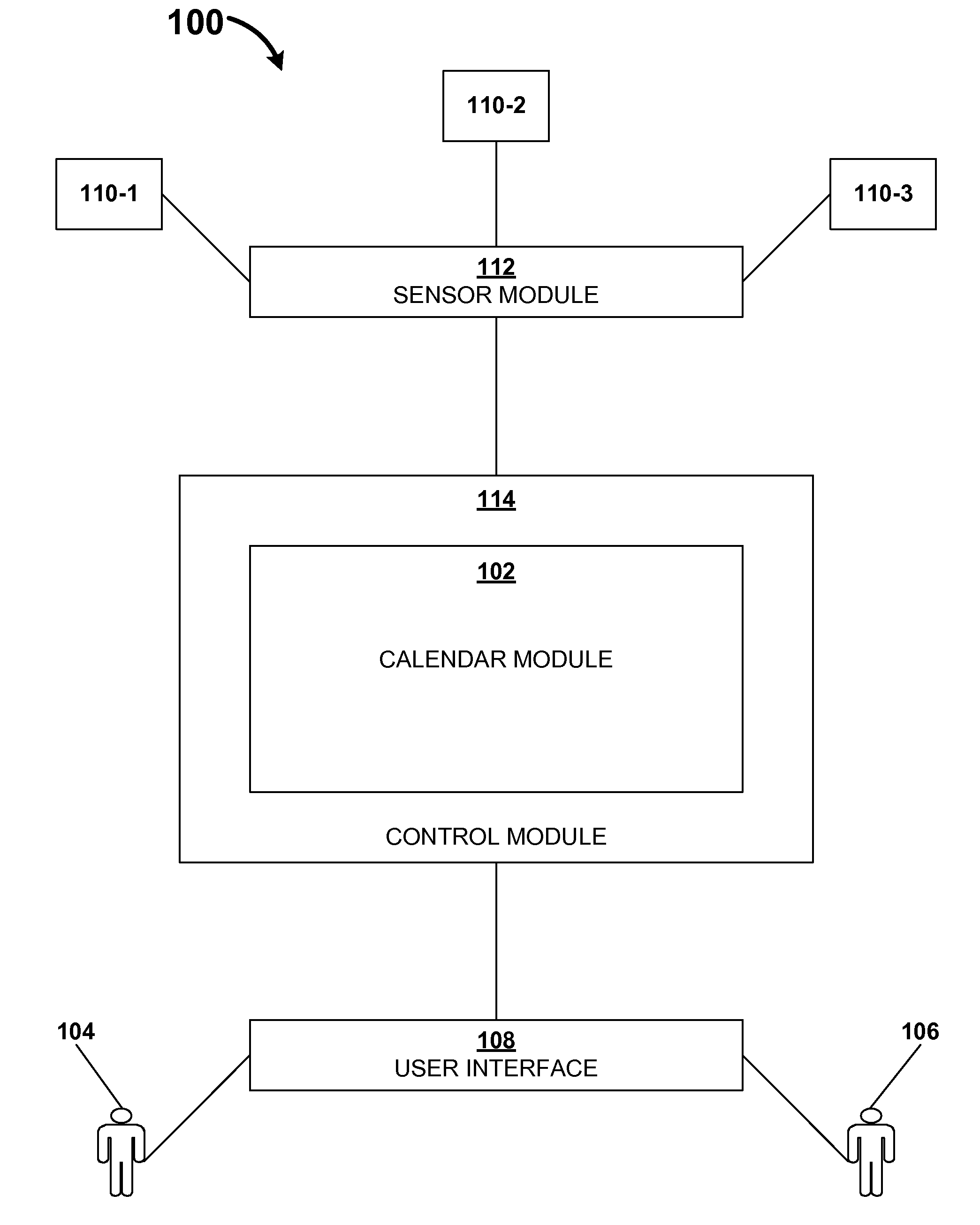
Presence-enhanced calendaring
InactiveUS20080244417A1Not accurateInput/output processes for data processingProviding presenceData science
Presence-enhanced calendaring is provided. A user can enter scheduled-activity information related to the user in a manner consistent with conventional calendaring systems. In addition to receiving scheduled-activity information related to a user, the presence-enhanced calendaring systems receive sensor-generated information related to a current activity of the user. The presence-enhanced calendaring system integrates the sensor-generated information related to a current activity of the user with the scheduled-activity information related to the user.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com