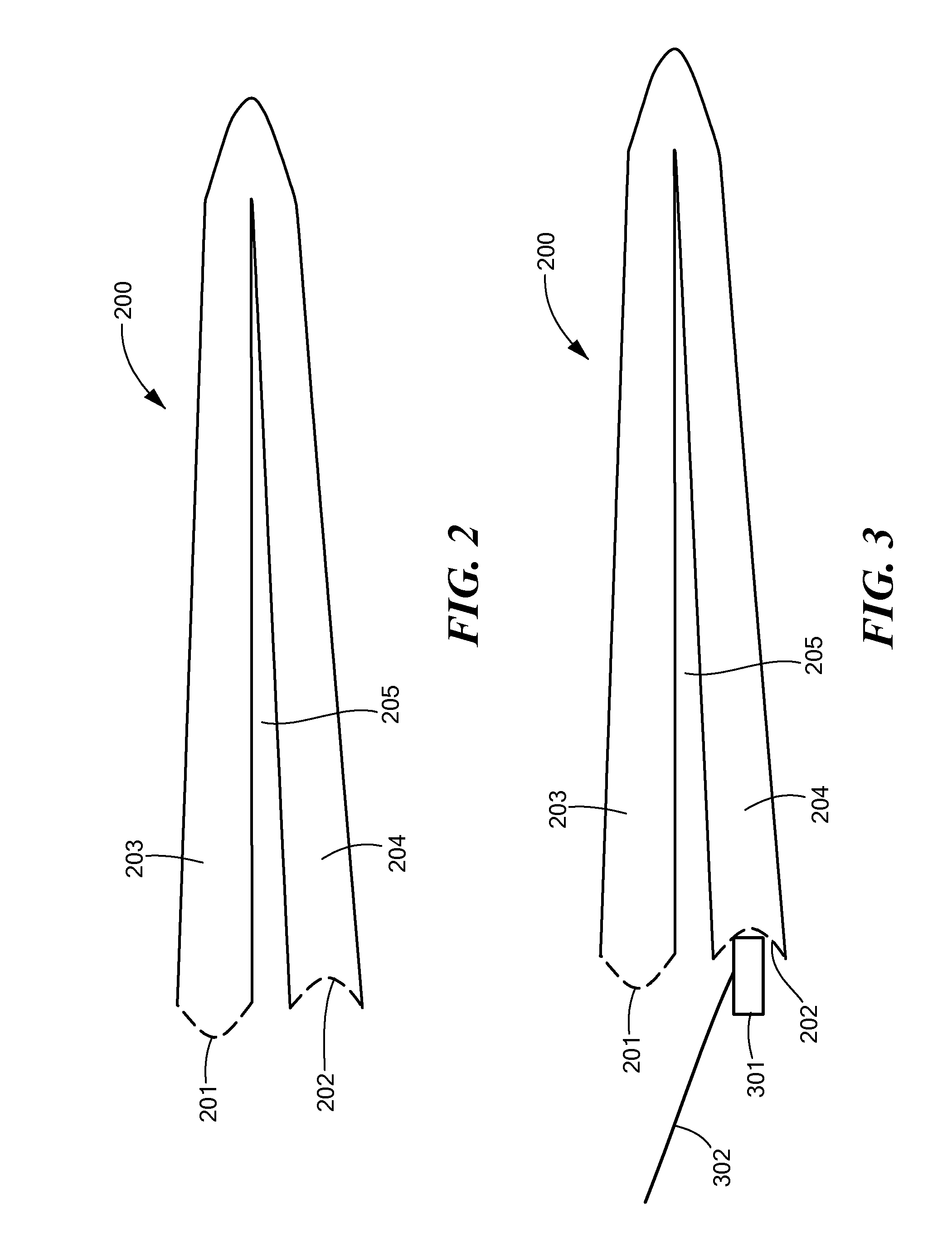
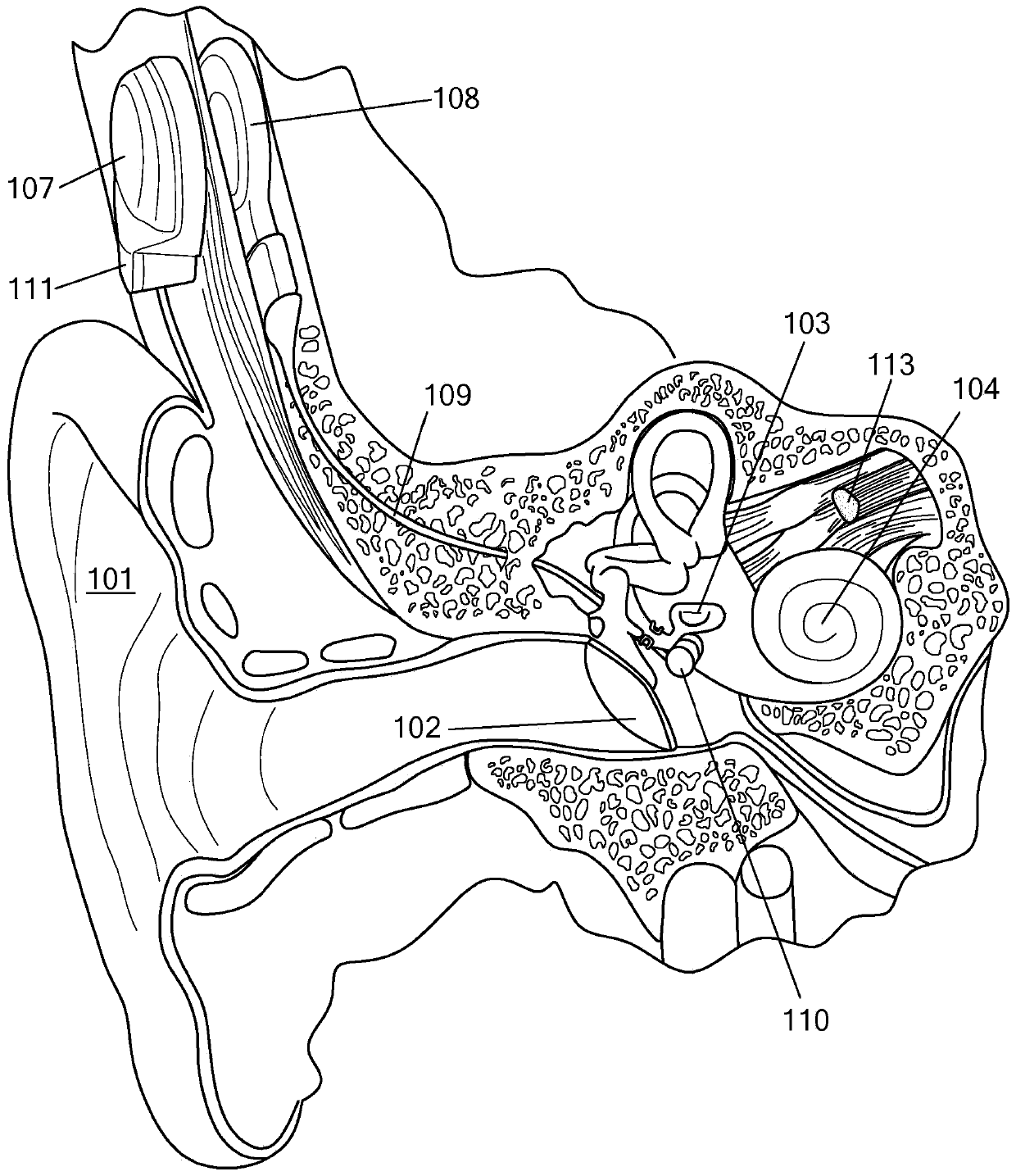
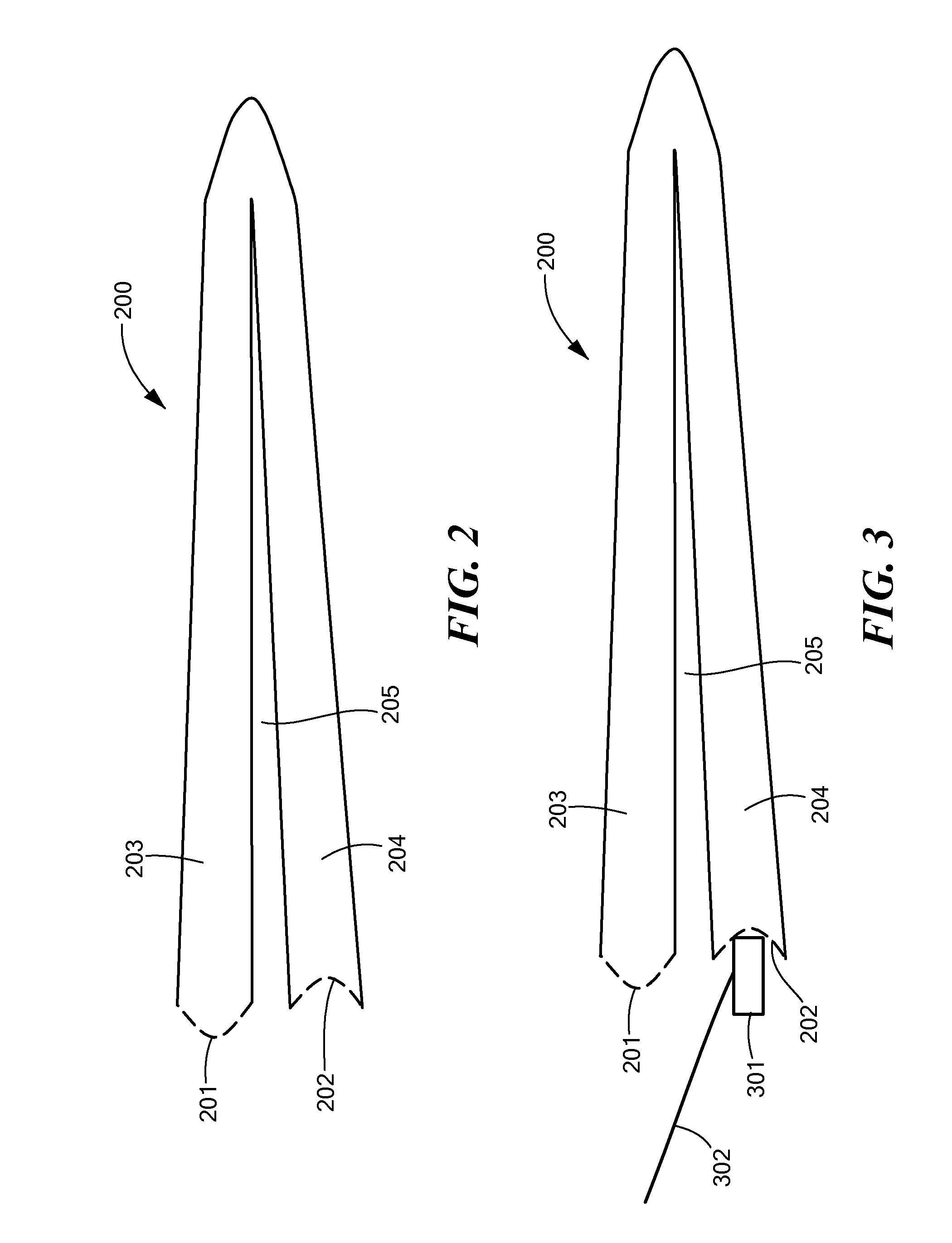
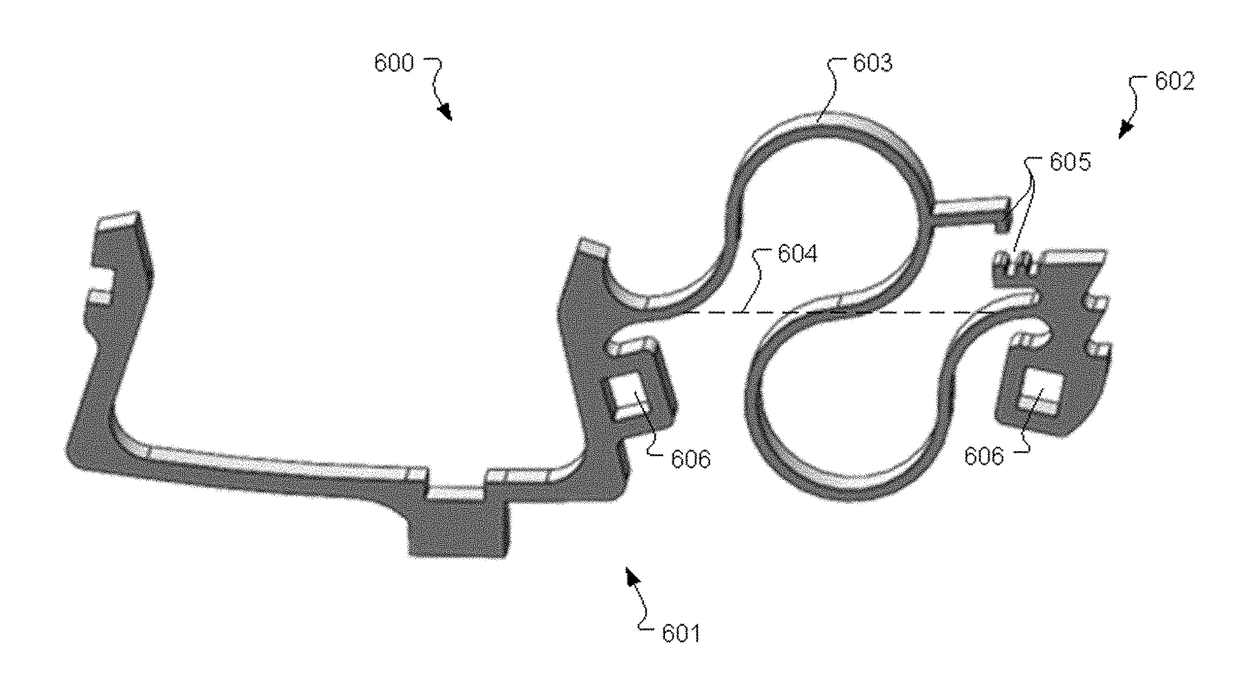
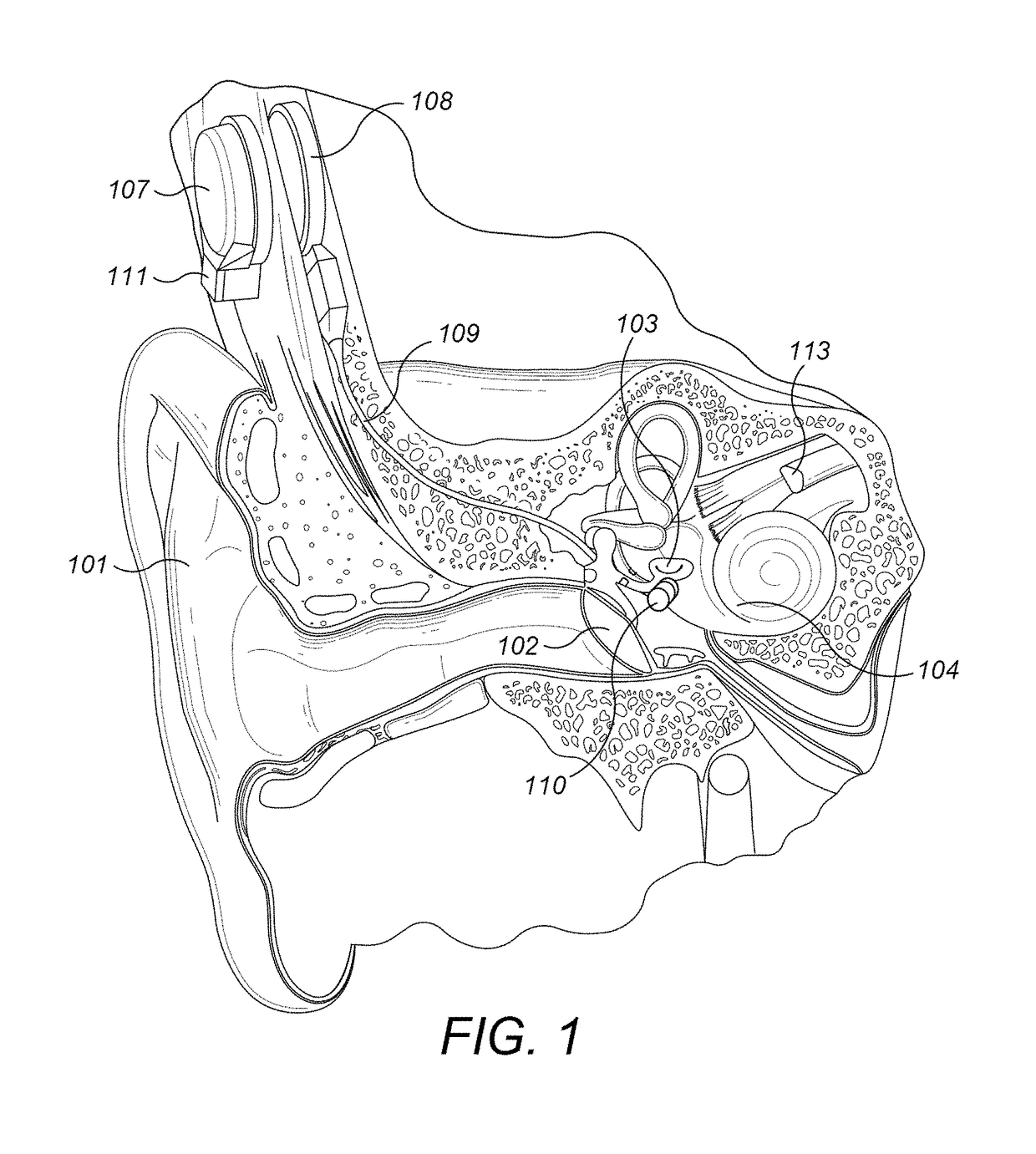
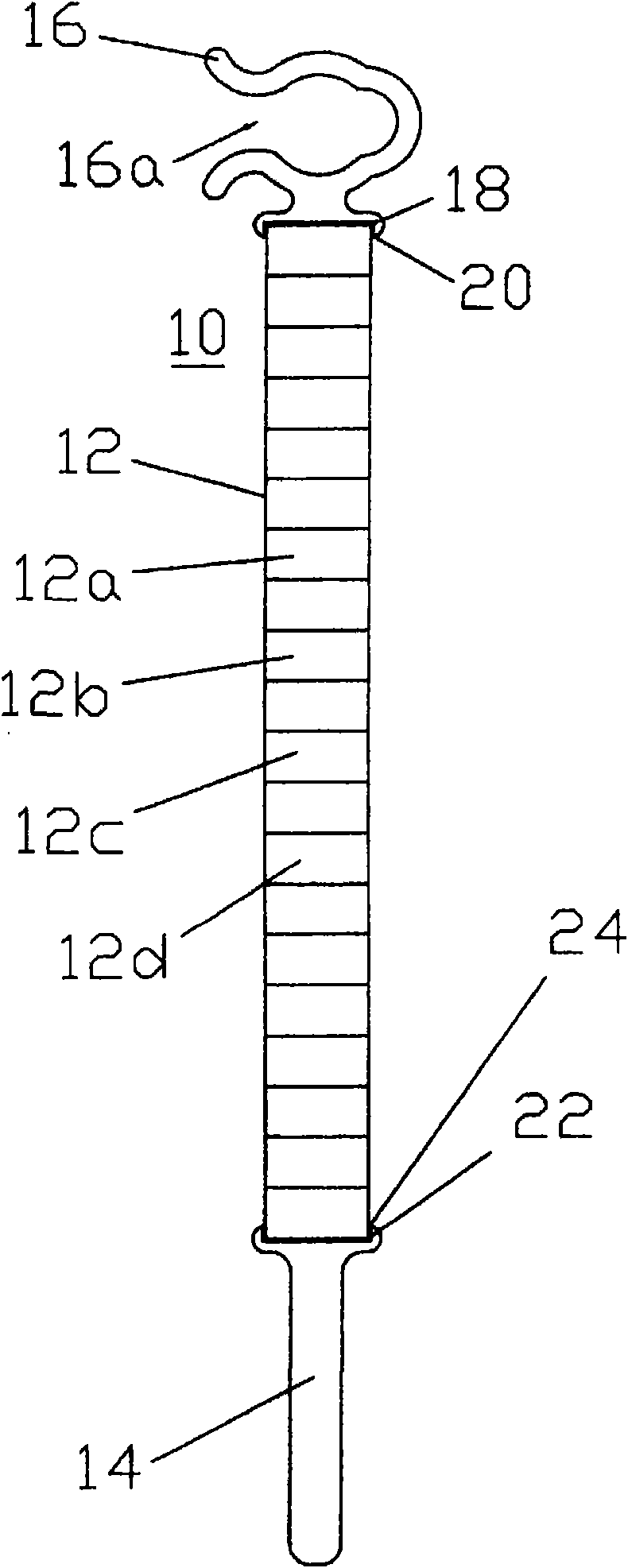
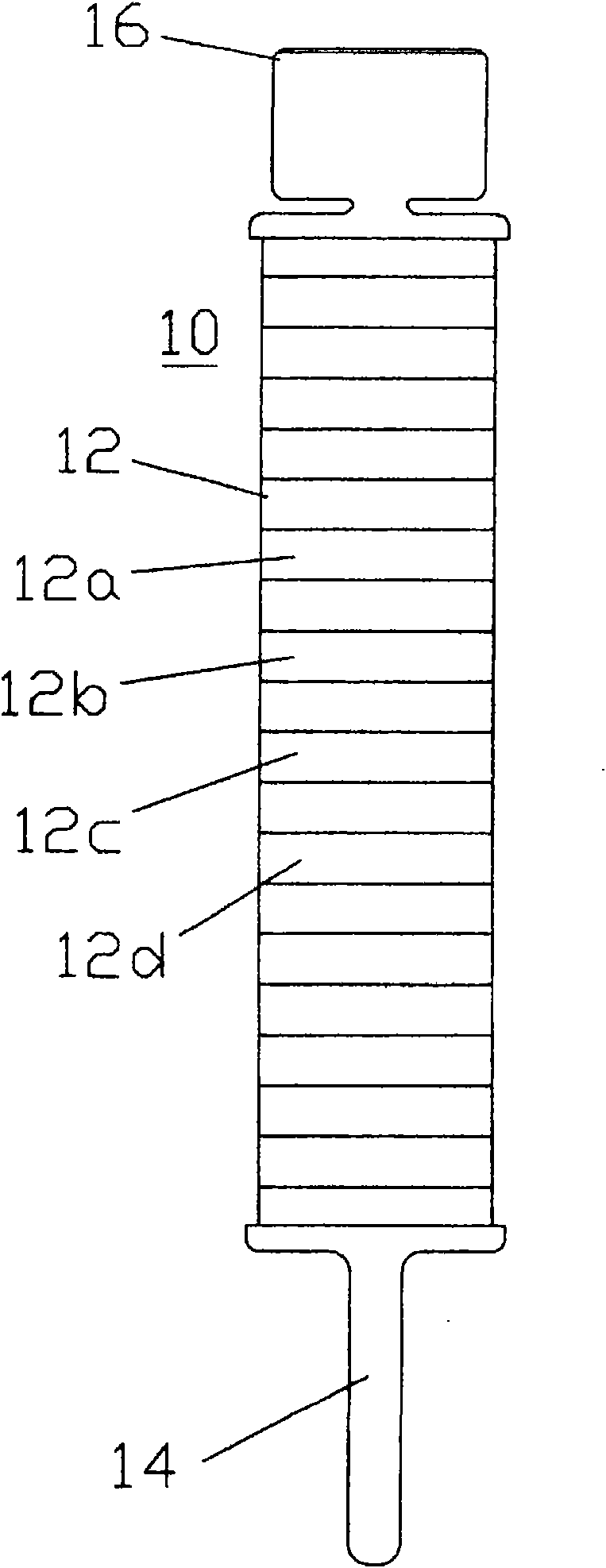
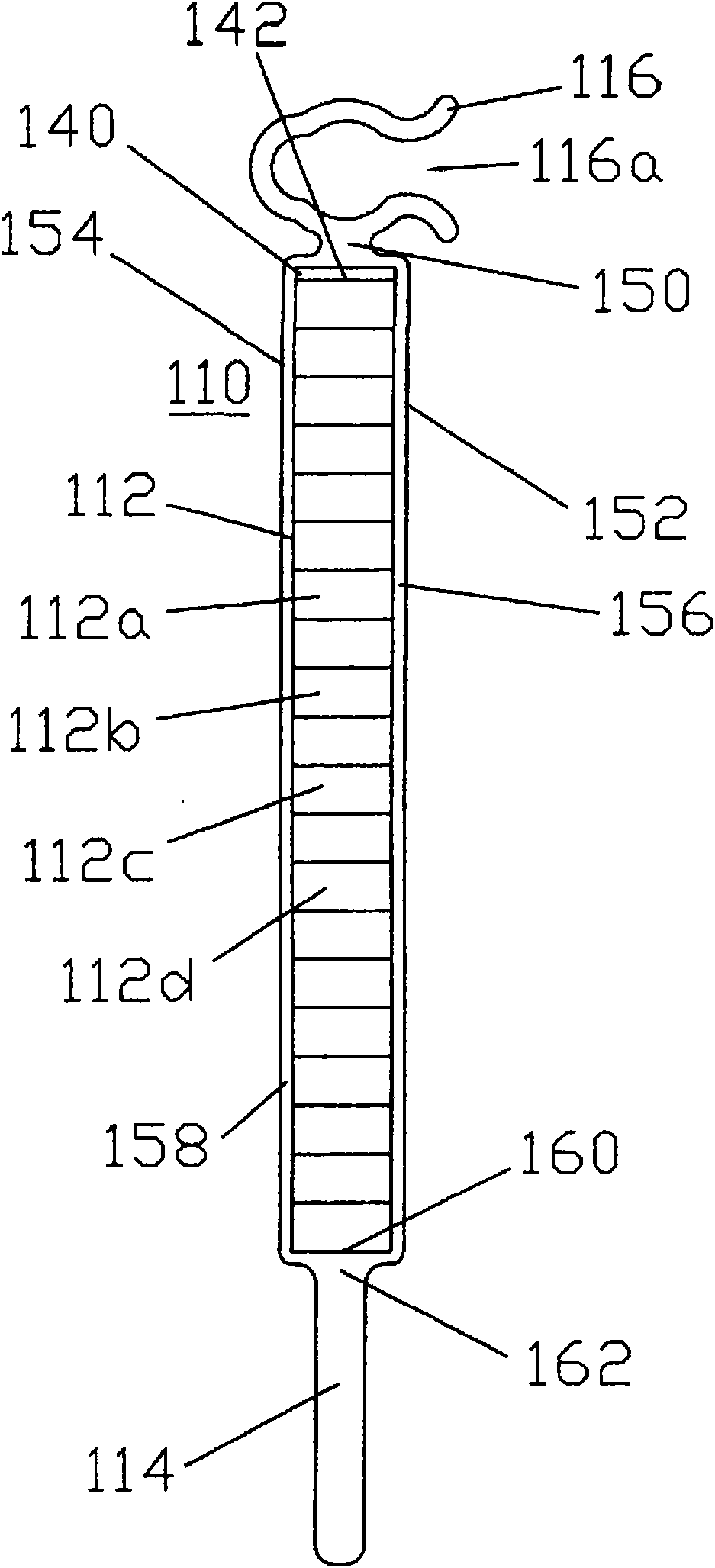
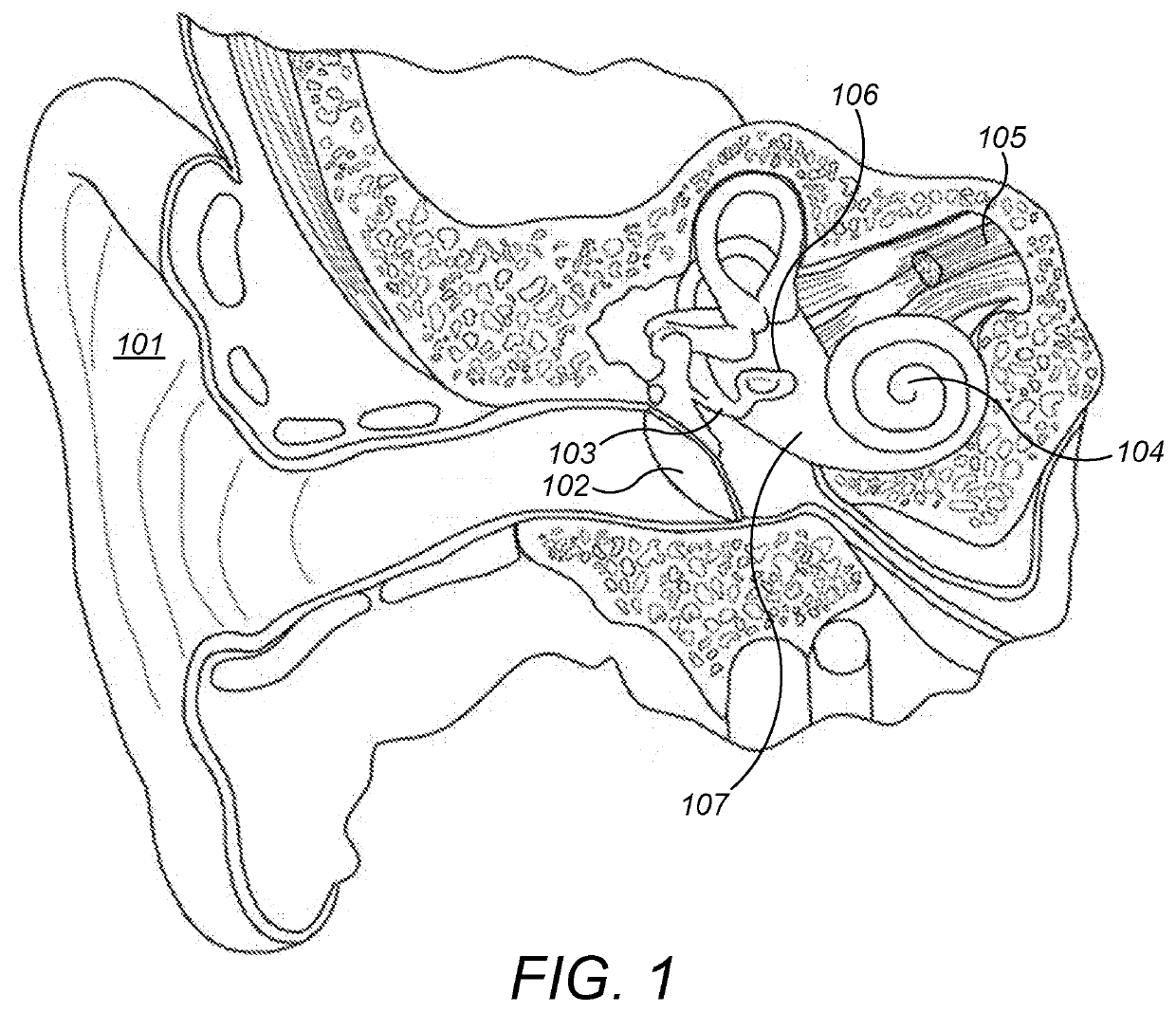
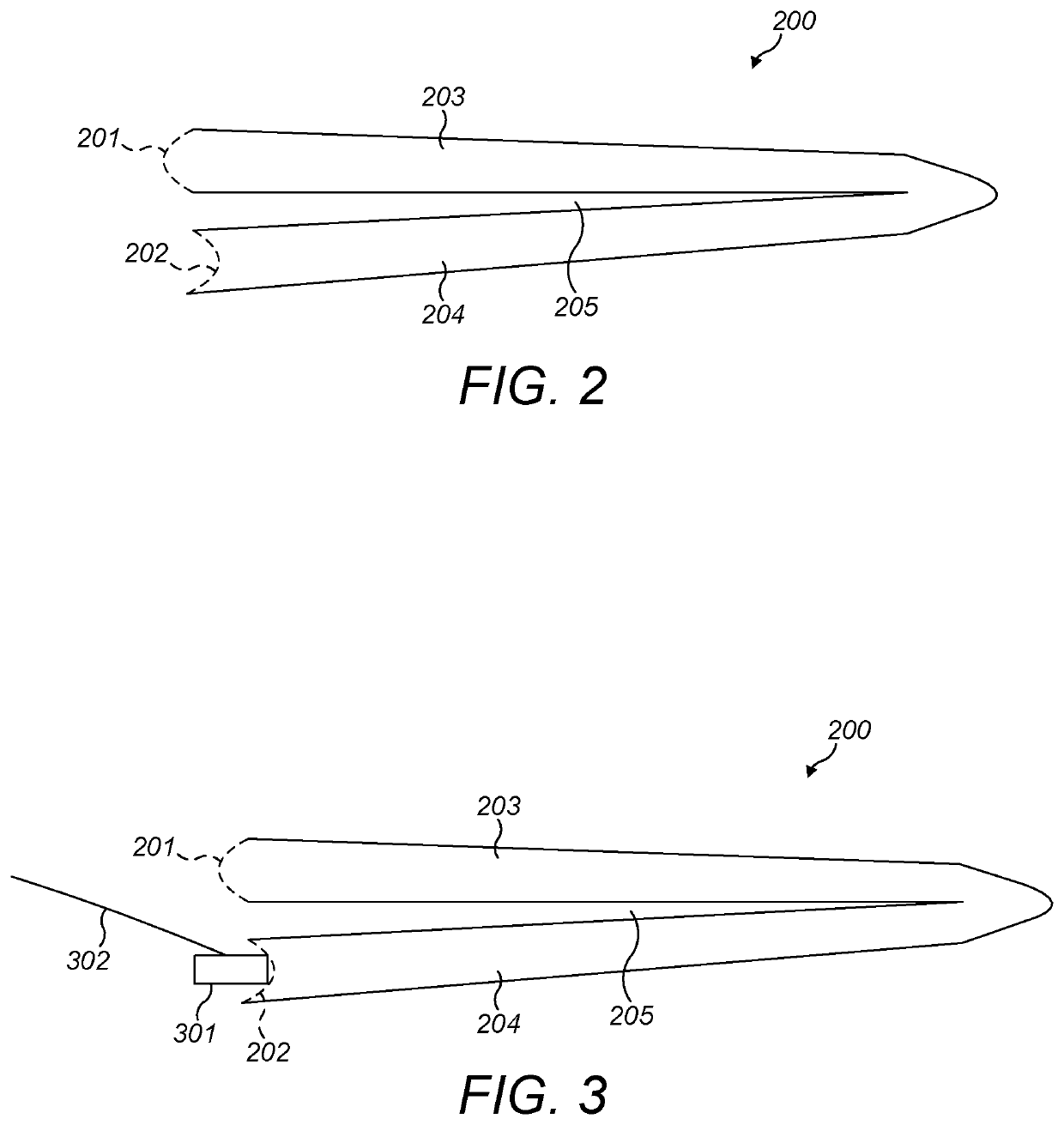
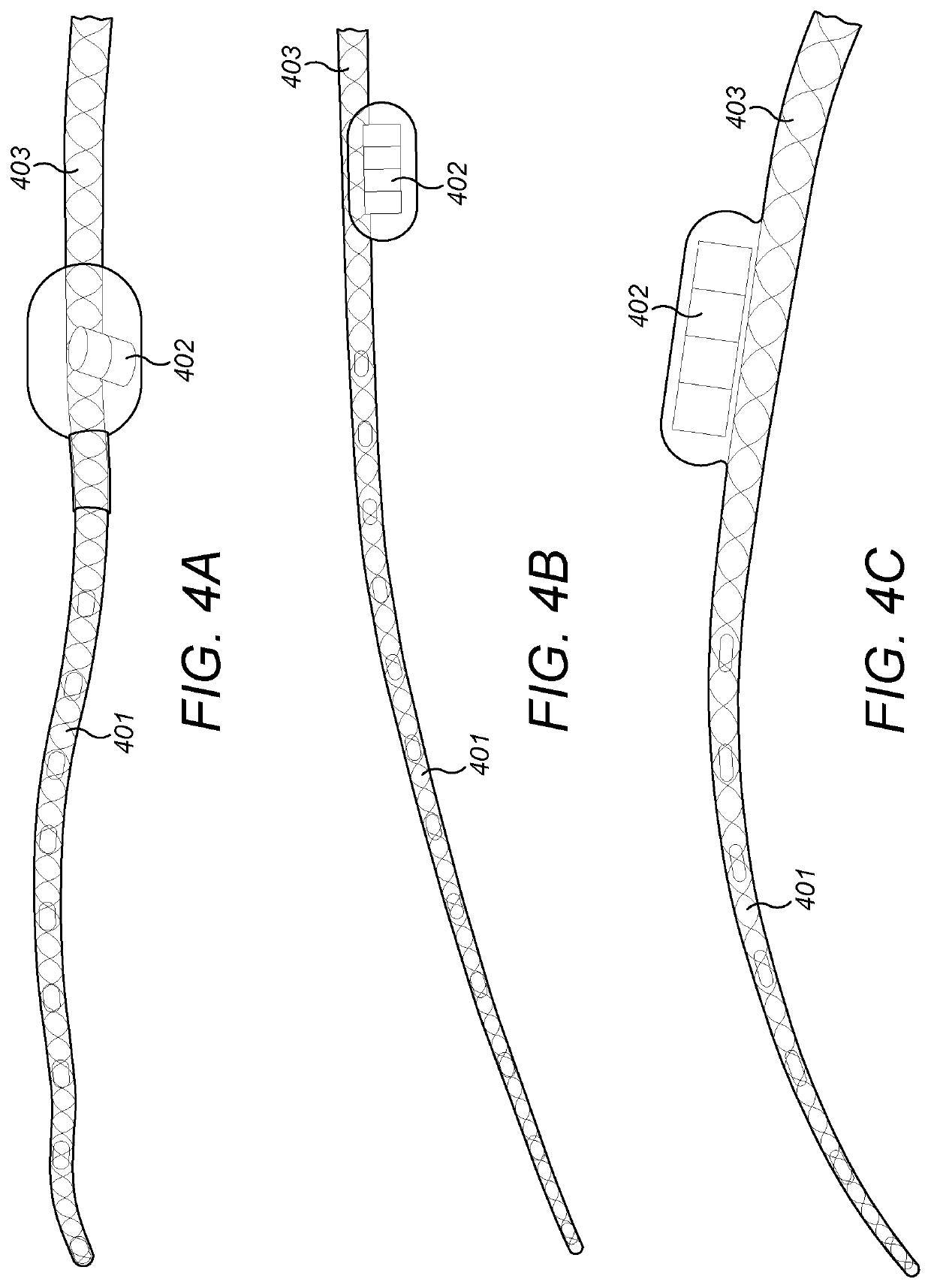
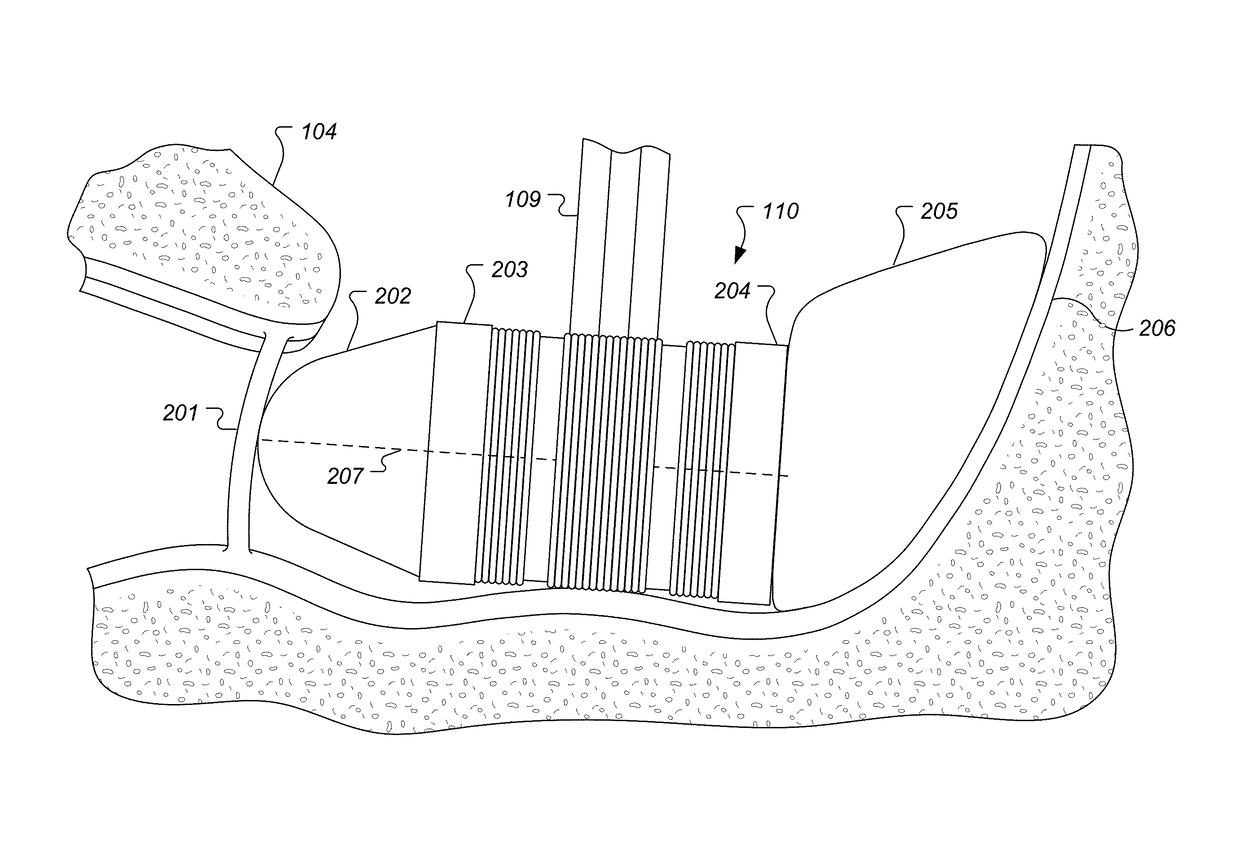
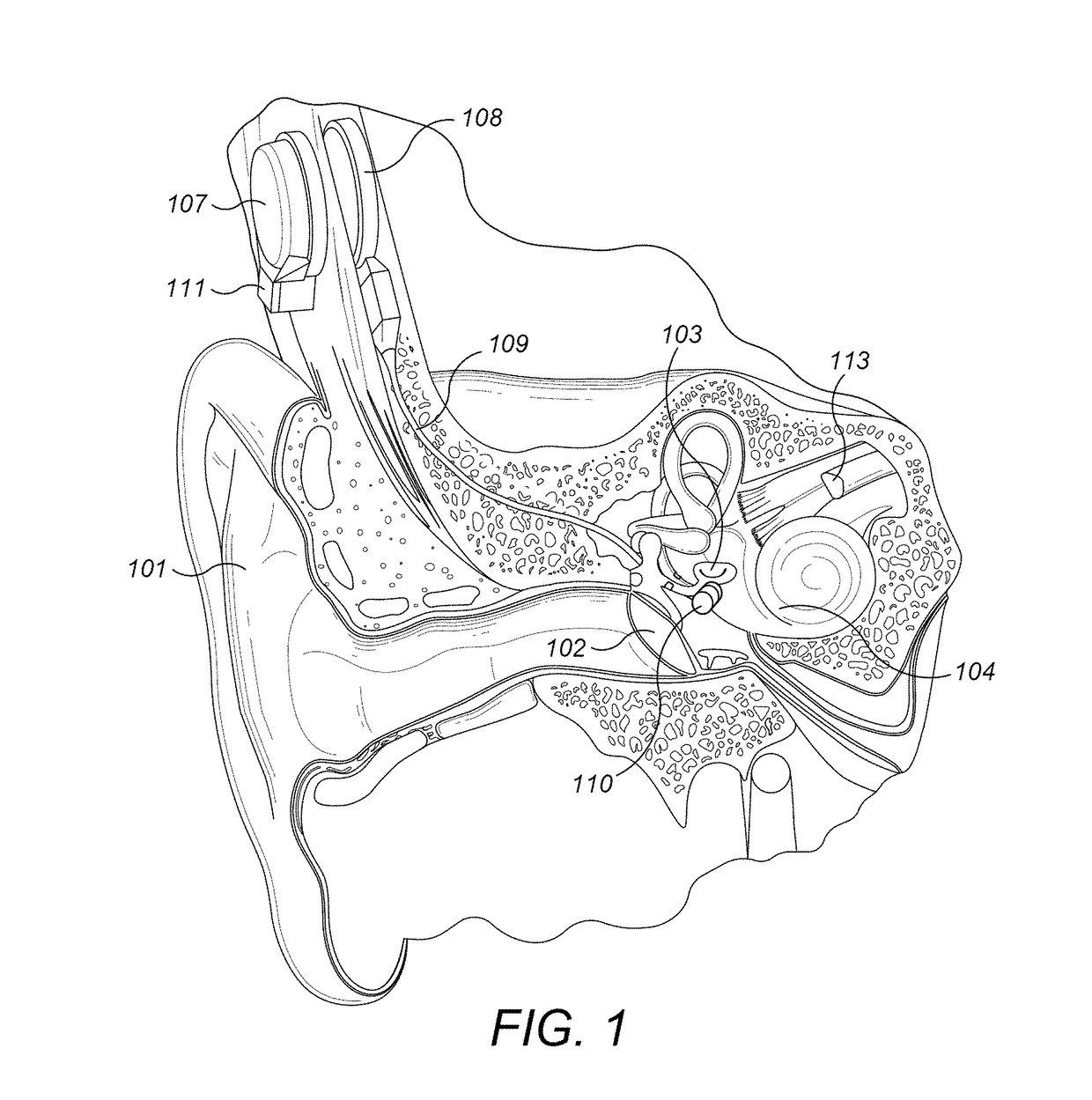
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Middle Ear Implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
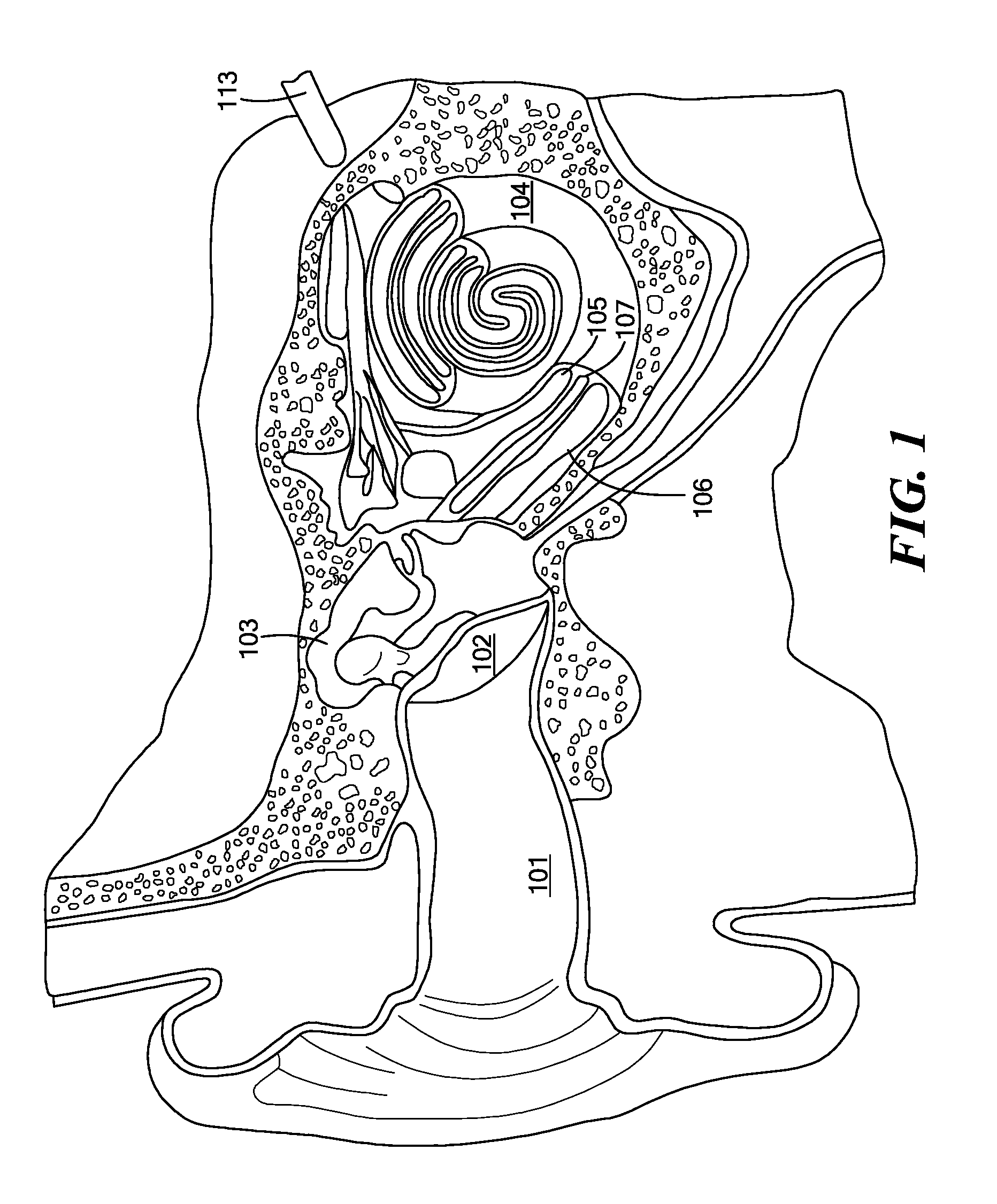
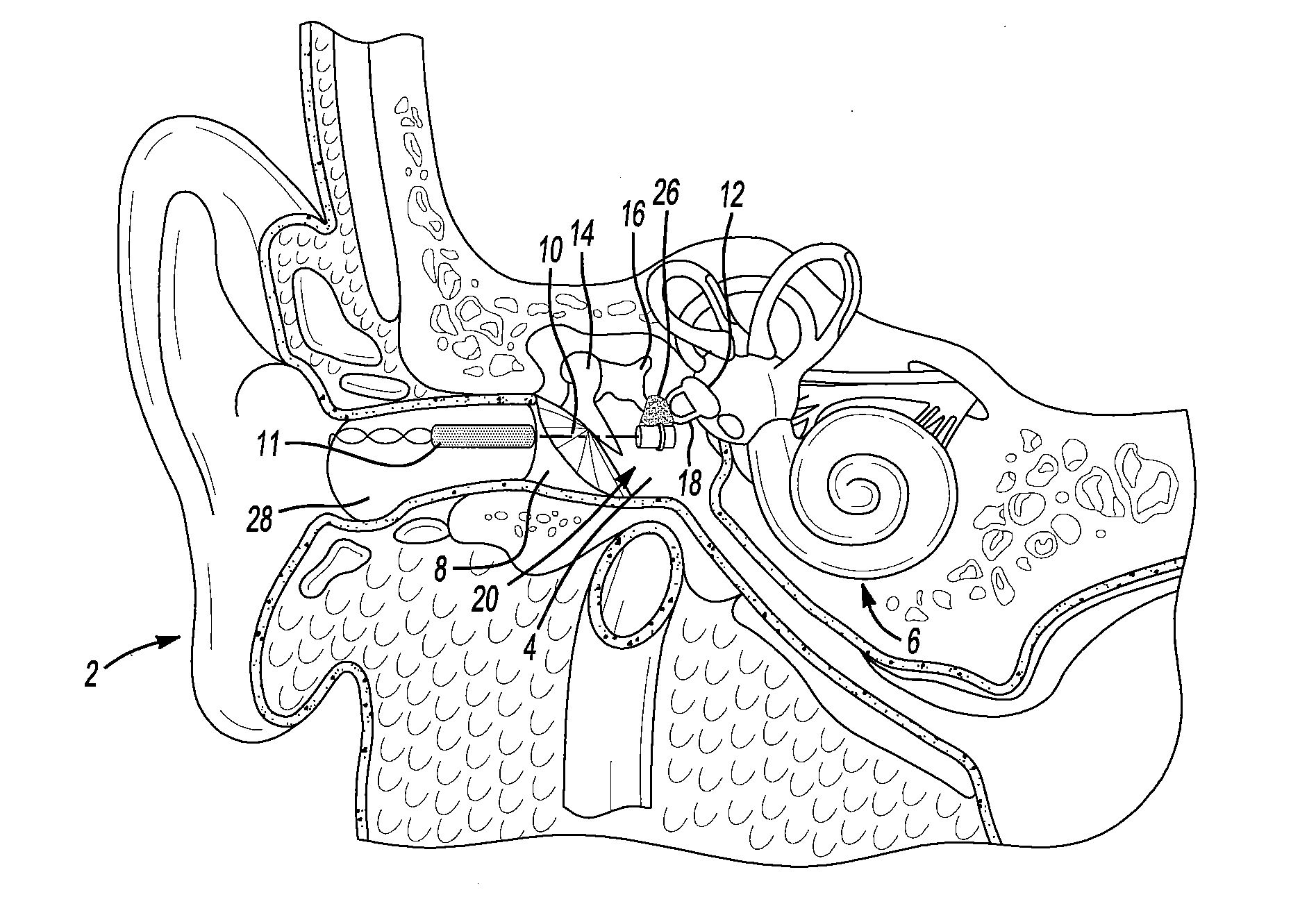
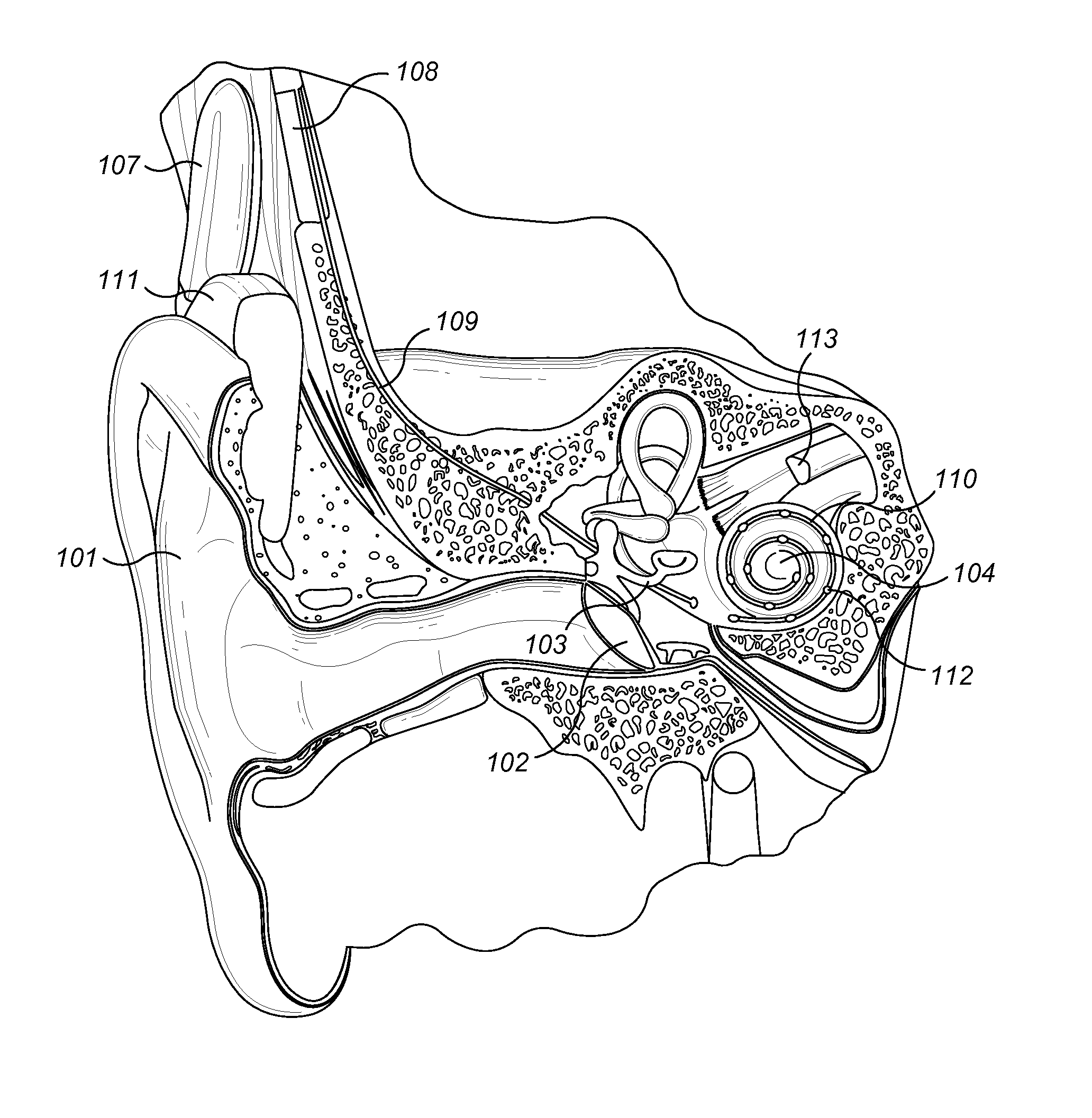
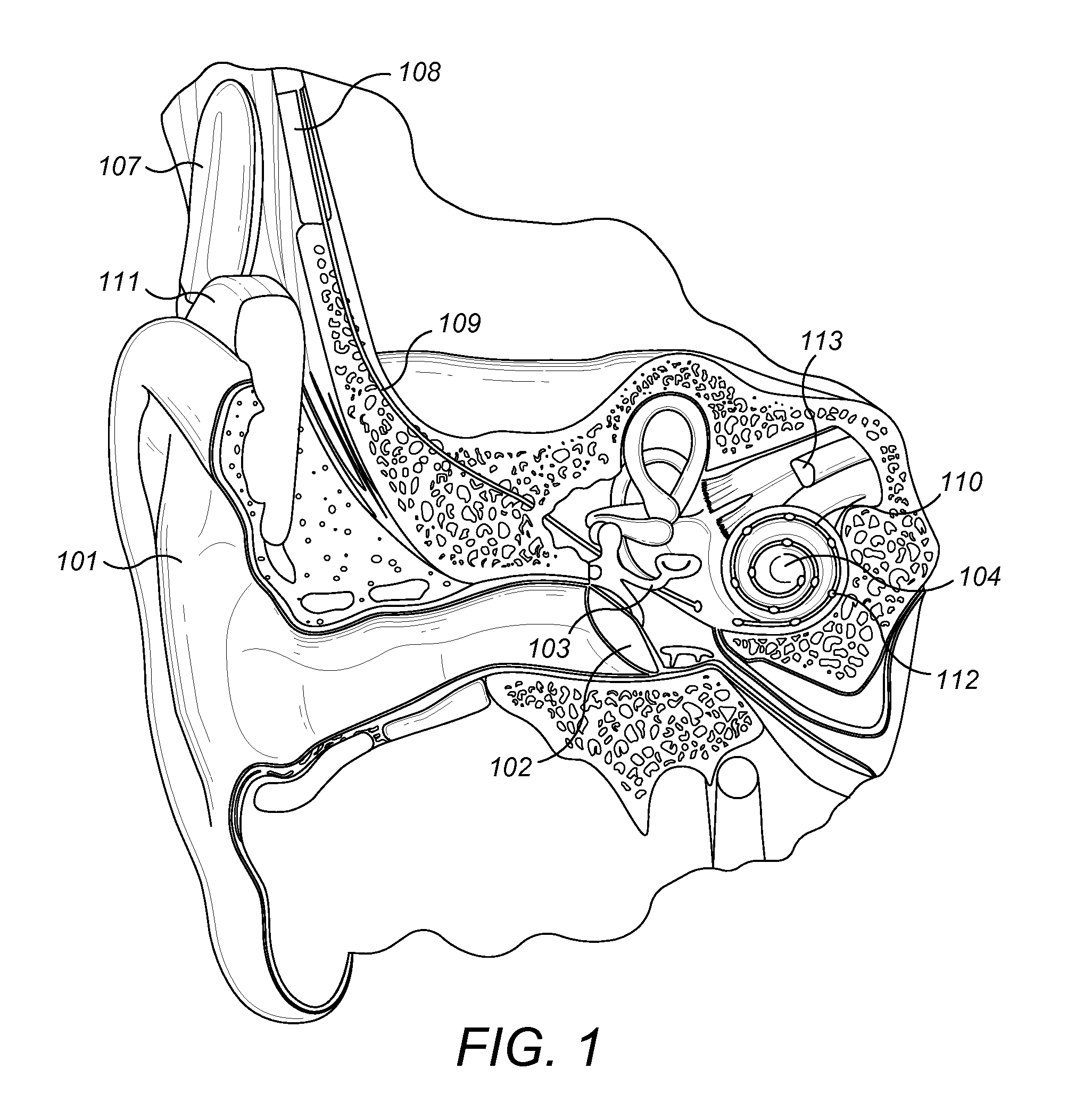
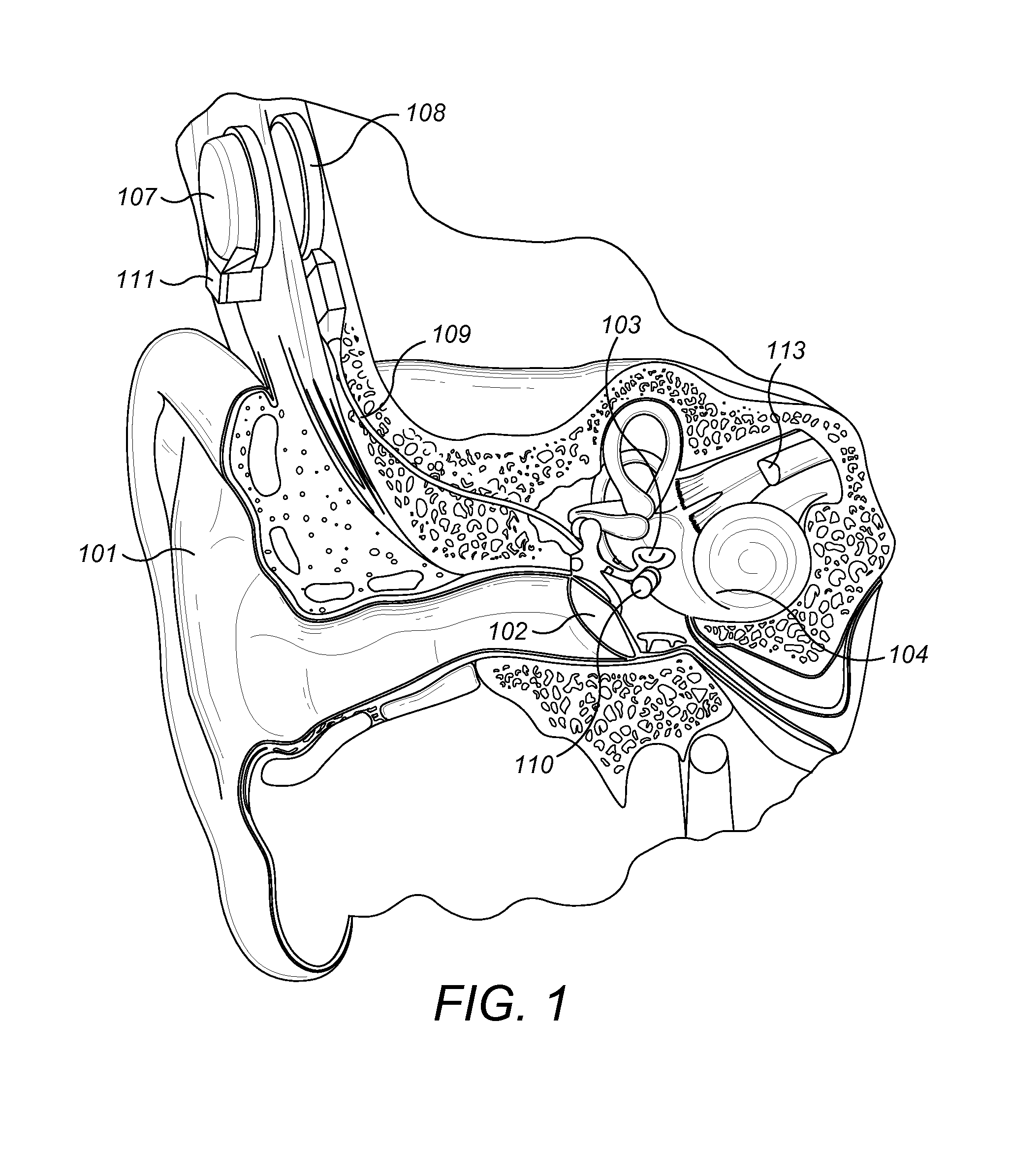
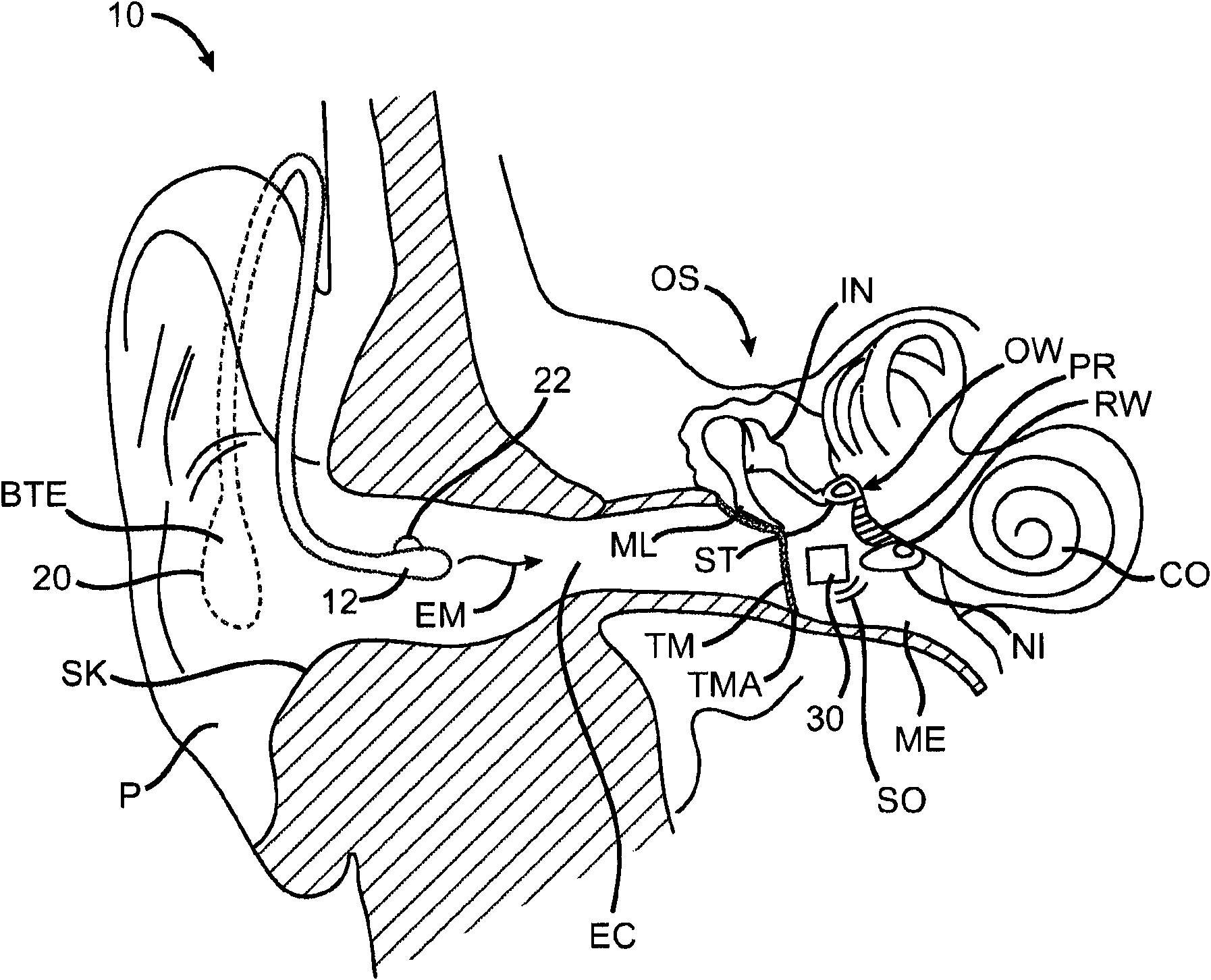
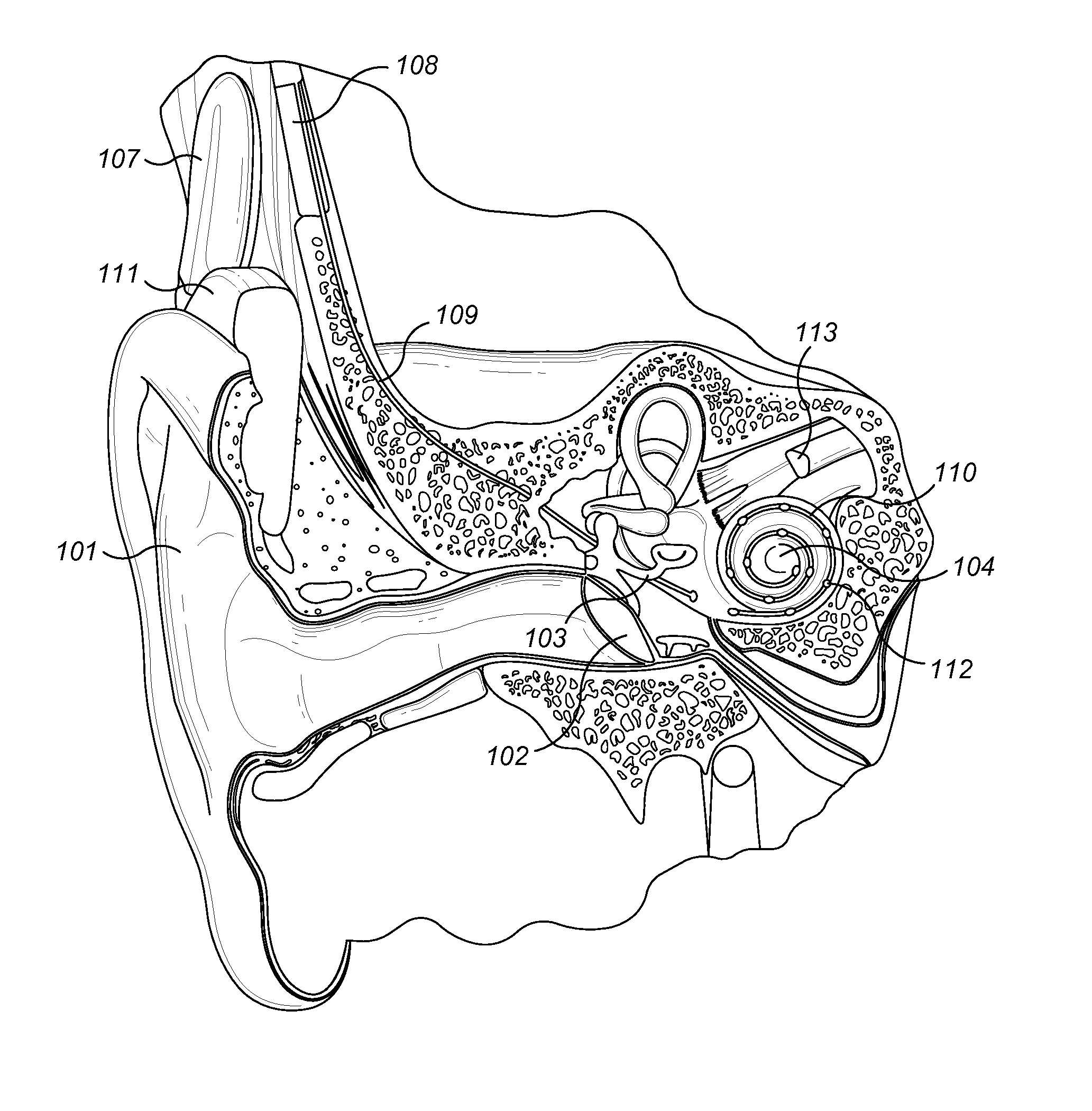
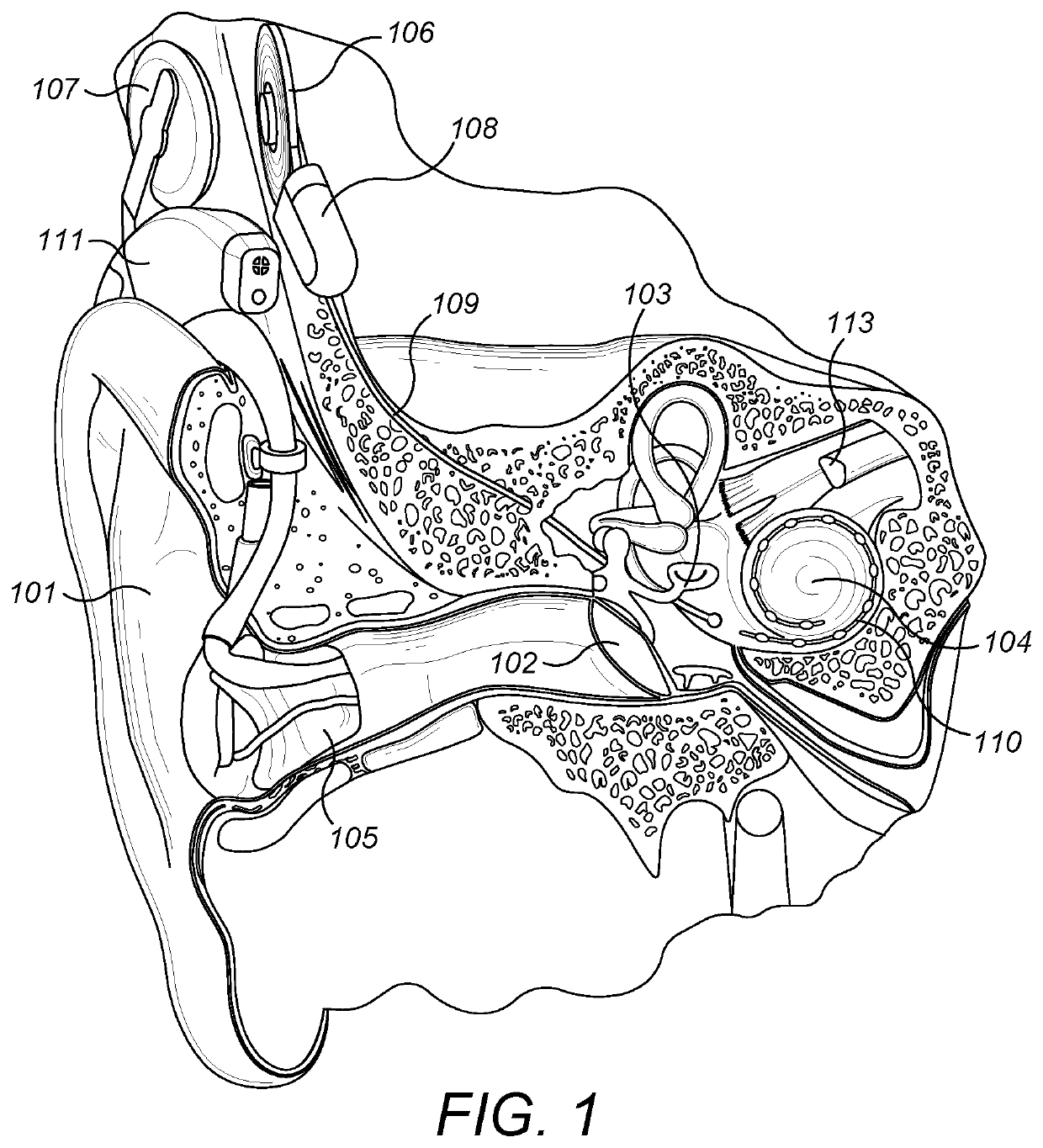
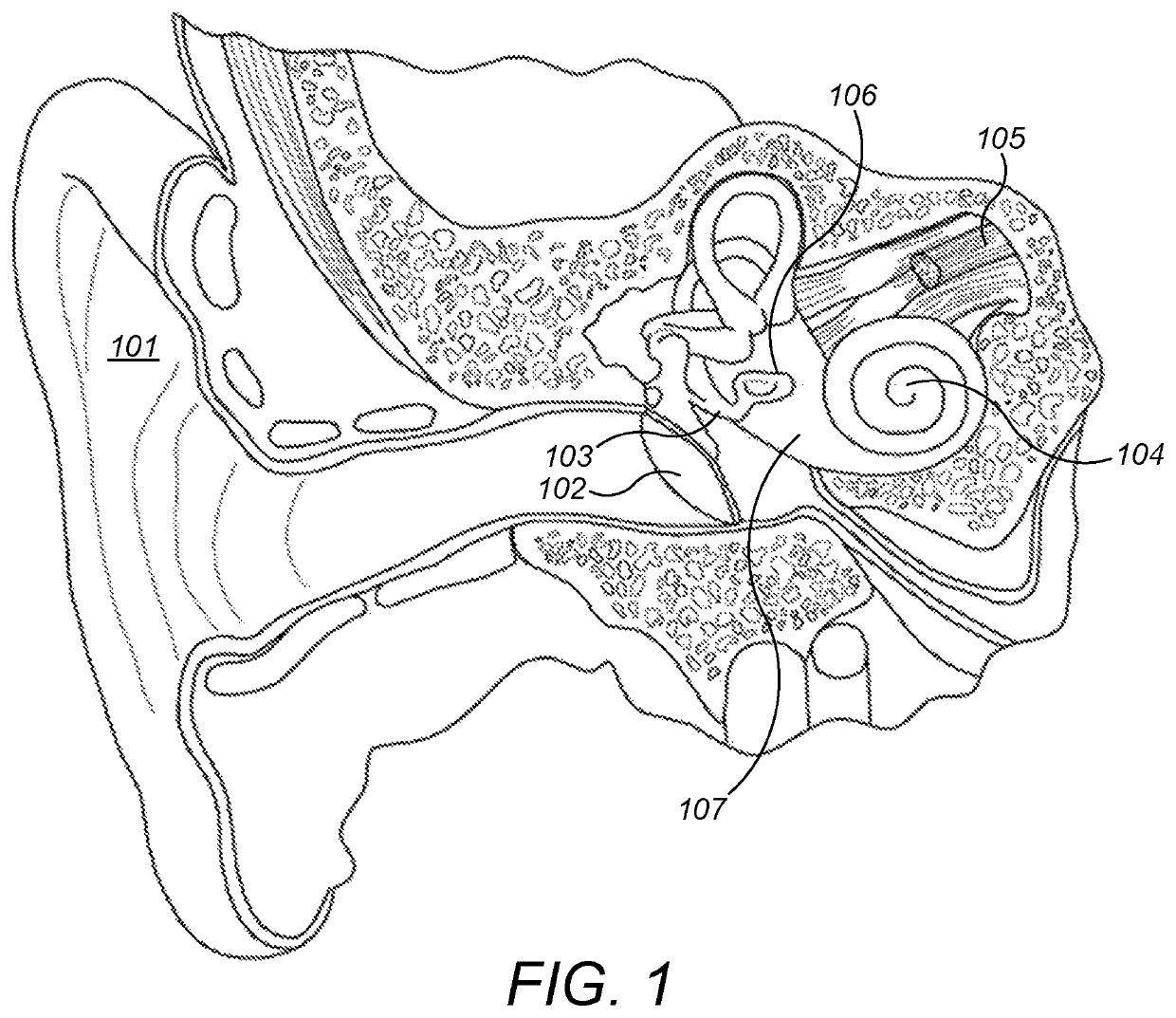
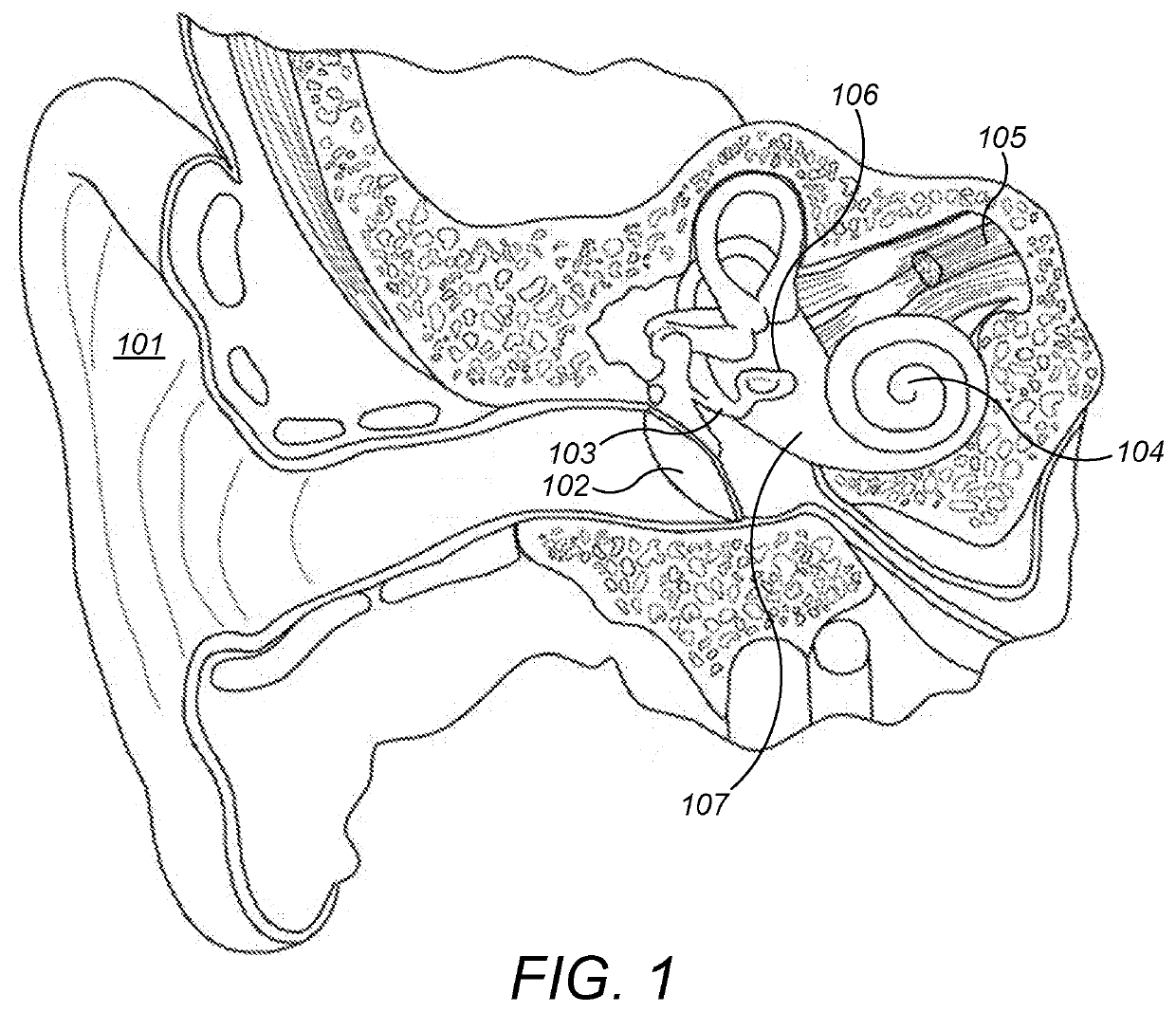
Advertisement. A middle-ear implant, or vibrating ossicular prosthesis, is designed for people with moderate to severe sensorineural hearing loss (permanent hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea, hair cells, or auditory nerve) who, for a variety of reasons, have not been helped by hearing aids.
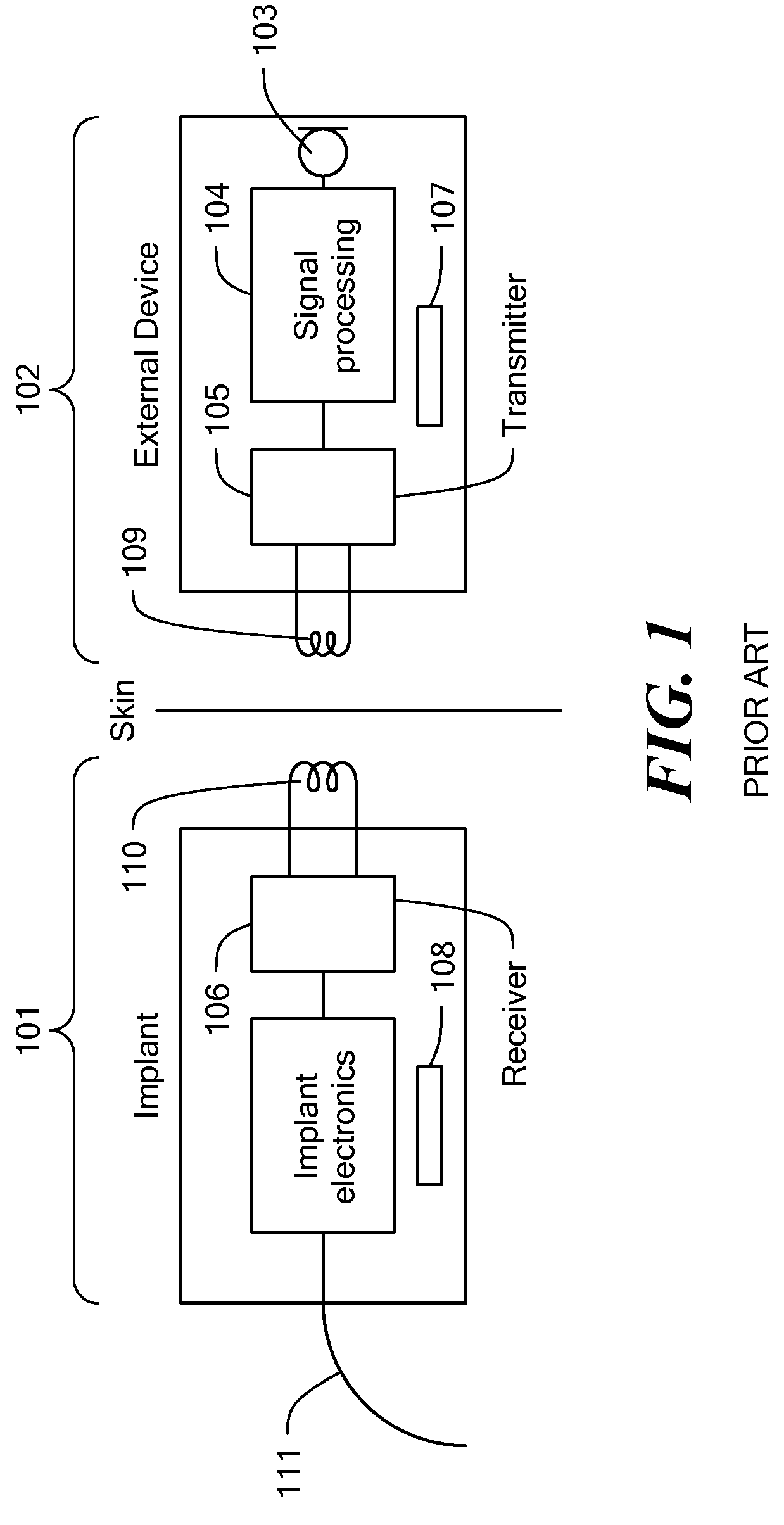
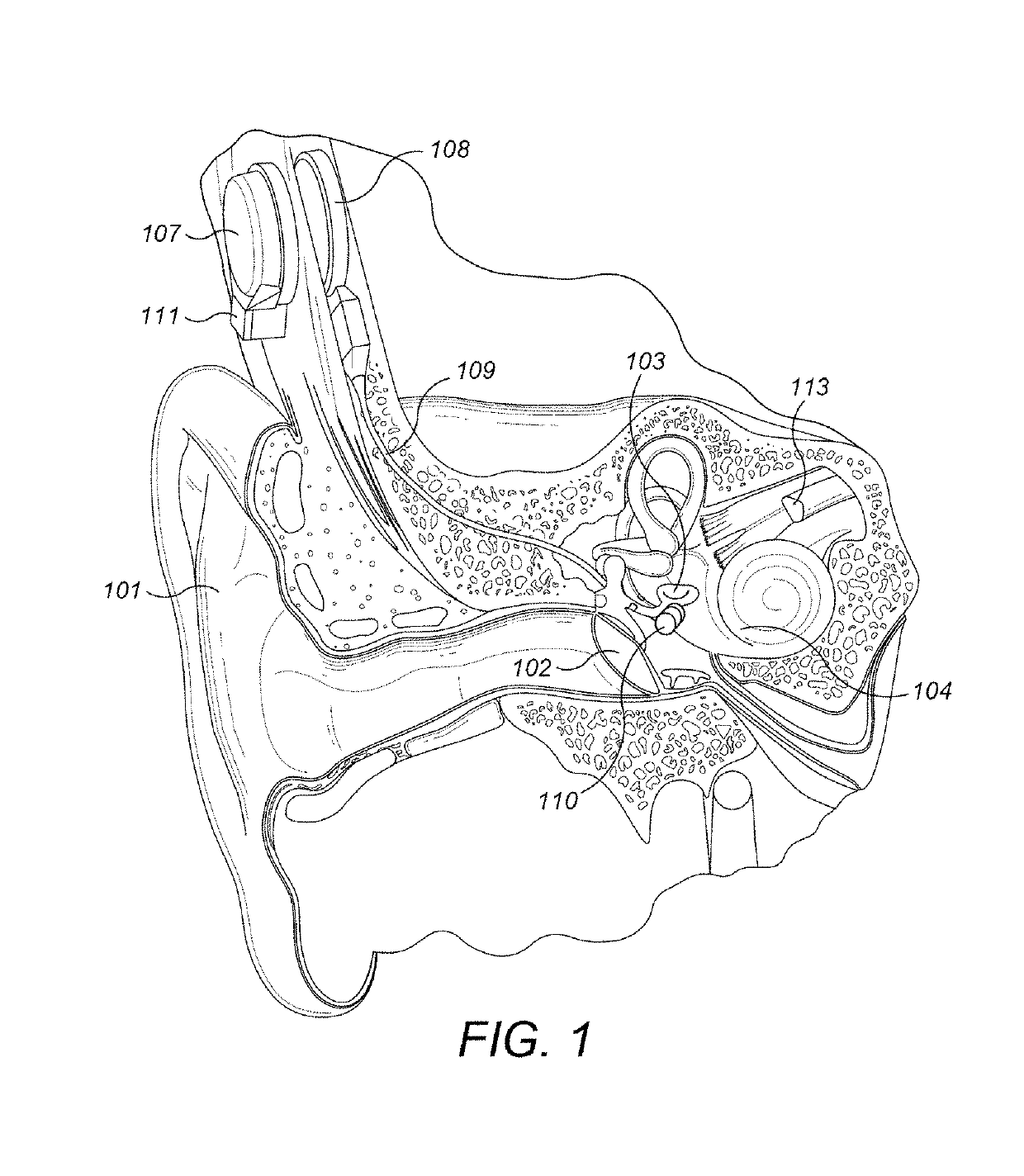
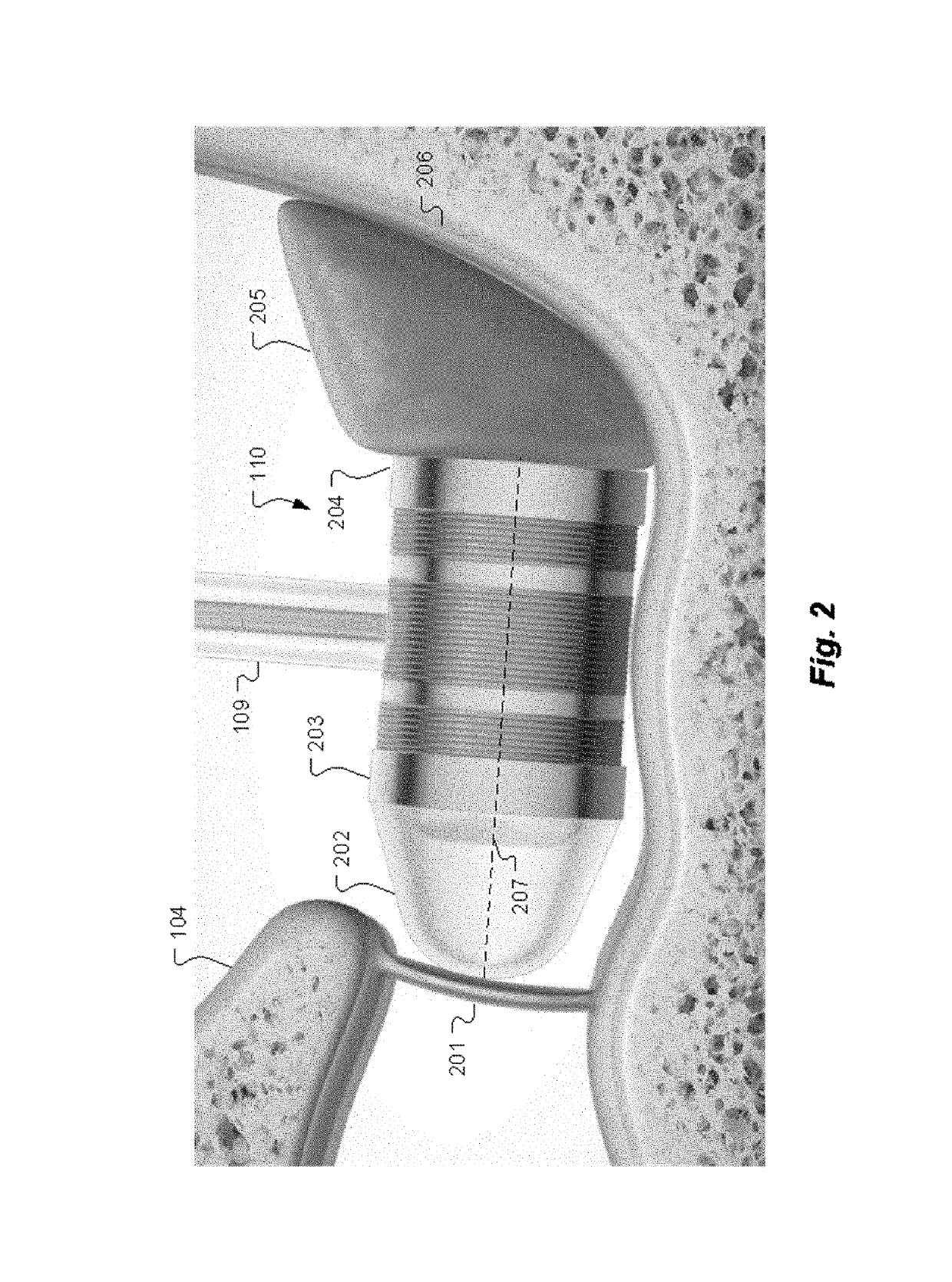
Hearing implant
InactiveUS7289639B2Not easily fall outAvoid cloggingCompletely in canal hearing aidsOptical signal transducersHearing aidLight signal
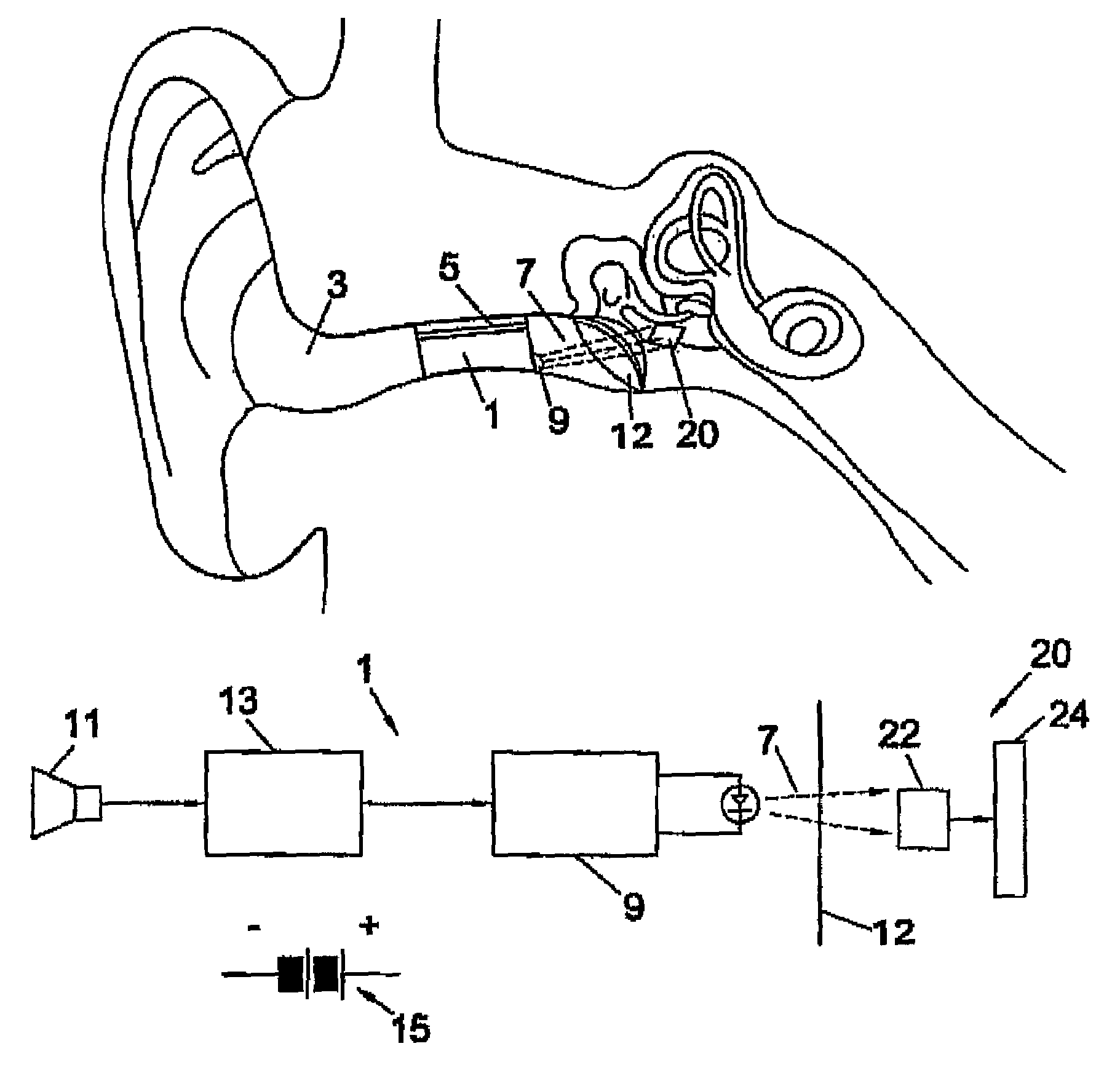
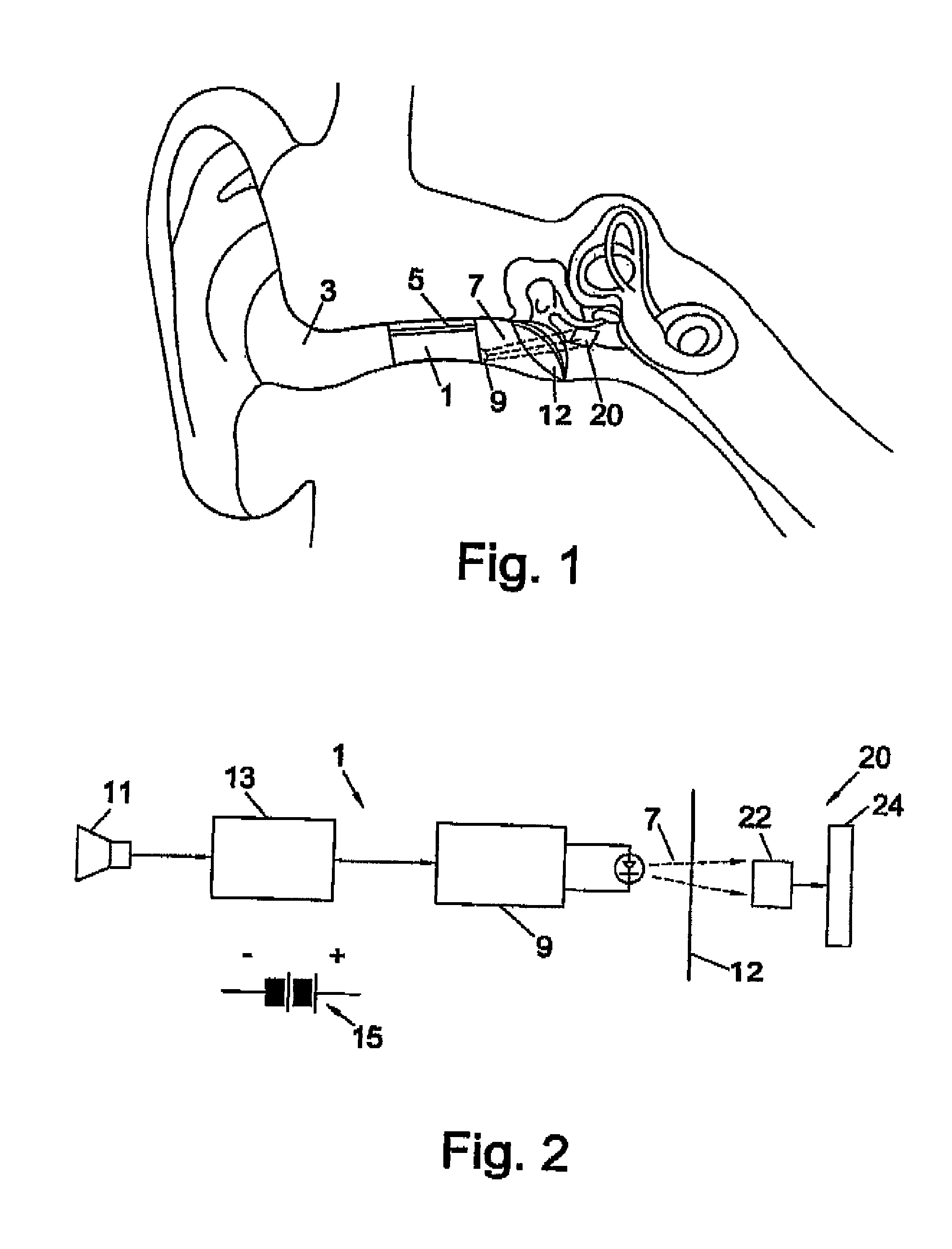
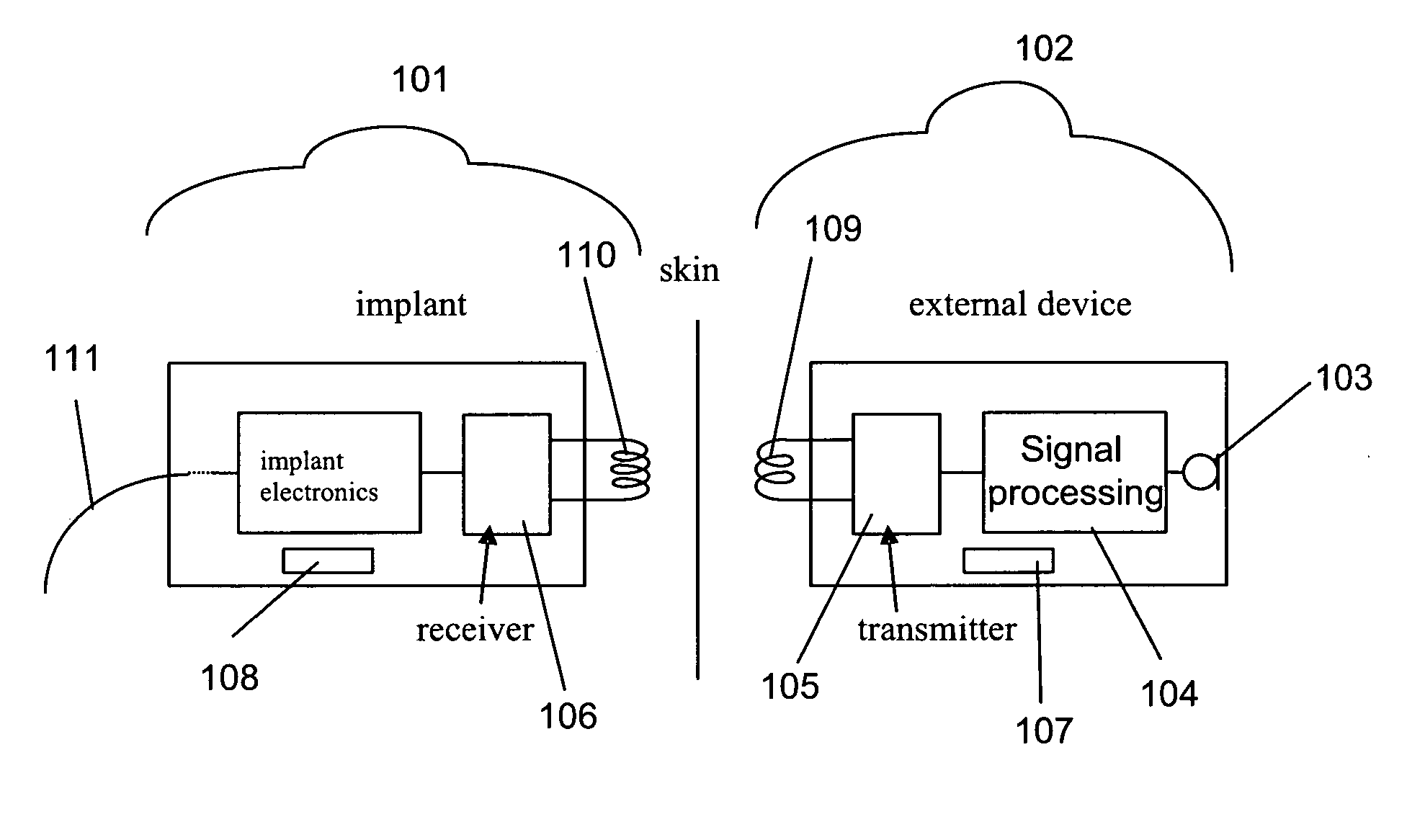
The present invention relates to a hearing aid system comprising a hearing implant and a method of powering a hearing implant, the system comprising an external ear canal module and an implant, wherein the signalling and / or powering of the ear implant is by way of a light signal being provided to the implant through the ear drum from, for example, the ear canal module.
Owner:EARLENS CORP
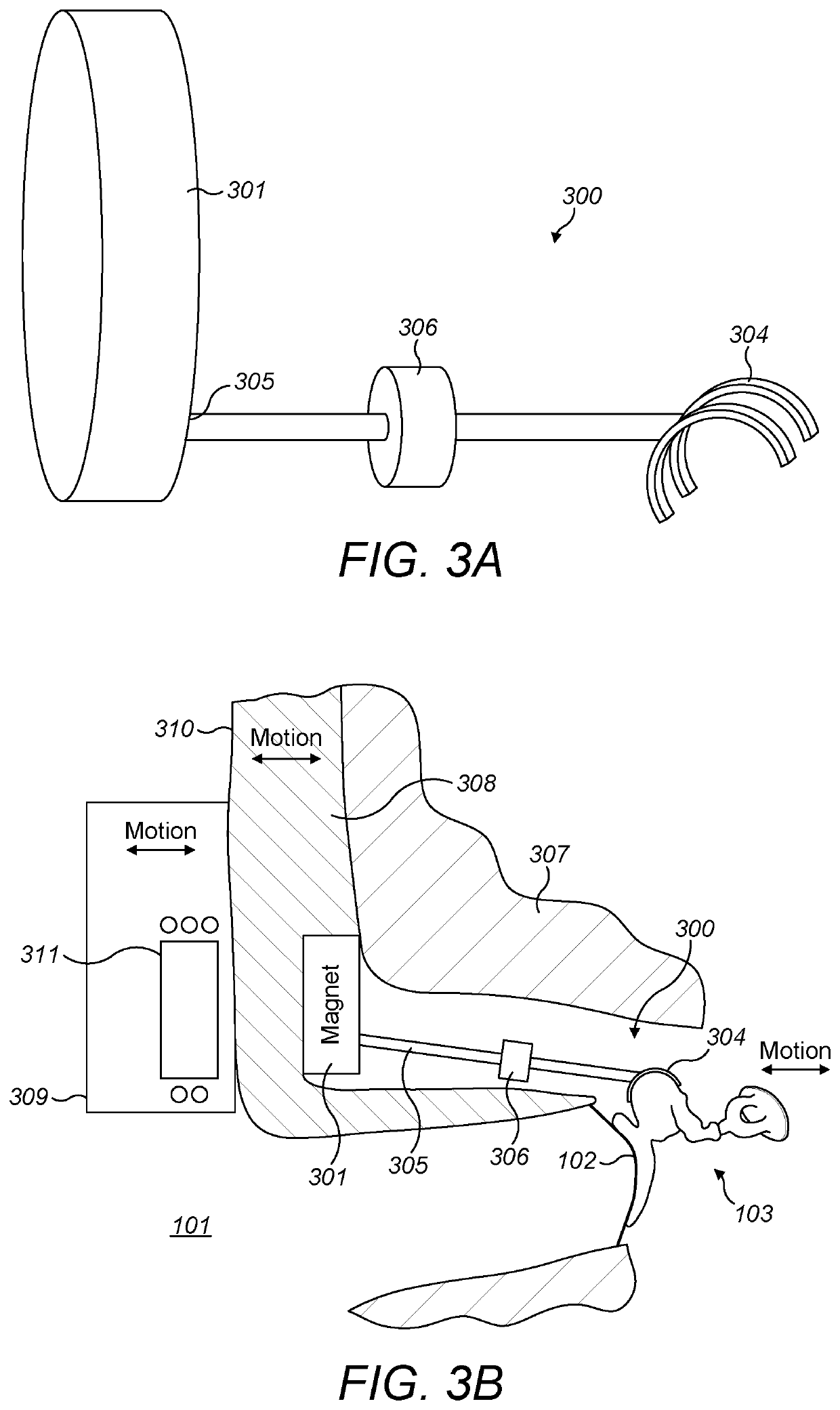
Moving Coil Actuator For Middle Ear Implants
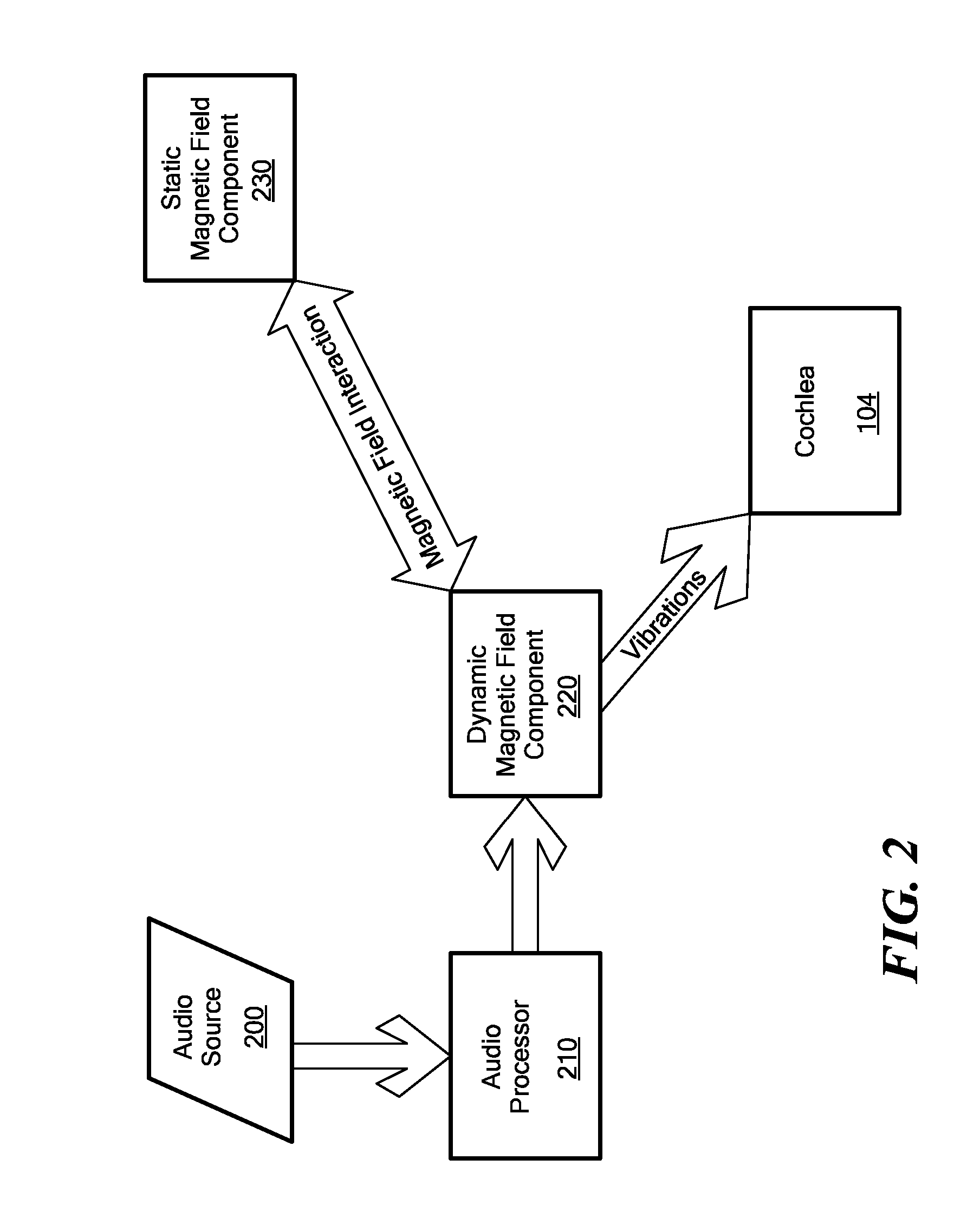
InactiveUS20080021518A1Improve hearingInternal electrodesMagnetostrictive transducersActuatorHearing perception
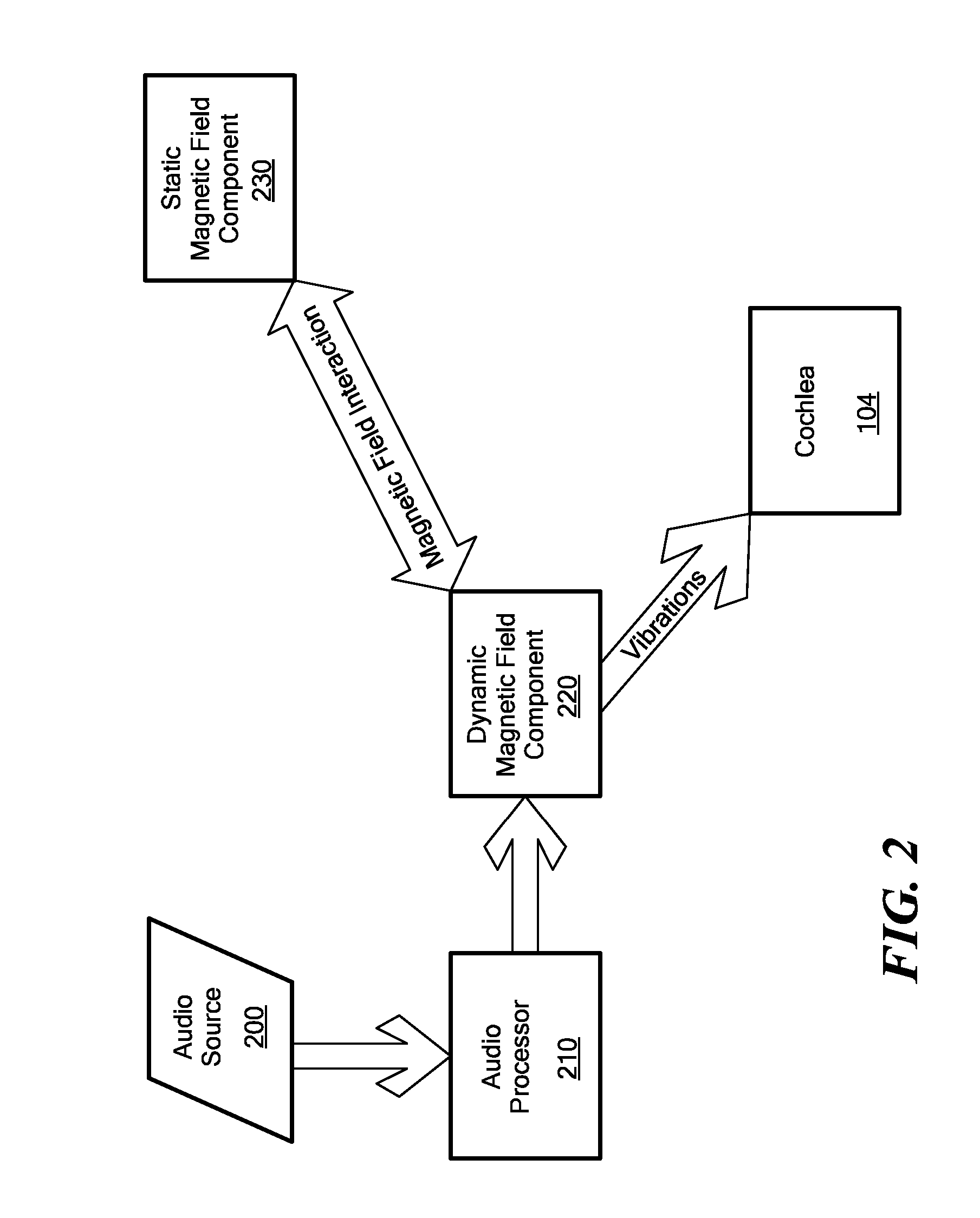
A hearing enhancement includes an audio processor that generates an electrical audio signal and transmits the signal to a coil. The coil is implanted into a patient in a position that results in transmission of mechanical stimulation to the inner ear when the coil is spatially displaced. A permanent magnet is placed in proximity to the coil so that when the coil receives the electrical audio signal form the processor, the induced coil magnetic field in the coil interacts with the magnetic field from the permanent magnet to spatially displace the coil and, as a result, transmit the mechanical stimulation to the inner ear.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
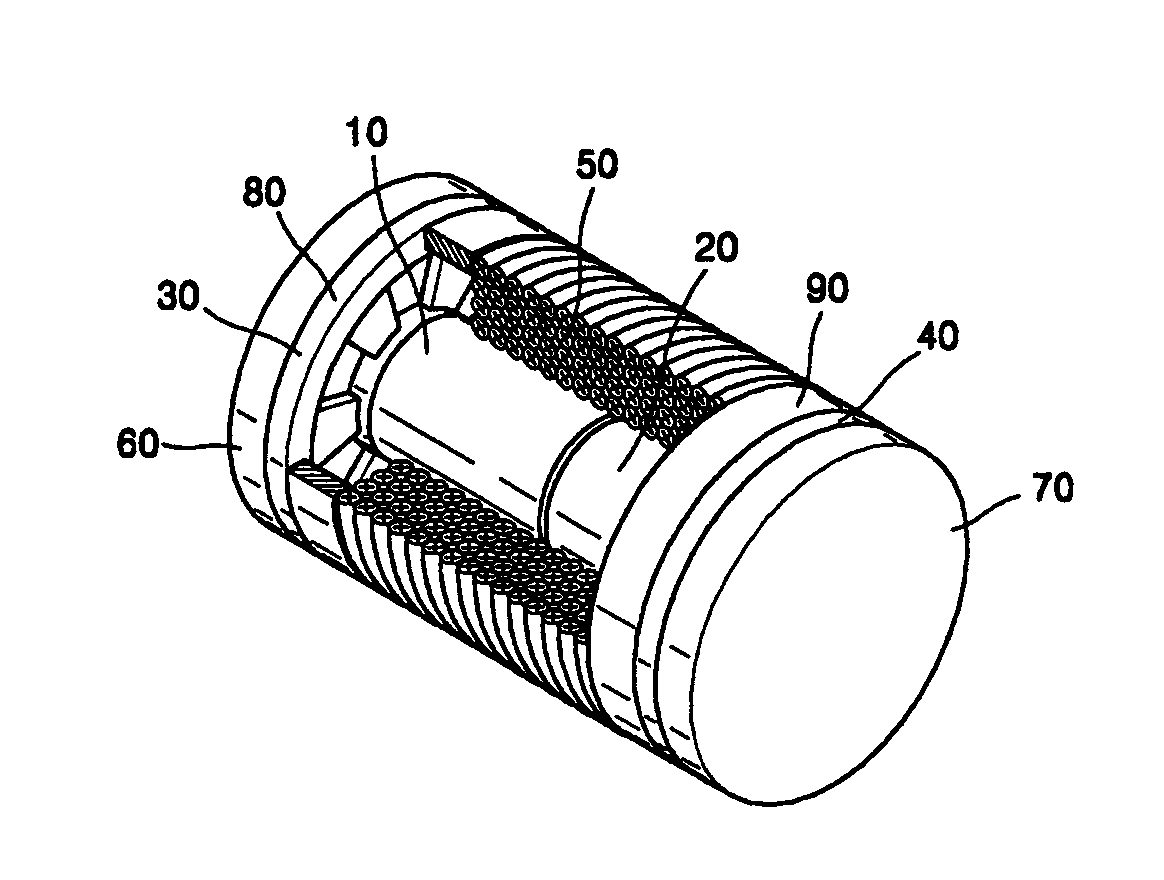
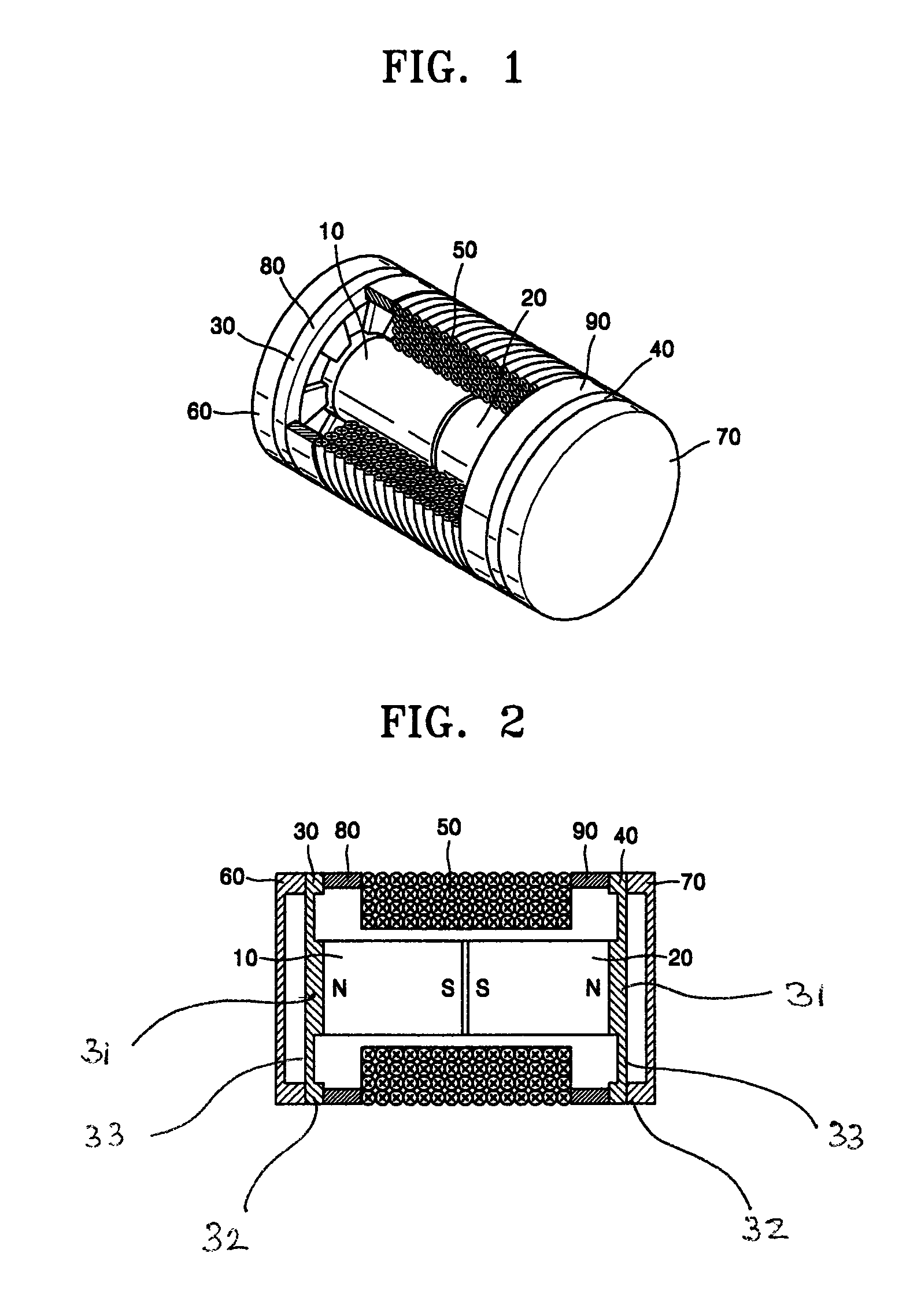
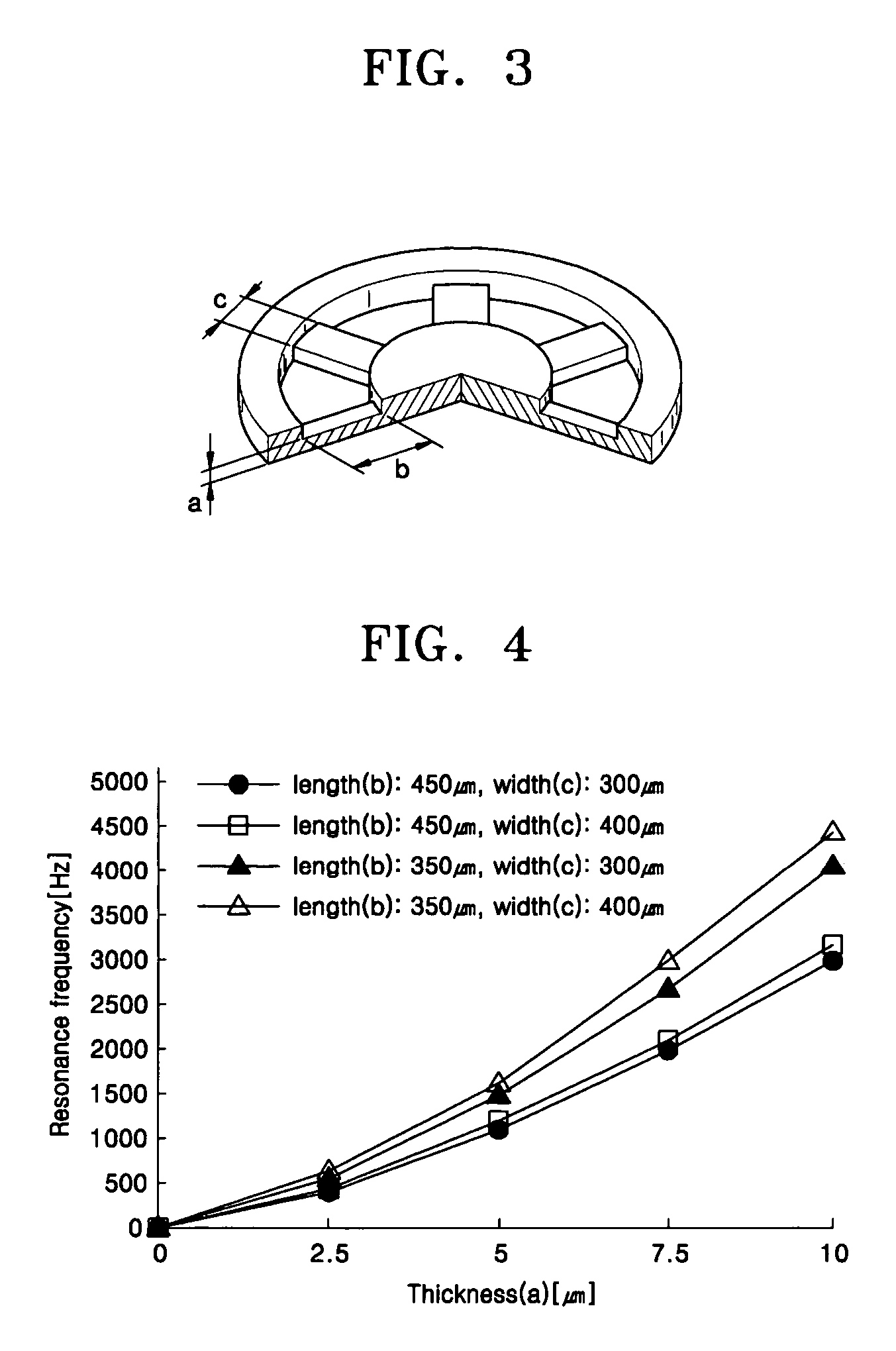
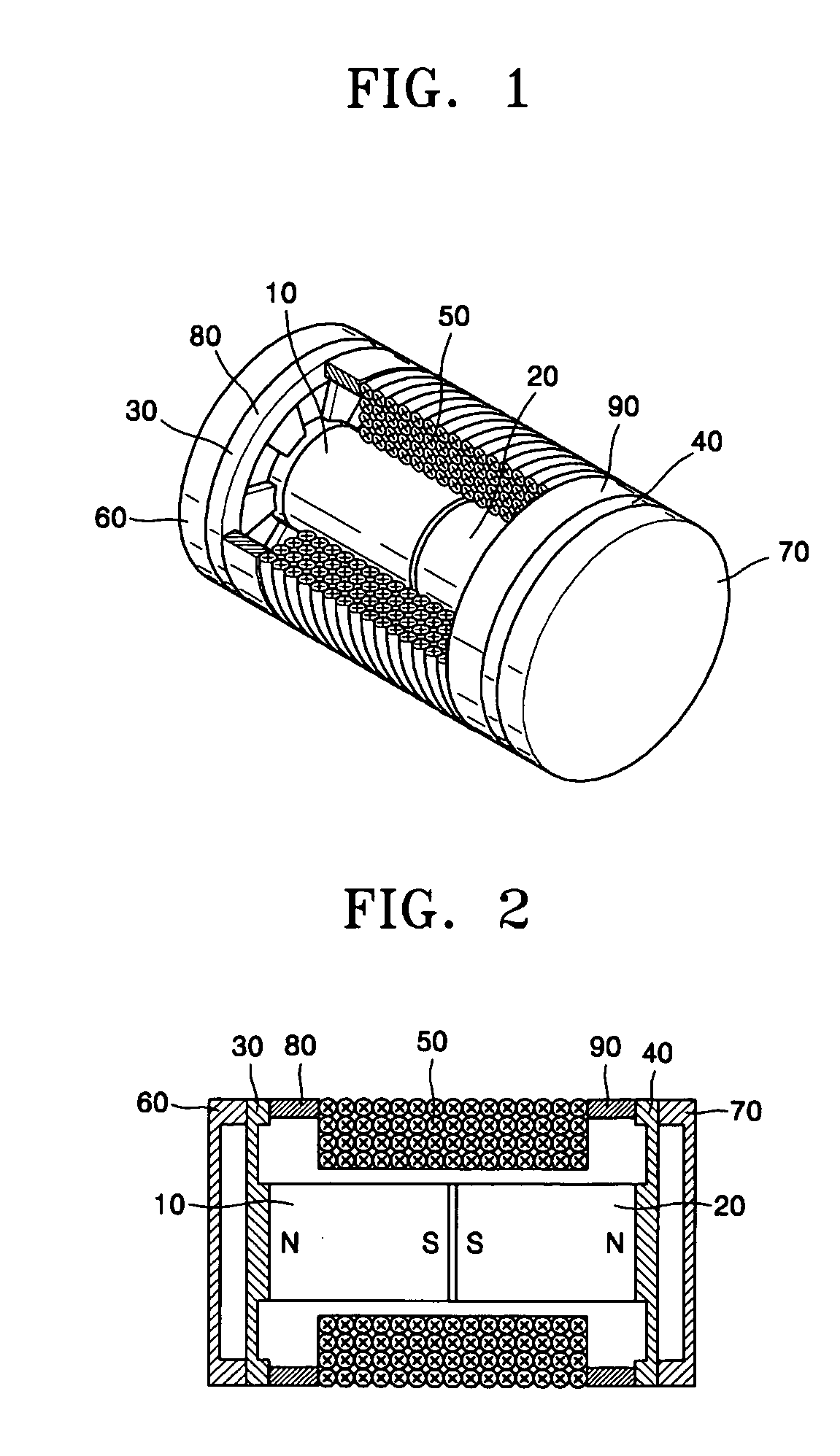
Middle ear implant transducer
A middle ear implant transducer of a hearing aid includes: first and second permanent magnets arranged such that the same poles of the first and second permanent magnets face each other; first and second vibrating members attached to both edges of the respective first and second permanent magnets; a coil enclosing the first and second permanent magnets and being separated a predetermined distance from the outer surfaces of the first and second permanent magnets between the first vibrating member and the second vibrating member; and first and second covers mounted on the outer surfaces of the first and second vibrating members, wherein the first and second vibrating members comprise couplers respectively attached to the first and second permanent magnets, rims respectively attached to the edges of the first and second covers, and support films respectively connecting the couplers to the rims and being thinner than the couplers and the rims.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
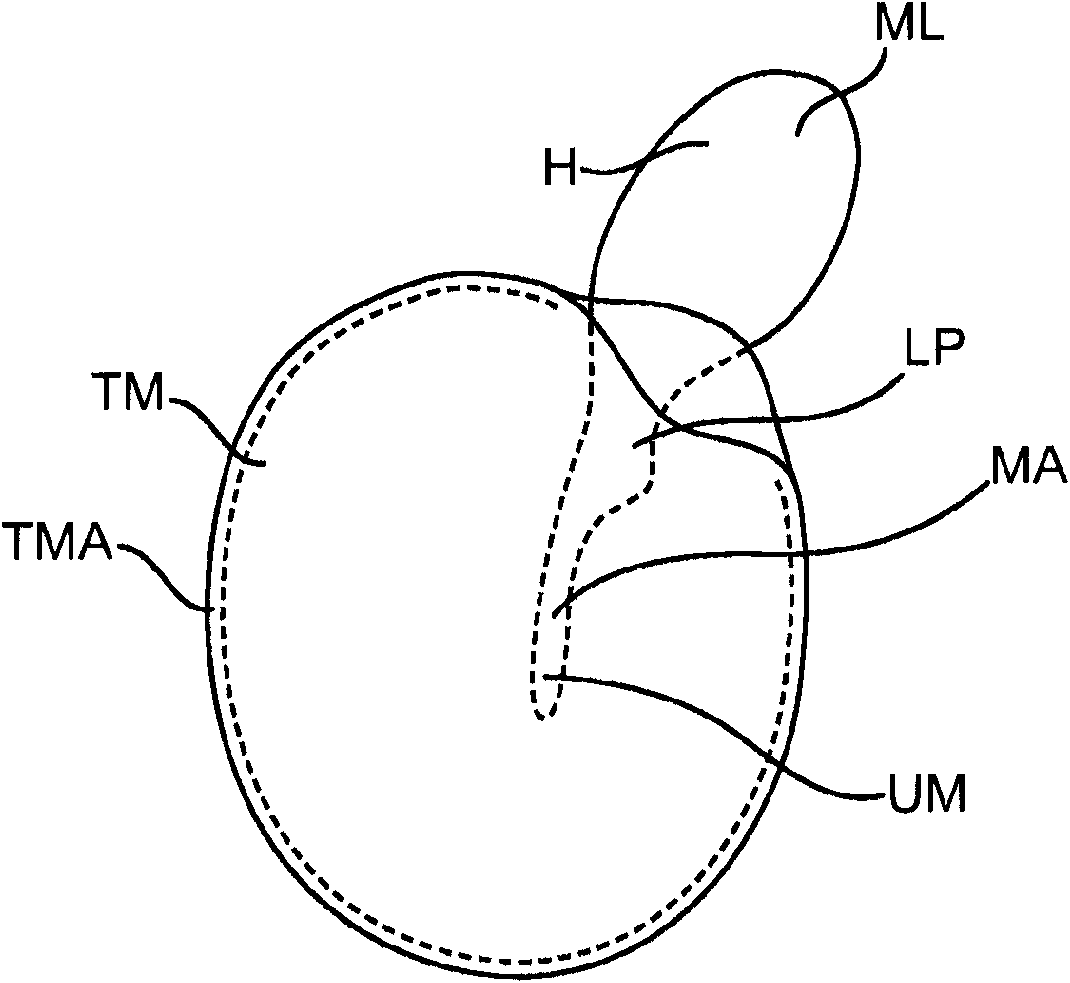
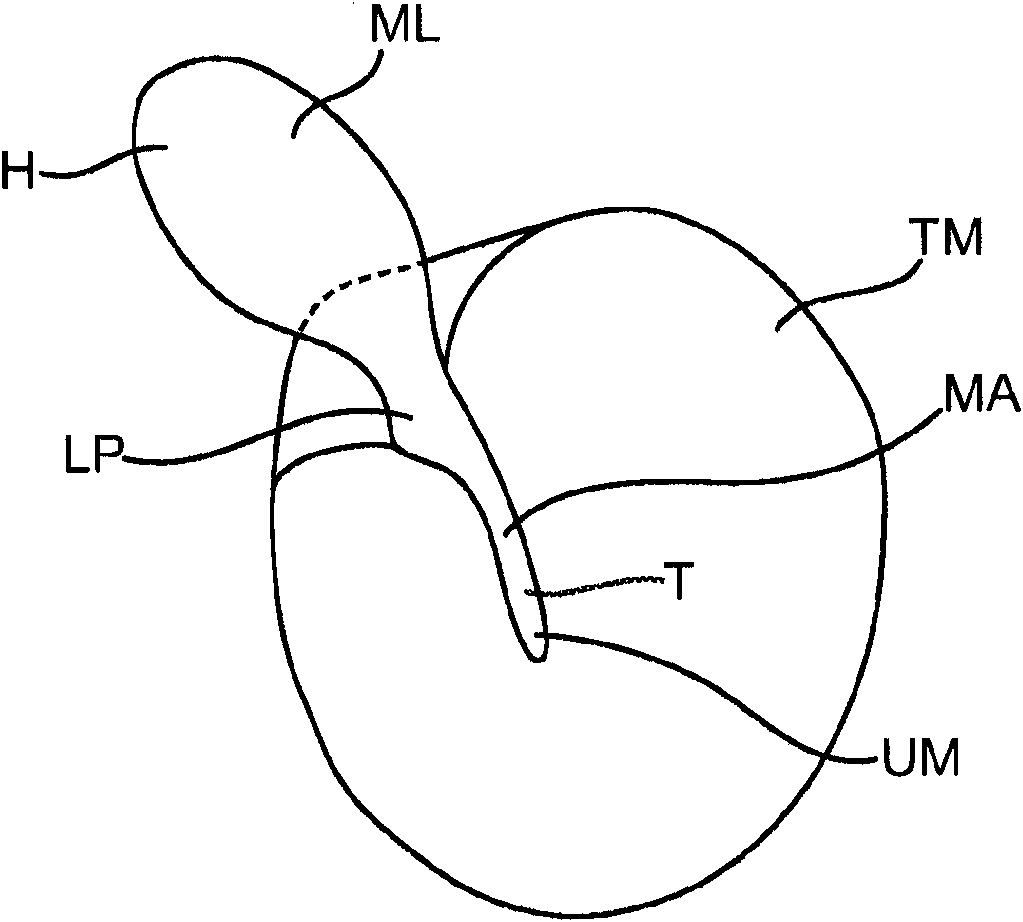
Middle ear implant and method
An improved middle ear implant and method are disclosed. The invention particularly relates to magnetic implants and to attachment devices and methods for mounting a magnet in the middle ear of a patient. The implant comprises a wire-form and a magnet disposed in a housing. The method may comprise the steps of: positioning a magnet in optimal alignment; and attaching said magnet to an ossicle in the middle ear. The method may further comprise the step of using a wire-form to attach the implant to the ossicle. Still further, the method may comprise the step of anchoring the implant to the ossicle with biological cement.
Owner:OTOTRONIX
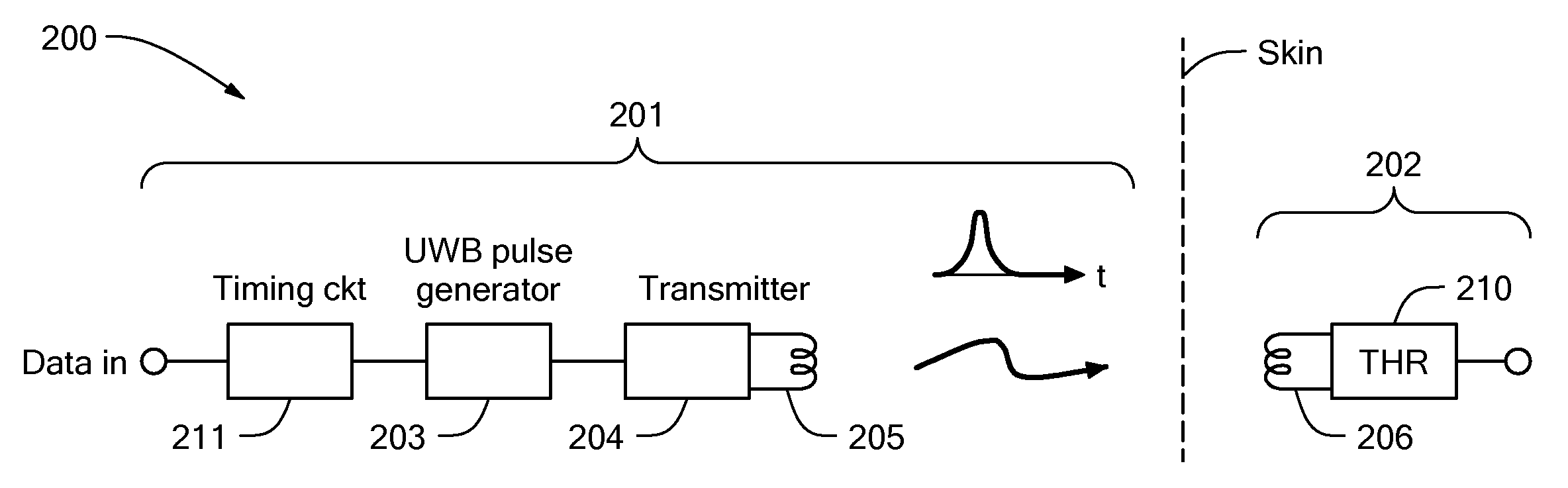
Low power signal transmission
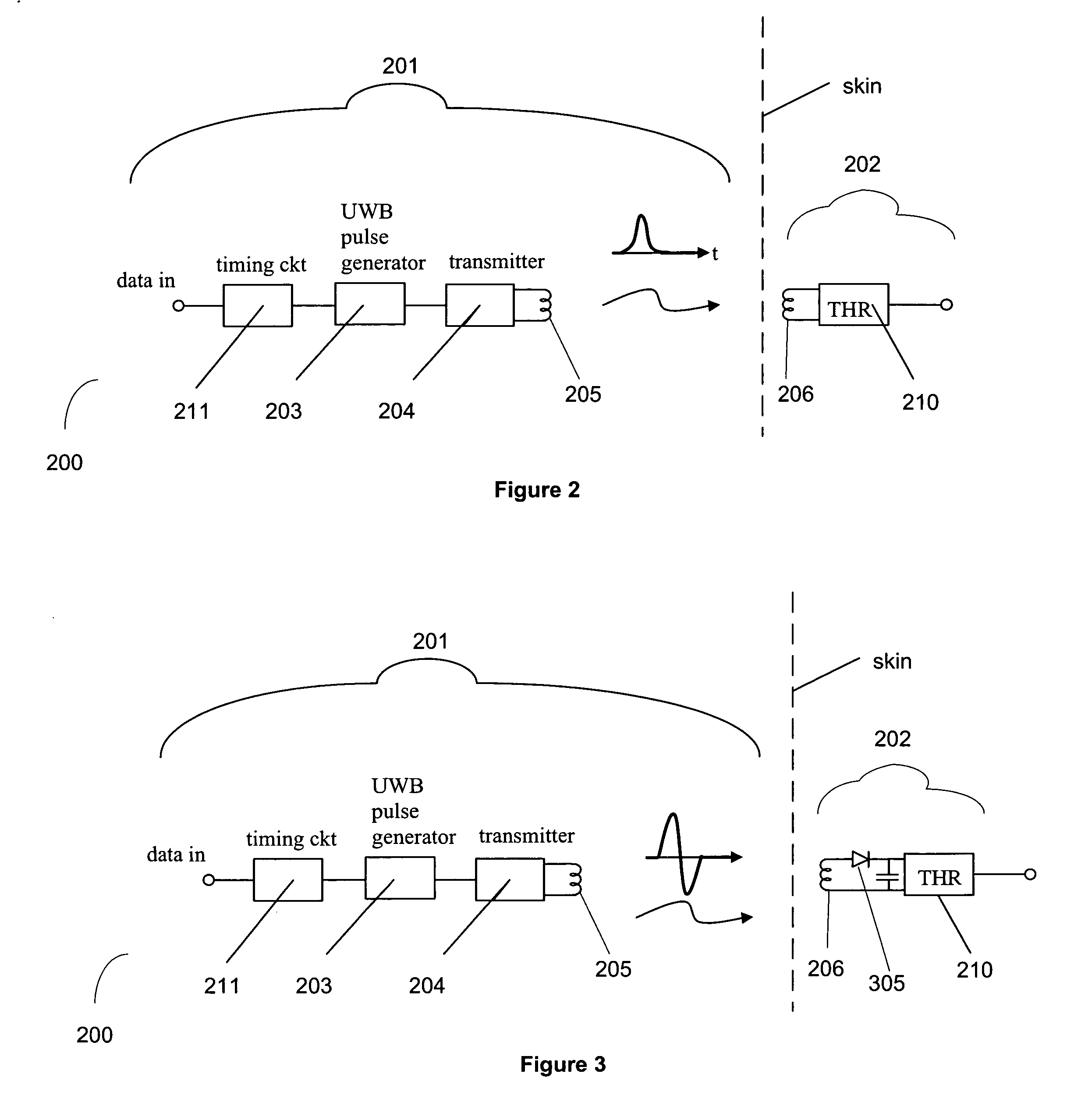
ActiveUS20050283207A1Eliminating low-frequency spectral componentComponent can be removedHead electrodesEar treatmentUltra-widebandAudio power amplifier
A low-power implant system. The system includes an implant for implantation into a person, such as a cochlear implant or a middle ear implant. The implant is capable of communicating with a device via transmission of ultra wideband pulses. The device may be adapted to be worn external to the person, or may be a second implant. So as to conserve battery power, the transmitted ultra wideband pulses may have a low duty cycle of approximately 1 / 1000 or less. Power savings may also be realized by using time-gating amplifiers in the implant and / or device receiver.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
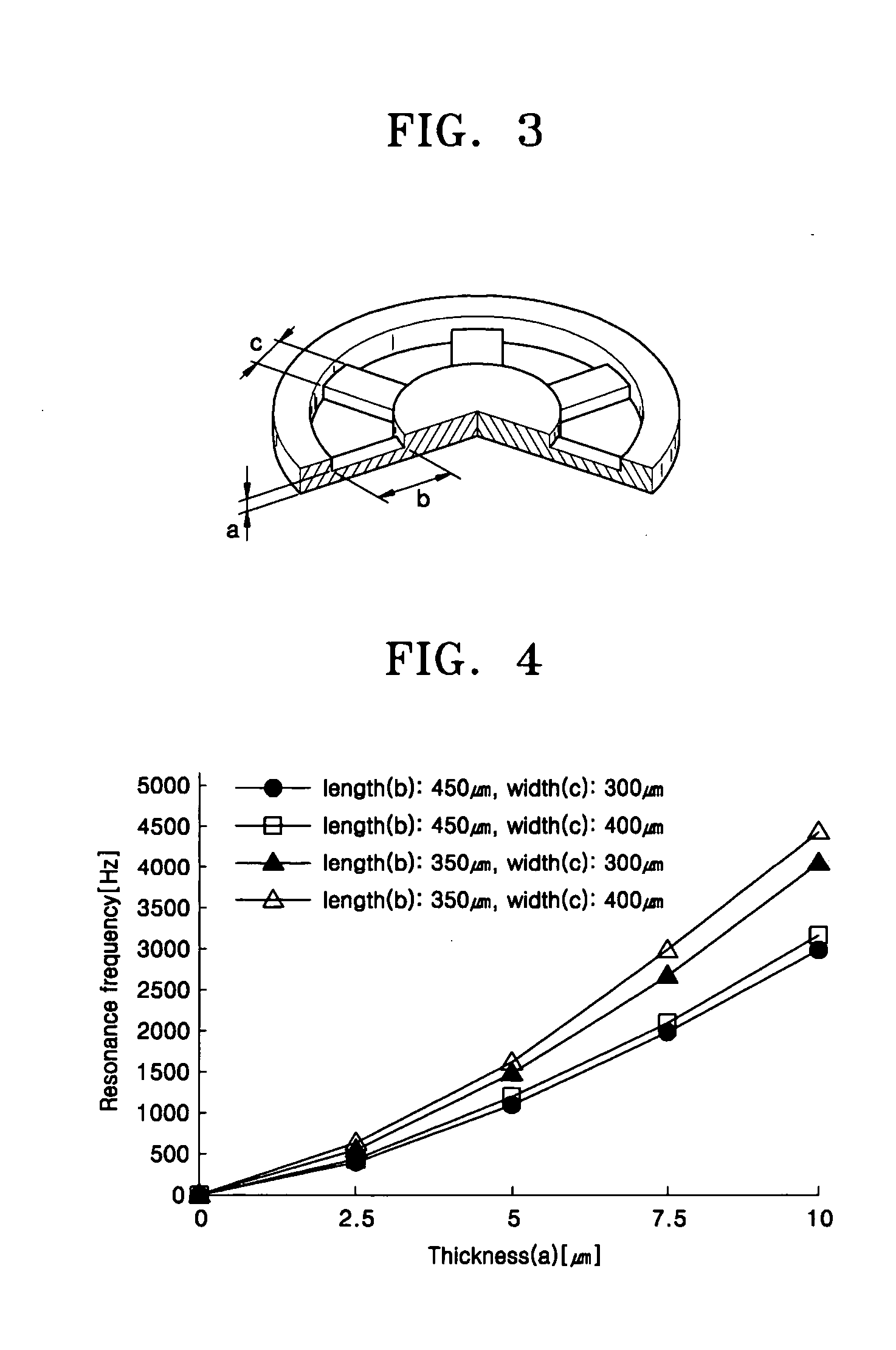
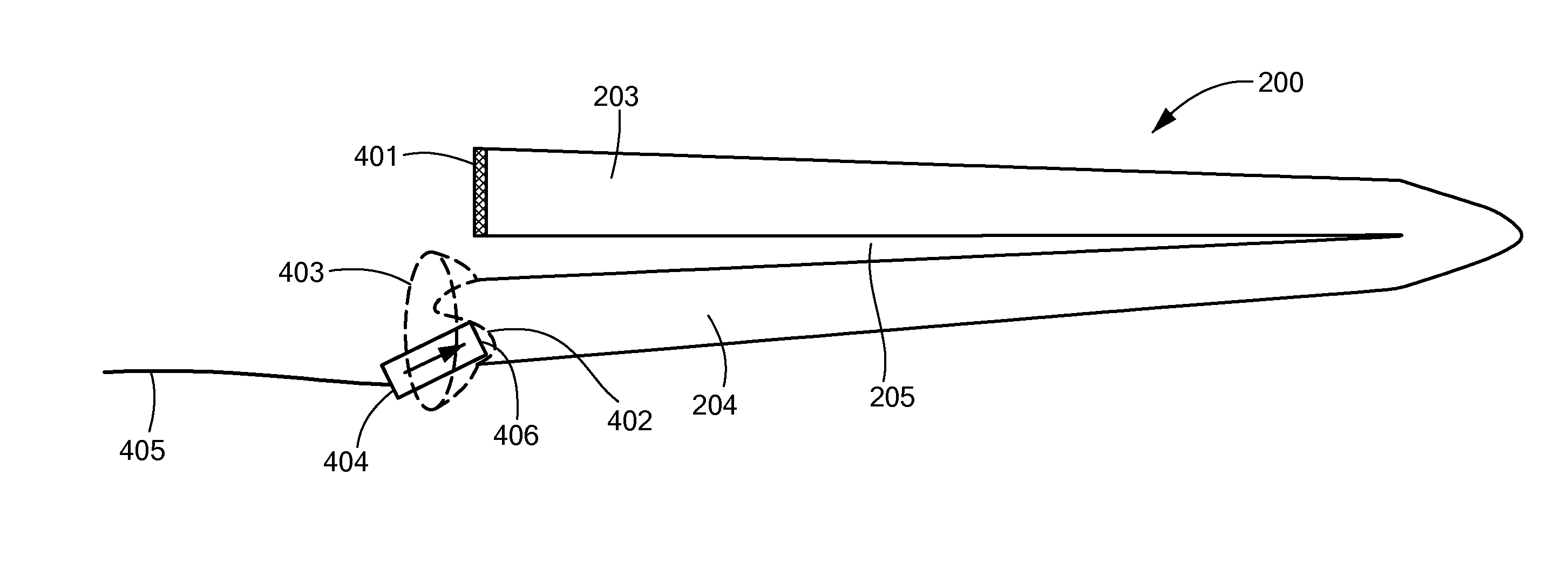
Optimal Pre-Load for Floating Mass Transducers
A middle ear implant arrangement is described which includes an implantable electromechanical transducer with an inner end and an outer end, for converting an input electrical stimulation signal into a corresponding output mechanical stimulation signal. A cochlear engagement member at the inner end of the transducer has a cochlear engagement surface for coupling the mechanical stimulation signal to an outer cochlear surface of a recipient patient. A transducer loading structure has: i. an inner end adapted to releasably engage the transducer, ii. an outer end elongated along a central end axis for engaging a fixed anatomical structure within the middle ear of the recipient patient, and iii. a center spring structure connecting the inner end and the outer end and adapted to expand along a central spring axis to develop a spring force between the fixed anatomical structure and the outer end of the transducer.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Middle ear implant transducer and vibrating member adapted thereto
Provided are a middle ear implant transducer and a method of manufacturing a vibrating member adapted to the transducer. The middle ear implant transducer of a hearing aid includes: first and second permanent magnets arranged such that the same poles of the first and second permanent magnets face each other; first and second vibrating members attached to both edges of the respective first and second permanent magnets; a coil enclosing the first and second permanent magnets and being separated a predetermined distance from the outer surfaces of the first and second permanent magnets between the first vibrating member and the second vibrating member; and first and second covers mounted on the outer surfaces of the first and second vibrating members, wherein the first and second vibrating members comprise couplers respectively attached to the first and second permanent magnets, rims respectively attached to the edges of the first and second covers, and support films respectively connecting the couplers to the rims and being thinner than the couplers and the rims.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Low power signal transmission
A low-power implant system. The system includes an implant for implantation into a person, such as a cochlear implant or a middle ear implant. The implant is capable of communicating with a device via transmission of ultra wideband pulses. The device may be adapted to be worn external to the person, or may be a second implant. So as to conserve battery power, the transmitted ultra wideband pulses may have a low duty cycle of approximately 1 / 1000 or less. Power savings may also be realized by using time-gating amplifiers in the implant and / or device receiver.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
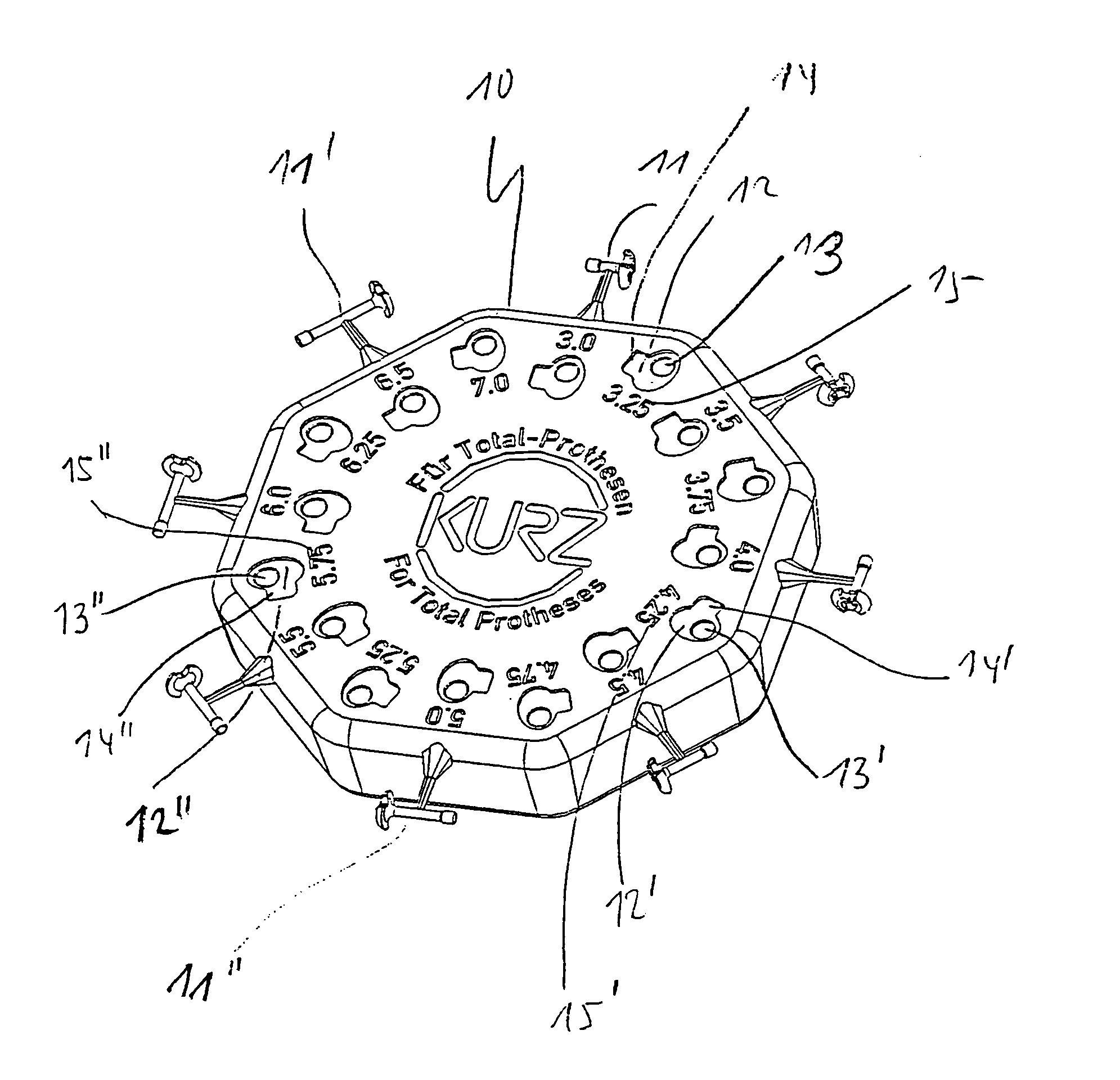
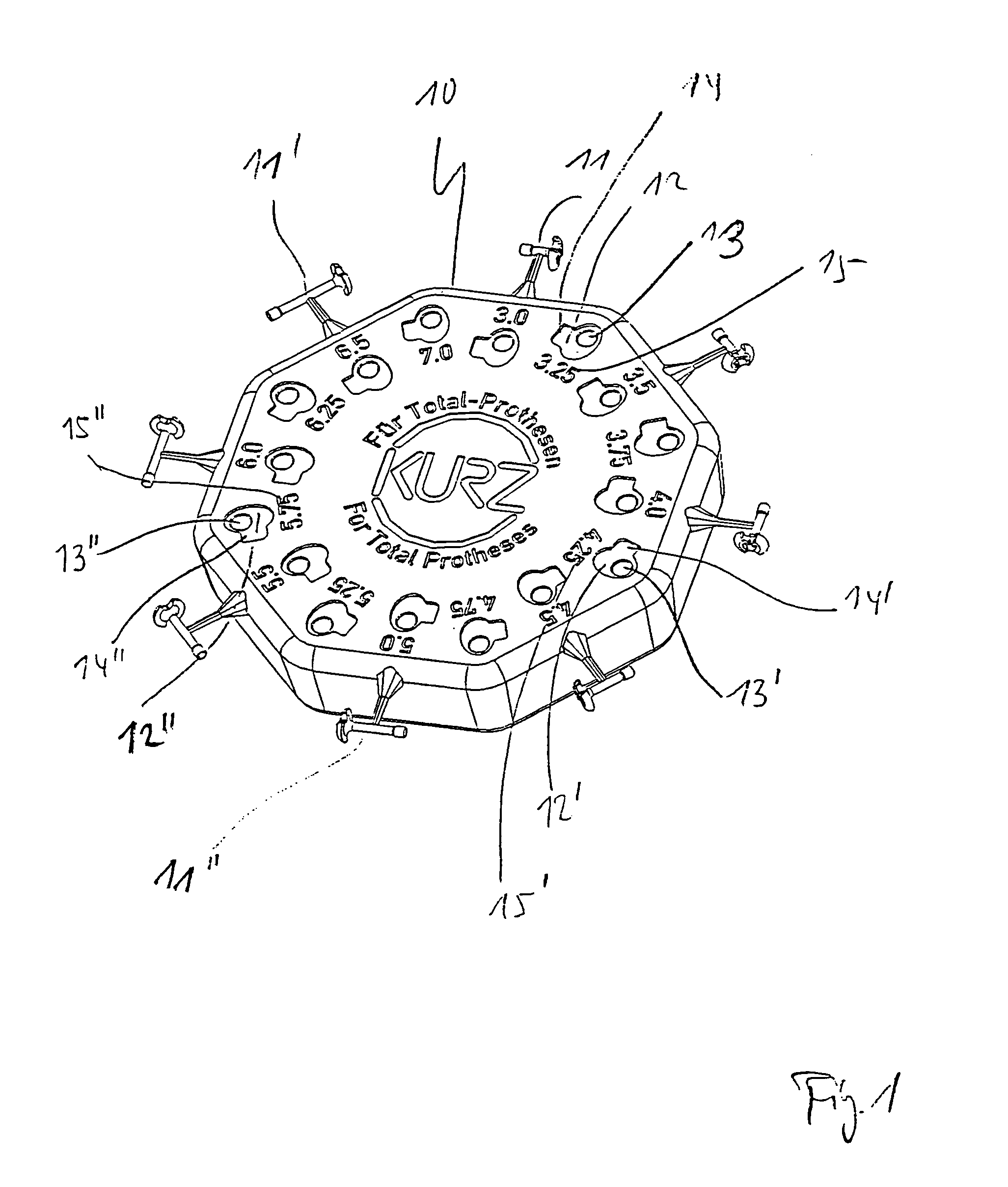
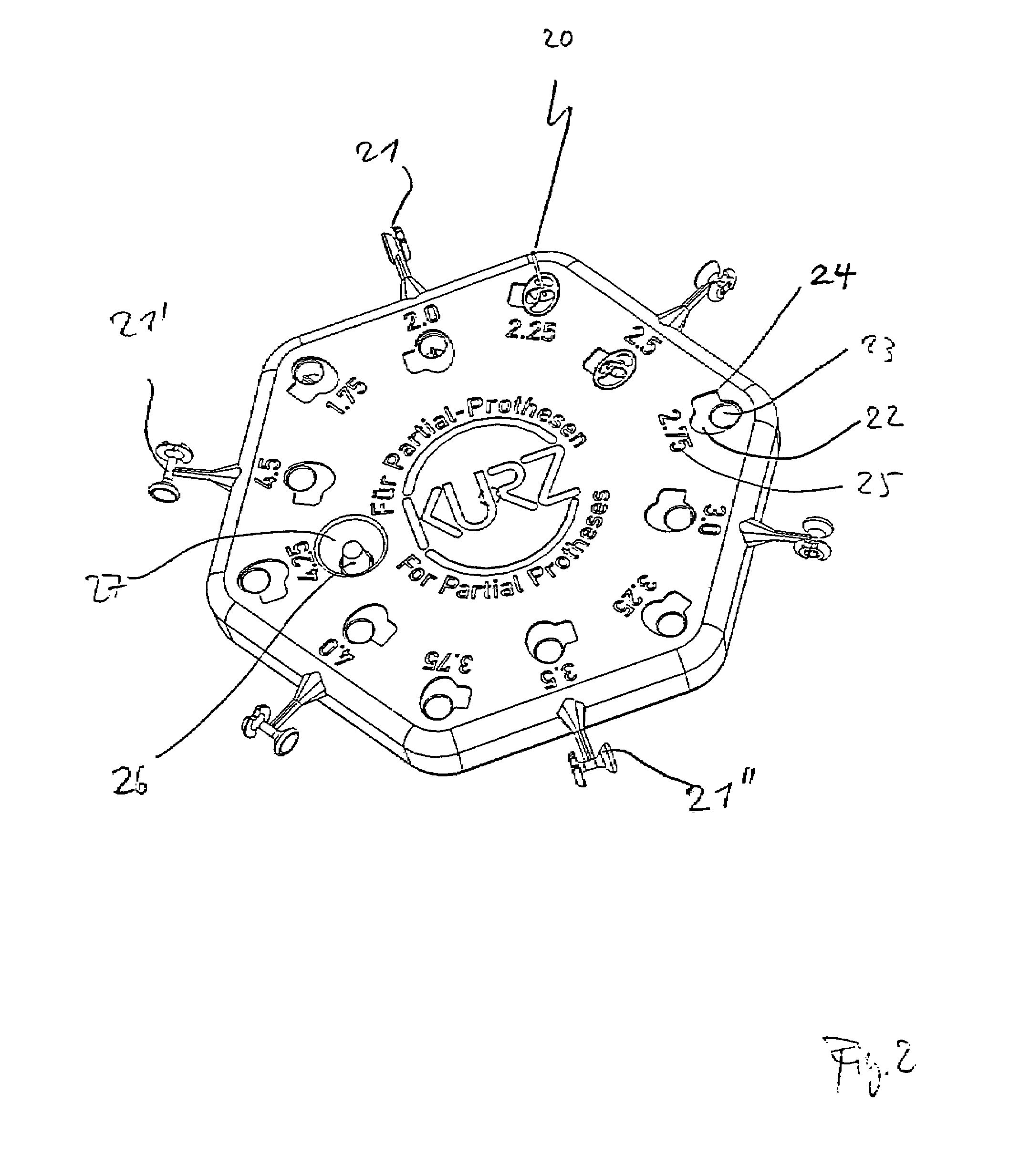
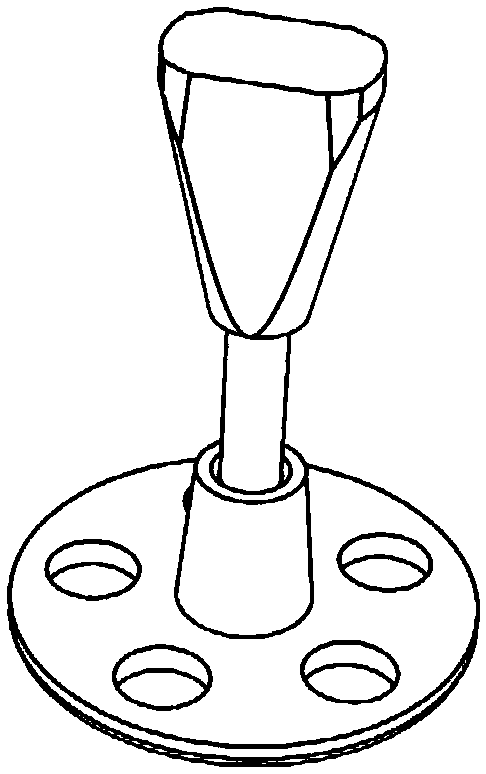
Device for adjusting the length of middle ear implants
ActiveUS7603788B2Easy to operateSimple wayElectrotherapySurgical furnitureMiddle ear functionProsthesis
A device for determining the required length of a middle ear prosthesis, having a disk-shaped base part to which prosthesis mockups or prostheses of different lengths are fastened, which, after being detached from the base part, can be inserted by an applicator into the middle ear of a patient during an operation for length determination purposes, in which the base part is provided with accessories for measuring and / or shaping the middle ear prosthesis to be inserted, so that this provides the operator with an even more simplified handling of prosthesis mockups or prostheses during the operation; no additional separate parts have to be used and instead, the handling means are compactly provided on or integrated into the device itself.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Impact Protection for Implantable Electric Lead
ActiveUS20140214145A1Improve energy absorptionHead electrodesExternal electrodesCochlear implantationMiddle Ear Implant
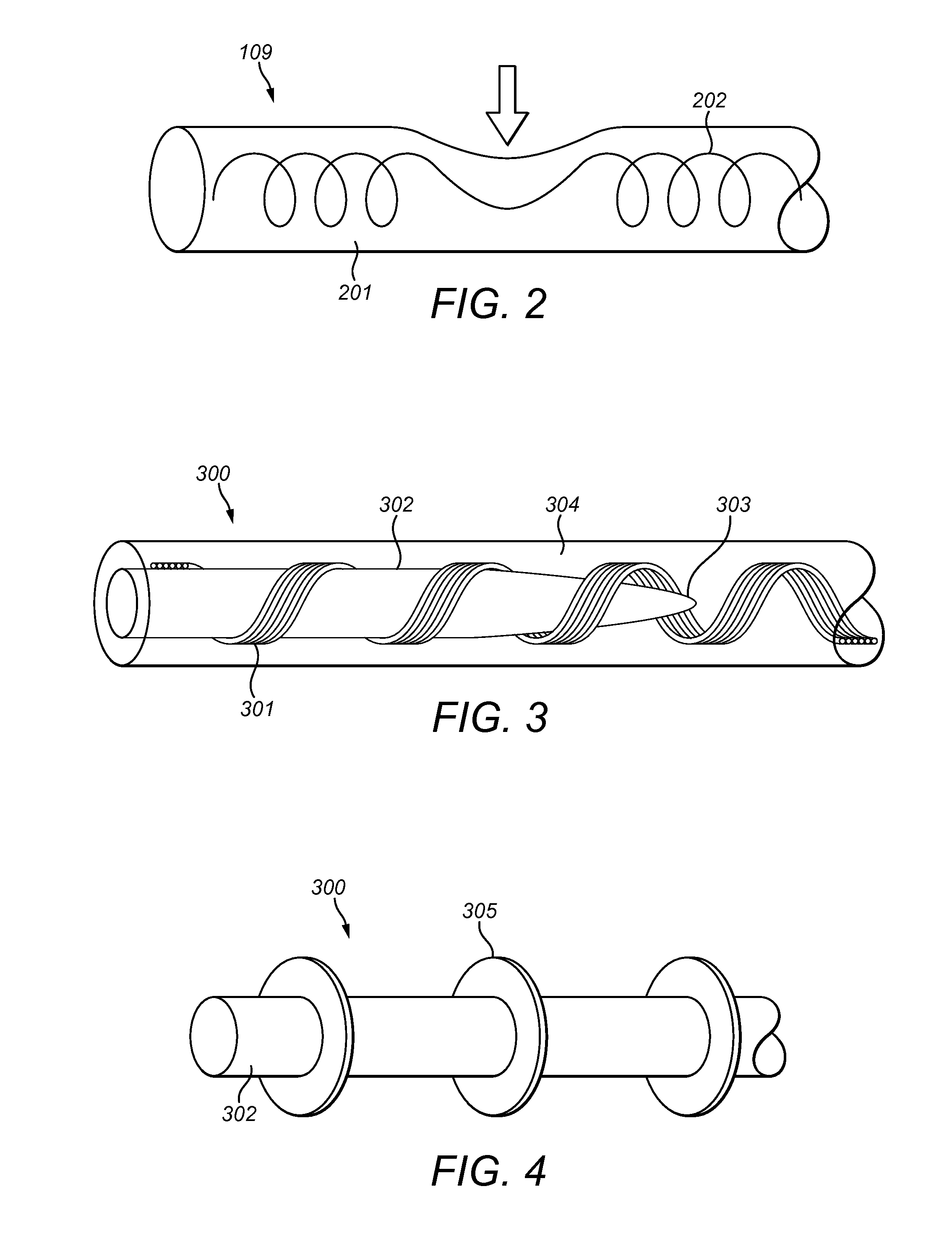
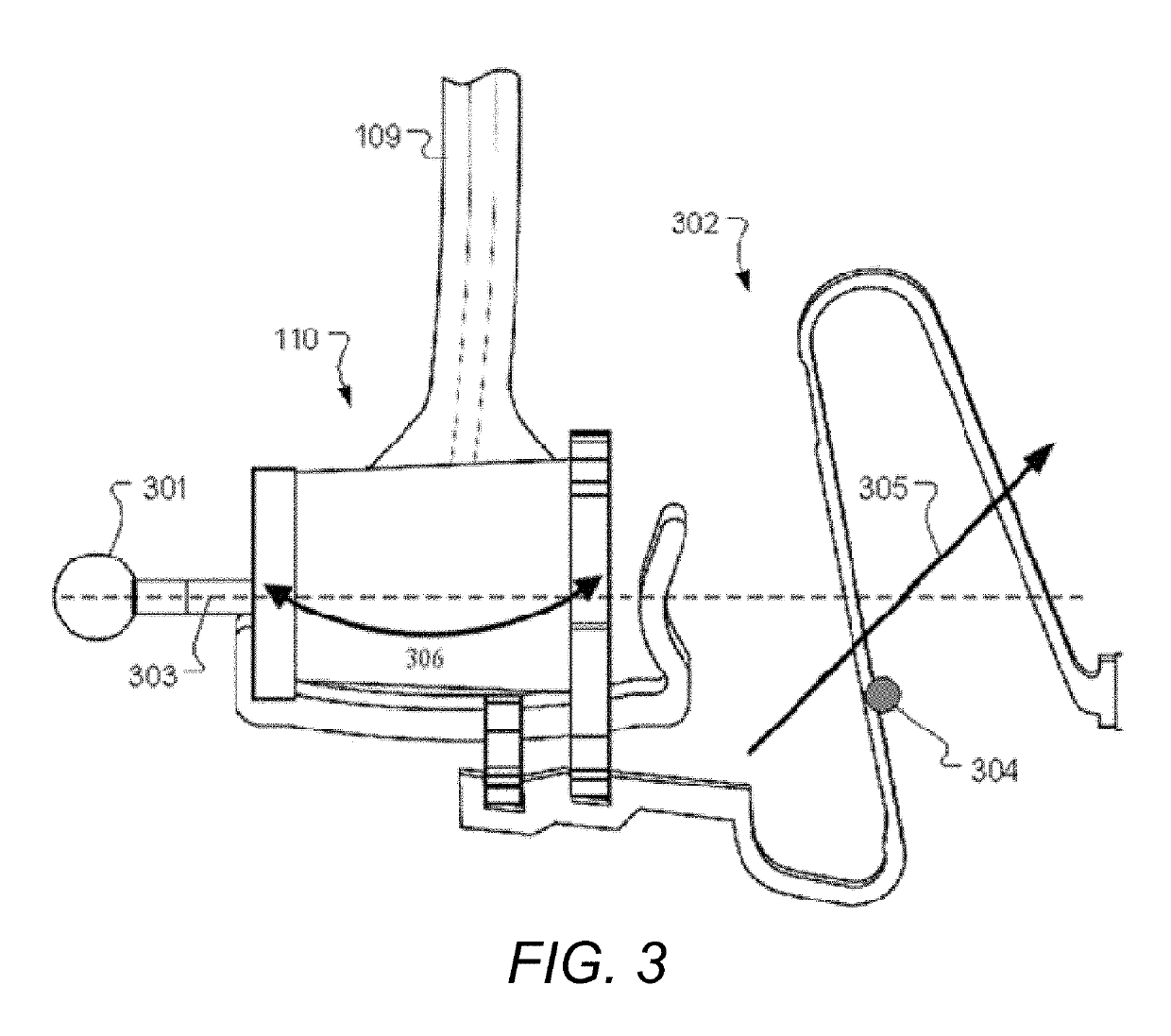
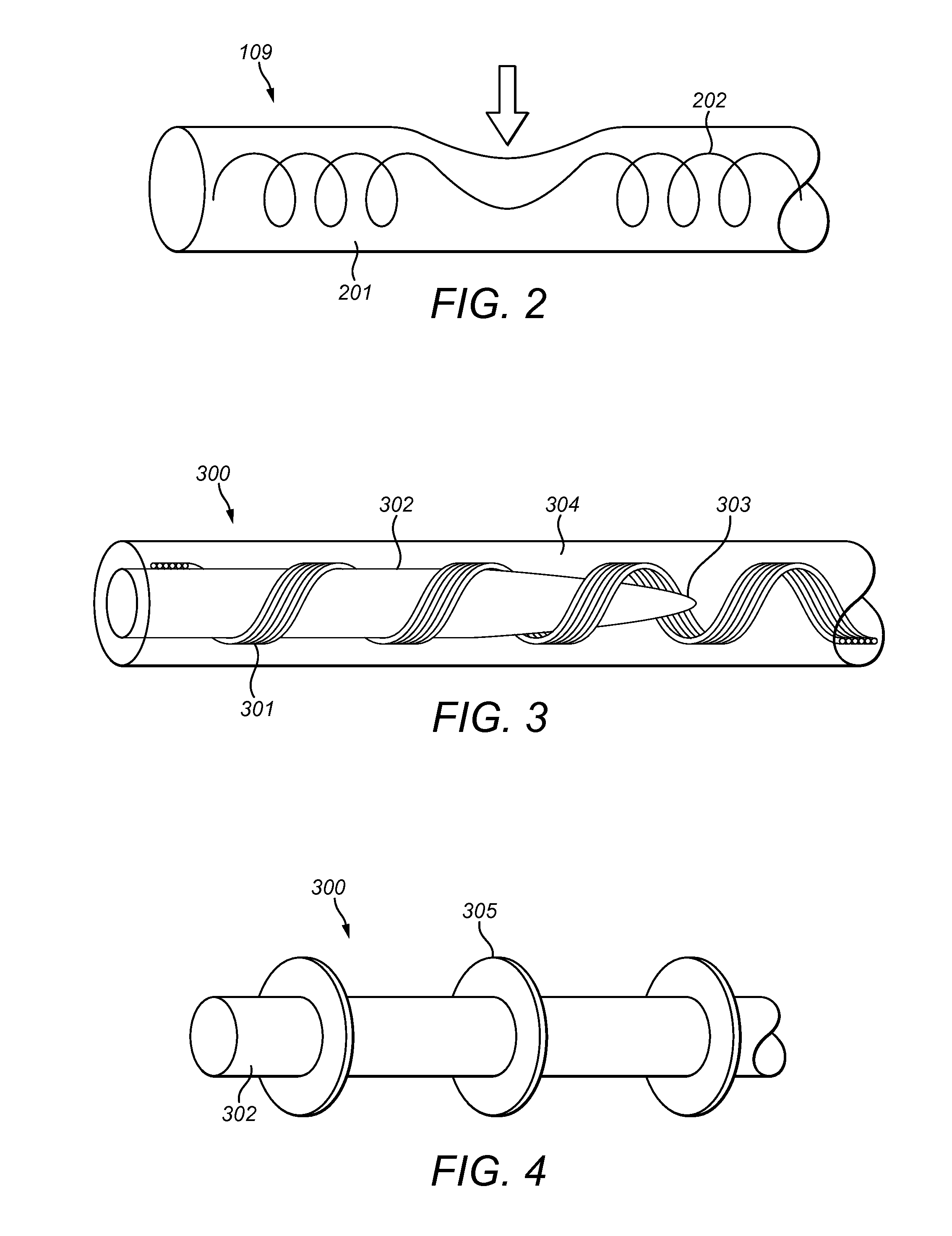
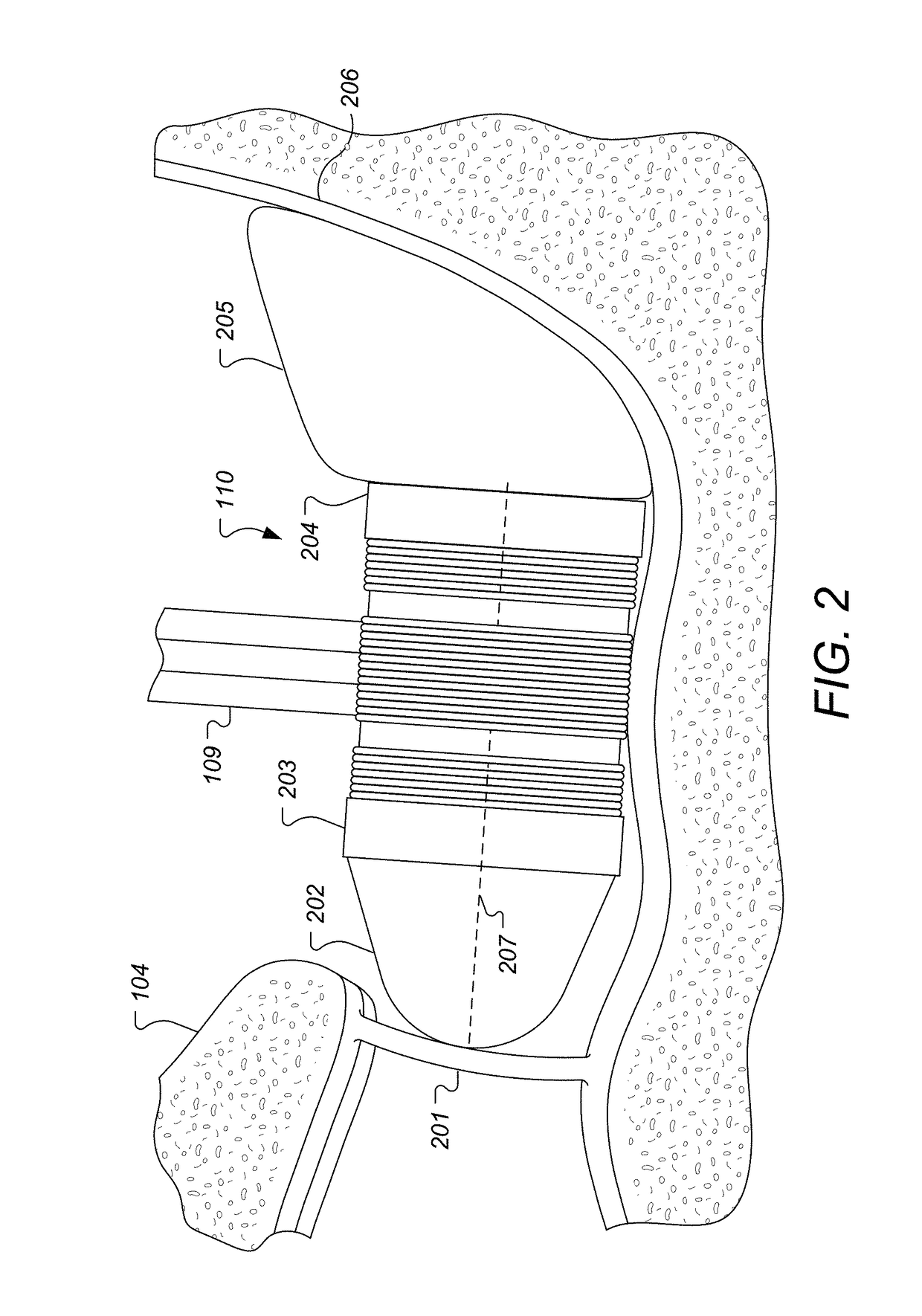
A novel implantable electric lead arrangement is described for medical implant systems such as middle ear implants (MEI), cochlear implants (CI) and vestibular implants (VI). An electric lead contains parallel lead wires wound in an elongated helix about a central longitudinal axis. A lead core is fixed and enclosed within the wire helix for providing impact strain relief to the lead wires by resisting radial and / or axial deformation from external impact force.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Optimal pre-load for floating mass transducers
A middle ear implant arrangement is described which includes an implantable electromechanical transducer with an inner end and an outer end, for converting an input electrical stimulation signal into a corresponding output mechanical stimulation signal. A cochlear engagement member at the inner end of the transducer has a cochlear engagement surface for coupling the mechanical stimulation signal to an outer cochlear surface of a recipient patient. A transducer loading structure has: i. an inner end adapted to releasably engage the transducer, ii. an outer end elongated along a central end axis for engaging a fixed anatomical structure within the middle ear of the recipient patient, and iii. a center spring structure connecting the inner end and the outer end and adapted to expand along a central spring axis to develop a spring force between the fixed anatomical structure and the outer end of the transducer.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
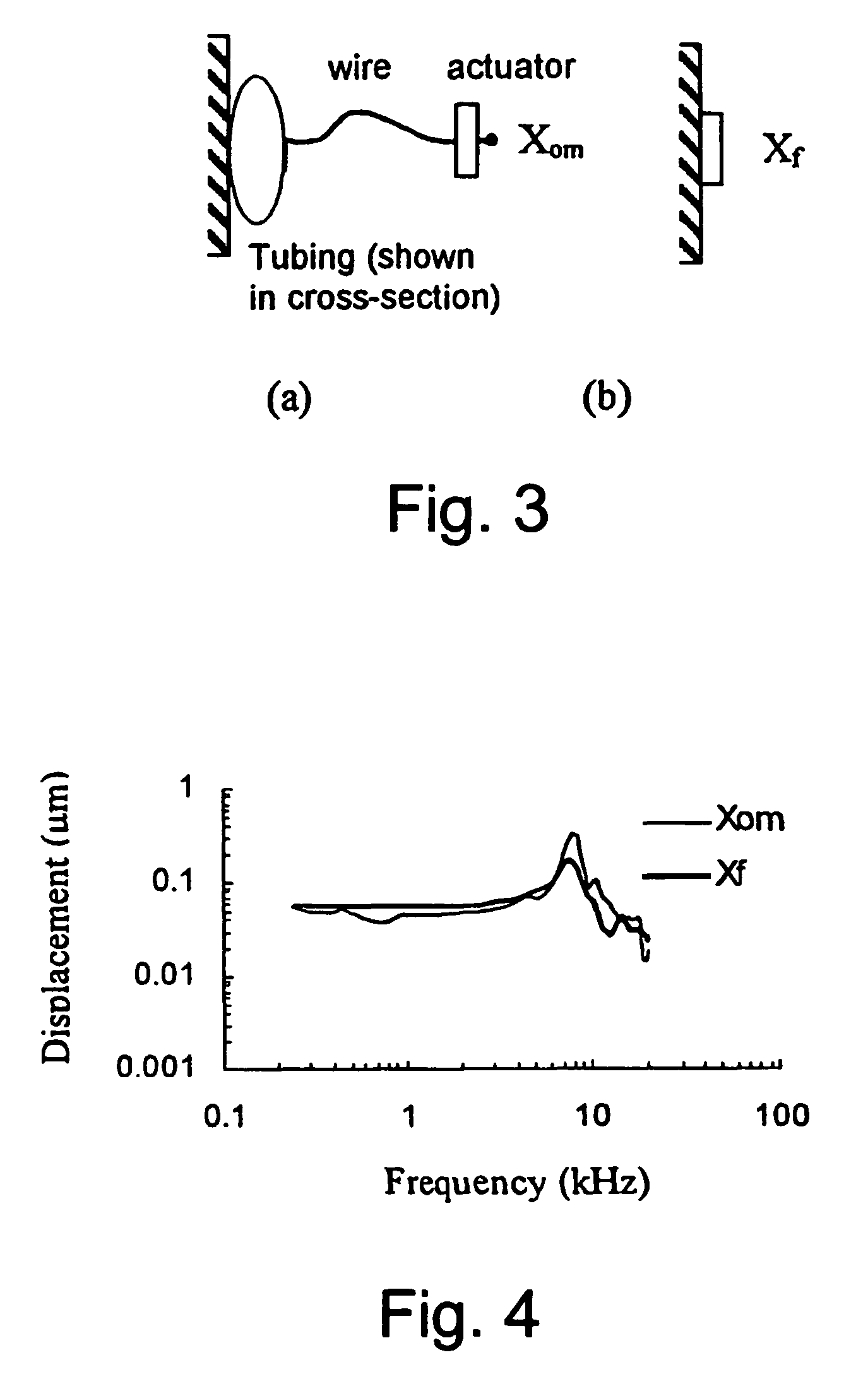
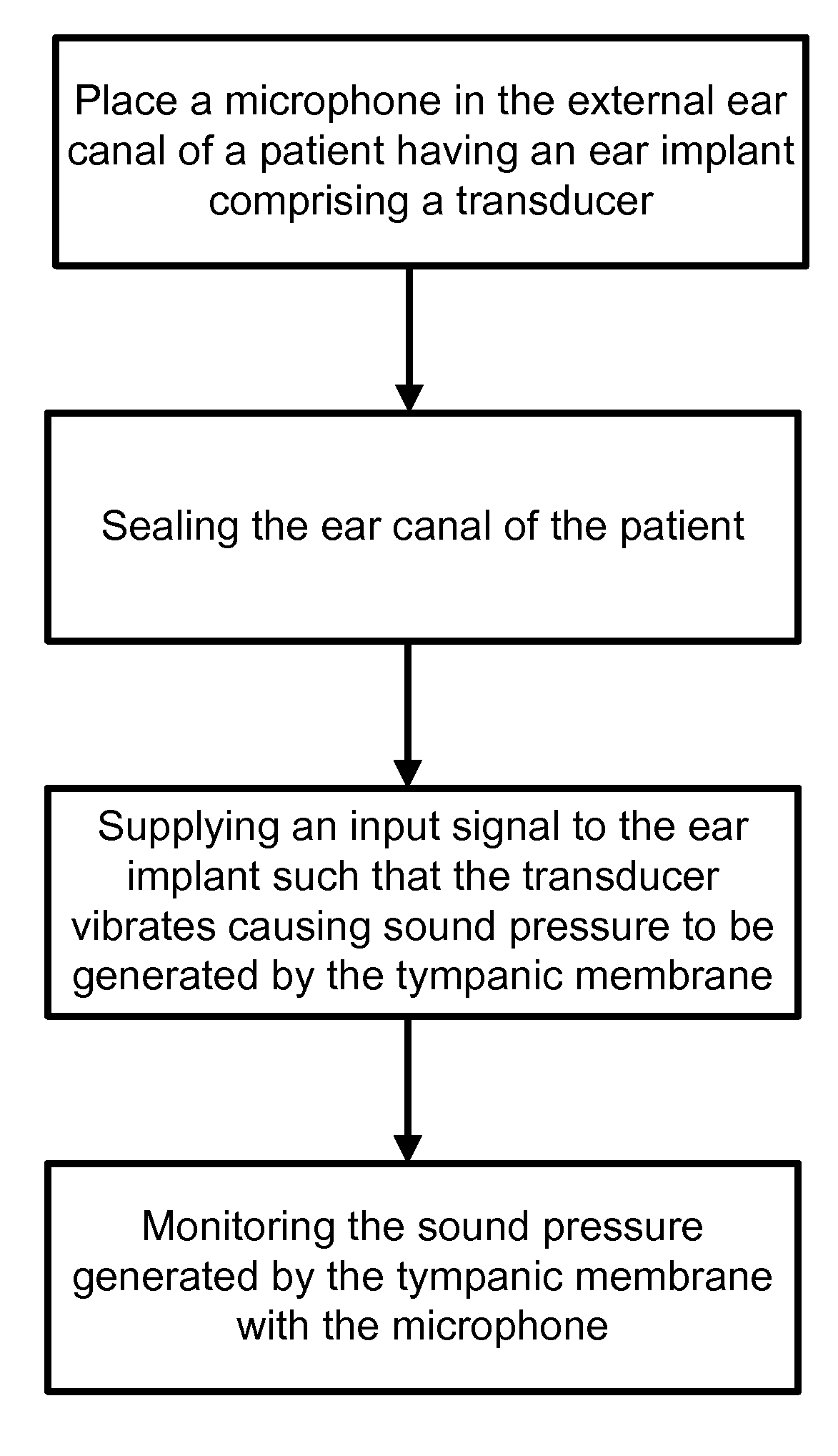
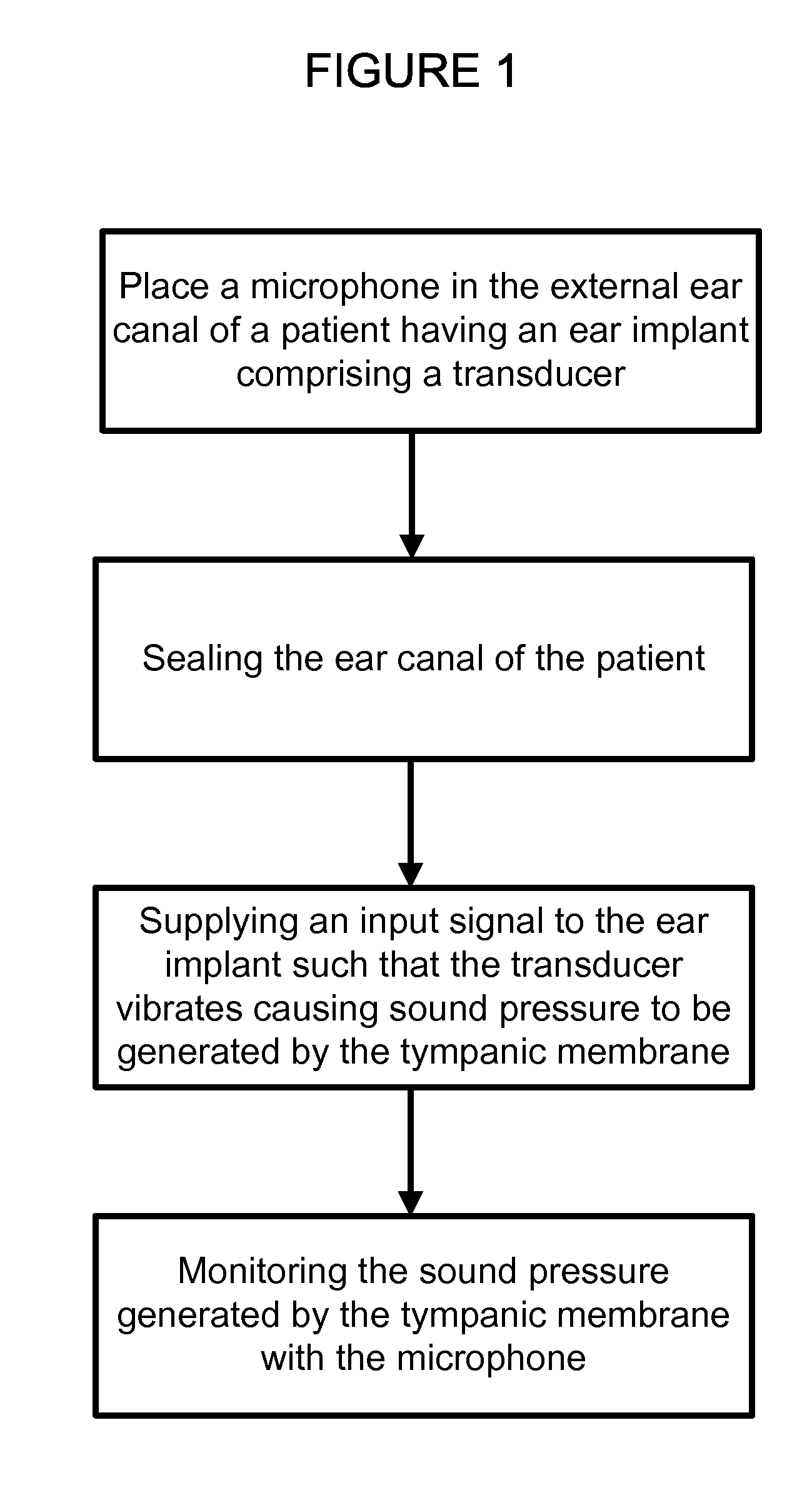
Soundbridge test system
The present invention relates to the field of devices and methods for improving testing of hearing devices, including soundbridges and direct drive middle ear implants. In particular, the present invention provides a microphone system utilizing reverse transfer function to assess the operability of implanted hearing improvement devices, including but not limited to soundbridges and direct drive middle ear implants.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Soundbridge test system
The present invention relates to the field of devices and methods for improving testing of hearing devices, including soundbridges and direct drive middle ear implants. In particular, the present invention provides a microphone system utilizing reverse transfer function to assess the operability of implanted hearing improvement devices, including but not limited to soundbridges and direct drive middle ear implants.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Improved middle ear implant and method
InactiveCN102696243AHas superelastic propertiesHave plastic propertiesEar supported setsImplantable hearing aidsBone tissueBioadhesive
Owner:OTOTRONIX
Middle Ear Implant for Otosclerosis
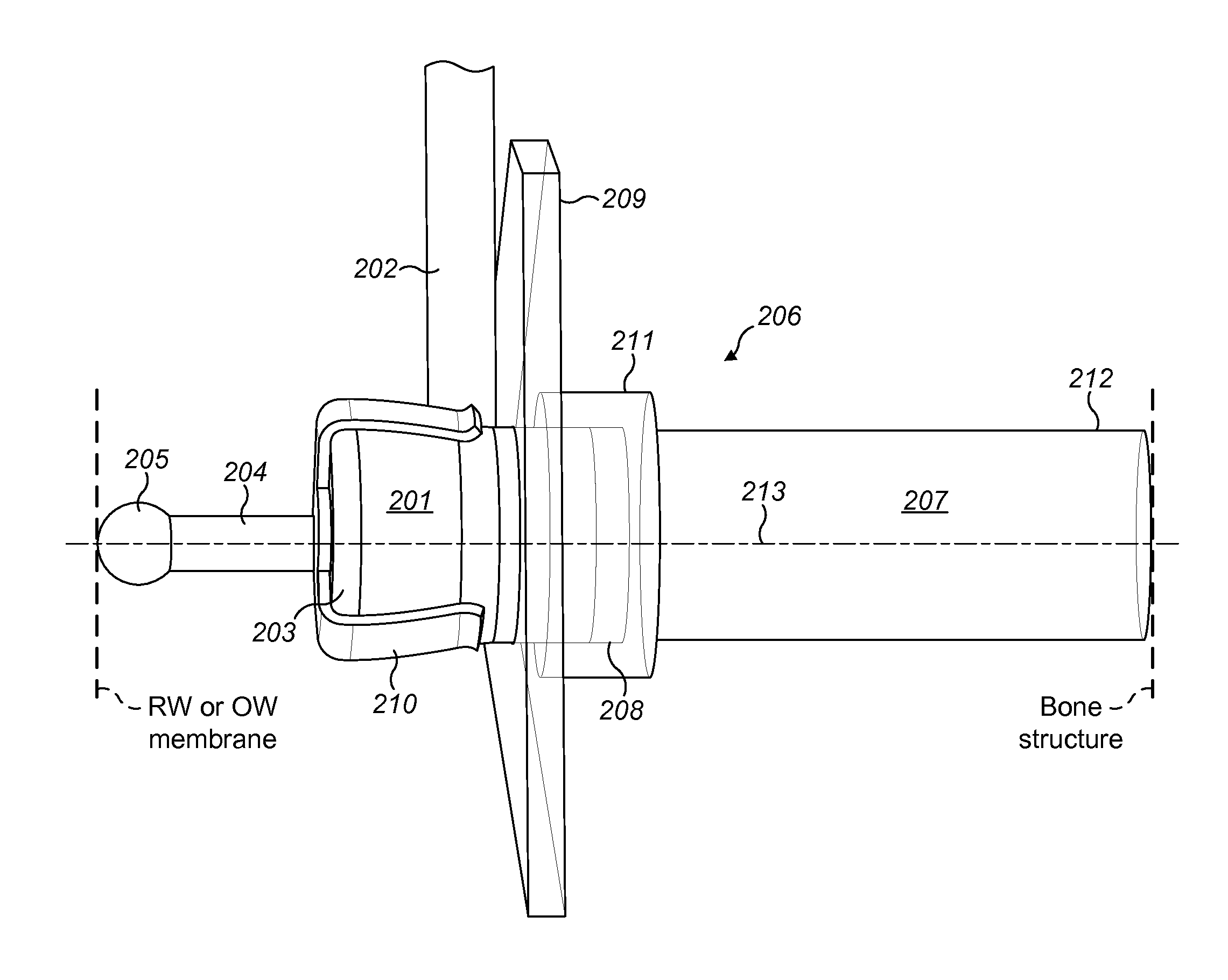
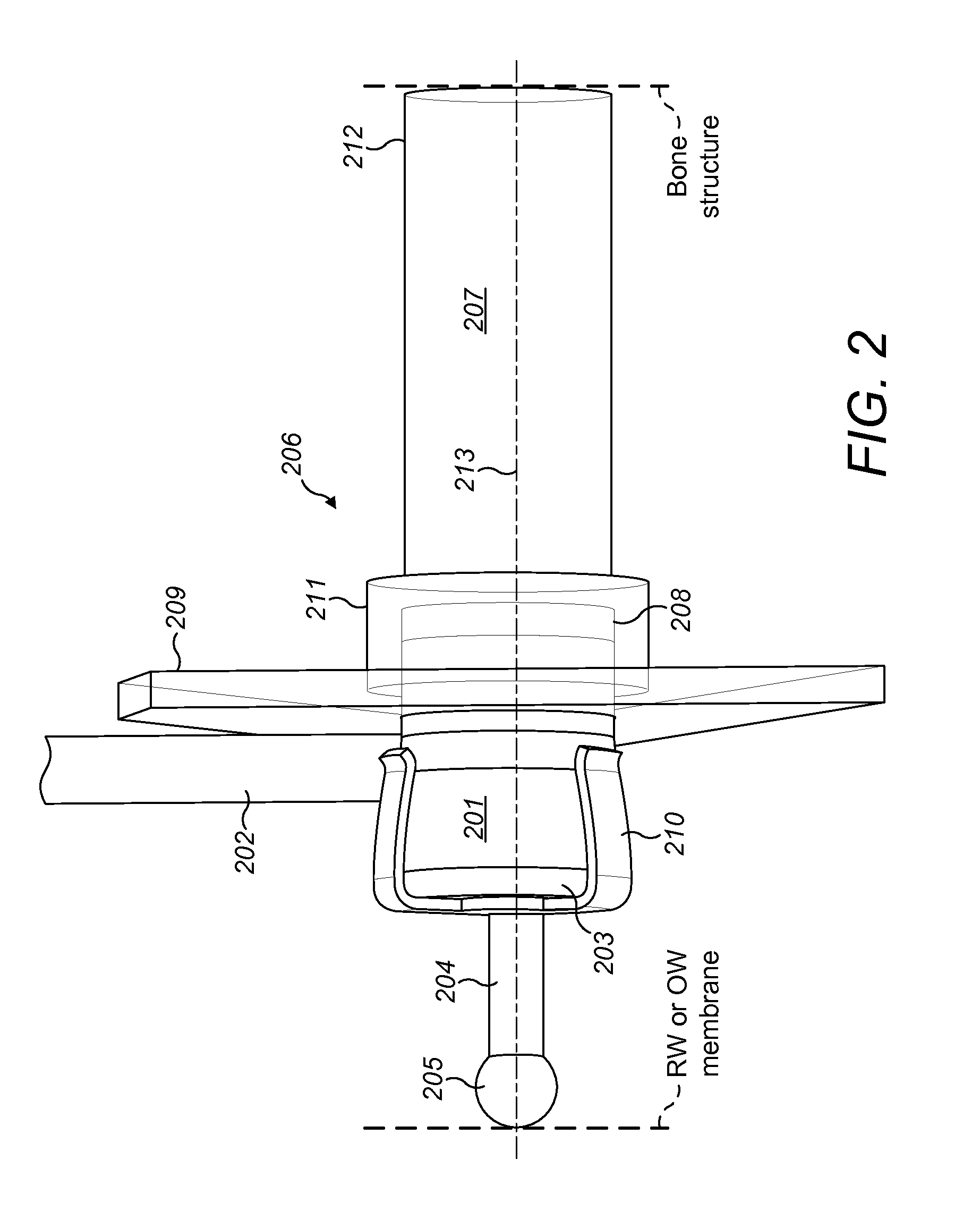
A middle ear transducer arrangement is described for engaging a round window membrane of a patient cochlea. A mechanical transducer is surgically implantable into a fixed position in the round window niche of the patient cochlea adjacent to the round window membrane. A drive face on the outer surface of the transducer has a diameter less than half the diameter of the round window membrane. The fixed position of the transducer engages the drive face against a side section of the round window membrane without engaging the center point to generate an acoustic stimulation signal for perception as sound.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Middle ear implant for otosclerosis
A middle ear transducer arrangement is described for engaging a round window membrane of a patient cochlea. A mechanical transducer is surgically implantable into a fixed position in the round window niche of the patient cochlea adjacent to the round window membrane. A drive face on the outer surface of the transducer has a diameter less than half the diameter of the round window membrane. The fixed position of the transducer engages the drive face against a side section of the round window membrane without engaging the center point to generate an acoustic stimulation signal for perception as sound.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Optically coupled acoustic middle ear implant systems and methods
An assembly comprising a sound transducer can be implanted in the middle ear in a manner that simplifies surgery. The assembly may comprise a narrow cross-sectional profile such that the assembly can be positioned in the middle ear through an incision in the eardrum, for example without cutting bone. The incision can be closed and electromagnetic energy transmitted through the closed incision to a transducer configured to vibrate the ear in response to the electromagnetic energy. In many embodiments, the sound transducer comprises a speaker positioned in the middle ear, and the sound transducer can couple to vibratory structure of the ear with air so as to simplify surgery. The assembly may be affixed to a substantially fixed structure of the ear, for example the promontory, so as to inhibit user perceivable occlusion and inhibit motion of the assembly, such that the user can perceive clear sound with little occlusion.
Owner:SOUNDBEAM
Middle ear implant for otosclerosis
A middle ear transducer arrangement is described for engaging a round window membrane of a patient cochlea. A mechanical transducer is surgically implantable into a fixed position in the round window niche of the patient cochlea adjacent to the round window membrane. A drive face on the outer surface of the transducer has a diameter less than half the diameter of the round window membrane. The fixed position of the transducer engages the drive face against a side section of the round window membrane without engaging the center point to generate an acoustic stimulation signal for perception as sound.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Moving coil actuator for middle ear implants
A hearing enhancement includes an audio processor that generates an electrical audio signal and transmits the signal to a coil. The coil is implanted into a patient in a position that results in transmission of mechanical stimulation to the inner ear when the coil is spatially displaced. A permanent magnet is placed in proximity to the coil so that when the coil receives the electrical audio signal form the processor, the induced coil magnetic field in the coil interacts with the magnetic field from the permanent magnet to spatially displace the coil and, as a result, transmit the mechanical stimulation to the inner ear.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
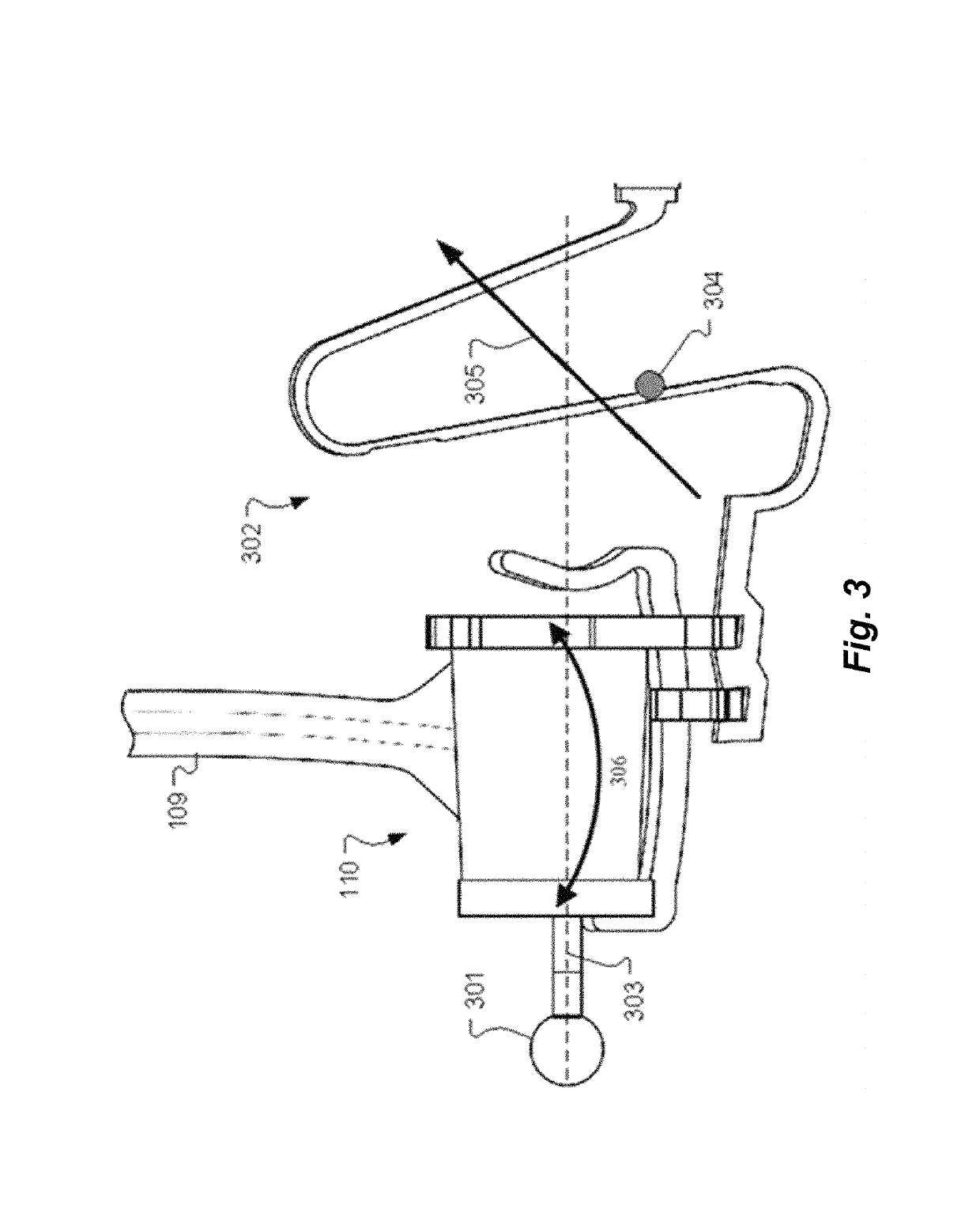
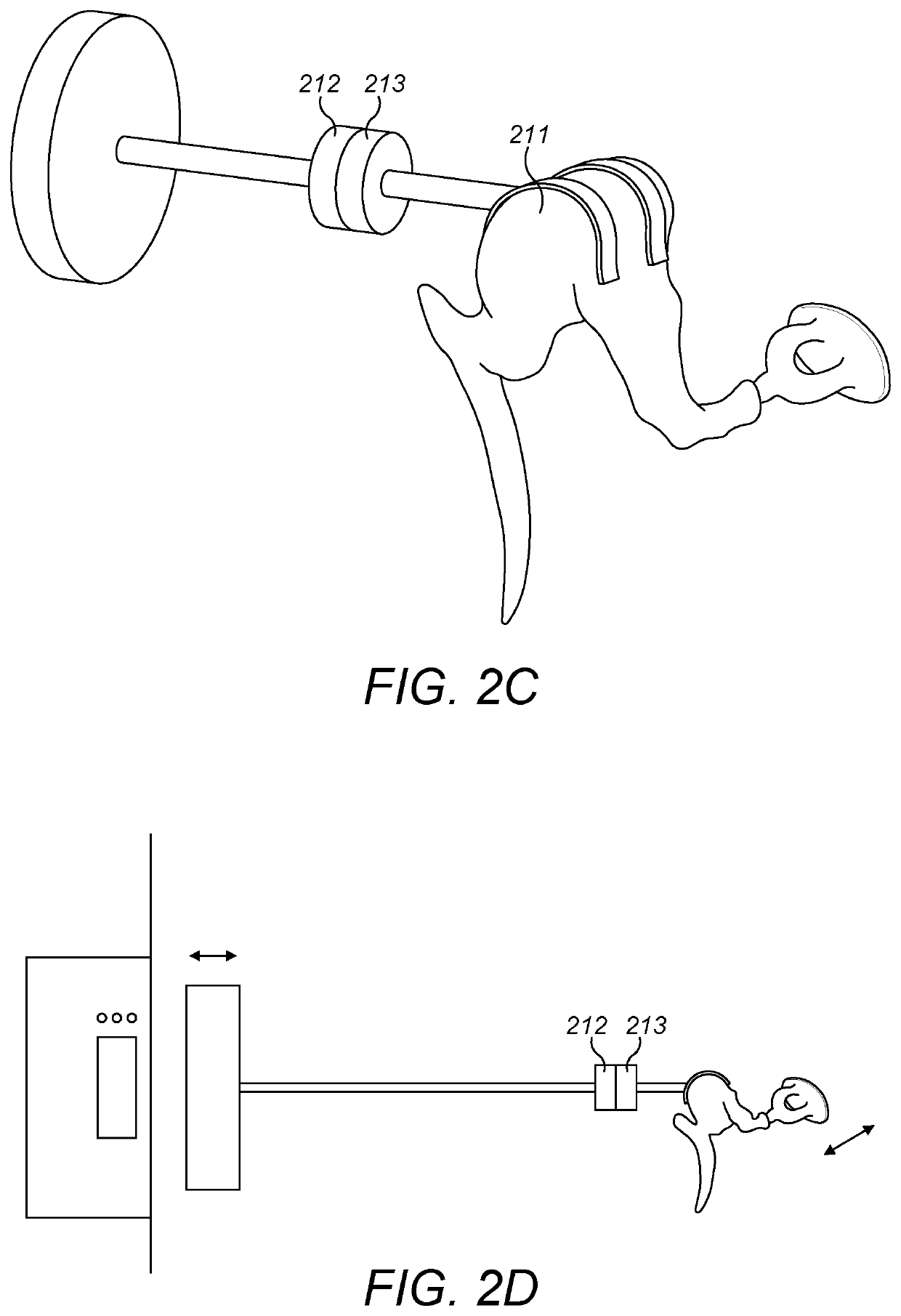
Pre-Load Feedback of a Middle-Ear Coupler
A coupling device for a middle ear implant includes a transducer end configured to engage an implantable electromechanical transducer, a bone engagement end configured to engage a temporal bone surface of a recipient patient, a planar loading spring located between the transducer end and the bone engagement end and configured for compression by displacement of the transducer end and the bone engagement end in towards each other, and compression indicators configured to provide visual indication of a pre-load force created on the temporal bone surface by the compression of the loading spring.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Middle ear implant
ActiveCN101690266BPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersDeaf-aid setsMiddle ear functionTransducer
A hearing actuator (10) for implantation in the middle ear of a user. The actuator comprises transducer means (for example a piezoelectric device) (12) for converting electrical input signals into mechanical vibrations, and attachment means (16) for attaching one end of the transducer means to a first part of the middle ear. The actuator also comprises contacting means (14) which extends from an opposite end of the transducer means such that a longitudinal axis of the contacting means is substantially parallel to a longitudinal axis of the transducer means. The contacting means is for contacting a second part of the middle ear (to which it may be attached), so as to transmit the mechanical vibrations of the transducer means thereto.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Universal Bone Conduction and Middle Ear Implant
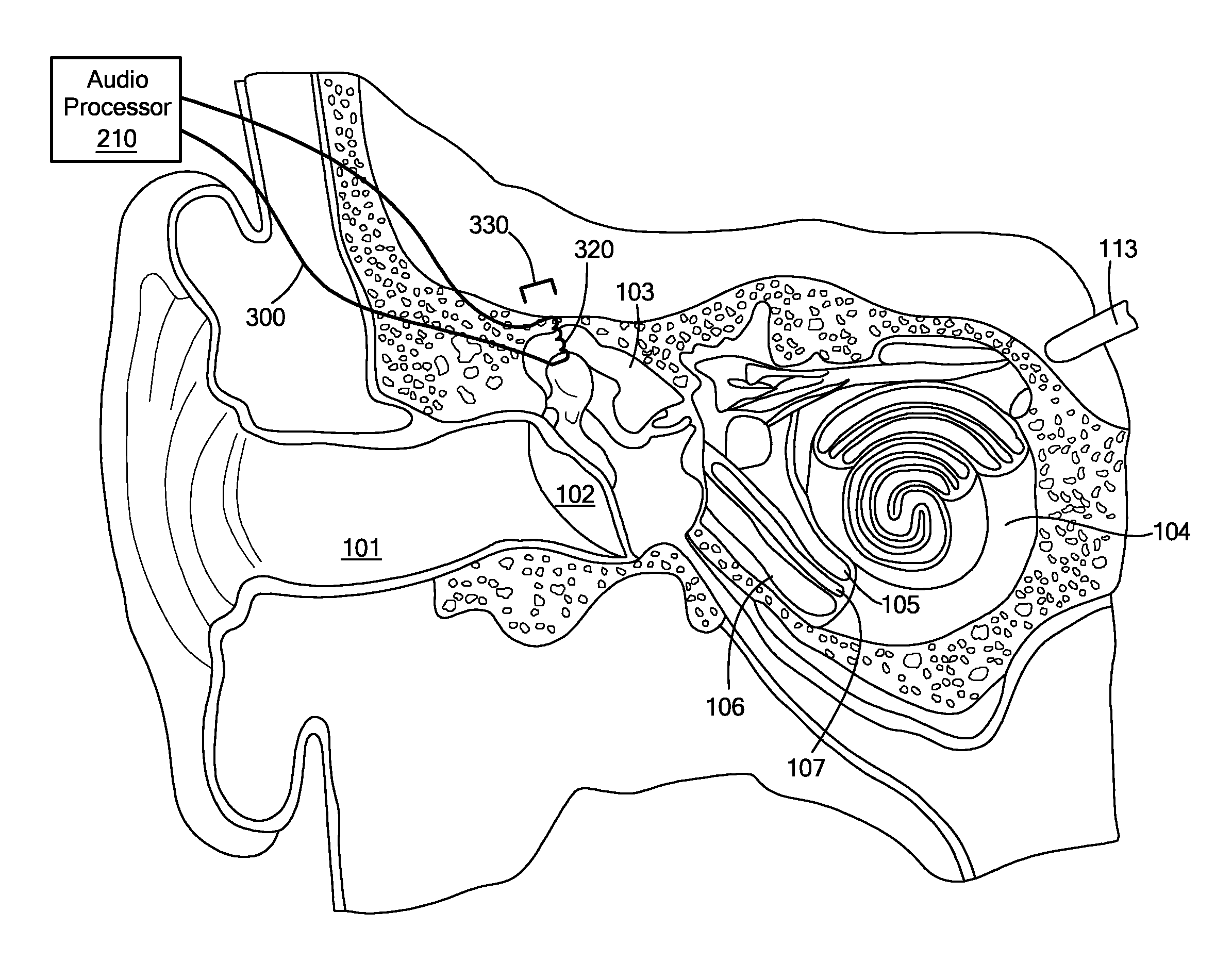
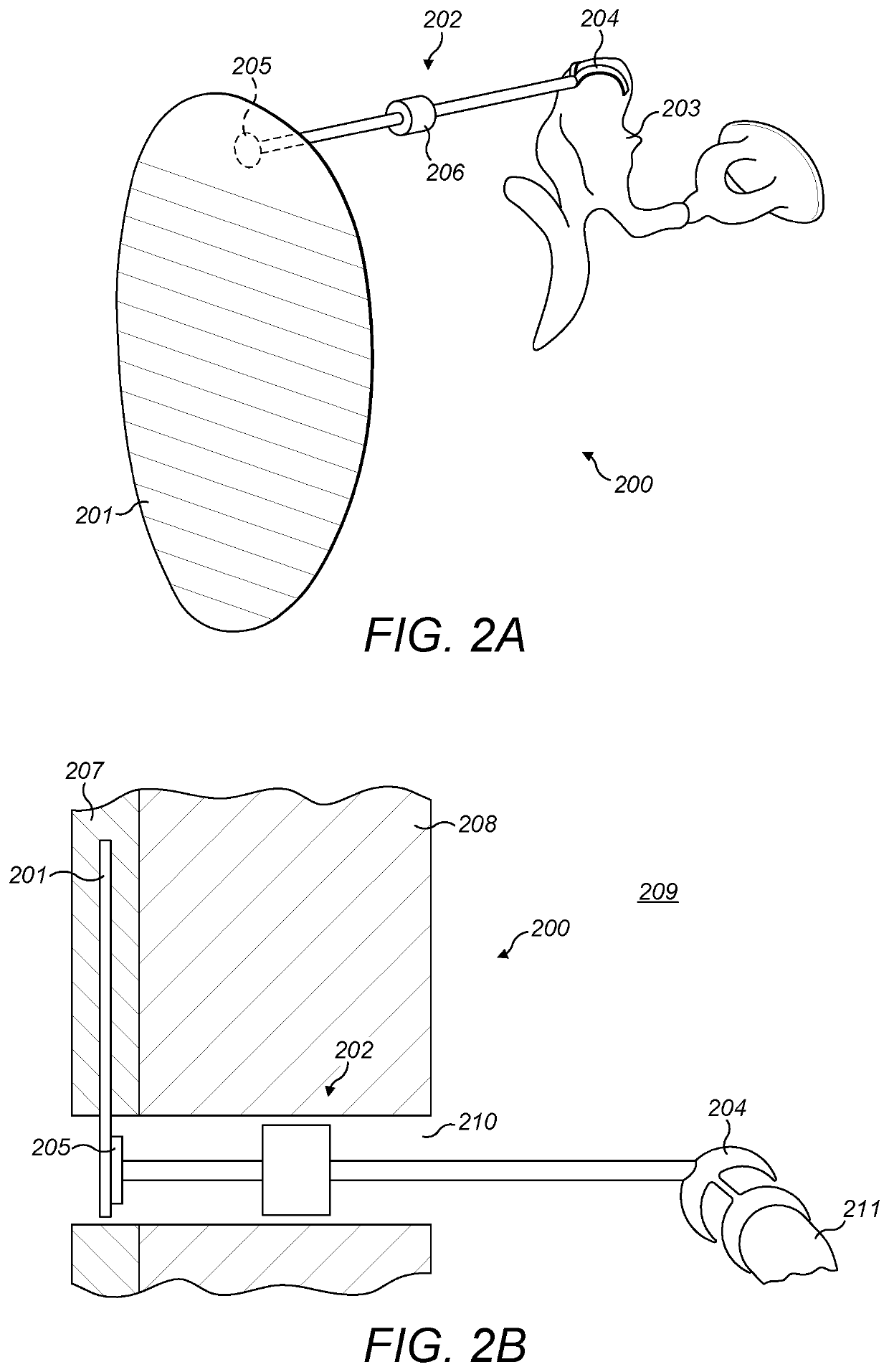
ActiveUS20220053277A1Bone conduction transducer hearing devicesImplantable hearing aidsSound perceptionSkull bone
A middle ear implant system includes a bone conduction transducer configured for fixed attachment to skull bone of a patient beneath the skin behind the ear, and for generating sound vibrations from an external communications signal received through the skin for coupling to the skull bone for bone conduction sound perception by the patient. A malleable ossicle connector is connected to the bone conduction transducer and a middle ear hearing structure of the patient. And one or more isolation springs are configured for placement at the fixed attachment of the bone conduction transducer to the skull bone to acoustically decouple the bone conduction transducer from the skull bone to avoid bone conduction sound perception so that sound perception from the external communications signal is solely via the middle ear sound perception from vibrations coupled to the middle ear hearing structure by the ossicle connector.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
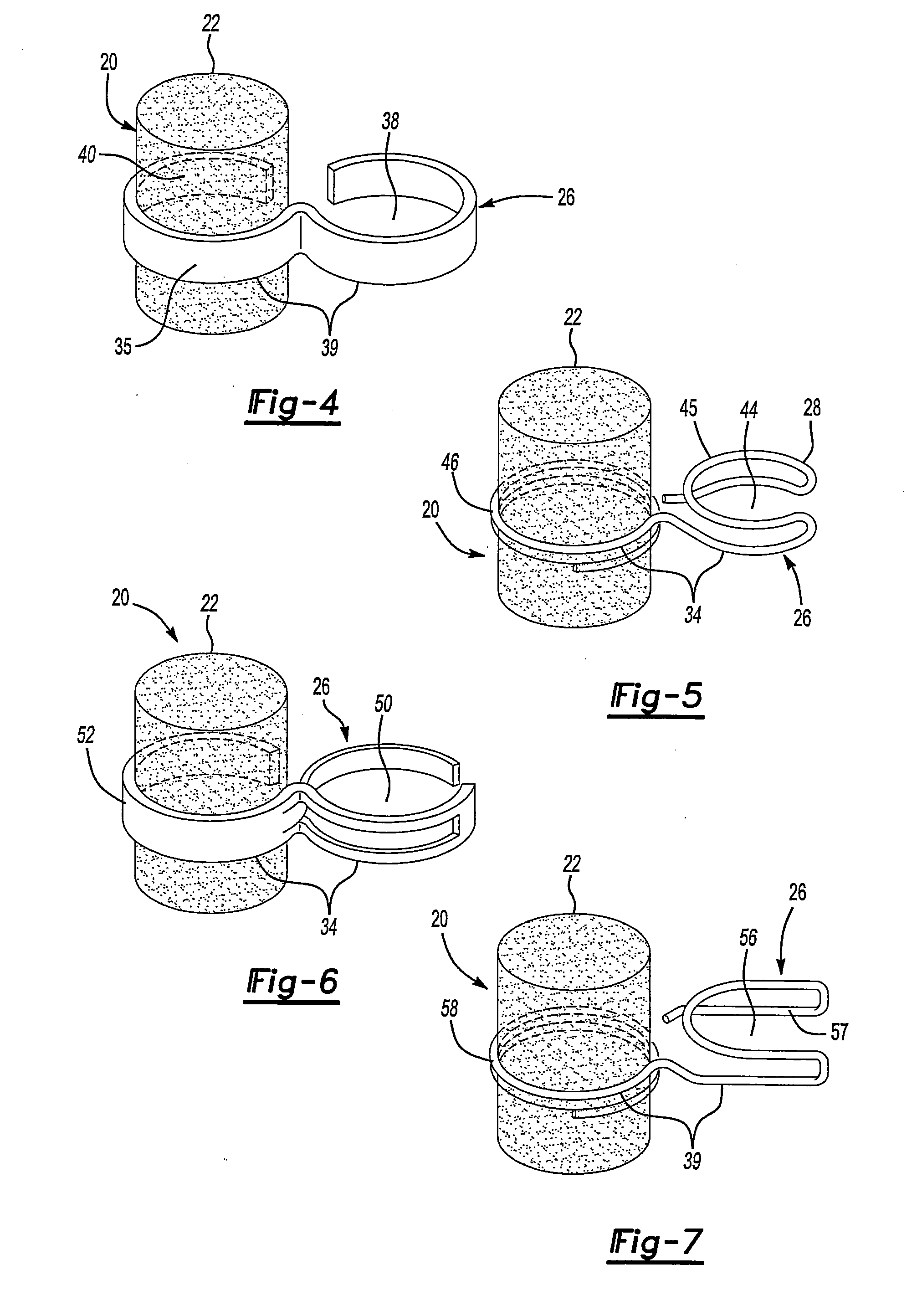
S-shaped coupling spring for middle ear implants
A loading spring has an inner end that engages the outer end of a middle ear transducer, an outer end that engages a fixed anatomical structure within the middle ear of the recipient patient, and a center of mass located on a common line between the inner end and the outer end. The loading spring also has an s-shape with a central spring axis along the common line. And the loading spring is configured for displacement of the inner end and the outer end along the central spring axis to fit the loading spring between the transducer and the fixed anatomical structure with a loading force that is within a defined range and entirely along a center axis of the middle ear transducer and the central spring axis.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Impact protection for implantable electric lead
ActiveUS9174039B2Improve energy absorptionHead electrodesExternal electrodesCochlear implantationElectric conductance
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Middle Ear Implant Coupler for Mechanical Cochlea Stimulation via the Round Window
A round window coupling device is described for a hybrid electric-mechanical stimulation hearing implant system. A rigid outer shell securely fits into a round window niche in a cochlear outer surface of a recipient patient. An electrode groove in the outer surface of the outer shell snuggly fits around a portion of a cochlear implant electrode array passing through the round window niche. A coupling filling is enclosed within the outer shell to couple mechanical vibrations from the proximal end to the distal end with minimal attenuation. A transducer receiver at the proximal end connects to and receives vibrations from a drive surface of a mechanical transducer. And a drive face at the distal end interfaces to perilymph fluid within the cochlea of the recipient patient to deliver vibrations from the coupling filling to the perilymph fluid with minimal attenuation for perception as sound.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
S-Shaped Coupling Spring for Middle Ear Implants
A loading spring has an inner end that engages the outer end of a middle ear transducer, an outer end that engages a fixed anatomical structure within the middle ear of the recipient patient, and a center of mass located on a common line between the inner end and the outer end. The loading spring also has an s-shape with a central spring axis along the common line. And the loading spring is configured for displacement of the inner end and the outer end along the central spring axis to fit the loading spring between the transducer and the fixed anatomical structure with a loading force that is within a defined range and entirely along a center axis of the middle ear transducer and the central spring axis.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Pre-load feedback of a middle-ear coupler
A coupling device for a middle ear implant includes a transducer end configured to engage an implantable electromechanical transducer, a bone engagement end configured to engage a temporal bone surface of a recipient patient, a planar loading spring located between the transducer end and the bone engagement end and configured for compression by displacement of the transducer end and the bone engagement end in towards each other, and compression indicators configured to provide visual indication of a pre-load force created on the temporal bone surface by the compression of the loading spring.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Universal bone conduction and middle ear implant
ActiveUS11425514B2Bone conduction transducer hearing devicesImplantable hearing aidsSound perceptionSkull bone
A middle ear implant system includes a bone conduction transducer configured for fixed attachment to skull bone of a patient beneath the skin behind the ear, and for generating sound vibrations from an external communications signal received through the skin for coupling to the skull bone for bone conduction sound perception by the patient. A malleable ossicle connector is connected to the bone conduction transducer and a middle ear hearing structure of the patient. And one or more isolation springs are configured for placement at the fixed attachment of the bone conduction transducer to the skull bone to acoustically decouple the bone conduction transducer from the skull bone to avoid bone conduction sound perception so that sound perception from the external communications signal is solely via the middle ear sound perception from vibrations coupled to the middle ear hearing structure by the ossicle connector.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
A kind of passive middle ear implant device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106563808BGuaranteed liquidityAvoid difficultiesTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusBiocompatibility TestingMechanical property
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical engineering, and specifically relates to a passive middle ear implantation device and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method steps are as follows: uniformly mix pure titanium powder and a binder and granulate, and perform injection molding treatment to obtain an injection Then carry out water debonding, drying, thermal debonding and pre-sintering treatment in sequence; then carry out sintering treatment and post-treatment, and finally obtain the passive middle ear implant device. The method adopts the Micro MIM process, and has made adjustments and improvements in the preparation of fine pure titanium powder injection materials, mold-assisted filling design, debonding process, and sintering process. The prepared passive middle ear implant has bone conduction and metal titanium Excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, as well as strength, toughness, elastic modulus, and fatigue resistance that match human bone tissue, can overcome the high cost and low efficiency of existing technologies.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
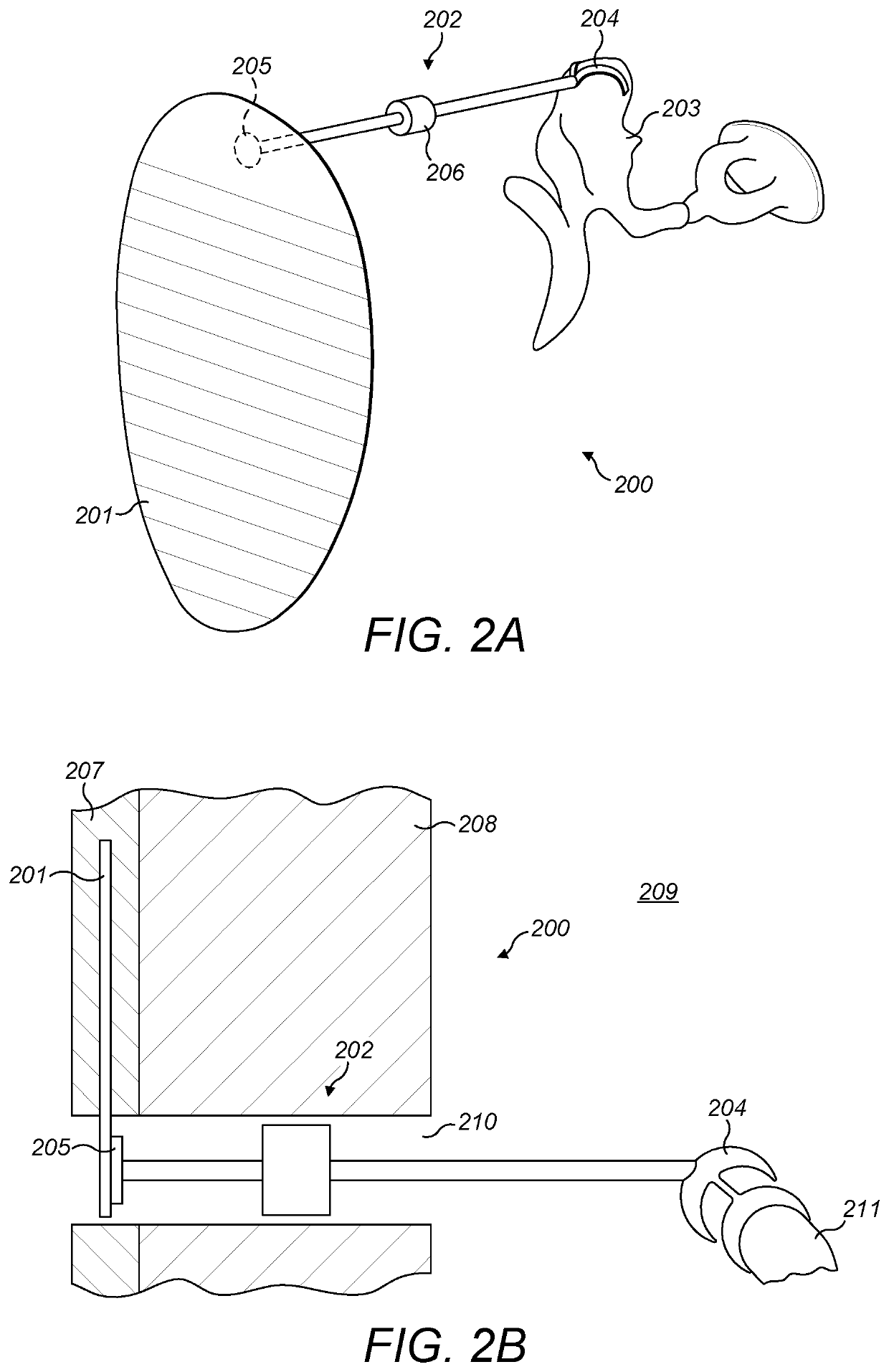
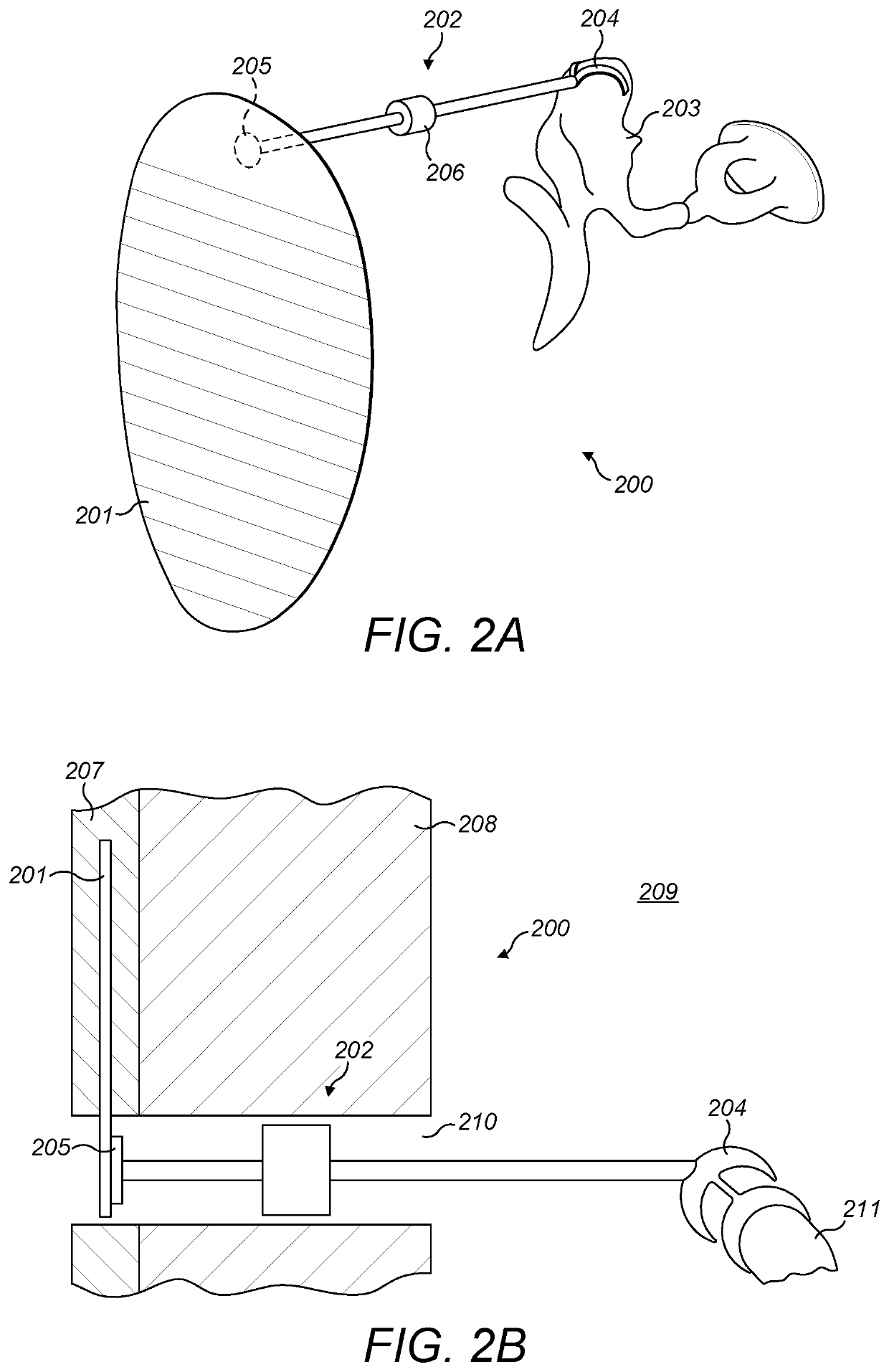
Passive Hearing Implant
PendingUS20220201411A1Adjustable lengthBone conduction transducer hearing devicesImplantable hearing aidsSkull boneHearing aid
A middle ear implant system includes a disc-shape vibration surface that is configured for implantation within skin lying over skull bone of a patient, with the disc-shape vibration surface parallel to an outer surface of the skin and to the skull bone so that sound vibrations striking the outer surface of the skin create corresponding vibrations in the disc-shape vibration surface within the skin. A rigid ossicle connector has a proximal end connected to the disc-shape vibration surface and a distal end connected to an ossicle in the middle ear of the patient so that vibrations of the disc-shape vibration surface are mechanically coupled to the ossicle for perception by the patient as sound.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com