Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Ossicular prosthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
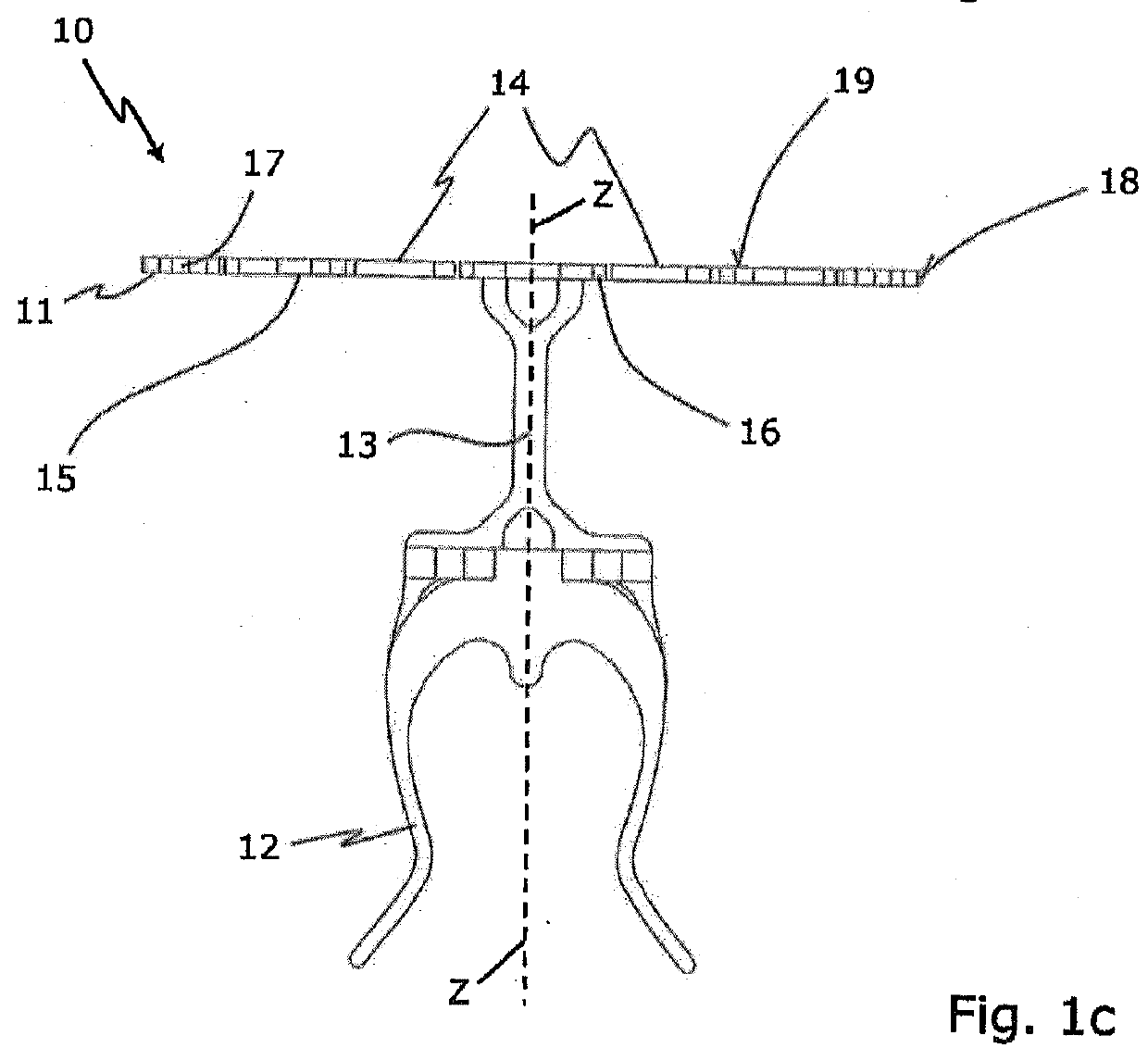
In medicine, an ossicular replacement prosthesis is a device intended to be implanted for the functional reconstruction of segments of the ossicles and facilitates the conduction of sound waves from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear.
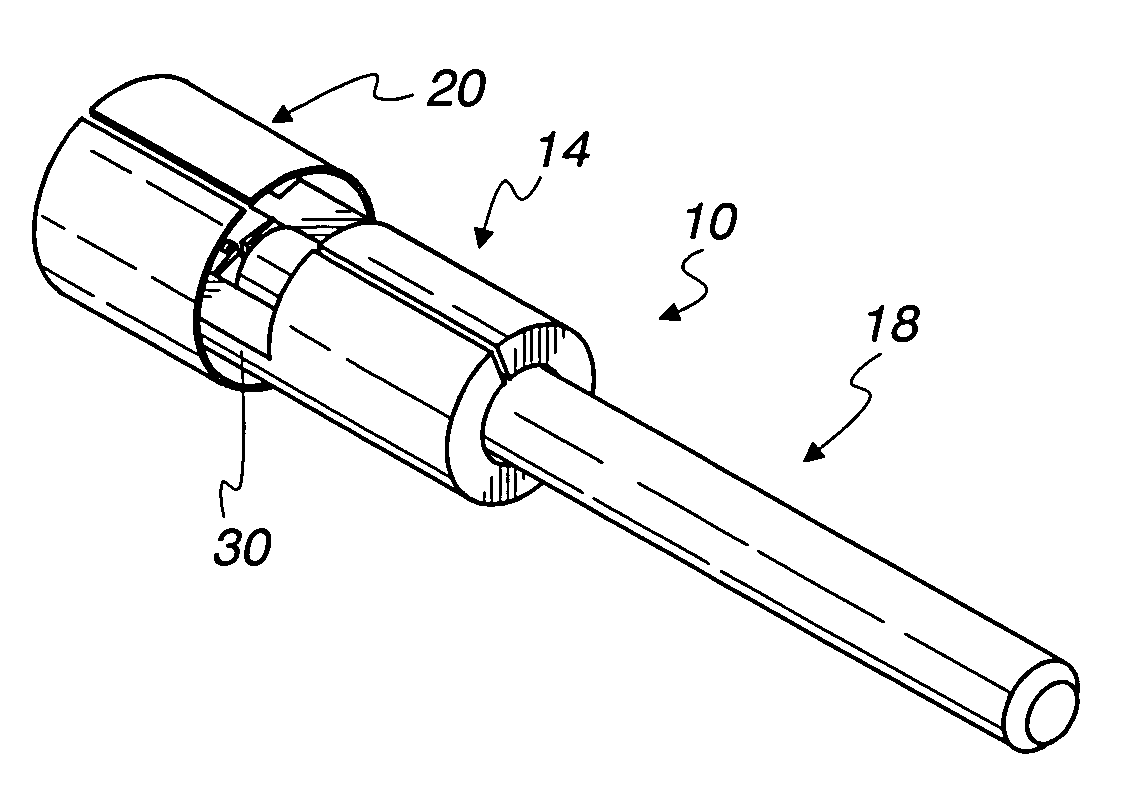
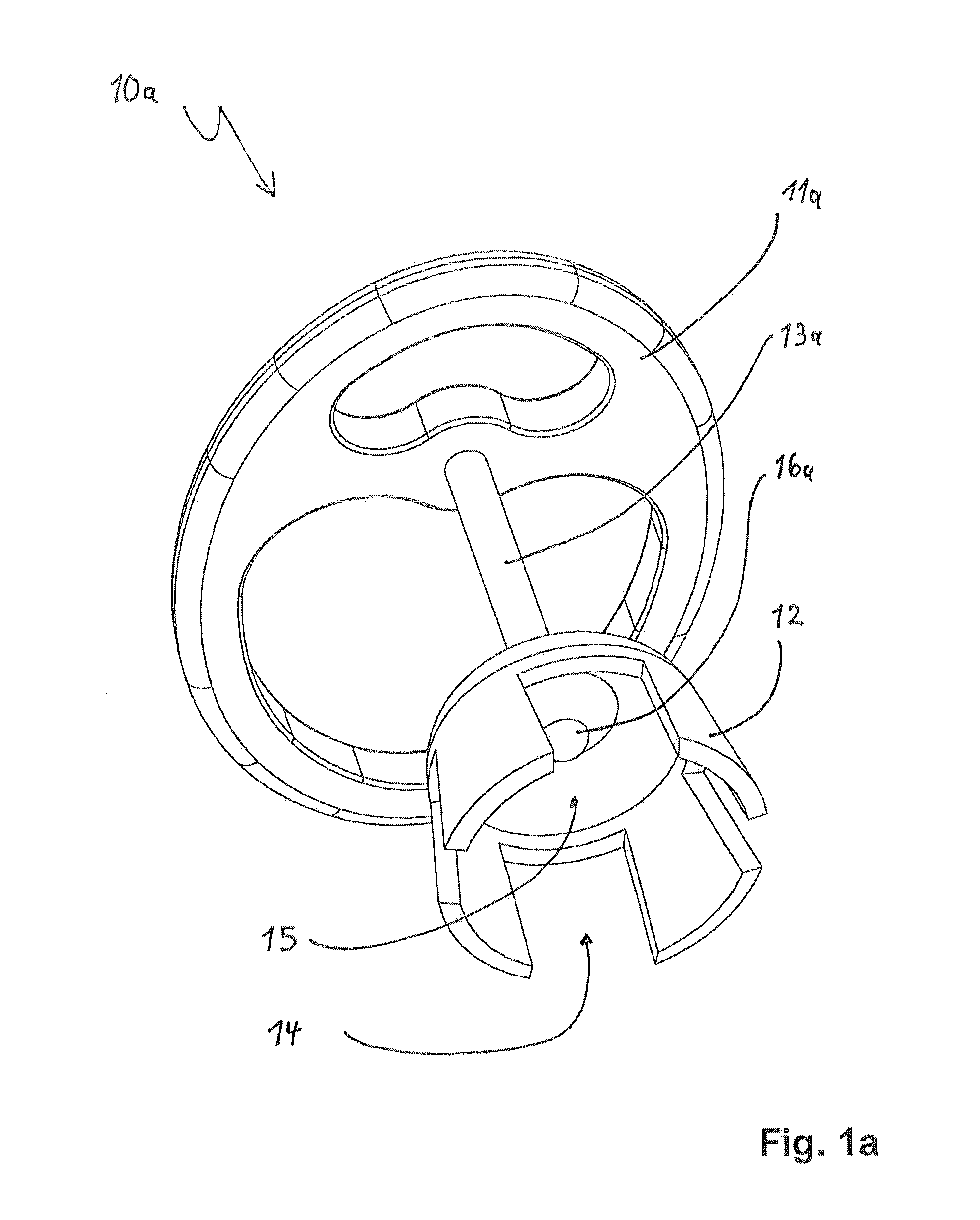
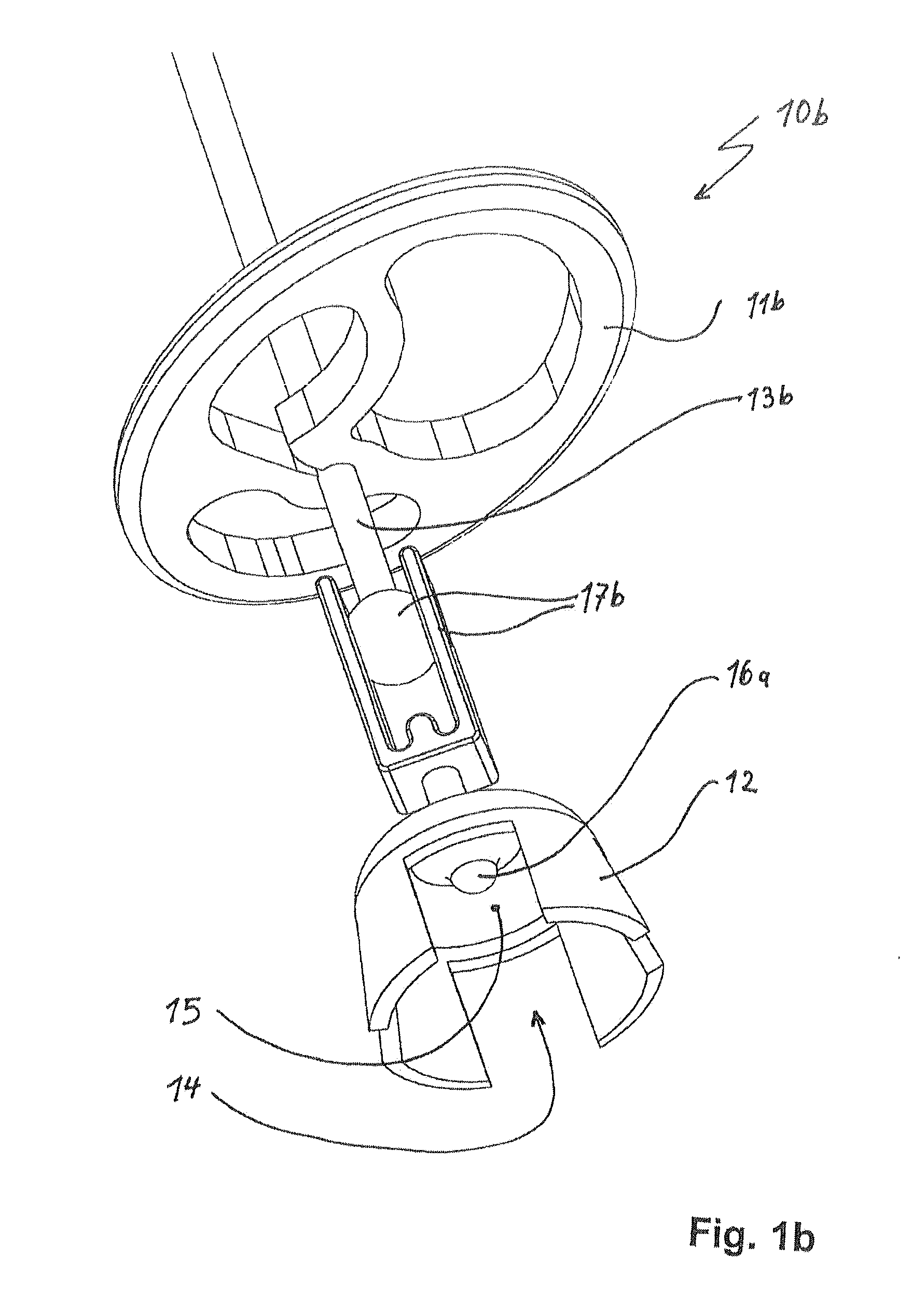
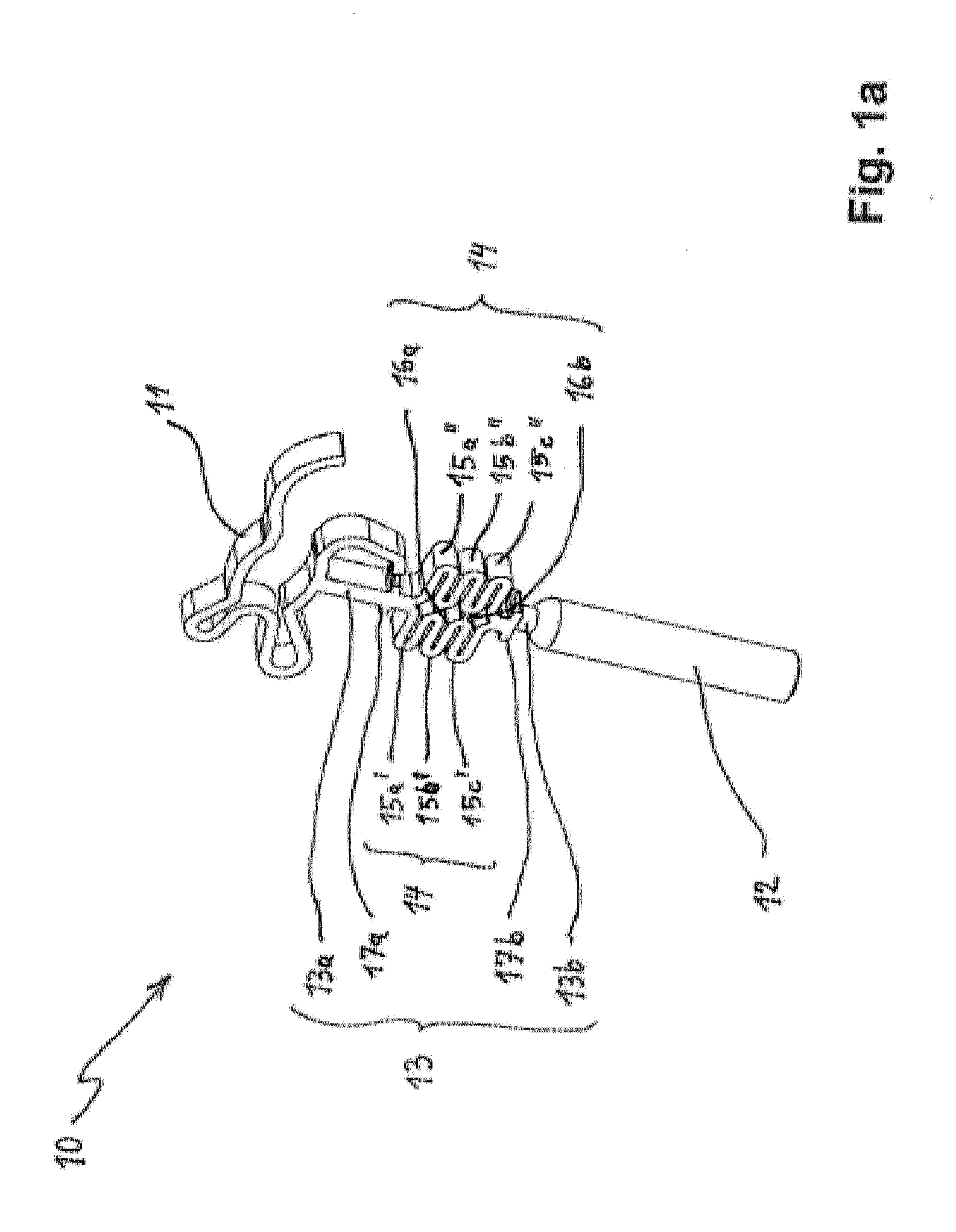
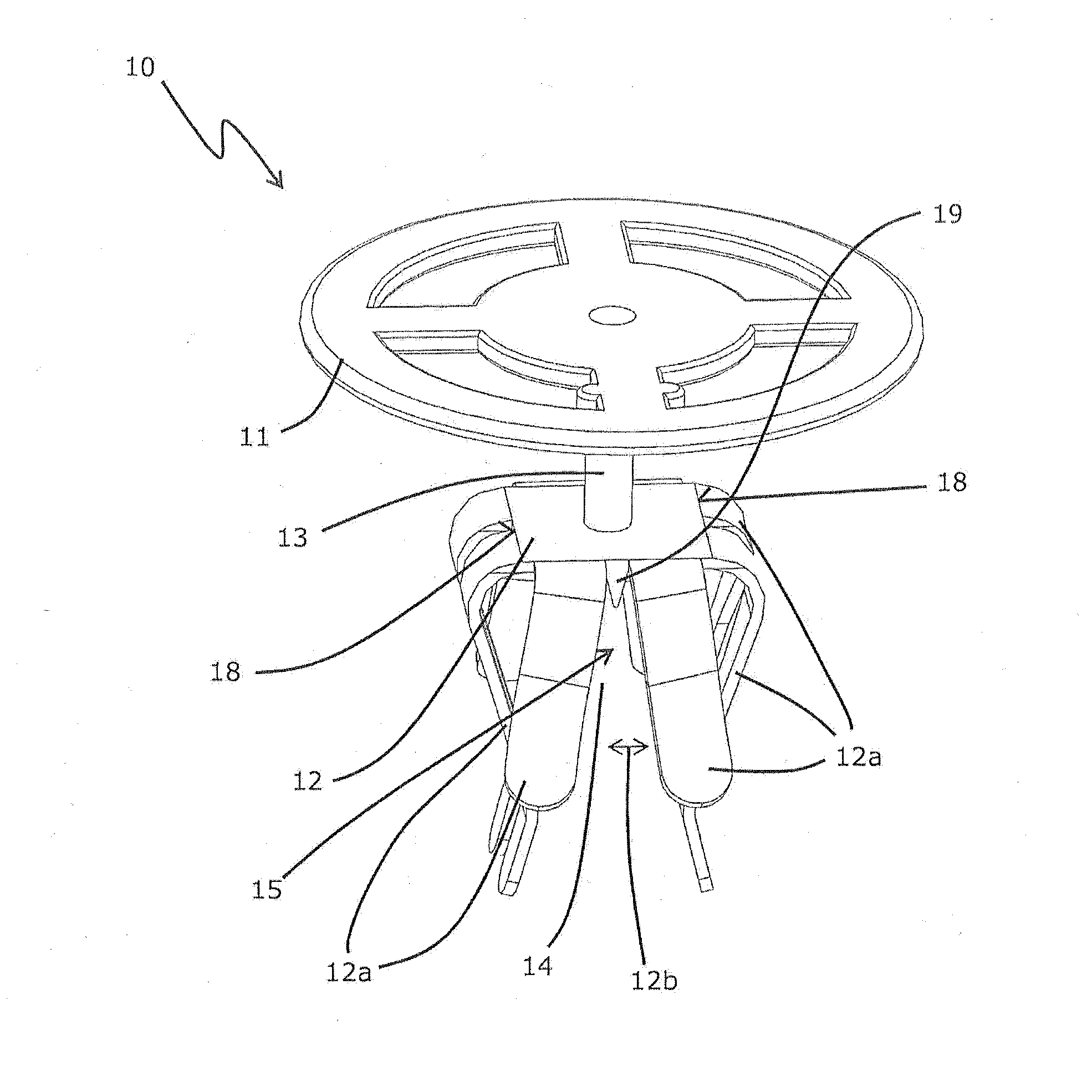
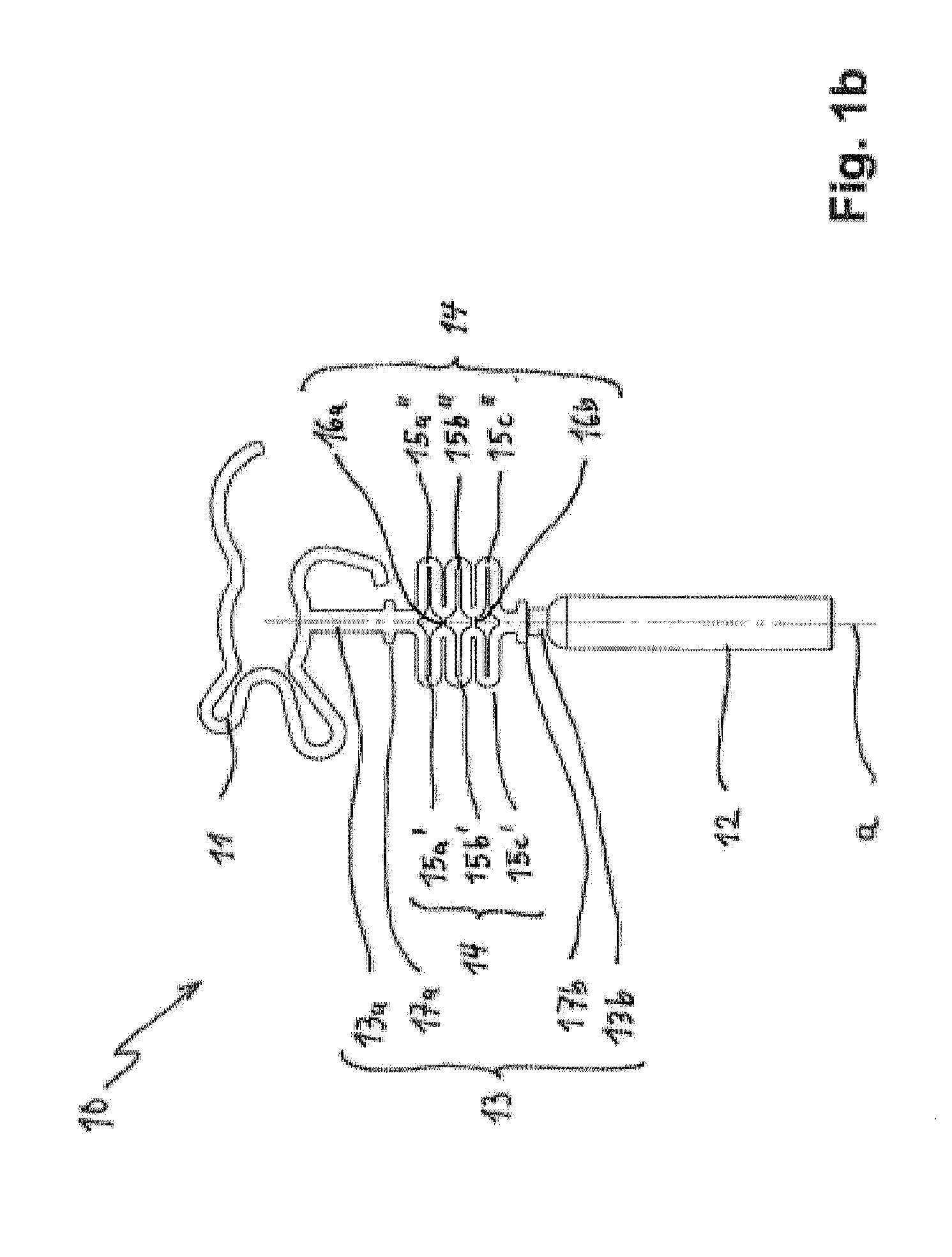
Ossicular prosthesis adjusting device
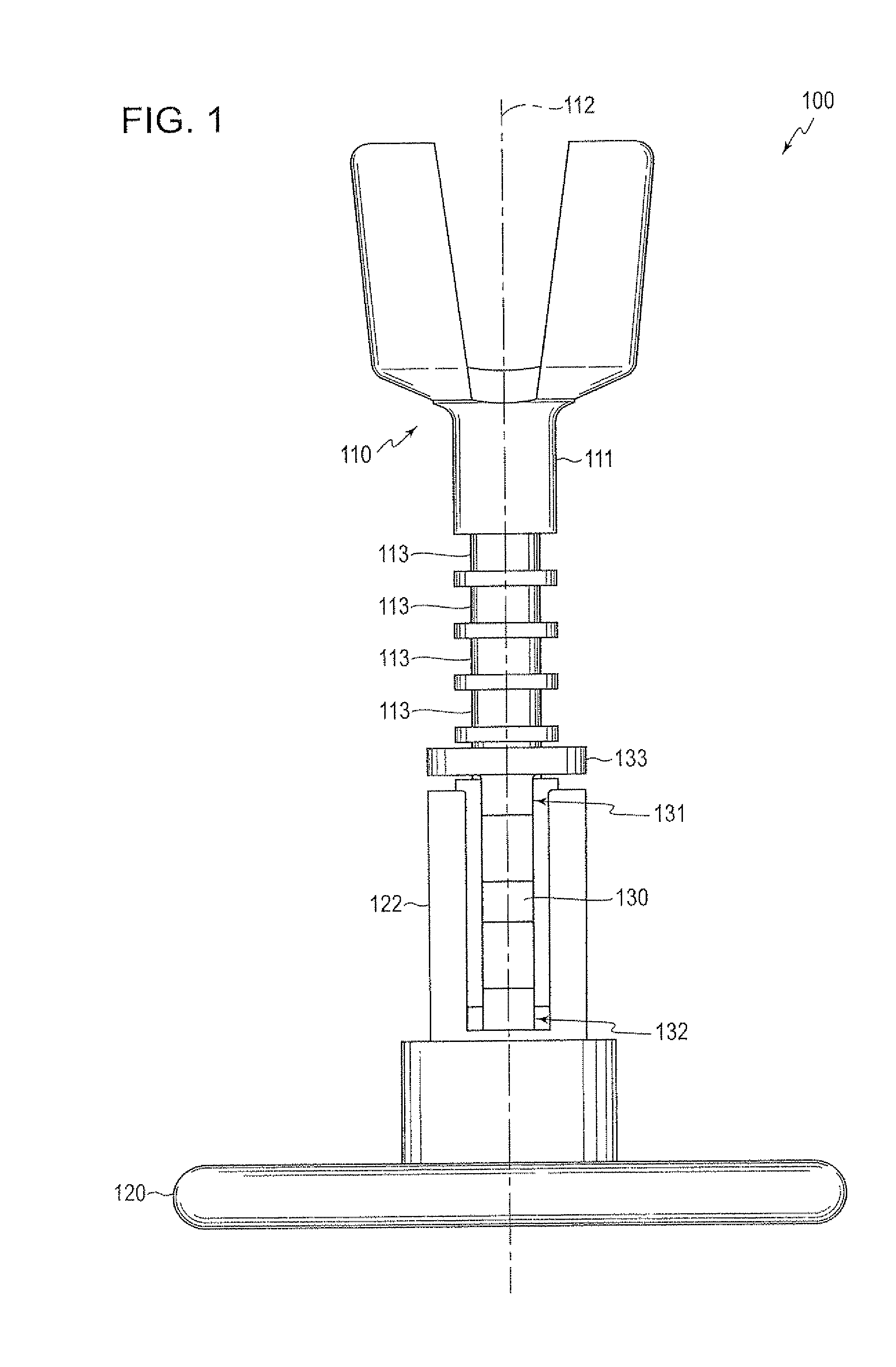
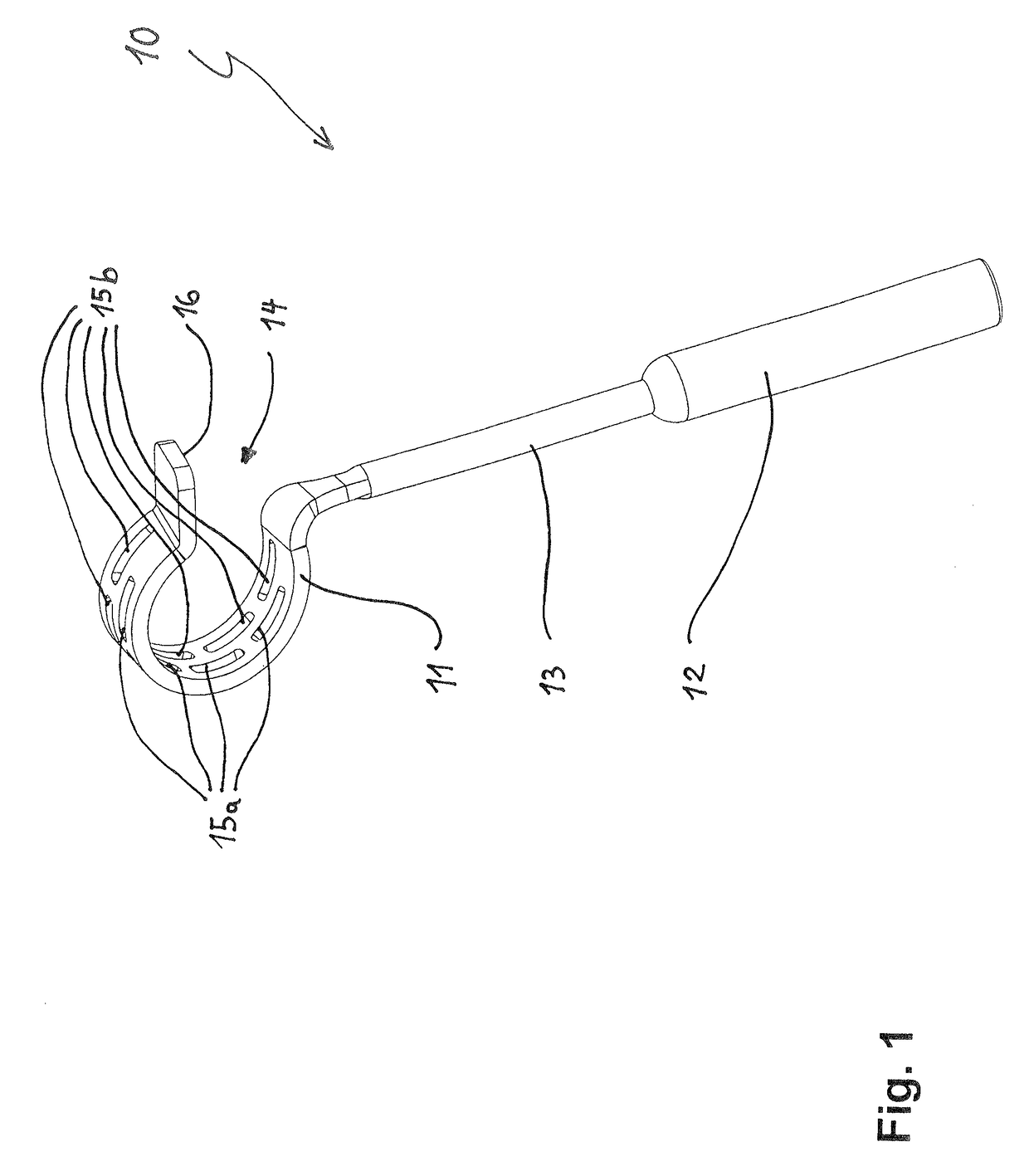
An ossicular prosthesis delivery system having an ossicular prosthesis including an enlarged head and a shaft axially, moveably mounted to the head to adjust shaft length. An elongate main body having an operating portion, including a cylindrical through bore, connected to an adjusting portion, including a generally semi-cylindrical upwardly opening channel coaxial with the bore. An end wall at a distal end of the adjusting portion includes a through passage coaxial with the channel and an upwardly opening cavity. An elongate cylindrical plunger has a claw at one end. The plunger is received in the bore with the claw in the channel and an opposite end extending outwardly of the operating portion. The ossicular prosthesis' shaft is positioned in the channel with the head received in the cavity and the plunger is rotatable in the bore to capture the shaft and is reciprocally moveable in the bore to adjust shaft length of the ossicular prosthesis.
Owner:CLARITY
Variable-length passive ossicular prosthesis
ActiveUS20140094910A1Avoid reactionPrecise and reproducibleEar implantsEngineeringTympanic Membranes
A passive ossicular prosthesis includes a first and second fastening element for connection to the tympanic membrane. A connecting element connects the fastening elements in a sound-conducting manner. The connecting element includes a receiving part and an insertion part. The insertion part is inserted into a receiving opening of the receiving part. The receiving part encloses an end section of the insertion part in the manner of a clamp by way of two opposing, parallel legs disposed parallel to a shank axis of the connecting element. The legs have catch devices that fix the enclosed end section discrete spatial positions relative to the shank axis.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Incus Replacement Partial Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis
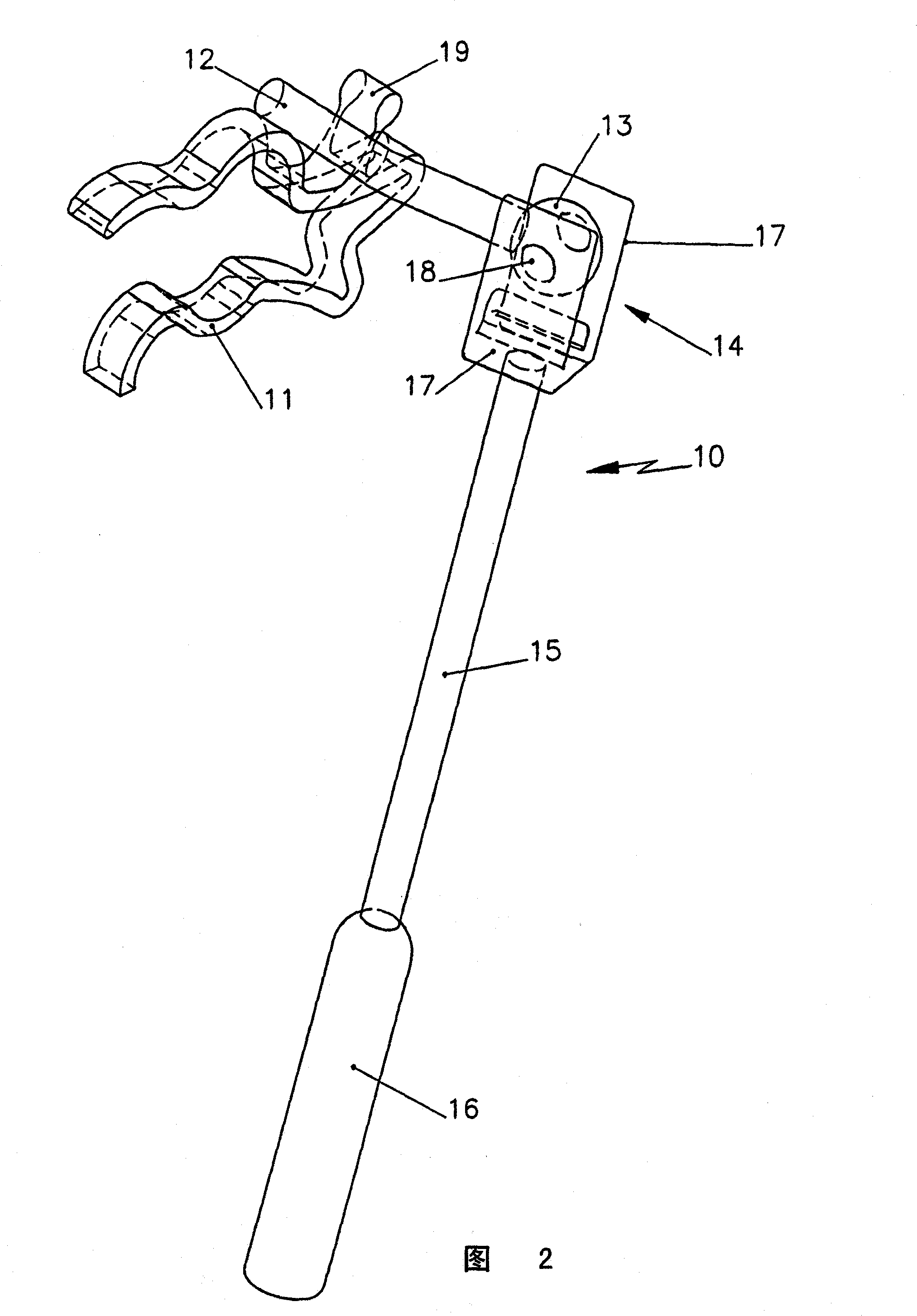
An ossicular prosthesis is described which includes an elongated prosthesis member having a proximal end and a distal end. A cochlea striker mass is at the distal end of the prosthesis member and includes an outer striking surface for coupling vibration of the striker mass to an outer cochlea surface of a recipient patient. A locking clamp is at the proximal end of the prosthesis member and includes a clamp strap having a fixed end and a free end, and a locking head at the fixed end of the clamp strap which has a strap opening for insertion of the free end of the clamp strap. The clamp strap passes around an ossicle of the middle ear in a closed loop and is fixedly engaged by the locking head such that acoustic vibration of the ossicle is coupled by the prosthesis member to the cochlea surface.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
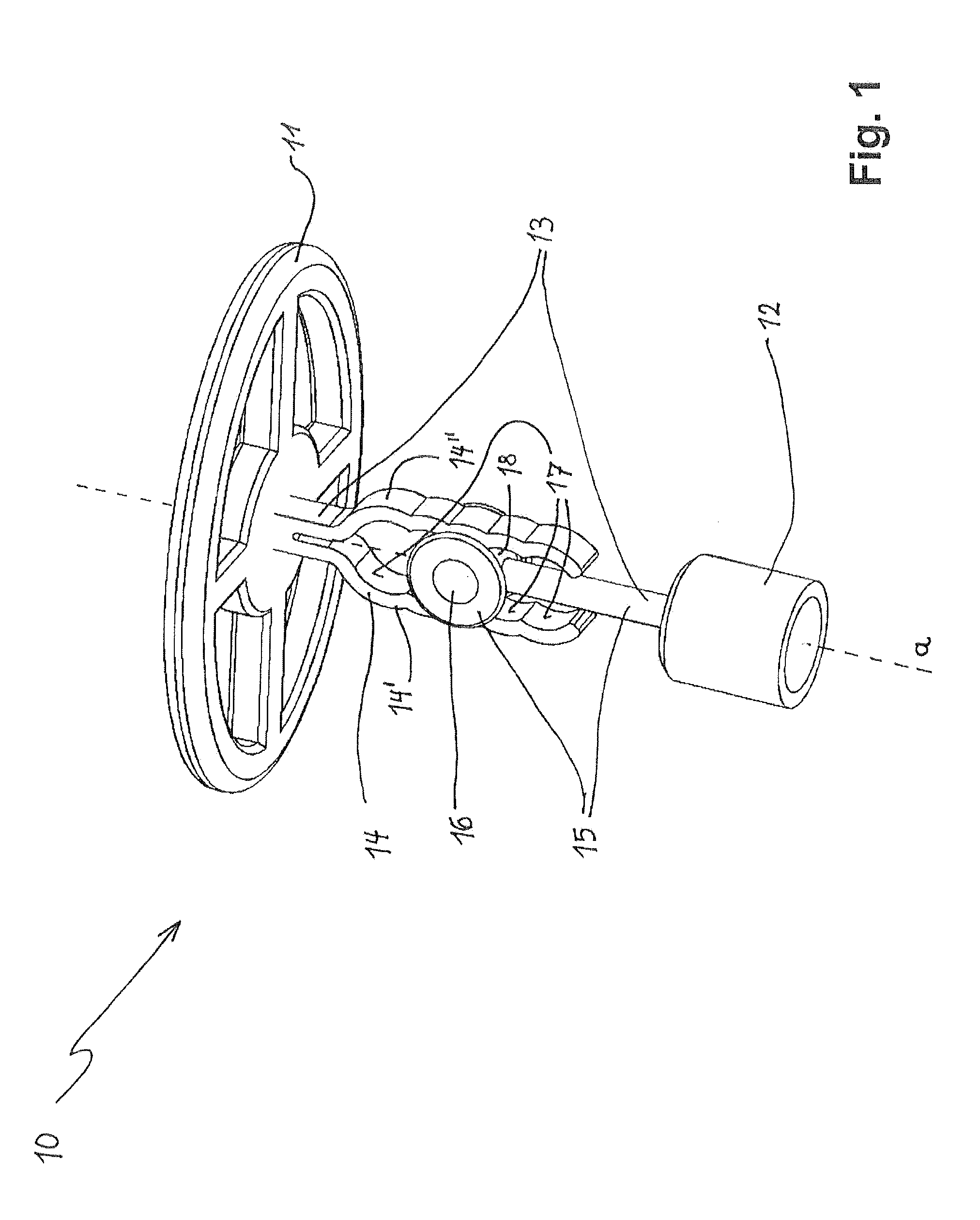
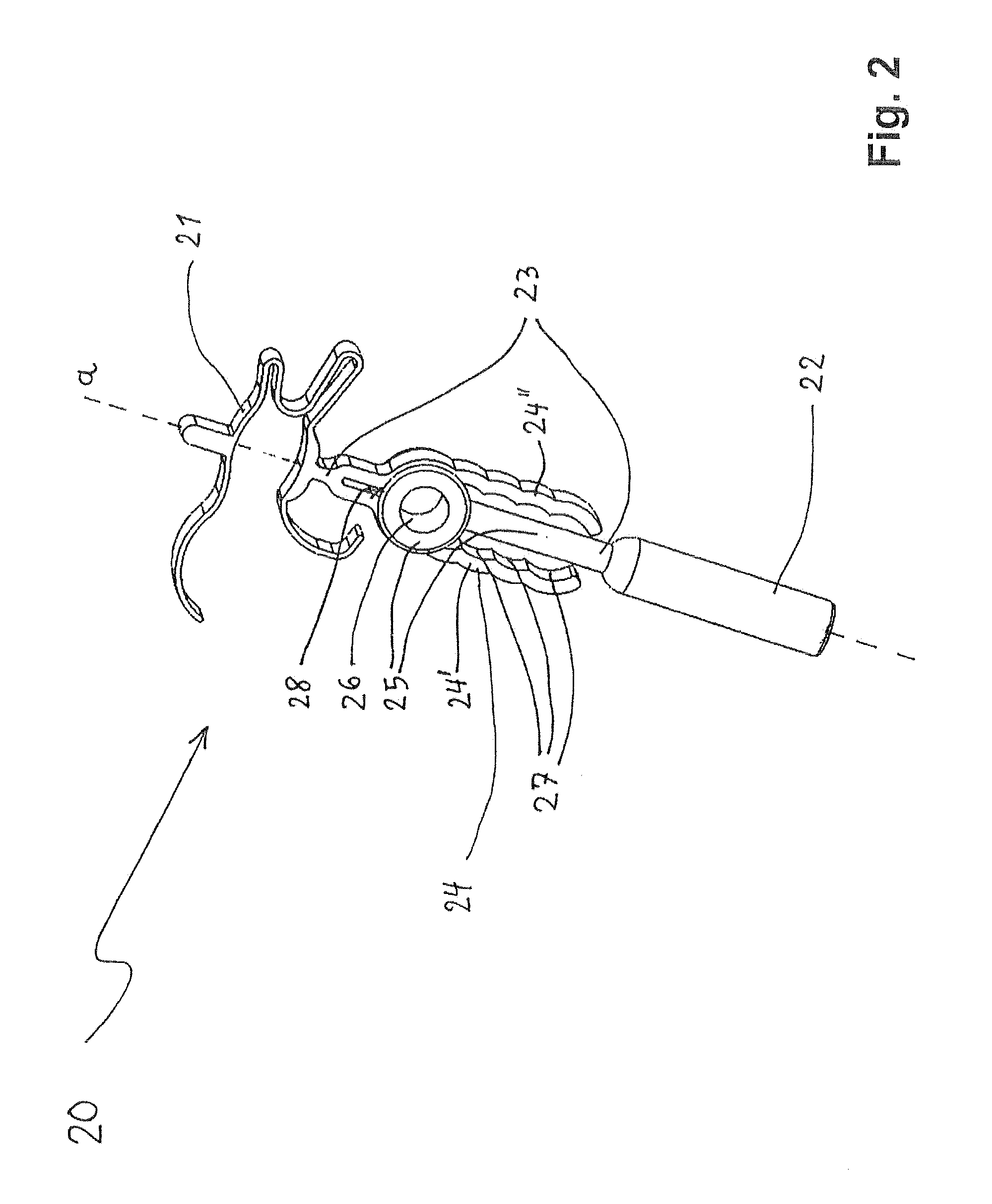
Ossicle prosthesis comprising a built-up attaching element
An ossicular prosthesis formed as a sound-conducting, elongated prosthesis body has a first coupling element designed as a tympanic membrane top plate or a clip or a connecting piece to an actuator end piece of an active hearing implant and a second coupling element provided with an access opening into a receiving space designed as a bell or a clip for a mechanical connection of the prosthesis to the head of the stapes. The second coupling element has a backing section on an inner surface of the receiving space as an axial extension of the prosthesis body. The backing section protrudes from the prosthesis body into the receiving space. In an implanted state, the backing section bears against a head of the stapes and prevents a formation of a hollow space between the stapes and an inner surface of the receiving space in an axial extension of the elongated prosthesis body. As a result, additional degrees of freedom are obtained for individualized adaptation to anatomical circumstances of a specific patient in terms of shape, size and position of the patient's stapes bone.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Middle ear prosthesis having discrete projections for purposes of ossicular attachment
Owner:SCHEURER MARK MATTHEW
Variable-length ossicular prosthesis
An ossicular prosthesis has a first fastening element for connection to the tympanic membrane or a component of the ossicular chain, a second fastening element for connection to a further component of the ossicular chain, or directly to the inner ear, an elongated connecting element that connects the two fastening elements in a sound-conducting manner and includes an adjusting device for adjusting the axial length of the prosthesis and including at least two partial strands that extend symmetrically to the longitudinal axis of the connecting element, are extendable and / or compressible in the axial direction, are permanently plastically deformable, and are folded into a plurality of loops transversely to the longitudinal axis before being deformed. As a result, a relatively simple design of the adjusting device considerably reduces the number of different prostheses that must be kept on hand, while ensuring that the prosthesis may be optimally adapted for a specific case.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Ossicular prosthesis having spikes
An ossicular prosthesis comprising a sound-conducting prosthesis body formed with a first coupling element and a second coupling element. The second coupling element is designed as a clip or a slotted bell and has an access opening into a receiving space having an inner surface in the axial extension of the prosthesis body.The inner surface is bounded by a peripheral outer edge having multiple interruptions. The second coupling element has, on an outer edge of the inner surface of the receiving space, at least two spikes distributed around the periphery of the outer edge, extending in a direction parallel to the axial extension of the elongate prosthesis body. In an implanted state, the spikes engage into the head of the stapes to effectuate a secure hold of the second coupling element.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Variable-length passive ossicular prosthesis
ActiveUS8936637B2Precise and reproducibleWithout a great deal of additional technical complexityDeaf-aid setsEar implantsEngineeringVariable length
A passive ossicular prosthesis includes a first and second fastening element for connection to the tympanic membrane. A connecting element connects the fastening elements in a sound-conducting manner. The connecting element includes a receiving part and an insertion part. The insertion part is inserted into a receiving opening of the receiving part. The receiving part encloses an end section of the insertion part in the manner of a clamp by way of two opposing, parallel legs disposed parallel to a shank axis of the connecting element. The legs have catch devices that fix the enclosed end section discrete spatial positions relative to the shank axis.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Transport device comprising device for ensuring safe transport of ossicular prosthesis
InactiveUS20110278188A1Compact dimensionsEasy to manufactureDiagnosticsSurgical needlesThin metalProsthesis
A transport device for receiving and securely holding an ossicular prosthesis for implantation in a middle ear to replace or bridge at least parts of a component of a human ossicular chain to an operating surgeon, has a substantially flat base plate of thin metal sheet having a thickness of substantially half a millimeter, a holding device integrated in the substantially flat base plate for holding the ossicular prosthesis, an outer packaging enclosing the base plate on all sides during transport, and the base plate has a device for ensuring safe transport provided with burr-shaped segments extending laterally outward from the base plate and clampable or braceable against inner walls of the outer packaging.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Ossicular Prostheses Fabricated From Shape Memory Polymers
Ossicular replacement prostheses are manufactured from a non-biodegradable shape memory polymer. Such prostheses can include TORPs, PORPs, and incudo-stapedial joints (ISJs). The prostheses are reshaped upon application of a stimulus to capture a portion of one or more ossicles. The force of capture of a reshaped polymeric prosthesis is less than a comparable reshaped shape memory alloy prosthesis and thereby prevents recipient discomfort and / or pressure induced necrosis of the bone. In addition, biocompatible shape memory polymers can be designed with recoverable strain that is orders of magnitude higher than shape memory alloys. Furthermore, prostheses can be manufactured in a single size and easily trimmed or otherwise modified by the surgeon during the implantation procedure to tailor the prosthesis in size and / or shape for the particular anatomy. Such modification does not negatively effect the ability of the prostheses to engage the ossicle.
Owner:GRACE MEDICAL
Ossicular replacement prosthesis
The invention provides an ossicular replacement prosthesis (ORP) for coupling a first point to a second point in the middle ear of a patient, to replace all or part of the ossicular chain. The ORP comprises a coupling having a variable configuration for accounting for pressure differentials, said coupling comprising a fluid filled chamber (28, 14) having two relatively moveable portions (12, 22) for varying the configuration of the coupling. The coupling comprises unsealed means constituting leak means and flowpath means for permitting displacement of the fluid (30). The relative movement of the relatively moveable portions is controlled by the movement of the fluid in said chamber. The chamber is configured to restrict the movement of the fluid such that relative movement of the moveableportions is permitted in response to quasi-static changes in pressure, and is substantially prevented in response to vibrational changes corresponding to sound frequencies.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Ossicular prosthesis and method and system for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20180311035A1Minimize impactIncrease success rateProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnatomical structuresBone tissue
Disclosed herein is a customized ossicular prosthesis suitable for treatment of conductive hearing loss due to ossicular chain defects, and a method and system for manufacturing the same. Medical imaging equipment can detect specifically designated landmarks in normal human middle ear ossicles, including significant anatomic differences in those structures. Those anatomic features are used to generate a customized ossicular prosthesis specifically configured for a particular patient's anatomy using 3D printing techniques and devices.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
In situ adjustable ossicular implant and instrument for implanting and adjusting an adjustable ossicular implant
ActiveUS20120065730A1Adjustable lengthDecrease stockSurgical pincettesSurgical forcepsBiomedical engineeringPosition fixing
A system for adjusting an adjustable ossicular prosthesis including an ossicular implant and an adjusting device is provided. The ossicular implant includes a first fixation element, an elongated member extending from the first fixation element with a plurality of notches, a receiving member receiving a portion of the elongated member, and a resilient arm coupled to the elongated member. The resilient arm has a locked position fixing the receiving member relative to the elongated member and the length of the implant, and an unlocked position. The adjusting device includes first and second arms having first and second sets of jaws coupled thereto, the first and second sets of jaws configured to selectively engage the implant, the second set of jaws being configured to position the resilient arm in the unlocked position when engaging the receiving member of the implant, and an adjustment mechanism to adjust the length of the implant.
Owner:GYRUS ENT
Adjustable length ossicular prosthesis with low profile resilient joint
An ossicular prosthesis is adjustable in length and temporarily and resiliently adjustable in angular orientation. The prosthesis includes a head for contacting a tympanic membrane, and a resilient sleeve is mounted within the head. An elongate shaft extends through the sleeve, and includes a distal end adapted to engage a footplate or stapes. The sleeve forms a resilient joint that allows the shaft to undergo an angular motion relative to the sleeve when subject to a non-axial force, and then subsequently return to its original position after the force is removed. The sleeve may also be longitudinally displaceable within the head of the prosthesis such that the shaft can undergo a damped linear motion. Also as a result of the arrangement of the sleeve, the prosthesis is adjustable to a very short length.
Owner:ENTEROPTYX
Ossicular prosthesis adjusting device
Owner:CLARITY
Ossicle prosthesis comprising a built-up attaching element
An ossicular prosthesis formed as a sound-conducting, elongated prosthesis body has a first coupling element designed as a tympanic membrane top plate or a clip or a connecting piece to an actuator end piece of an active hearing implant and a second coupling element provided with an access opening into a receiving space designed as a bell or a clip for a mechanical connection of the prosthesis to the head of the stapes. The second coupling element has a backing section on an inner surface of the receiving space as an axial extension of the prosthesis body. The backing section protrudes from the prosthesis body into the receiving space. In an implanted state, the backing section bears against a head of the stapes and prevents a formation of a hollow space between the stapes and an inner surface of the receiving space in an axial extension of the elongated prosthesis body. As a result, additional degrees of freedom are obtained for individualized adaptation to anatomical circumstances of a specific patient in terms of shape, size and position of the patient's stapes bone.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Auditory ossicle fixing stent
PendingCN109925093APrevent prolapseGuaranteed activityProsthesisIncreasing energy efficiencyOssicular chain reconstructionInsertion stent
The invention discloses an auditory ossicle fixing stent which comprises an elliptical disc. The elliptical disc is matched with the inner wall and the outer wall of the middle ear cavity and the elliptical pit above a tympanic nerve, a through hole is formed in the center of the elliptical disc, the through hole is arranged in a penetrating manner in the thickness direction of the elliptical disc, and the diameter of the through hole is 0.2-0.9 mm, the through hole is used for being matched with the rod portion of an ossicular prosthesis, the elliptical disc is provided with an empty groove,the empty groove extends from the periphery of the elliptical disc to the through hole, and the width of the empty groove is 0.1-0.5 mm. The auditory ossicle fixing stent is applied to clinical auditory ossicular chain reconstruction surgery, is suitable for auditory ossicle prosthesis implantation (aiming at the condition of total auditory ossicle replacement), corrects the movement direction ofan auditory ossicle prosthesis base when the auditory ossicle prosthesis base is separated from the center of an operation fixing position of the auditory ossicle prosthesis base, assists in fixing the auditory ossicle prosthesis, prevents the auditory ossicle prosthesis from escaping, meets the bone conduction of the auditory ossicle prosthesis and ensures the movement of the auditory ossicle prosthesis within a certain range.
Owner:四川华曙图灵增材制造技术有限责任公司 +1
Low-strain five-claw ossicular prosthesis
PendingCN109758265ALight in massExpand field of viewBone implantJoint implantsShear stressAcute angle
The invention discloses a low-strain five-claw ossicular prosthesis which comprises a top disc, a connecting rod and a stirrup bone clip. Fillets are arranged on the top disc, a sunken cavity is formed in the bottom of the top disc, the top disc is in a cover shape, and an annular edge is formed at the periphery of the top disc; the top disc and the connecting rod are connected through a socket joint; the stirrup bone clip is of a five-claw structure; by changing the structure of the top disc, when the top disc makes contact with a tympanic membrane, contact strain can be reduced, and damage caused by an acute angle generated during oblique placement to the tympanic membrane is avoided; the top disc and the connecting rod are connected through the socket joint, the angle formed between thetop disc and the connecting rod can be flexibly and conveniently adjusted, and the shearing stress of artificial otosteon to the tympanic membrane is buffered during different middle ear pressure changes; the stirrup bone clip is arranged to be of the five-claw specific thickness structure, the degree of tightness is suitable when the stirrup bone clip is connected with the stirrup bone, and thestirrup bone cannot be damaged due to excessive tightness and cannot be disengaged due to excessive looseness.
Owner:安徽奥弗智能微创医疗器械集团有限公司
Incus Replacement Partial Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Variable-length ossicular prosthesis
An ossicular prosthesis has a first fastening element for connection to the tympanic membrane or a component of the ossicular chain, a second fastening element for connection to a further component of the ossicular chain, or directly to the inner ear, an elongated connecting element that connects the two fastening elements in a sound-conducting manner and includes an adjusting device for adjusting the axial length of the prosthesis and including at least two partial strands that extend symmetrically to the longitudinal axis of the connecting element, are extendable and / or compressible in the axial direction, are permanently plastically deformable, and are folded into a plurality of loops transversely to the longitudinal axis before being deformed. As a result, a relatively simple design of the adjusting device considerably reduces the number of different prostheses that must be kept on hand, while ensuring that the prosthesis may be optimally adapted for a specific case.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Ossicular prosthesis and method and system for manufacturing same
ActiveUS10646331B2Minimize impactIncrease success rateProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnatomical structuresOssicles
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Ossicular prosthesis comprising foldable head plate
ActiveUS10278813B2High level of postoperative flexibility and variabilitySimple and cost-effective mannerOcculdersEar implantsCouplingProsthesis
An ossicular prosthesis has a head plate as a first fastening element, a second fastening element for the mechanical connection to the ossicular chain, or to the inner ear, and a connecting element. The head plate has a central coupling region and radially outward extending bridging elements which are connected to the coupling region via a radially inner end region and each transition into an outer free end section. The bridging elements are connected to the coupling region so that they fold together upon introduction of a force component parallel to the longitudinal axis, wherein their end sections are pivoted radially closer to the longitudinal axis and thereby also execute an axial movement. The bridging elements, without this force, extend from the coupling region at a predefined, fixed angle. The prosthesis can be inserted into the middle ear of the patient more easily and through a much smaller artificial opening.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Ossicular prosthesis comprising foldable head plate
ActiveUS20180104048A1High level of postoperative flexibility and variabilitySimple and cost-effective mannerOcculdersProsthesisCouplingProsthesis
An ossicular prosthesis has a head plate as a first fastening element, a second fastening element for the mechanical connection to the ossicular chain, or to the inner ear, and a connecting element. The head plate has a central coupling region and radially outward extending bridging elements which are connected to the coupling region via a radially inner end region and each transition into an outer free end section. The bridging elements are connected to the coupling region so that they fold together upon introduction of a force component parallel to the longitudinal axis, wherein their end sections are pivoted radially closer to the longitudinal axis and thereby also execute an axial movement. The bridging elements, without this force, extend from the coupling region at a predefined, fixed angle. The prosthesis can be inserted into the middle ear of the patient more easily and through a much smaller artificial opening.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
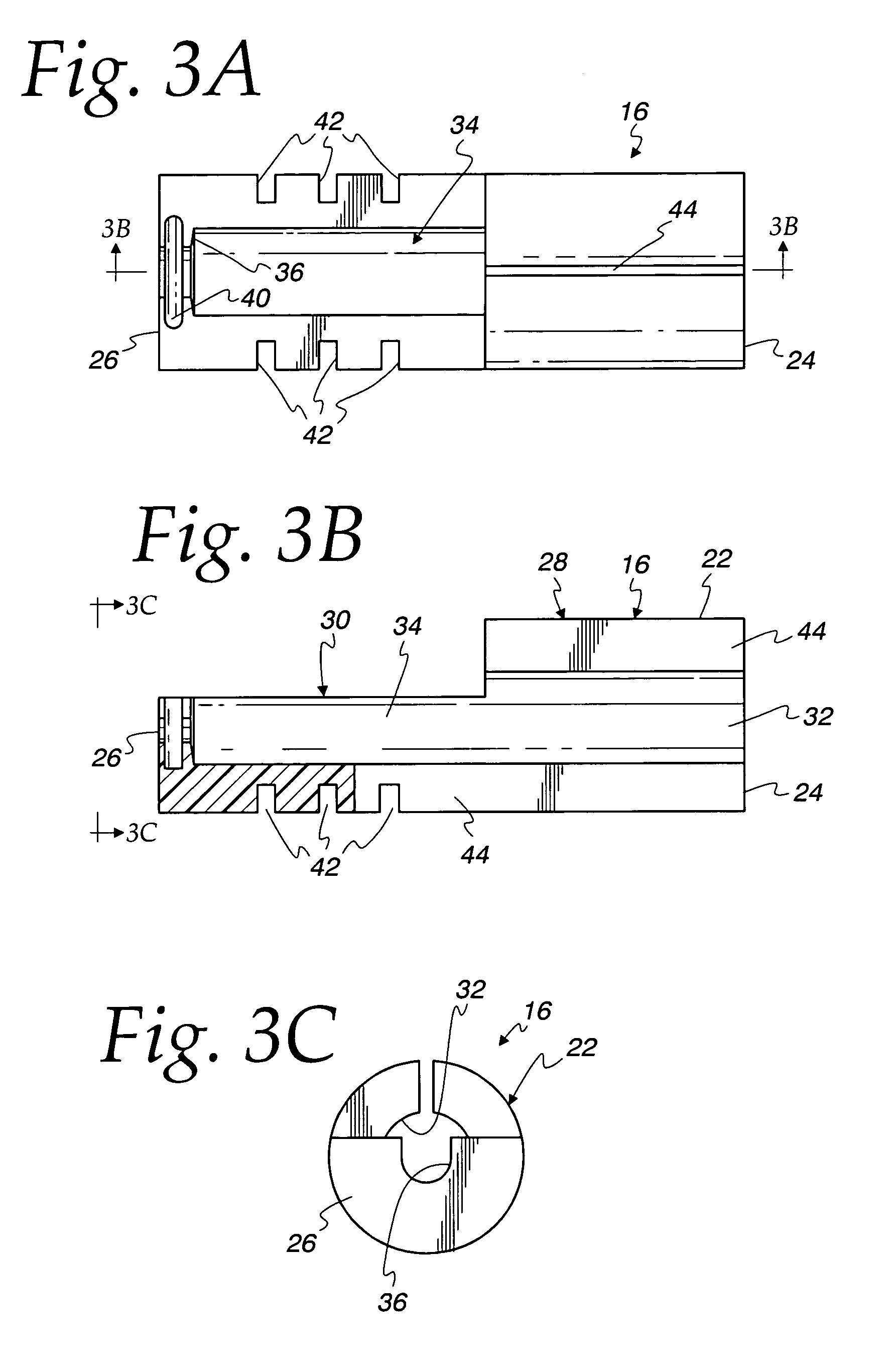
Ossicular prosthesis having a longitudinally perforated bight
A passive ossicular prosthesis has a sound-conducting prosthesis body with a first coupling element for mechanical connection to the incus, malleus, or an actuator end piece of an active hearing aid at one end. The bight is made of a strip-shaped metallic material, partially open toward the outside via a gap-type opening and is intraoperatively crimped in the middle ear for permanent attachment. There is a second coupling element at the other end of the prosthesis body for connection to a further component of the ossicular chain or directly to the inner ear. The bight includes elongated perforations with longitudinal axes extending, in the implanted state, along a curved trajectory at a right angle or slant relative to an axis parallel to the longitudinal axis (a) of the enclosed object to reduce spring action and stiffness and markedly reduce the force to be applied for the crimping.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Ossicular prostheses for middle ear reconstruction
PendingUS20200246135A1Reduce recurrenceImprove hearing-related outcomeAdditive manufacturing apparatusTomographyEngineeringEar ossicles
Ossicular prostheses, and methods for producing such, are disclosed for treatment of middle ear damage caused by a malady of the middle ear such as cholesteatoma. The ossicular prostheses comprises a strut component attached to a disc via a rigid or flexible connecting joint. The strut is attachable to a head or footplate of a subject's stapes. The disc is attachable to the subject's existing tympanic membrane, or, alternatively, to an artificial tympanic membrane graft. In some embodiments, a scaffold is used to support the ossicular prosthesis and the tympanic membrane graft.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Titanium periosteum-based auditory ossicle prosthesis
ActiveCN113367841AGuaranteed responseImprove the vibration effectBone implantEar implantsMedicinePostoperative recovery
The invention discloses an auditory ossicle prosthesis. The auditory ossicle prosthesis comprises a middle rod; a supporting plate and a connector are arranged at the two ends of the middle rod respectively; the supporting plate is used for being connected with the tympanic membrane; the connector is used for being connected with the stapes; the supporting plate and the connector are both integrally formed together with the middle rod; the included angle between the middle rod and the plane where the supporting plate is located is smaller than 90 degrees; the supporting plate is formed in an oval shape corresponding to the shape of the tympanic membrane; the connecting point of the supporting plate and the middle rod does not coincide with the circle center of the supporting plate; and the middle rod is a telescopic elastic rod-shaped piece. All the structures are integrally formed, the effect of transmitting vibration of the tympanic membrane is good, and the postoperative recovery effect of a patient is guaranteed.
Owner:中国人民解放军总医院第六医学中心
Ossicular prosthesis having a longitudinally perforated bight
A passive ossicular prosthesis has a sound-conducting prosthesis body with a first coupling element for mechanical connection to the incus, malleus, or an actuator end piece of an active hearing aid at one end. The bight is made of a strip-shaped metallic material, partially open toward the outside via a gap-type opening and is intraoperatively crimped in the middle ear for permanent attachment. There is a second coupling element at the other end of the prosthesis body for connection to a further component of the ossicular chain or directly to the inner ear. The bight includes elongated perforations with longitudinal axes extending, in the implanted state, along a curved trajectory at a right angle or slant relative to an axis parallel to the longitudinal axis (a) of the enclosed object to reduce spring action and stiffness and markedly reduce the force to be applied for the crimping.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Transport device for ossicular prosthesis
A transport device for receiving and securely holding an ossicular prosthesis for implantation in a middle ear during transport to an operating surgeon for replacing or bridging at least parts of a component of a human ossicular chain, the transport device has a flat base plate of thin metal sheet having a thickness of substantially half a millimeter, at least one suspending device connected to the base plate and twistable using fine segments and integrated in the base plate for receiving and holding the ossicular prosthesis, and the connecting element which connects a first fastening element of the ossicular prosthesis used for mechanical connection to a tympanic membrane or a component of the ossicular chain with a second fastening component on another end used for mechanical connection to a further component or parts of a component of the ossicular chain or directly to an inner ear so that the first and second fastening elements are connected by the connecting element in a sound-conducting manner, wherein the suspending device is configured so that it aligns with the surface of the base plate during manufacture of the transport device and for suspension of the ossicular prosthesis is rotatable relative to an ossicular prosthesis lying-flat production state by substantially 90° relative to the base plate by plastic deformation of the segments and then extends above the surface of the base plate.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
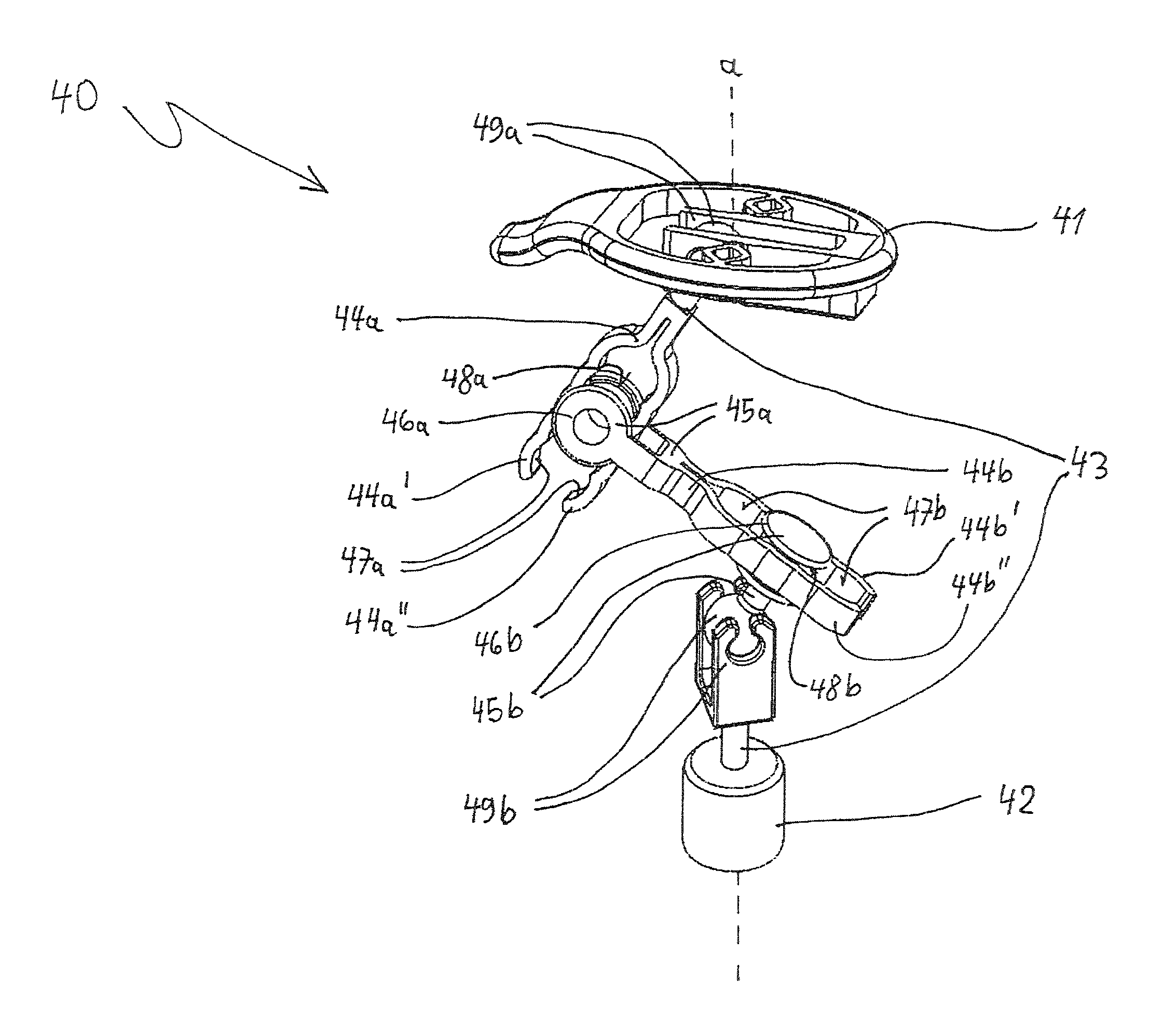
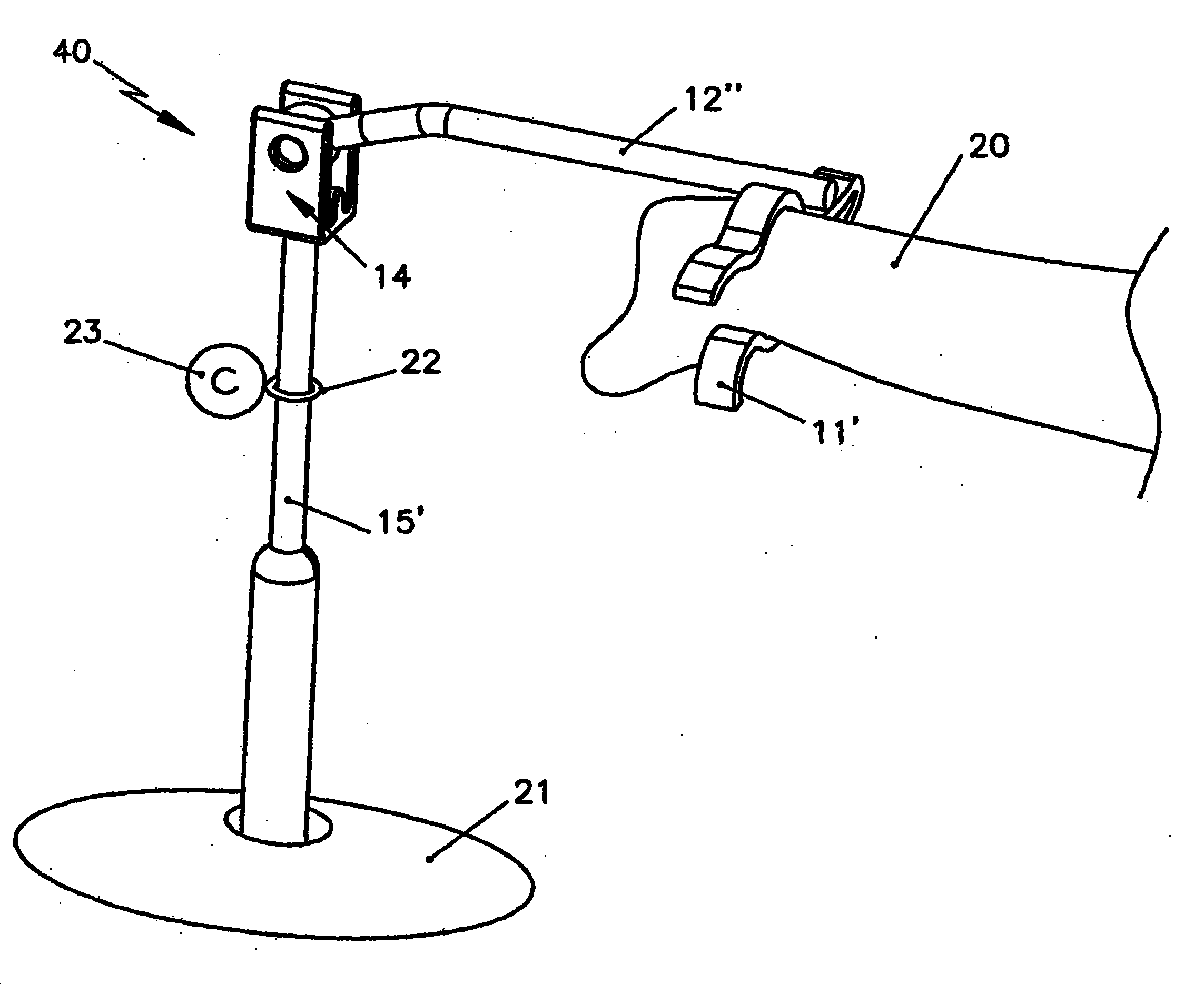
Auditory ossicle prosthesis comprising changeable frequency response function in middle ear
The invention relates to an ossicular prosthesis (40) which replaces or bridges at least one element of the human ossicular chain. The ossicular prosthesis (40) is made of an elastic material or from material having at least articular connection. The inventive prosthesis is characterised in that it is provided with means for adapting the frequency (tuning) for sound conduction in the middle ear, in particular in order to alter lift conditions in the ossicular chain. Sound conduction is considerably improved between the region of the middle ear and the inner ear of the human auditory channel, and enables, in particular, optimal adaptation to the individually different conditions and a tailor-made solution to problems and defects of each patient.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Replaceable artificial ossicular prosthesis device
Owner:苏州真懿医疗有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com