Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
156 results about "Coupled motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
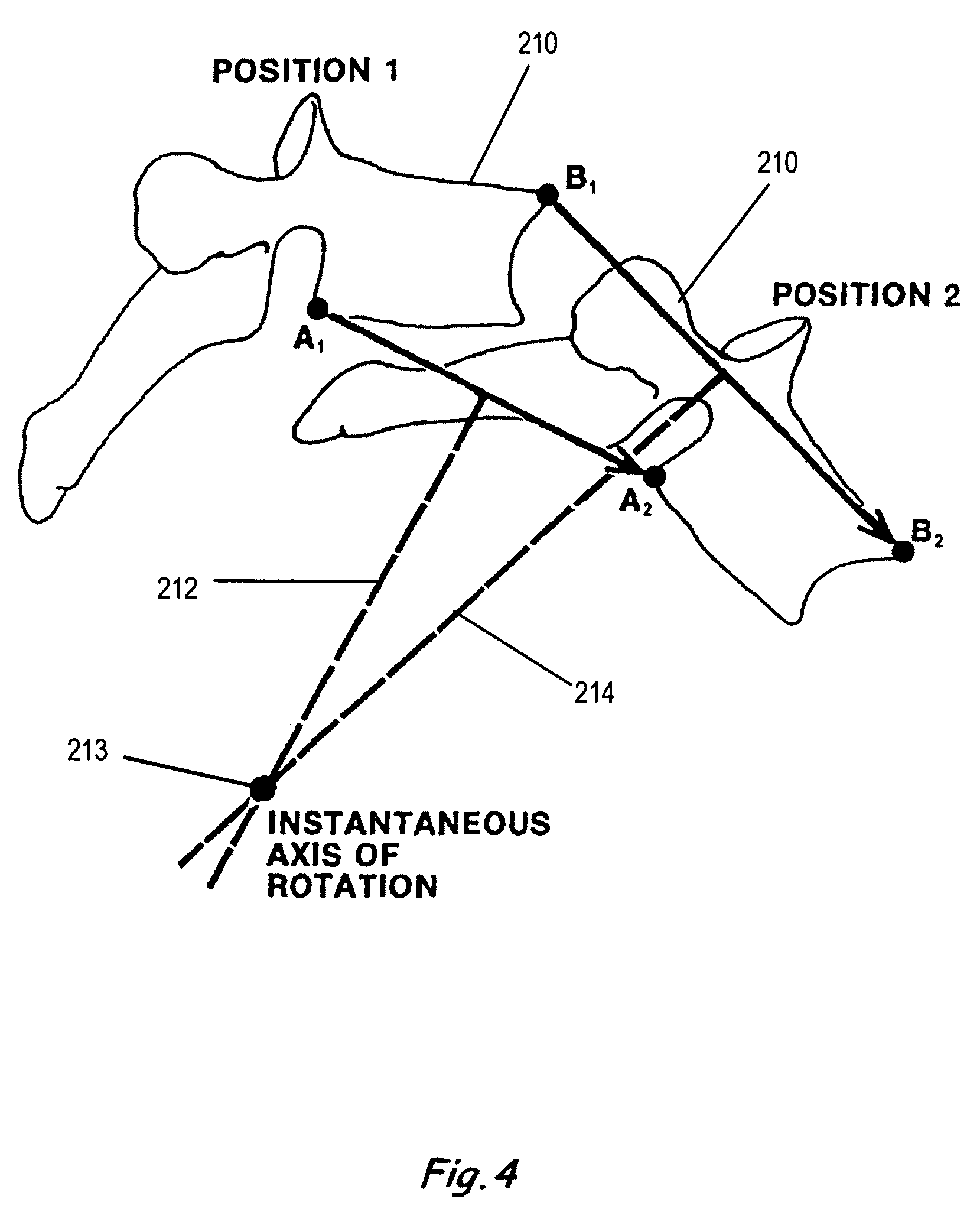
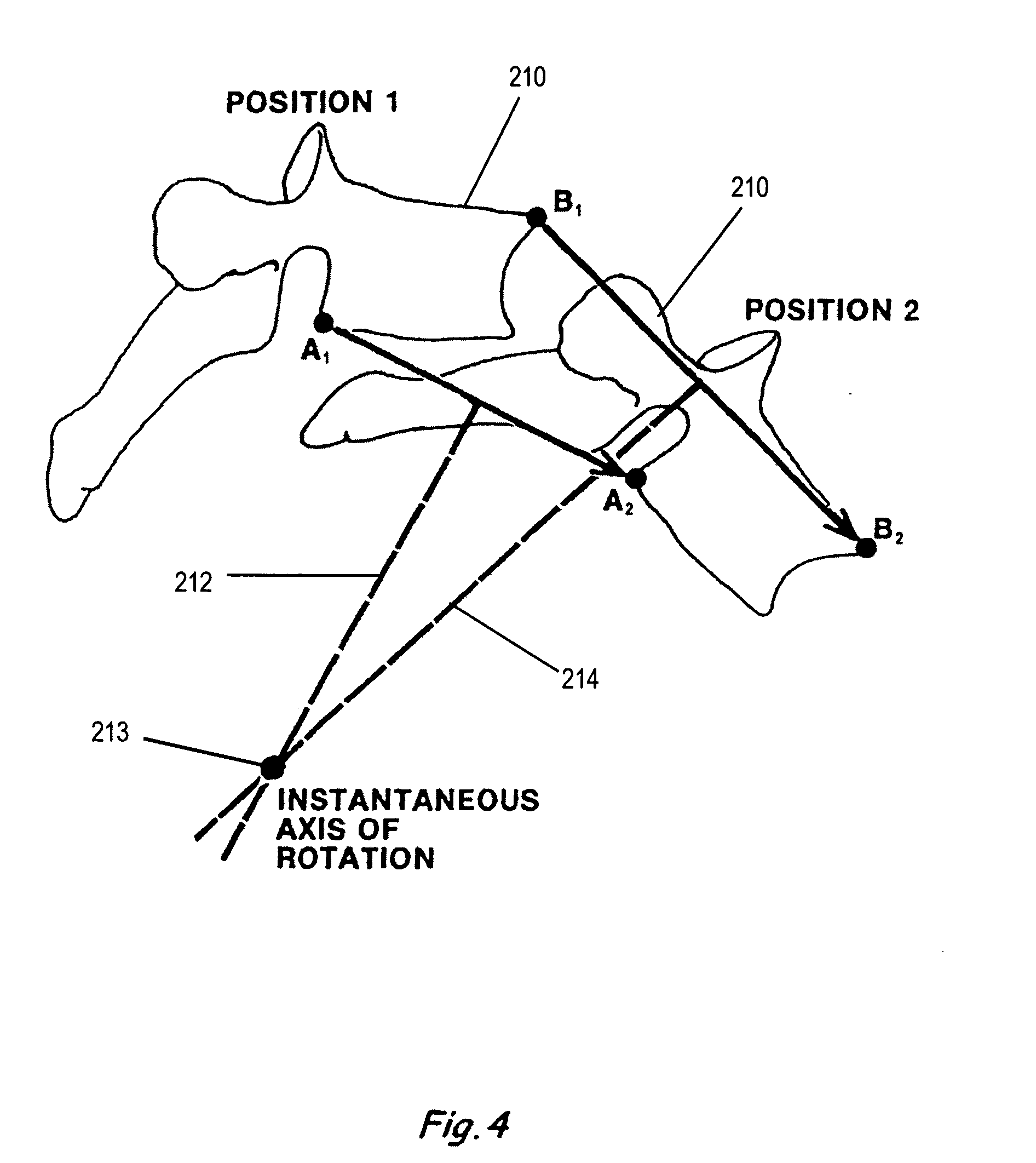
Coupled motion is when two processes of the vertebrae take place at the same time. In lateral flexion you bend to one side which is one act and the vertebrae also rotate right or left depending on their location in the spine which is the second act. If you bend your neck to the right all the cervical vertebrae also rotate to...
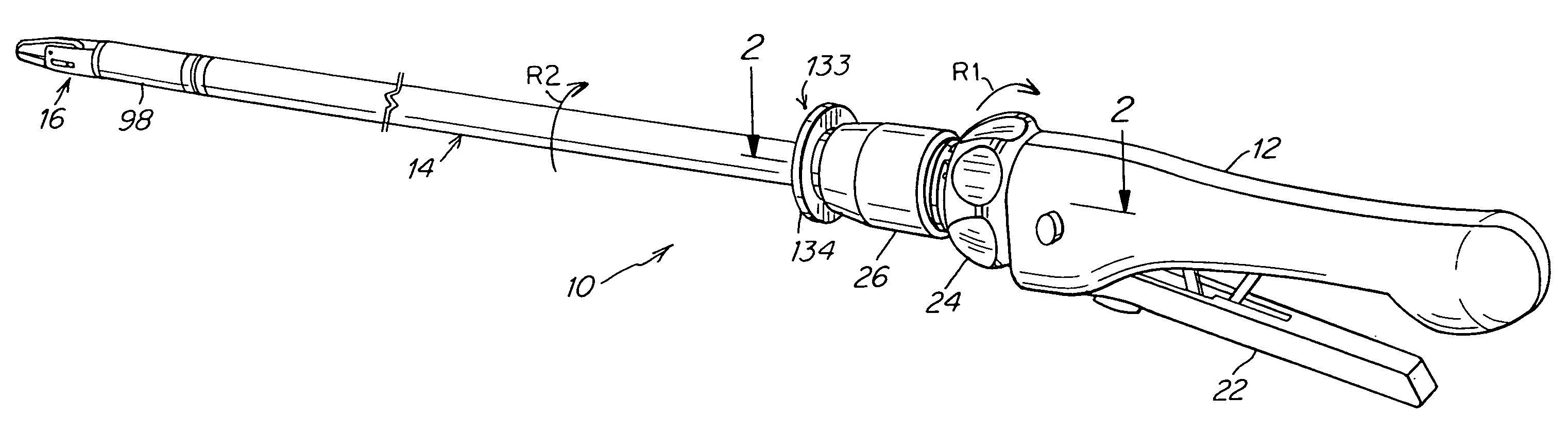
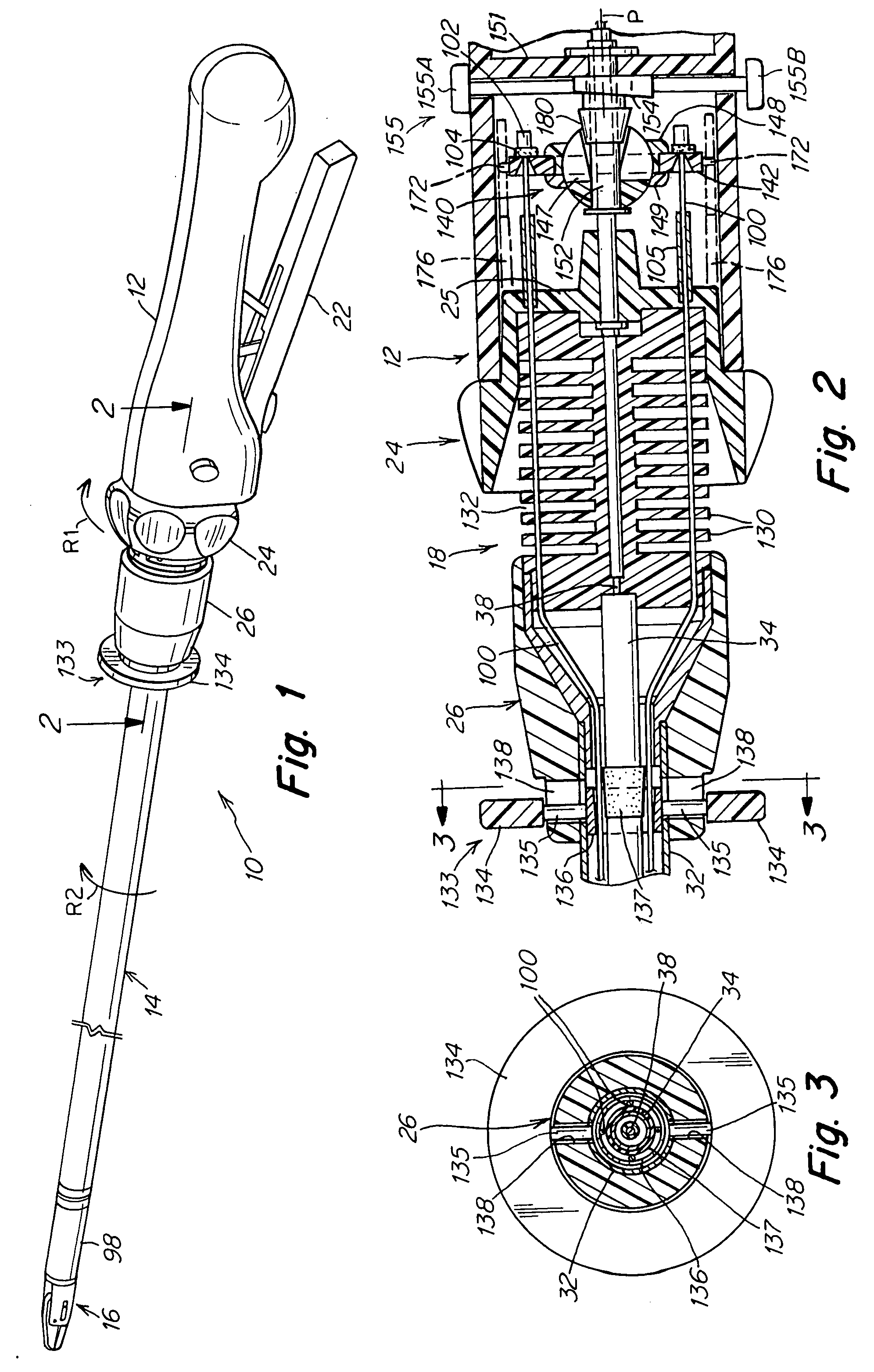
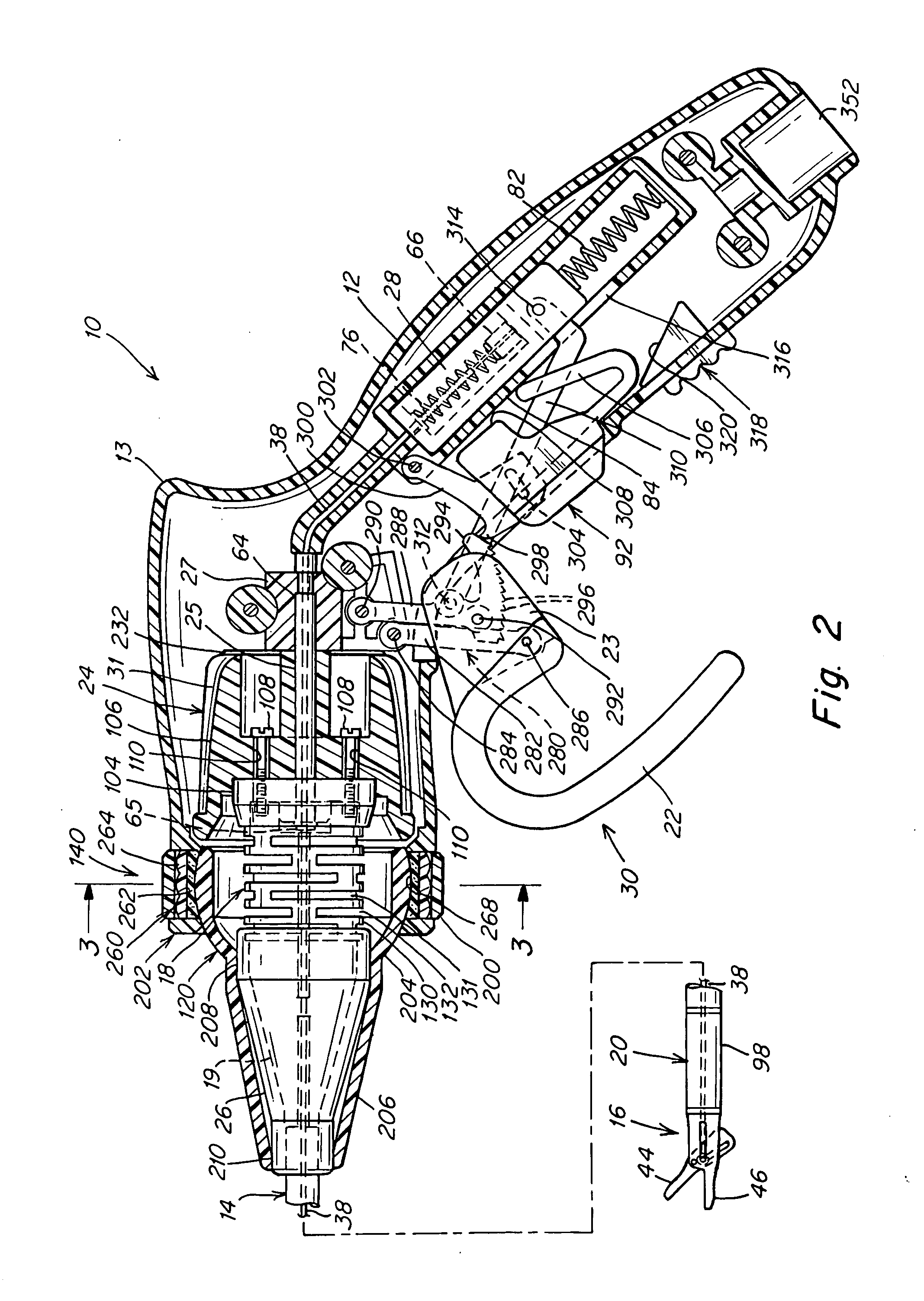
Surgical instrument
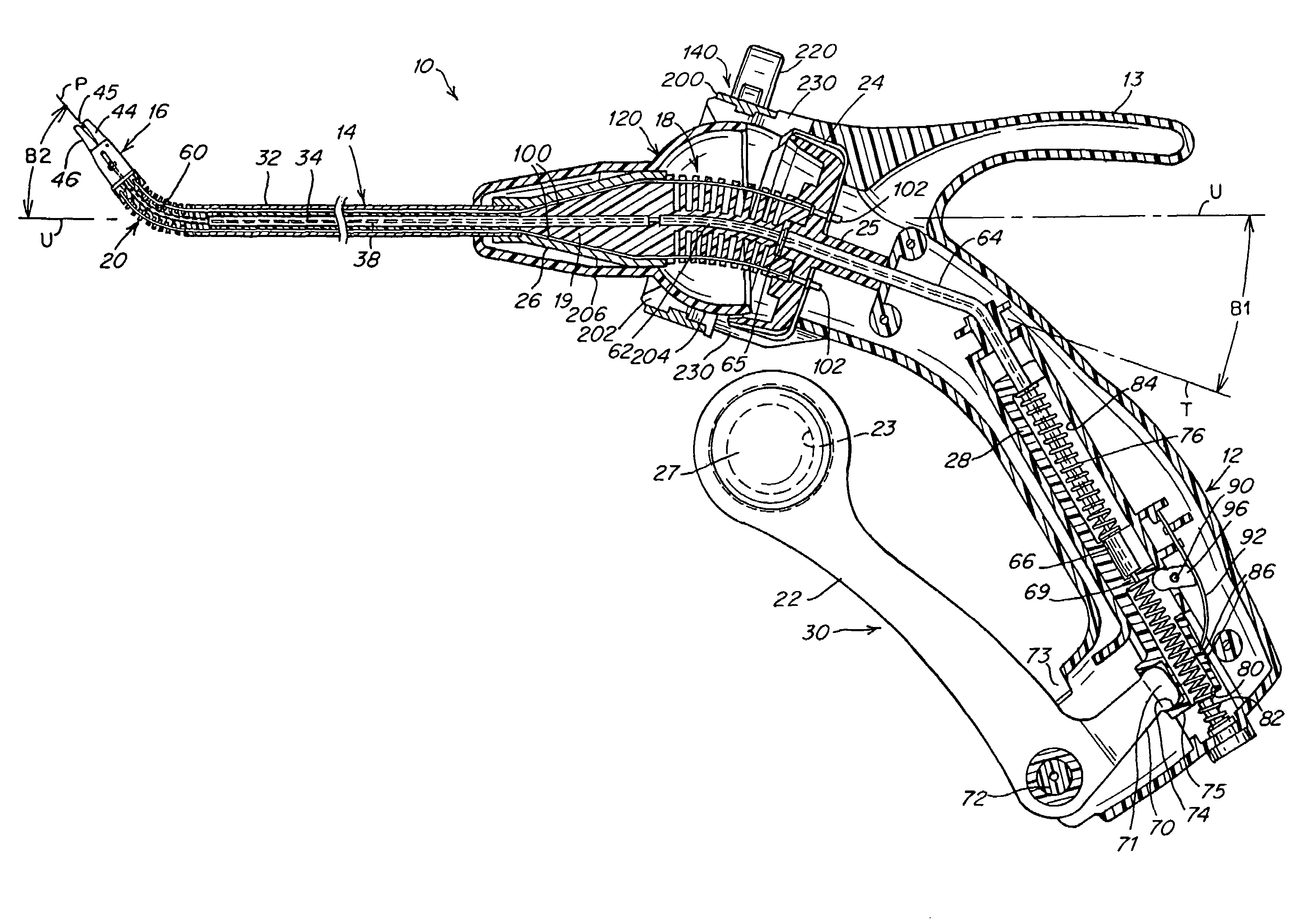
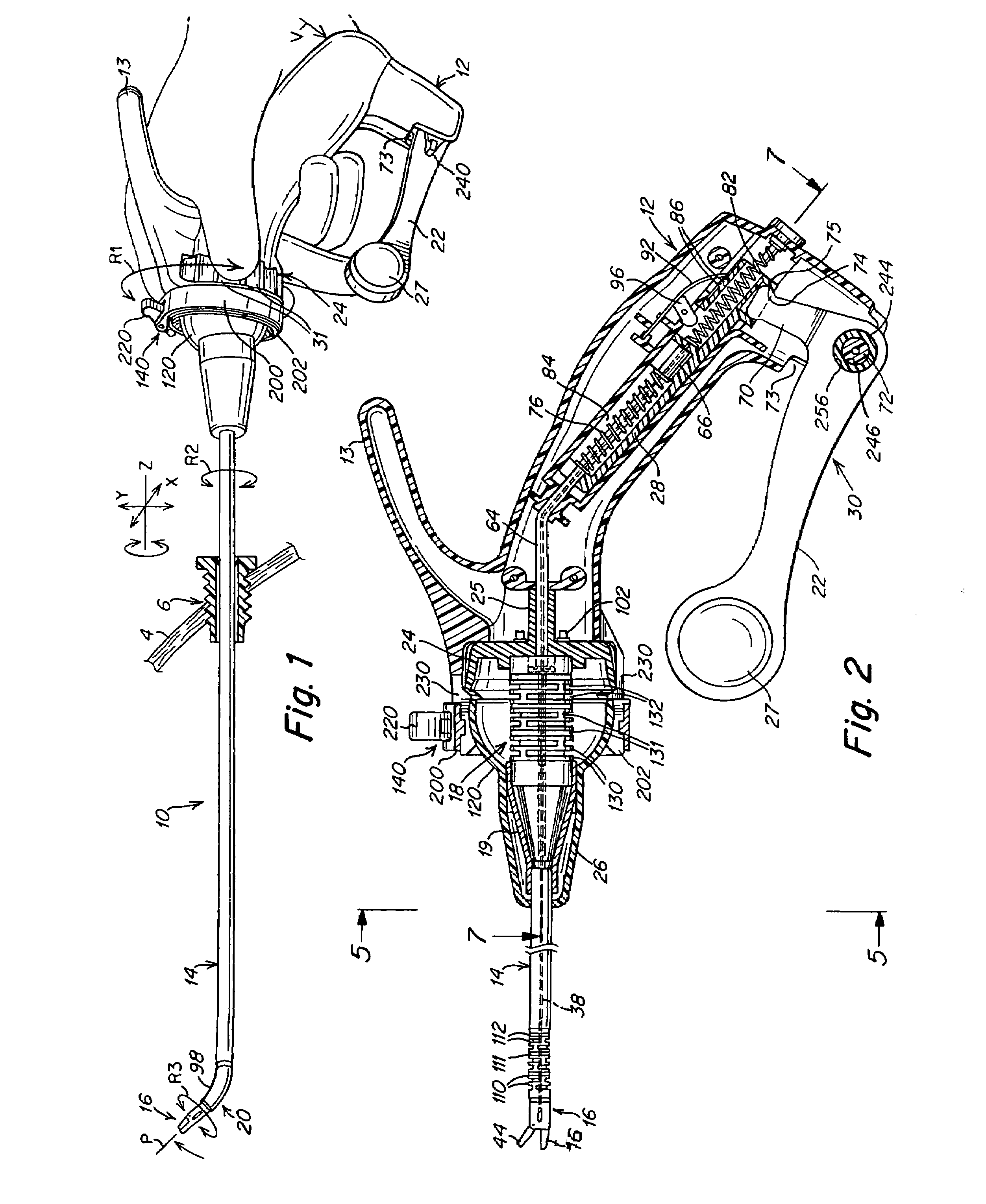
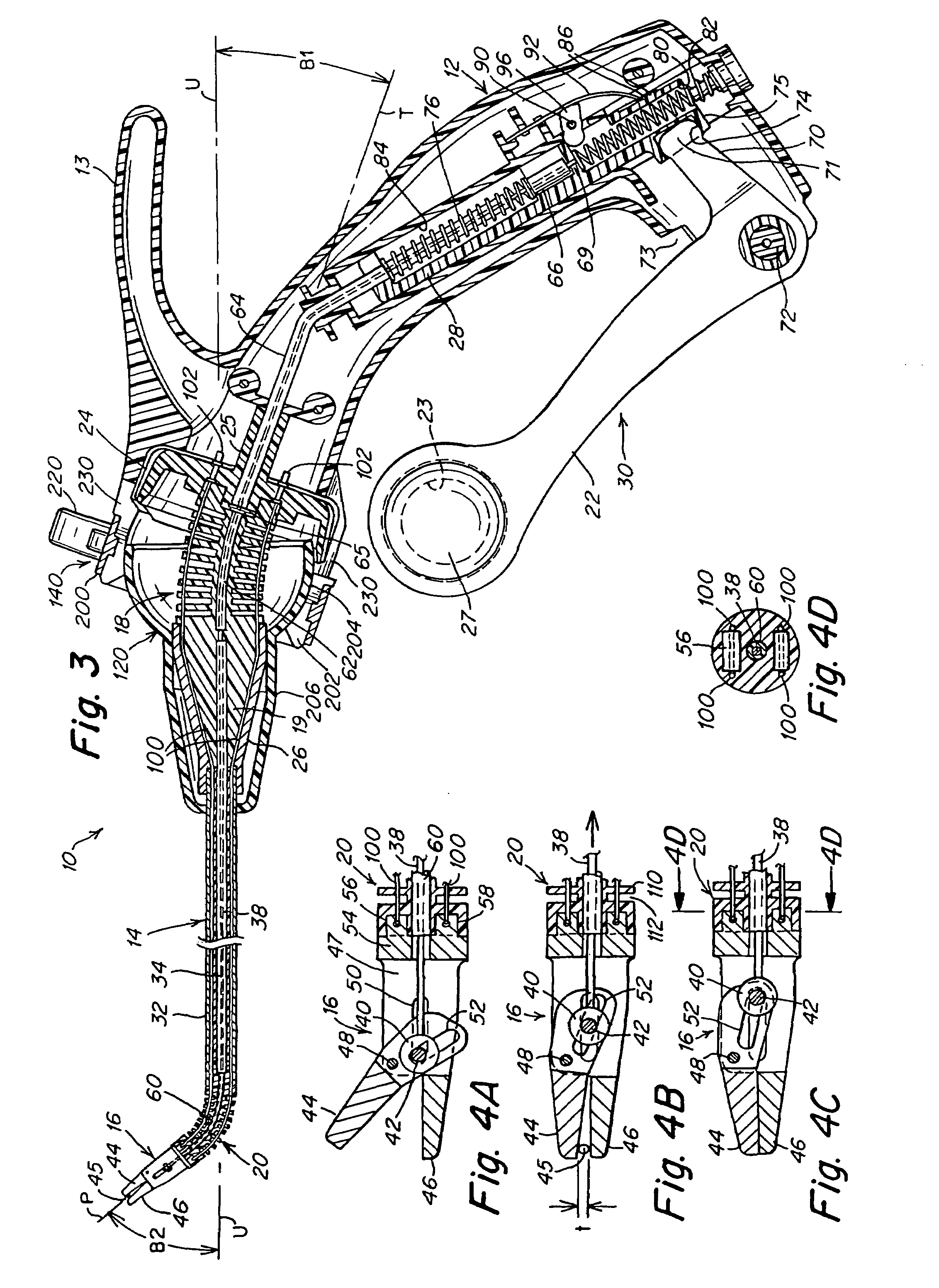
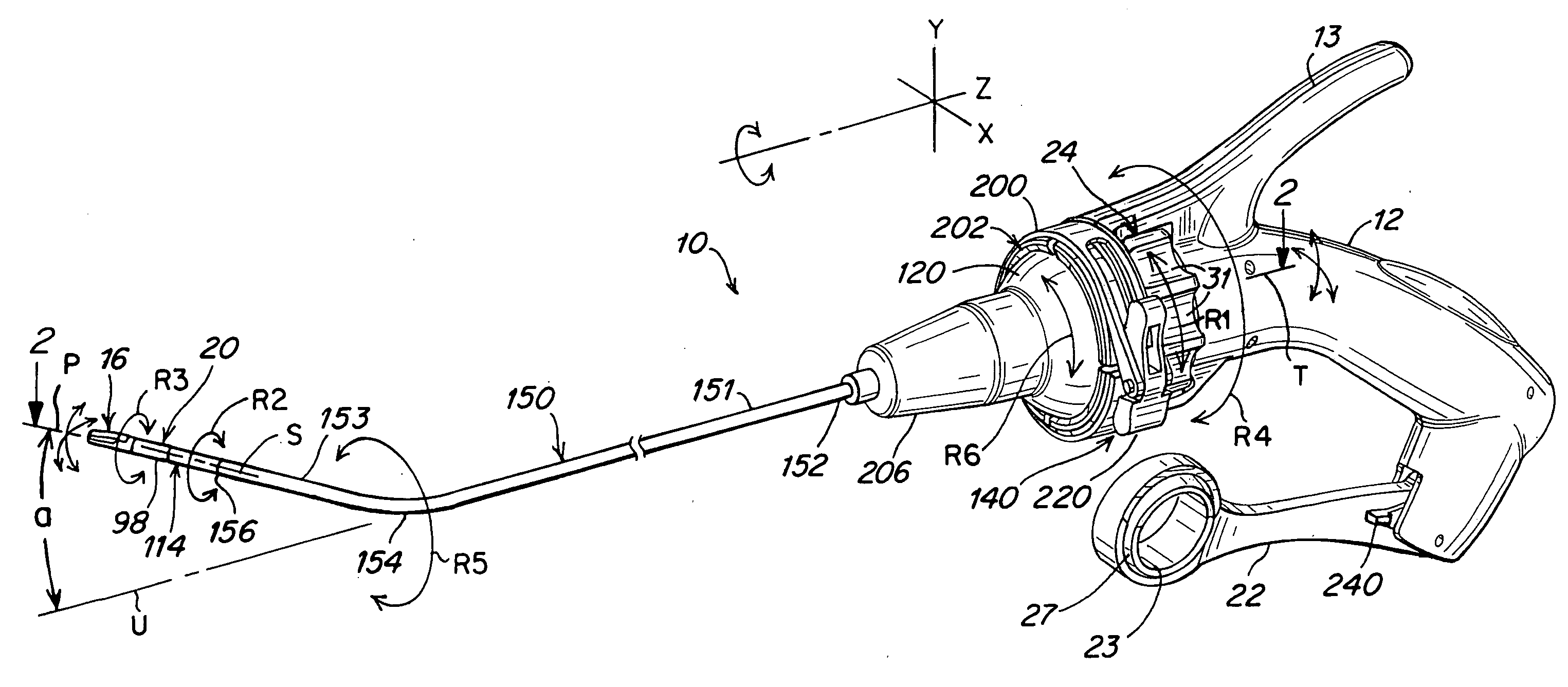
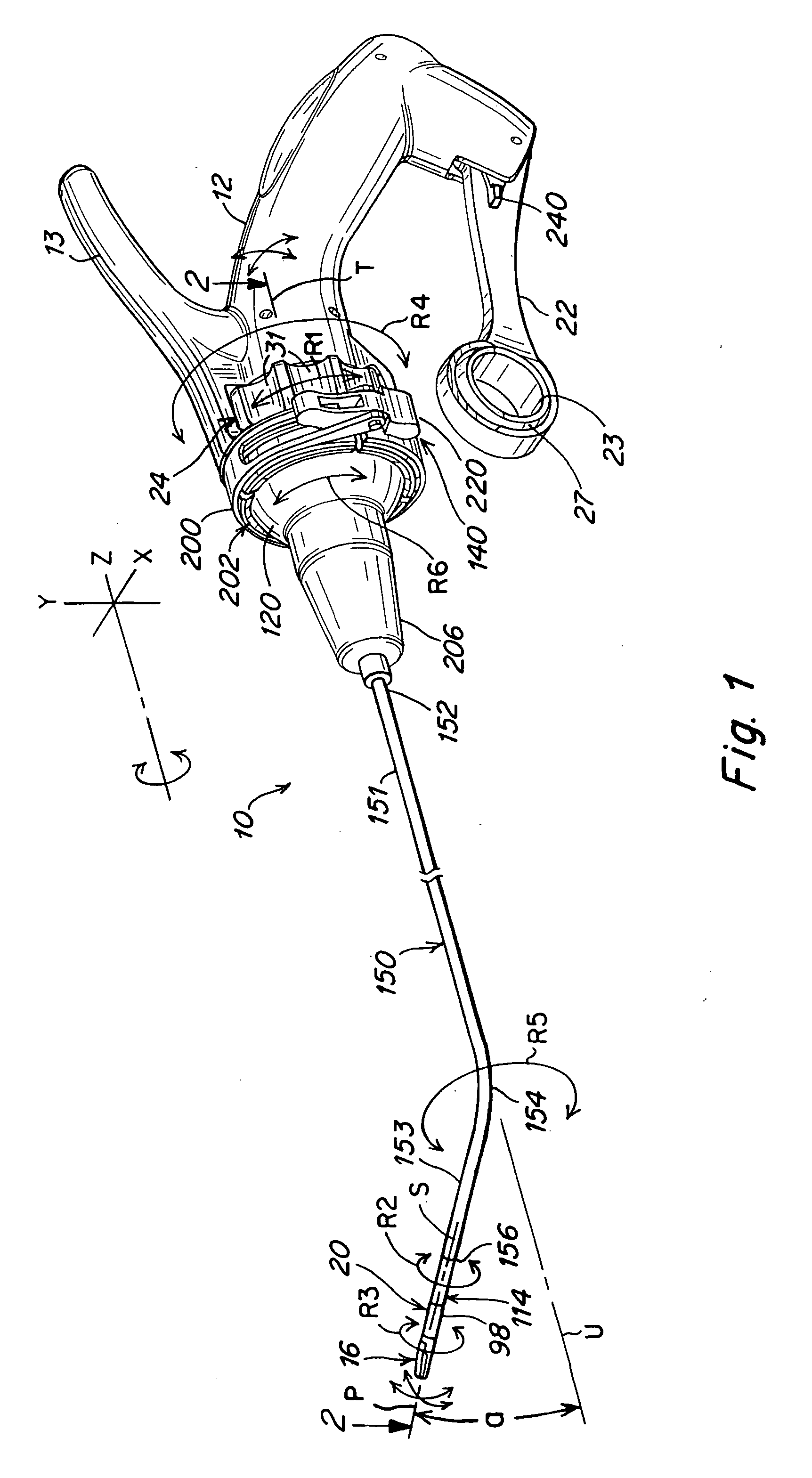
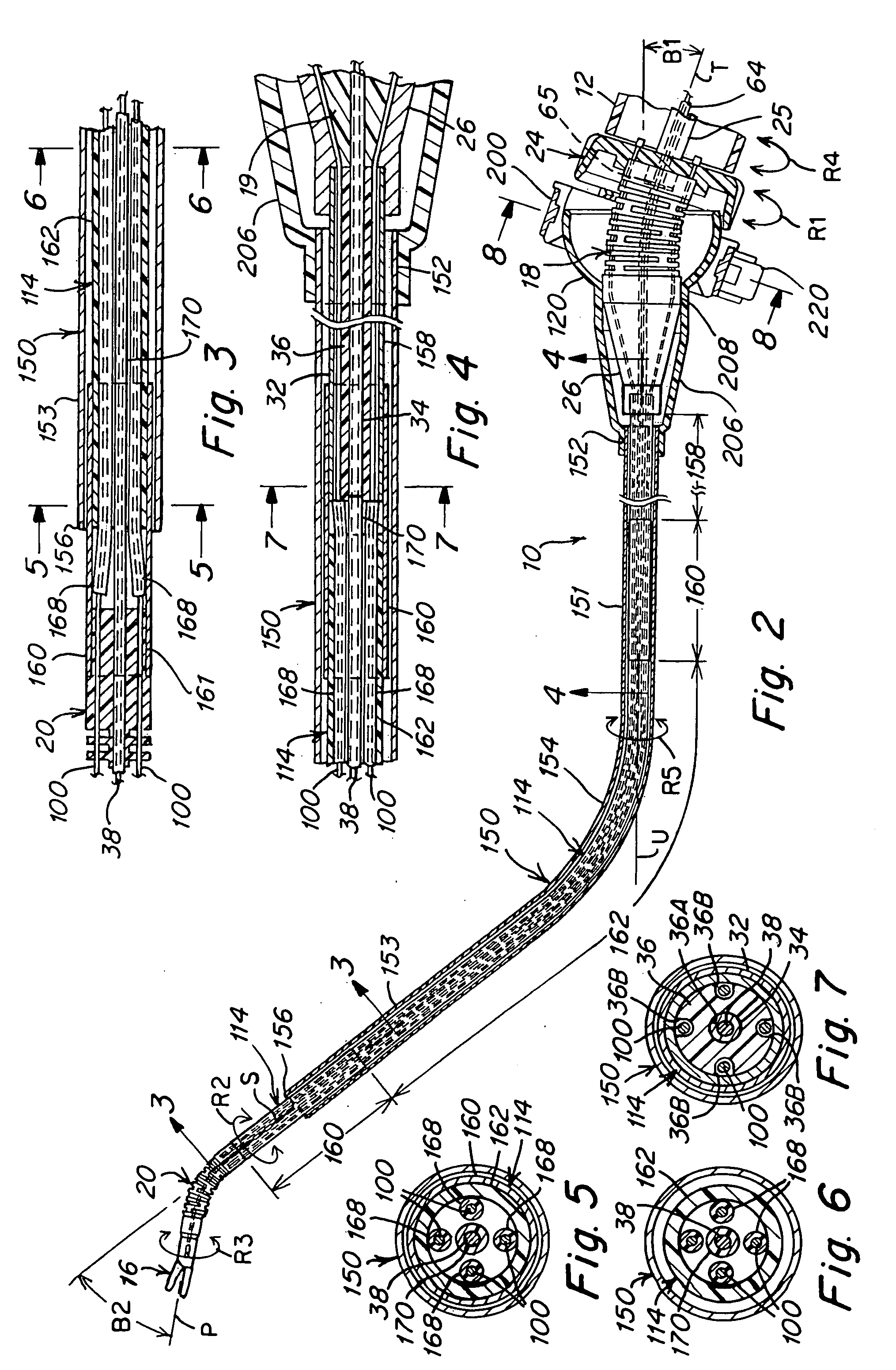
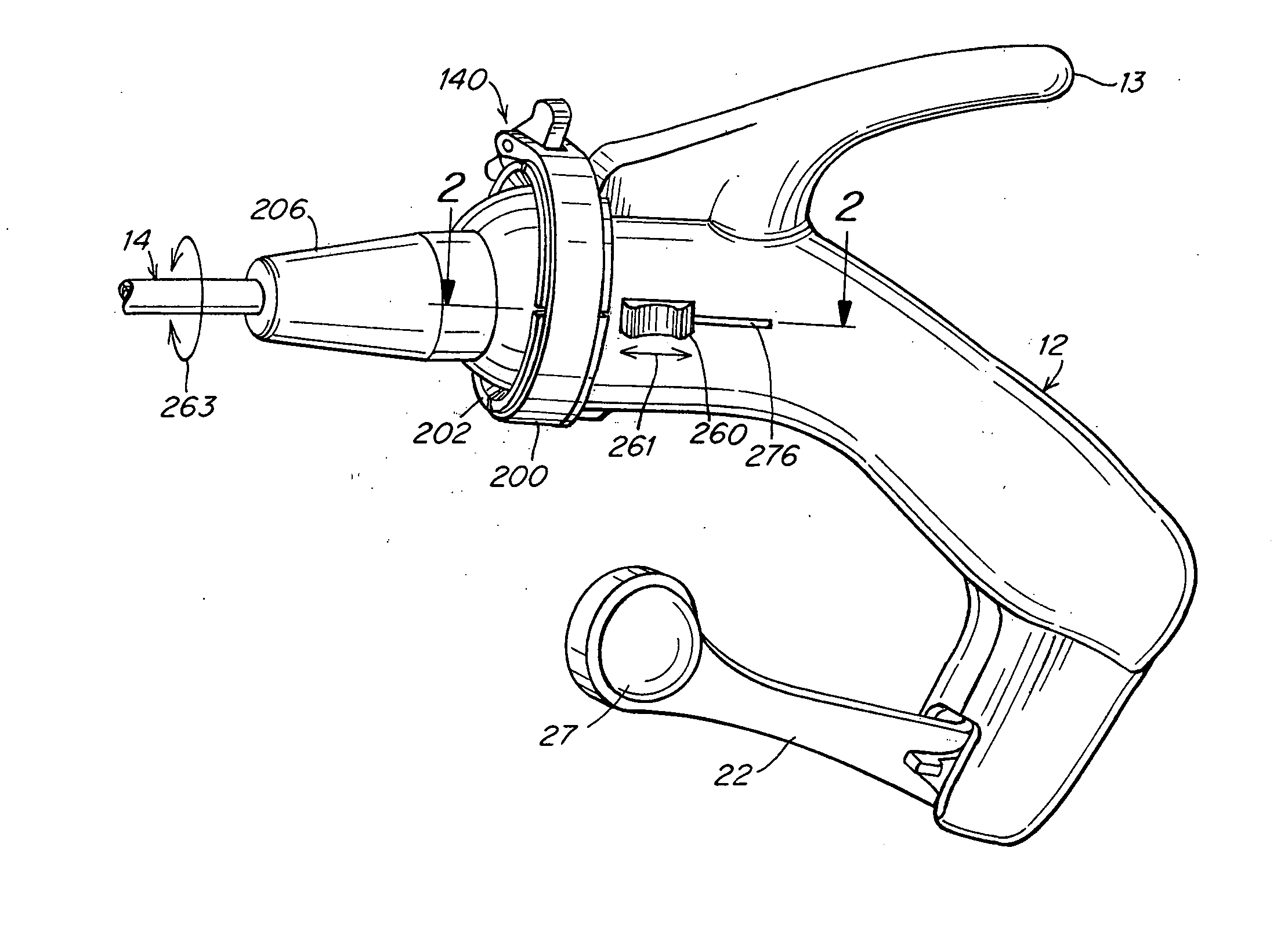
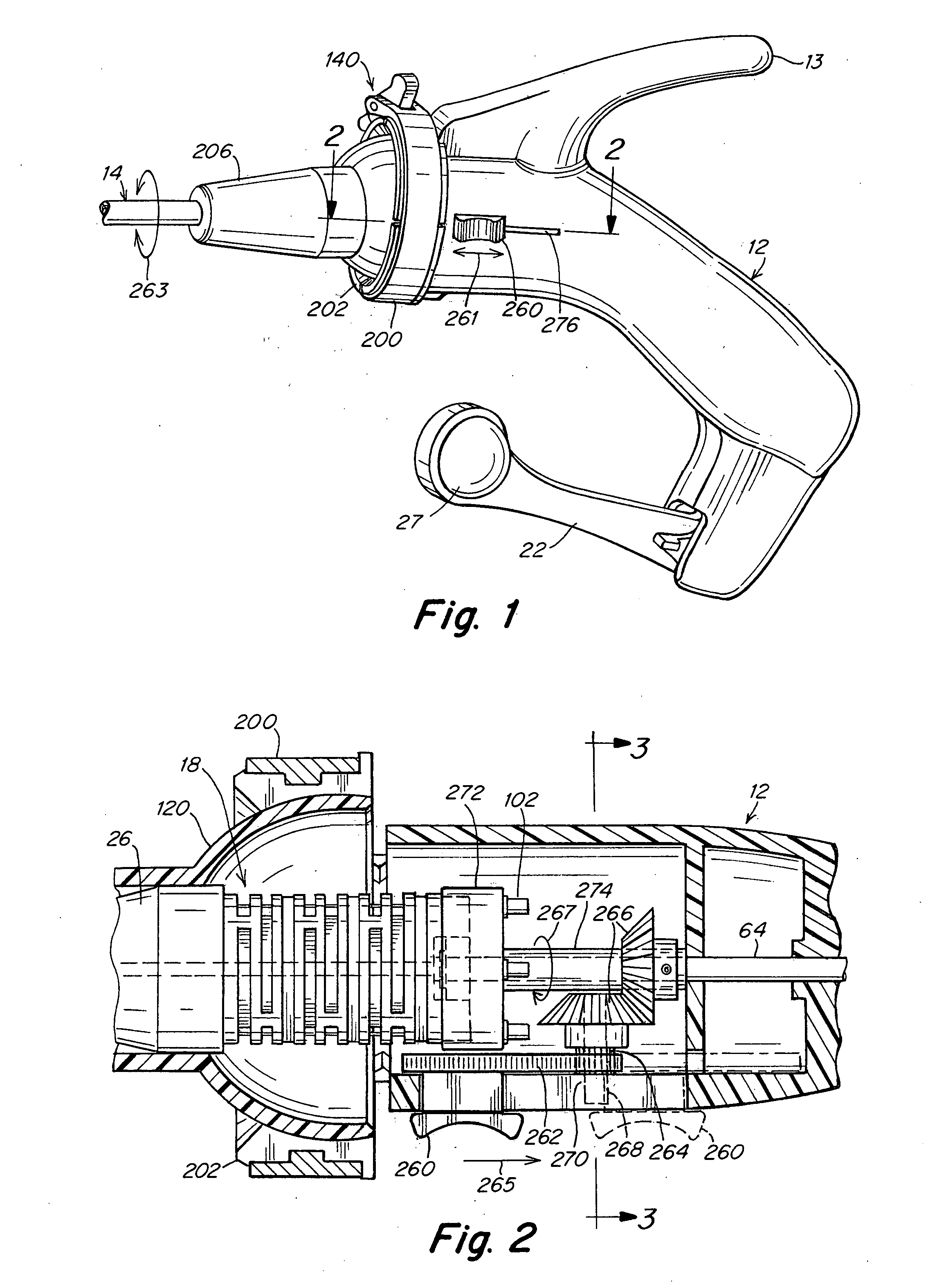
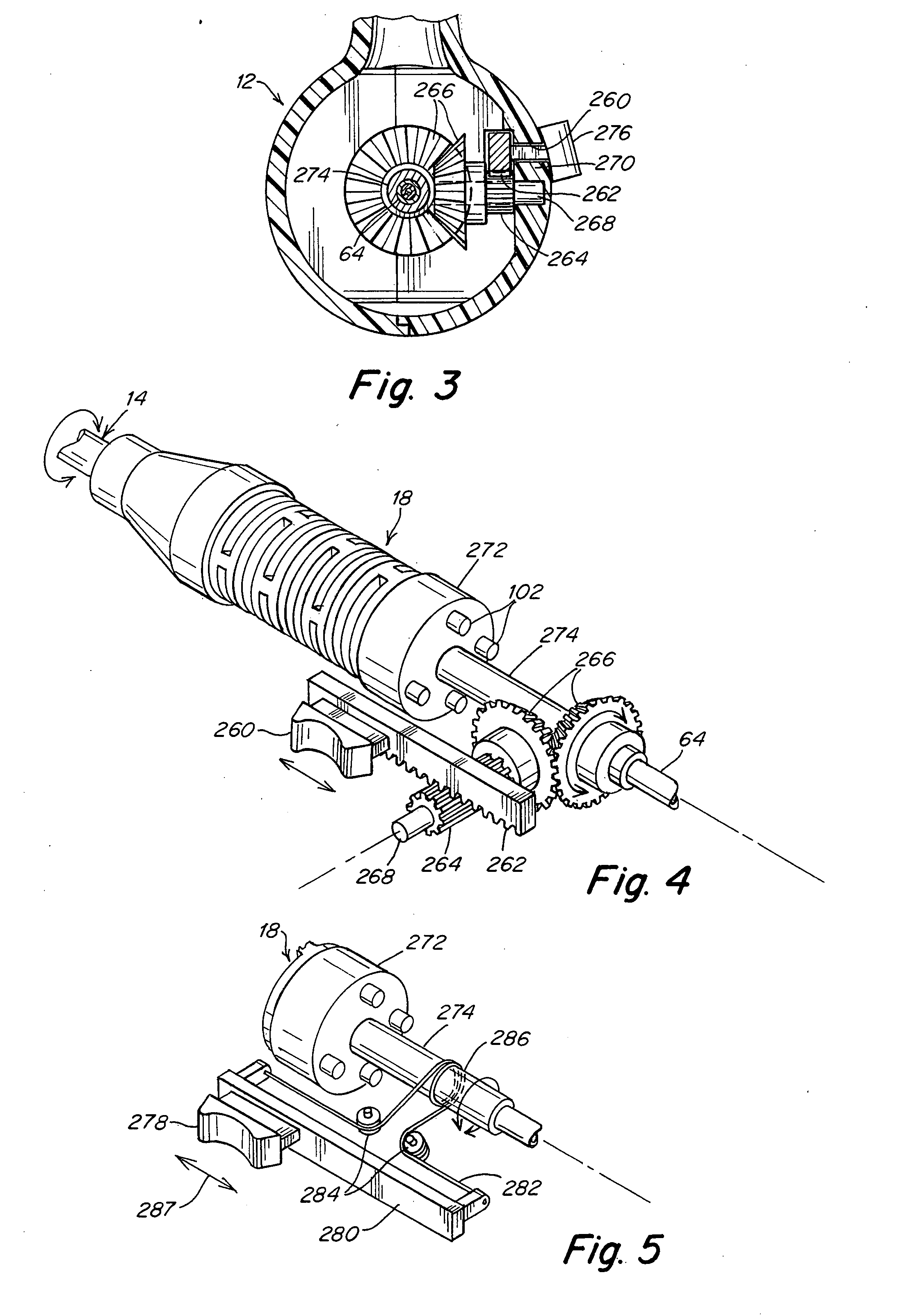
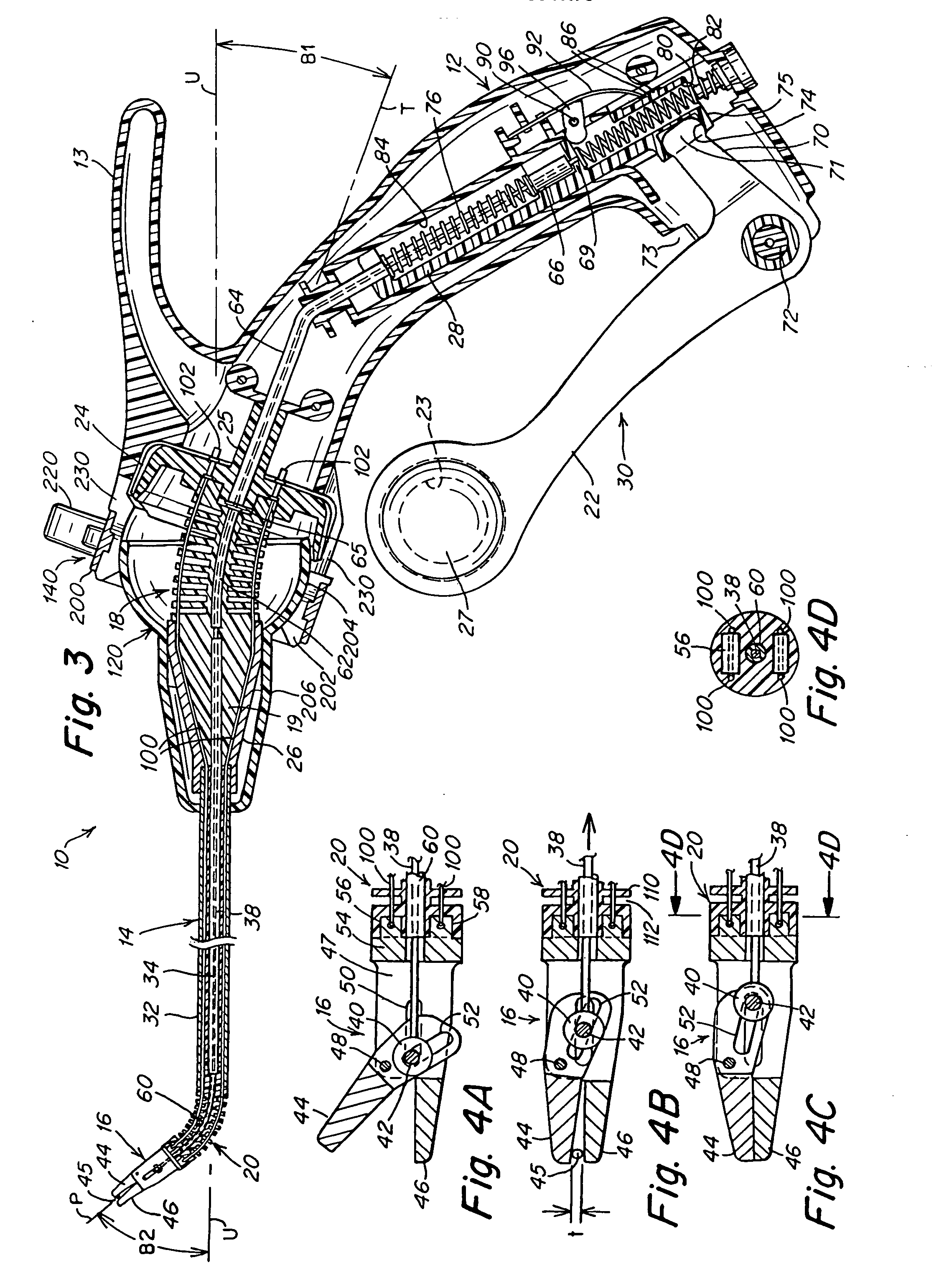
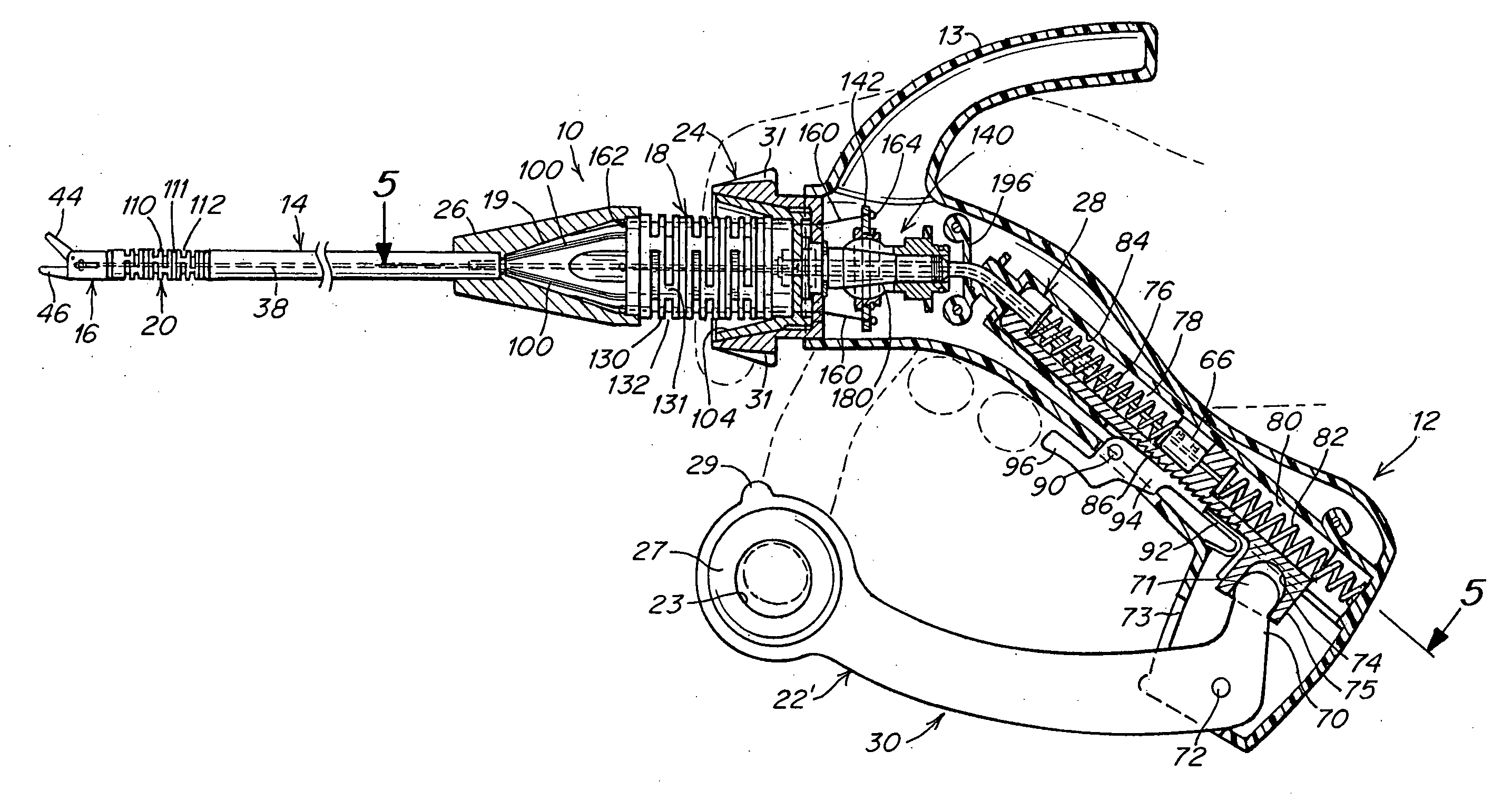
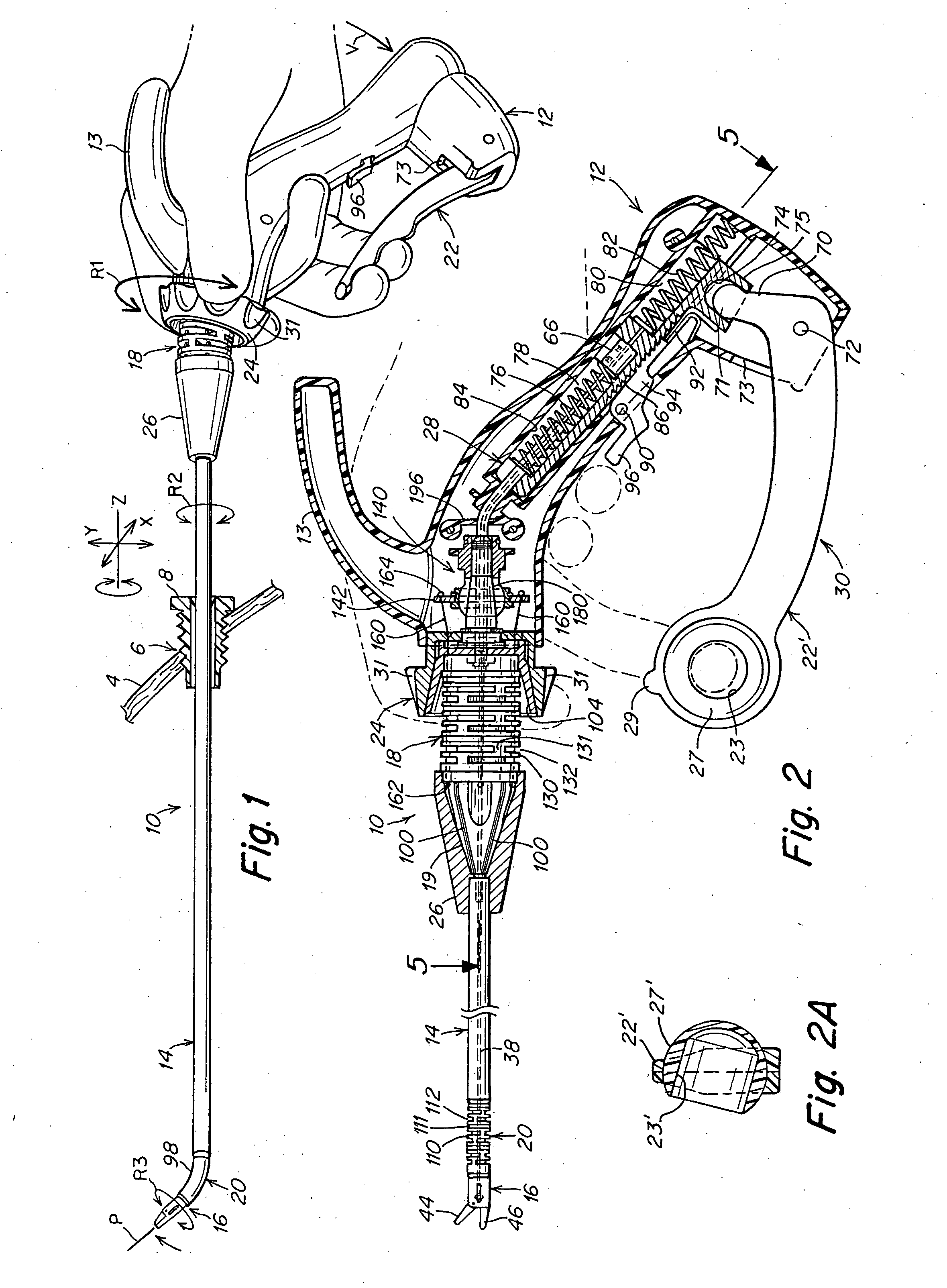
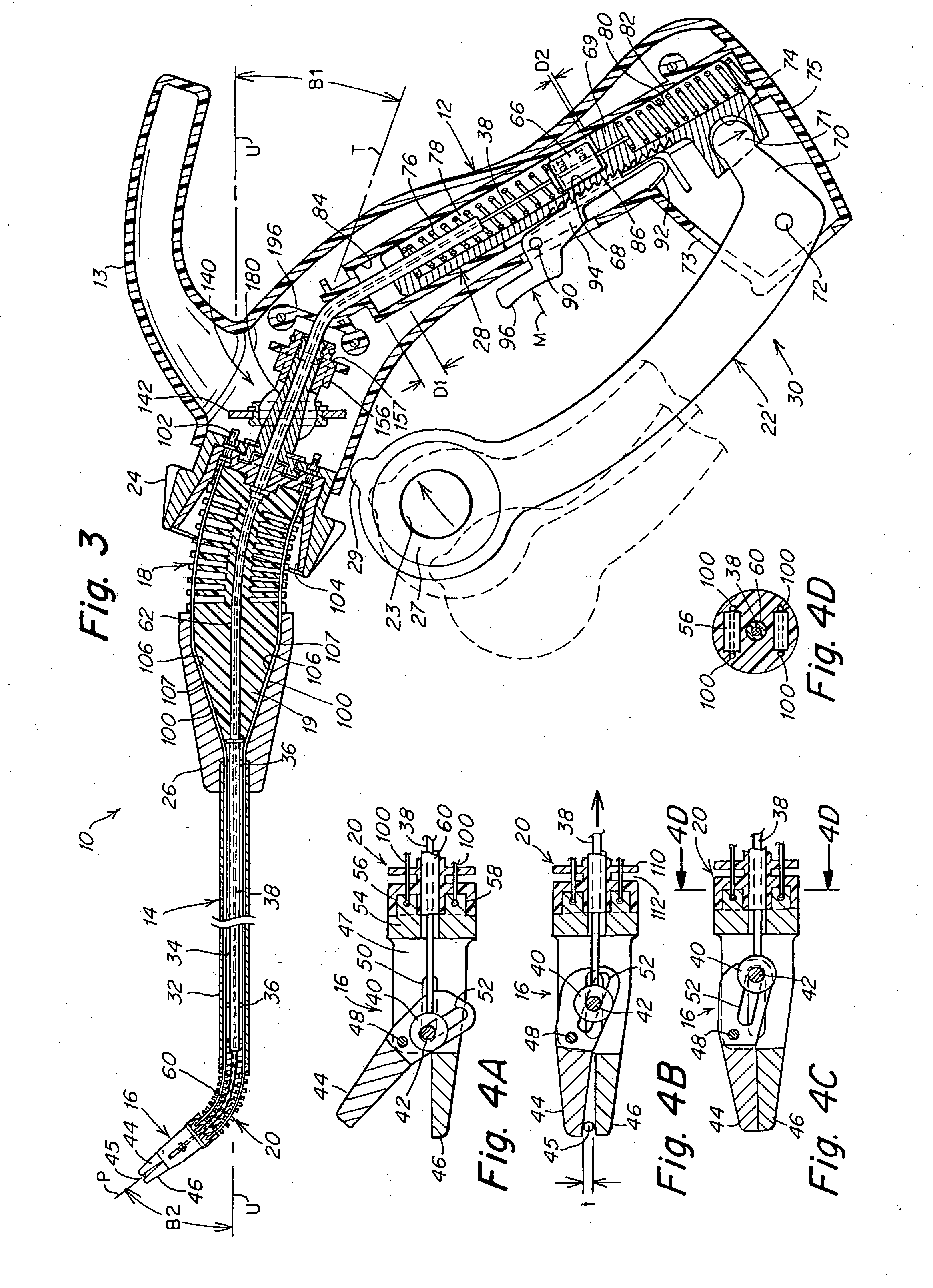
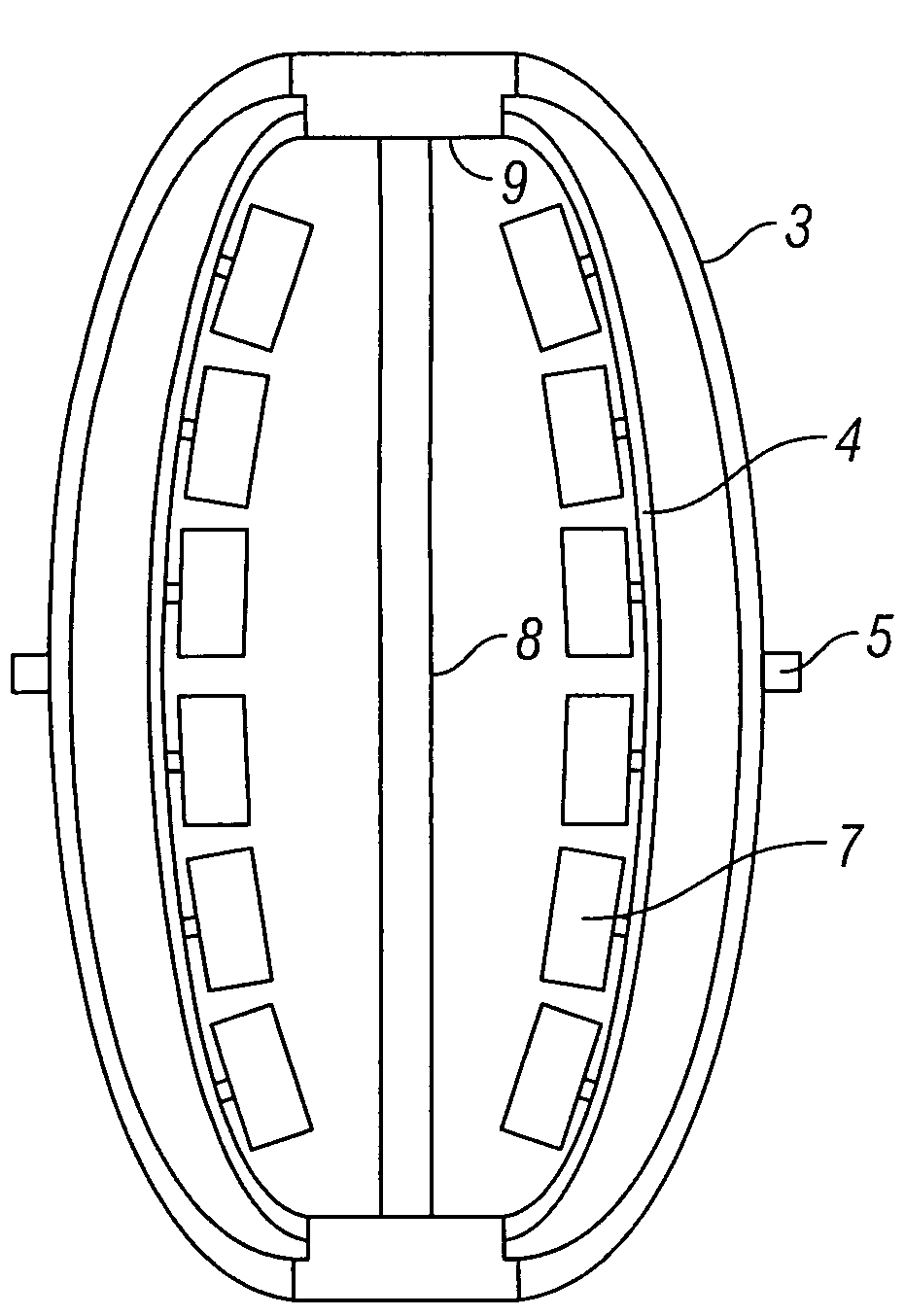
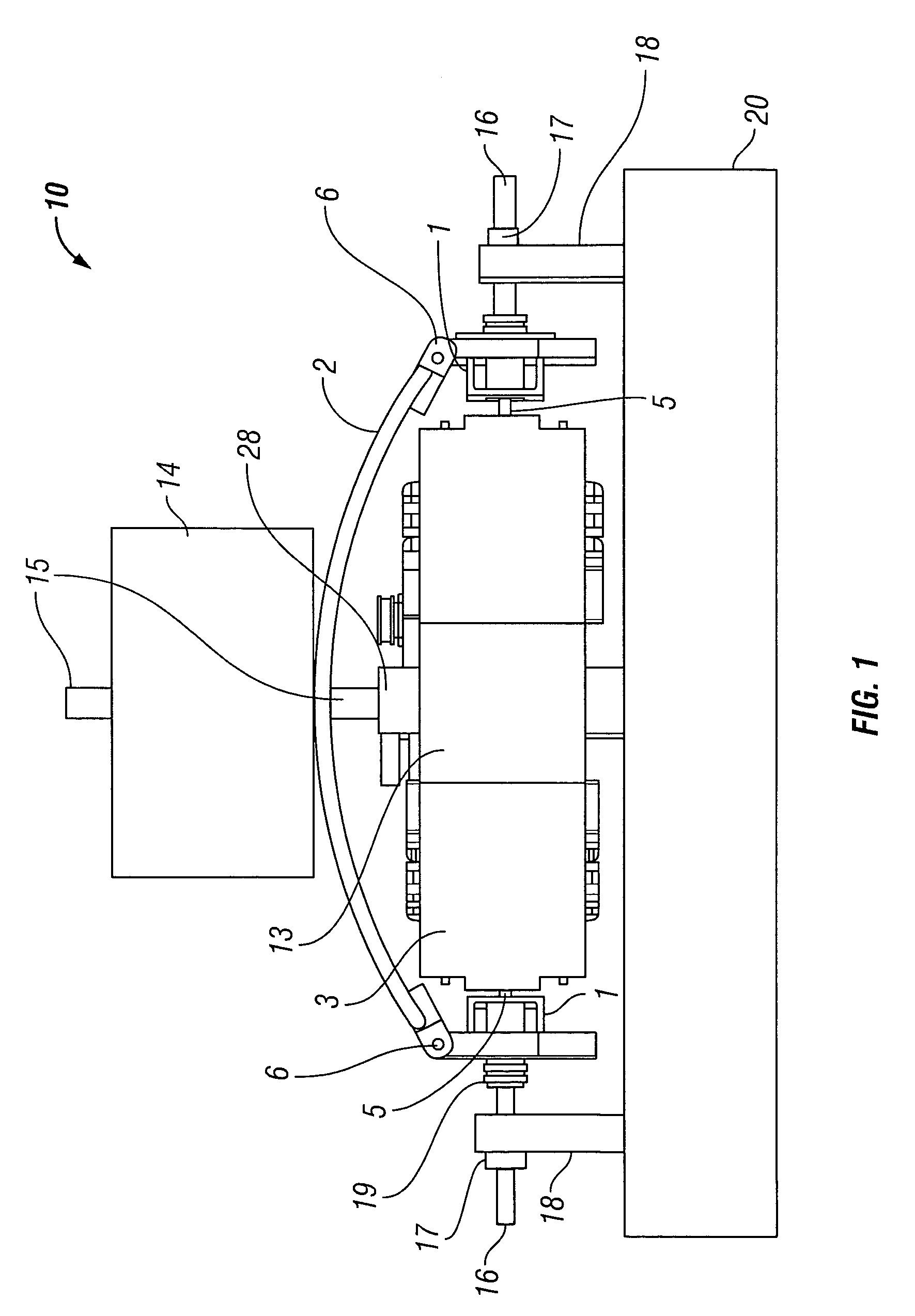
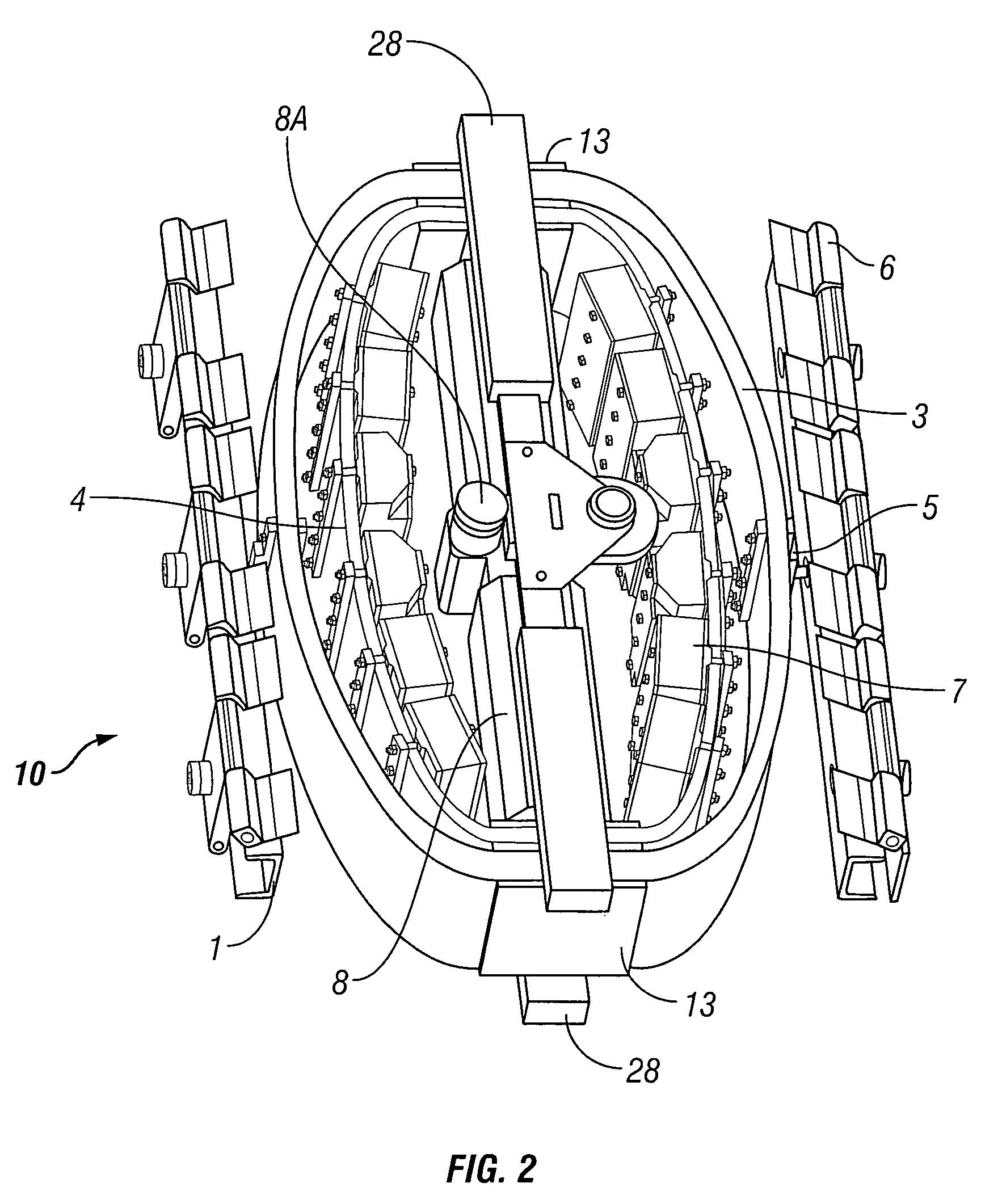
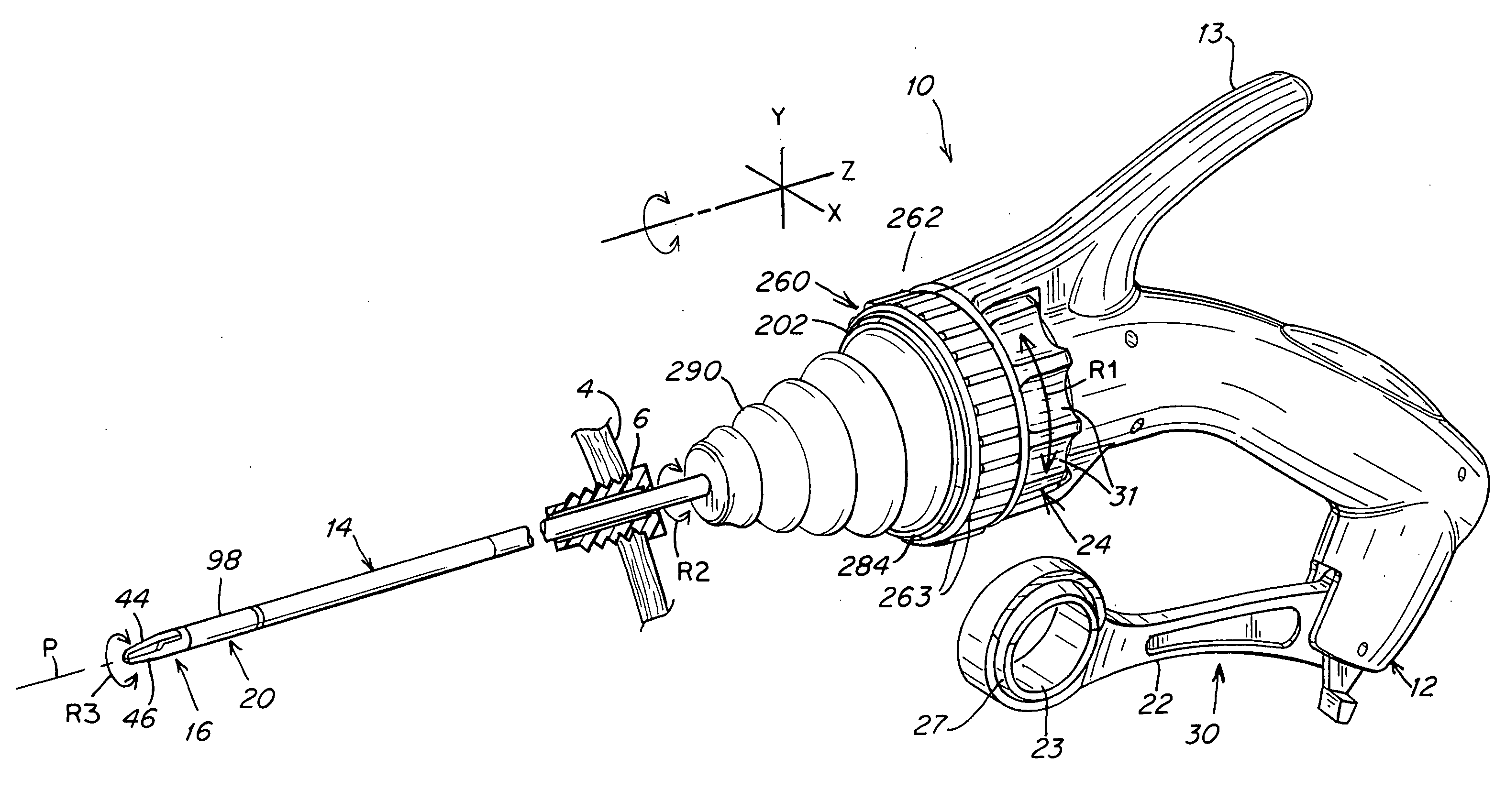
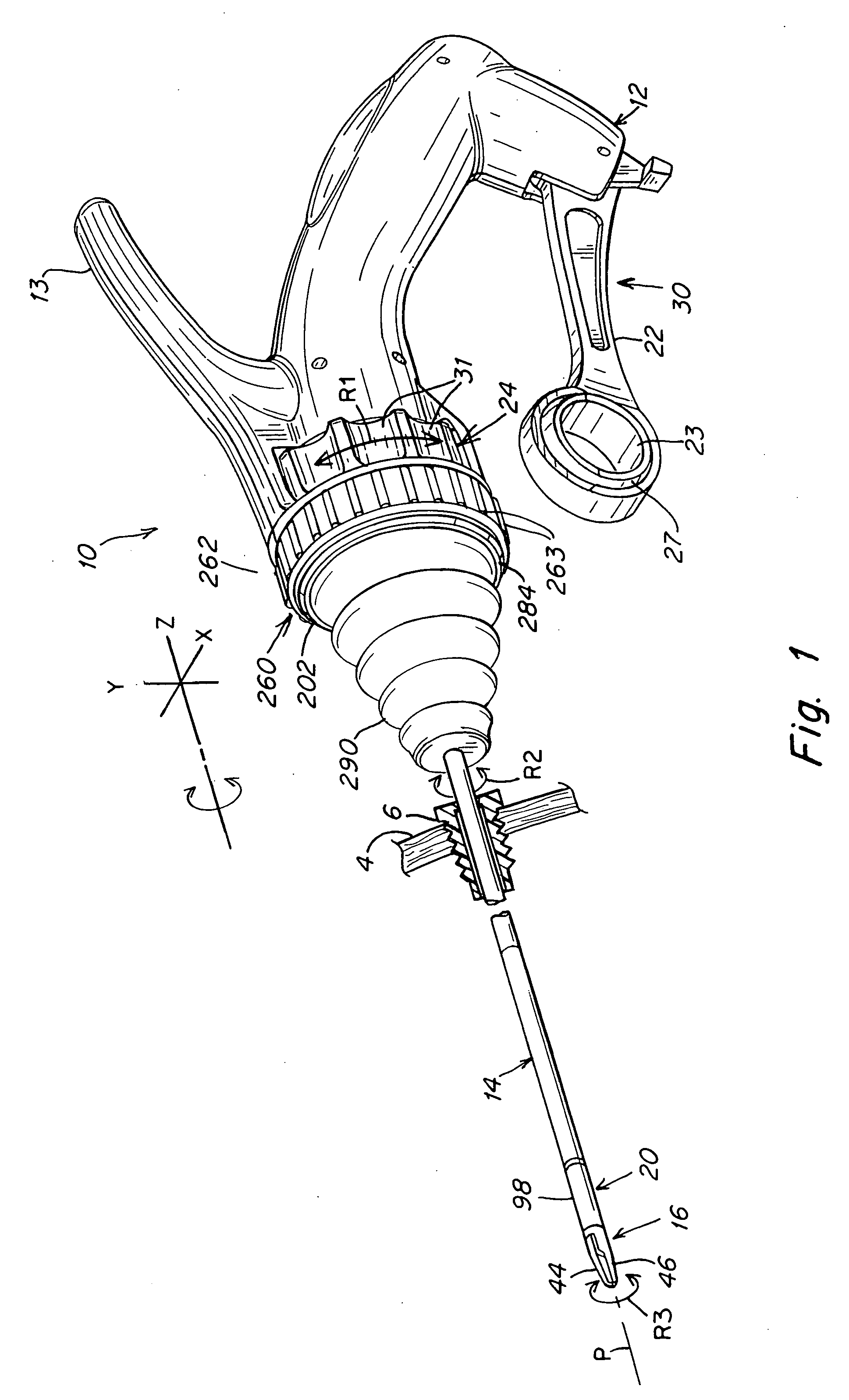
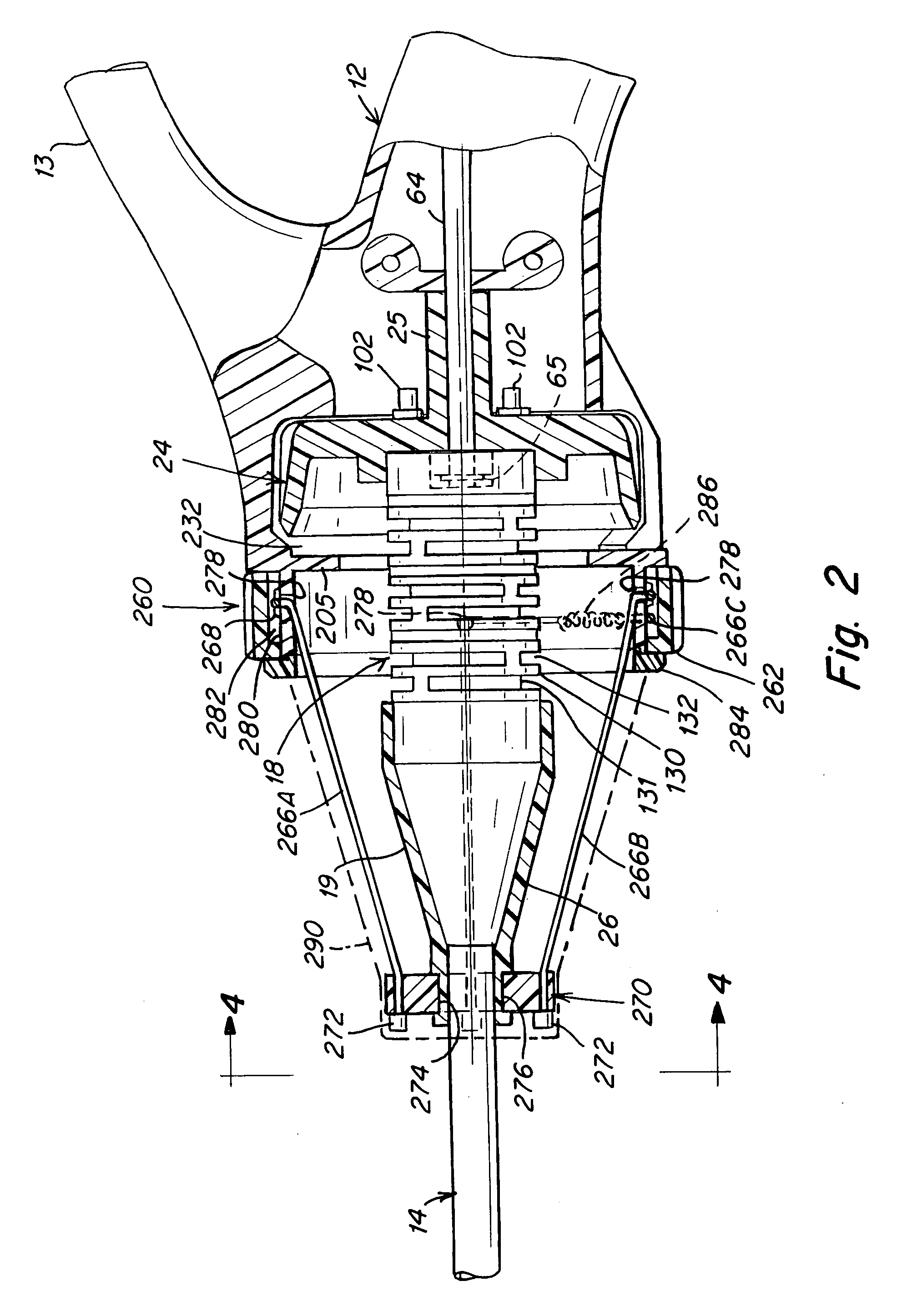
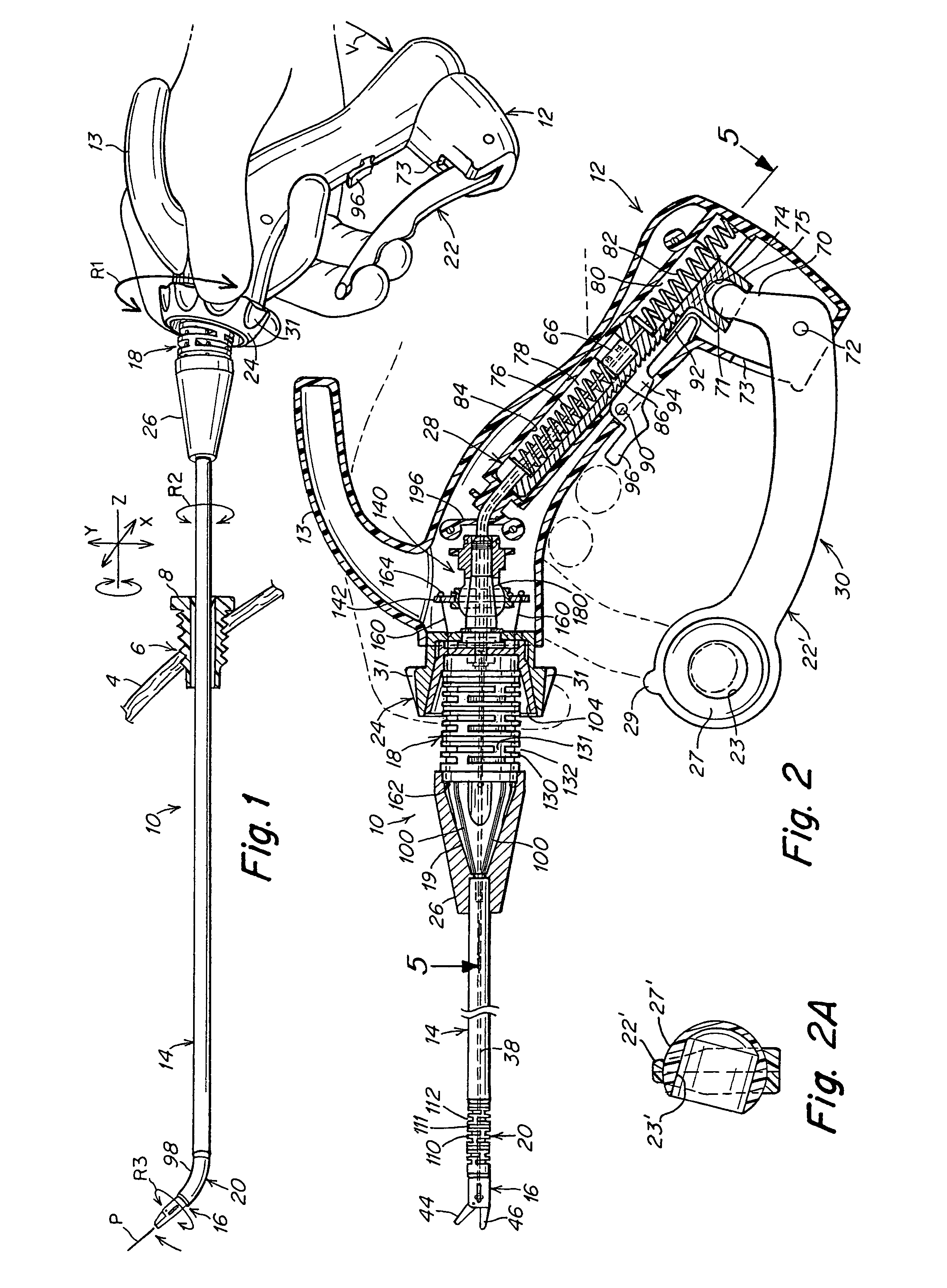
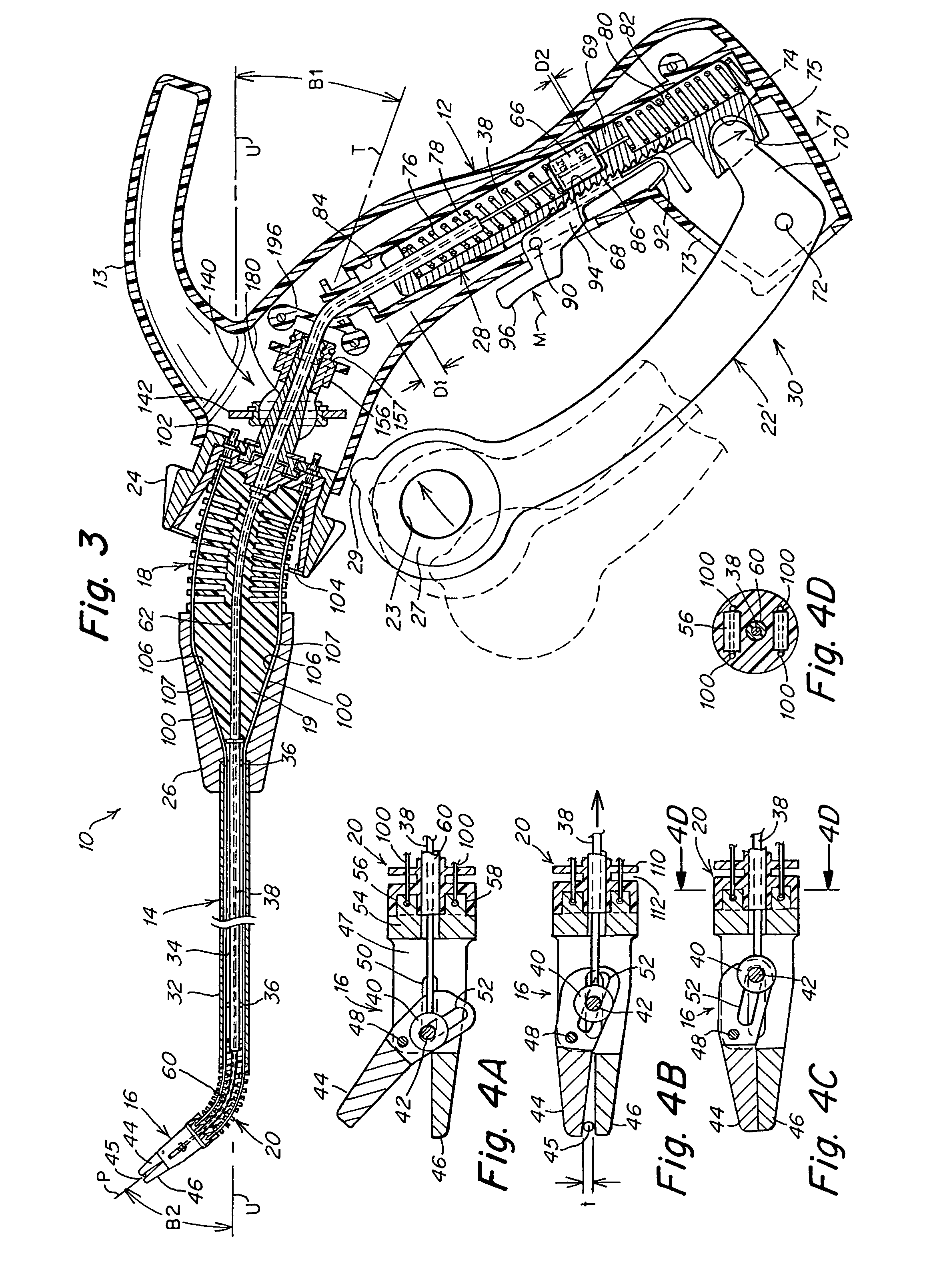
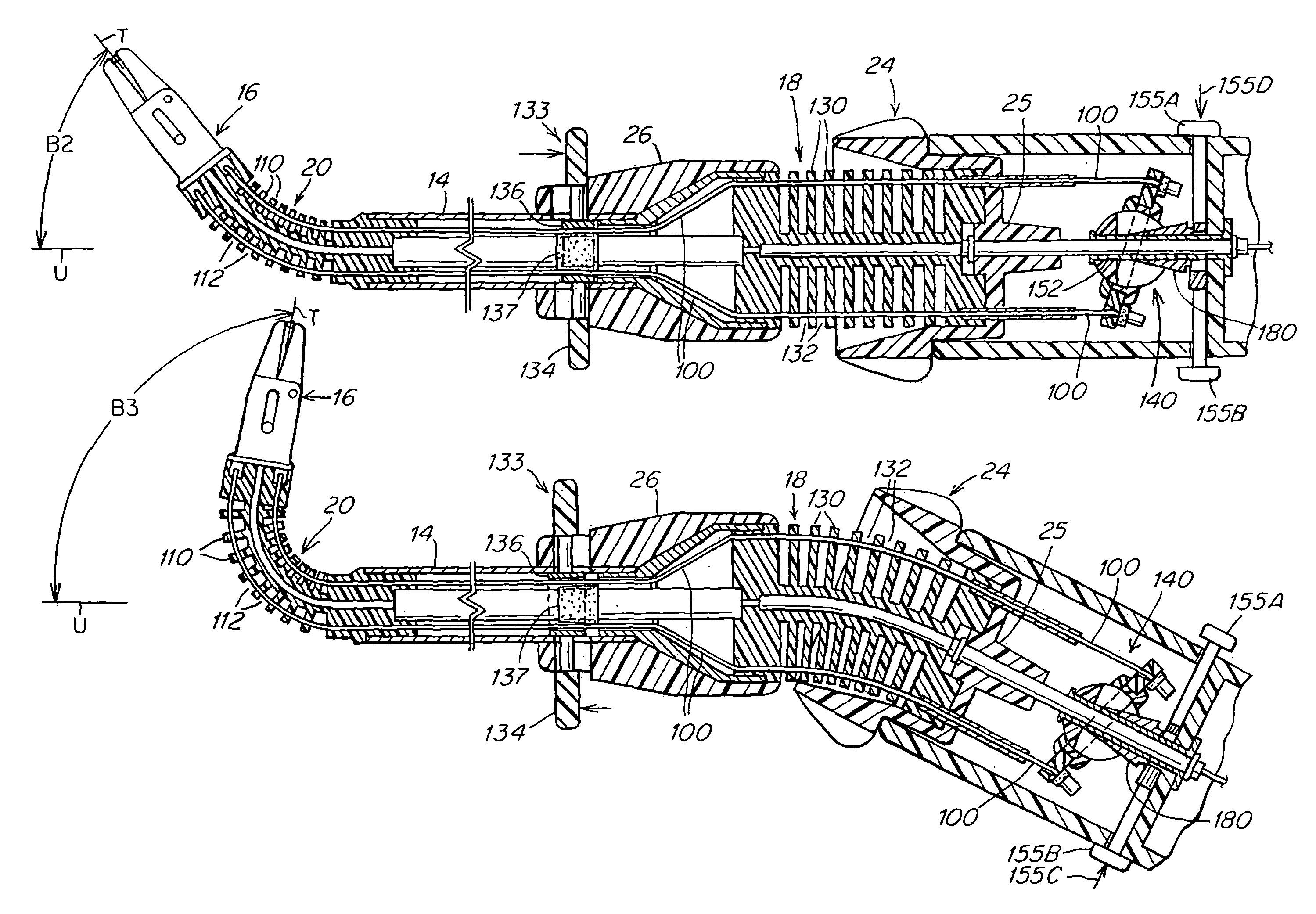
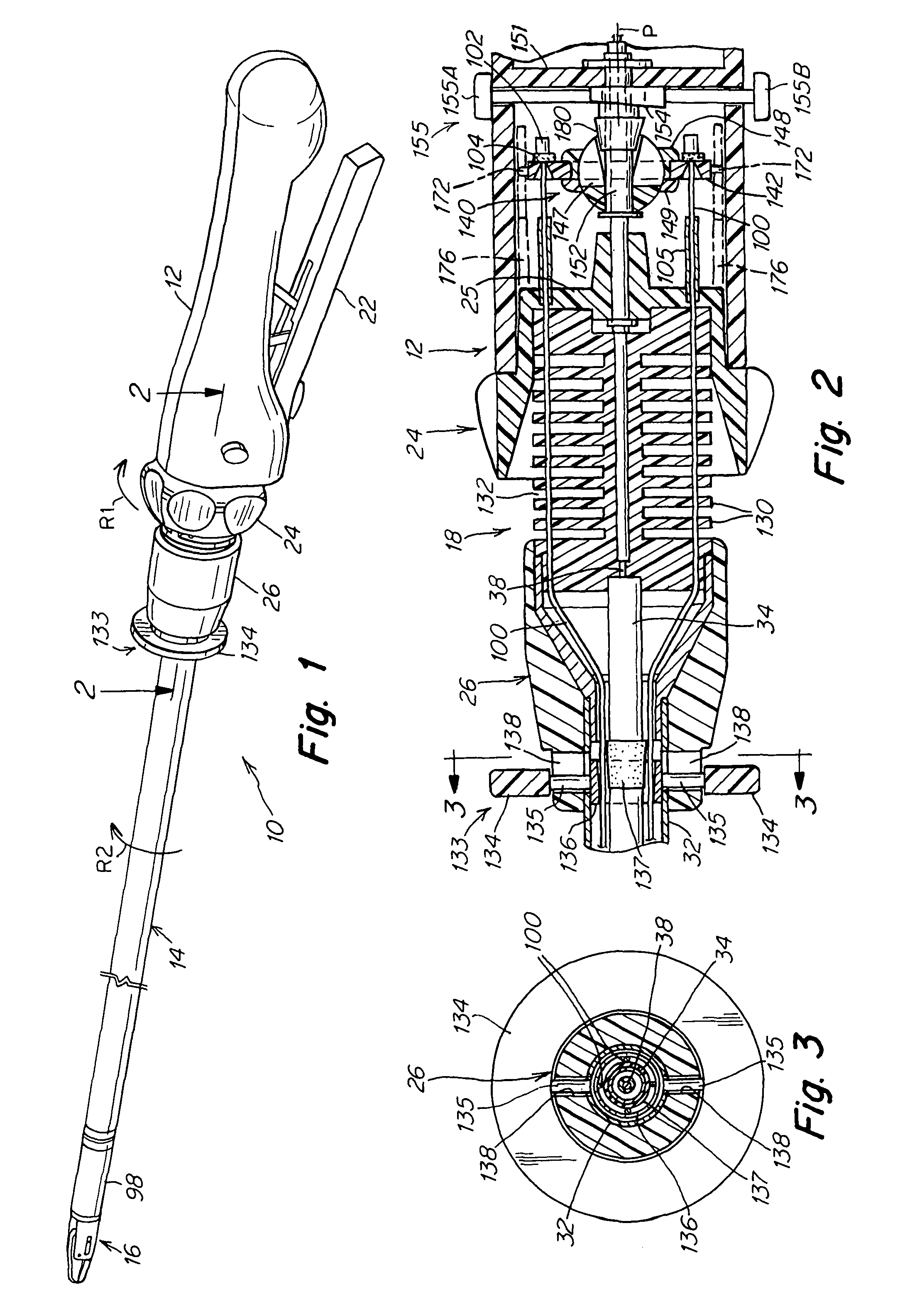
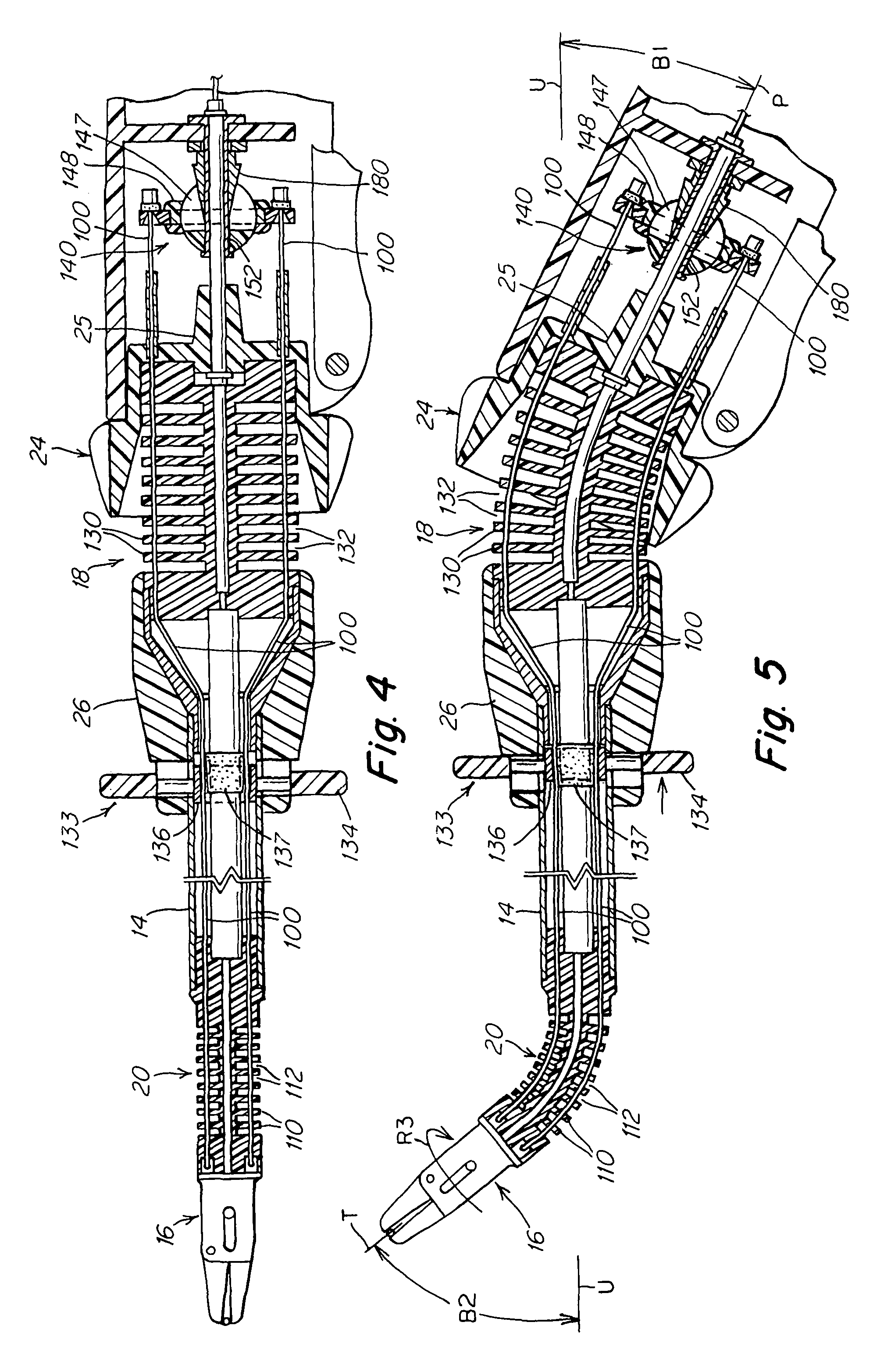
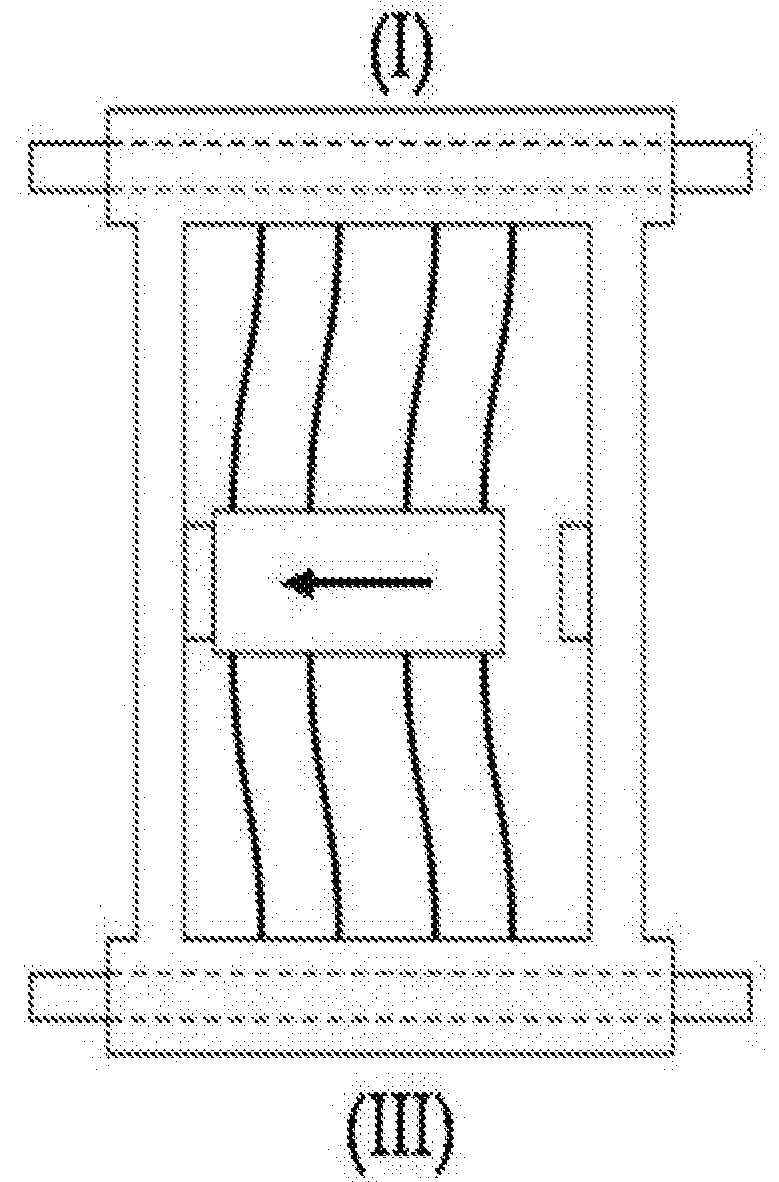
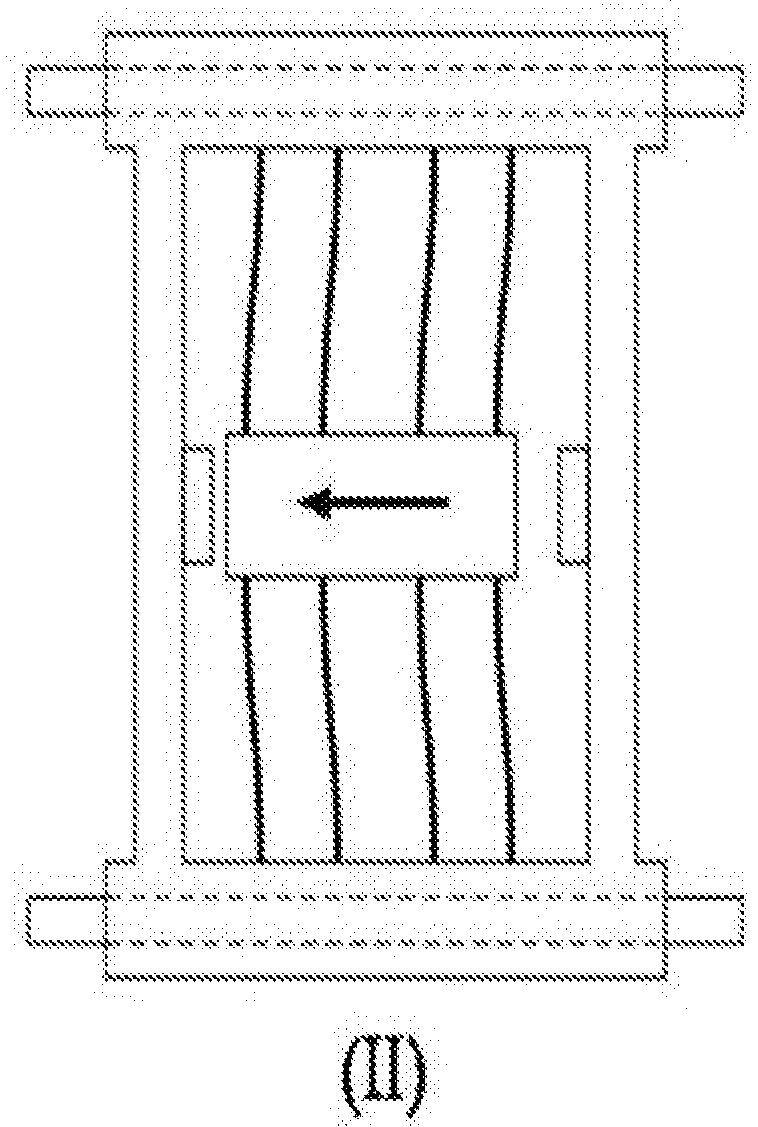
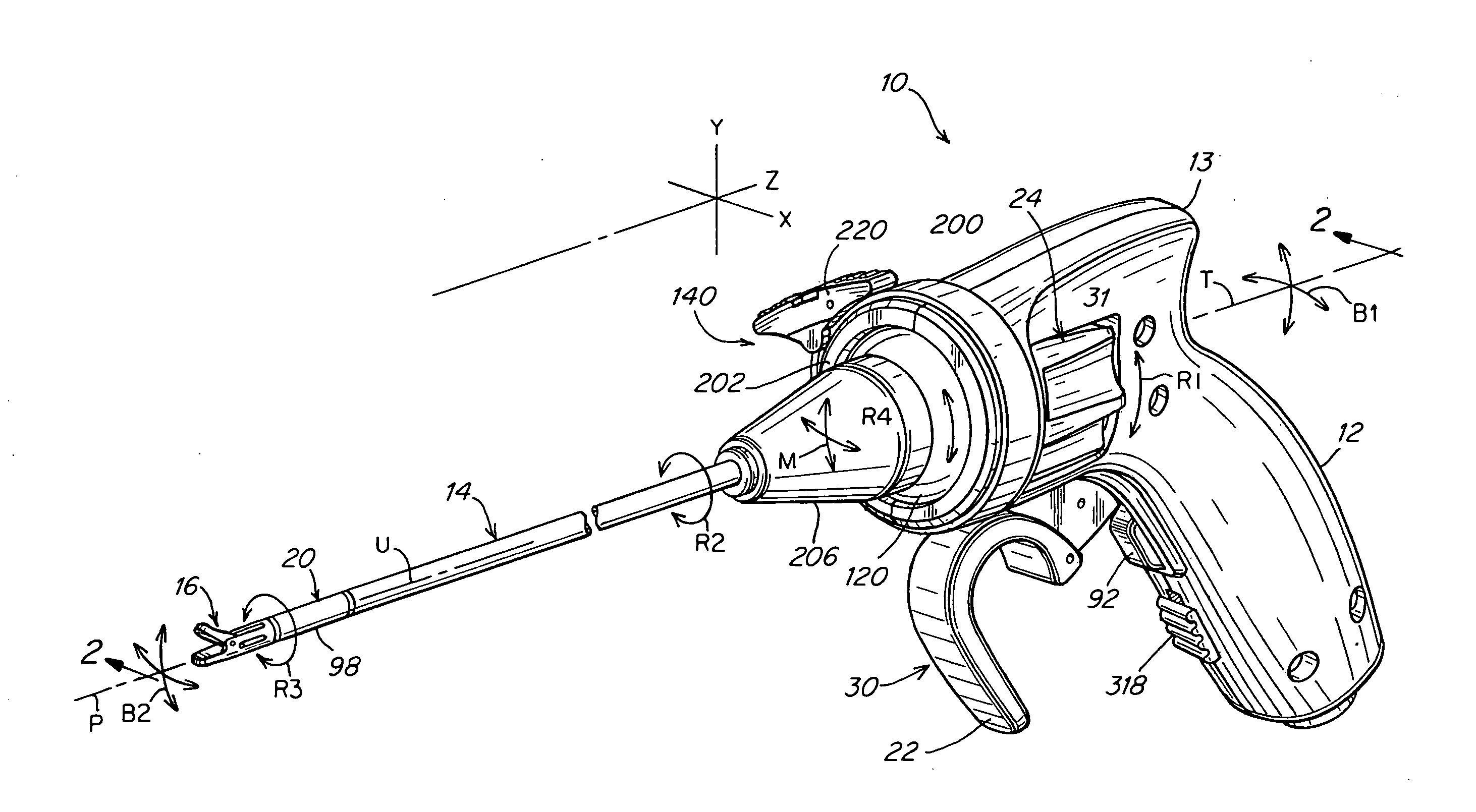
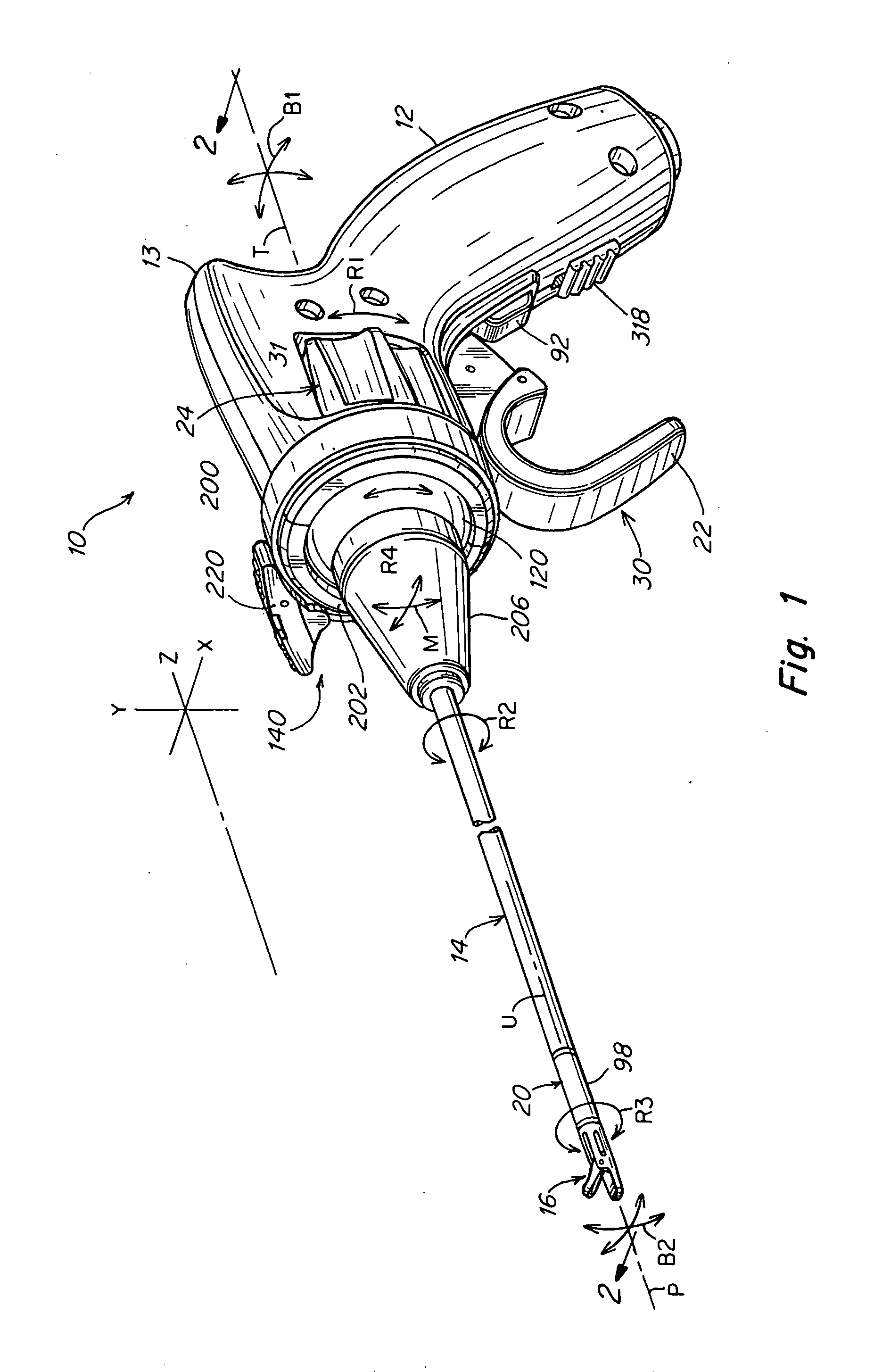
A surgical instrument that includes an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends, a tool disposed from the distal end of the instrument shaft, a control handle disposed from the proximal end of the instrument shaft, a distal motion member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool, a proximal motion member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the handle, actuation means extending between the distal and proximal motion members for coupling motion of the proximal motion member to the distal motion member for controlling the positioning of the tool and a locking mechanism for fixing the position of the tool at a selected position and having locked and unlocked states.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENDOSCOPIC DEVICES INC
Surgical instrument
A medical instrument that includes an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends; a tool for performing a medical procedure; a control handle; a distal motion member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool; a proximal motion member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the control handle; actuation means extending between the distal and proximal motion members for coupling motion of the proximal motion member to the distal motion member for controlling the positioning of the tool; a control tube through which the instrument shaft and tool extend; the control tube including, along the length thereof, a curved section; the curved section of the control tube, upon rotation thereof, providing an additional degree of freedom by displacing the tool out of a plane defined by the curved section of the control tube.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENDOSCOPIC DEVICES
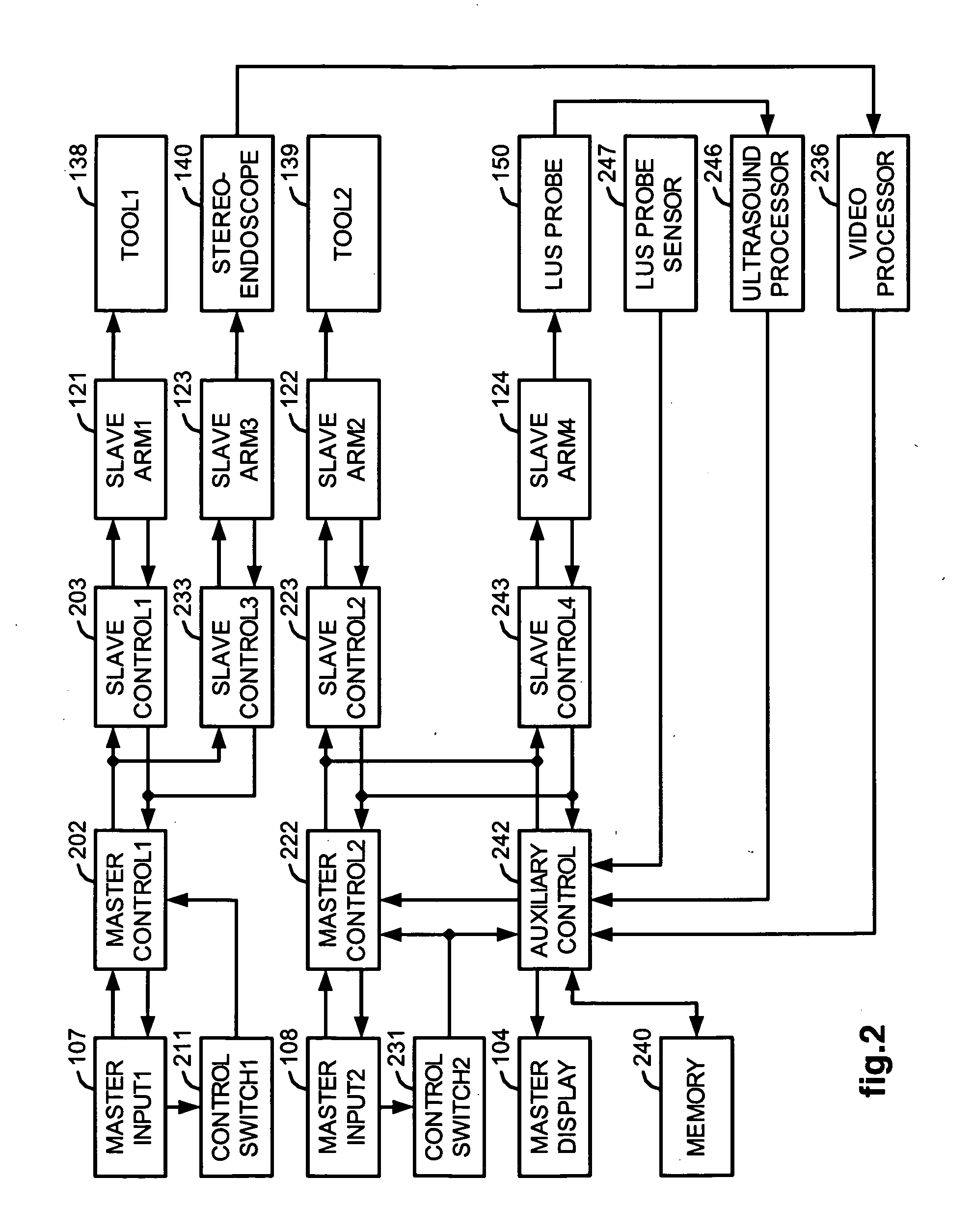
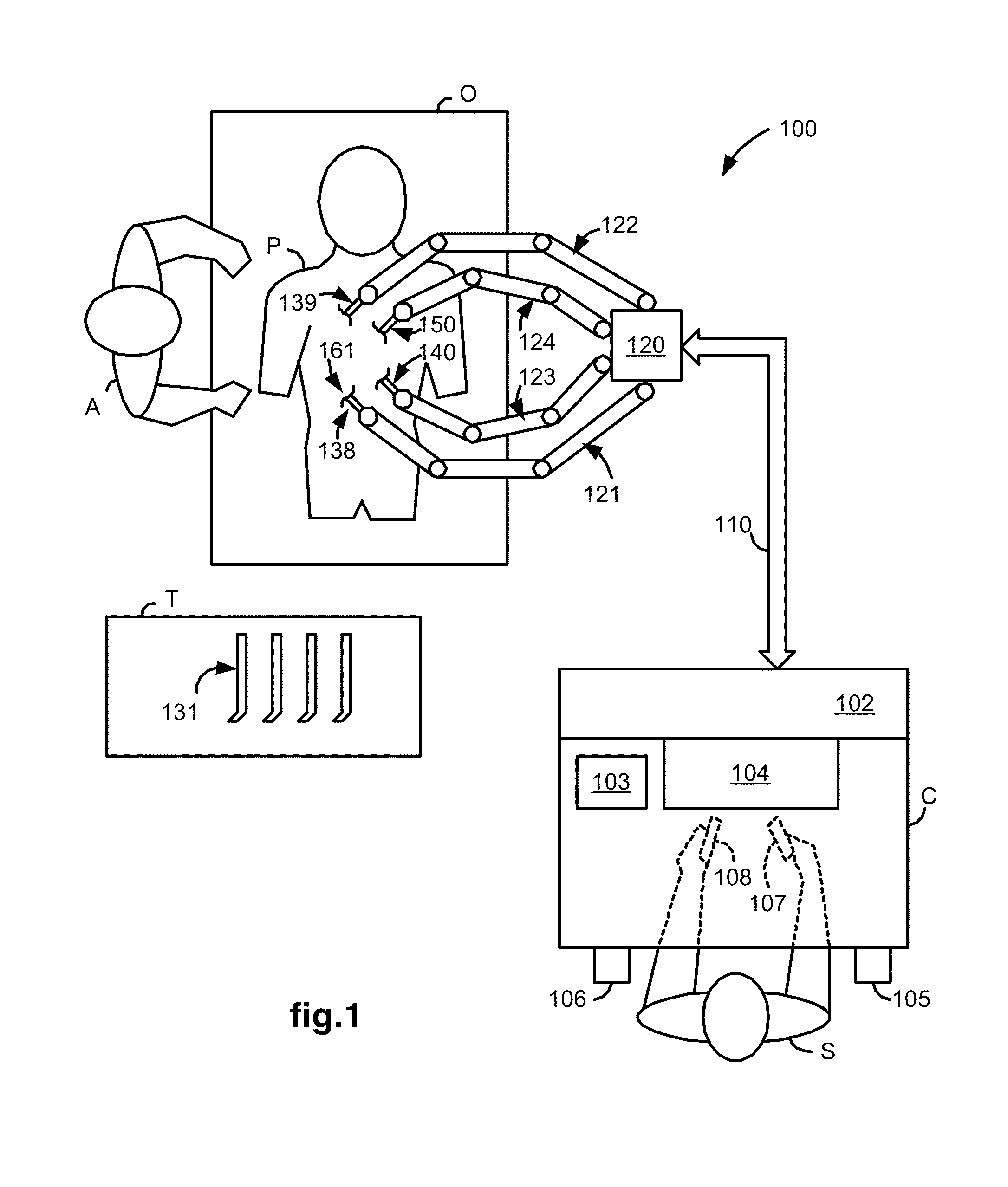
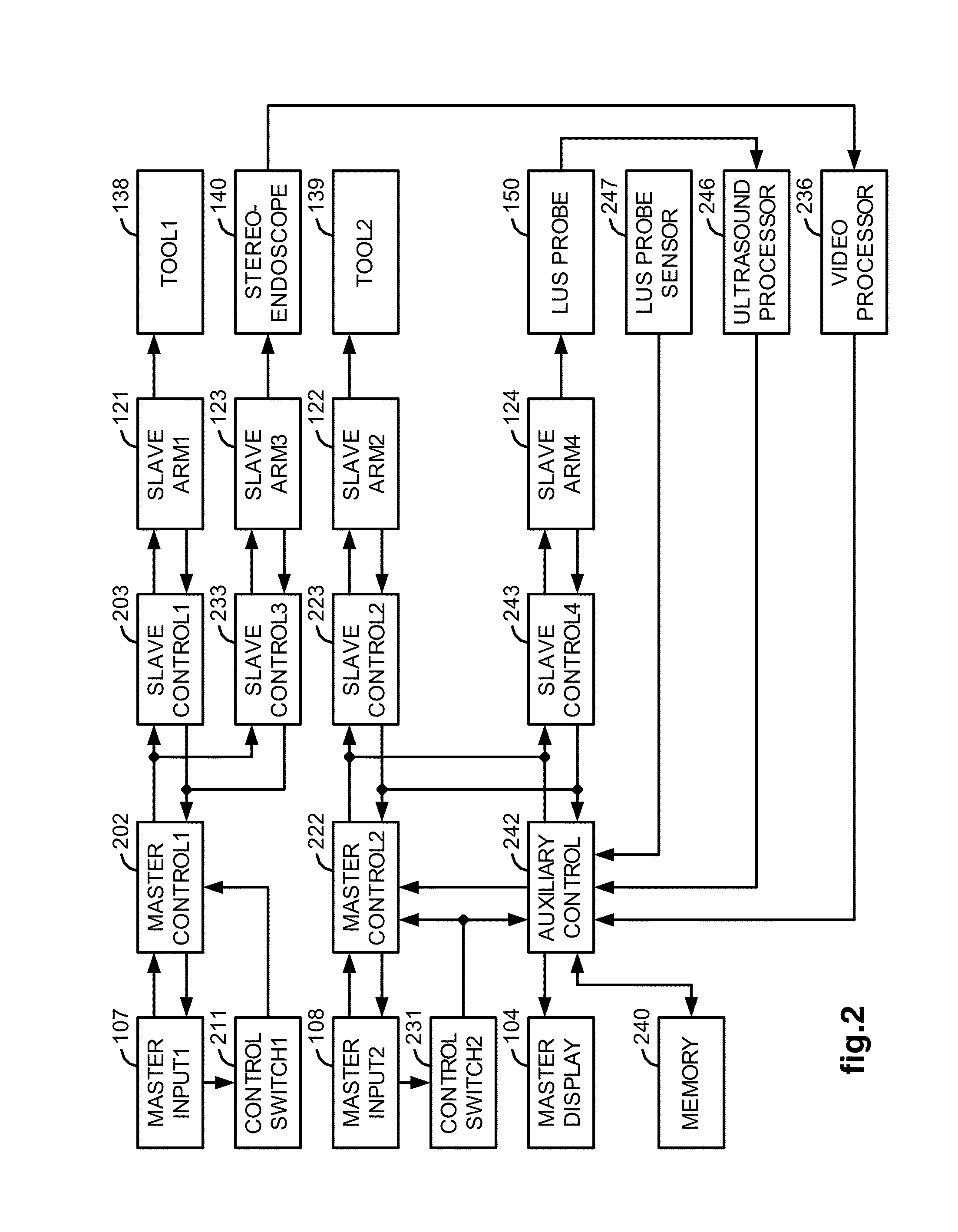
Interactive user interfaces for robotic minimally invasive surgical systems
ActiveUS20090036902A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDisplay deviceSurgical site
In one embodiment of the invention, a method for a minimally invasive surgical system is disclosed. The method includes capturing and displaying camera images of a surgical site on at least one display device at a surgeon console; switching out of a following mode and into a masters-as-mice (MaM) mode; overlaying a graphical user interface (GUI) including an interactive graphical object onto the camera images; and rendering a pointer within the camera images for user interactive control. In the following mode, the input devices of the surgeon console may couple motion into surgical instruments. In the MaM mode, the input devices interact with the GUI and interactive graphical objects. The pointer is manipulated in three dimensions by input devices having at least three degrees of freedom. Interactive graphical objects are related to physical objects in the surgical site or a function thereof and are manipulatable by the input devices.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Interactive user interfaces for robotic minimally invasive surgical systems
ActiveUS8398541B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMini invasive surgeryDisplay device
In one embodiment of the invention, a method for a minimally invasive surgical system is disclosed. The method includes capturing and displaying camera images of a surgical site on at least one display device at a surgeon console; switching out of a following mode and into a masters-as-mice (MaM) mode; overlaying a graphical user interface (GUI) including an interactive graphical object onto the camera images; and rendering a pointer within the camera images for user interactive control. In the following mode, the input devices of the surgeon console may couple motion into surgical instruments. In the MaM mode, the input devices interact with the GUI and interactive graphical objects. The pointer is manipulated in three dimensions by input devices having at least three degrees of freedom. Interactive graphical objects are related to physical objects in the surgical site or a function thereof and are manipulatable by the input devices.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Surgical instrument
A surgical instrument having an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends, a tool disposed from the distal end of the instrument shaft, a control handle coupled from the proximal end of the instrument shaft, a distal motion member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool, a proximal motion member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the handle and actuation means extending between distal and proximal motion members for coupling motion of the proximal motion member to the distal motion member for controlling the positioning of the tool. Rotation control and locking members are also disclosed.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENDOSCOPIC DEVICES
Surgical instrument
A surgical instrument that includes an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends, a tool disposed from the distal end of the instrument shaft, a control handle disposed from the proximal end of the instrument shaft, a distal motion member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool, a proximal motion member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the handle, actuation means extending between the distal and proximal motion members for coupling motion of the proximal motion member to the distal motion member for controlling the positioning of the tool and a locking mechanism for fixing the position of the tool at a selected position and having locked and unlocked states.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENDOSCOPIC DEVICES
Surgical instrument
A surgical instrument that includes an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends, a tool disposed from the distal end of the instrument shaft, a control handle disposed from the proximal end of the instrument shaft, a distal motion member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool, a proximal motion member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the handle, actuation means extending between the distal and proximal motion members for coupling motion of the proximal motion member to the distal motion member for controlling the positioning of the tool, a rotation knob disposed adjacent the control handle and rotatable relative to the control handle for causing a corresponding rotation of the instrument shaft and tool and a locking mechanism for fixing the position of the tool at a selected position and having locked and unlocked states. The rotation knob has a first position in which the locking mechanism is controlled to be in its locked state and a second position in which the locking mechanism is released to its unlocked state so as to allow tool positioning.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENDOSCOPIC DEVICES
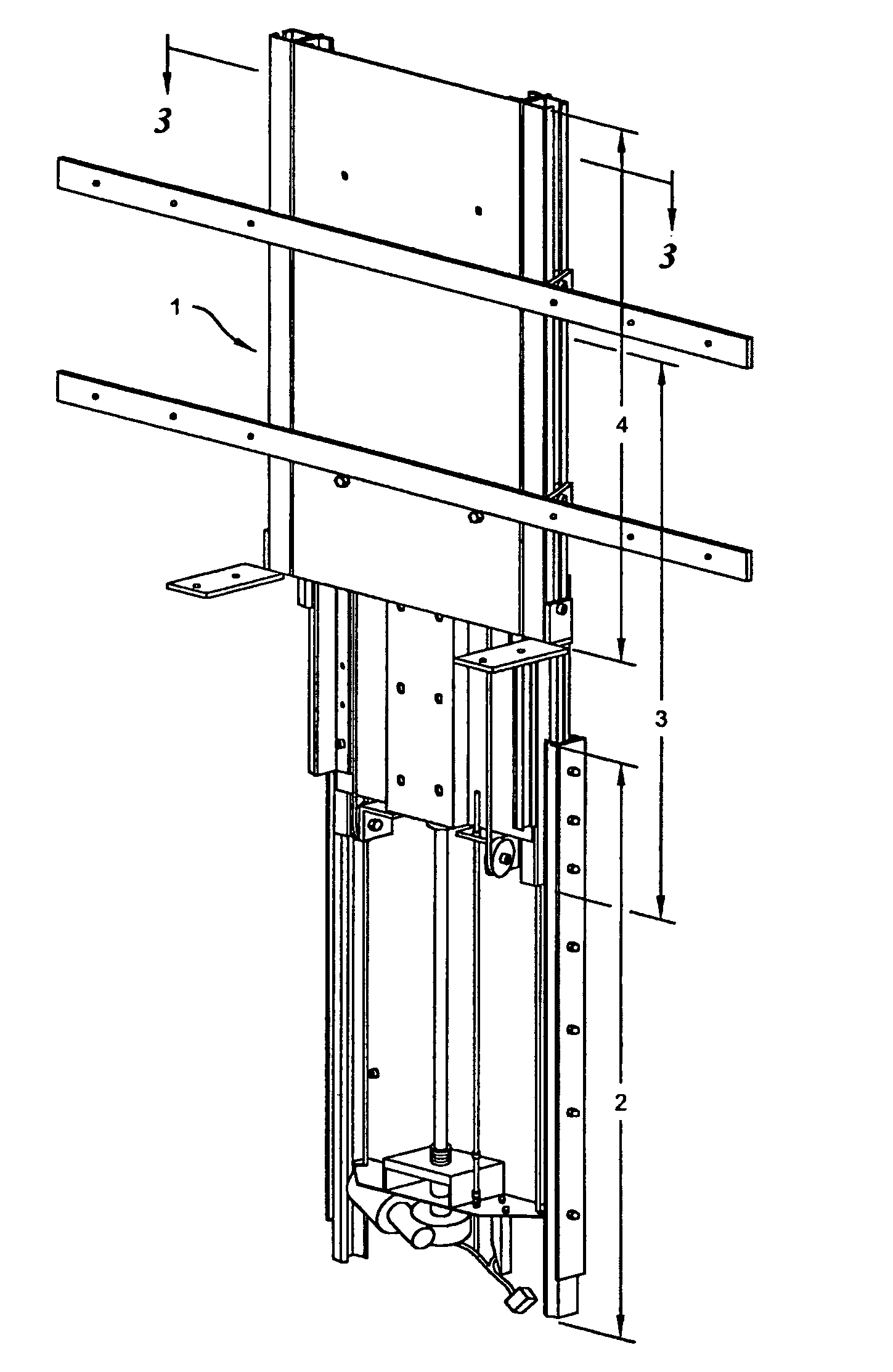
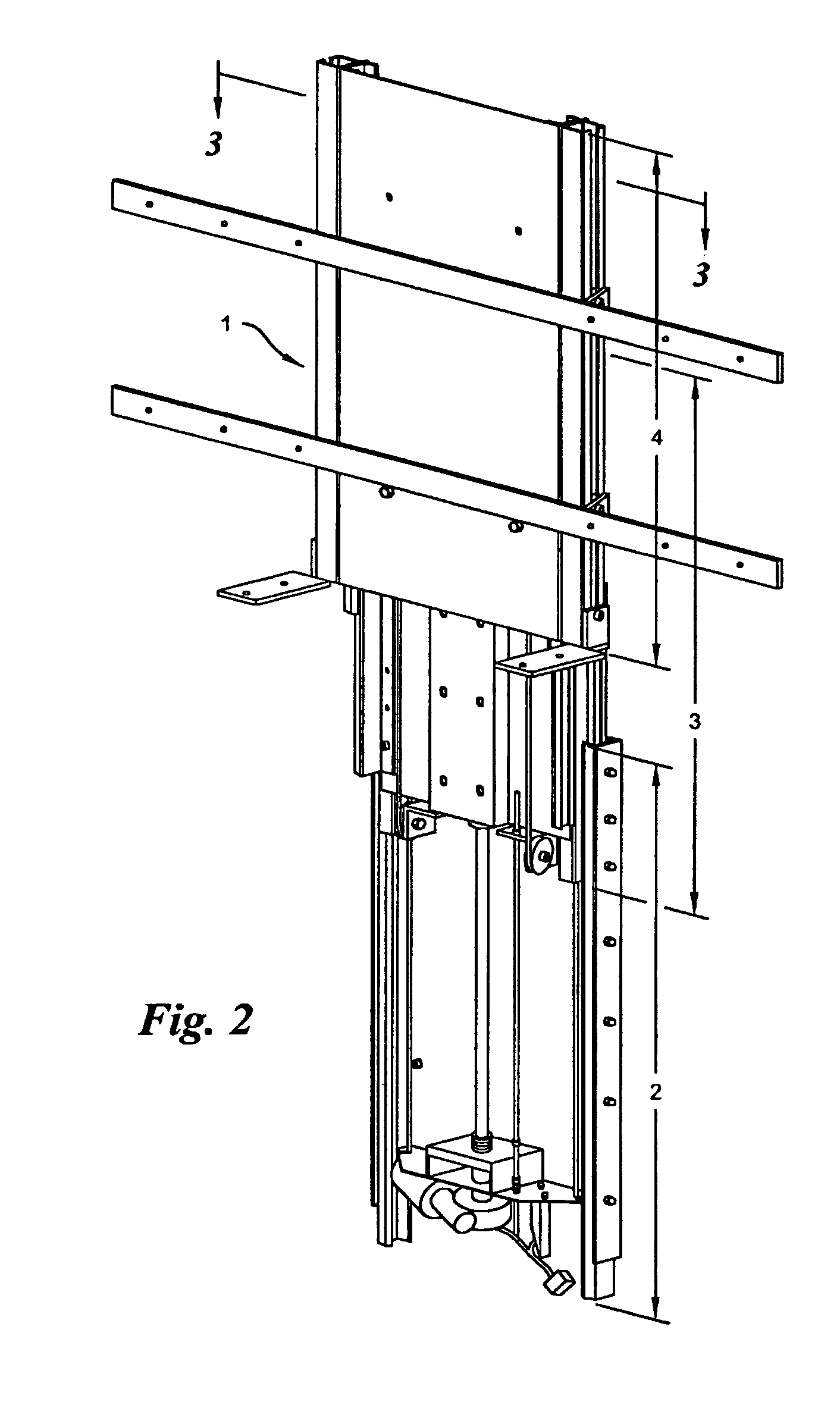
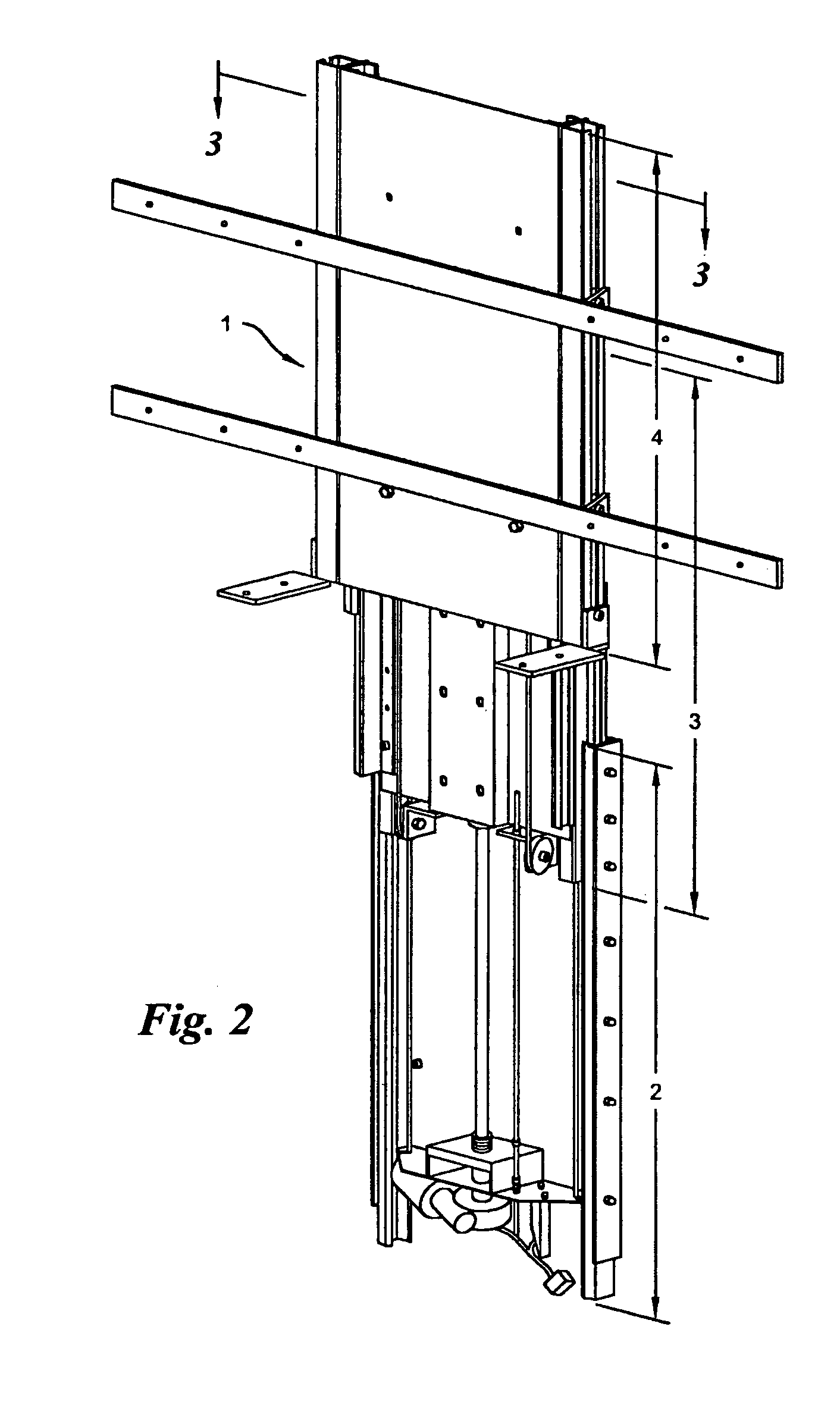
Compound lift device
InactiveUS7044423B2Compact storageFacilitating the uninterrupted and nearly noiseless movement of a low-profile televisionTelevision system detailsFurniture partsKinematic couplingMotor drive
The present invention is a compound motorized lift device facilitating the uninterrupted and nearly noiseless movement of a low-profile television. The invention is comprised of a base unit, an intermediate unit, and a support unit slidably disposed in a telescoping fashion in the described order. A pair of linearly extensible slides are fastened between base and intermediate units and between intermediate and support units. The intermediate unit is extended and retracted with respect to the base unit in a linear fashion via a motor driven screw. The support unit is extended and retracted in a linear fashion via a cable-pulley arrangement that couples motion by the intermediate unit in a likewise direction to the support unit.
Owner:BOBER WIESLAW
Surgical instrument
A surgical instrument that includes an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends, a tool disposed from the distal end of the instrument shaft, a control handle disposed from the proximal end of the instrument shaft, a distal motion member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool, a proximal motion member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the handle, actuation means extending between the distal and proximal motion members for coupling motion of the proximal motion member to the distal motion member for controlling the positioning of the tool and a locking mechanism for fixing the position of the tool at a selected position and having locked and unlocked states.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENDOSCOPIC DEVICES
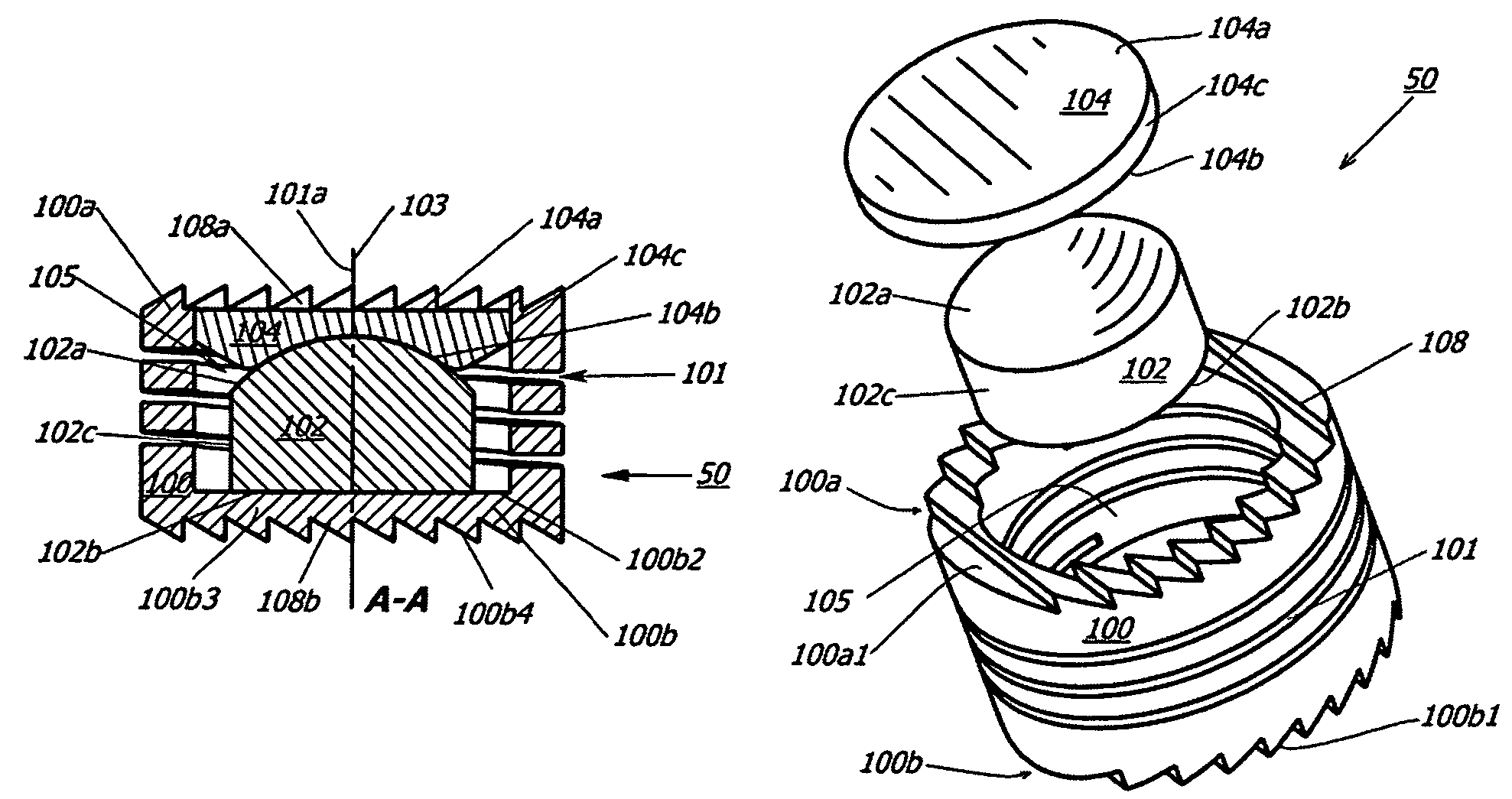
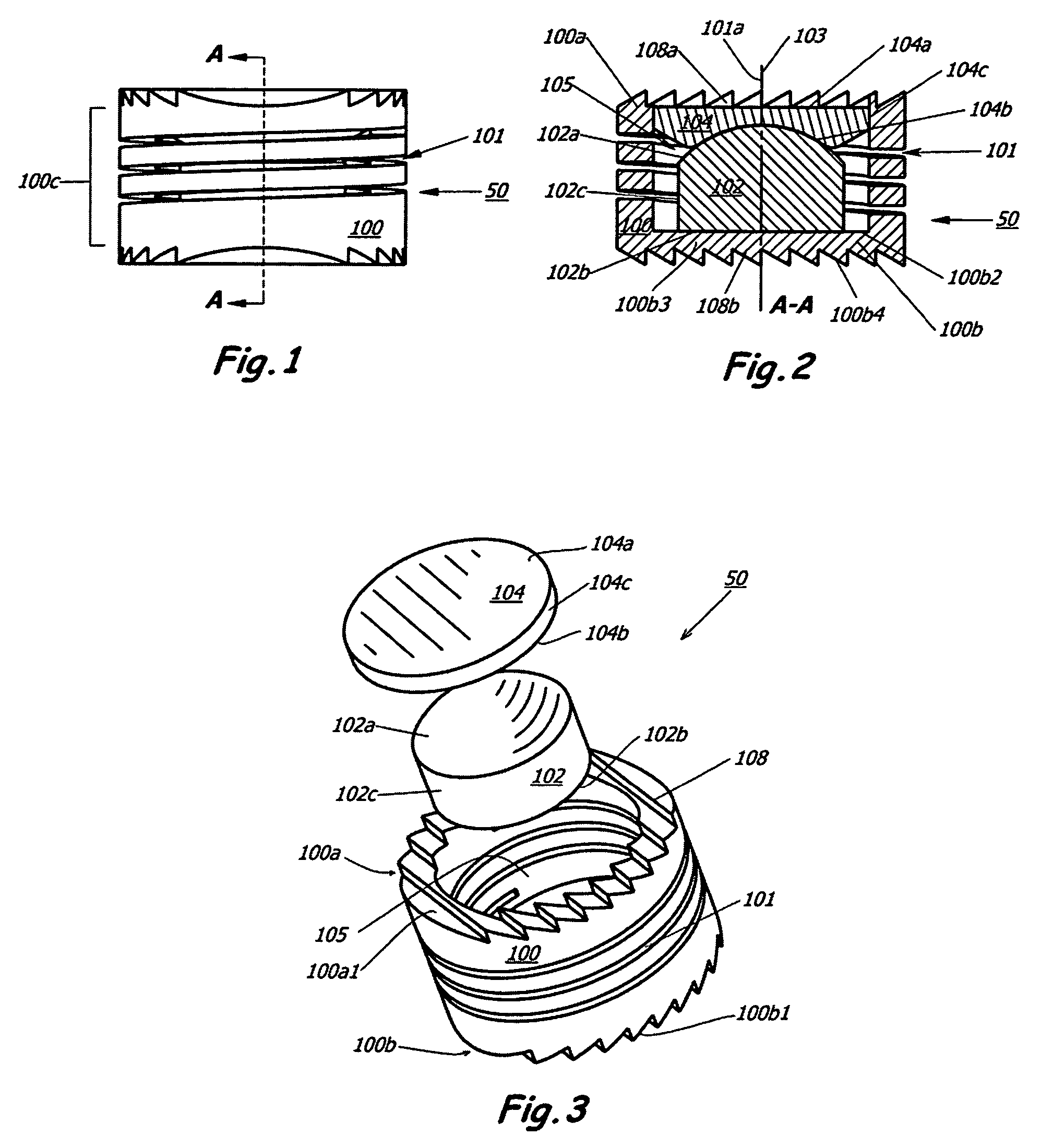
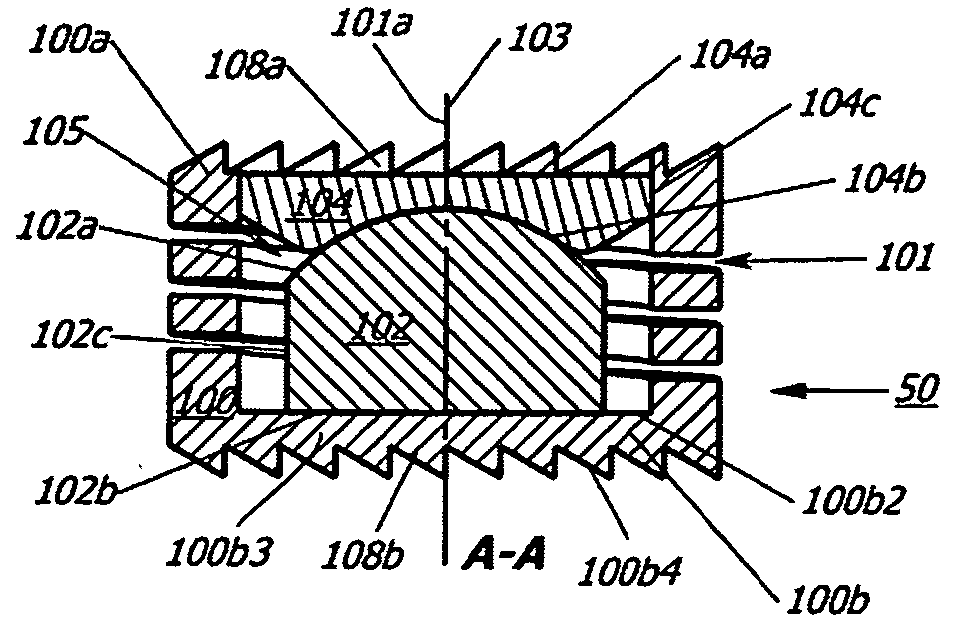
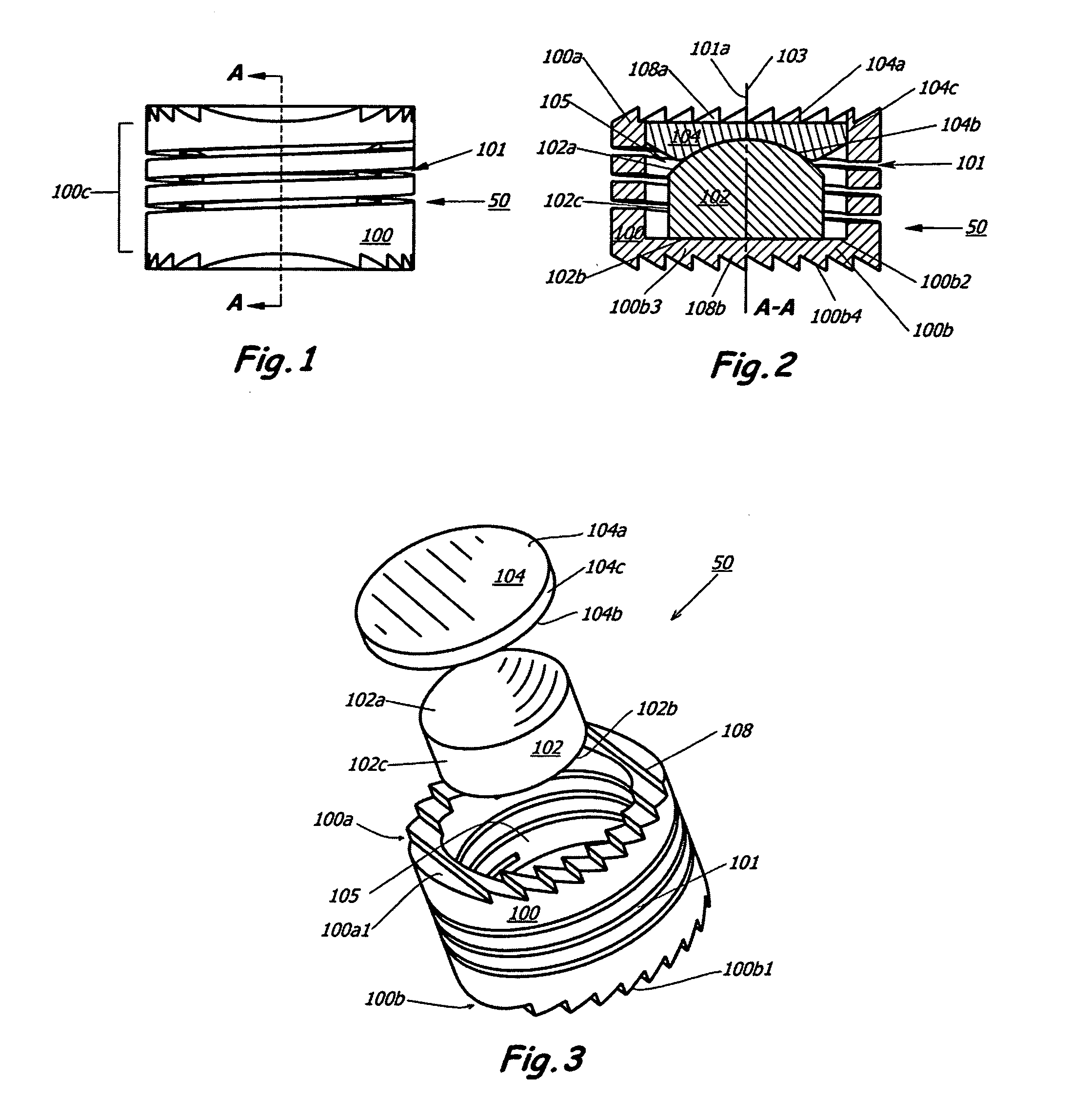
Intervertebral disc replacement prosthesis
An intervertebral disc prosthesis for placement between a first vertebra and a second vertebra adjacent to the first vertebra. In one embodiment, the intervertebral disc prosthesis includes a resilient member, a first support member and a second support member. The first support member and the second support member are housed into the resilient member that is arranged, in use, to be secured to the first vertebra and the second vertebra, respectively. The intervertebral disc prosthesis can generate a coupled motion in more than one possible direction responsive to a possible movement of at least one of the first vertebra and the second vertebra, among the resilient member, the first support member and the second support member.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Intervertebral disc replacement prosthesis
An intervertebral disc prosthesis for placement between a first vertebra and a second vertebra adjacent to the first vertebra. In one embodiment, the intervertebral disc prosthesis includes a resilient member, a first support member and a second support member. The first support member and the second support member are housed into the resilient member that is arranged, in use, to be secured to the first vertebra and the second vertebra, respectively. The intervertebral disc prosthesis can generate a coupled motion in more than one possible direction responsive to a possible movement of at least one of the first vertebra and the second vertebra, among the resilient member, the first support member and the second support member.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Compound lift device
InactiveUS20050109892A1Minimizes cabinet sizeReduce weightTelevision system detailsFurniture partsMotor driveEngineering
The present invention is a compound motorized lift device facilitating the uninterrupted and nearly noiseless movement of a low-profile television. The invention is comprised of a base unit, an intermediate unit, and a support unit slidably disposed in a telescoping fashion in the described order. A pair of linearly extensible slides are fastened between base and intermediate units and between intermediate and support units. The intermediate unit is extended and retracted with respect to the base unit in a linear fashion via a motor driven screw. The support unit is extended and retracted in a linear fashion via a cable-pulley arrangement that couples motion by the intermediate unit in a likewise direction to the support unit.
Owner:BOBER WIESLAW
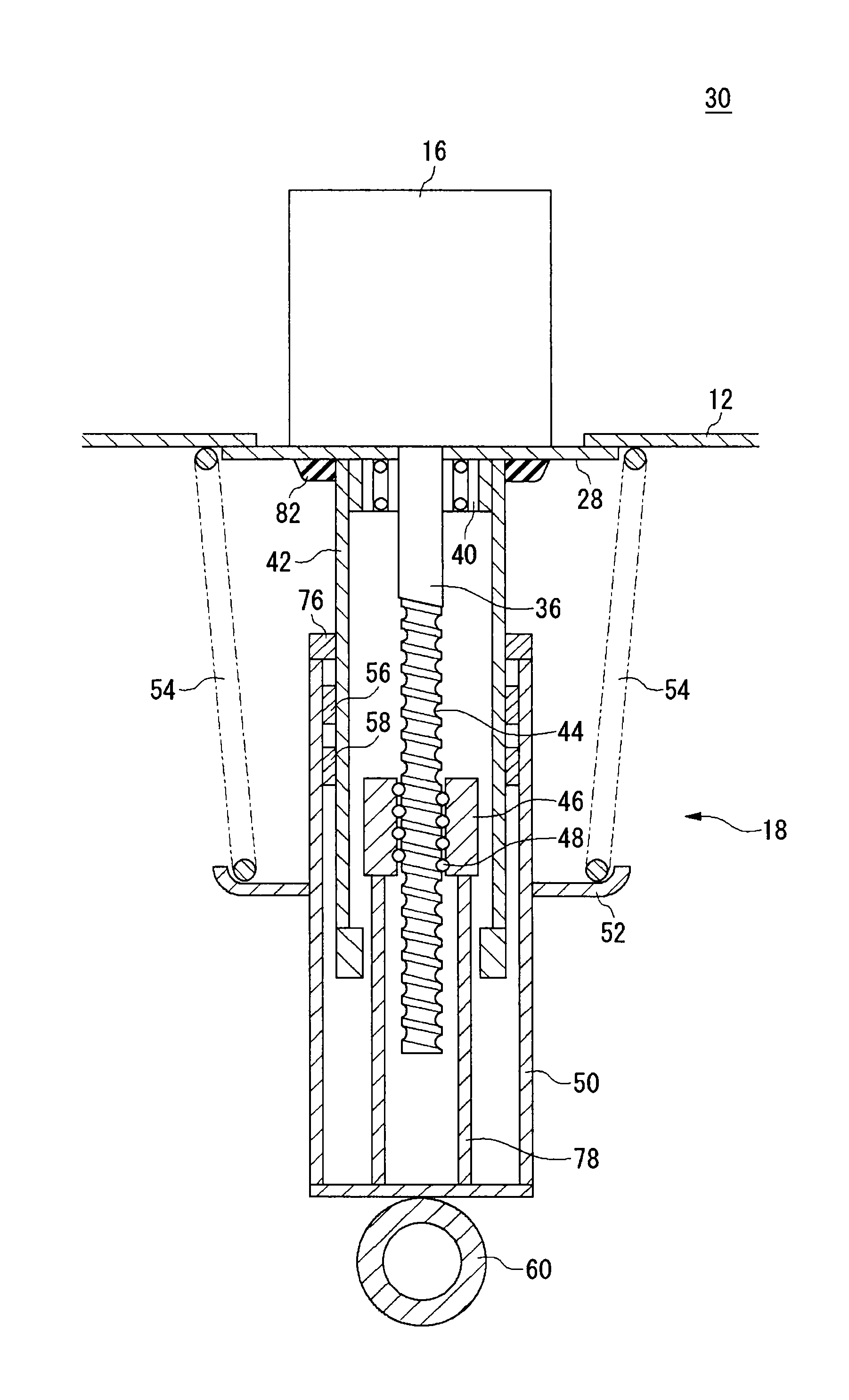
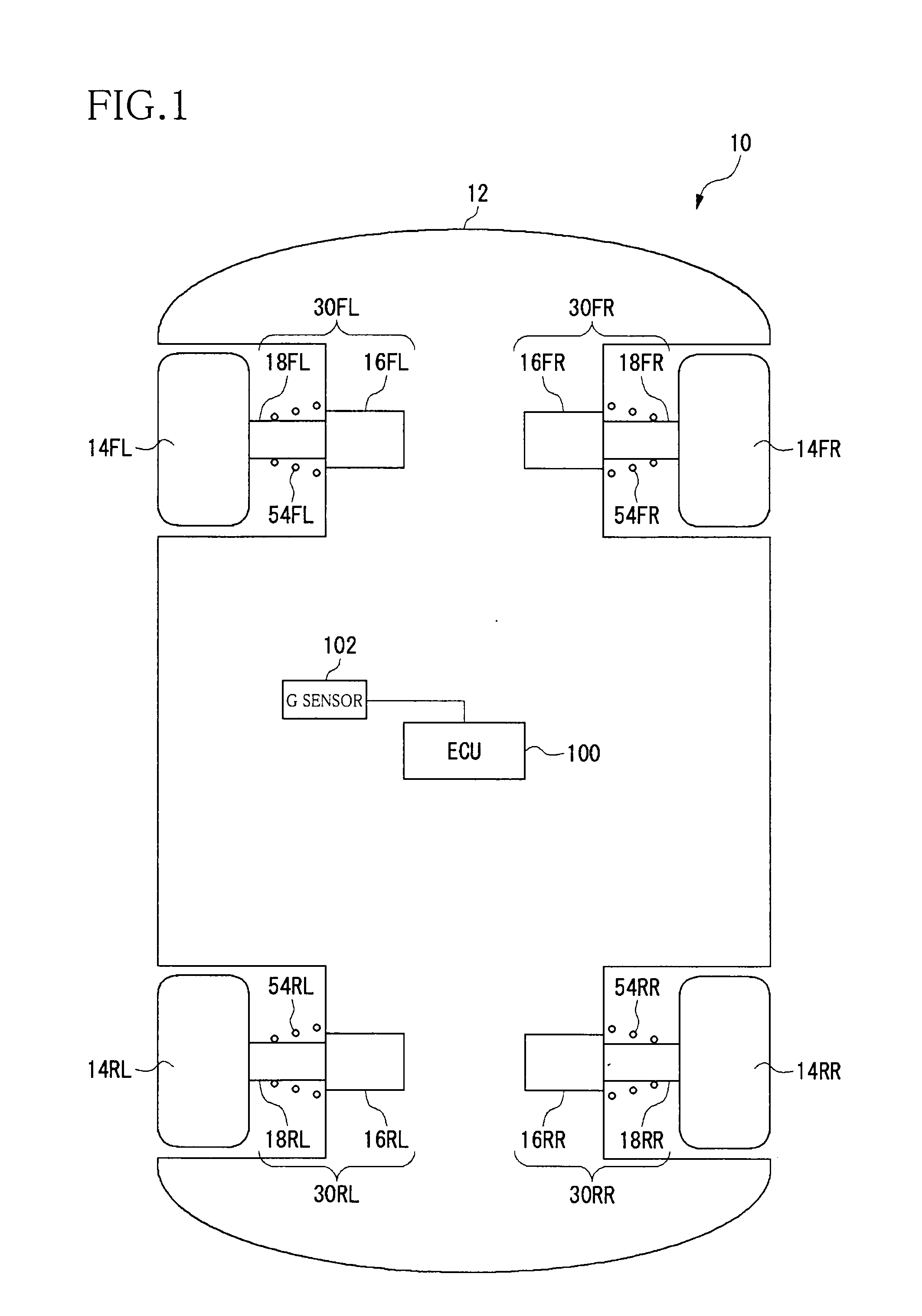
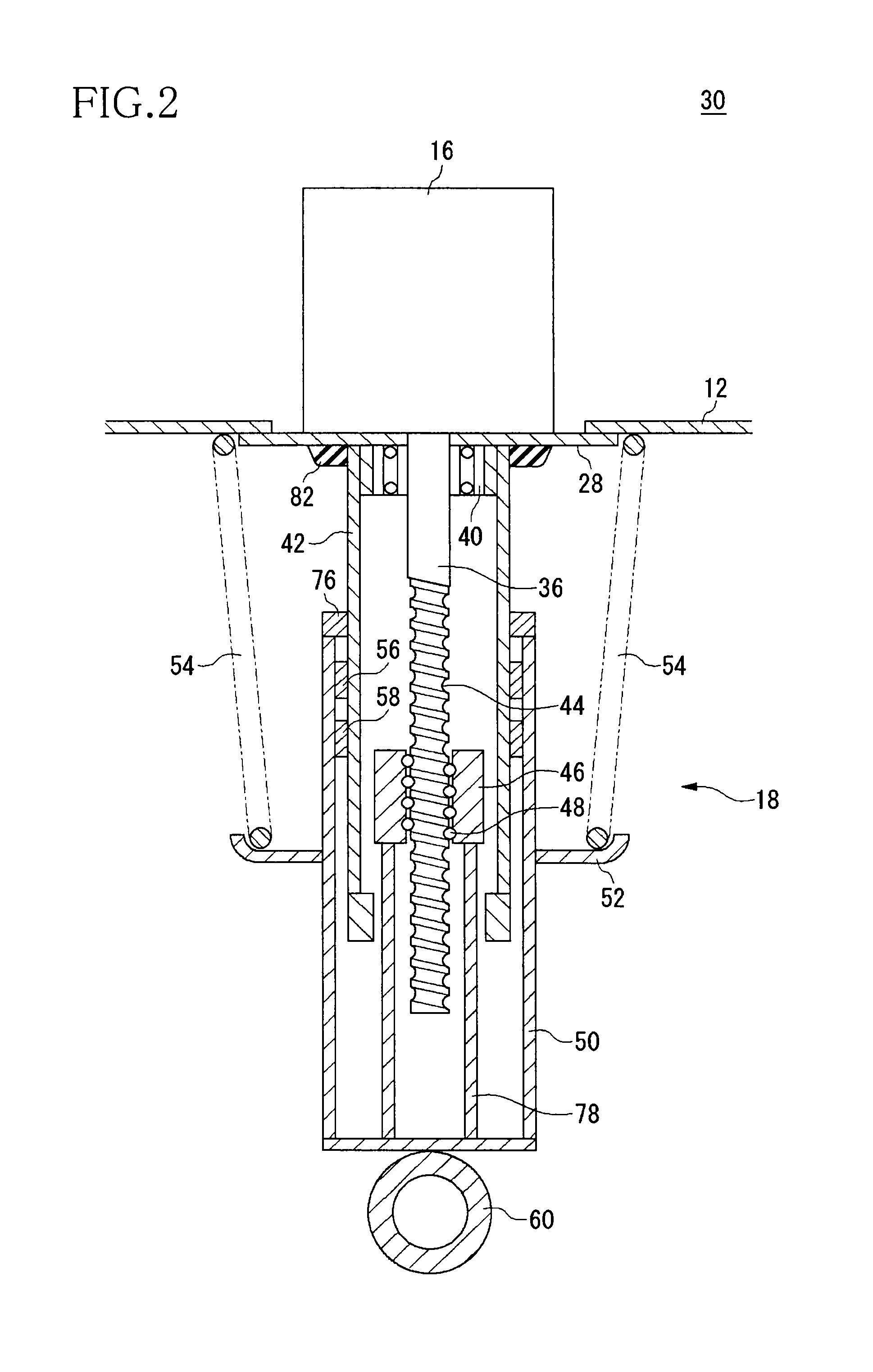
Suspension system for vehicle
ActiveUS20090273147A1Simple structureReduce voltageNon-rotating vibration suppressionDigital data processing detailsElectromagnetic absorbersClosed loop
In a system including four electromagnetic absorbers for respective four vehicle wheels, motor coils of two respective electromagnetic absorbers disposed corresponding to two diagonally located wheels are connected forming a closed loop including the coils. A generated damping force magnitude can be made different between an instance directions of respective movements of the diagonally located two wheels with respect to the vehicle body are the same, and an instance the directions are opposite each other. Each electromagnetic absorber includes a resistor cooperating with the corresponding coil forming a closed loop, and selectively establishes: a connected state in which one of the four coils and any of the other three coils are connected to form a closed loop; and a non-connected state in which the one of the four coils is not connected to any other coil. An appropriate vibration suppressing action is exhibited with respect to a coupled motion.
Owner:KYB CORP +2
Seismic vibrator having multiple resonant frequencies in the seismic frequency band using multiple spring and mass arrangements to reduce required reactive mass
InactiveUS7881158B2Seismic energy generationMagnetostrictive transducersTransducerClassical mechanics
A seismic vibrator includes a transducer, a reactive mass, a base plate to couple motion of the reactive mass to subsurface formations and a linkage system configured to couple motion of the transducer to the reactive mass and the base plate. The linkage system cooperates with the reactive mass and the transducer to define a first resonant frequency and a second resonant frequency within a range of 1 to 300 Hz.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Surgical instrument
InactiveUS20100286480A1Easy to relocateComfortable to useSurgical needlesEndoscopesLocking mechanismEngineering
A surgical instrument that includes an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends, a tool disposed from the distal end of the instrument shaft, a control handle disposed from the proximal end of the instrument shaft, a distal motion member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool, a proximal motion member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the handle, actuation means extending between the distal and proximal motion members for coupling motion of the proximal motion member to the distal motion member for controlling the positioning of the tool and a locking mechanism for fixing the position of the tool at a selected position and having locked and unlocked states.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENDOSCOPIC DEVICES
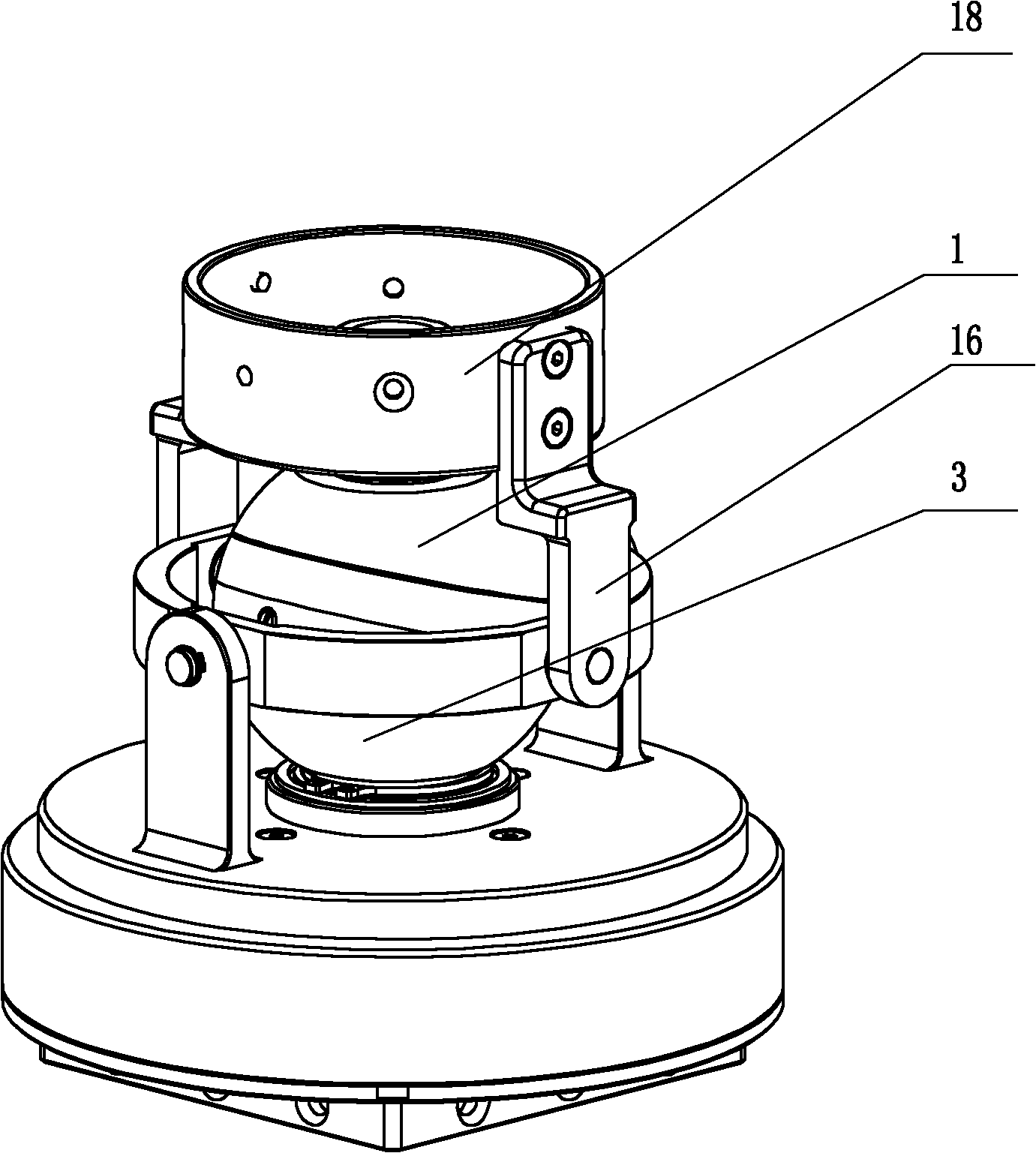
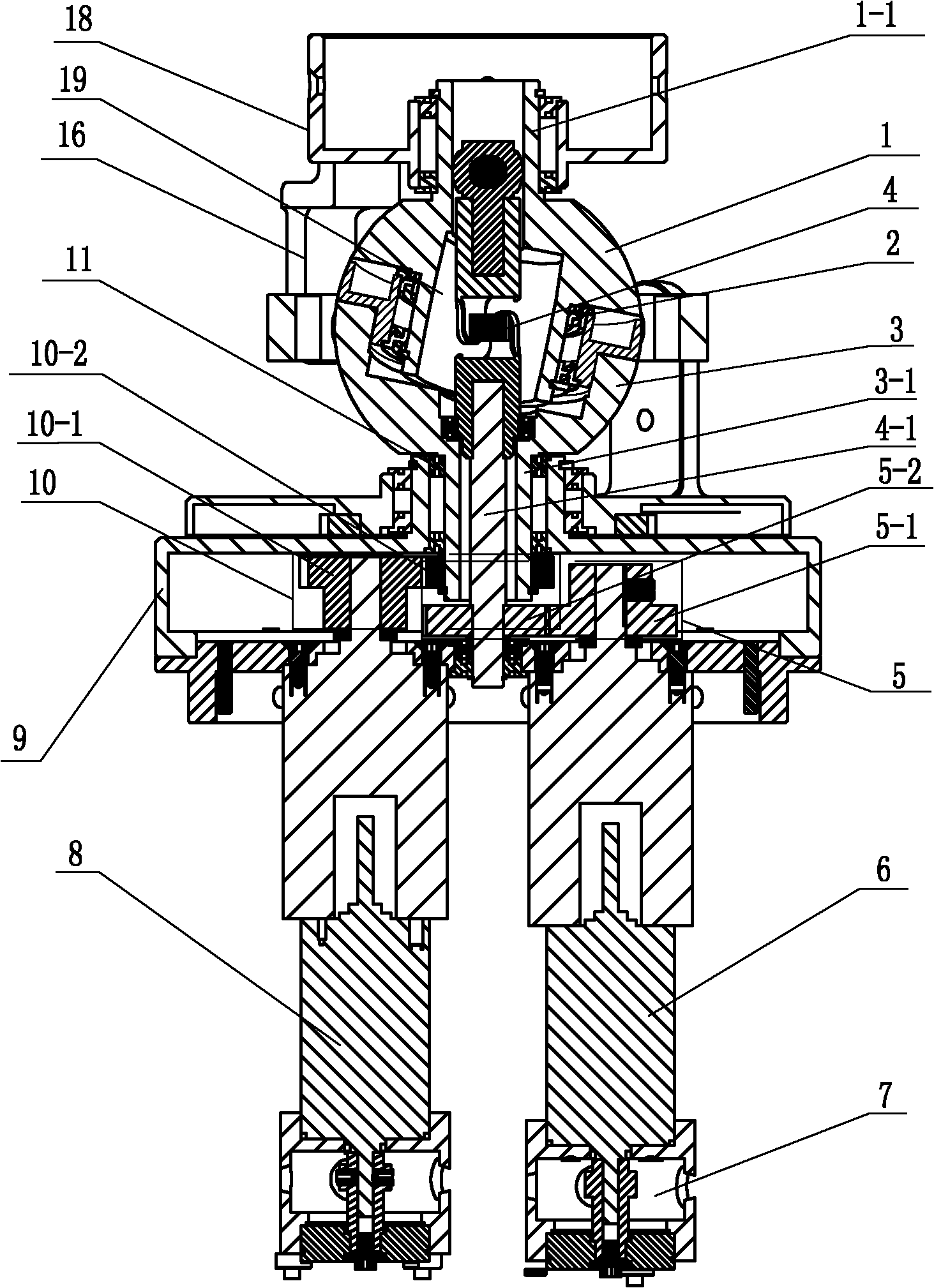
Three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist
InactiveCN102029614AEasy to adjust directionAchieve large-angle rotationJointsSpherical spaceThree degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist and relates to a robot wrist. The three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist solves the problems of complex structure, low integrated level, large own weight and coupling motion of the three-degree-of-freedom robot wrist. In the three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist, an upper semisphere shaft is rotationally connected with an interface of an end effector; an upper semisphere is rotationally connected with a lower semisphere; the contact surface of the upper semisphere and the lower semisphere is an offset inclined plane; the angle between the offset inclined plane and the horizontal plane is 10 to 25 degrees; an upper semisphere motor and a speed reducing mechanism are fixedly connected with a universal joint shaft through an upper semisphere gear transmission mechanism; the universal joint shaft is fixedly connected with the upper semisphere shaft through an internal universal joint; the upper semisphere shaft is rotationally connected with the interface of the end effector; a lower semisphere motor and the speed reducing mechanism are fixedly connected with a lower semisphere shaft through a lower semisphere gear transmission mechanism; a rotation motor and the speed reducing mechanism are fixedly connected with a turnplate through a rotation gear transmission mechanism; and the turnplate is in transmission connection with the interface of the end effector through an external universal joint. The three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist is applied to aerospace robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Analysis method for reducing rolling motion of ship
ActiveCN103387038AReduced rolling motionAdjust navigation statusVessel stability improvementMovement controllersCouplingThree degrees of freedom
The invention discloses an analysis method for reducing rolling motion of a ship. The analysis method comprises the following steps of according to an established three-dimensional stimulation image of the ship, calculating instant restoring force and instant wave incidence force of the ship under any waves, calculating a rolling angle and a ship rolling probability according to the ship heaving, pitching and rolling three degrees of freedom coupling motion differential equation to obtain the probability that the rolling angle of the ship is smaller than a flooding angle, thereby judging whether the ship runs at a safe state; and by regulating a navigational state of the ship, obtaining a numerical simulation result of the motion of the ship in any wave directions under the action of random waves and the probability that the rolling angle is smaller than the flooding angle, so that a navigation state of the ship corresponding to the maximum of the probability that the rolling angle is smaller than the flooding angle can be found out, and the rolling motion of the ship can be reduced by selecting the navigation state or changing the model line of a ship body at a design stage. According to the analysis method for reducing the rolling motion of the ship, which is disclosed by the invention, the rolling angle and the rolling probability are calculated, so that the rolling motion of the ship under any waves is reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Motion and resistance testing device for ship and marine structures
The invention is designed for providing a motion and resistance testing device for ship and marine structures, which comprises surge-motion sliding rails, sway-motion sliding rails, a heaving rod, a longitudinal motion block and transverse motion blocks, wherein the longitudinal motion block is arranged on the surge-motion sliding rail, the transverse motion blocks are arranged on the sway-motion sliding rails, the numbers of the surge-motion sliding rails, the sway-motion sliding rails and the transverse motion blocks are respectively two, the two surge-motion sliding rails are arranged in an up-and-down mode between the two transverse motion blocks, the two sway-motion sliding rails constitute a quadrilateral structure by two rods, the heaving rod is arranged on the longitudinal motion block, an end point of the heaving rod is located at the center of gravity of a tested marine structure and connected with the tested marine structure, and the heaving rod is provided with a line displacement sensor. The device disclosed by the invention can simultaneously measure the six-DOF (degrees of freedom) coupled motions such as rolling, pitching, yawing, heaving, surging and swaying of ship and marine structures in waves and the resistances of ship and marine structures in waves.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Surgical instrument
A surgical instrument that includes an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends, a tool disposed from the distal end of the instrument shaft, a control handle disposed from the proximal end of the instrument shaft, a distal motion member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool, a proximal motion member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the handle, actuation means extending between the distal and proximal motion members for coupling motion of the proximal motion member to the distal motion member for controlling the positioning of the tool, a rotation knob disposed adjacent the control handle and rotatable relative to the control handle for causing a corresponding rotation of the instrument shaft and tool and a locking mechanism for fixing the position of the tool at a selected position and having locked and unlocked states. The rotation knob has a first position in which the locking mechanism is controlled to be in its locked state and a second position in which the locking mechanism is released to its unlocked state so as to allow tool positioning.
Owner:ENDOBOTICS LLC
Surgical instrument
A surgical instrument that includes an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends, a tool disposed from the distal end of the instrument shaft, a control handle disposed from the proximal end of the instrument shaft, a distal motion member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool, a proximal motion member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the handle, actuation means extending between the distal and proximal motion members for coupling motion of the proximal motion member to the distal motion member for controlling the positioning of the tool and a locking mechanism for fixing the position of the tool at a selected position and having locked and unlocked states.
Owner:ENDOBOTICS LLC
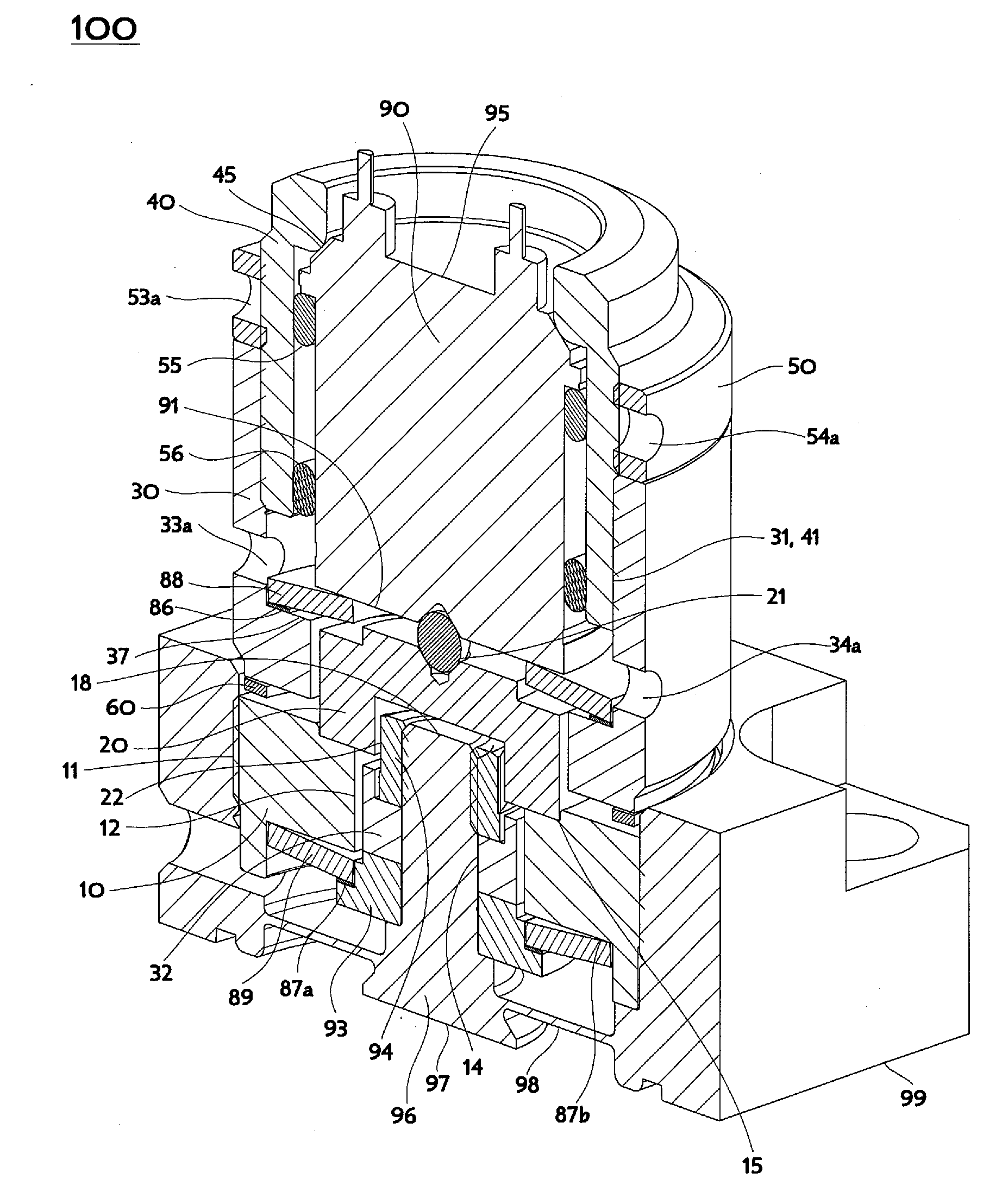
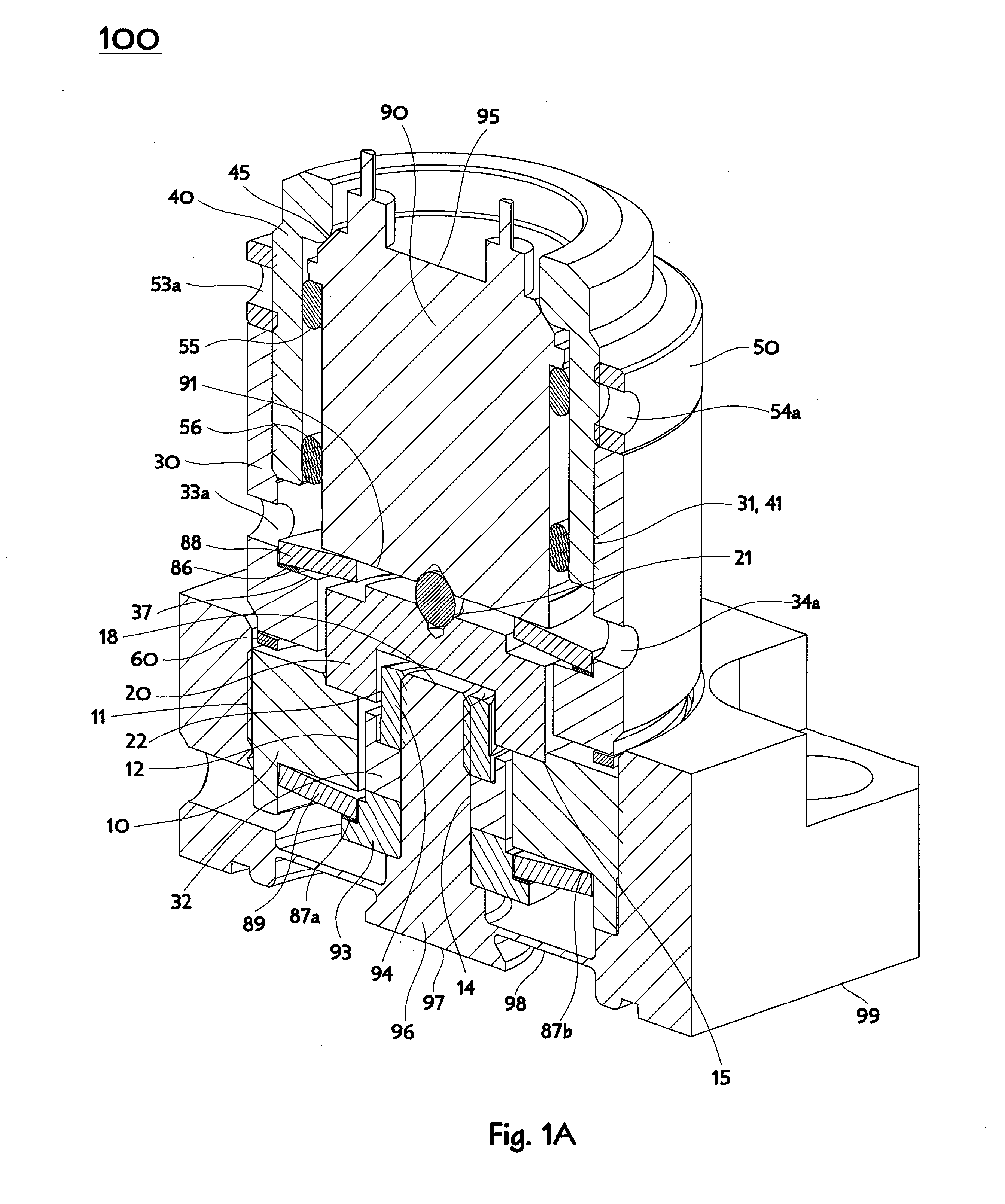
Interlace lifting mechanism
ActiveUS20150059877A1Assisting understandingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesHysteresisPiezoelectric actuators
A mechanism for coupling motion of a piezoelectric actuator in axisymmetric devices like modulating proportional valves uses actuator extension motion to cause translation away from a mechanism mounting plane and thereby enables lifting open of a valve element instead of the usual pushing closed of the valve element. The mechanism does not contain any gears nor leadscrew threads, and in usual practice is constantly loaded, so apparent change of direction is achieved without mechanical backlash introducing hysteresis. The mechanism surrounds a piezoelectric stack actuator by contacting opposite ends of the piezoelectric stack, whereby extension motion lengthening the actuator causes a lifting portion of the mechanism to translate toward the bulk of the actuator while the proximally adjacent mounting portion of the mechanism remains at a fixed location.
Owner:HORIBA STEC CO LTD
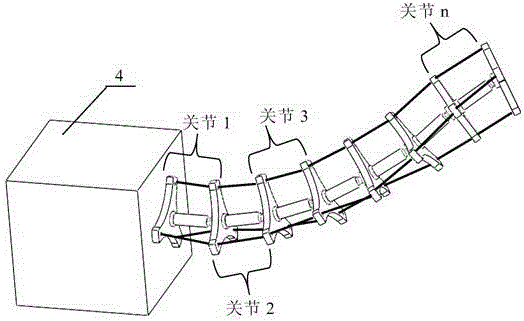
Rigid-flexible coupled trunk-shaped continuous robot
InactiveCN105729458AAchieve continuous motion outputSmall inertiaProgramme-controlled manipulatorReducerEngineering
The invention discloses a rigid-flexible coupled trunk-shaped continuous robot, and relates to the technical fields of robots and advanced manufacturing. The robot comprises a control box and a group of joints which are mounted on one side of the control box, have completely the same structure and are connected end to end, wherein each joint comprises a movable platform, a fixed platform, and a supporting rod and three driving ropes which connect the movable platform and the fixed platform; one end of the supporting rod is fixedly connected with the fixed platform vertically, and the other end of the supporting rod is connected with the movable platform through a ball pair; one ends of the three driving ropes are fixedly connected with three endpoints of the movable platform respectively, and the other ends of the three driving ropes penetrate through three endpoints of the fixed platform to be connected with the ropes in the control box; and the ropes are connected with a motor through a speed reducer. According to the rigid-flexible coupled trunk-shaped continuous robot, working platforms of each joint can achieve motion output of three-dimensional rotation under a cartesian coordinate system; and the motion output of each movable platform is achieved through transmission of the rigid supporting rod and the three driving ropes, so that the rigid-flexible coupled motion characteristic is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Vertical elevating device with deadweight balancing capability
The invention discloses a vertical elevating device with a deadweight balancing capability. The vertical elevating device is characterized in that a parallelogram transmission mechanism is arranged; a first rocking lever and a second rocking lever are articulated on top frames on both sides respectively; the first rocking lever is connected with the second rocking lever through a pull rod; the outer side rod ends of the first rocking lever and the second rocking lever are provided with a first slide block and a second slide block which are positioned at the same height; the first slide block and the second slide block are connected with a horizontal elevating framework through a sliding pair; and meanwhile, a crank rocker mechanism serving as a driving mechanism, a vertical elevating forked mechanism and a deadweight stabilizing unit constructed by a hydraulic cylinder are arranged. Through coupled movement of each mechanism, horizontal and vertical elevation for carried objects is realized; and the vertical elevating device is simple in structure, and has a high loading capability.
Owner:ANHUI JEE AUTOMATION EQUIP CO LTD
Thumb mechanism for under-driven adaptive prosthetic hand
InactiveCN101057791AImprove motor flexibilityHigh movement reliabilityArtificial handsEngineeringBiological activation
The invention discloses a thumb device for artificial hand. The driving device (1) is in rotary connection with the back part of near knuckle (4), the front part of near knuckle is in rotary connection with back part of middle knuckle (3), and the front end of middle knuckle is in rotary connection with the back part of far knuckle (2). The middle knuckle and near knuckle imitate deficient activation motion of real hand driven by middle knuckle shaft disk, the middle knuckle and far knuckle imitate coupling motion of real hand driven by coupling rod; and the knuckle number of thumb is imitative to that of real hand. The invention is characterized by simple structure, real-like appearance and flexible motion of each knuckle.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
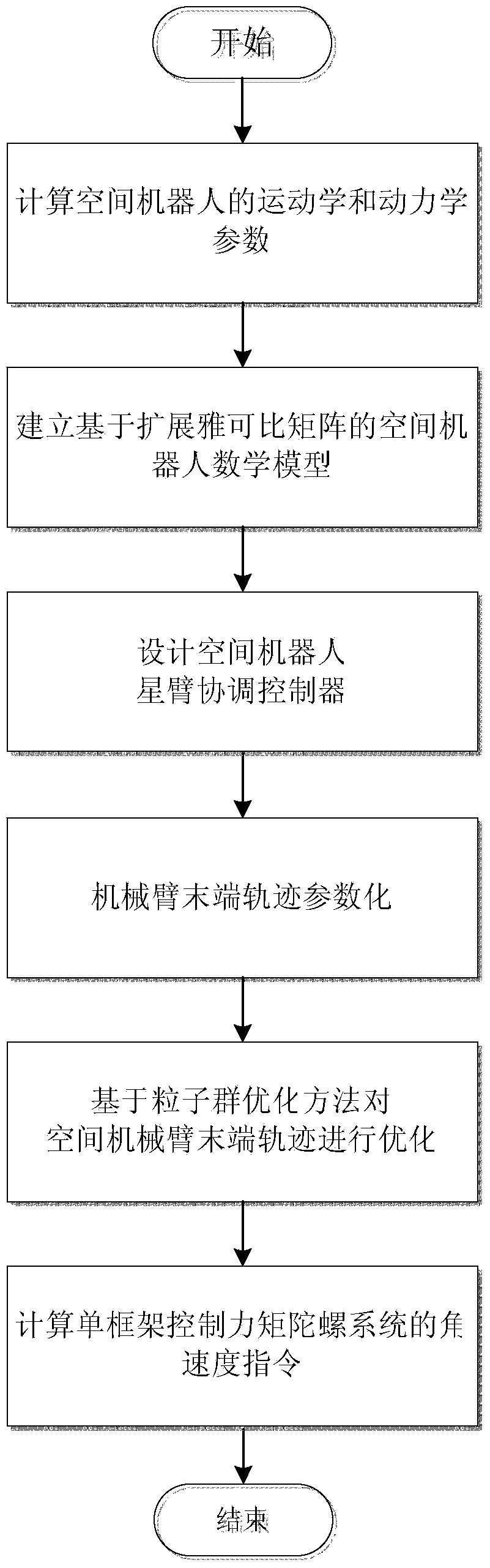
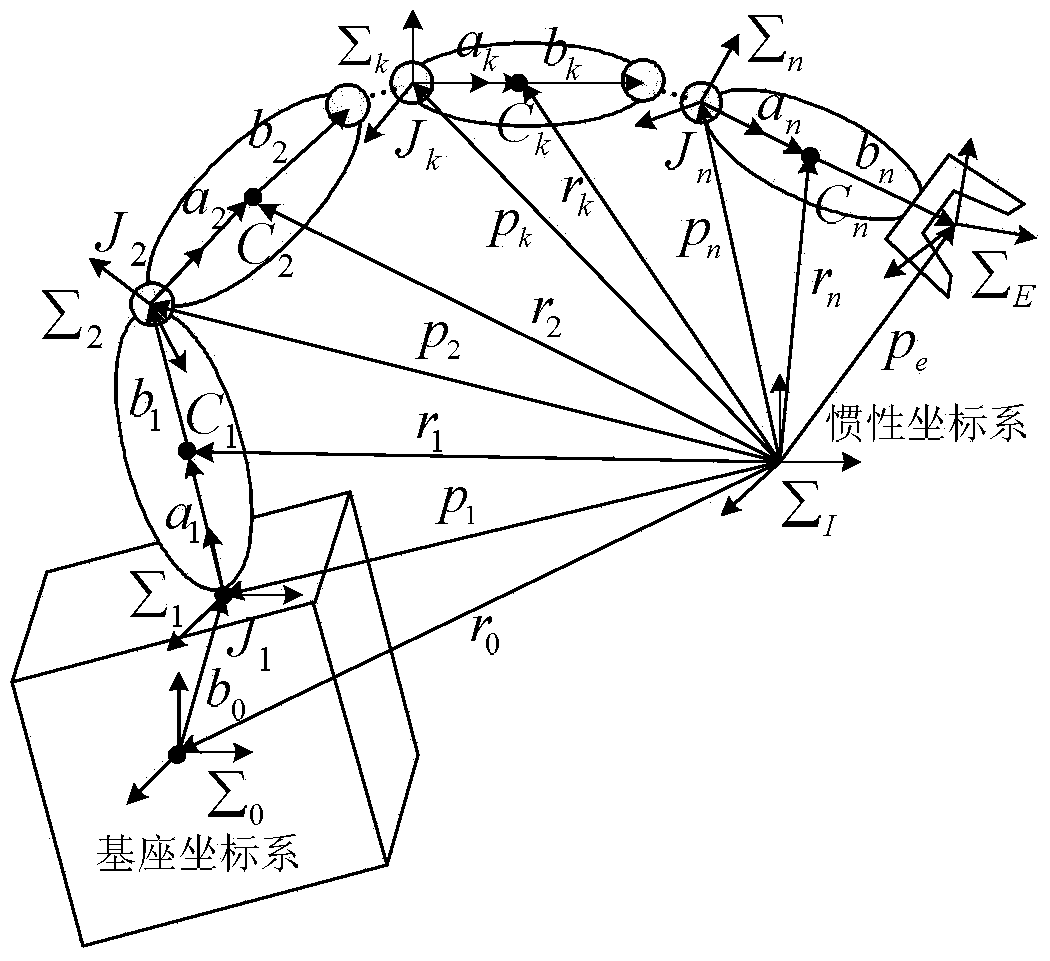
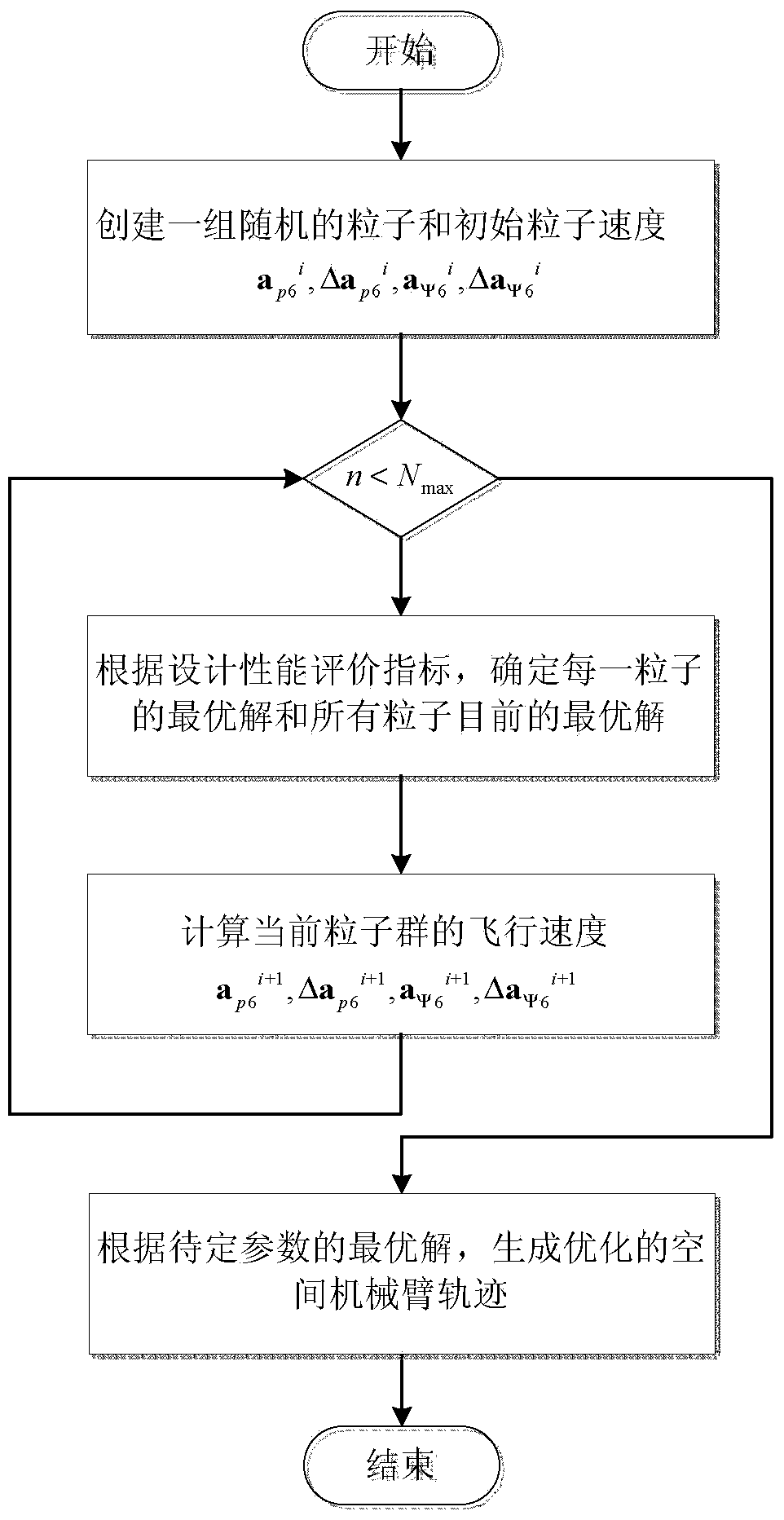
Method for coordination control over satellite arms of space robot based on expanded Jacobian matrix
InactiveCN103869704ARealize coordinated controlReduce consumptionAdaptive controlMathematical modelAngular velocity
The invention discloses a method for coordination control over satellite arms of a space robot based on an expanded Jacobian matrix. The method achieves integrated coordination control over a space manipulator operating in orbit and a base satellite. The method comprises the steps of computing kinetic parameters and dynamic parameters of the space robot, establishing a mathematical model of the space motor based on the expanded Jacobian matrix, designing a coordination controller of the satellite arms of the space robot, conducting parameterization on the trajectory of the tail end of the manipulator, optimizing the trajectory of the manipulator, and computing an angular velocity instruction of a single gimbal control moment gyro system of the space robot. According to the method, hysteretic feedback control conducted by a satellite according to attitude measurement is not needed, overall mathematical modeling is conducted on the coupled motion of the satellite arms, the angular velocity instruction of the single gimbal control moment gyro system is directly computed according to the input trajectory of the tail end of the manipulator, the single gimbal control moment gyro system is used for compensation, needed by the satellite, for manipulator motion, and then overall coordination control over the satellite arms is realized; the trajectory of the tail end of the manipulator is optimized, so that the energy consumed by a satellite state control system for compensating for the restoring torque of the manipulator is small.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
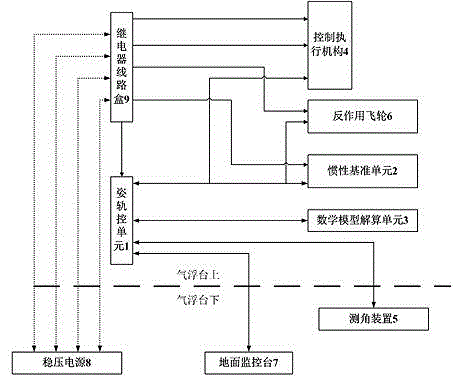
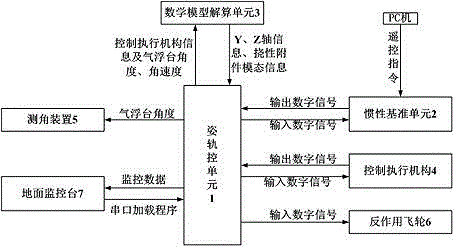
Test system and method for simulating flexible satellite three-axis attitude coupling movement with single-axis air bearing table
ActiveCN104133479AThe test results are real and effectiveAttitude controlAir bearingSpace environment
The invention discloses a test system for simulating flexible satellite three-axis attitude coupling movement with a single-axis air bearing table. The single-axis air bearing table is adopted for simulating the attitude movement of one axis of the satellite. The system comprises an attitude track control unit, an inertia reference unit, a mathematic model resolving unit, a control execution mechanism, an angle measuring device and a force moment output device, wherein the inertia reference unit is connected with the attitude track control unit, the mathematic model resolving unit is connected with the attitude track control unit, the control execution mechanism is connected with the attitude track control unit and the inertia reference unit, the angle measuring device is connected with the attitude track control unit, and the force moment output device is connected with the attitude track control unit. According to the test system for simulating flexible satellite three-axis attitude coupling movement, function extension is carried out on the single-axis air bearing table, the physical property and a mathematic model are combined, and resolving is carried out through the mathematic model, so that three-axis coupling force moment, flexible attachment disturbance force moment and space environment disturbance force moment borne by the satellite in the single-axis attitude movement process are achieved through a force moment output device, the effectiveness for verifying the flexible satellite single-axis attitude movement with the single-axis air bearing table can be improved, and the satellite ontrack single-axis attitude movement can be reflected more really.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
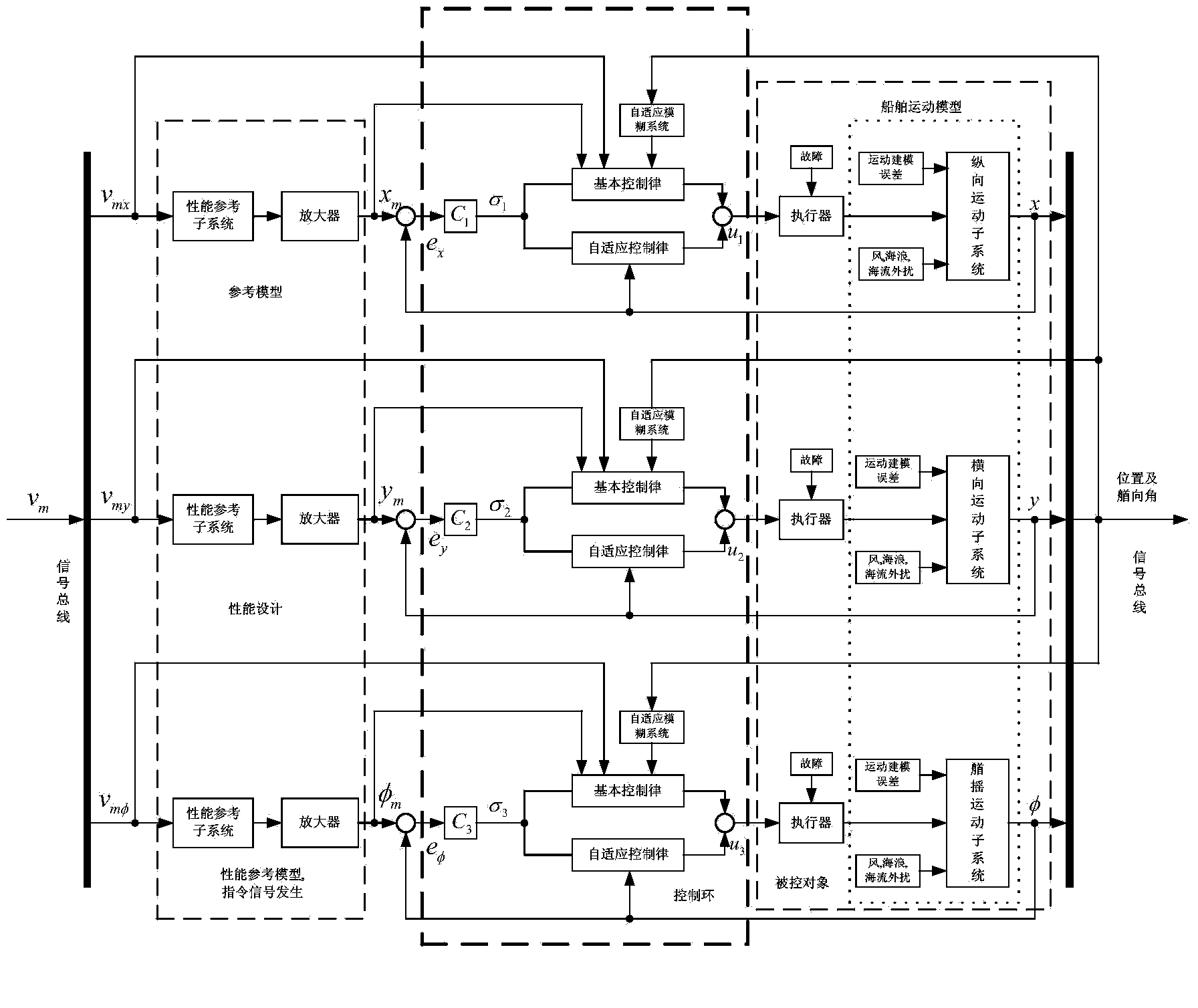
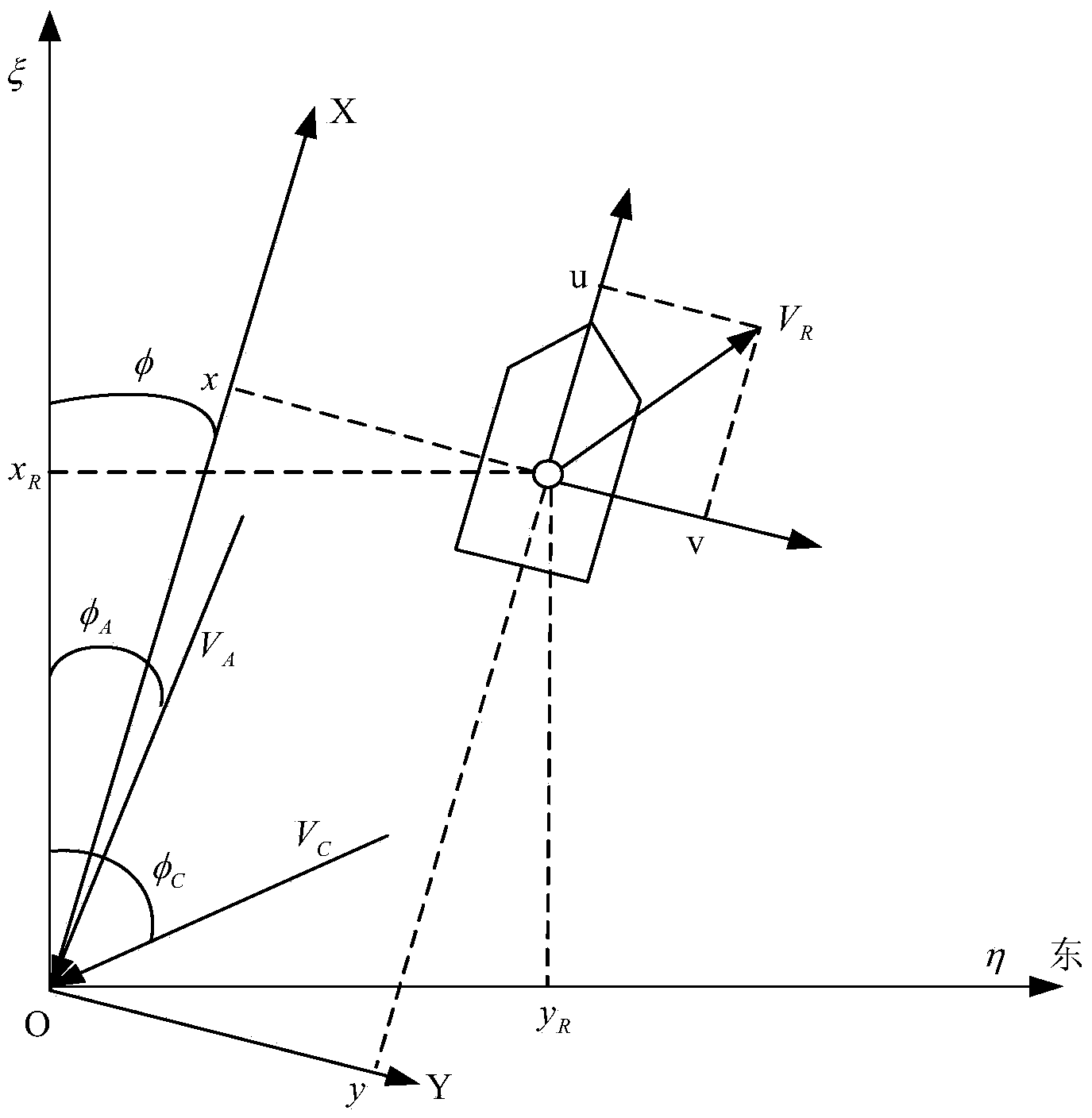
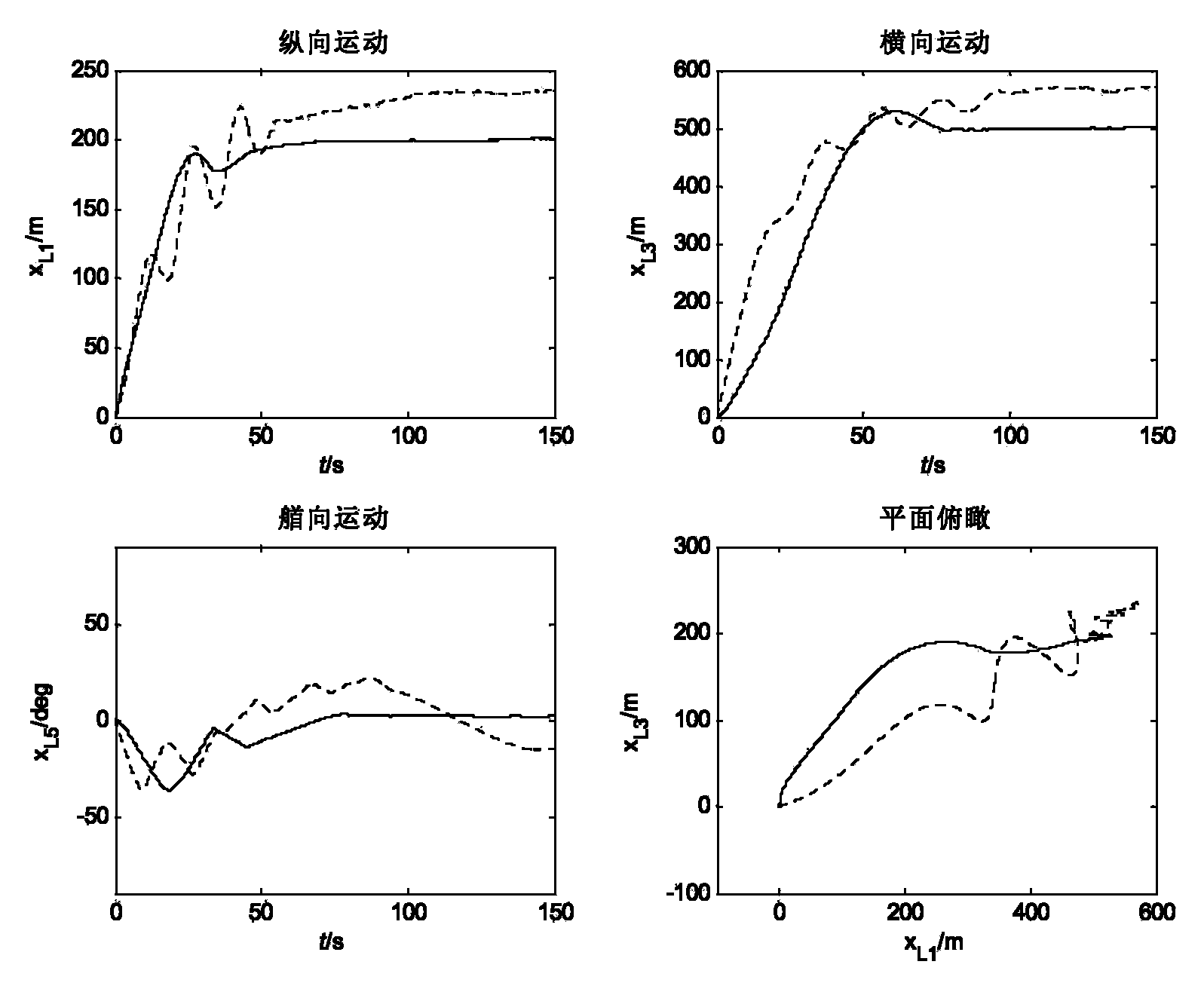
Self-adaptive positioning and tracking fault-tolerant control method of non-linear power system of ship
The invention discloses a self-adaptive positioning and tracking fault-tolerant control method of a non-linear power system of a ship. Firstly, a coupling motion model of a ship under the inertial coordinate system and a dynamic equation of state variable of the ship are established; Secondly, a performance reference decoupling sub-model signal generator is designed according to the positioned static and dynamic characters of ship; finally, a self-adaptive fuzzy logic device is designed and used for estimating unknown terms of the ship and a self-adaptive tracking fault-tolerant controller is designed, so that positioning control of the power system of the ship in normal operation or under the circumstance that boundary failures of an actuator occur under the sea conditions of wind, wave and current can be realized . The self-adaptive positioning and tracking fault-tolerant control method of the non-linear power system of the ship has the advantages that the control method is independent of known terms of each subsystem model of the ship, a single subsystem is controlled through directly utilizing the independent state of each subsystem, so that situations related to global variable of the ship is incorporated into the uncertainty to be handled; besides, impacts of the uncertainty of the ship and failures of the actuator can be compensated dynamically through the fuzzy logic device and the self-adaptive fault-tolerant controller, and positioning and tracking uncertainty caused by human estimates can be reduced.
Owner:嘉之会(青岛)智能科技有限公司
Upper limb rehabilitation training device based on grouping coupling drive
The invention discloses an upper limb rehabilitation training device based on grouping coupling drive. The upper limb rehabilitation training device based on the grouping coupling drive comprises a shoulder three-degree-of-freedom self-adapting mechanism, a first coupling movement mechanism, a shoulder connecting component, a second coupling movement mechanism and a wrist two-degree-of-freedom self-adapting mechanism, the first coupling movement mechanism is firmly connected with the shoulder three-degree-of-freedom self-adapting mechanism, the shoulder connecting component is rotationally connected with the first coupling movement mechanism, the second coupling movement mechanism is firmly connected with the shoulder connecting component, and the wrist two-degree-of-freedom self-adapting mechanism is firmly connected with the second coupling movement mechanism. The upper limb rehabilitation training device based on the grouping coupling drive is capable of regulating automatically according to the affected limb sizes of different patients and the concrete use situations, the human body can coordinate with the mechanism, the human body comfort and safety coefficient are greatly improved, and the movements transit smoothly and coordinate with each other so that the upper limb rehabilitation training device based on the grouping coupling drive is capable of finishing various complex active and passive training actions.
Owner:湖北英特搏智能机器有限公司
Single-drive rigid-flexible coupling precision motion platform and realization method and application thereof
ActiveUS20180104779A1Avoid displacementSimple designDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCouplingEngineering
The present invention discloses a single-drive rigid-flexible coupling precision motion platform, including a machine base, a linear guide rail, a rigid-flexible coupling motion platform, a linear driver and a displacement sensor, wherein the rigid-flexible coupling motion platform includes a rigid frame, flexible hinges and a core motion platform; and the core motion platform of the rigid-flexible coupling motion platform is connected with the rigid frame through the flexible hinges. In this arrangement, the single-drive rigid-flexible coupling precision motion platform disclosed by the present invention can realize high-accuracy continuous change displacements of the platform, thereby avoiding displacement “jitter” caused by sudden change of acceleration. The present invention further discloses a realization method and an application including the above platform.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Surgical instrument
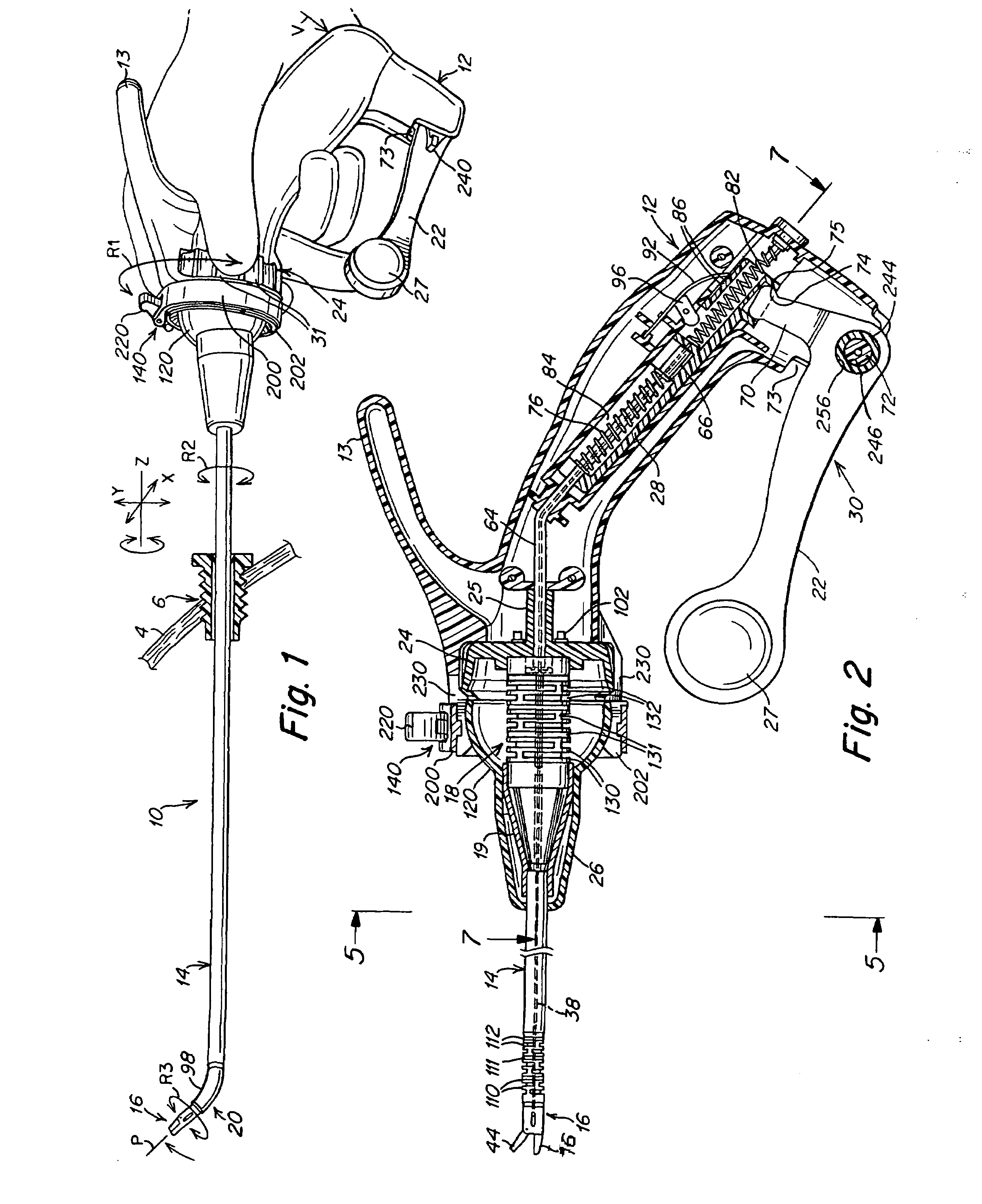
A surgical instrument that includes an instrument shaft having proximal and distal ends; a tool disposed from the distal end of the instrument shaft; a control handle coupled from the proximal end of the instrument shaft; a distal bendable member for coupling the distal end of the instrument shaft to the tool; a proximal bendable member for coupling the proximal end of the instrument shaft to the control handle; actuation means extending between the distal and proximal bendable members for coupling motion of the proximal bendable member to the distal bendable member for controlling the positioning of the tool and a locking mechanism for fixing the position of the tool at a selected position. The locking mechanism includes a ball and socket arrangement disposed about the proximal bendable member and a locking member for locking the ball and socket arrangement and having locked and unlocked states. The ball and socket arrangement includes a compression ring supported from the control handle, having an outer surface for support of the locking member thereabout and having an inner surface defining an at least partially spherical shaped socket. The ball and socket arrangement further includes a hollow ball member having an internal hollow chamber and an outer at least partially spherical shaped surface which mates with the at least partially spherical shaped socket.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENDOSCOPIC DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com