Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
247 results about "Paiute language" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
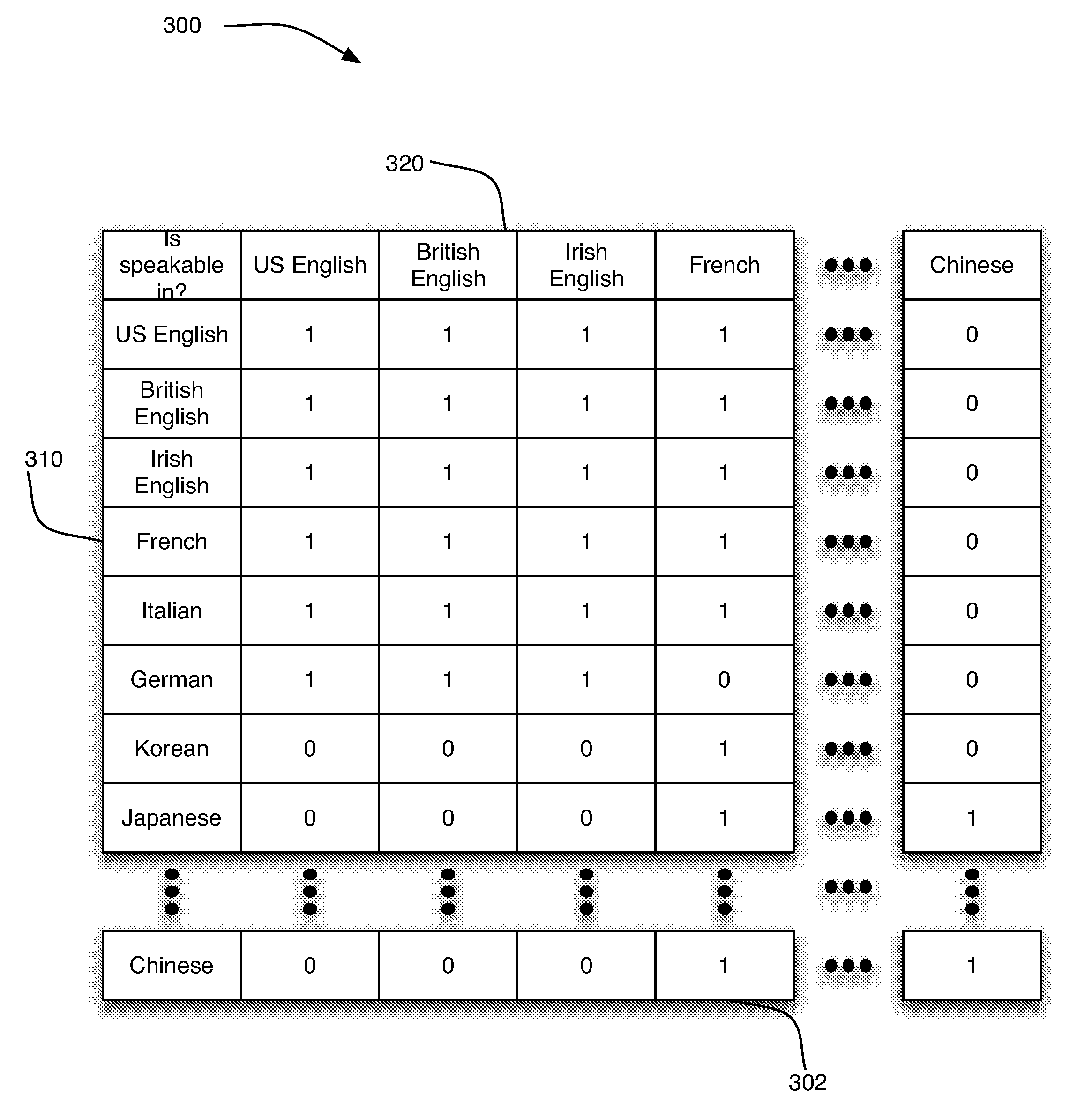
Paiute--sometimes called Northern Paiute to distinguish it from Ute--is a Uto-Aztecan language of the Western Plateau. The language is spoken natively by more than 1000 Paiute Indians in Nevada, California, Oregon and Idaho and also by some Shoshone-Bannock people in Idaho.
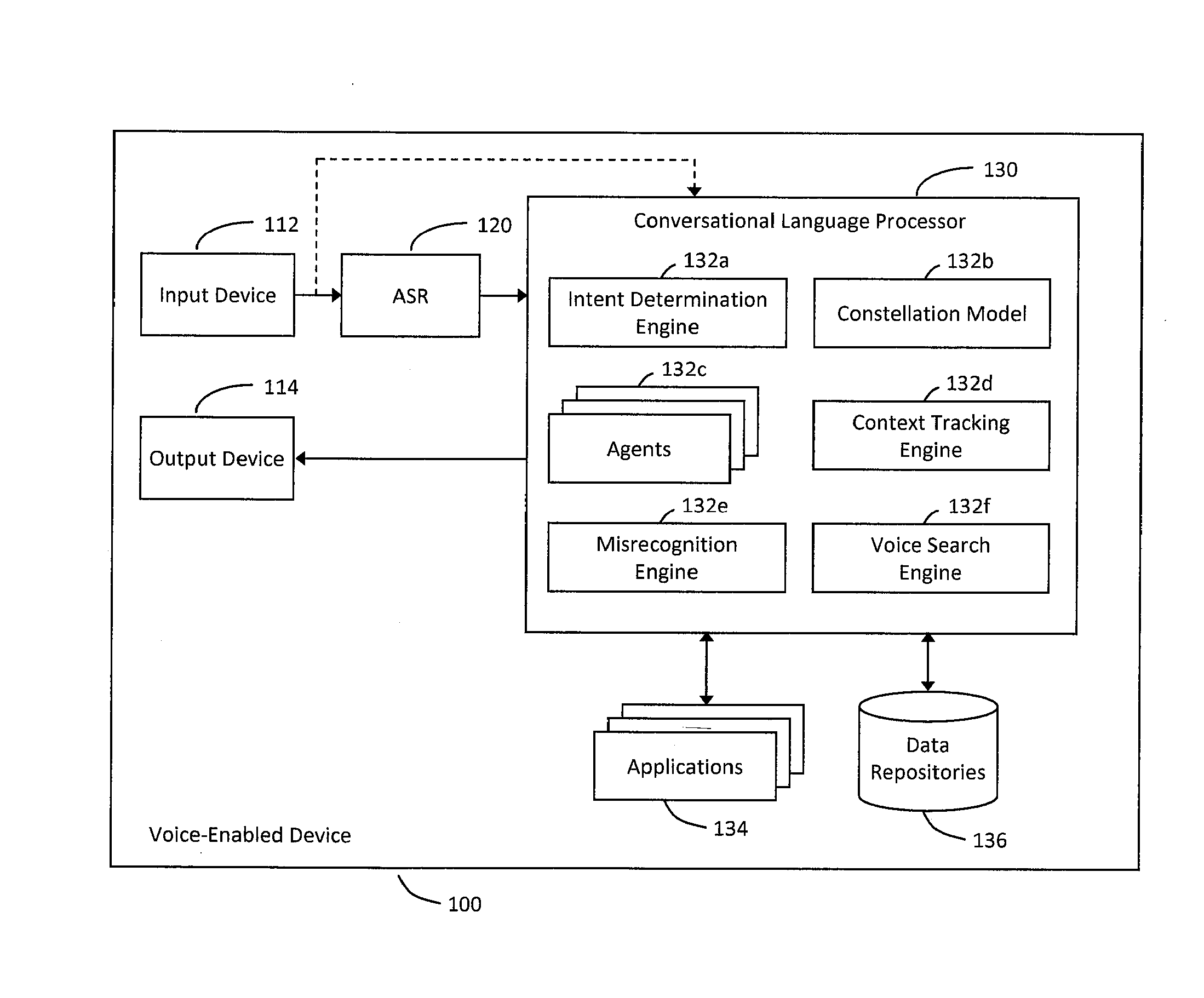
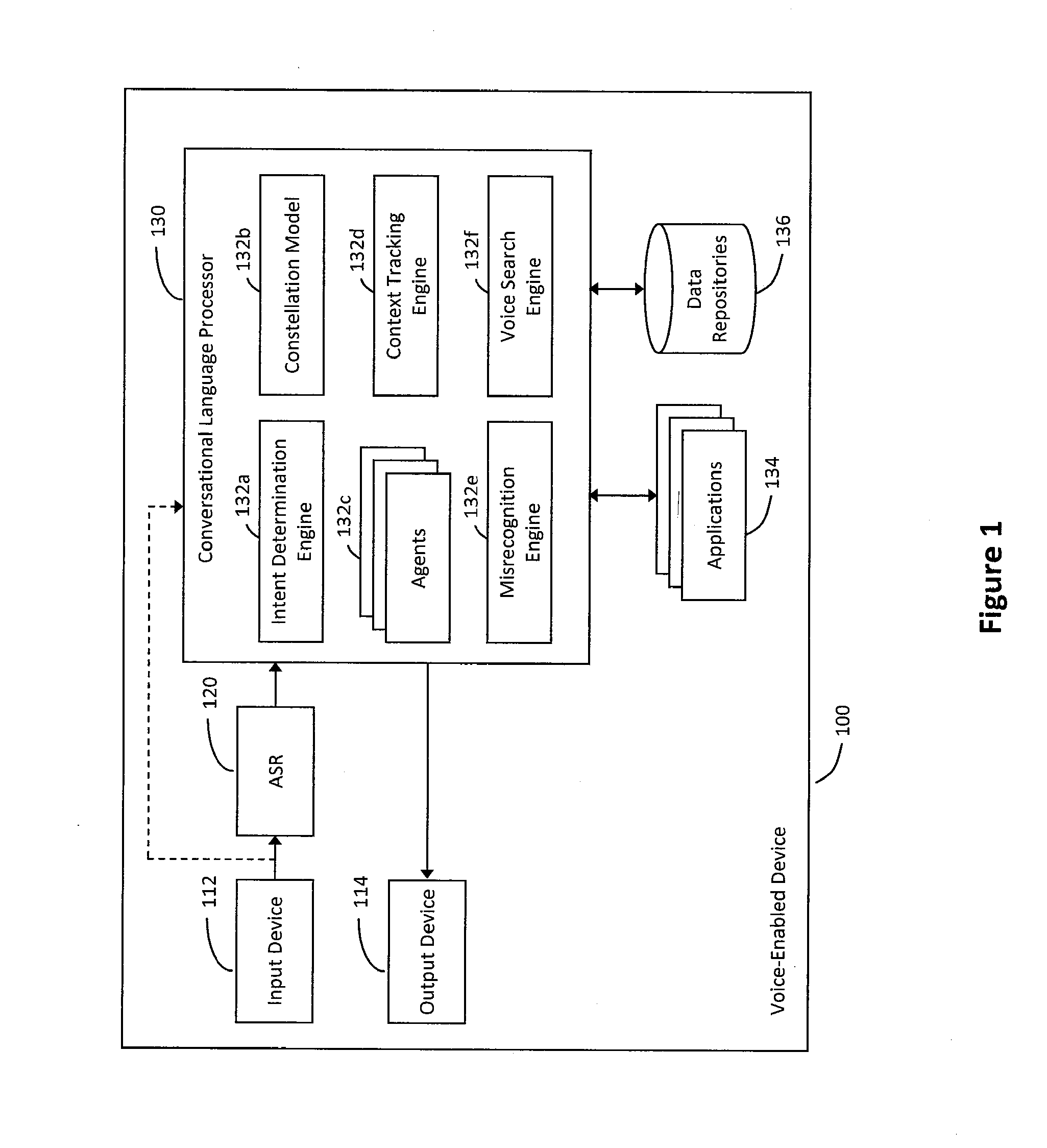
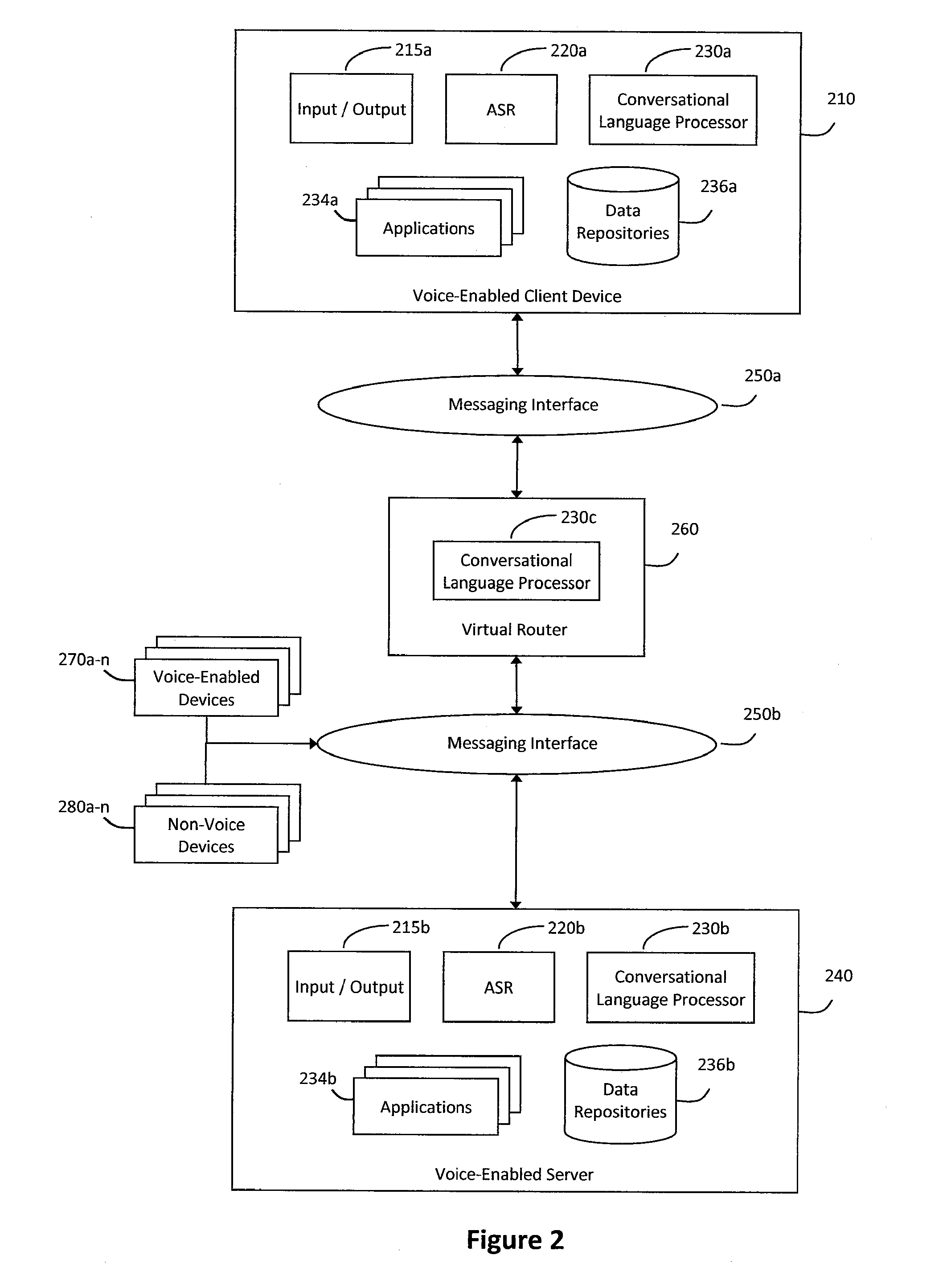
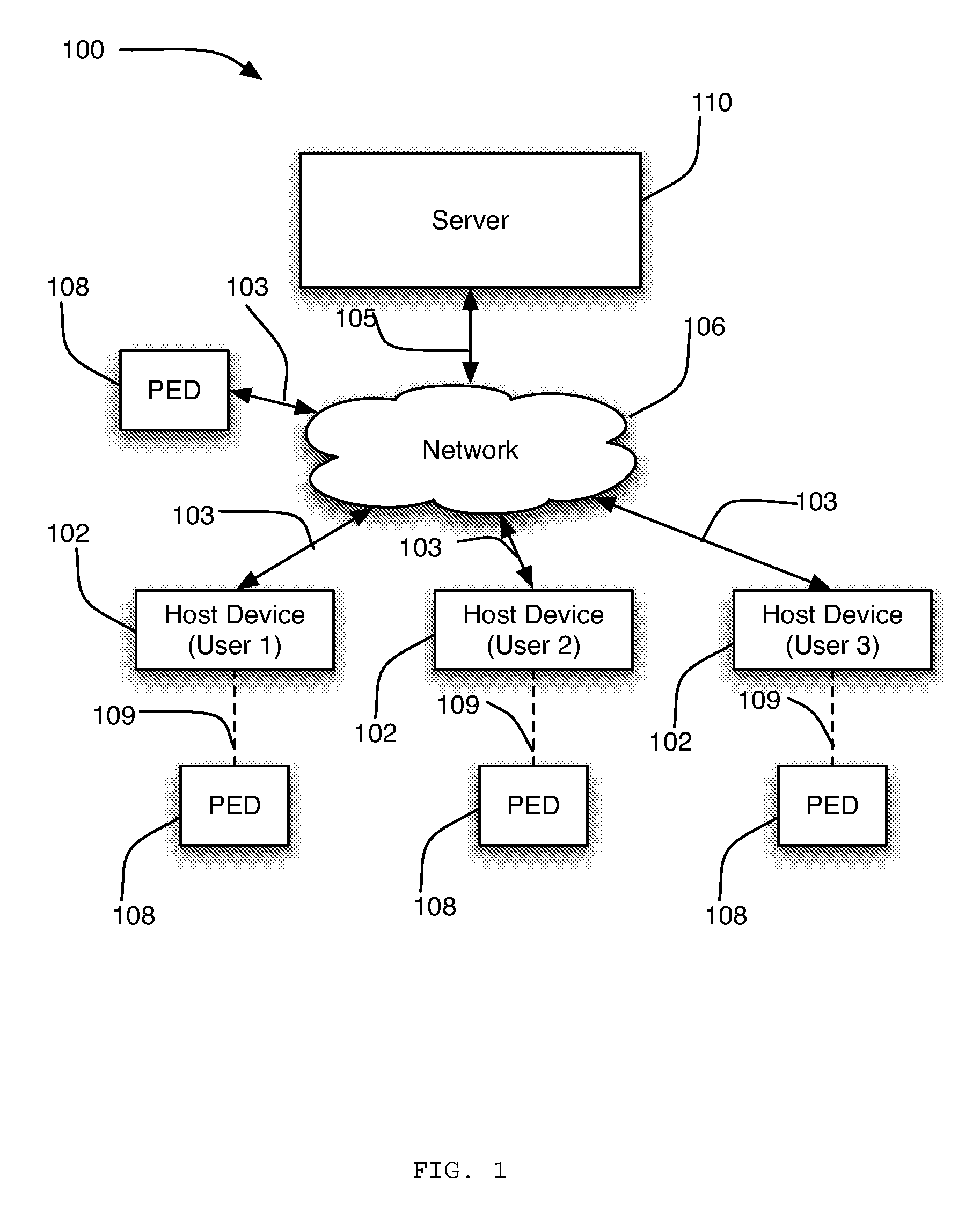
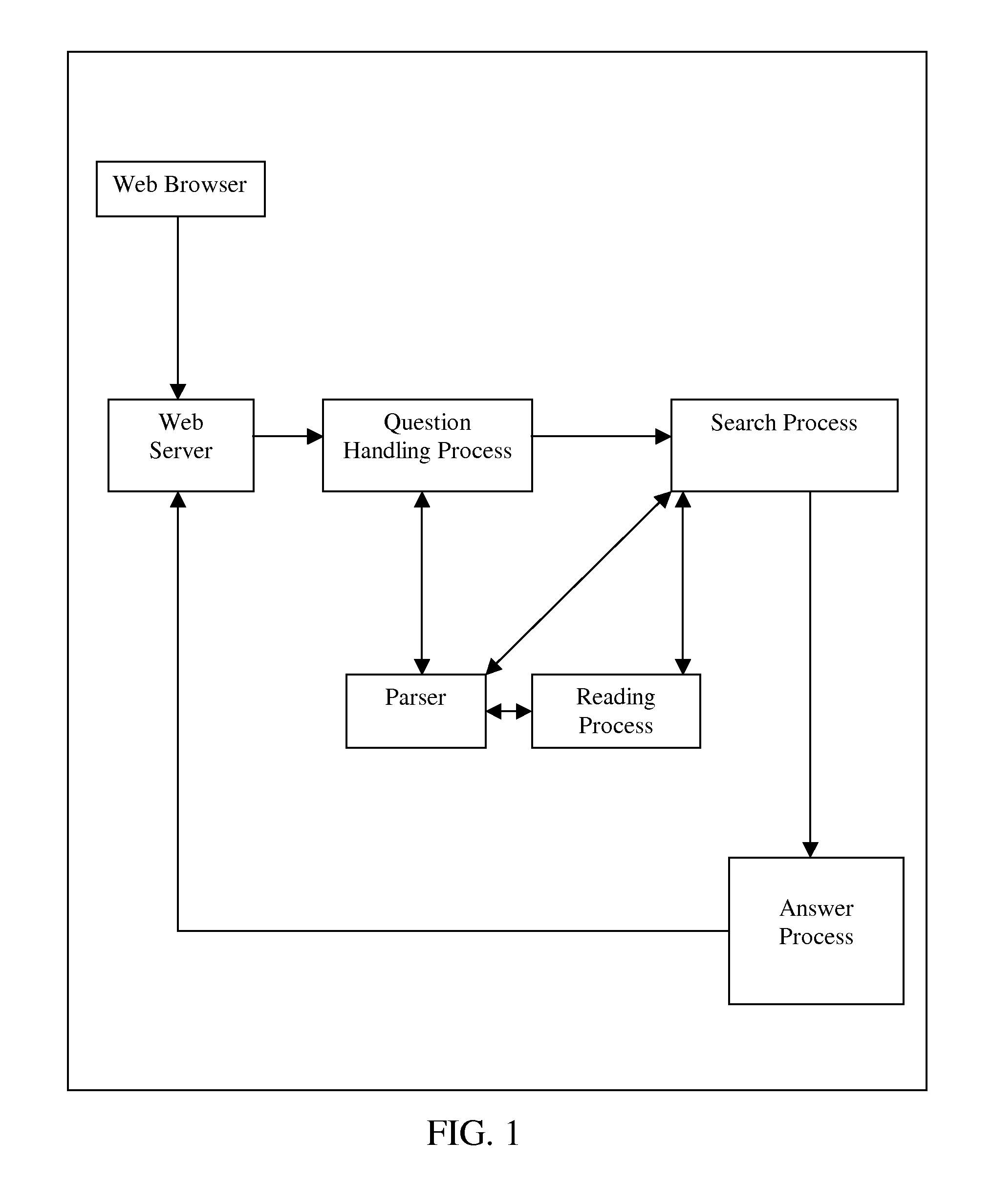
System and method for providing a natural language content dedication service
ActiveUS20110112921A1Less chargeNatural language translationSpeech recognitionSpeech soundWorld Wide Web
The system and method described herein may provide a natural language content dedication service in a voice services environment. In particular, providing the natural language content dedication service may generally include detecting multi-modal device interactions that include requests to dedicate content, identifying the content requested for dedication from natural language utterances included in the multi-modal device interactions, processing transactions for the content requested for dedication, processing natural language to customize the content for recipients of the dedications, and delivering the customized content to the recipients of the dedications.
Owner:VB ASSETS LLC
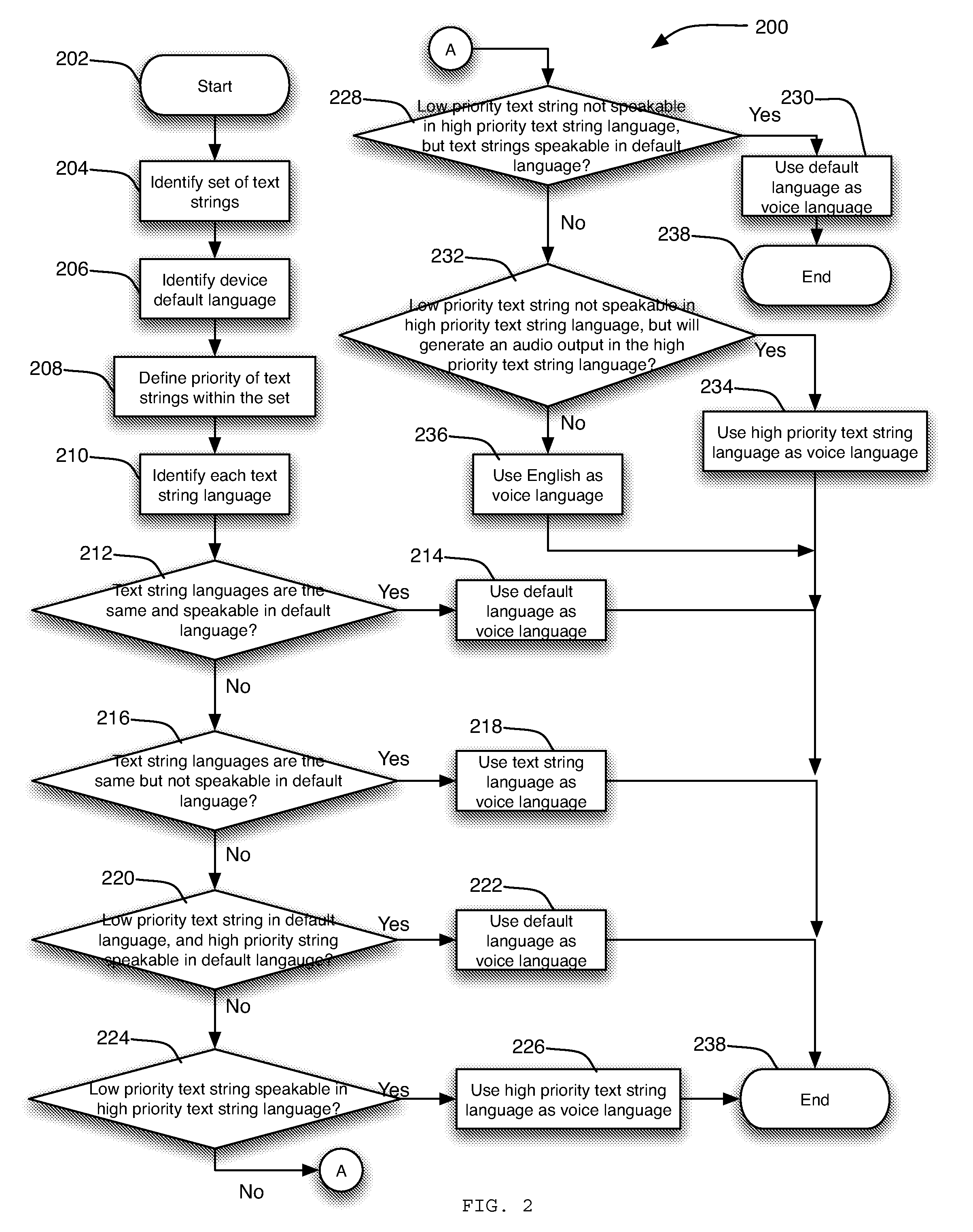
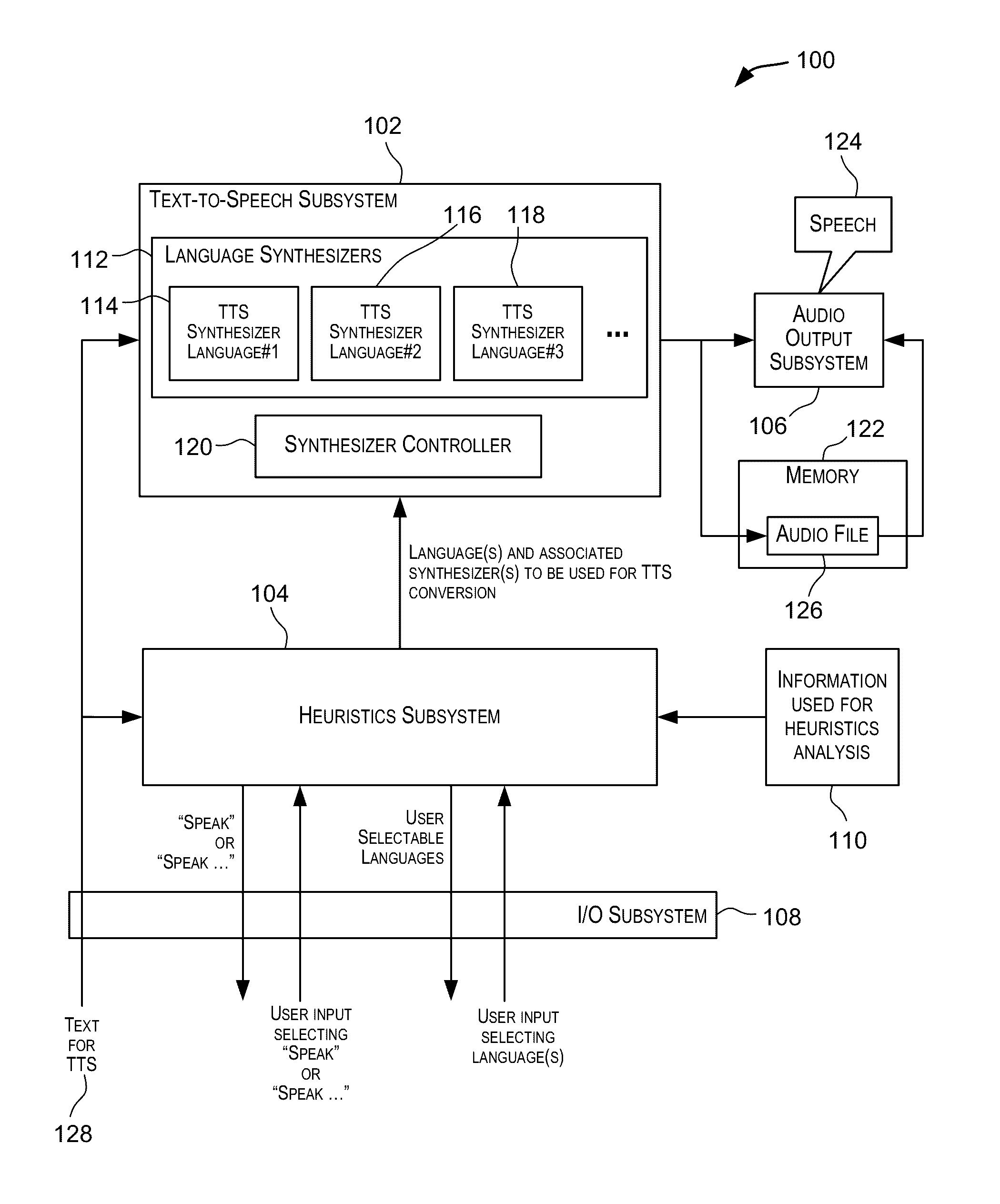
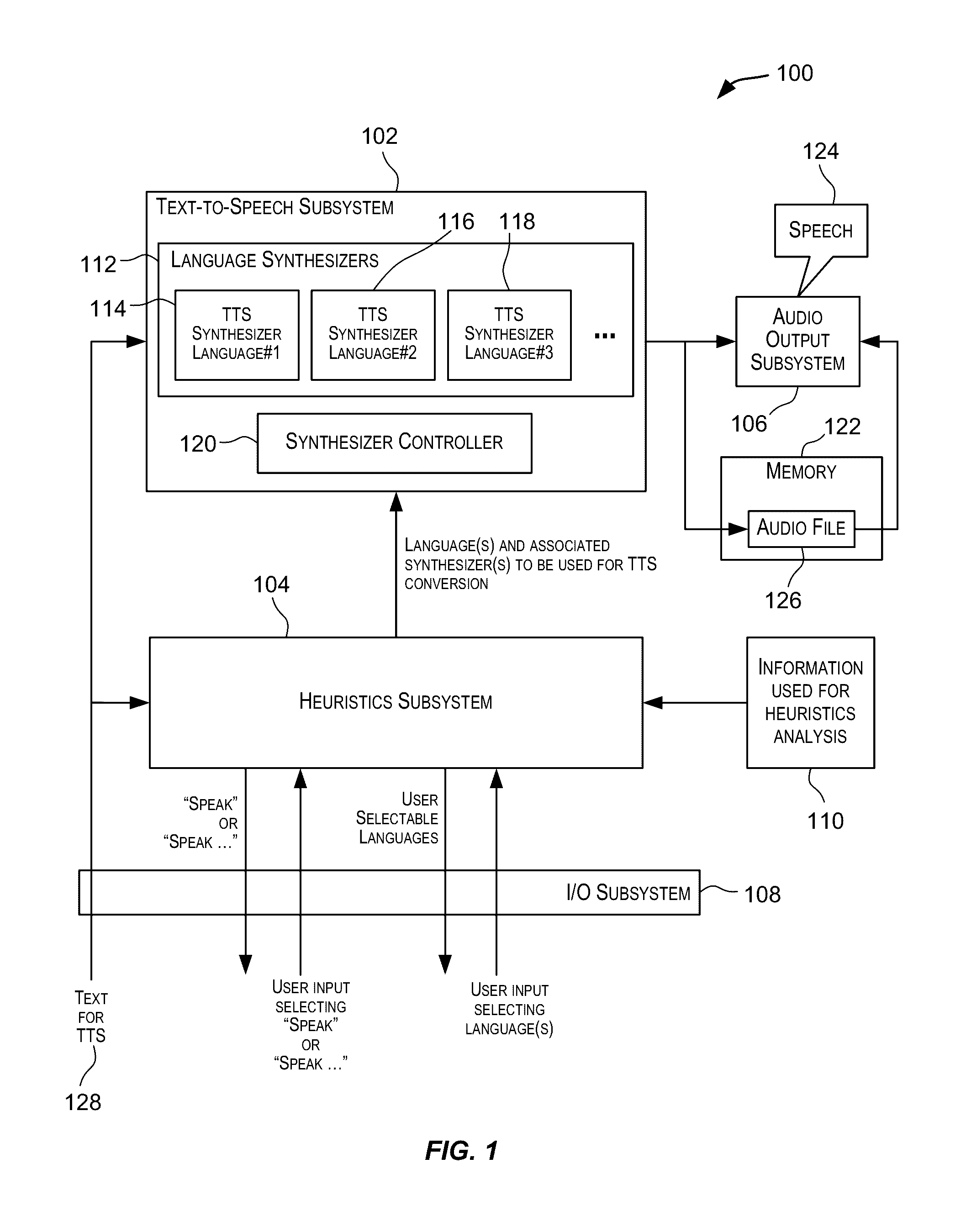
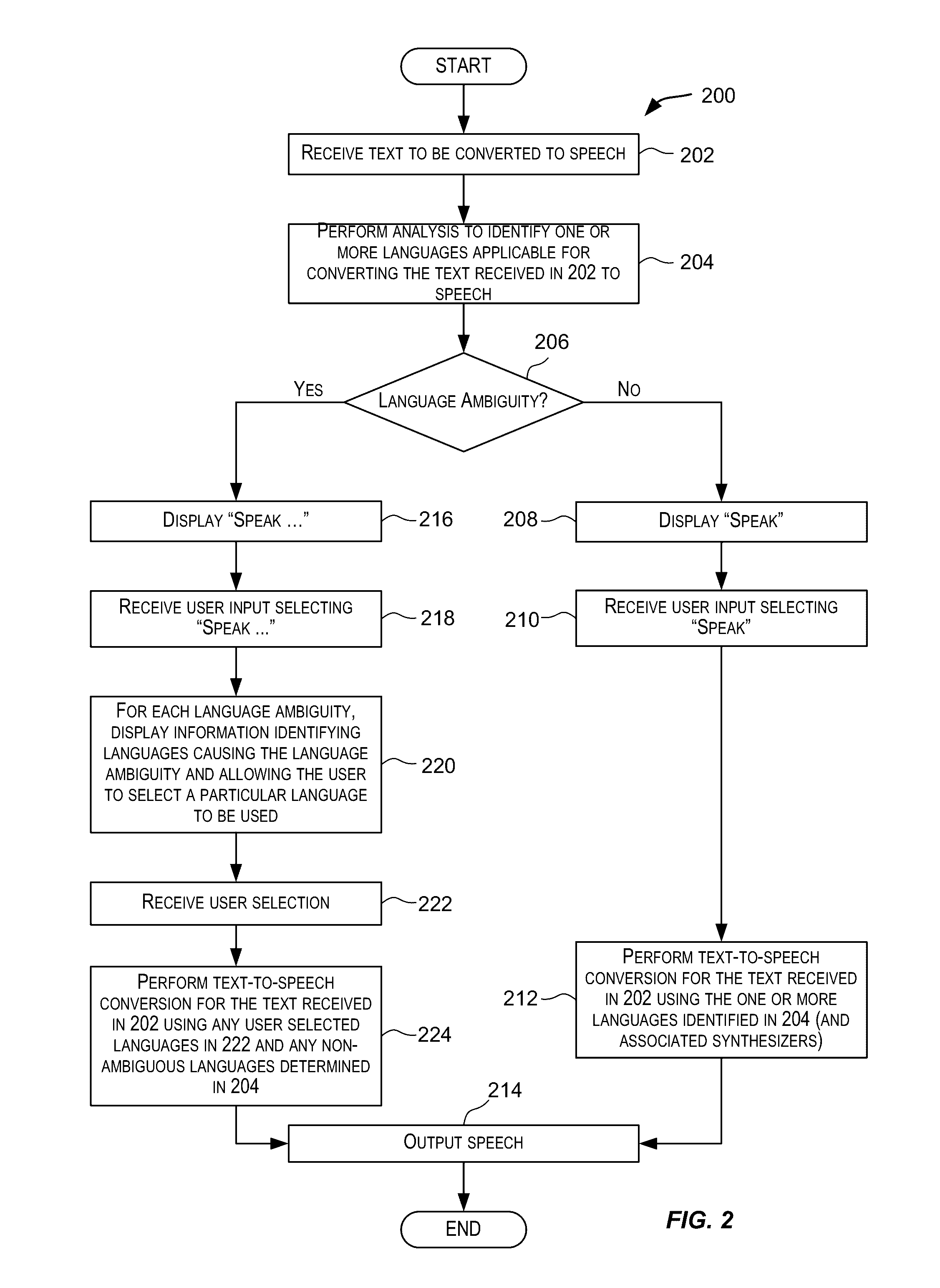
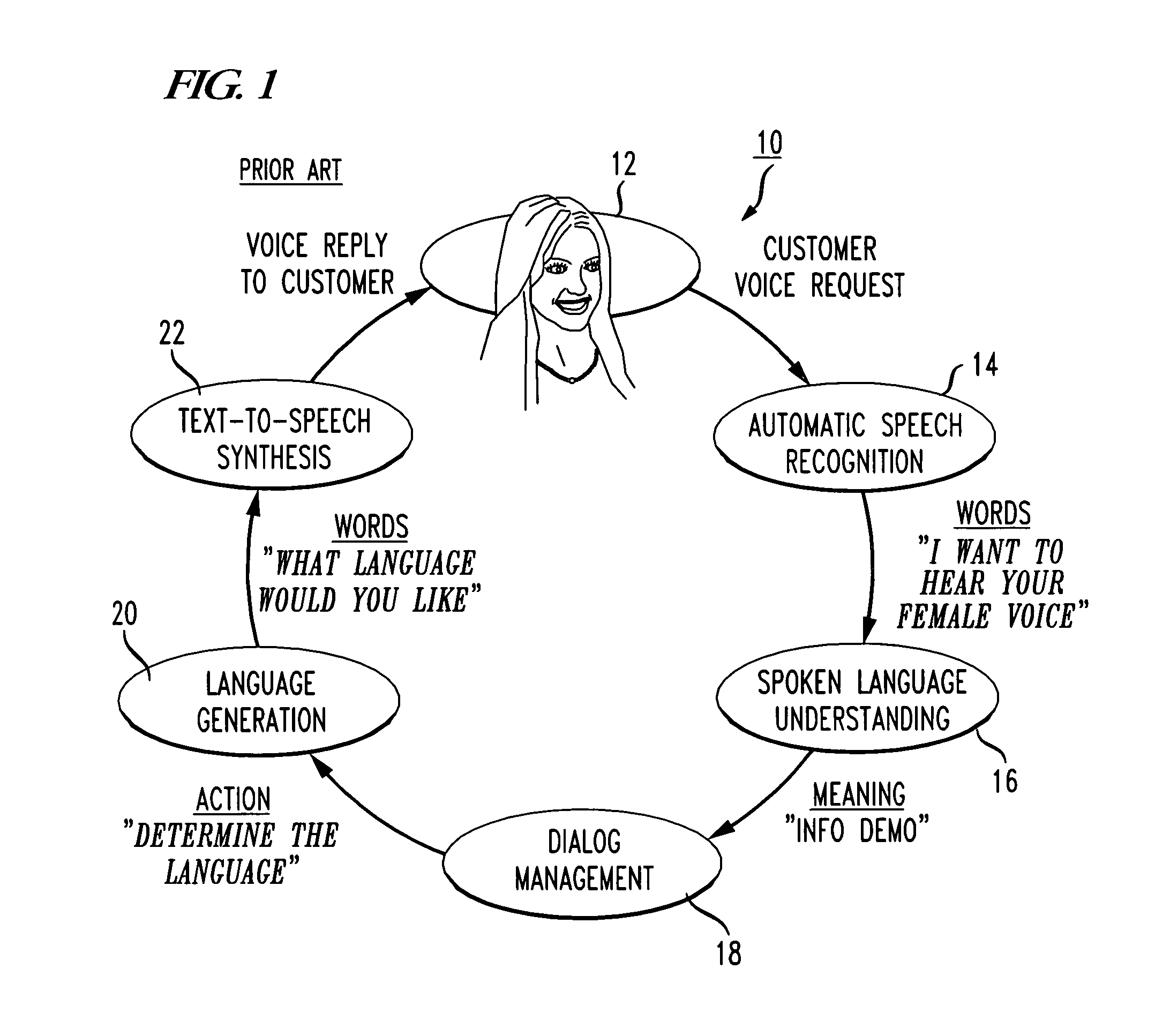
Systems and methods for determining the language to use for speech generated by a text to speech engine
Owner:APPLE INC
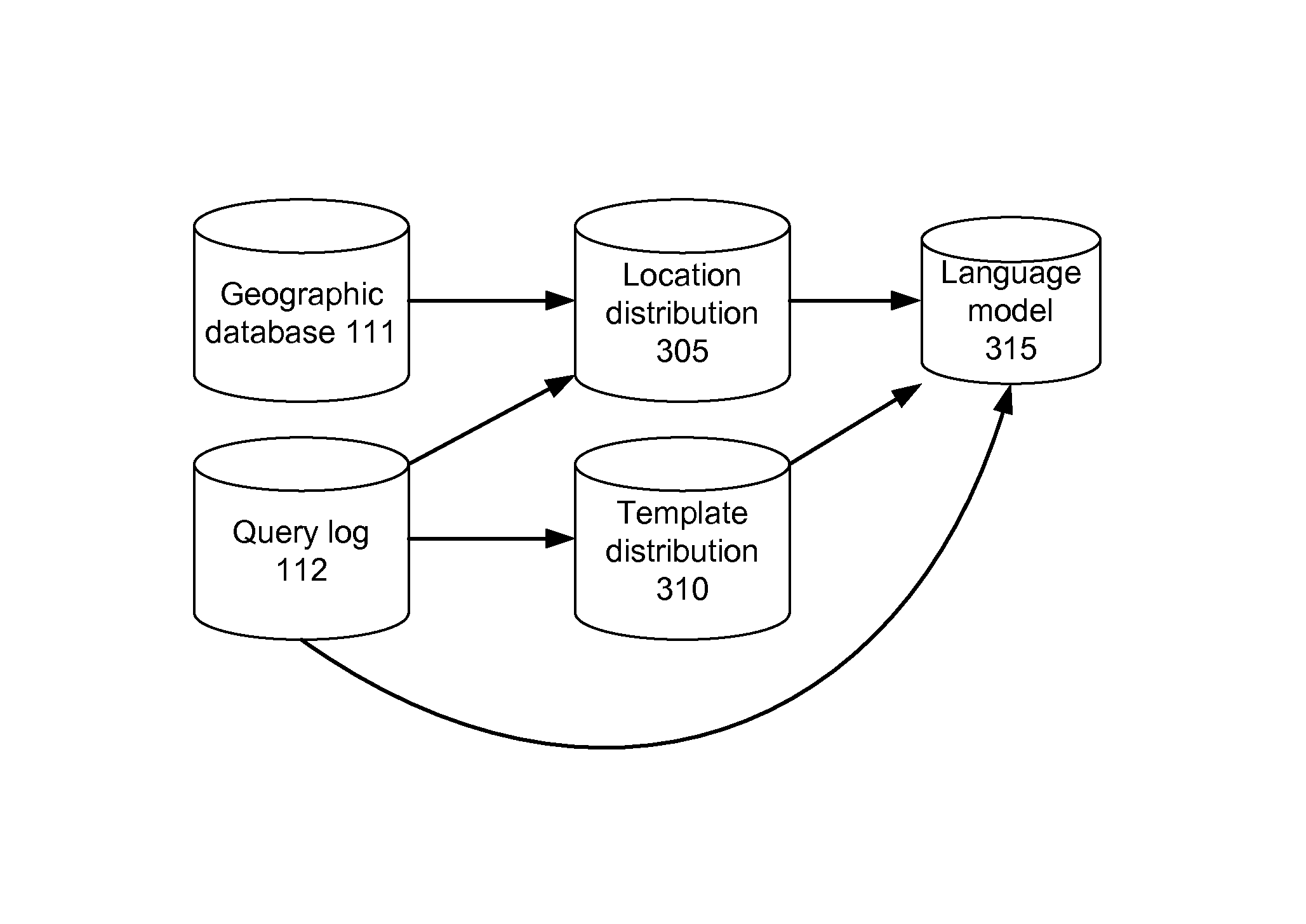
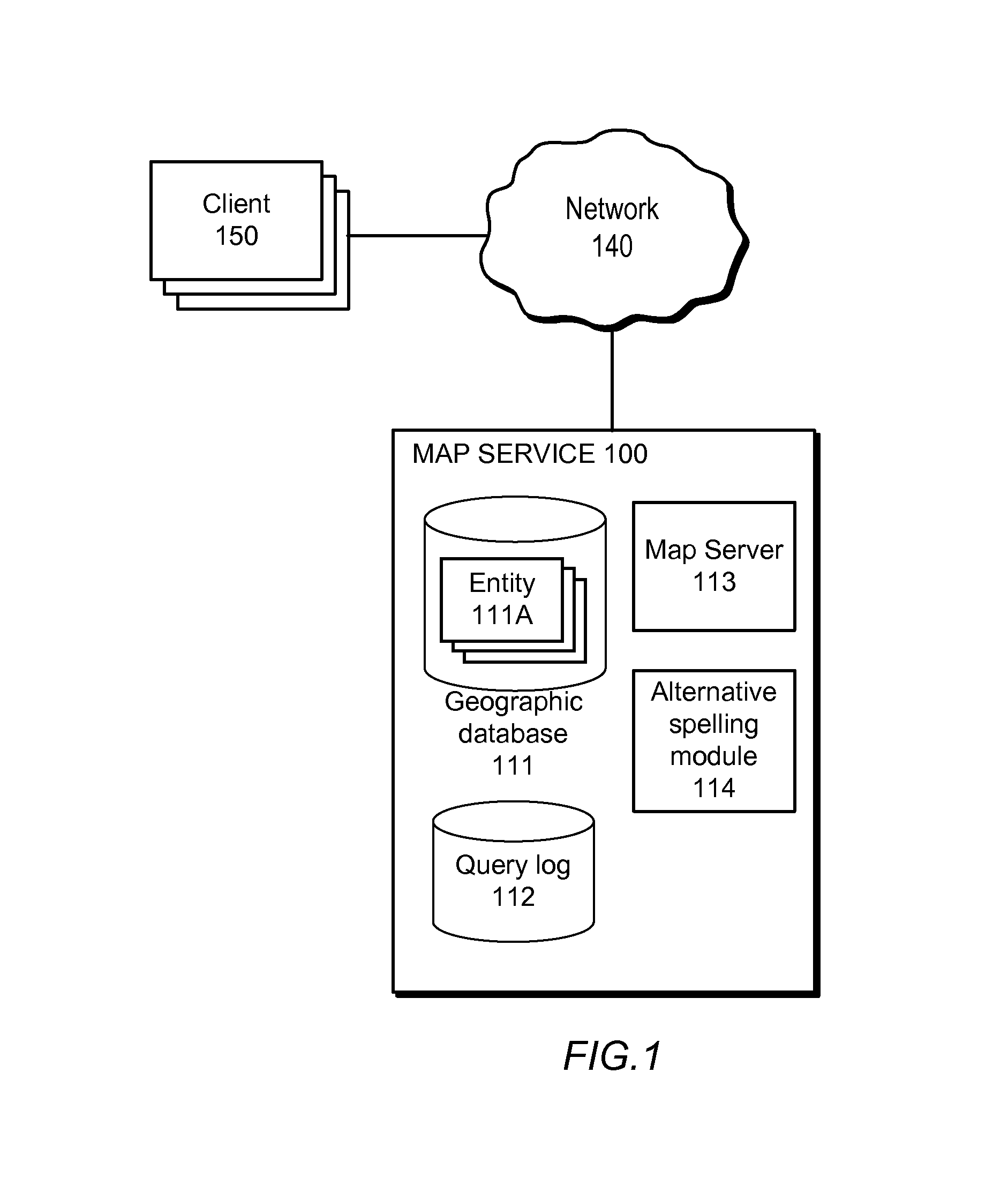
Training a probabilistic spelling checker from structured data
InactiveUS8626681B1Increase the number ofDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingEntity typeAlgorithm
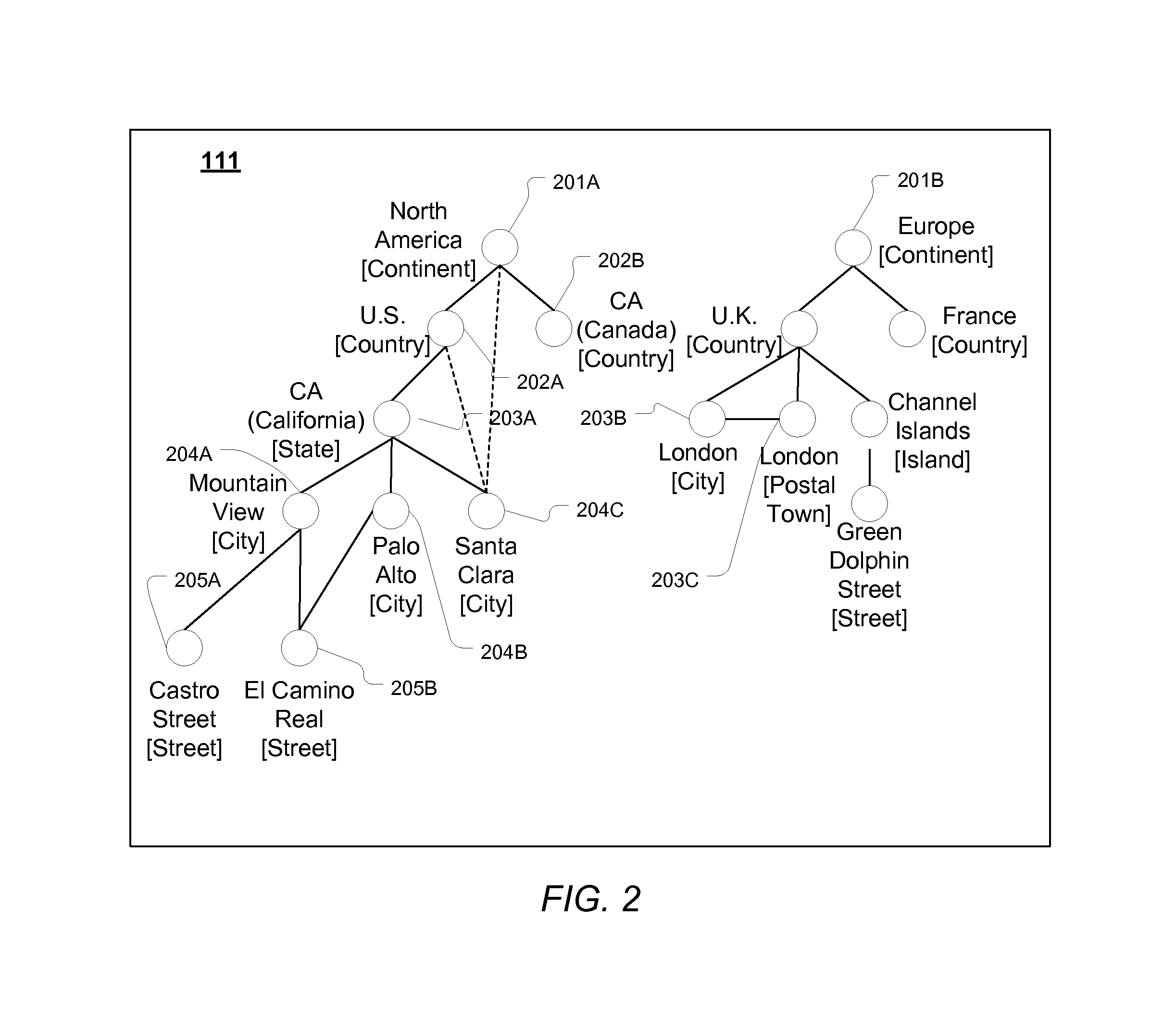
A spelling system derives a language model for a particular domain of structured data, the language model enabling determinations of alternative spellings of queries or other strings of text from that domain. More specifically, the spelling system calculates (a) probabilities that the various query entity types—such as STREET, CITY, or STATE for queries in the geographical domain—are arranged in each of the various possible orders, and (b) probabilities that an arbitrary query references given particular ones of the entities, such as the street “El Camino Real.” Based on the calculated probabilities, the spelling system generates a language model that has associated scores (e.g., probabilities) for each of a set of probable entity name orderings, where the total number of entity name orderings is substantially less than the number of all possible orderings. The language model can be applied to determine probabilities of arbitrary queries, and thus to suggest alternative queries more likely to represent what a user intended.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Generating Topic-Specific Language Models
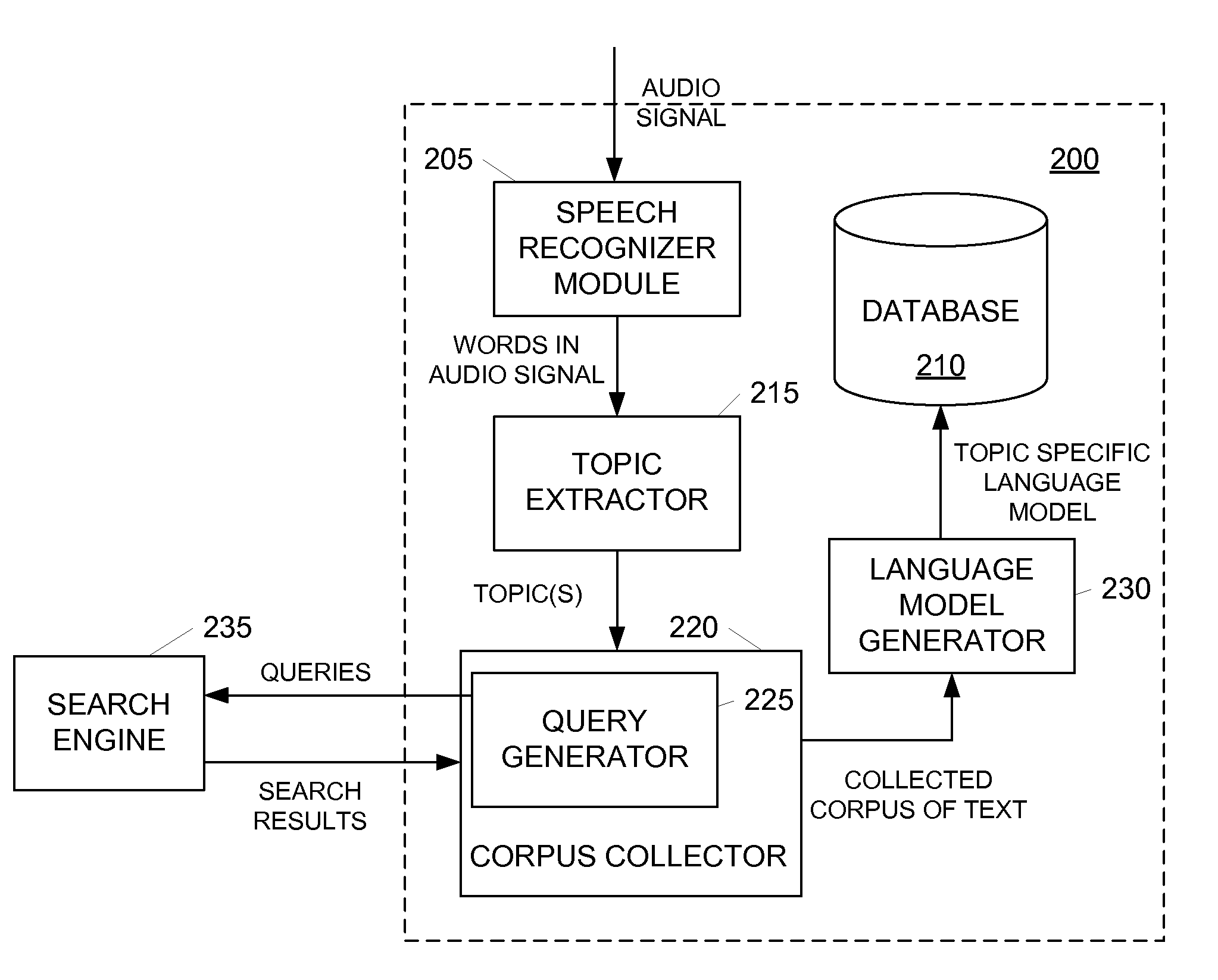
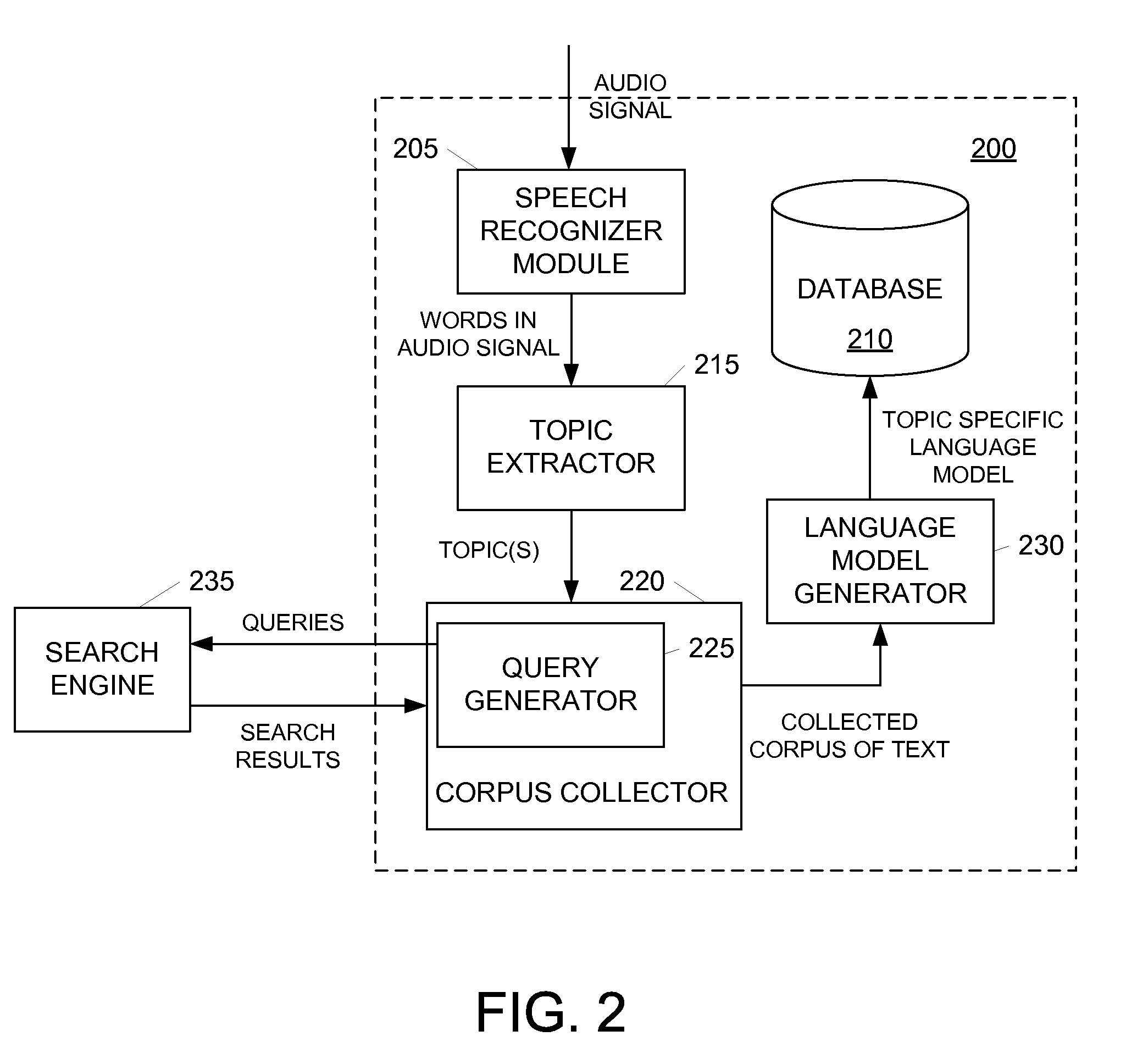
ActiveUS20110004462A1Improve accuracyEliminate needDigital data processing detailsSpeech recognitionSpeech identificationAudio signal flow
Speech recognition may be improved by generating and using a topic specific language model. A topic specific language model may be created by performing an initial pass on an audio signal using a generic or basis language model. A speech recognition device may then determine topics relating to the audio signal based on the words identified in the initial pass and retrieve a corpus of text relating to those topics. Using the retrieved corpus of text, the speech recognition device may create a topic specific language model. In one example, the speech recognition device may adapt or otherwise modify the generic language model based on the retrieved corpus of text.
Owner:TIVO CORP
Handling speech synthesis of content for multiple languages
Owner:APPLE INC
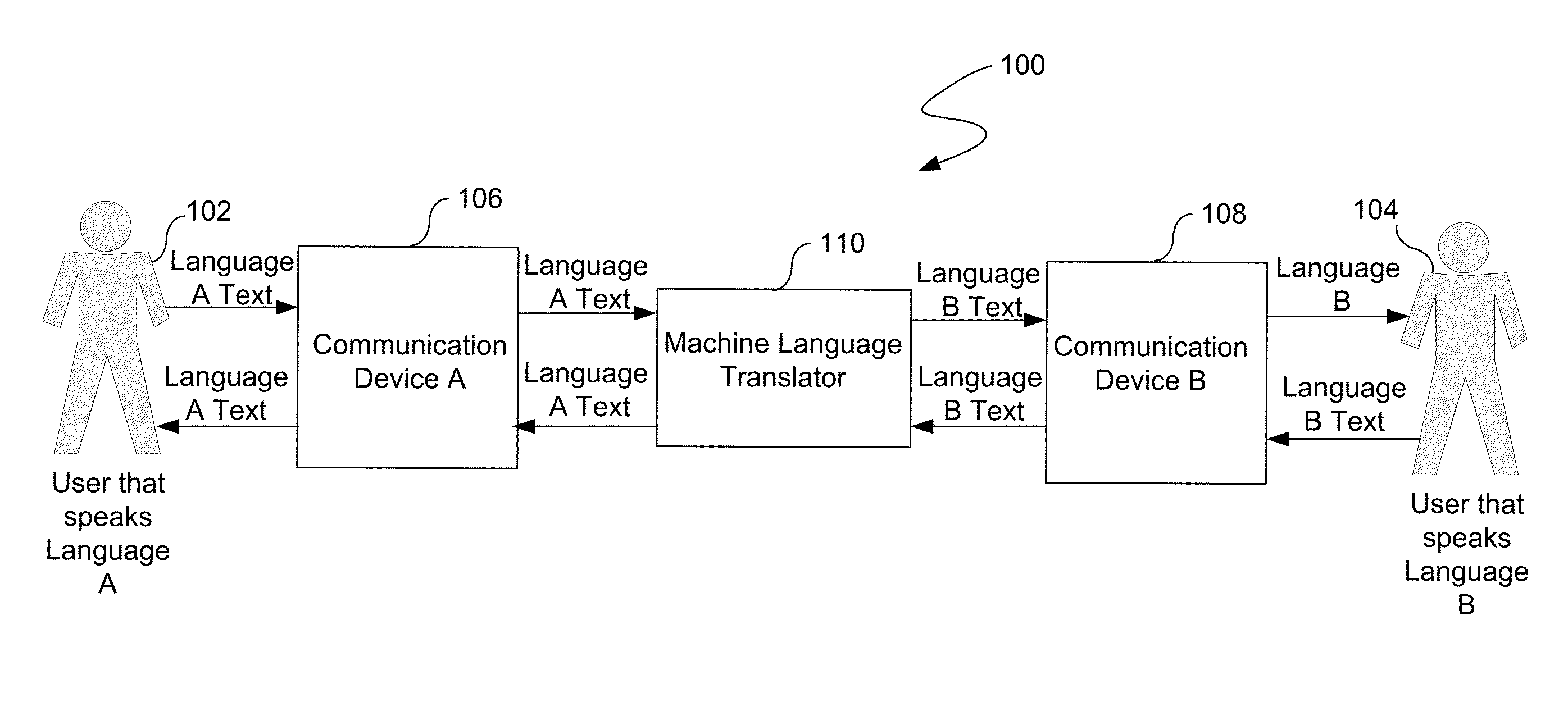
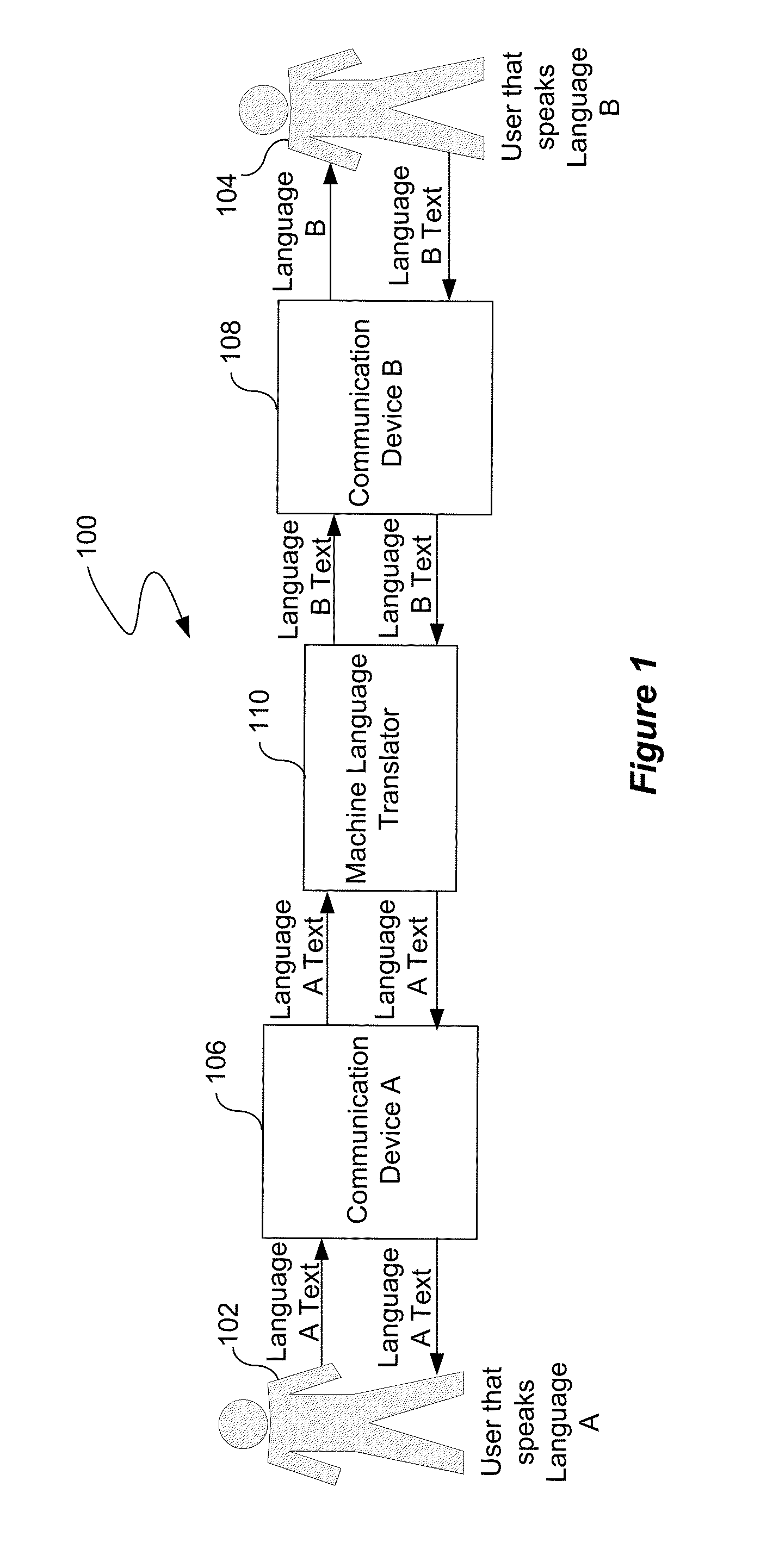
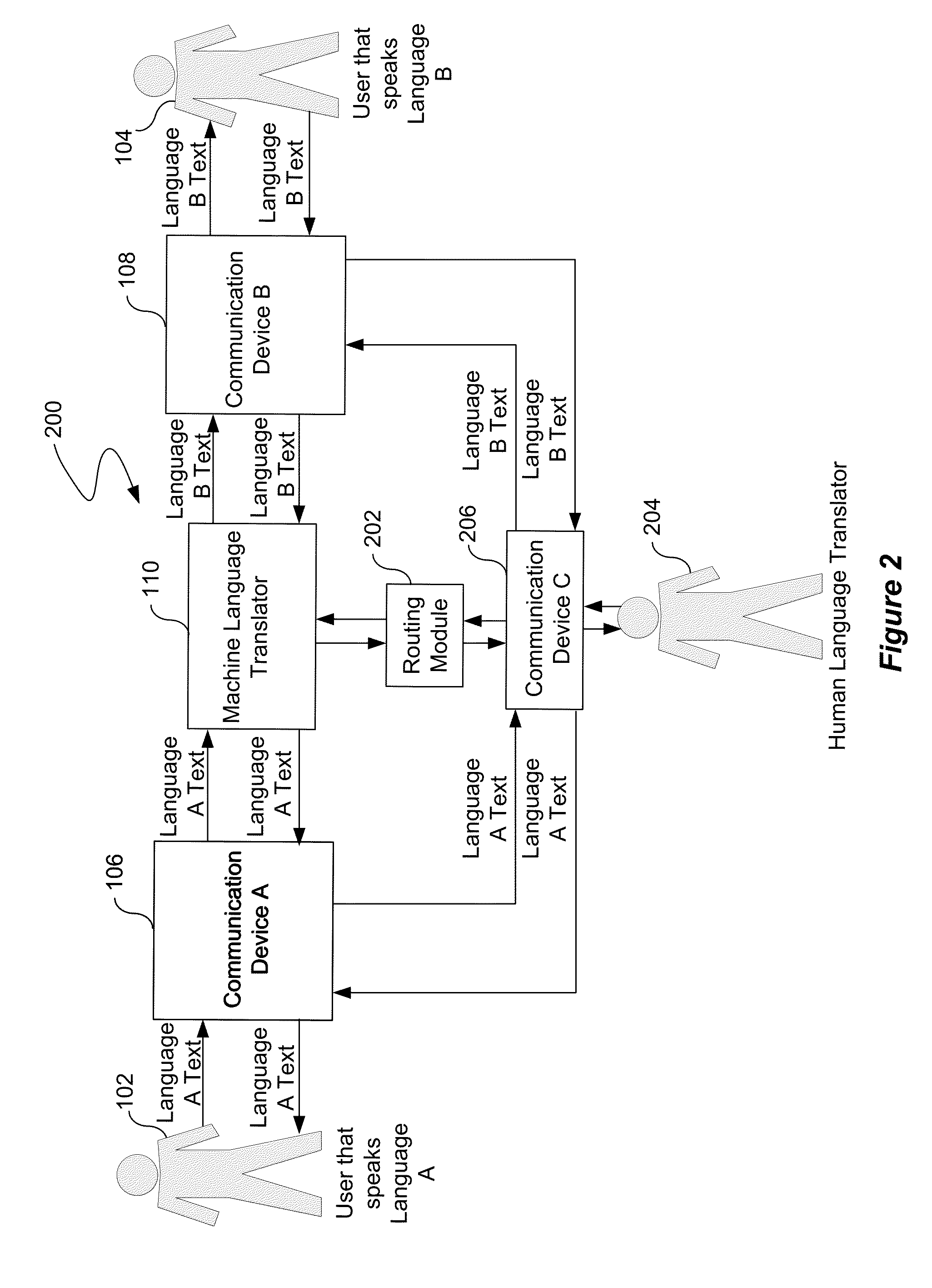
Routing of machine language translation to human language translator
InactiveUS20140142917A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman languageLanguage translation
A language translation system receives a request for a translation of a set of text from a first language to a second language. Further, the language translation system provides the request to a machine language translator. In addition, the machine language translator performs a machine translation of the set of text from the first language to the second language. The machine language translator determines that the machine translation should be modified by a human translator. Further, the machine translation is provided to the human translator for modification after the determination.
Owner:LANGUAGE LINE SERVICES
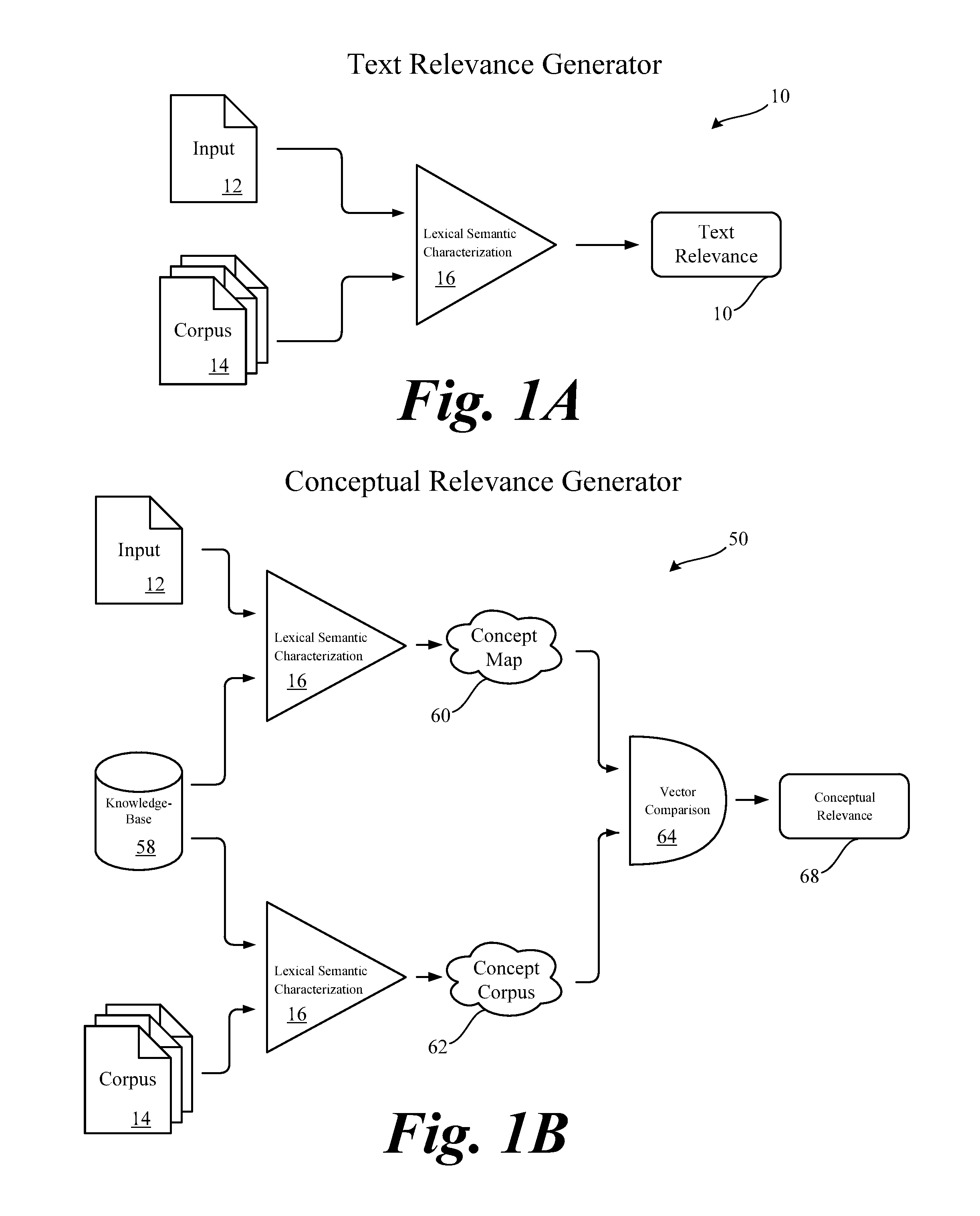
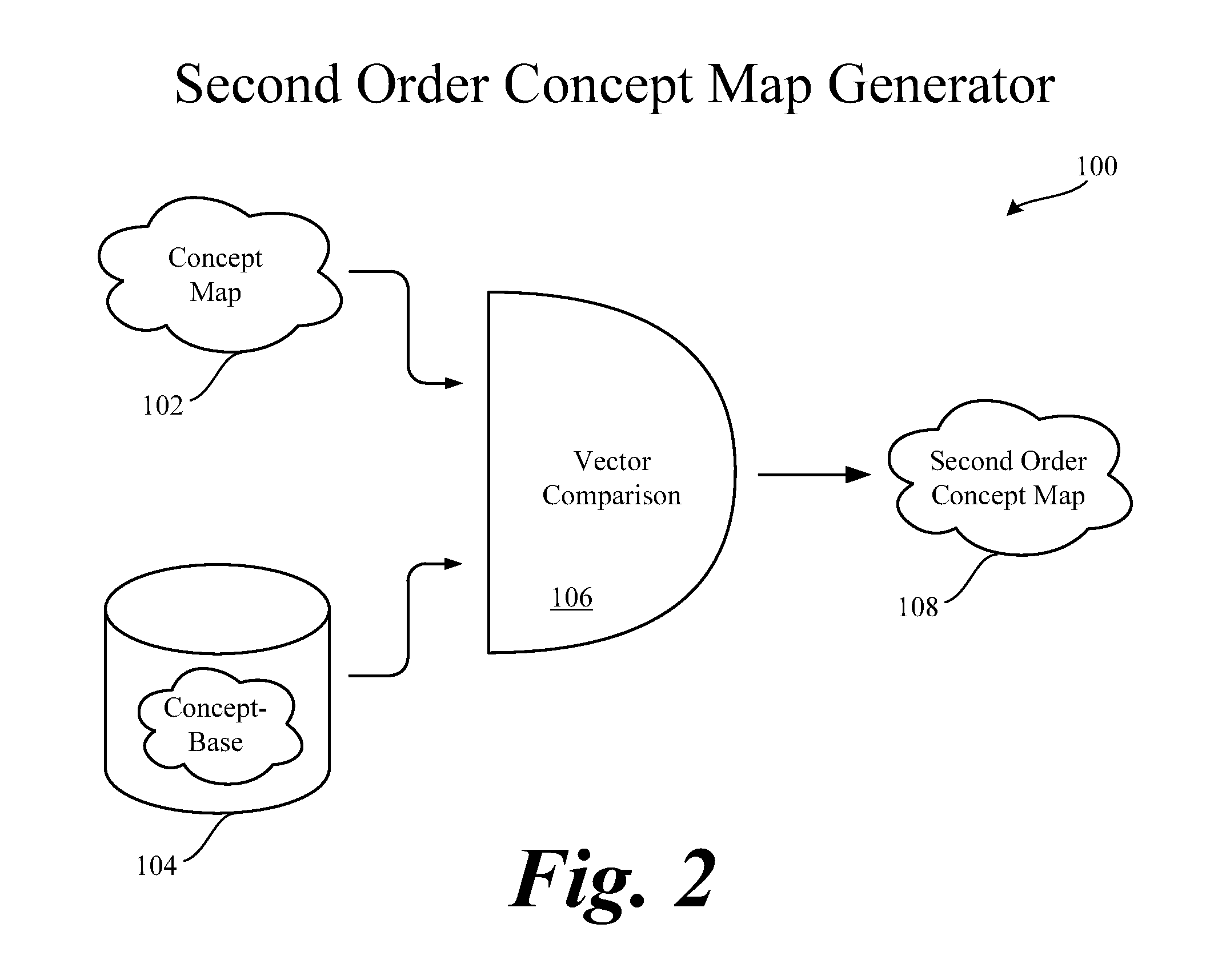
Systems and methods to determine and utilize conceptual relatedness between natural language sources
ActiveUS20160232160A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productivityText processingRelational databasesGraphicsHuman language
A microprocessor executable method and system for determining the semantic relatedness and meaning between at least two natural language sources is described in a prescribed context. Portions of natural languages are vectorized and mathematically processed to express relatedness as a calculated metric. The metric is associable to the natural language sources to graphically present the level of relatedness between at least two natural language sources. The metric may be re-determined with algorithms designed to compare the natural language sources with a knowledge data bank so the calculated metric can be ascertained with a higher level of certainty.
Owner:VETTD INC
Natural language dialogue method and natural language dialogue system
ActiveUS20140188478A1Easy to useNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionSpeech inputSpeech sound
A natural language dialogue method and a natural language dialogue system are provided. In the method, a first speech input is received and parsed to generate at least one keyword included in the first speech input, so that a candidate list including at least one report answer is obtained. According to a properties database, one report answer is selected from the candidate list, and a first speech response is output according to the report answer. Other speech inputs are received, and a user's preference data is captured from the speech inputs. The user's preference data is stored in the properties database.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Systems Methods Circuits and Associated Computer Executable Code for Deep Learning Based Natural Language Understanding
InactiveUS20160350655A1Semantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsNatural language understandingUser input
Disclosed are systems, methods, circuits and associated computer executable code for deep learning based natural language understanding, wherein training of one or more neural networks, includes: producing character strings inputs ‘noise’ on a per-character basis, and introducing the produced ‘noise’ into machine training character strings inputs fed to a ‘word tokenization and spelling correction language-model’, to generate spell corrected word sets outputs; feeding machine training word sets inputs, including one or more ‘right’ examples of correctly semantically-tagged word sets, to a ‘word semantics derivation model’, to generate semantically tagged sentences outputs. Upon models reaching a training ‘steady state’, the ‘word tokenization and spelling correction language-model’ is fed with input character strings representing ‘real’ linguistic user inputs, generating word sets outputs that are fed as inputs to the word semantics derivation model for generating semantically tagged sentences outputs.
Owner:EVATURE TECH 2009 LTD
Language Processing And Knowledge Building System
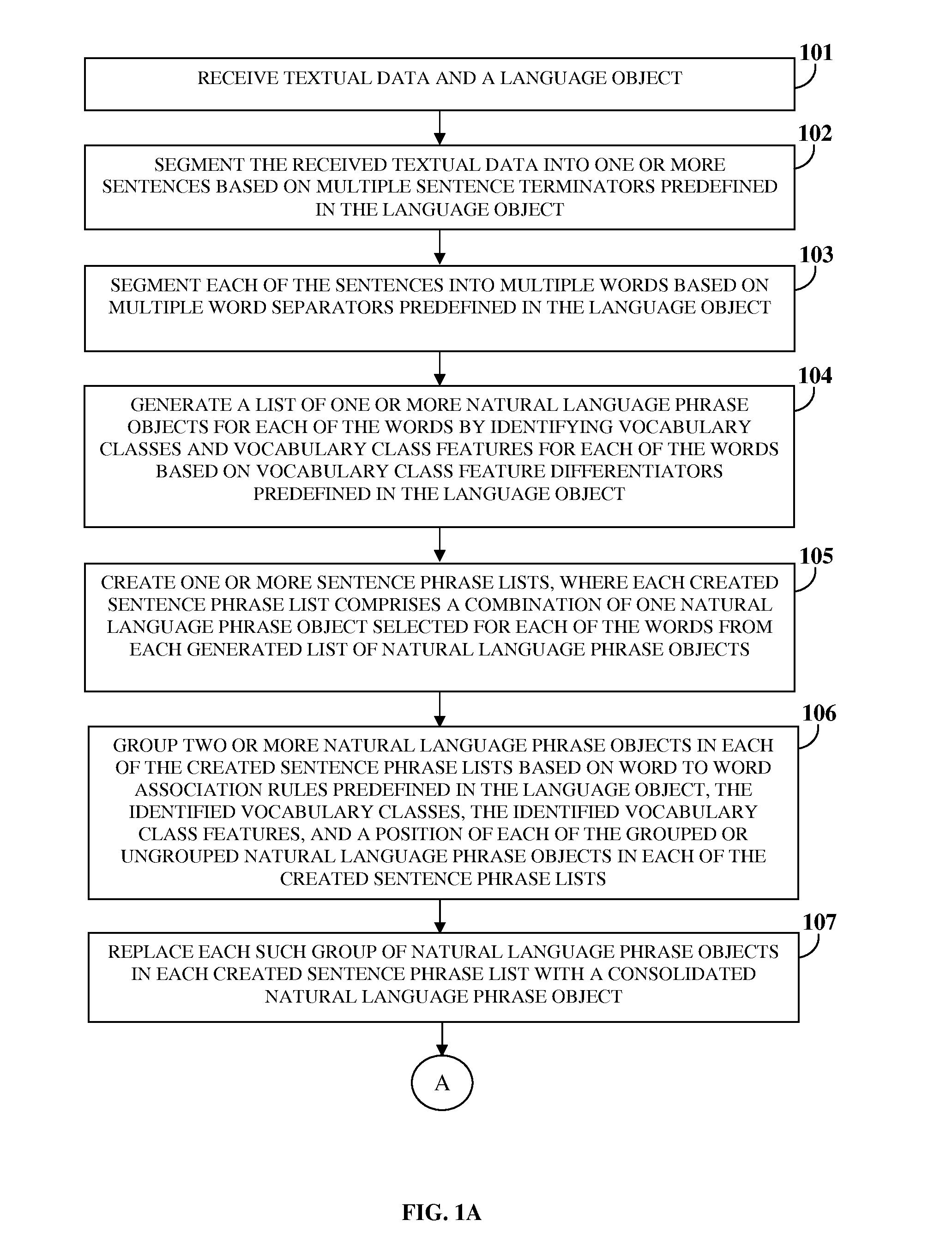
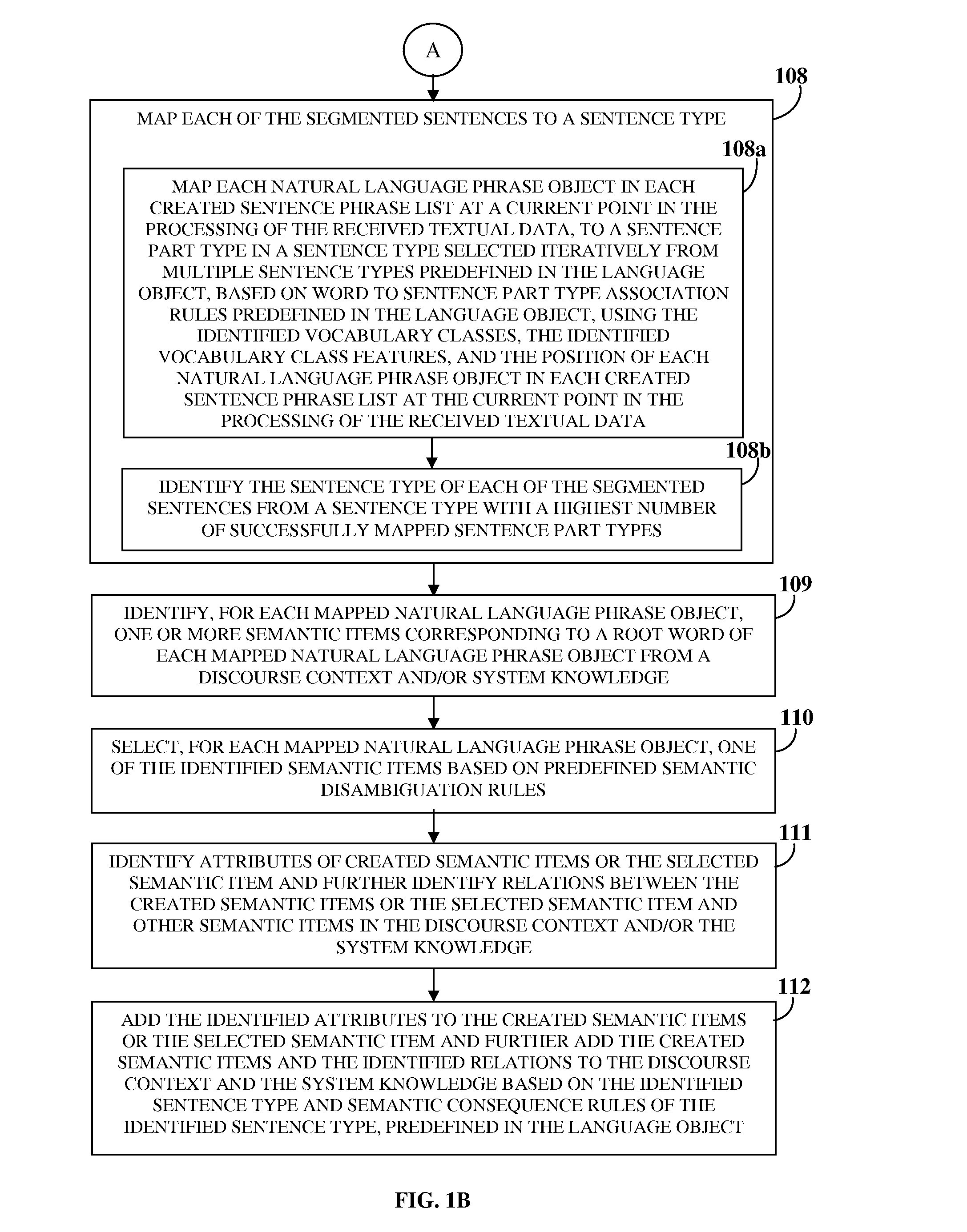
ActiveUS20160364377A1Cost and time-effective developmentEliminates effort and costSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsDifferentiatorKnowledge building
A method and a language processing and knowledge building system (LPKBS) for processing textual data, receives textual data and a language object; segments the textual data into sentences and each sentence into words; generates a list of one or more natural language phrase objects (NLPOs) for each word by identifying vocabulary classes and vocabulary class features for each word based on vocabulary class feature differentiators; creates sentence phrase lists, each including a combination of one NLPO selected per word from each list of NLPOs; groups two or more NLPOs in each sentence phrase list based on word to word association rules, the vocabulary classes, the vocabulary class features, and a position of each NLPO; replaces each such group of NLPOs with a consolidated NLPO; maps each segmented sentence to a sentence type; identifies a semantic item for each mapped NLPO; and identifies and stores associated attributes and relations.
Owner:KRISHNAMURTHY SATYANARAYANA
Automatic spoken language identification based on phoneme sequence patterns
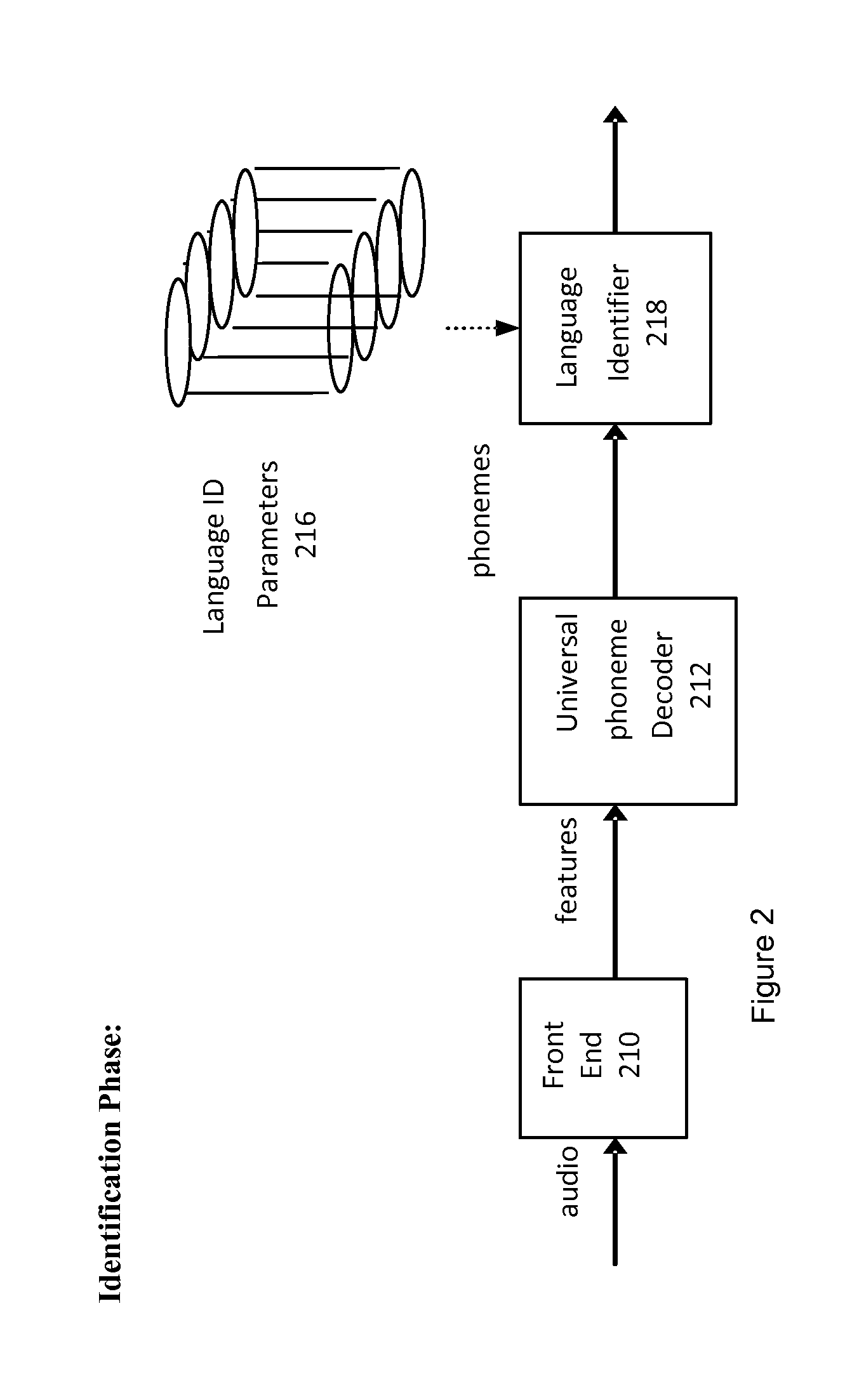
ActiveUS20110035219A1Digital data processing detailsNatural language data processingSpoken languageRunning time
A language identification system that includes a universal phoneme decoder (UPD) is described. The UPD contains a universal phoneme set representing both 1) all phonemes occurring in the set of two or more spoken languages, and 2) captures phoneme correspondences across languages, such that a set of unique phoneme patterns and probabilities are calculated in order to identify a most likely phoneme occurring each time in the audio files in the set of two or more potential languages in which the UPD was trained on. Each statistical language models (SLM) uses the set of unique phoneme patterns created for each language in the set to distinguish between spoken human languages in the set of languages. The run-time language identifier module identifies a particular human language being spoken by utilizing the linguistic probabilities supplied by the one or more SLMs that are based on the set of unique phoneme patterns created for each language.
Owner:LONGSAND
System for natural language understanding
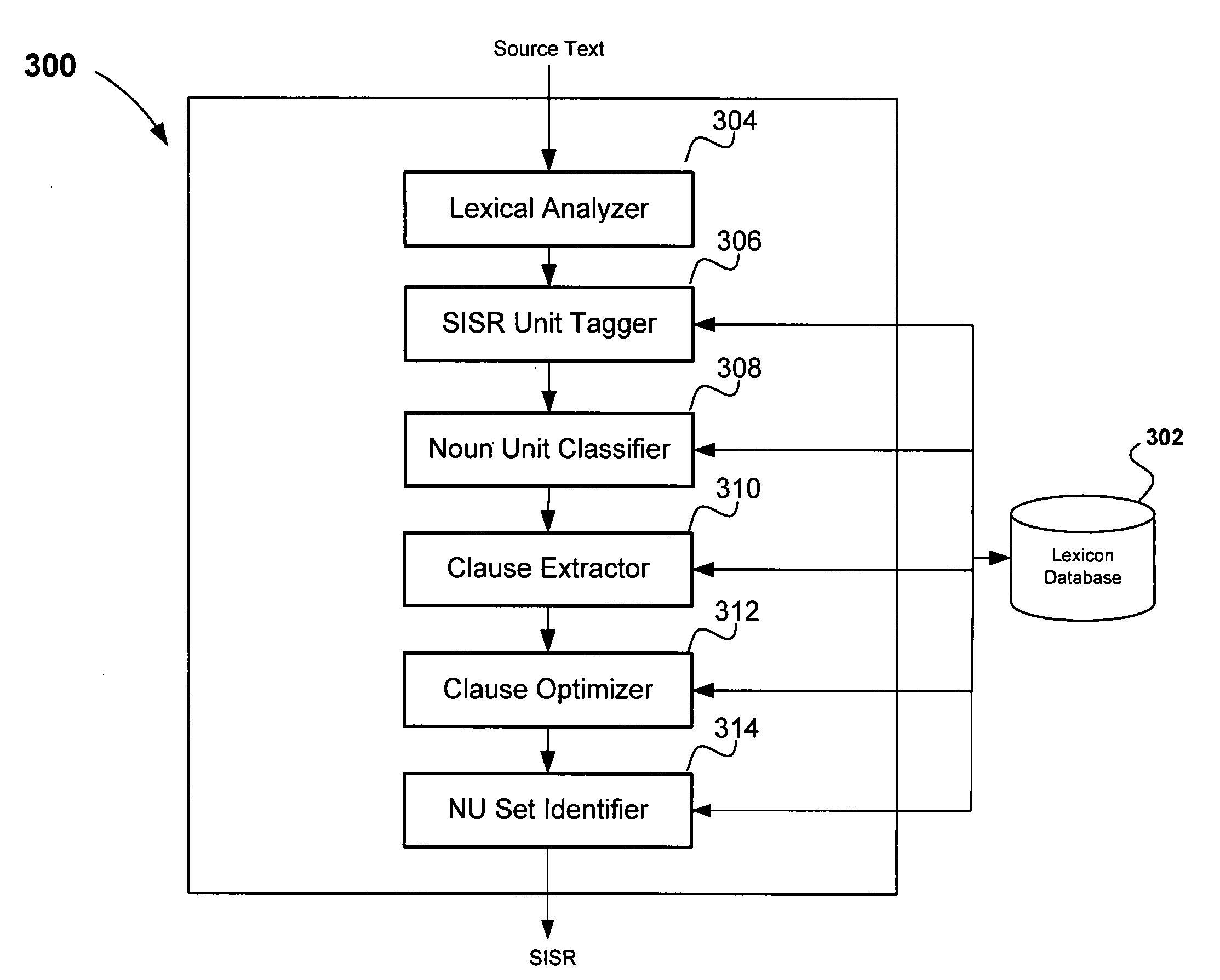
ActiveUS20120253793A1Wide rangeNatural language translationDigital data information retrievalGeneral purposeNatural language understanding
A general-purpose apparatus for analyzing natural language text that allows for the implementation of a broad range of natural language understanding applications. The apparatus for natural language understanding analyzes a source text and transforms the source text into a semantically-interpretable syntactic representation (SISR), comprising a syntax template and semantic clause annotations. The general-purpose apparatus for natural language understanding is adaptable to various source text natural languages and is adaptable to various natural language understanding applications, such as query answering, translation, summarization, information extraction, disambiguation, and parsing. A natural language query answering apparatus for answering questions about a source text, whereby the query answering apparatus utilizes the general-purpose apparatus for transforming the natural language query into SISR format.
Owner:GHANNAM RIMA +1
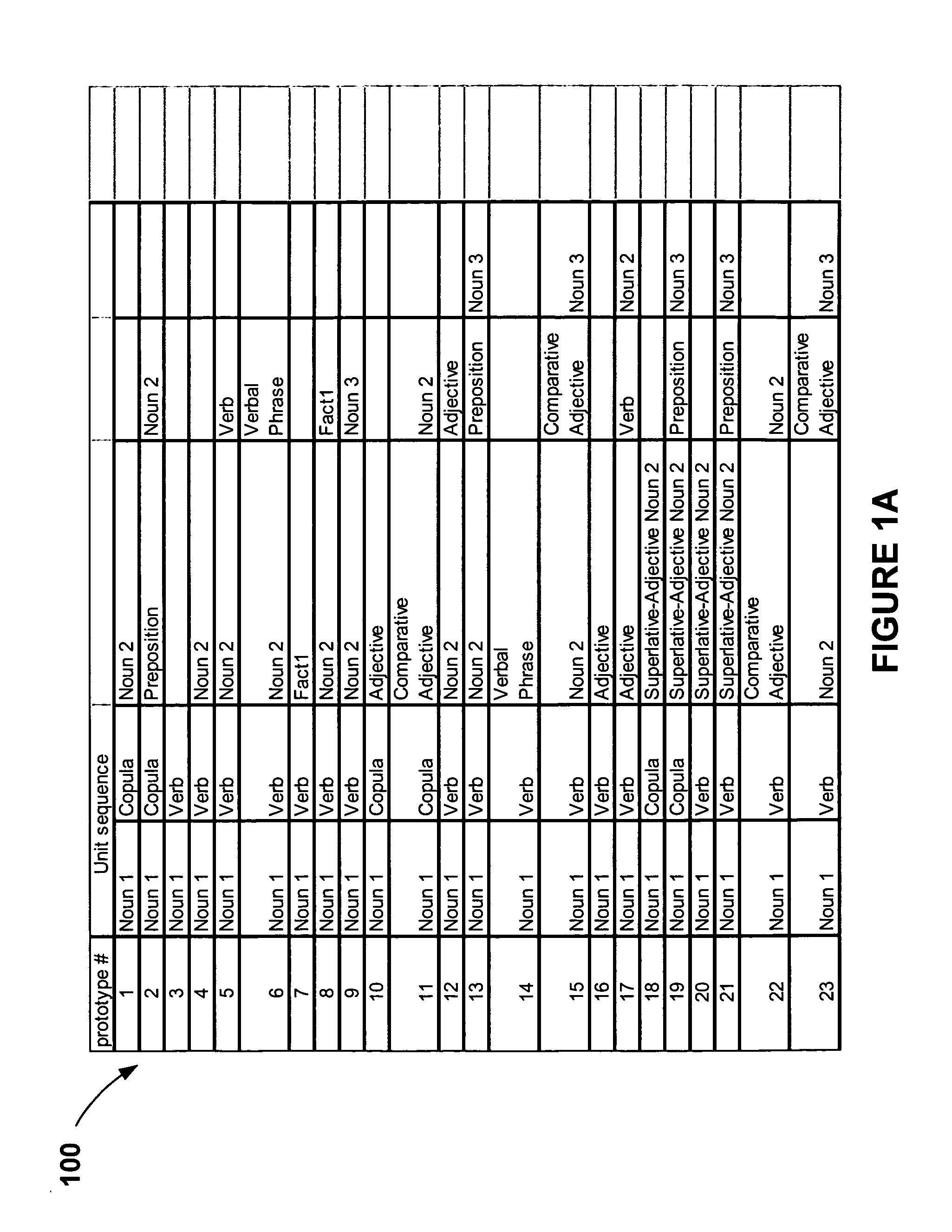
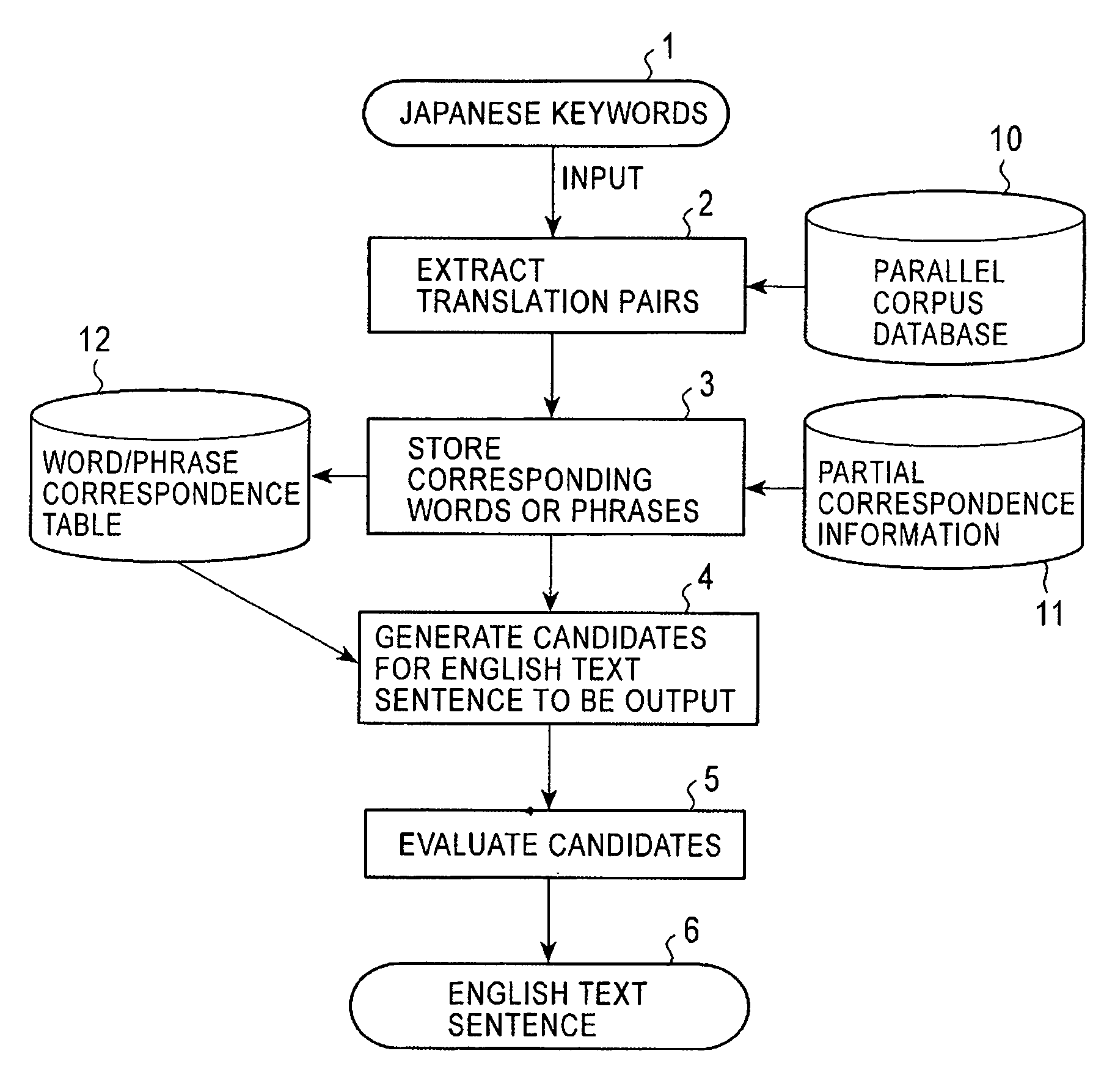
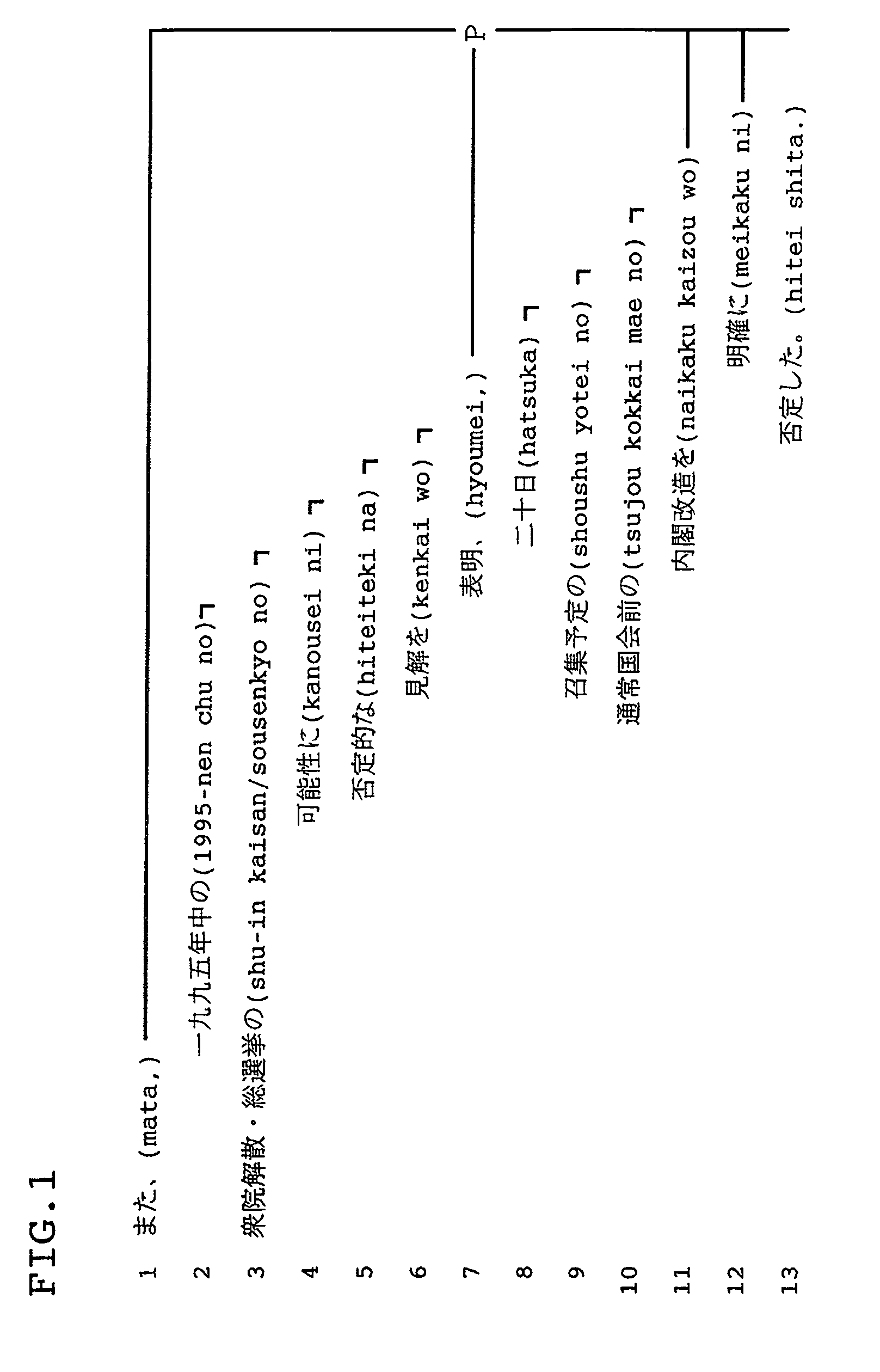
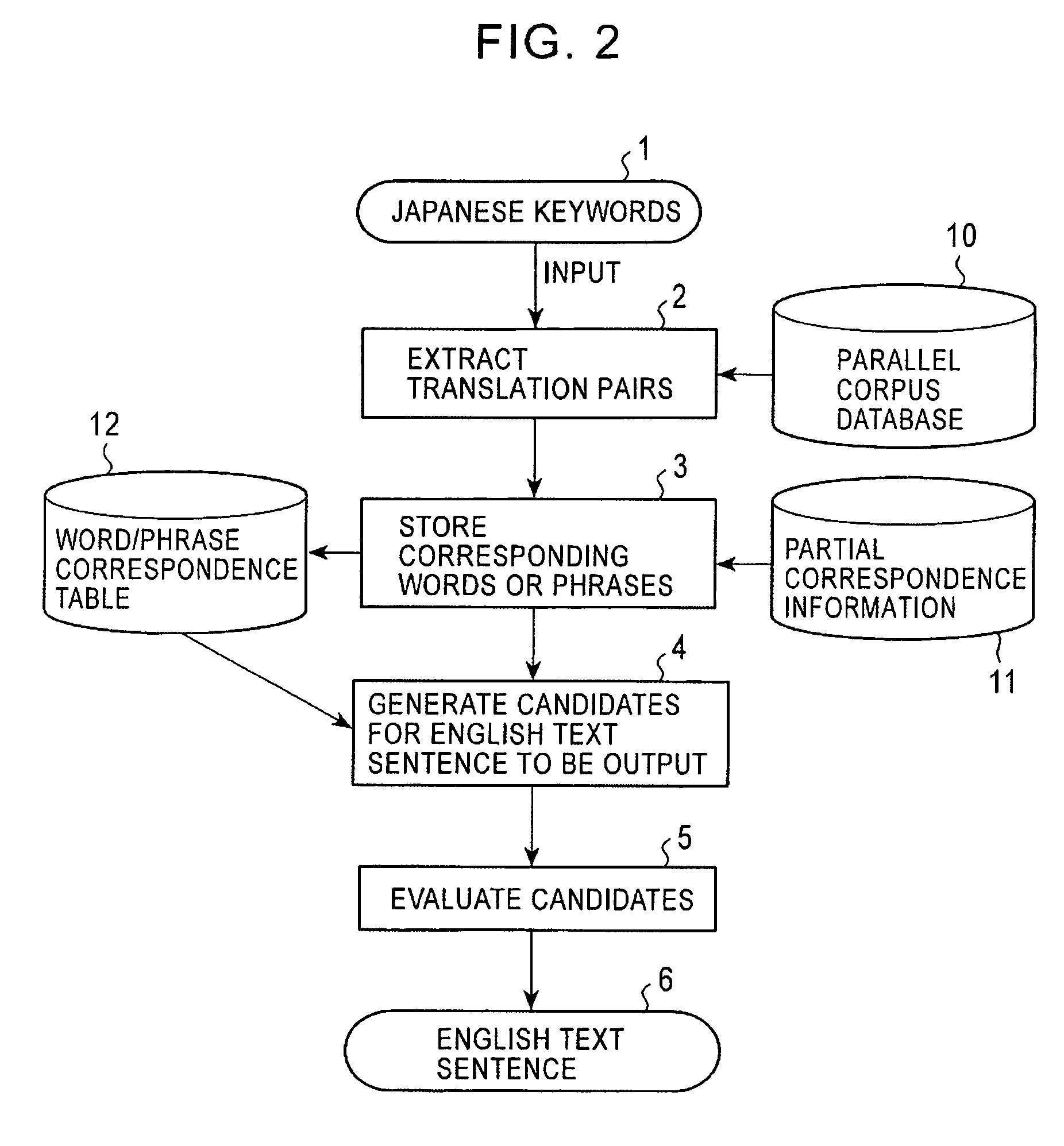
Method for generating a text sentence in a target language and text sentence generating apparatus
InactiveUS8386234B2Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsSentence generationHuman language
By inputting words of source language as a keyword (31), a translation pairs are extracted (50) from a parallel corpus database including source language and target one. From the partially corresponding information on the translation sentence, a corresponding phrase group table formed by the corresponding phase of the target language corresponding to the source language phrase including a keyword phrase f the source language is stored (60). Text generator (70) assumes a relationship between the phrases of different language contained in the corresponding phrase group table and generates a text sentence candidate (32) of the target language.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
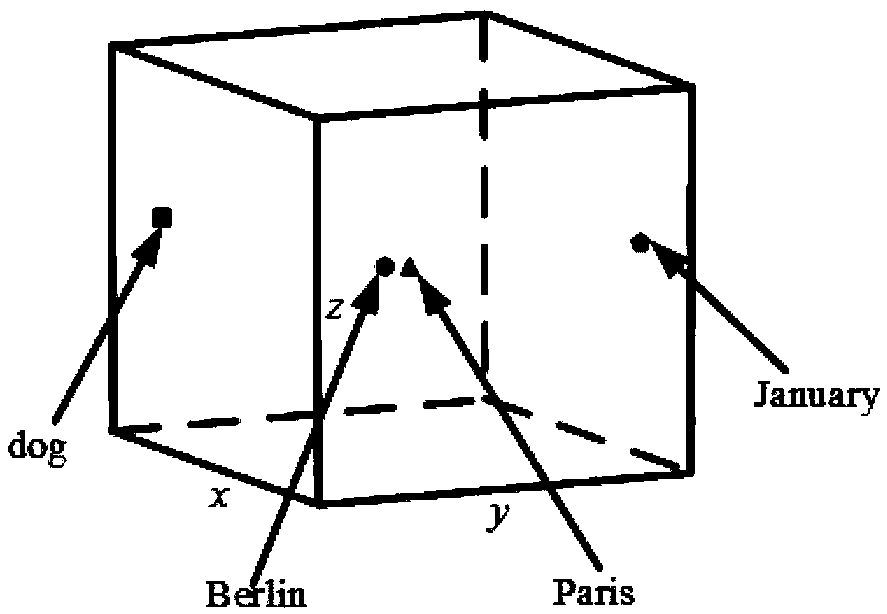
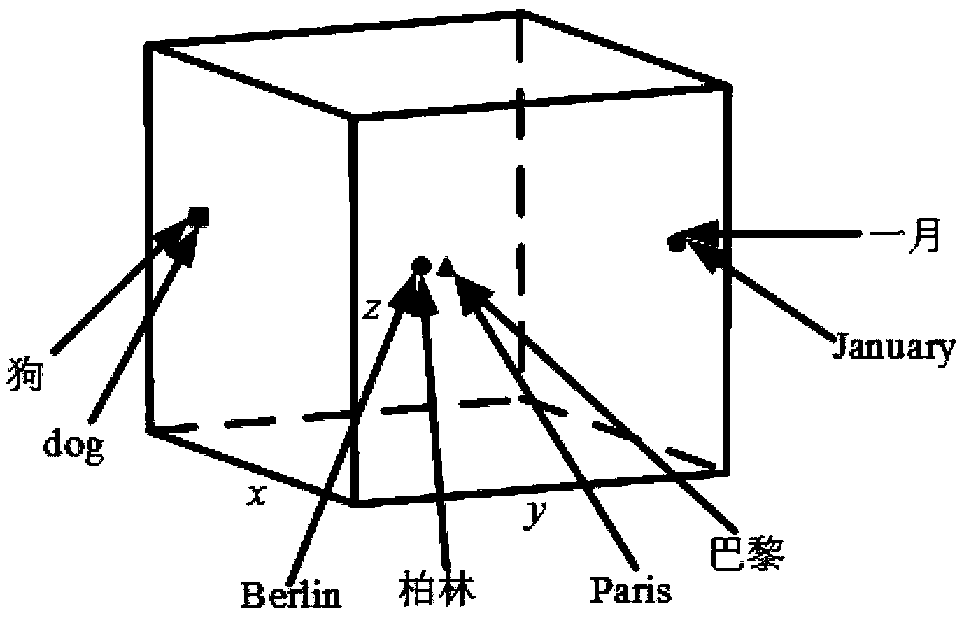
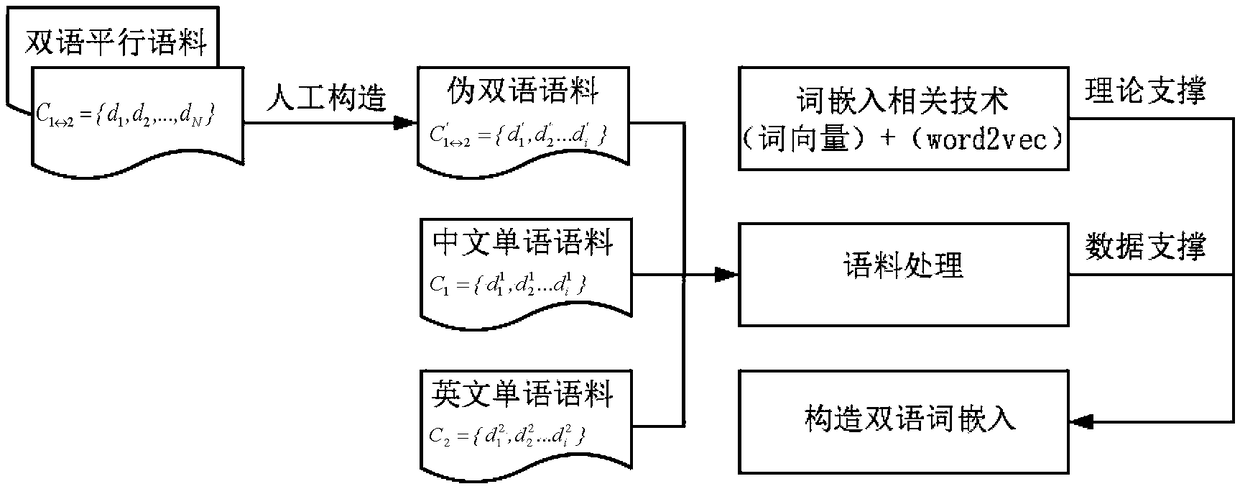
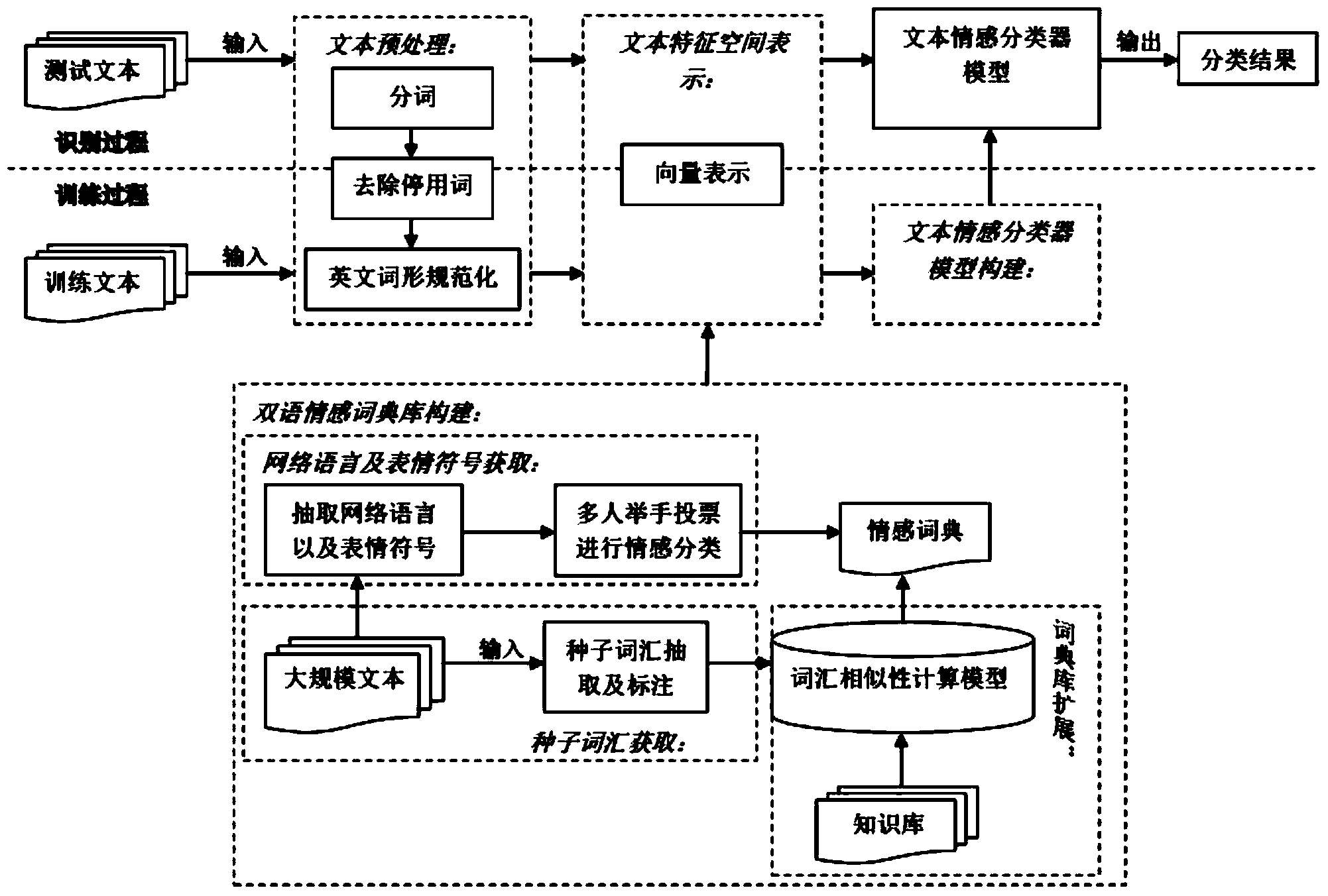
A bilingual word embedding-based cross-language text similarity assessment technique
The invention belongs to the field of language processing, in particular to a cross-language text similarity evaluation technology based on bilingual word embedding. The technical route and workflow of cross-language text similarity evaluation technology based on bilingual word embedding can be divided into three stages: the construction of bilingual word embedding model, the construction of textsimilarity calculation framework based on multi-neural network, and the cross-language similarity calculation. Through this model, a bilingual shared word embedding representation can be generated, which is based on the word vector correlation theory and Skip-Gram model is used to train word vectors on artificially constructed pseudo-bilingual corpus. Secondly, in order to make the generated wordembedding space as complete as possible, monolingual corpus is used as a supplement to learn additional word embedding knowledge. The similarity score of sentences is obtained by combining several neural network structures to learn the semantic representation of sentences. By dividing short text into paragraphs and treating paragraphs as long sentences as sequence input, the similarity iteration on a larger scale can be realized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method and apparatus for using directed reasoning to respond to natural language queries
ActiveUS8719005B1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPattern matchingConcept search
A method and apparatus are presented for using directed reasoning to provide natural language responses to questions and commands in natural language. The directed reasoning process uses concepts in the natural language sentence to identify relevant response concepts in a knowledge base, by creating a continuous chain of logic from the input concept to the response concept and limiting the creation of the logic chains to only those consistent with the context of the natural language sentence and information in the knowledge base. The invention allows the identification of relevant concepts that elude traditional concept searching based on pattern matching, while focusing computational resources on only those logic calculations relevant to the natural language sentence and knowledge base. The invention will automatically identify the relevant source documents to use and create a knowledge base during run time, without requiring preprogrammed ontologies or knowledge bases.
Owner:LEE RUSTY SHAWN +1
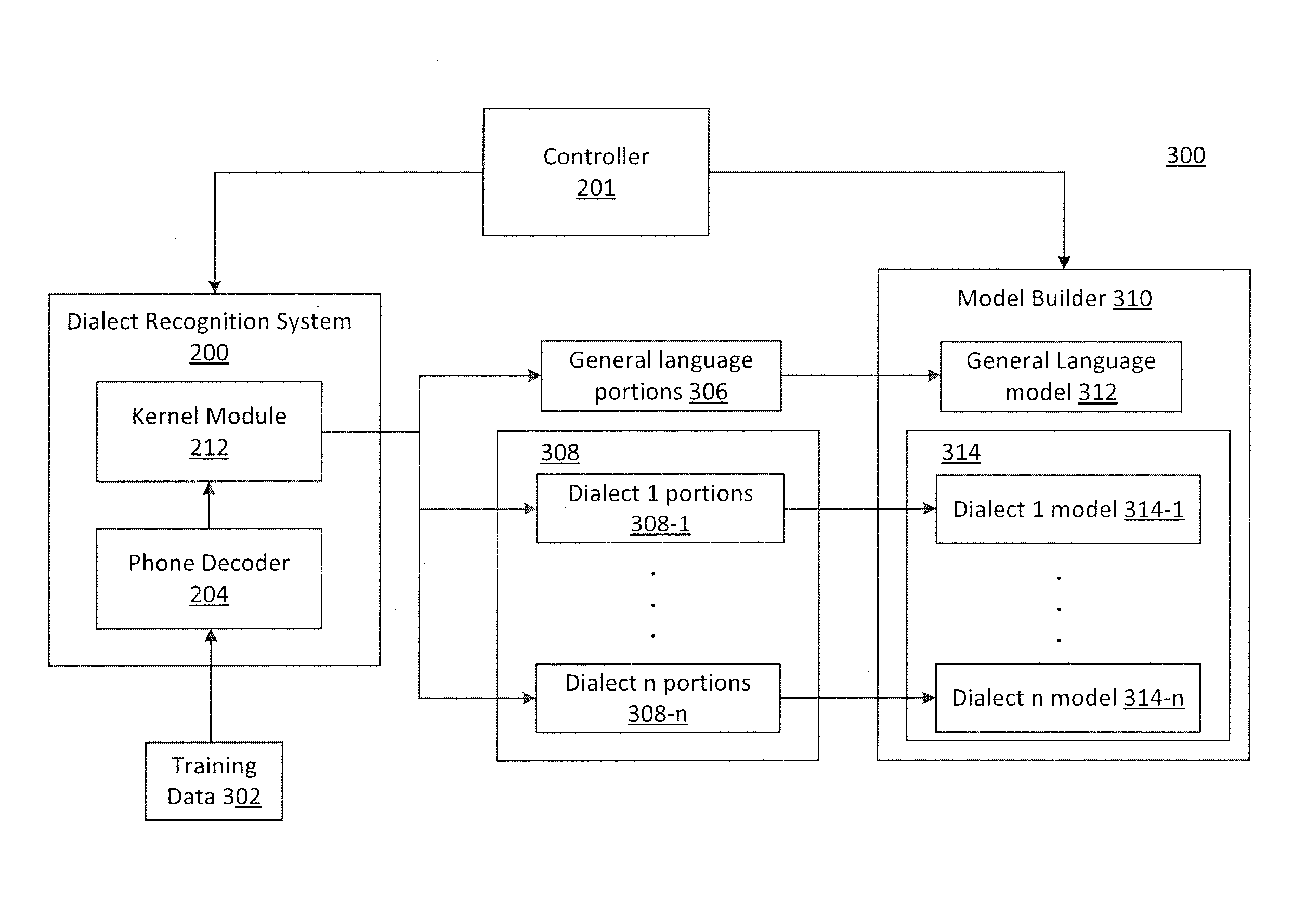
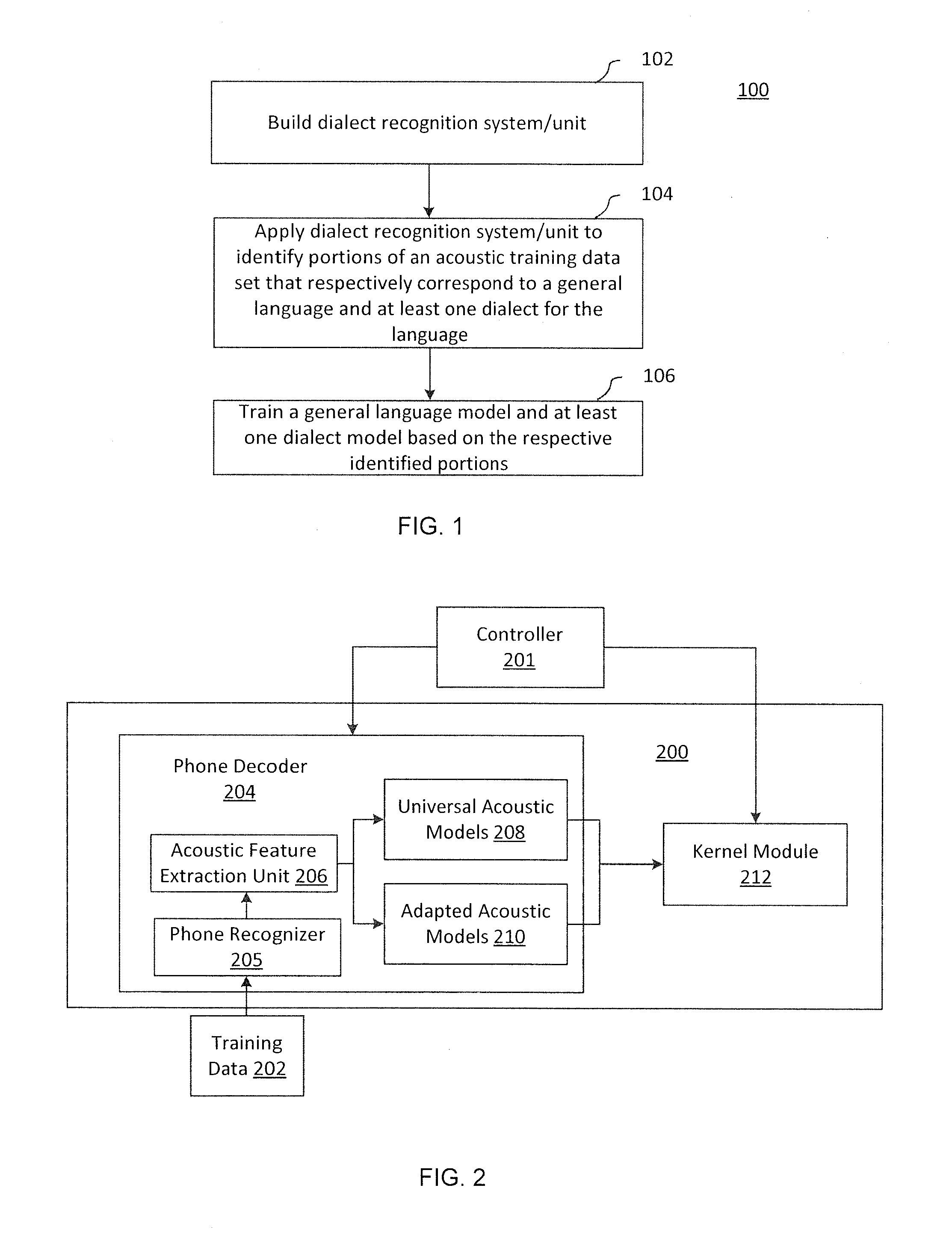
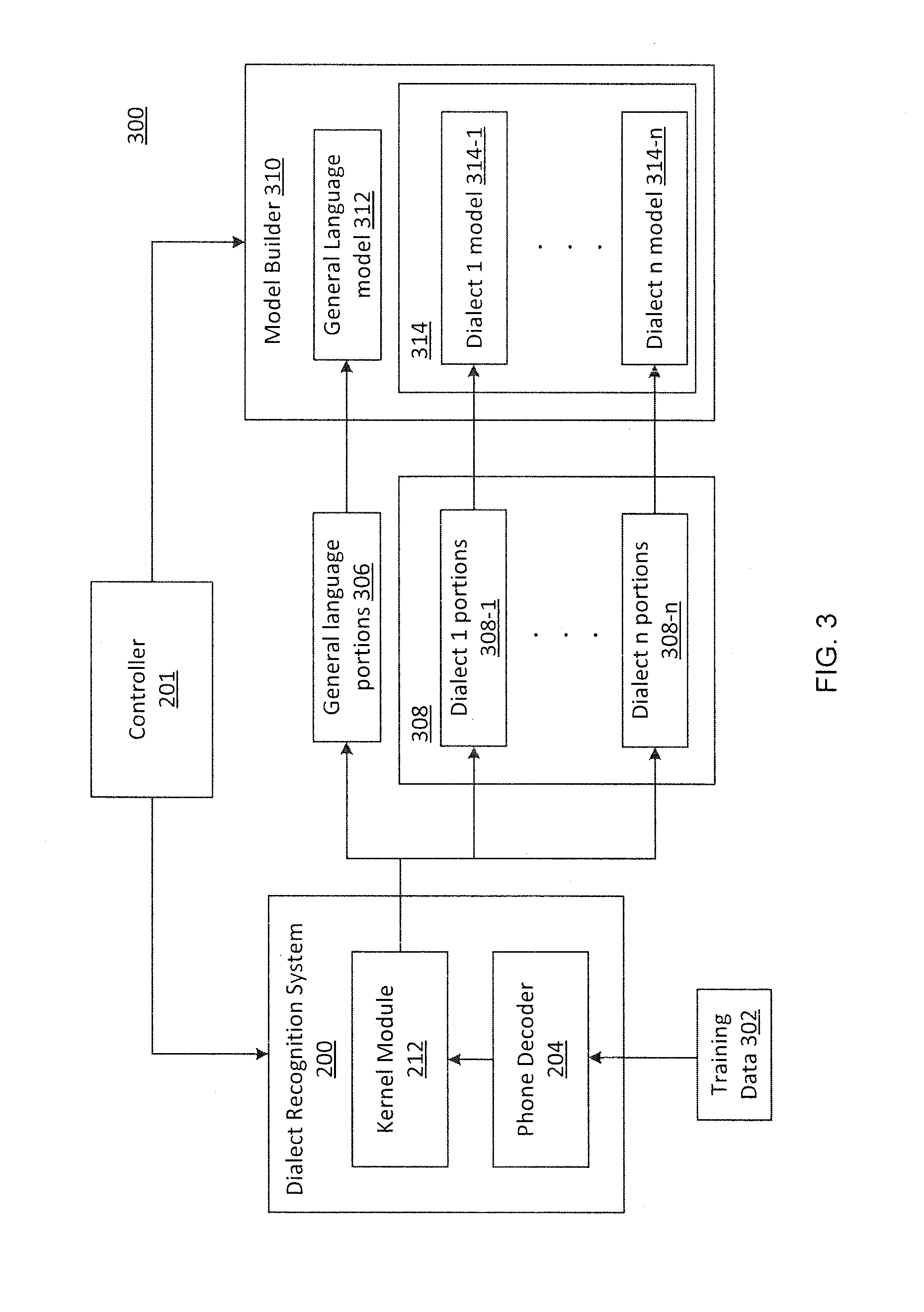
Dialect-specific acoustic language modeling and speech recognition
InactiveUS8583432B1Speech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsAutomatic speechGeneral-purpose language
Methods and systems for automatic speech recognition and methods and systems for training acoustic language models are disclosed. One system for automatic speech recognition includes a dialect recognition unit and a controller. The dialect recognition unit is configured to analyze acoustic input data to identify portions of the acoustic input data that conform to a general language and to identify portions of the acoustic input data that conform to at least one dialect of the general language. In addition, the controller is configured to apply a general language model and at least one dialect language model to the input data to perform speech recognition by dynamically selecting between the models in accordance with each of the identified portions.
Owner:IBM CORP
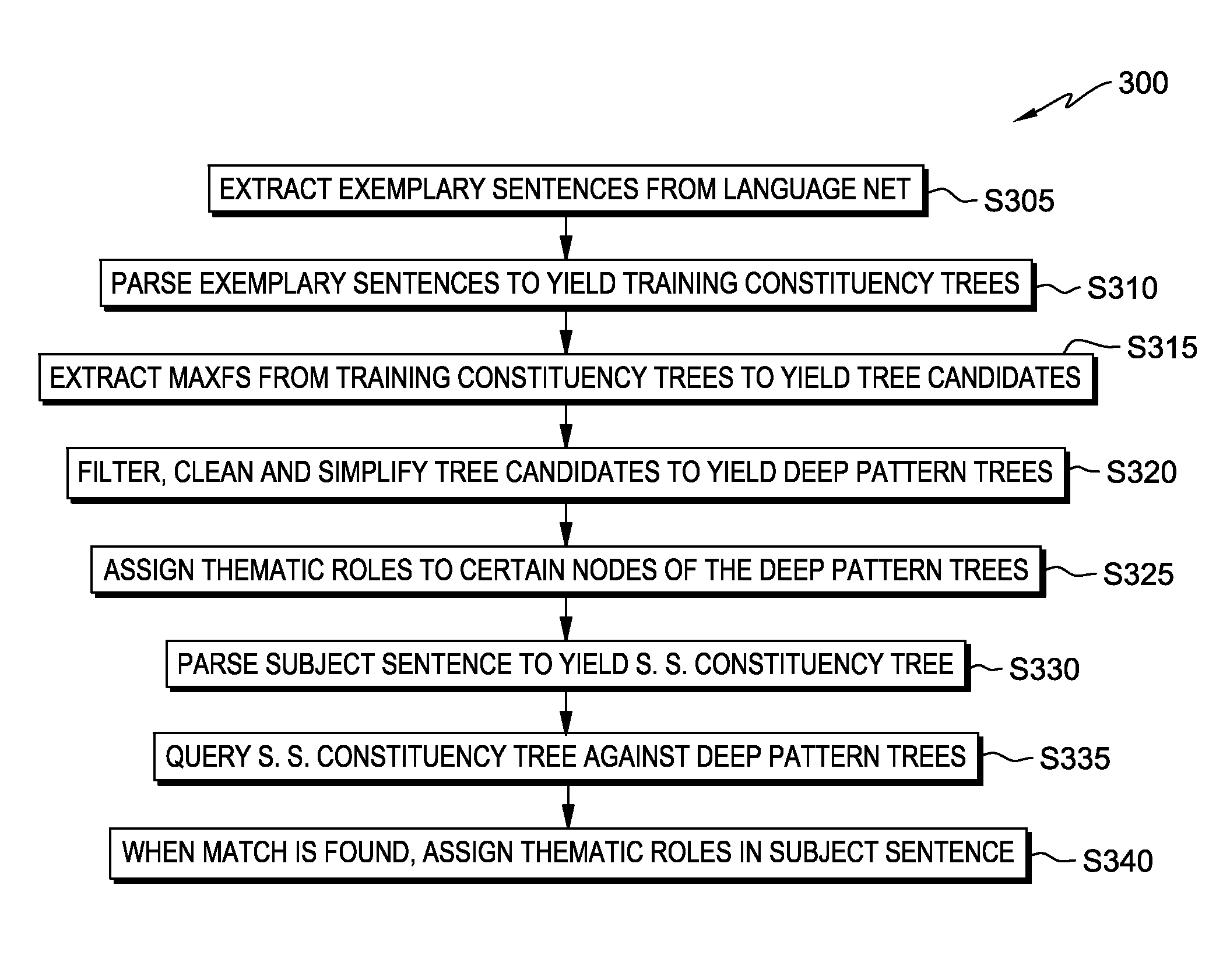
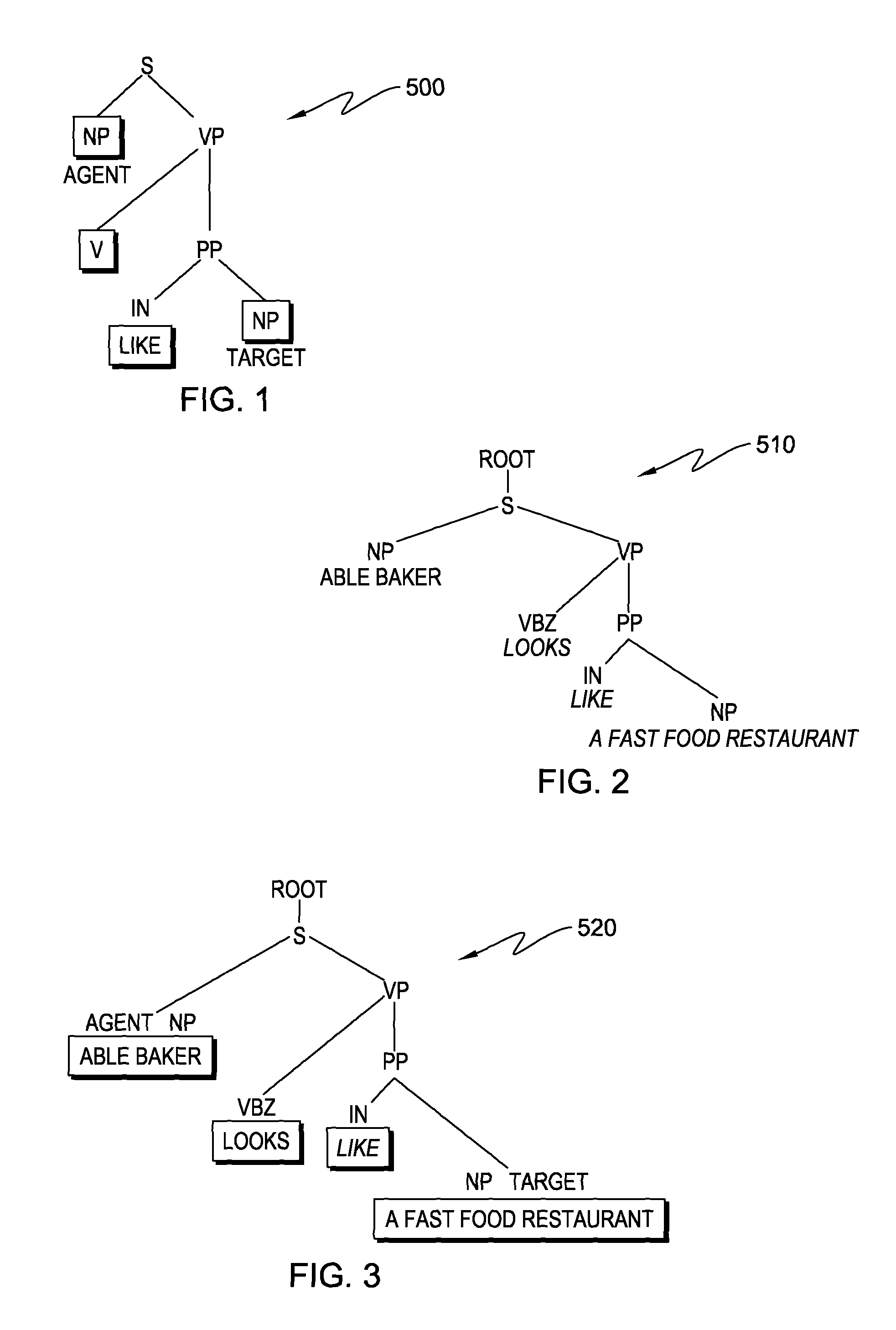
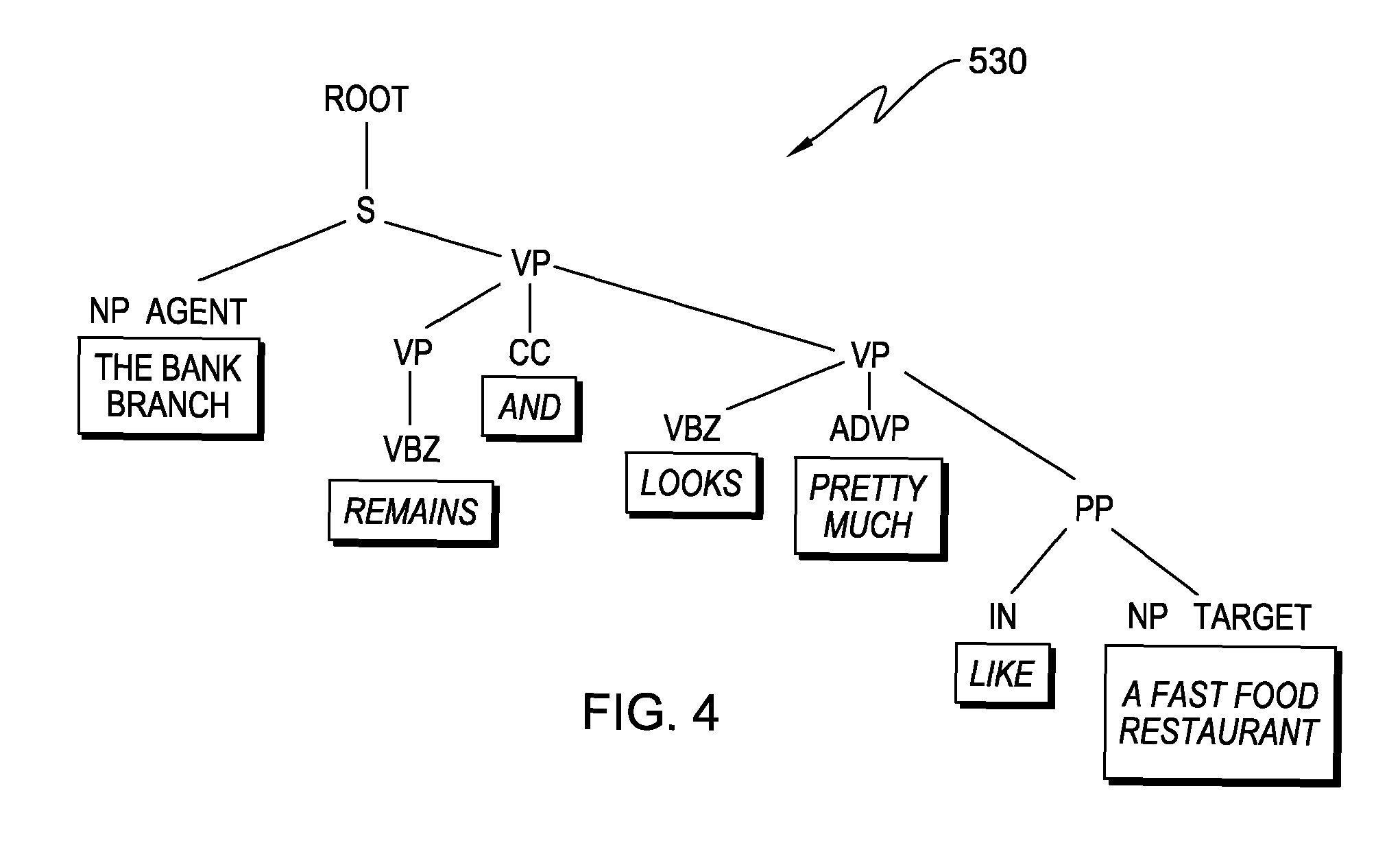
Unsupervised learning of deep patterns for semantic parsing
InactiveUS9292490B2Semantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsUnsupervised learningParsing
Using exemplary sentences, usage patterns and thematic roles ascribed in VerbNet to generate “deep pattern trees” for the exemplary sentences. Then, when an arbitrary natural language subject sentence is input, these deep pattern trees can be matched to the natural language subject sentence in order to assign thematic roles to at least some of the “grammatical portions” of the natural language subject sentence.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
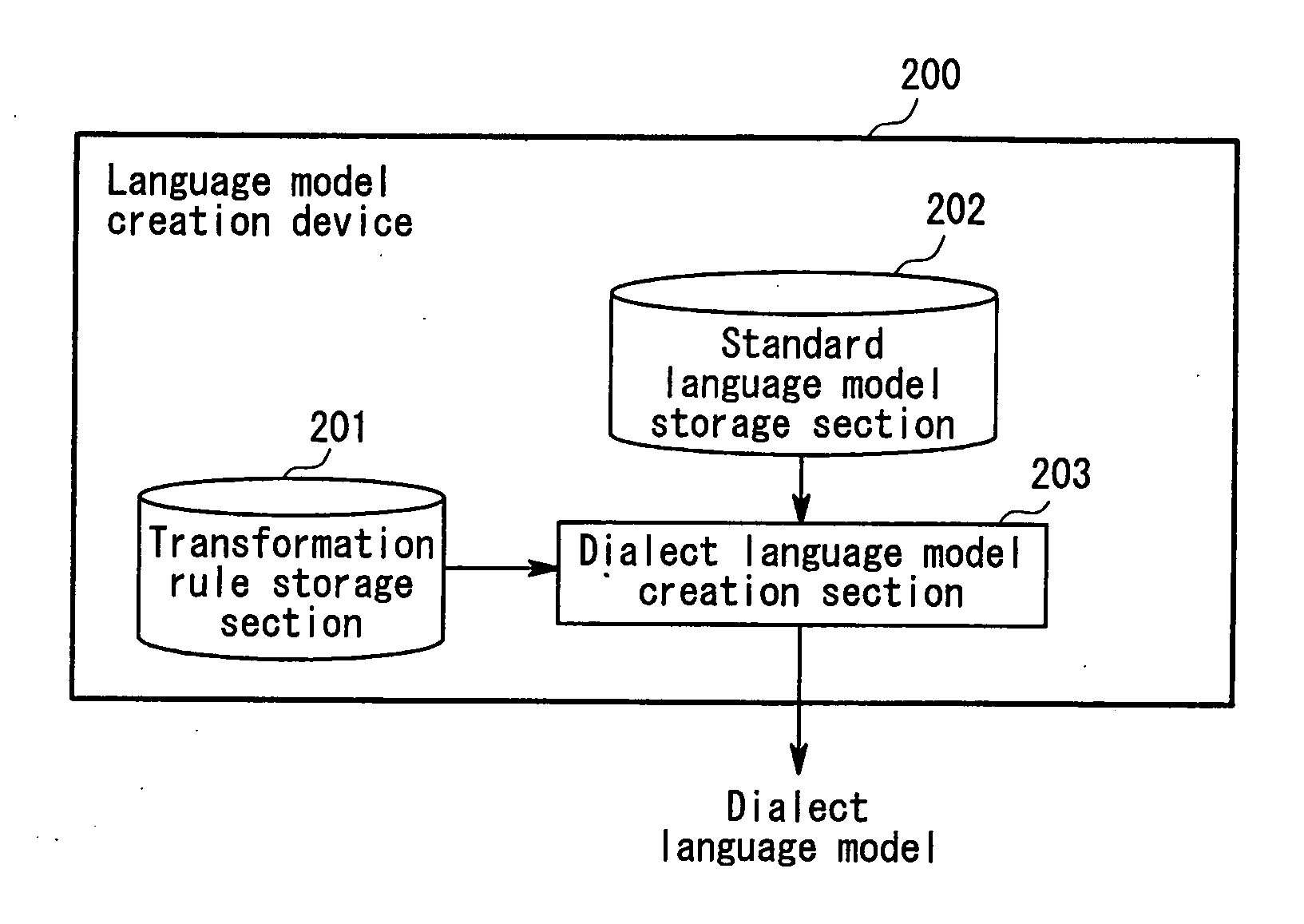
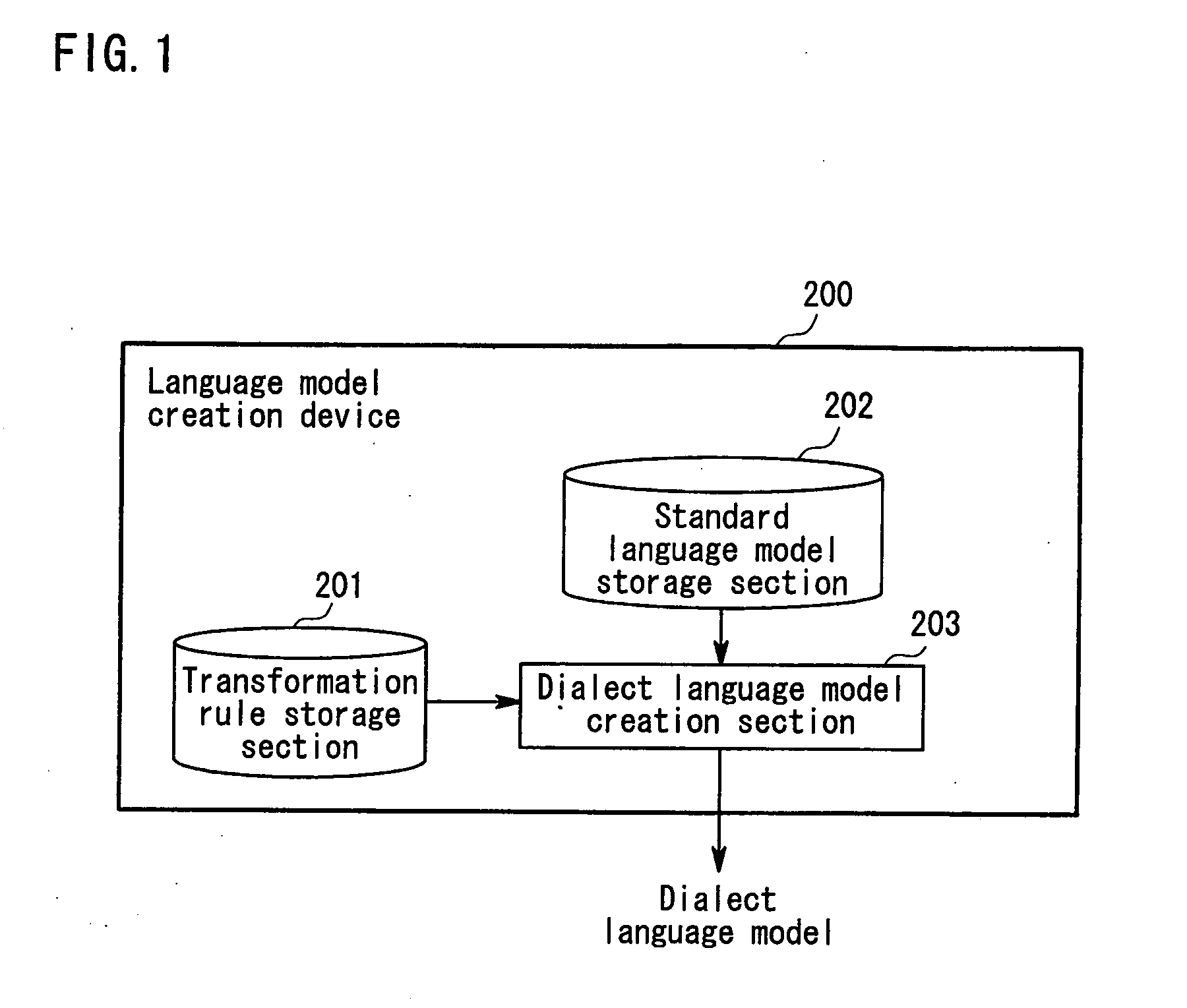
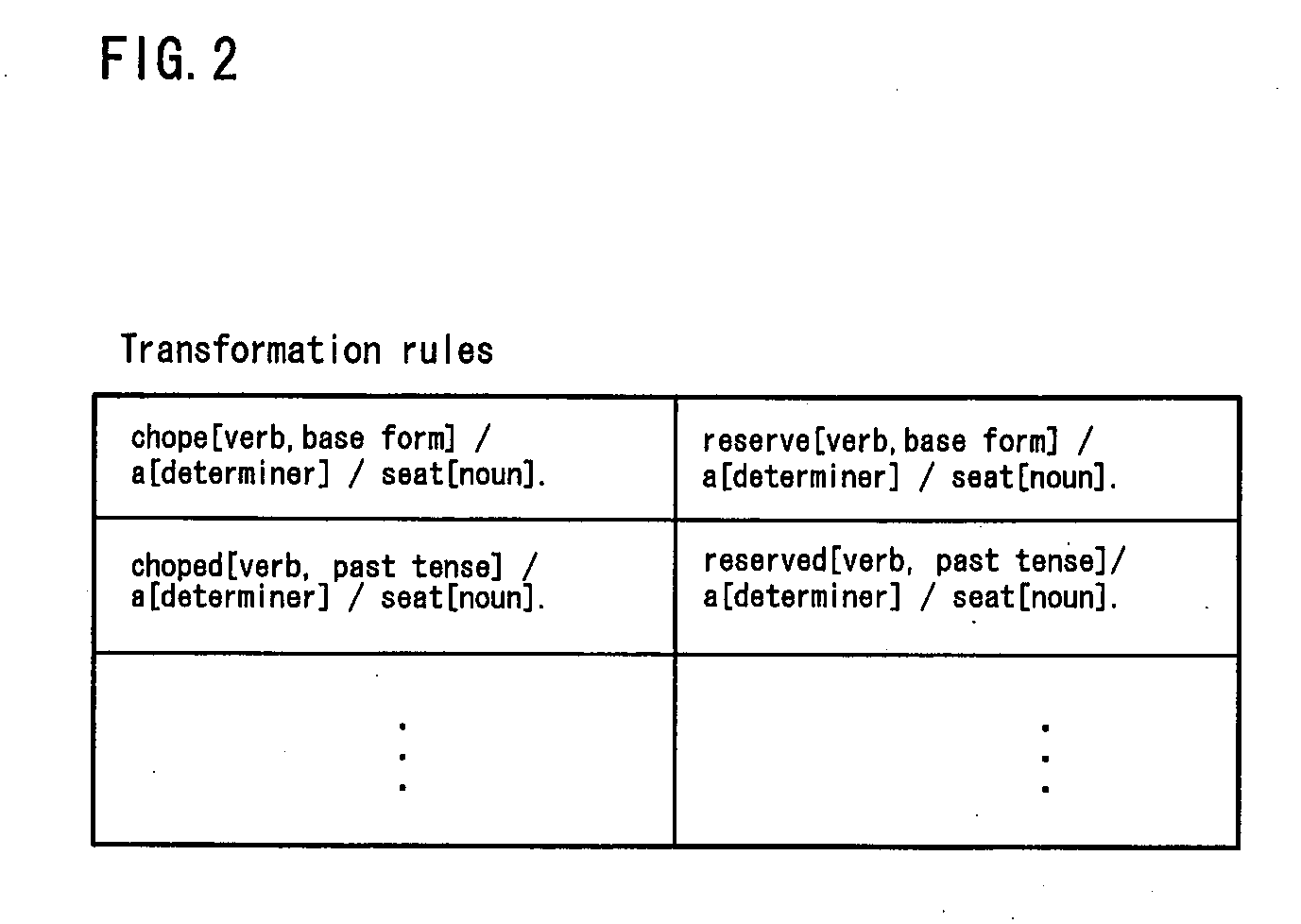
Language model creation device, language model creation method, and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveUS20120035915A1Robust recognitionSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsStandard Boolean modelHuman language
The present invention uses a language model creation device 200 that creates a new language model using a standard language model created from standard language text. The language model creation device 200 includes a transformation rule storage section 201 that stores transformation rules used for transforming dialect-containing word strings into standard language word strings, and a dialect language model creation section 203 that creates dialect-containing n-grams by applying the transformation rules to word n-grams in the standard language model and, furthermore, creates the new language model (dialect language model) by adding the created dialect-containing n-grams to the word n-grams.
Owner:NEC CORP
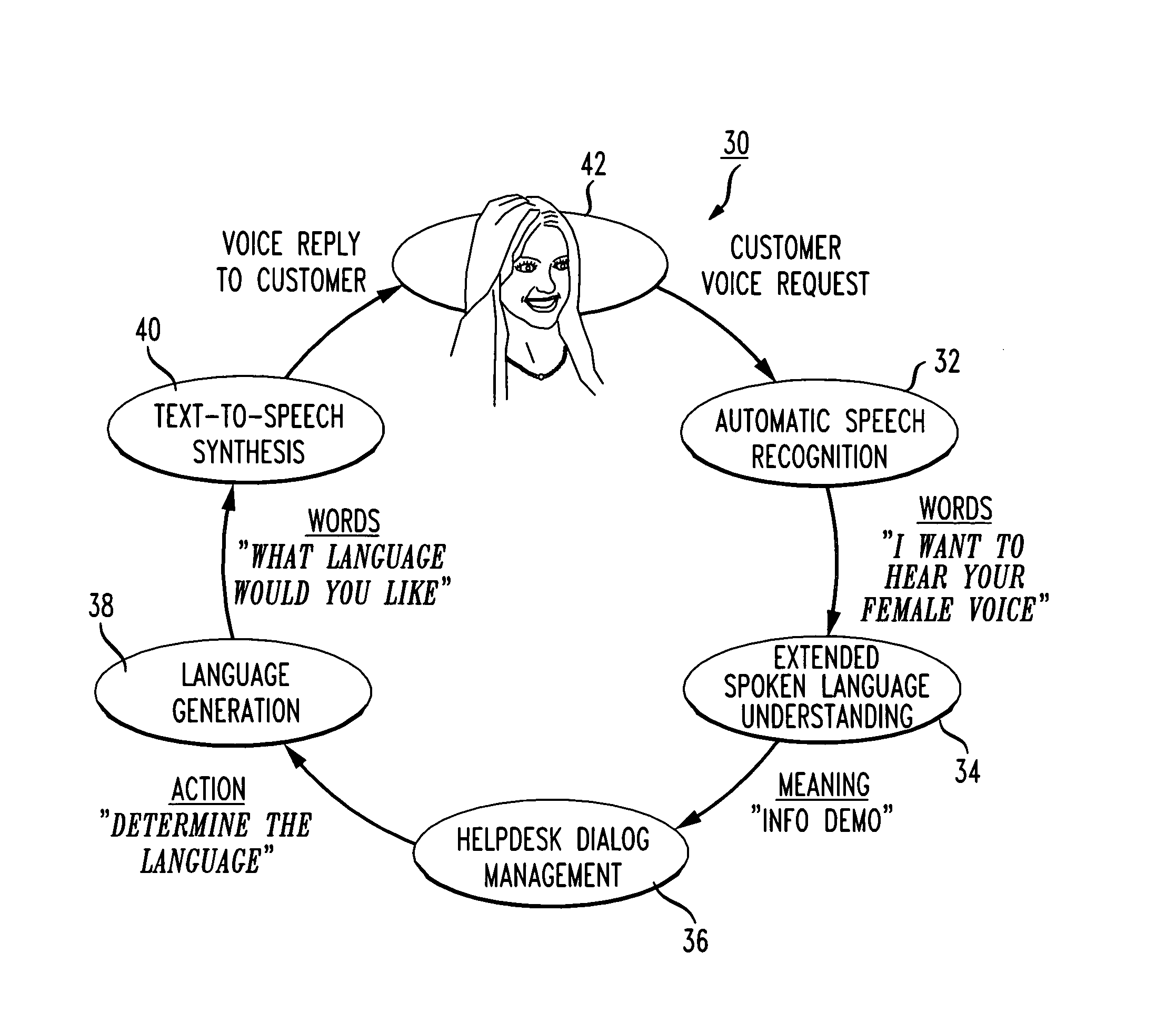
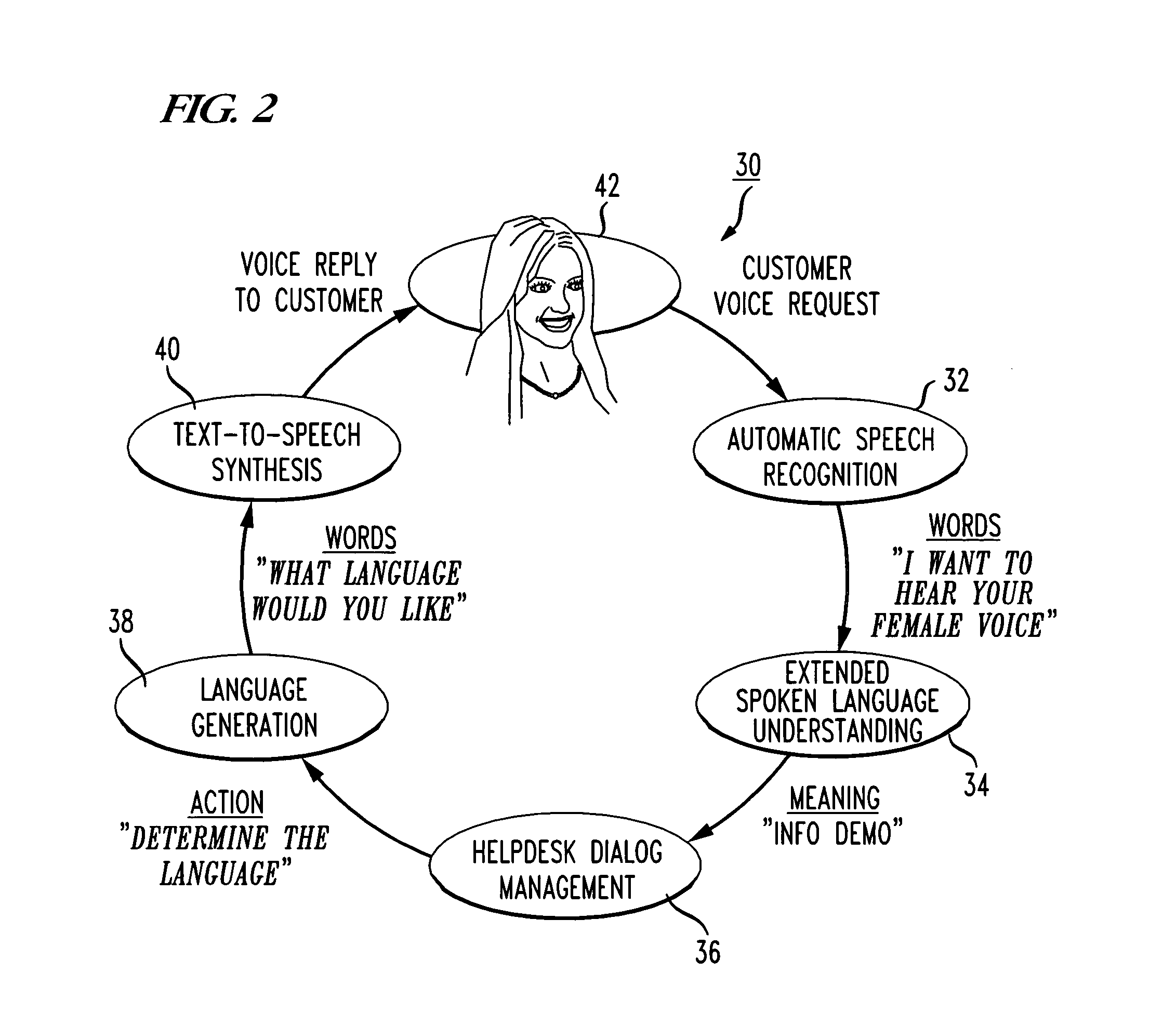
Method of handling frequently asked questions in a natural language dialog service
ActiveUS8645122B1Improve customer relationshipEfficient mannerNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionSpoken languageDialog management
A voice-enabled help desk service is disclosed. The service comprises an automatic speech recognition module for recognizing speech from a user, a spoken language understanding module for understanding the output from the automatic speech recognition module, a dialog management module for generating a response to speech from the user, a natural voices text-to-speech synthesis module for synthesizing speech to generate the response to the user, and a frequently asked questions module. The frequently asked questions module handles frequently asked questions from the user by changing voices and providing predetermined prompts to answer frequently asked questions.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
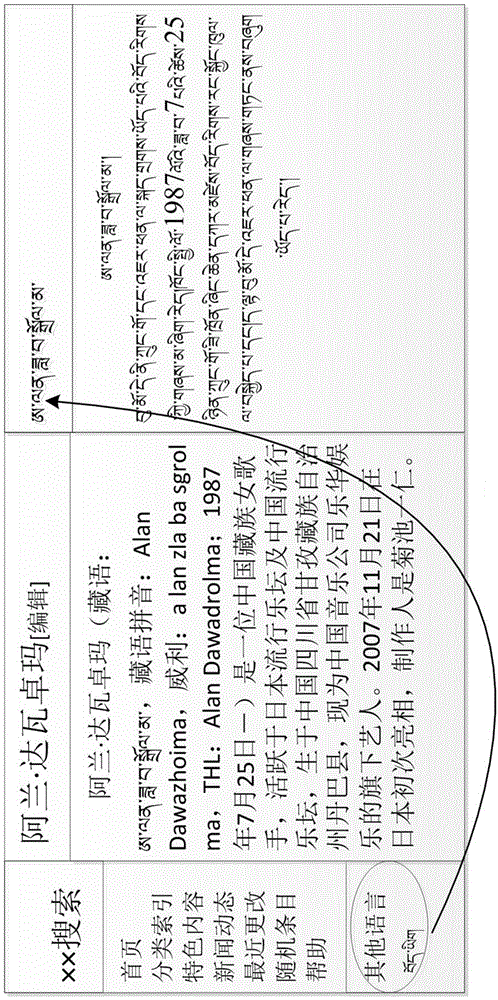
Tibetan language entity knowledge information extraction method
ActiveCN104133848AAvoid missingImplement miningNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsMachine translationTibetan language
The invention relates to a Tibetan language entity knowledge information extraction method, which comprises the following steps that: Tibetan and Chinese comparable language material information is extracted from Tibetan and Chinese text language material information; entity equivalence pairs are extracted from the Tibetan and Chinese comparable language material information; the Tibetan and Chinese cross-language entity relationship is extracted from the entity equivalence pairs; a Tibetan language "entity-attribute-value" triad is extracted from the Tibetan and Chinese cross-language entity relationship; and the triad is stored into a Tibetan language entity knowledge semantic resource library. The Tibetan language entity knowledge information extraction method solves the problem of Tibetan language training language material deficiency to a certain degree, promotes the knowledge sharing among different languages, and provides support for the study in the fields of Tibetan and Chinese cross-language knowledge questions, information retrieval, machine translation and the like.
Owner:MINZU UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
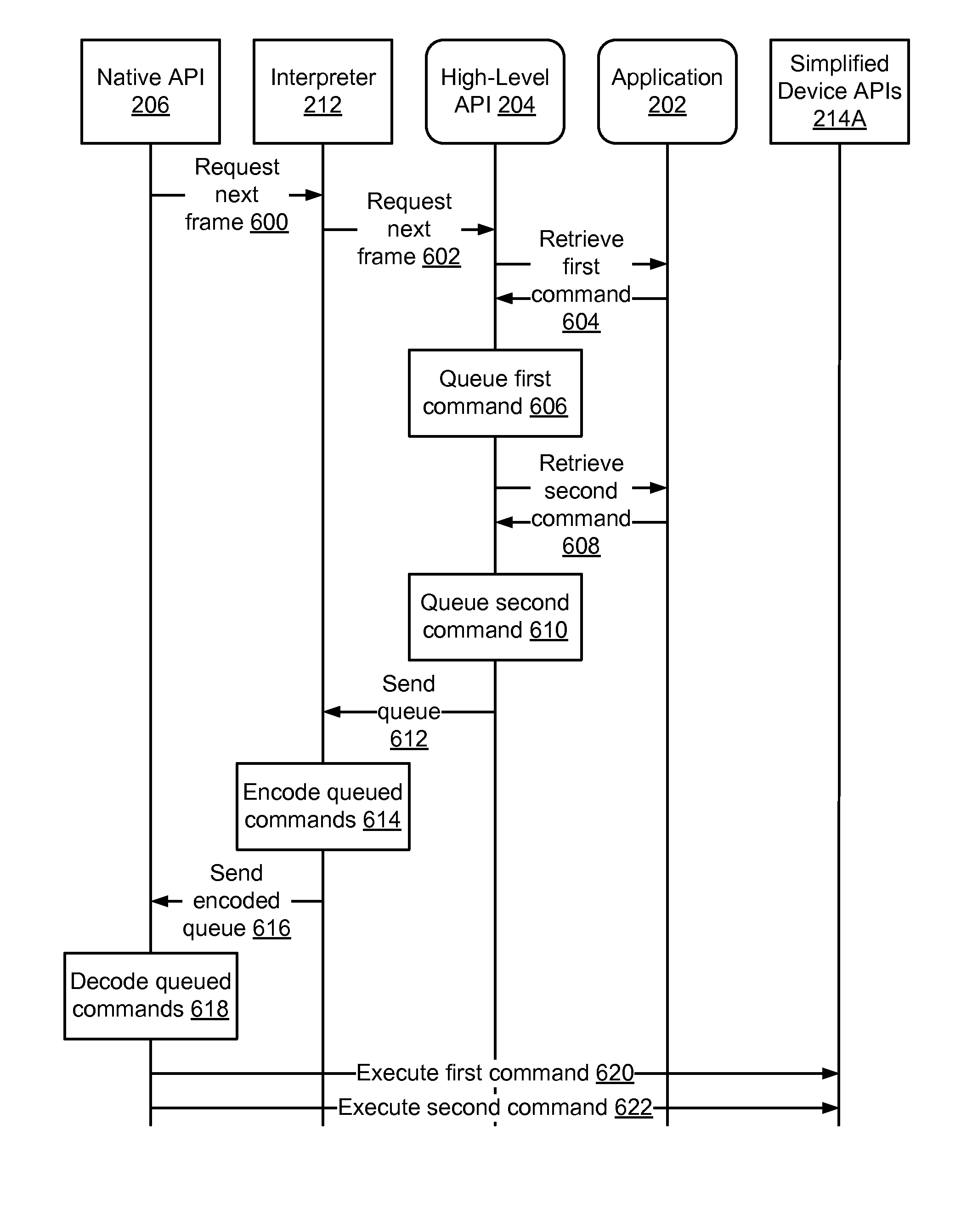
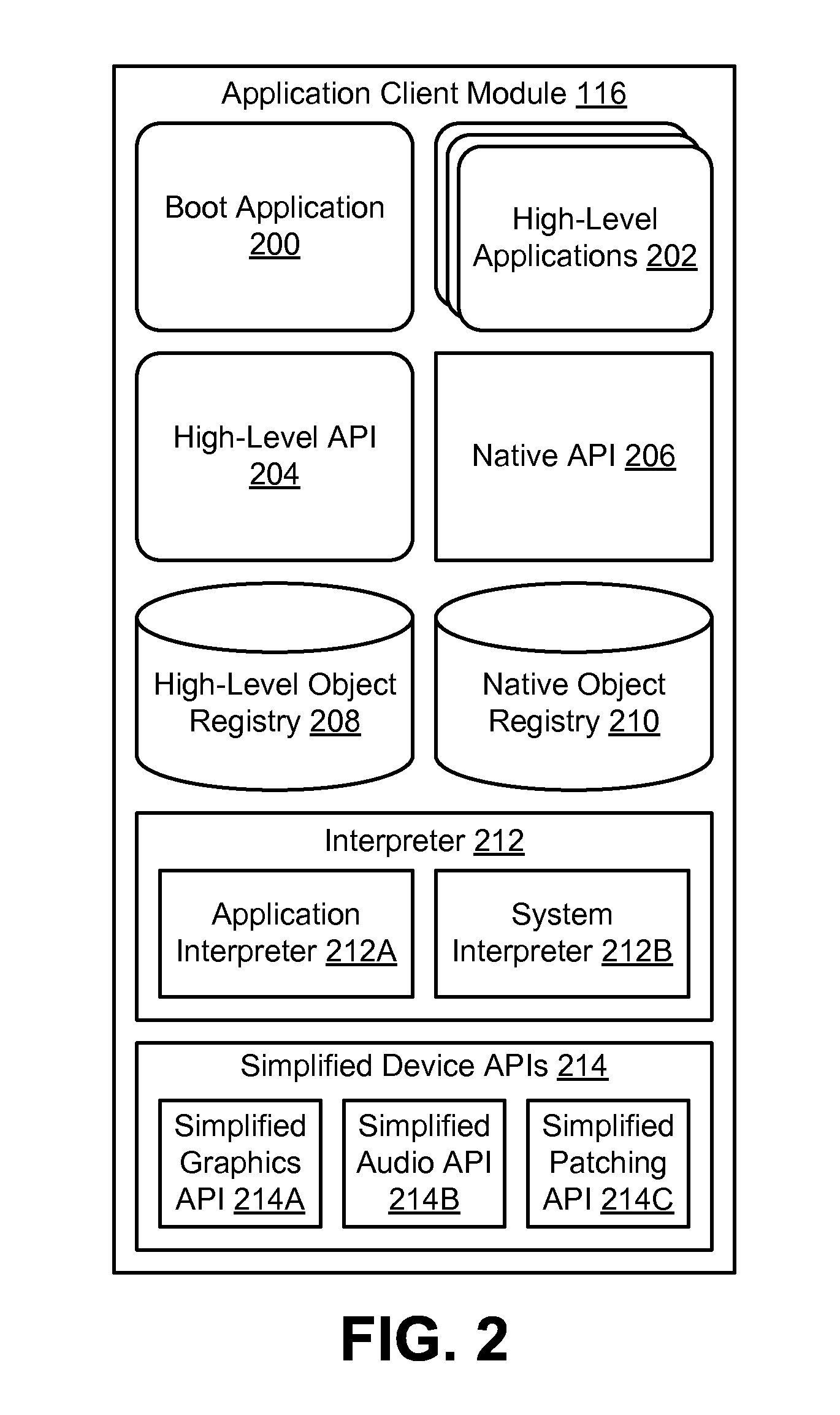
Communication protocol between a high-level language and a native language
InactiveUS20120167063A1Transformation of program codeInterprogram communicationCode writingOperational system
A system and a method are disclosed for communicating between two programming languages on a client device. Commands in a high-level language are encoded as character string containing a series of numbers separated by delimiters, with each component of the command encoded as a different number. The encoded character strings are passed to compiled code that runs natively on the client device, and the native code decodes the character strings into corresponding native commands and executes the native commands. This communication protocol allows applications written in high-level code to perform functions that are typically set aside for native code, such as communicating with web servers and modifying files saved in memory. High-level code may also be transferred to client devices without being subjected to the restrictions that some operating systems place on the transfer for application binaries, which allows application developers to automatically send application updates to users.
Owner:NGMOCO
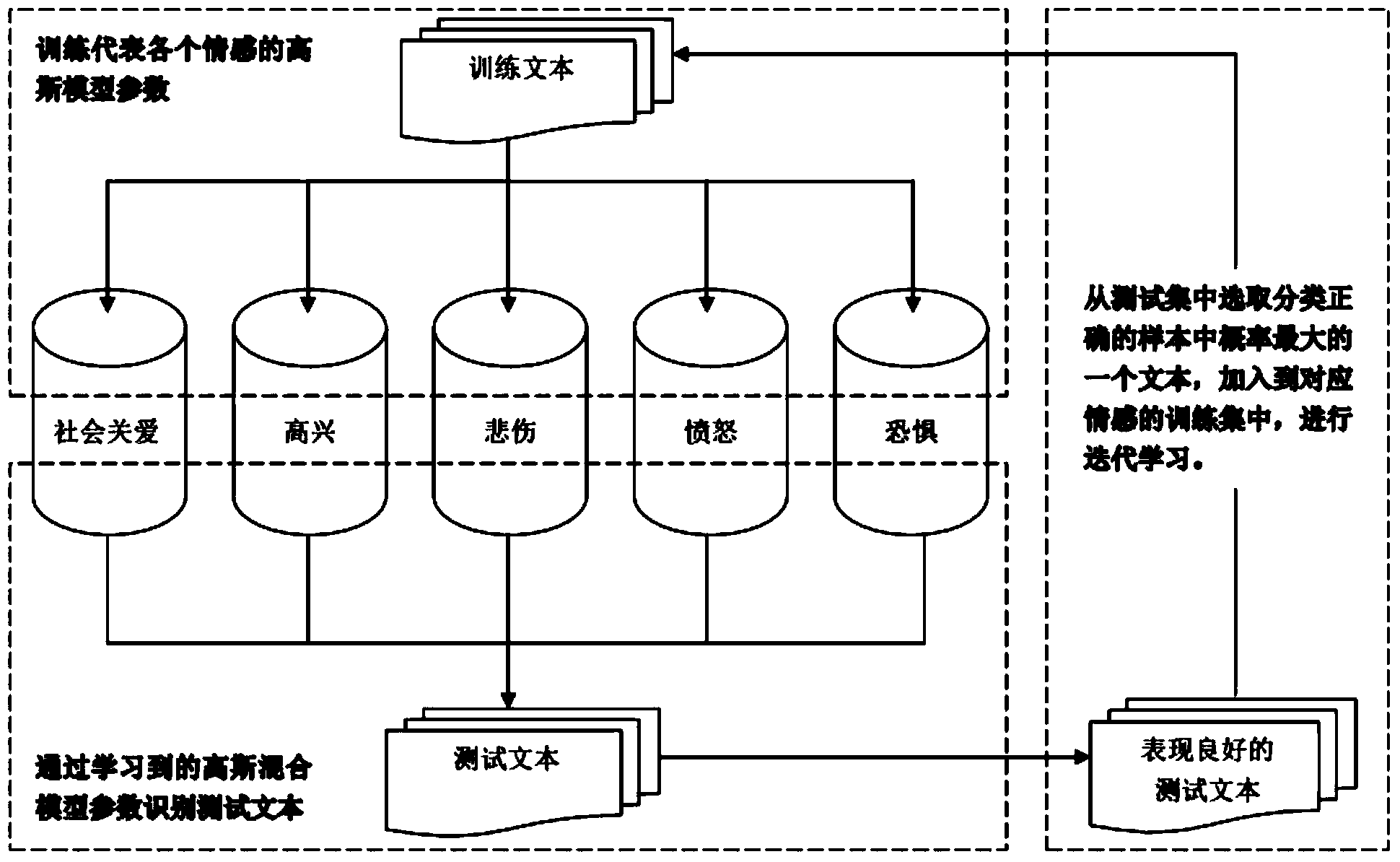
Multiclass emotion analyzing method and system facing bilingual microblog text
InactiveCN104331506AEasy to classifyNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsClass modelClassification methods
The invention relates to a multiclass emotion analyzing method and a system facing a bilingual microblog text and belongs to the technical field of microblog text emotion analysis. The method comprises the following steps that (1) bilingual dictionary construction: corpus with an emotion inclination of a certain size is first collected, high frequent words with the emotion inclination can be extracted from the corpus, an emotional dictionary is then expanded by using an existing knowledge database and a vocabulary similarity calculating model, and finally network language and emotional signs are added in the emotional dictionary; (2) text pretreatment: the words are divided in a to-be-identified text, stop words are removed, and standardization treatment is conducted on English word shapes; (3) text characteristic space expression: the bilingual emotional dictionary is used for conducting vectorization on the text; (4) an emotional identifying task of the corpus text is realized through a multi emotion class model. The accurate rate and the F1 valve of the method are higher than those of a traditional classification method, and particularly the classification effect of a semi-supervised Gaussian mixture model classification algorithm in a small-scale training set is obviously better than that of the other methods.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and portable system for phonetic language translation using brain interface
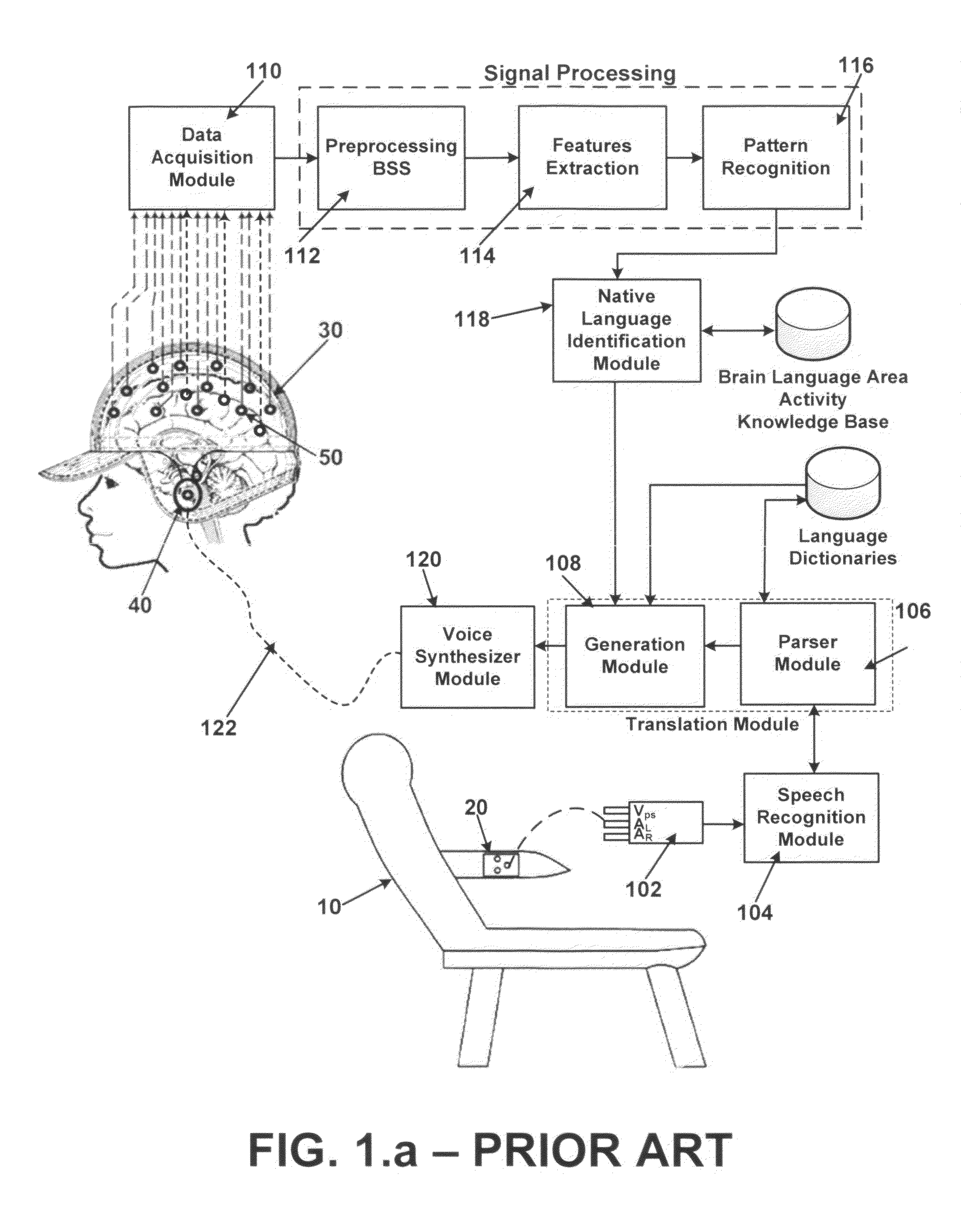
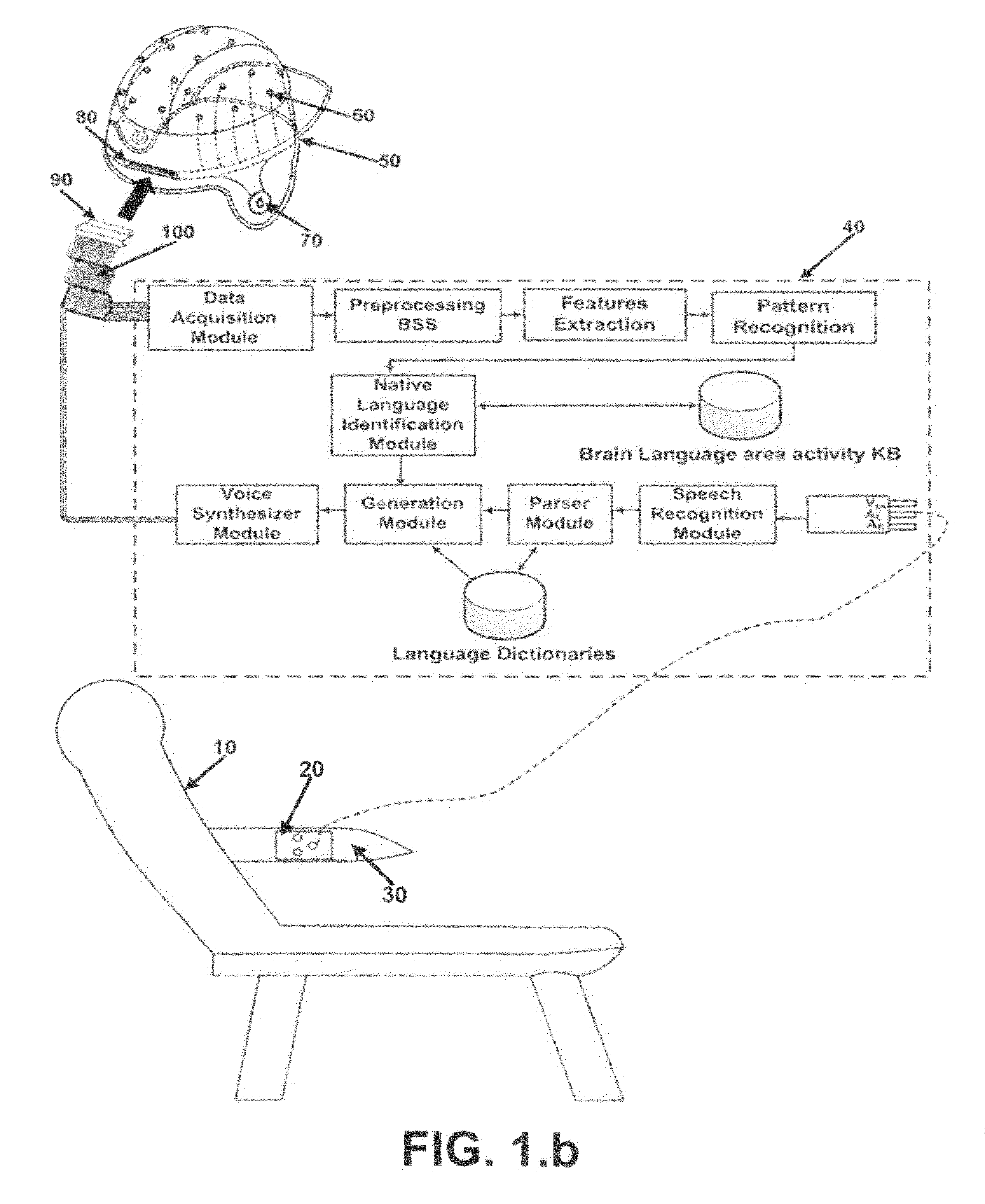
InactiveUS8548814B2Overcomes drawbackNatural language translationSpeech analysisSpoken languageSpeech synthesis
A phonetic language translation system receives audio output from an audible program presented to the user, so as to identify any speech signal contained within the audio output. The speech signals are broken down into recognizable phonemes which make up the most basic elements of speech in spoken languages. The sequentially generated phonemes are then regrouped to form recognizable words in one of native languages spoken around the world. While watching the audible program, the activity of language area of user's brain is recorded using electrodes in the cap. The recorded language area brain signals are analyzed and compared with brain language area activity knowledge base to identify the native language of user. Sentences are formed using the grammatical rules of the native language. Each sentence is then translated into the identified native language and broadcast to the user using a voice synthesizer.
Owner:MANUEL DEVADOSS JOHNSON
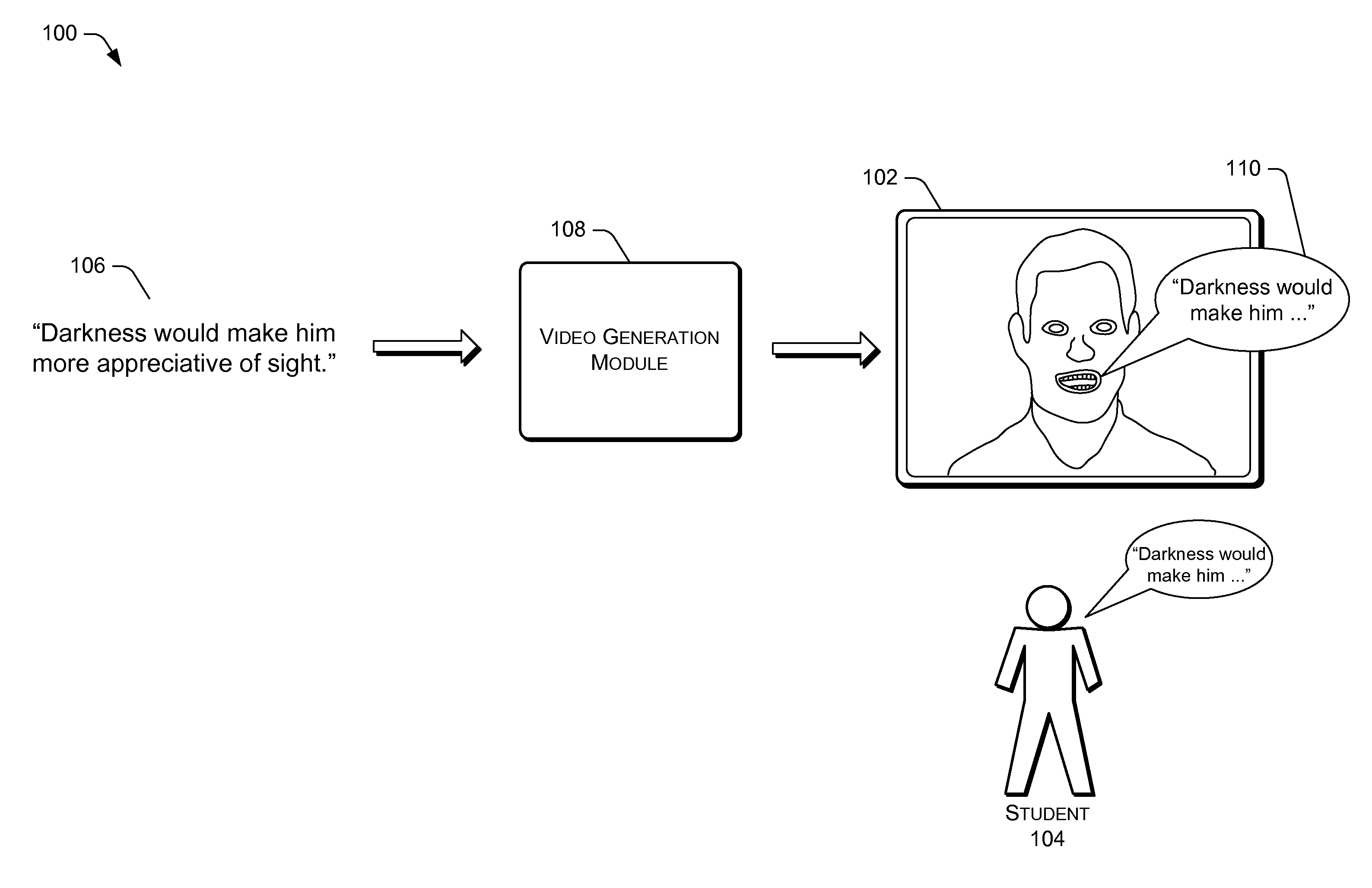
Talking Teacher Visualization for Language Learning
A representation of a virtual language teacher assists in language learning. The virtual language teacher may appear as a “talking head” in a video that a student views to practice pronunciation of a foreign language. A system for generating a virtual language teacher receives input text. The system may generate a video showing the virtual language teacher as a talking head having a mouth that moves in synchronization with speech generated from the input text. The video of the virtual language teacher may then be presented to the student.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for classifying legal texts by adopting semi-supervised convolutional neural network (SSC)
InactiveCN108009284AAbility to understand literal meaningHave logical reasoningNatural language data processingNeural architecturesNatural language understandingMulti-label classification
The invention relates to a method for classifying legal texts by adopting a semi-supervised convolutional neural network (SSC) and belongs to the field of neural networks. According to the method, natural languages are processed by utilizing the SSC to achieve the main objective of a system; and through the processing on the legal case description, the problems that what rights and interests of parties does the legal case description violate or which laws and regulations does the parties violate are preliminarily solved, probably more than one rights and interests of the parties is violated orthe parties violate a plurality of laws and regulations at the same time and multi-label classification is realized. Through the legal service platform, case handlers are helped to efficiently handlevarious legal cases and the various legal cases are subjected to semantic analysis to achieve classification to ensure that not only the ability to understand literal meanings but also the ability tologically reason and understand deep meanings are provided in the aspect of the natural language understanding function.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
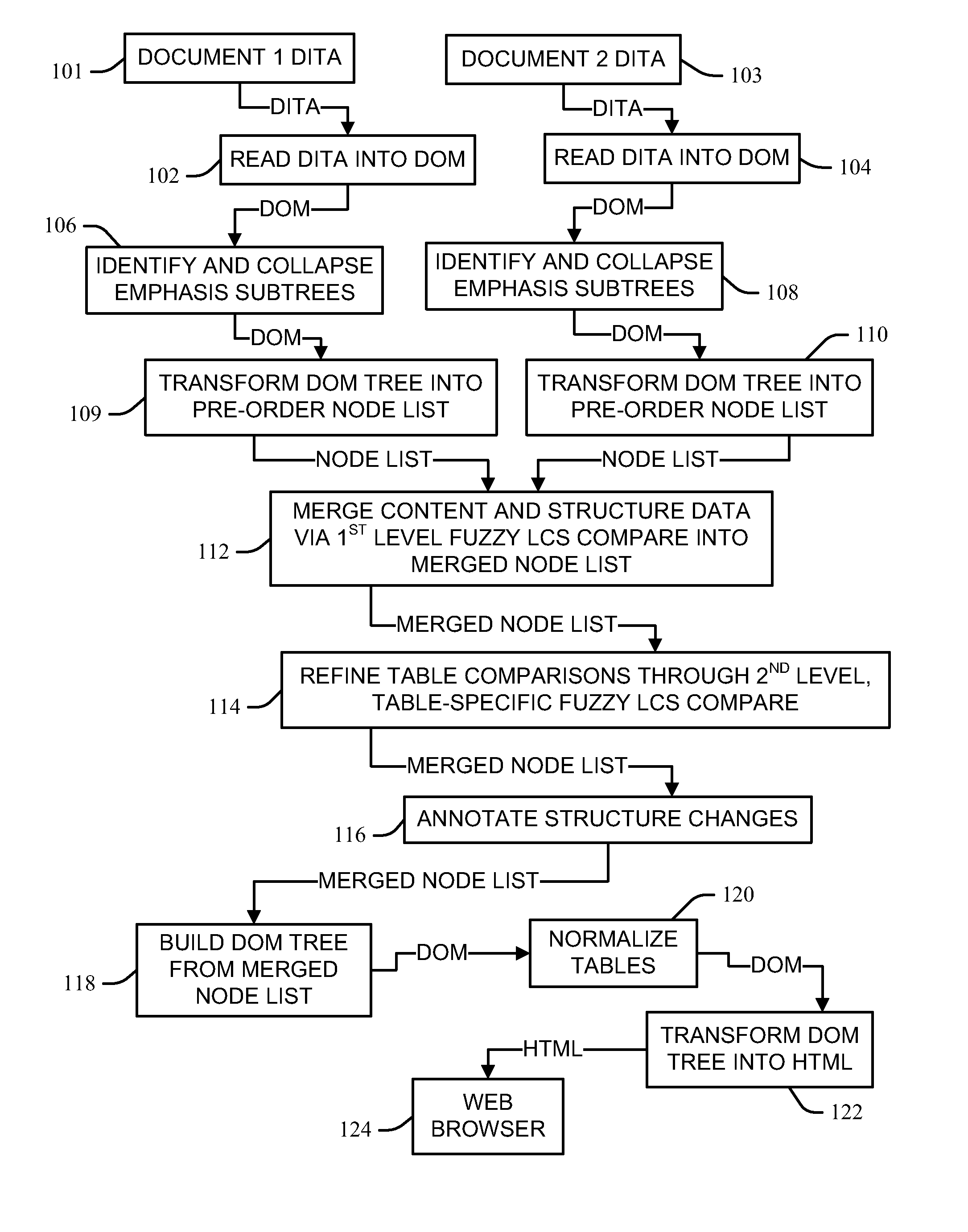
Automated document revision markup and change control
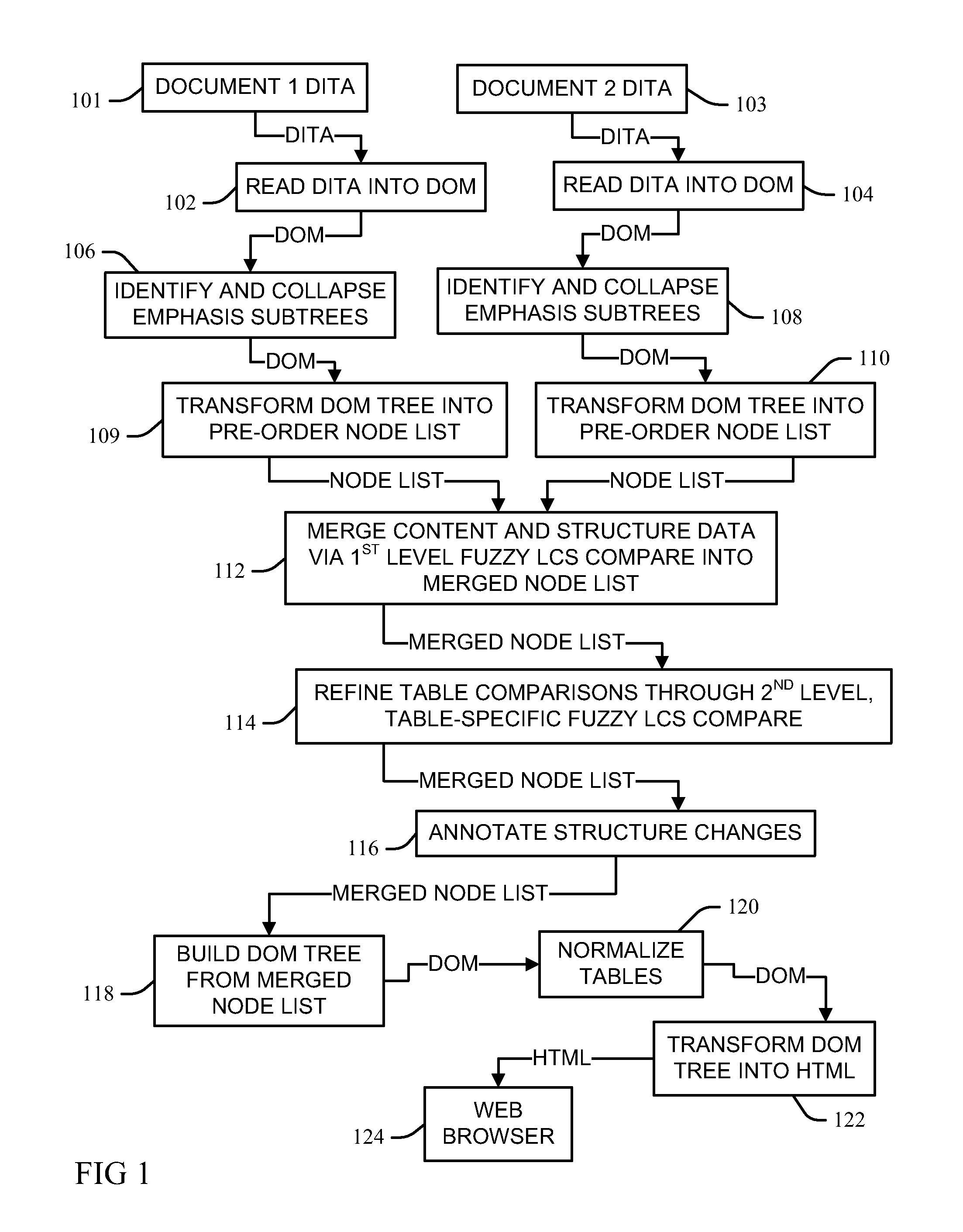
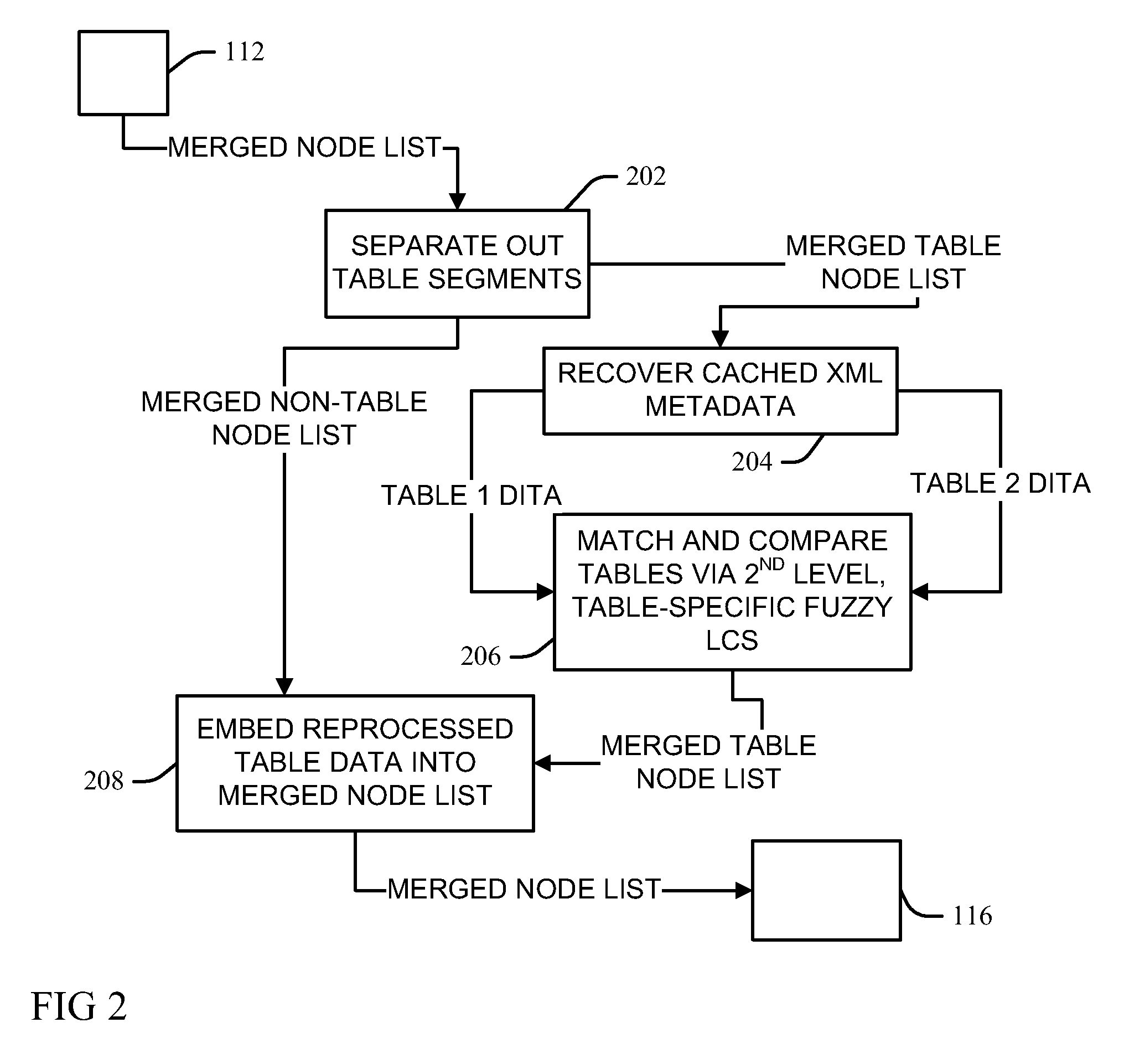
InactiveUS8381095B1Digital data processing detailsNatural language data processingDarwin Information Typing ArchitectureLongest common subsequence problem
Automated comparison of Darwin Information Typing Architecture (DITA) documents for revision mark-up includes reading document data from first and second DITA documents into respective document object model trees of nodes, and identifying and collapsing emphasis subtree nodes in the trees into their parent nodes, the collapsing caching emphasis data from the identified subtree nodes. A preorder traversal transforms the model trees into respective pre-order node lists and captures adjacent sibling emphasis subtree nodes as single text nodes. The node lists are merged into a merged node list via a longest common subsequence process that recognizes matches node pairs having primary sort key information and document structure metadata meeting a match threshold, with differences between matching tokens of the node pairs saved. A merged document object model built from the refined merged node list is transformed into a hypertext mark-up language document.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for providing a natural language content dedication service
The system and method described herein may provide a natural language content dedication service in a voice services environment. In particular, providing the natural language content dedication service may generally include detecting multi-modal device interactions that include requests to dedicate content, identifying the content requested for dedication from natural language utterances included in the multi-modal device interactions, processing transactions for the content requested for dedication, processing natural language to customize the content for recipients of the dedications, and delivering the customized content to the recipients of the dedications.
Owner:VB ASSETS LLC
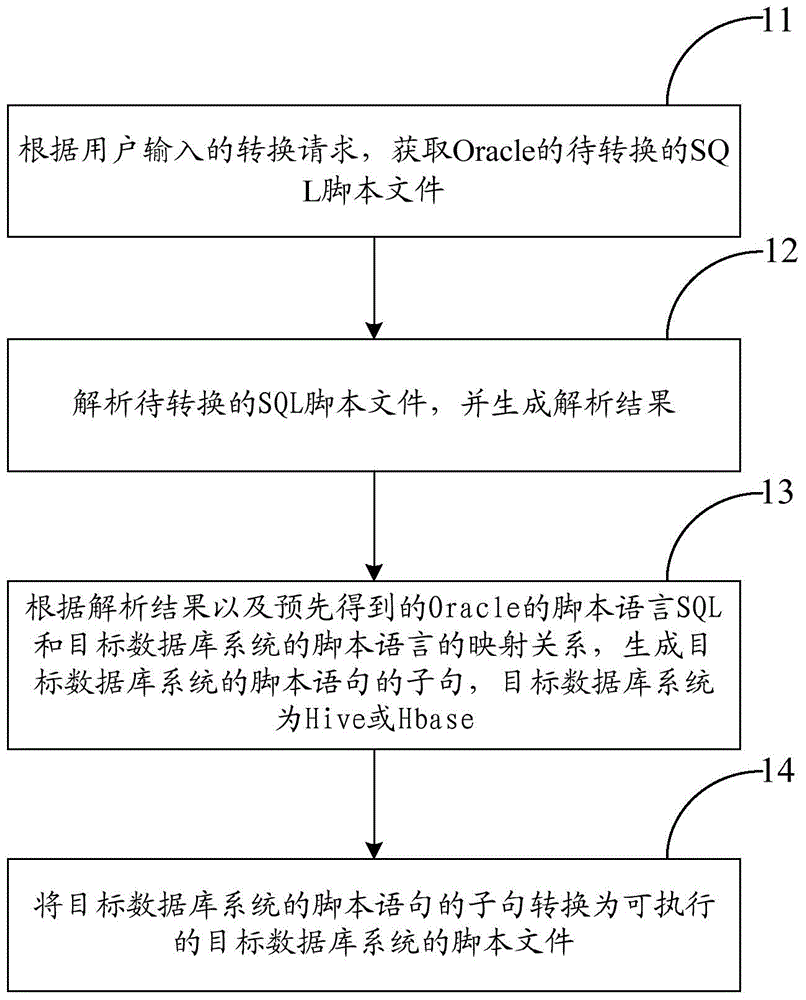
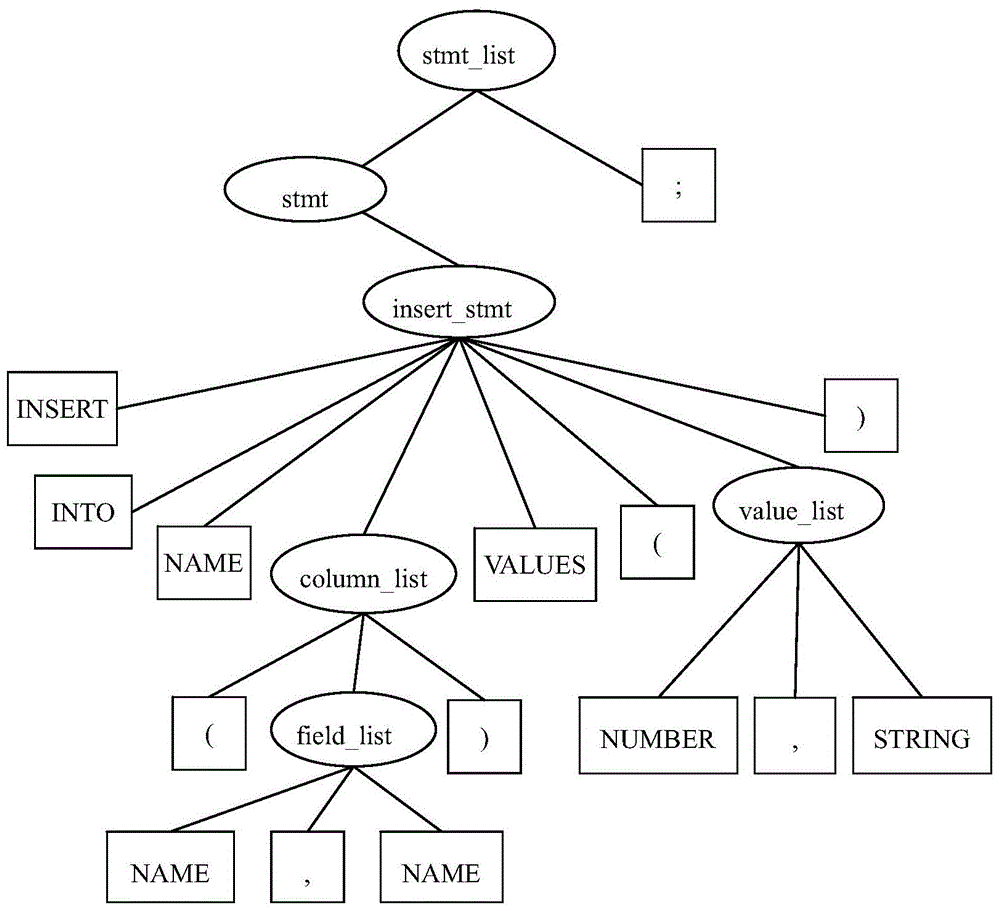
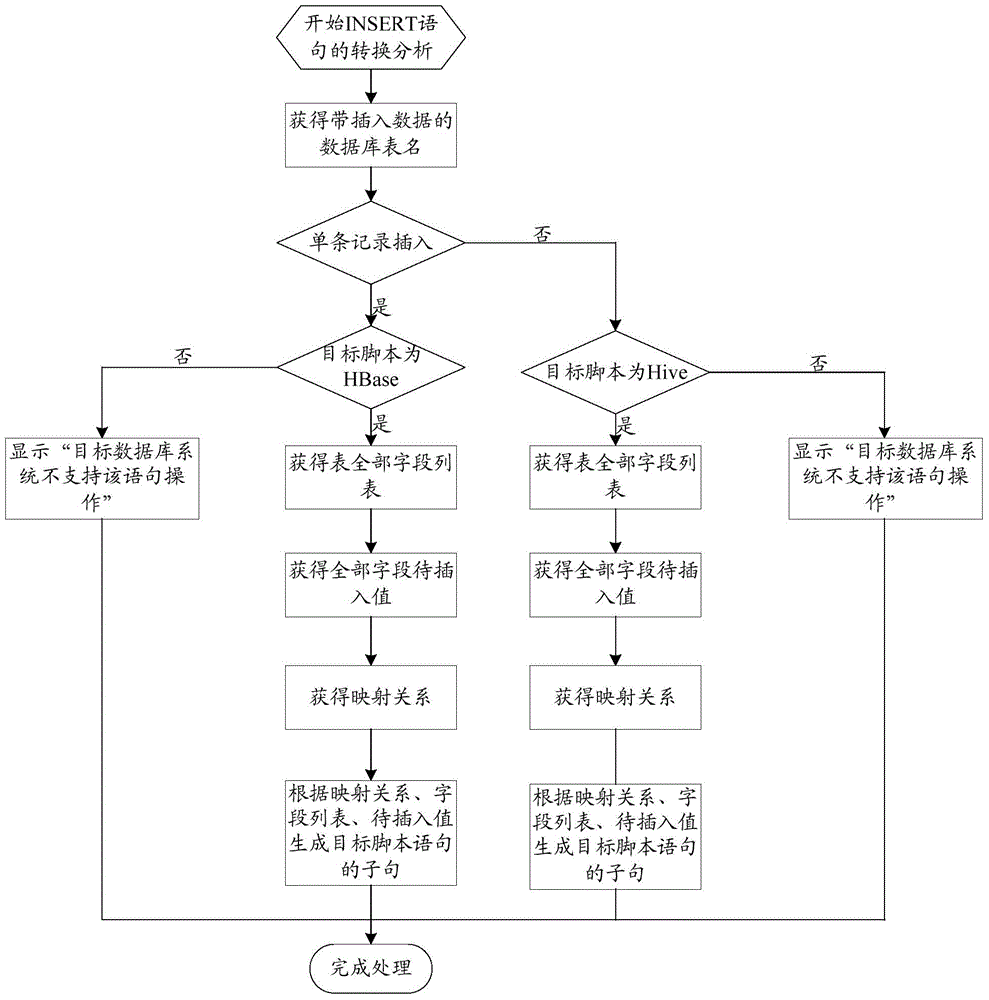
Method and apparatus for converting script language SQL of Oracle
The invention provides a method and an apparatus for converting a script language SQL of Oracle. The method comprises the steps of according to a conversion request input by a user, obtaining a to-be-converted SQL script file of Oracle; analyzing the to-be-converted SQL script file to generate an analytic result; according to the analytic result and a pre-obtained mapping relationship between the script language SQL of Oracle and a script language of a target database system, generating clauses of a script statement of the target database system, wherein the target database system is Hive or Hbase; and converting the clauses of the script statement of the target database system into an executable script file of the target database system. According to the method for converting the script language SQL of Oracle, the SQL script file of Oracle can be conveniently and quickly converted into script files of other database systems.
Owner:中移信息技术有限公司
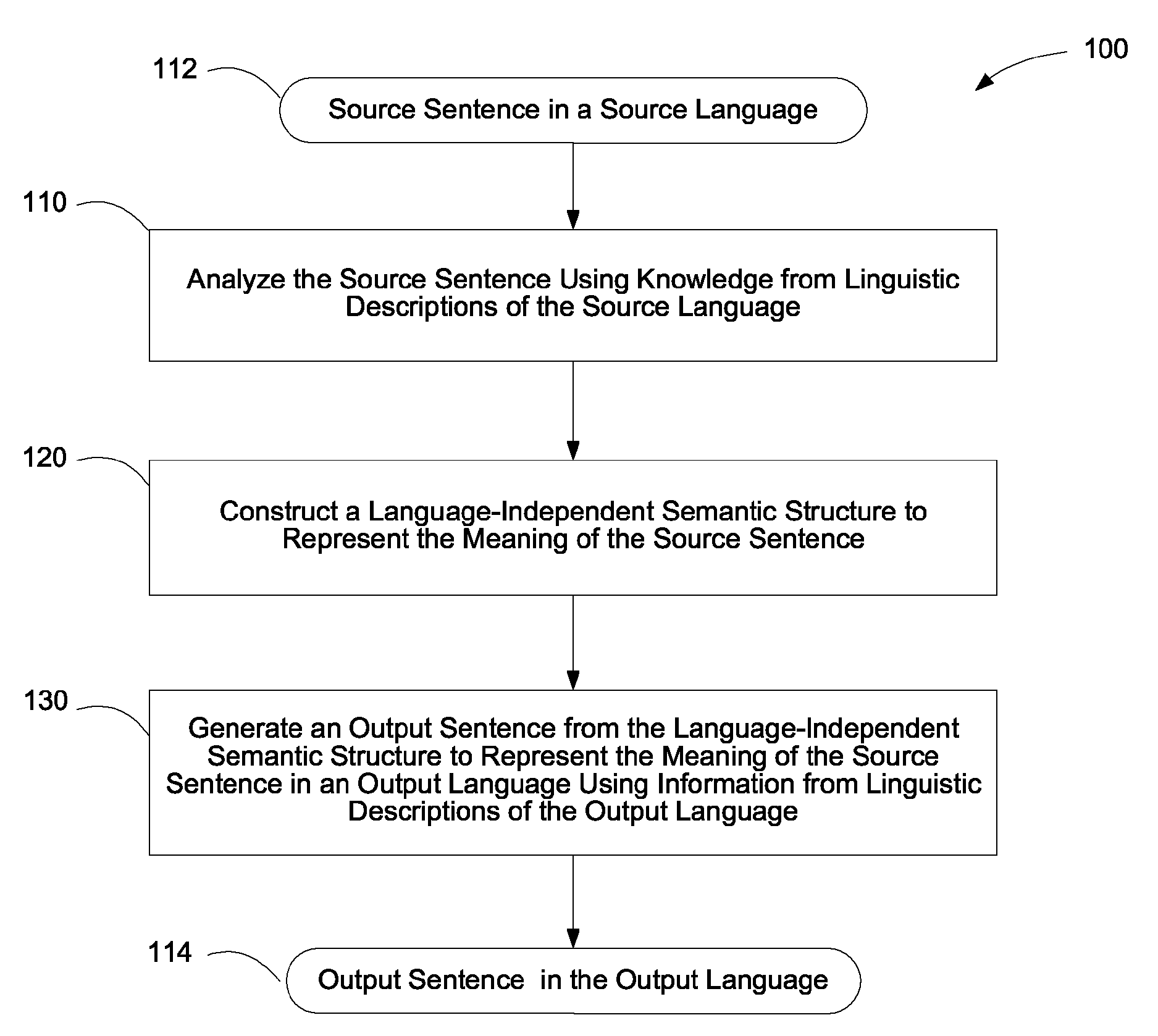
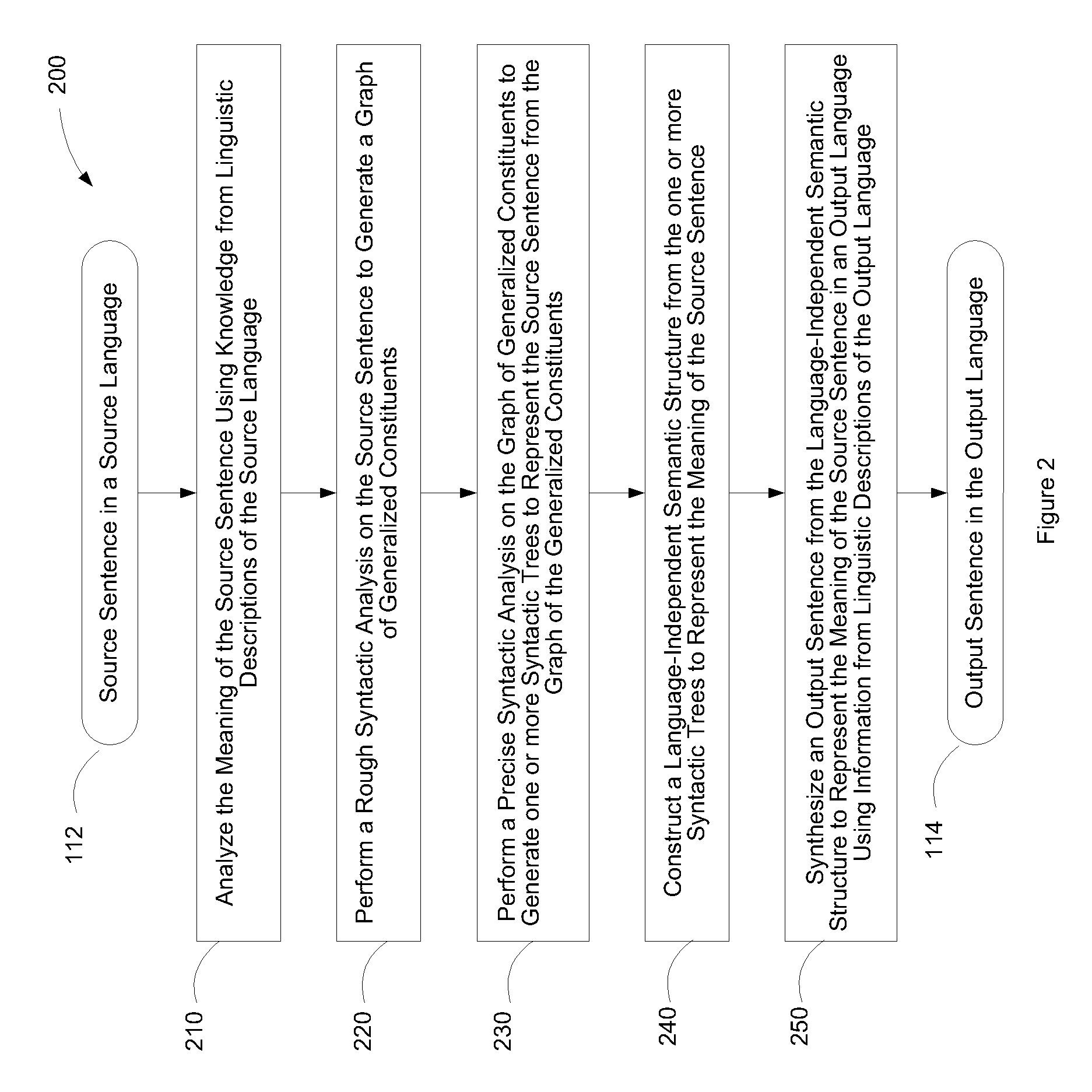
Systems for translating sentences between languages using language-independent semantic structures and ratings of syntactic constructions
ActiveUS8214199B2Natural language translationSemantic analysisTranslation languageIntermediate language
A method and computer system for translating sentences between languages from an intermediate language-independent semantic representation is provided. On the basis of comprehensive understanding about languages and semantics, exhaustive linguistic descriptions are used to analyze sentences, to build syntactic structures and language independent semantic structures and representations, and to synthesize one or more sentences in a natural or artificial language. A computer system is also provided to analyze and synthesize various linguistic structures and to perform translation of a wide spectrum of various sentence types. As result, a generalized data structure, such as a semantic structure, is generated from a sentence of an input language and can be transformed into a natural sentence expressing its meaning correctly in an output language. The method and computer system can be applied to in automated abstracting, machine translation, natural language processing, control systems, Internet information retrieval, etc.
Owner:ABBYY DEV INC
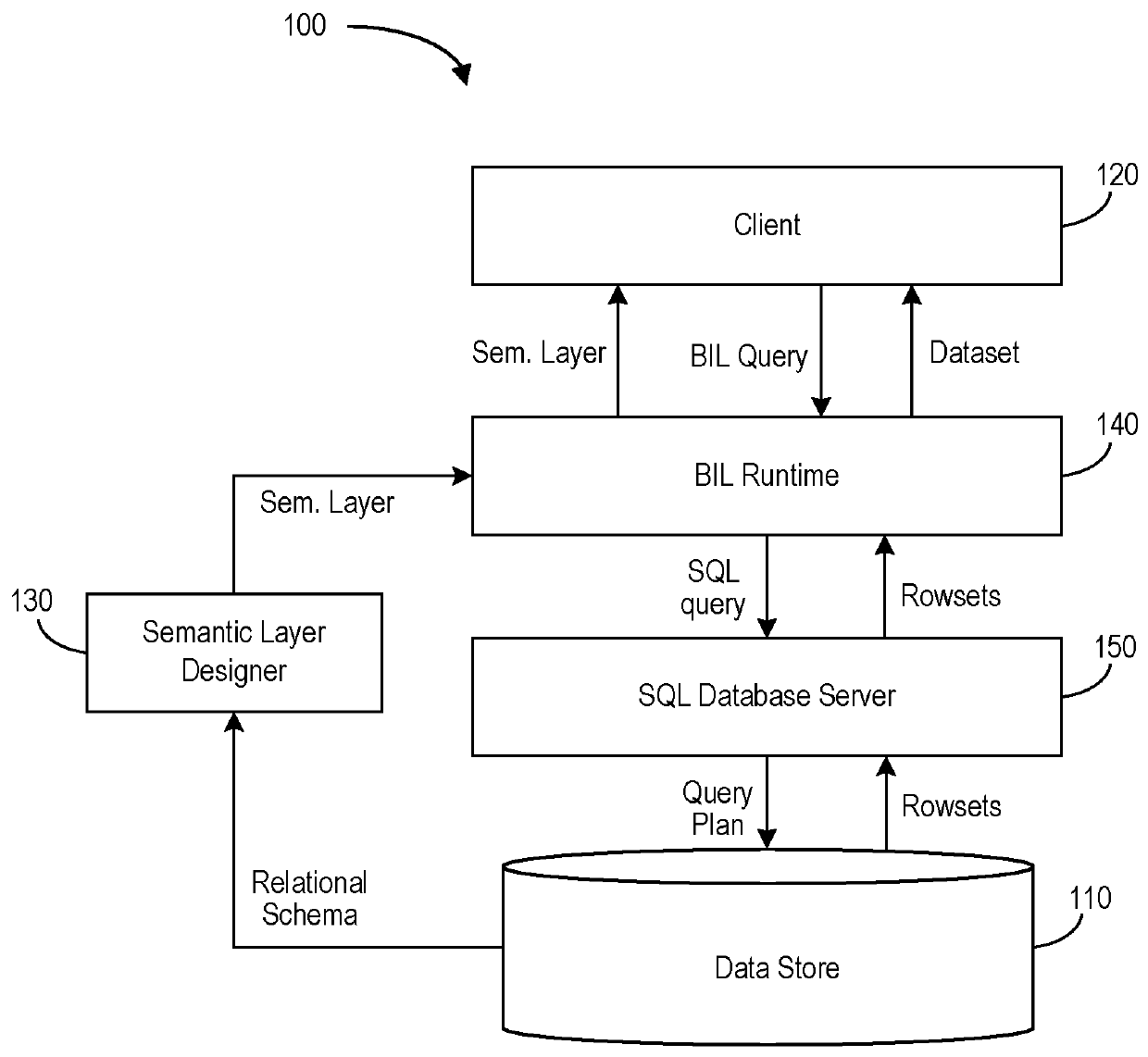
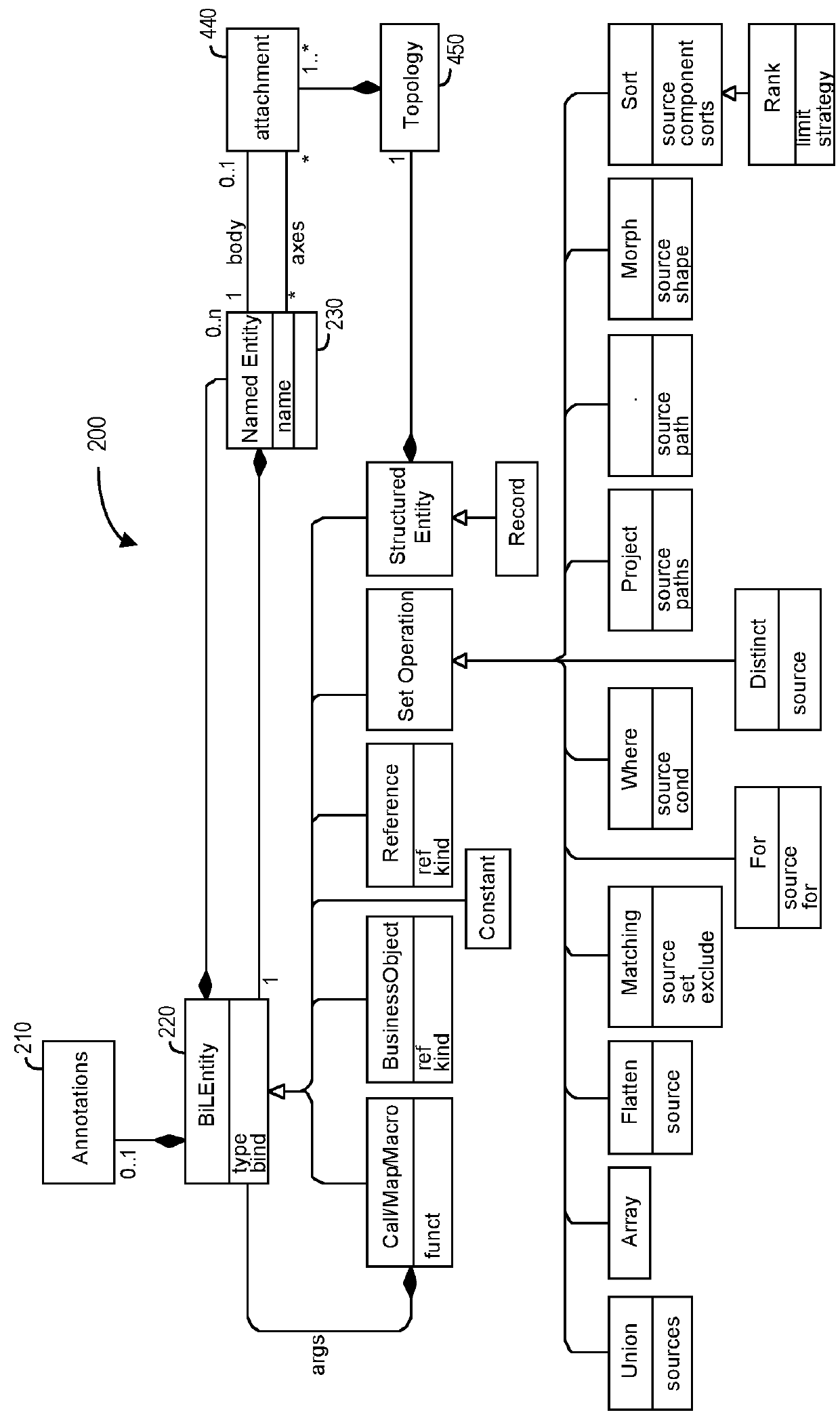
Business intelligence language macros
ActiveUS20180165610A1Easy to useNatural language translationDigital data information retrievalData sourceNative Queries
According to some embodiments, a business intelligence language expansion and compilation platform may receive a business intelligence language expression, containing at least one macro sub-expression from a user. Information may then be accessed in a business and data models data store to perform expansion and compilation operations on the received business intelligence language expression. As a result of these operations, the system may provide a native query to a data source database. A business intelligence language result set manager may retrieve data from a data source database responsive to the native query and output a business intelligence language result set to the user in response to the business intelligence language expression. According to some embodiments, the business intelligence language is reentrant such that the received business intelligence language expression is evaluated in one context and uses a result of another business intelligence language expression evaluated in a possibly different context.
Owner:BUSINESS OBJECTS SOFTWARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com