Patents
Literature
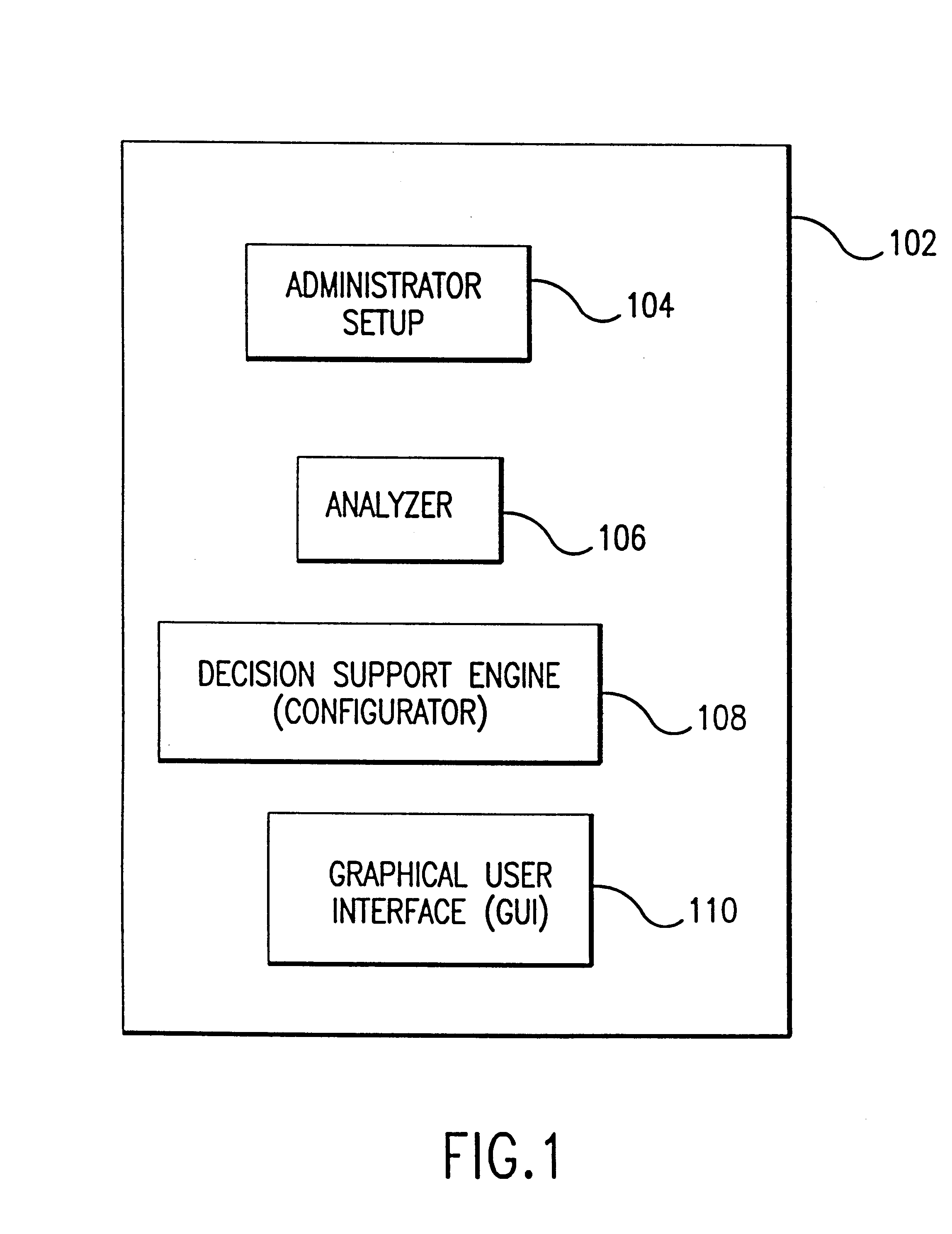
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Activity scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Activity Scheduling is a tool for combating passivity and gradually re-engaging the depressed person in some of the routines of his/her daily life. The first step in Activity Scheduling is simply to monitor the activity over the course of a week by recording on a grid (see below).
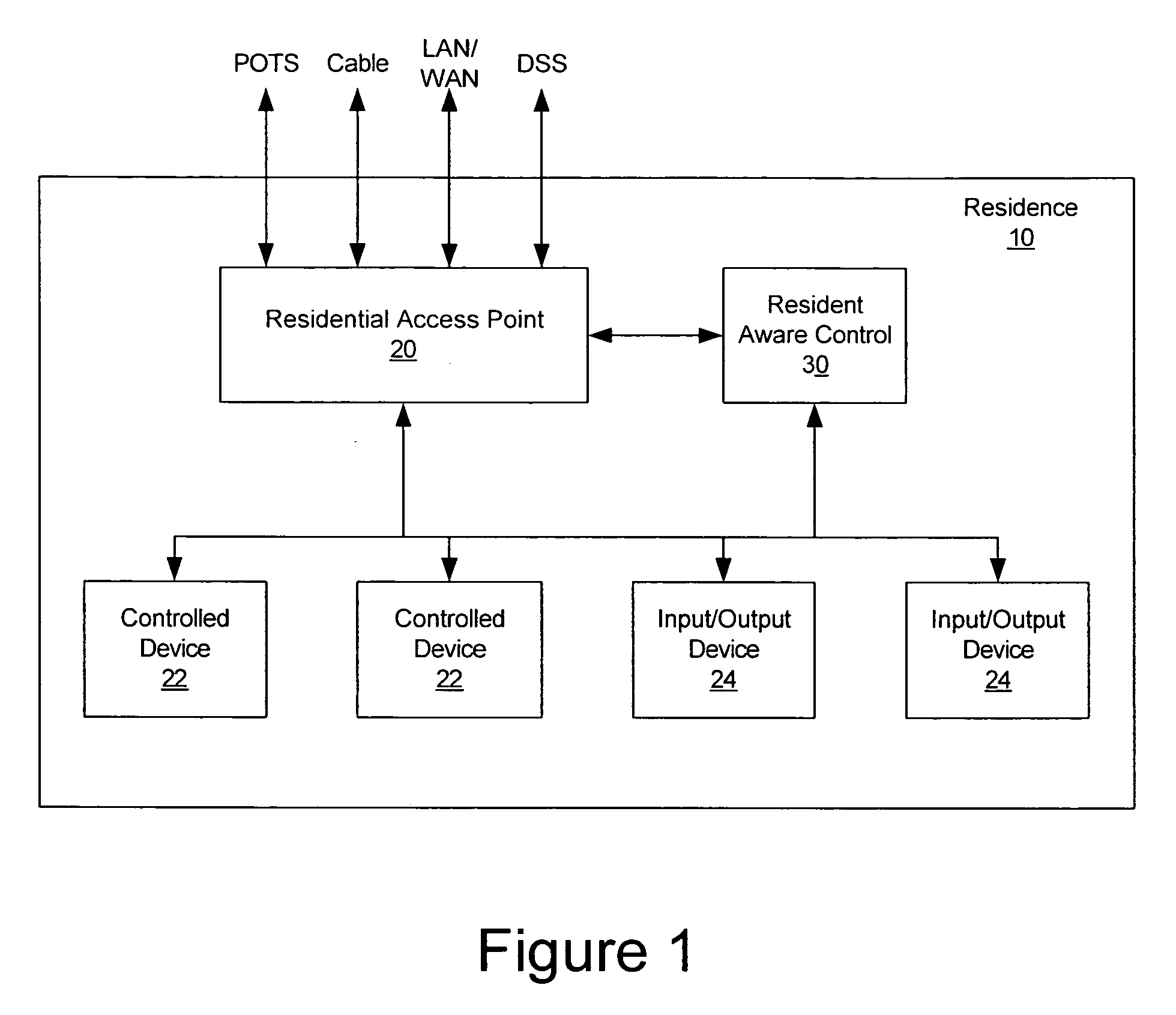
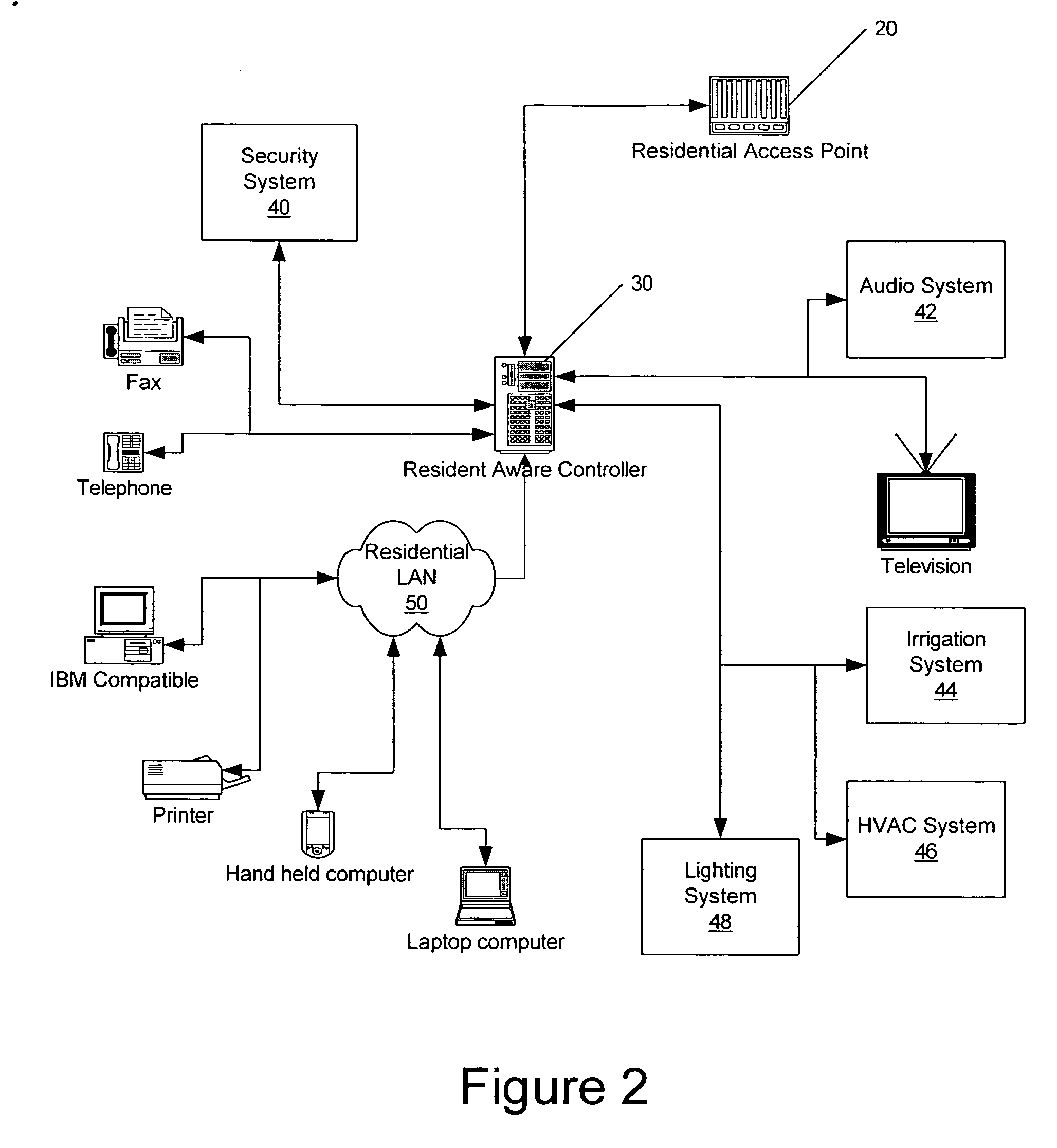
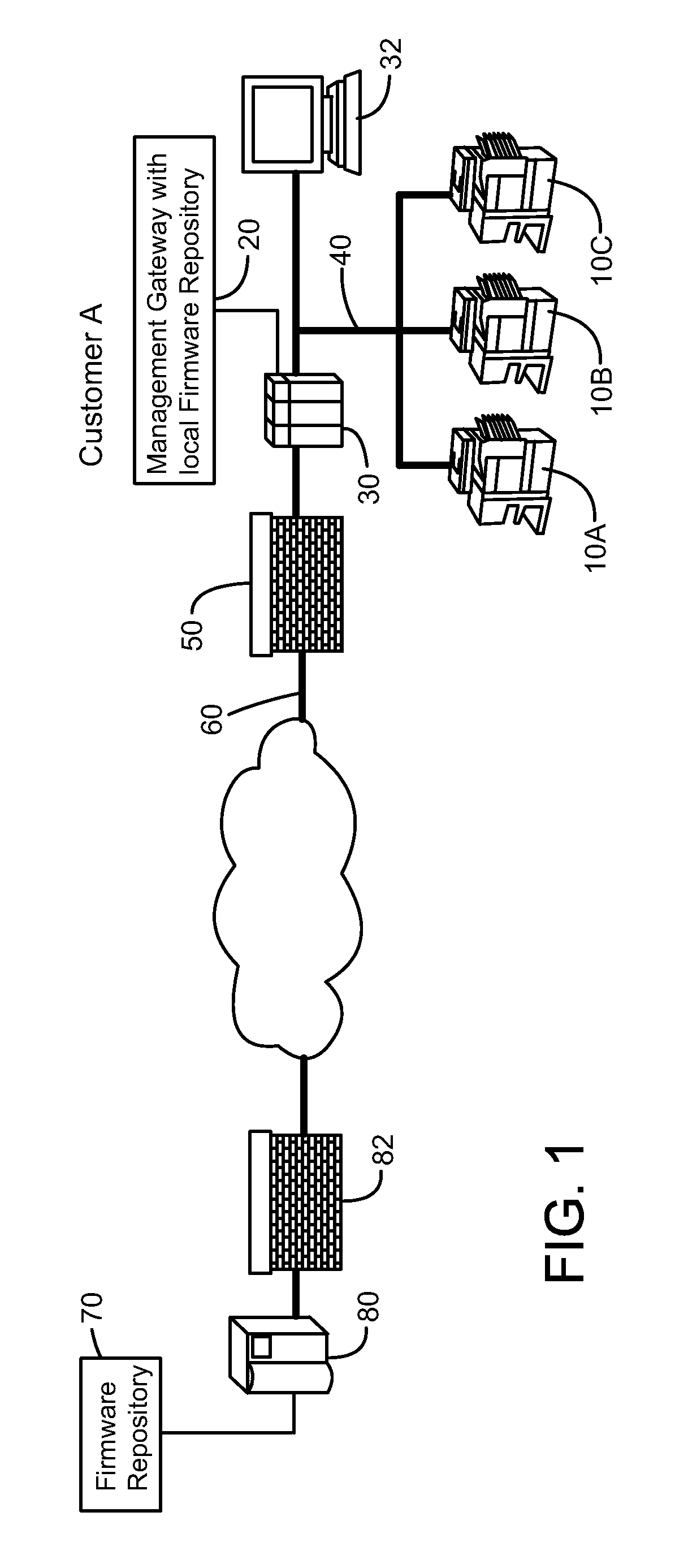
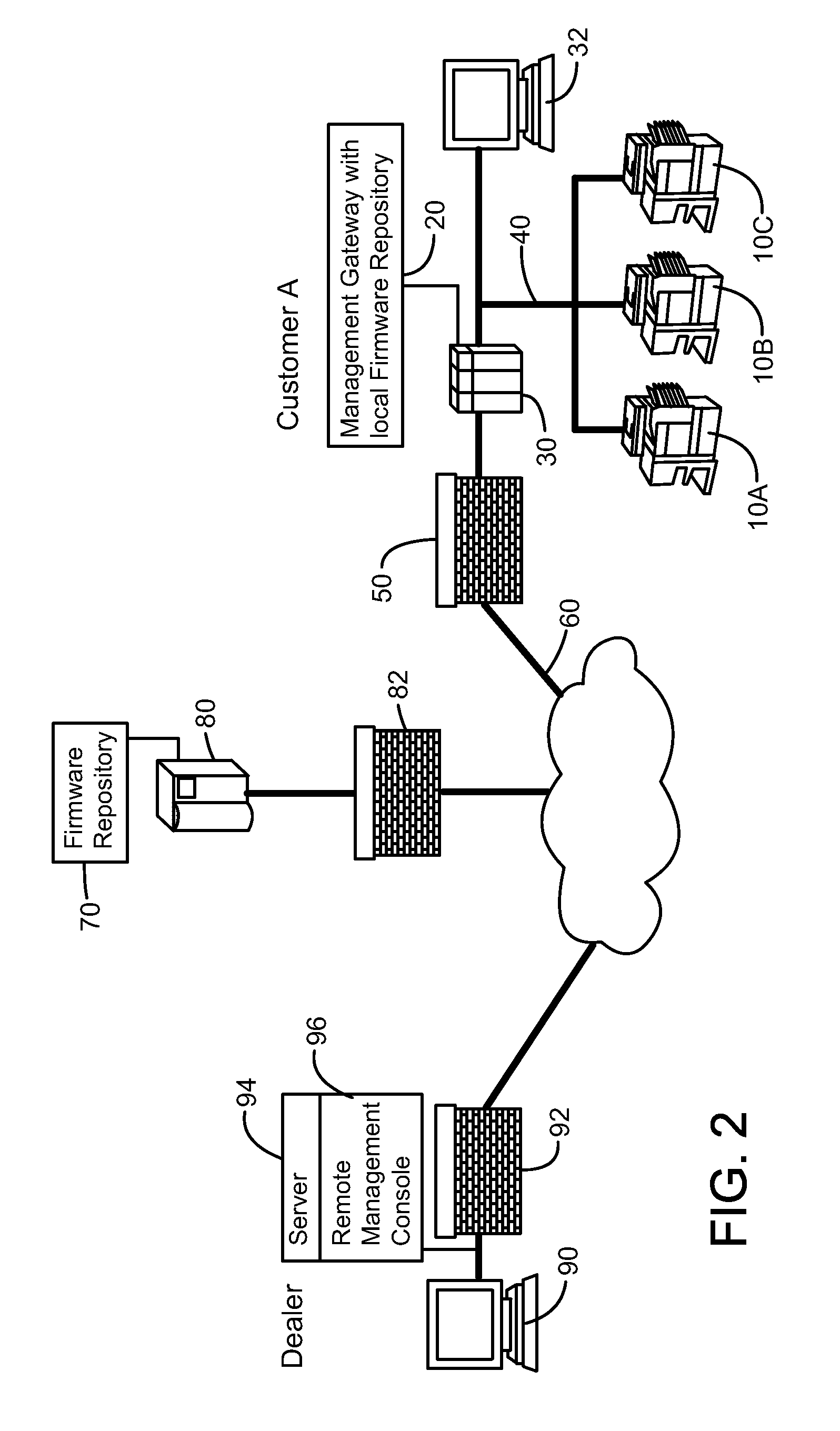
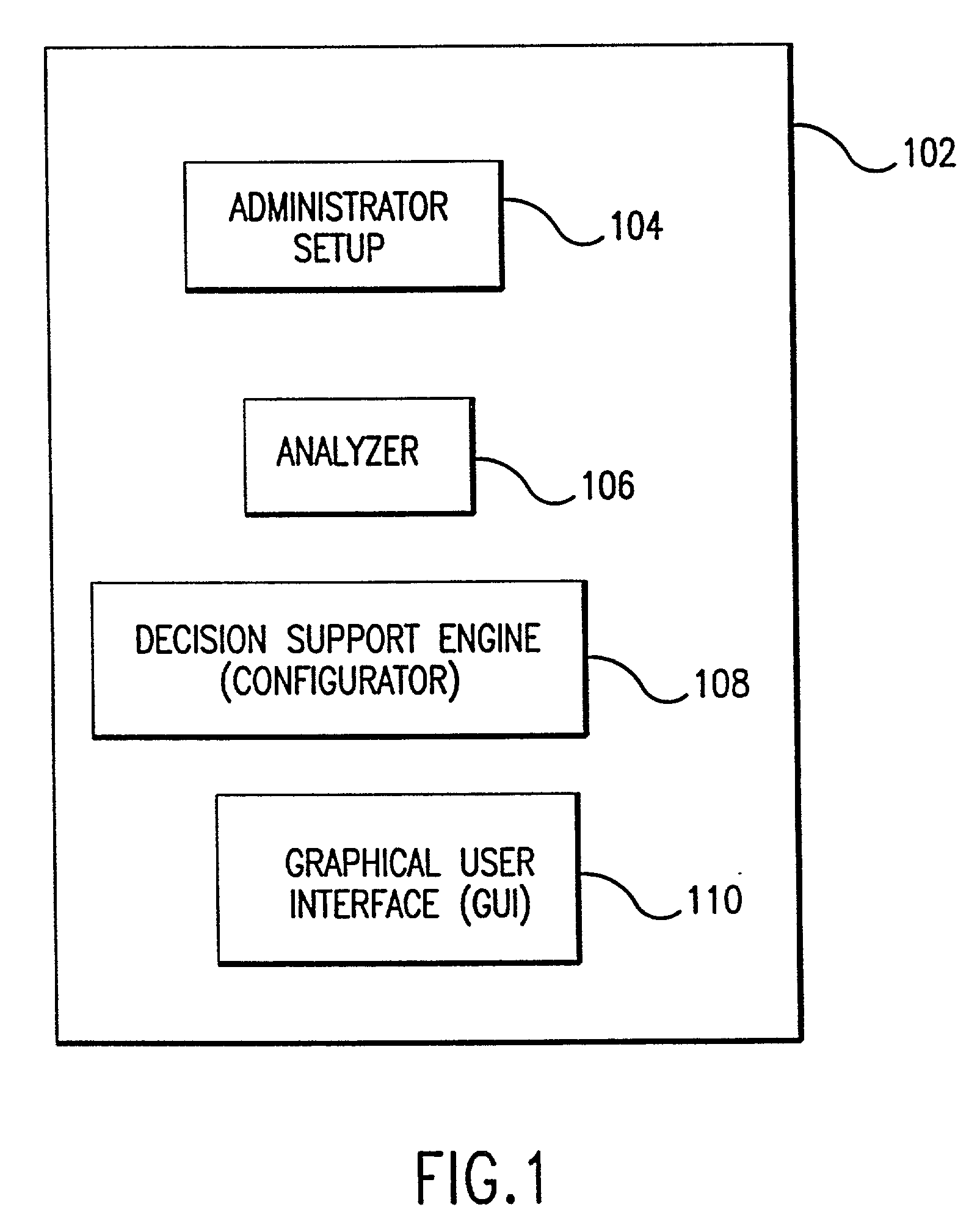
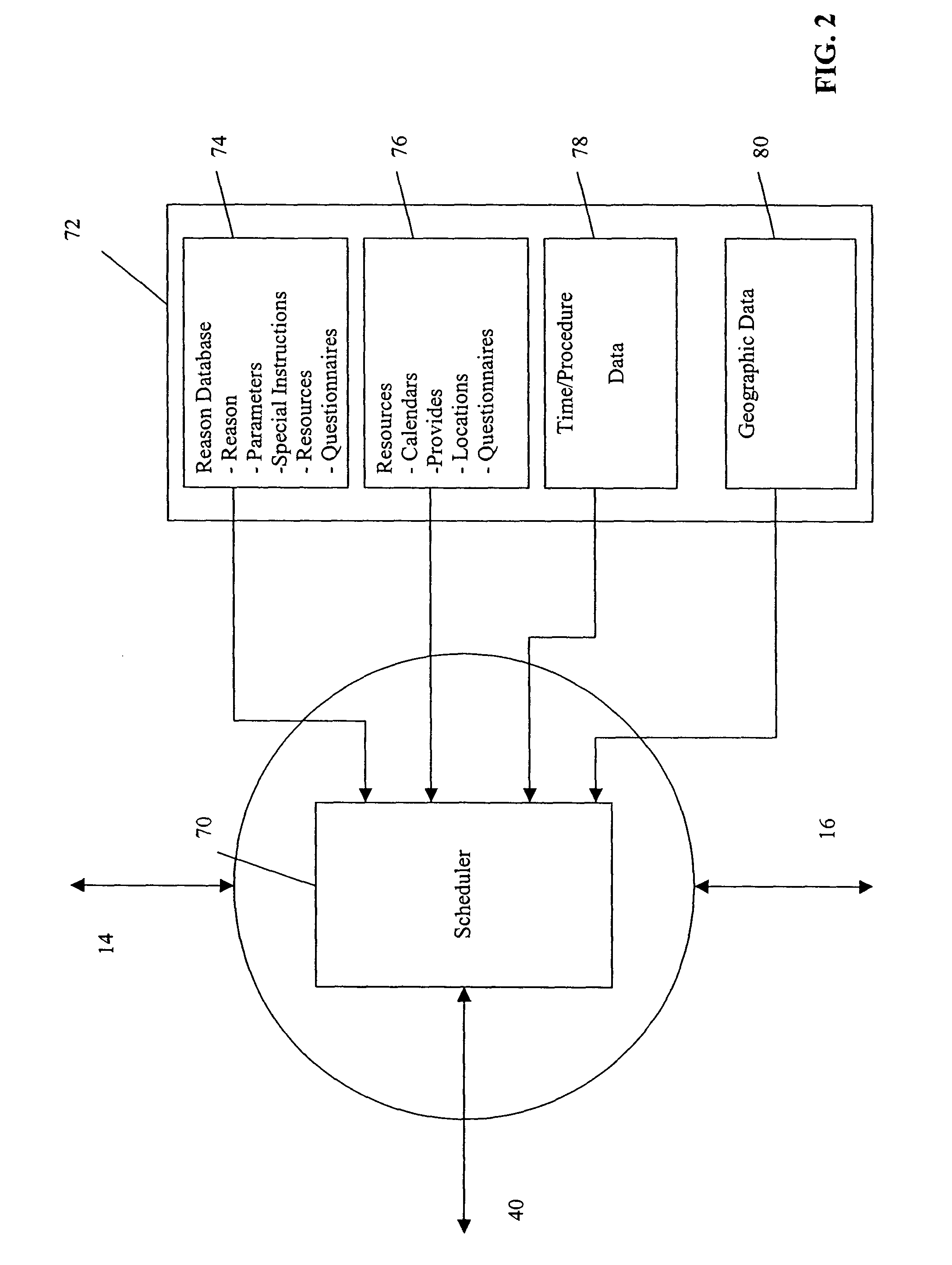
Methods, systems and computer program products for providing resident aware home management
InactiveUS20050108091A1Two-way working systemsSelective content distributionActivity schedulingProgram planning
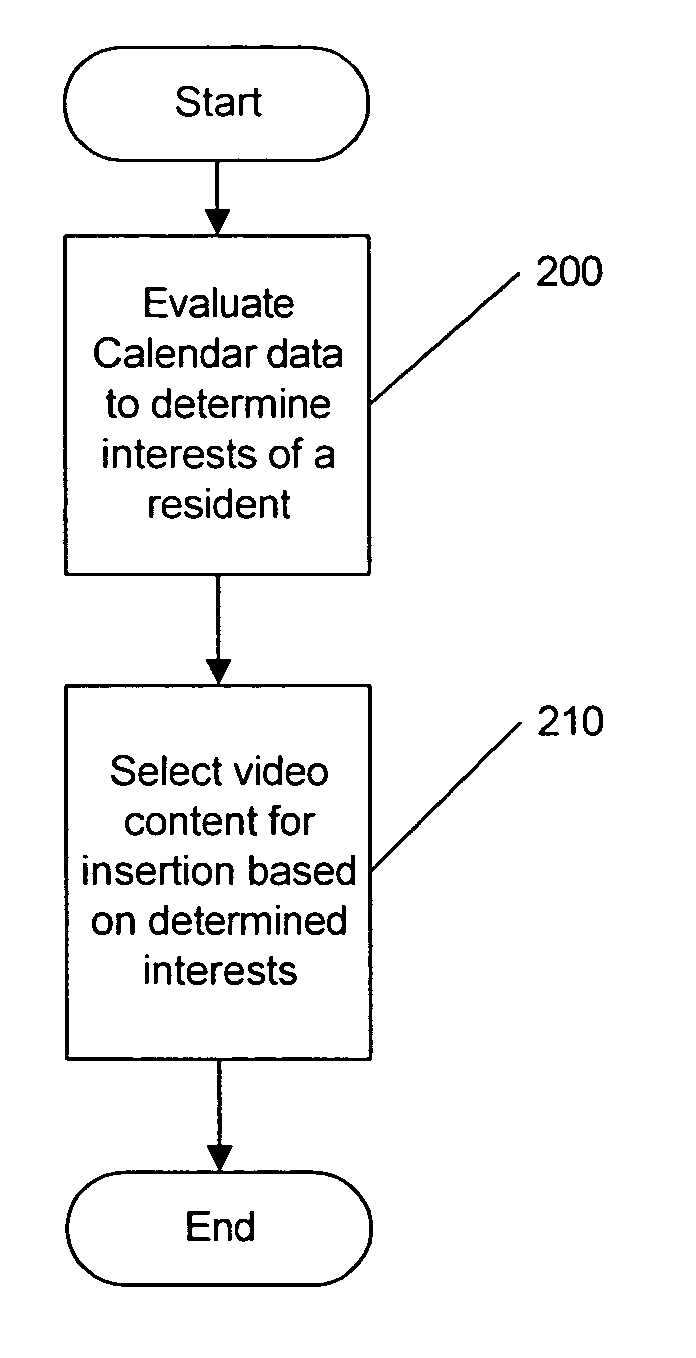
Resident activities and / or activity schedules are used to control a home management system. Resident activities and / or activity schedules may be monitored using a calendar application. A common repository may be provided for storing residential information used by multiple applications. Control of the home management system may include the selection of advertising video clips that may replace commercial advertisements in a vide stream. Advertising portions of a video stream may also be replaced with a locally generated video insertion. An architecture and / or system for home management is also provided.
Owner:RESINETICS
Remote firmware management for electronic devices
Owner:SHARP KK
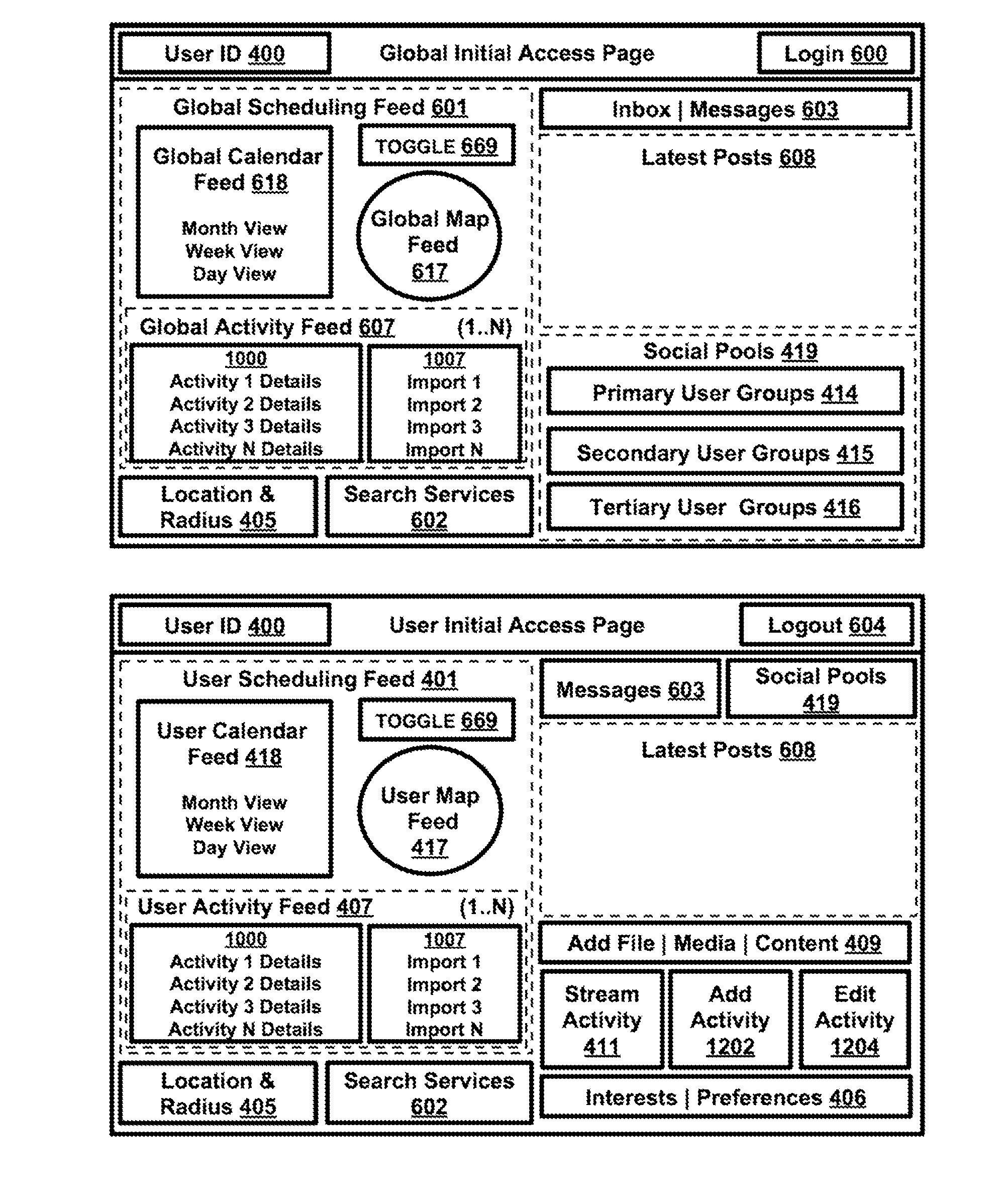
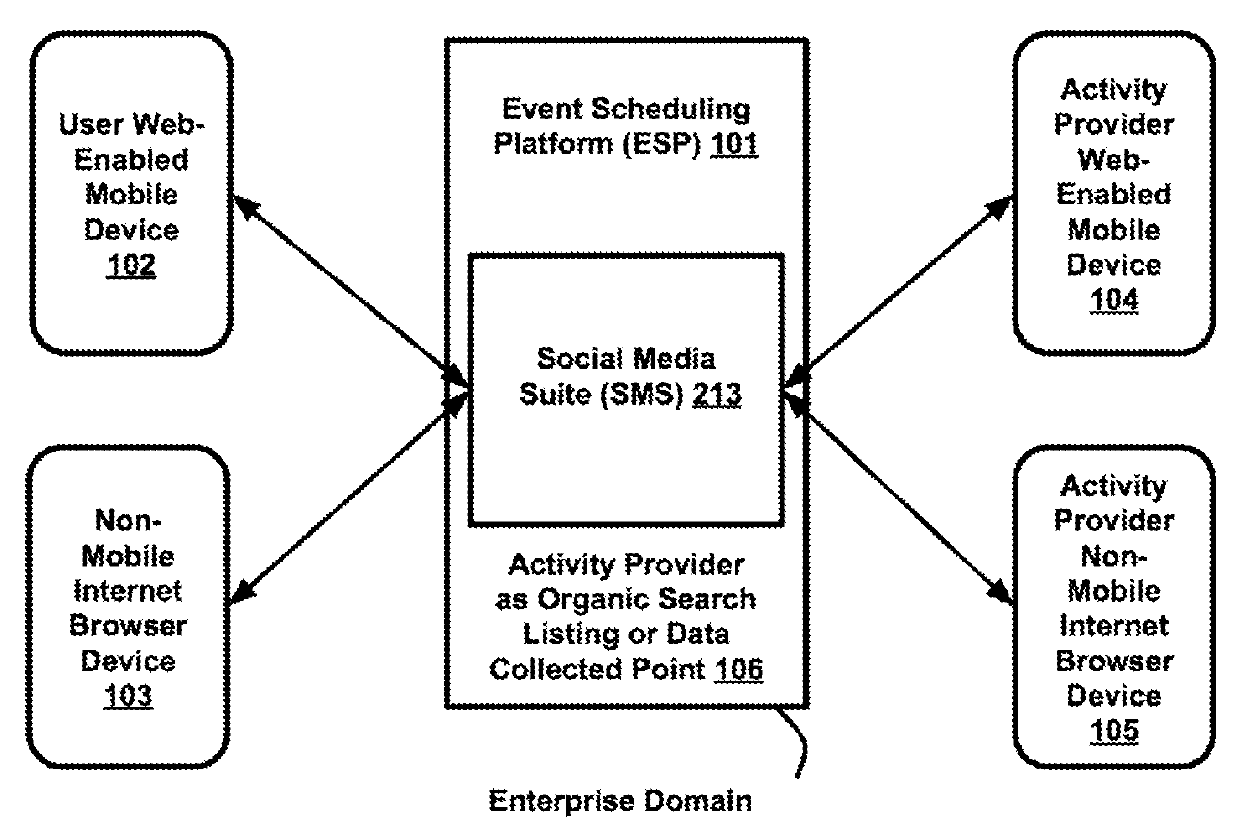
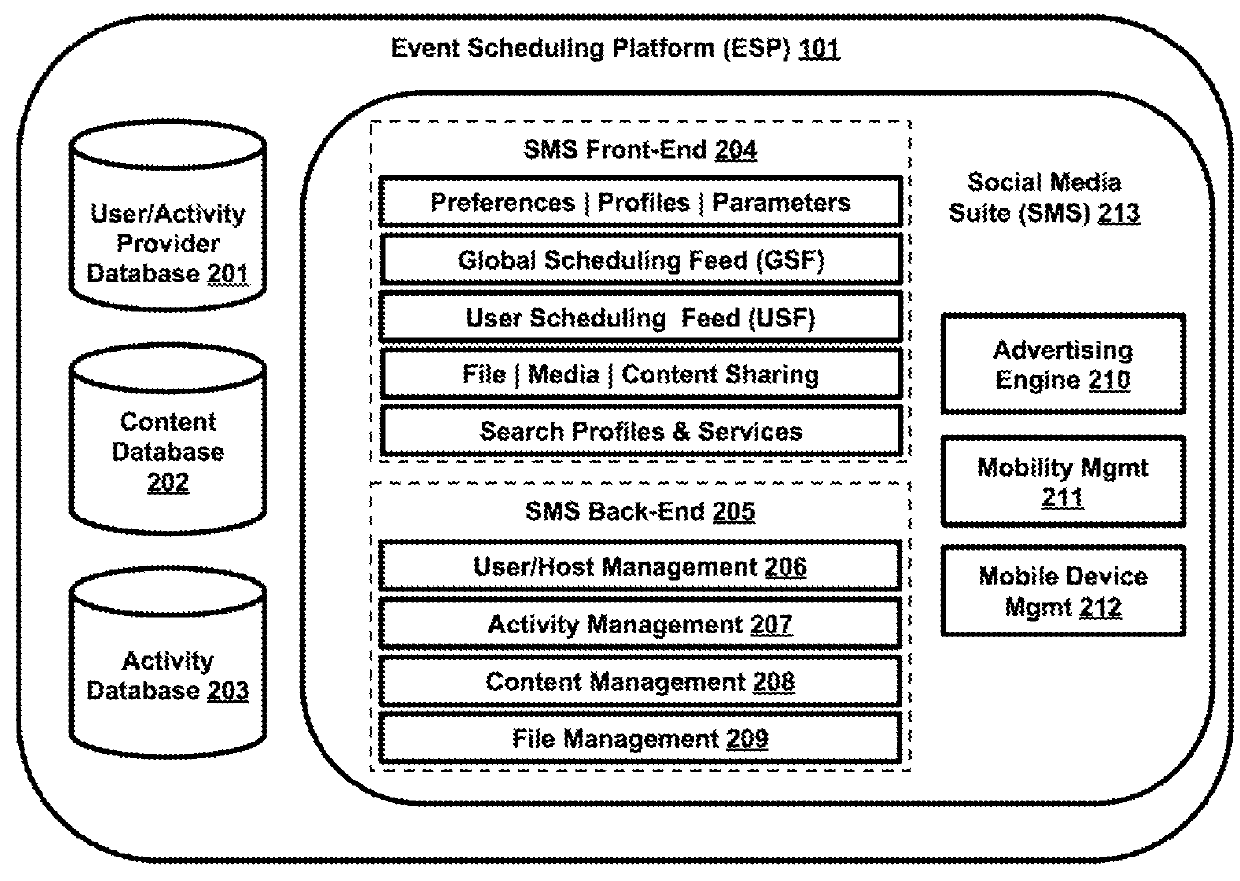
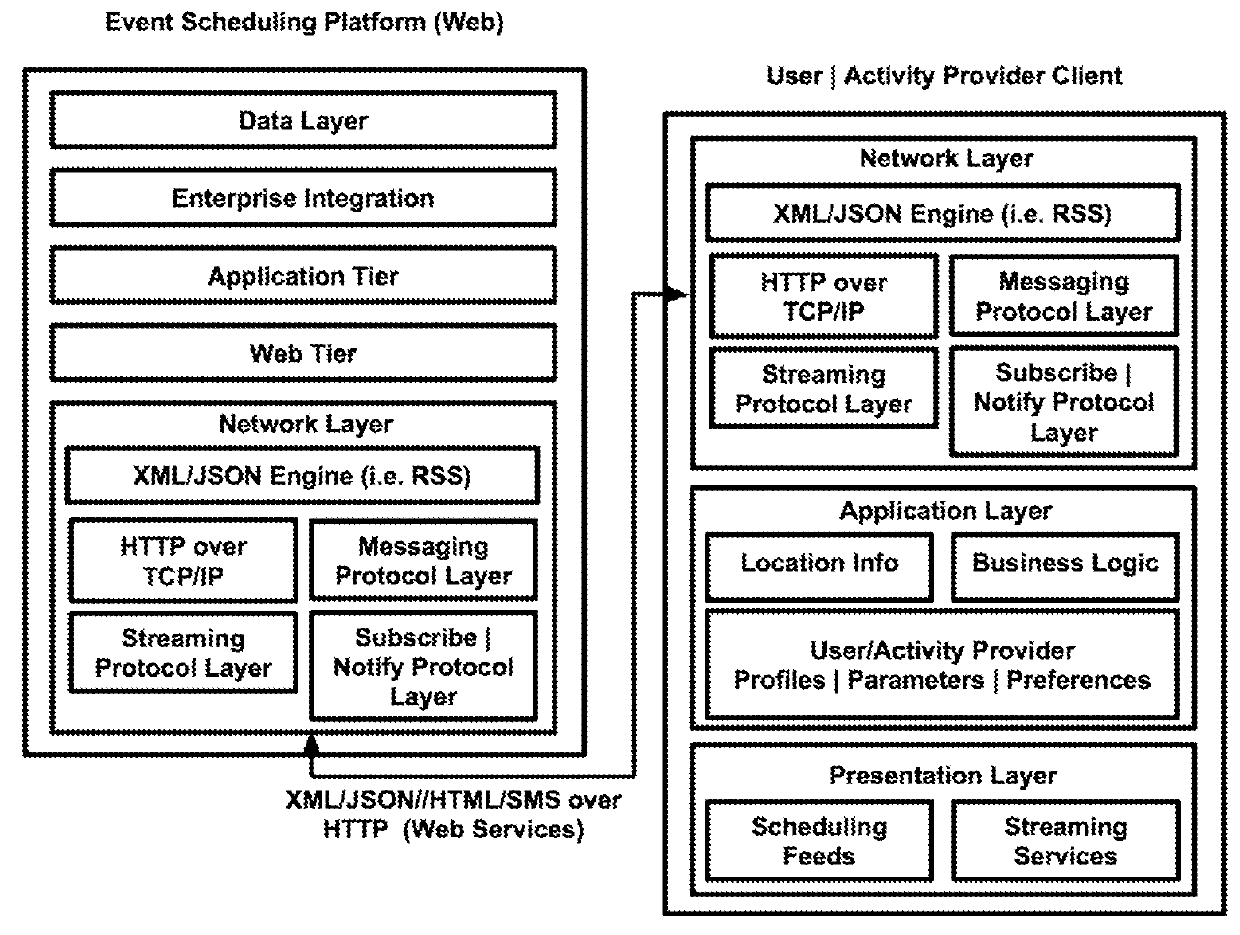
Systems and methods of enabling integrated activity scheduling, sharing and real-time social connectivity through an event-sharing platform
InactiveUS20150058324A1New levelFacilitate adding activitySpecial service provision for substationData processing applicationsWeb siteActivity scheduling
Embodiments herein provide for an interactive event-scheduling platform (ESP), wherein locating activities via location data, notifying and alerting of them via real-time feeds and encouraging interaction through a full-service social media suite (SMS), enhanced with live streaming and “always-on” connectivity, could provide a fresh experience for users and hosts. A real-time data procuring system and method may solve problems with stale or incomplete activity data within a geographic area, bridge gaps between users and hosts by shortening time periods—from activity announcement, to discovery, to launch, to response—create buzz, maximize venue attendance, boost sales and ensure promotional success. Software crawlers may mine public Web sites for thorough activity data coverage. Stored activities, profiles and collected user interaction data may produce behavioral reports to increase ROMI. Security packages, installations and access controls may incite users to safely register themselves in the SMS to engage, interact and transact.
Owner:KAUWE JOSEPH GREGORY
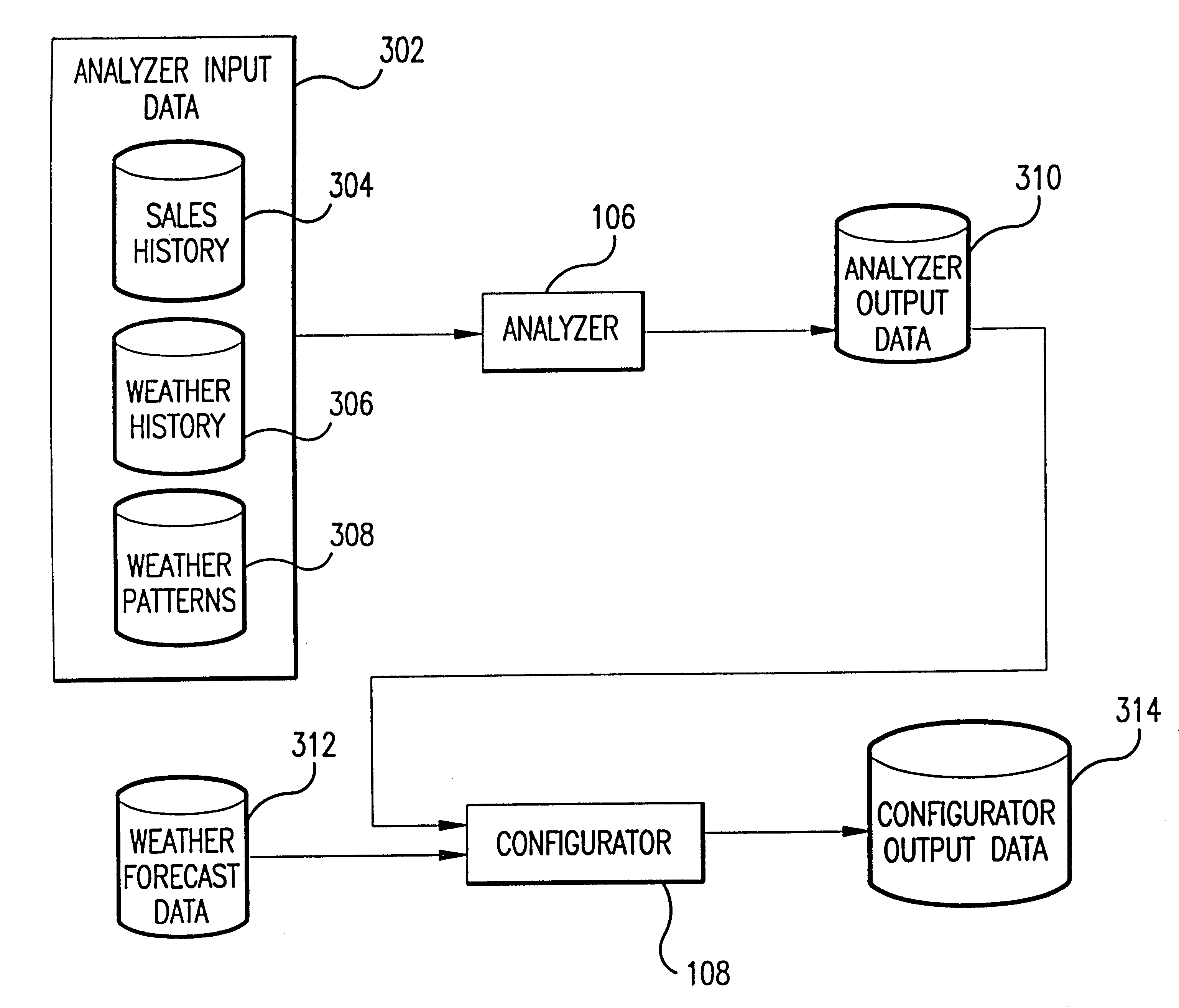
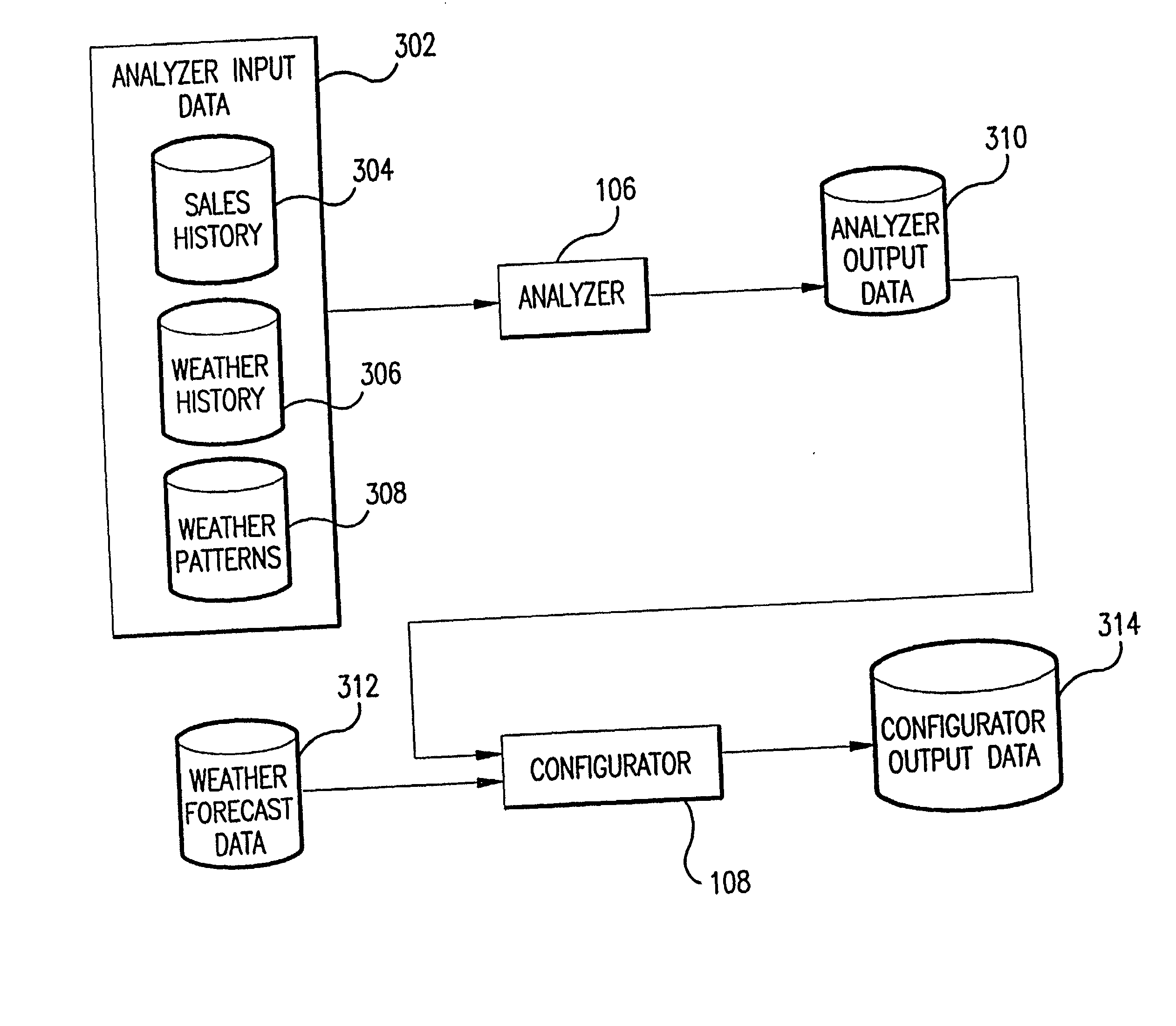
Method and computer program product for weather adapted, consumer event planning
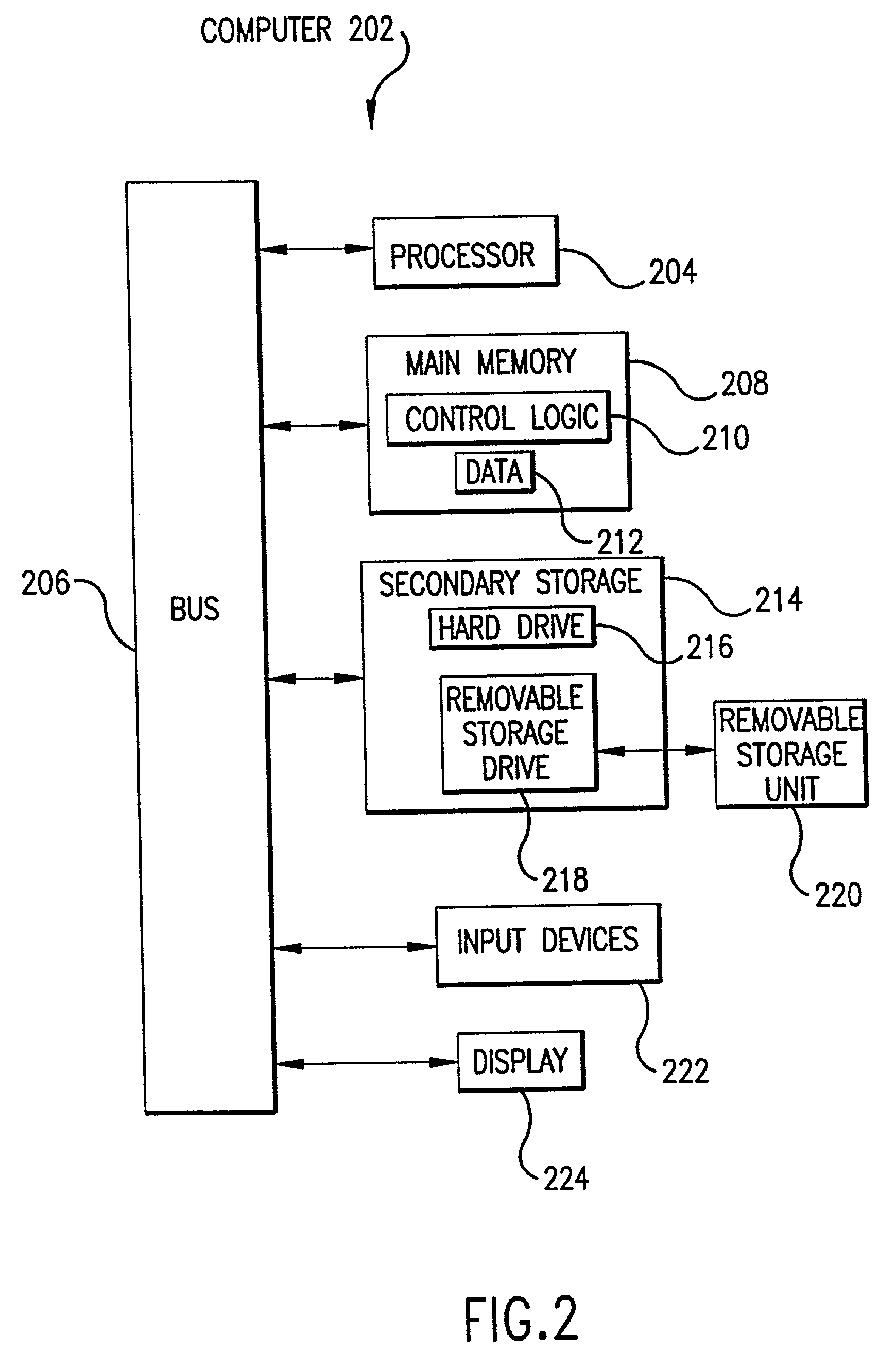
A system and method for forecasting future retail performance are described herein. The system includes a storage device that stores a sales history database, a weather history database, and a weather forecast database. An analyzer determines the extent to which past retail performance of a plurality of products at a plurality of locations was affected by weather using the sales history database and the weather history database. A configurator, coupled to the analyzer, estimates expected future retail performance of the products at the stores for a plurality of future time periods using the weather forecast database and results produced by the analyzer. A graphical user interface, coupled to the analyzer and the configurator, enables users to view and manipulate results produced by the analyzer and the configurator to thereby forecast future retail performance of the products at the locations. In an embodiment of the present invention, a consumer weather planner system allows consumers to perform weather-based planning for future events (e.g., golfing, vacations, weddings, etc.).
Owner:PANALEC
Method, Apparatus and Computer Program Product for Providing Route Planning Based on Personal Activity Plans of Multiple Individuals
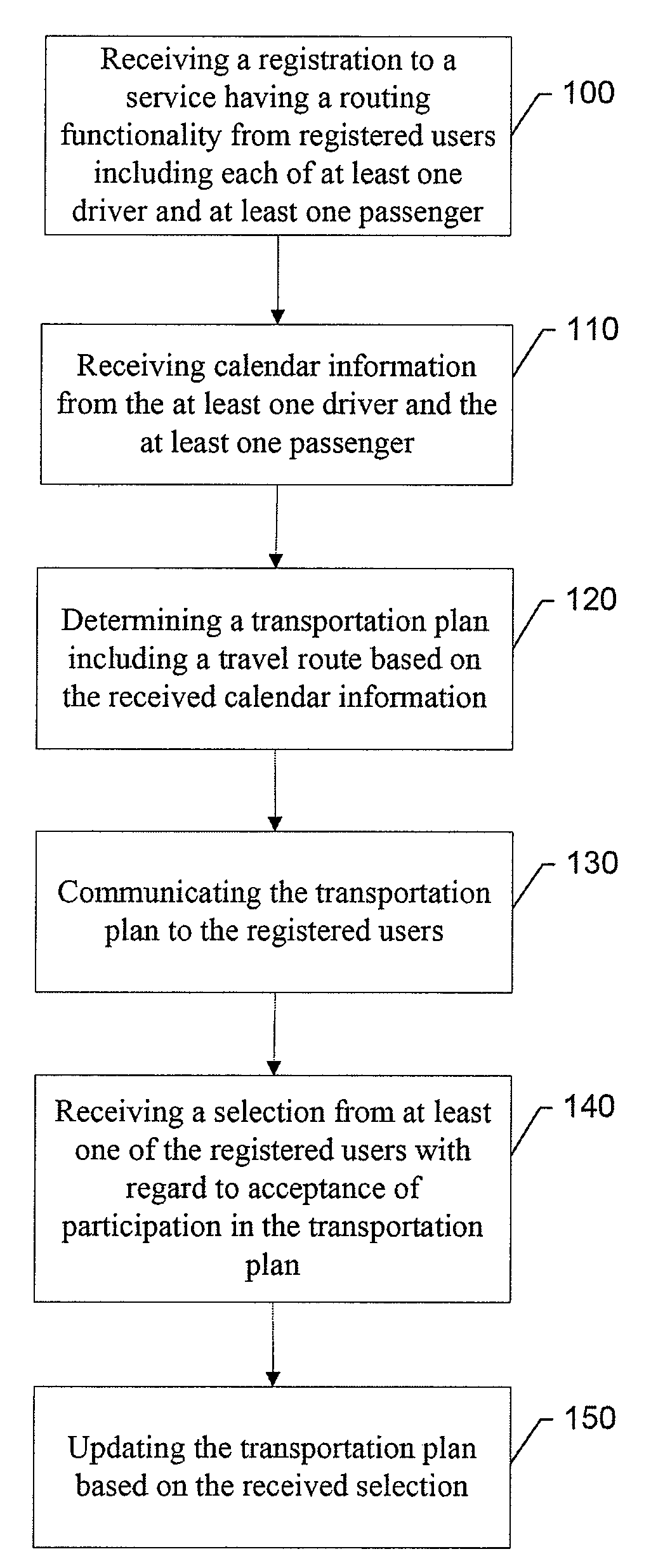
InactiveUS20090005963A1Reduce overheadInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlActivity schedulingDriver/operator
An apparatus for providing improved route planning may include a processing element. The processing element may be configured to receive calendar information from at least one driver and at least one passenger that are each registered to a service having a routing functionality, and determine a transportation plan including a travel route based on the received calendar information.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
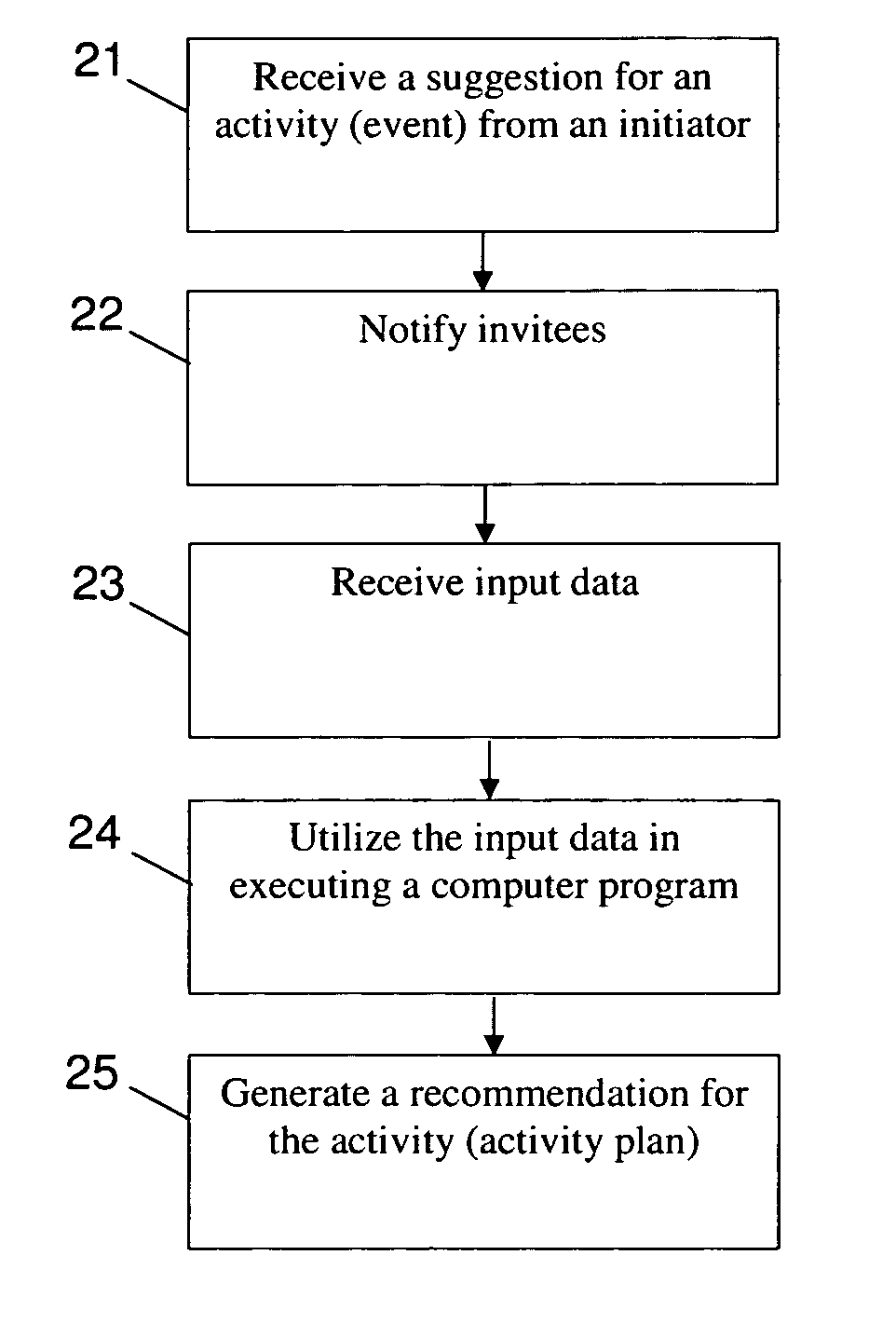
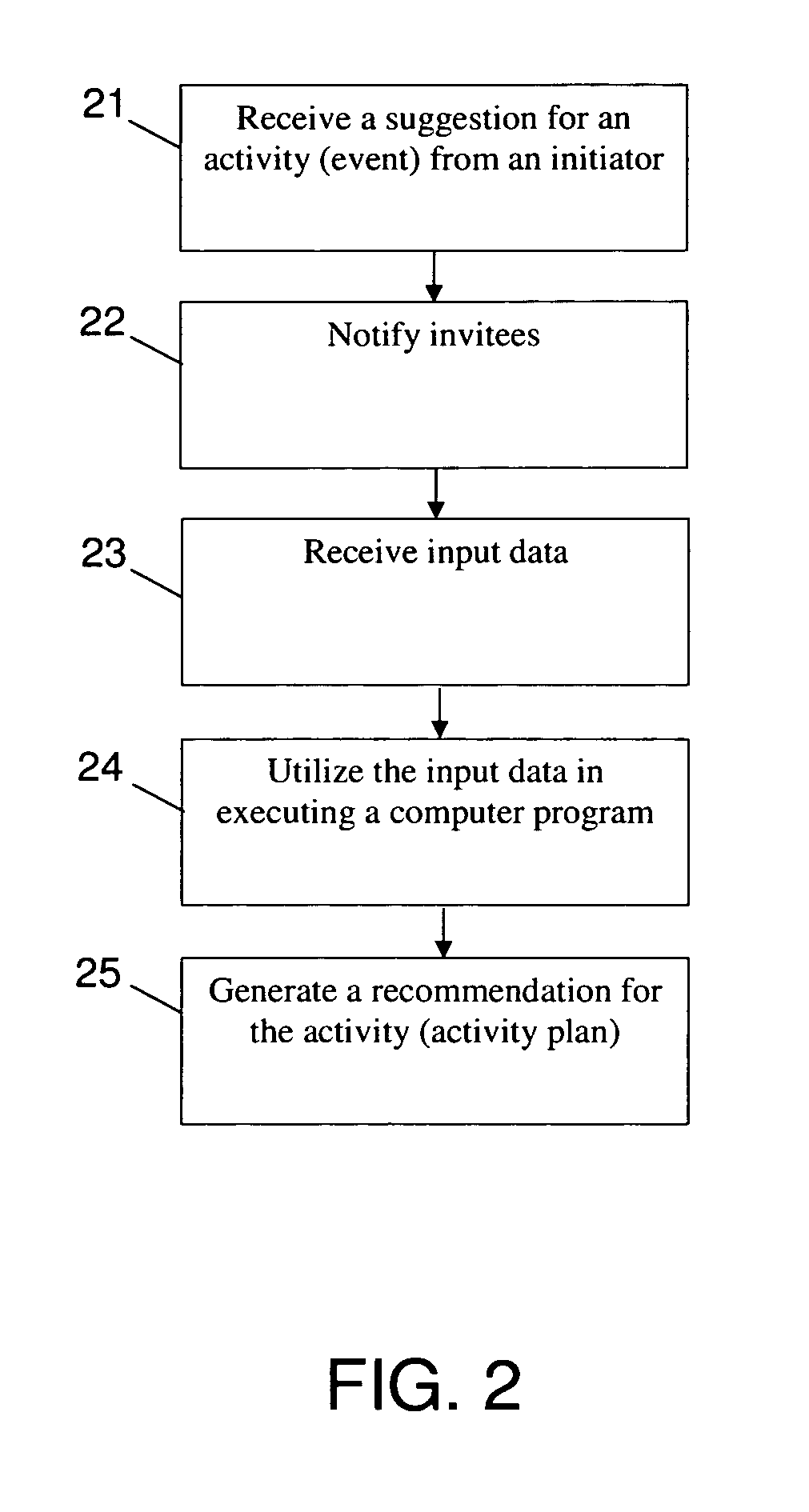
Activity planning method and system
InactiveUS20070094065A1Digital computer detailsElectric digital data processingActivity schedulingProgram planning
A computer-implemented method for planning an activity is disclosed. The method includes receiving a suggestion pertaining to the activity from an initiator and receiving a list of invitees, the list of invitees including at least two invitees. The method further includes executing a decision program, using input data, to generate an activity plan. The input data includes at least one of initiator preference data pertaining to preferences of the initiator and invitee preference data pertaining to preferences of at least one of the invitees. The activity plan includes at least one of a list of suggested participants for the activity, a recommended time slot for the activity, and a recommended location for the activity.
Owner:WU CHENGHSIU +2
Method and computer program product for weather adapted, consumer event planning
A system and method for forecasting future retail performance are described herein. The system includes a storage device that stores a sales history database, a weather history database, and a weather forecast database. An analyzer determines the extent to which past retail performance of a plurality of products at a plurality of locations was affected by weather using the sales history database and the weather history database. A configurator, coupled to the analyzer, estimates expected future retail performance of the products at the stores for a plurality of future time periods using the weather forecast database and results produced by the analyzer. A graphical user interface, coupled to the analyzer and the configurator, enables users to view and manipulate results produced by the analyzer and the configurator to thereby forecast future retail performance of the products at the locations. In an embodiment of the present invention, a consumer weather planner system allows consumers to perform weather-based planning for future events (e.g., golfing, vacations, weddings, etc.).
Owner:FOX FREDERIC D +4
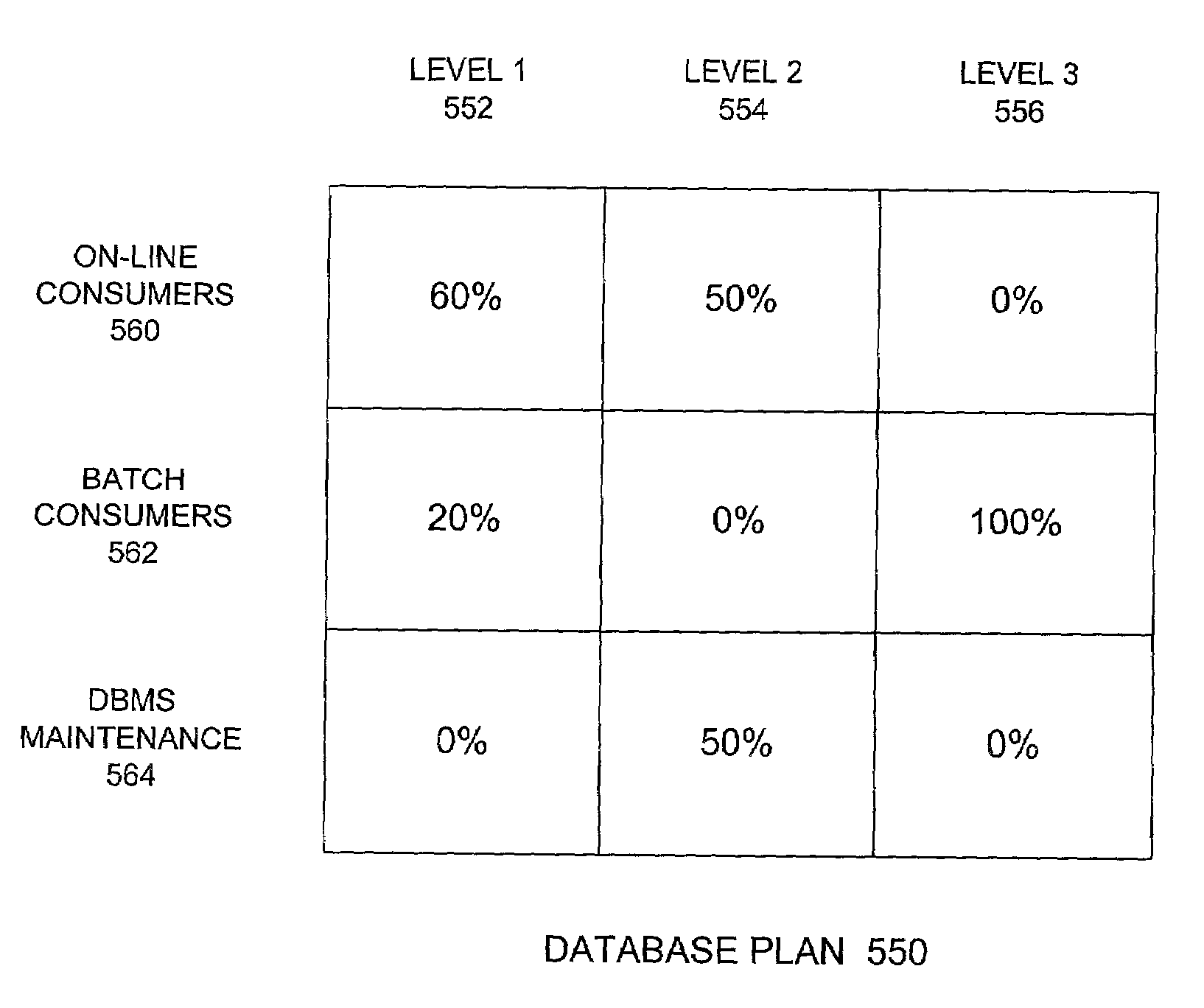
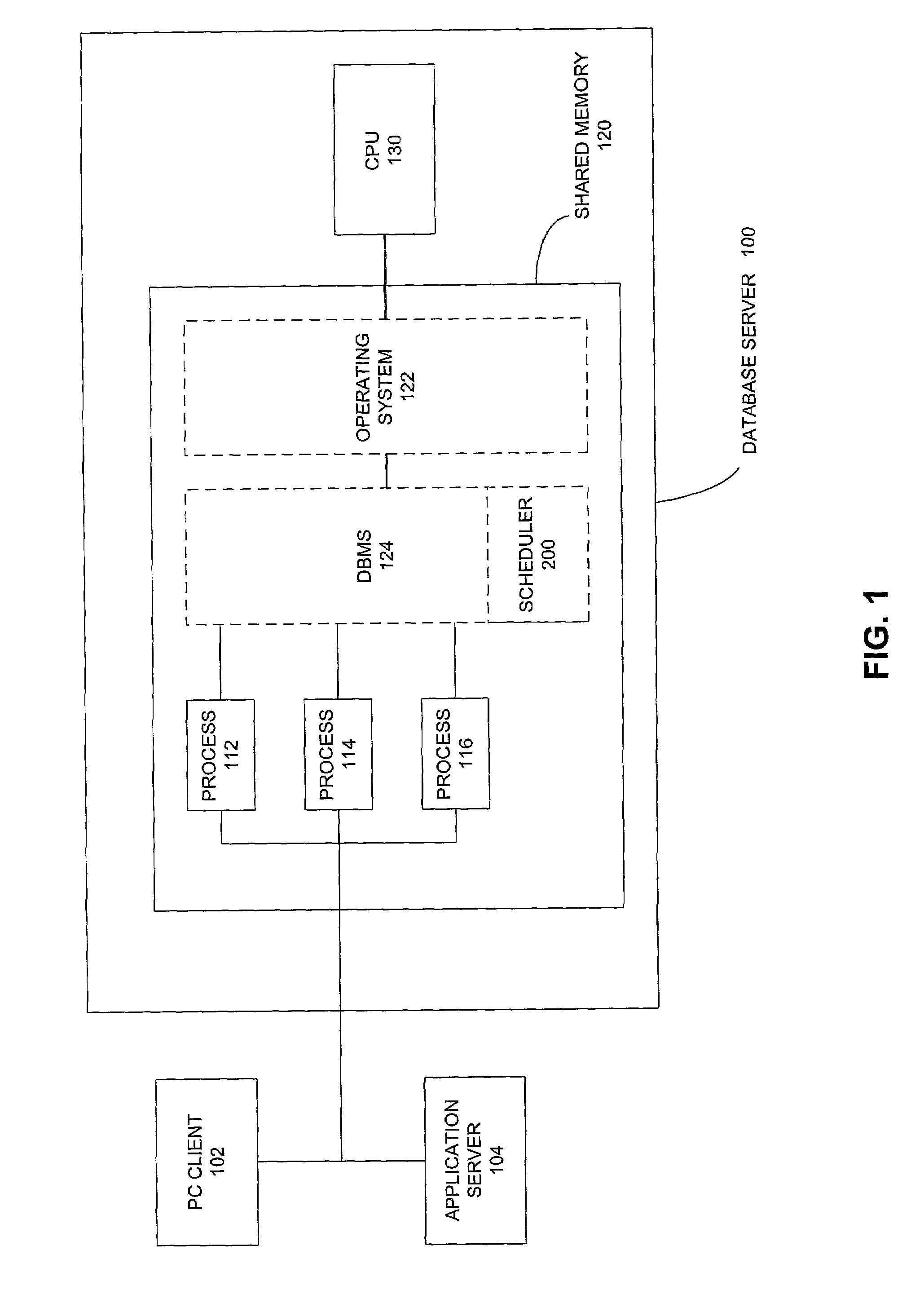
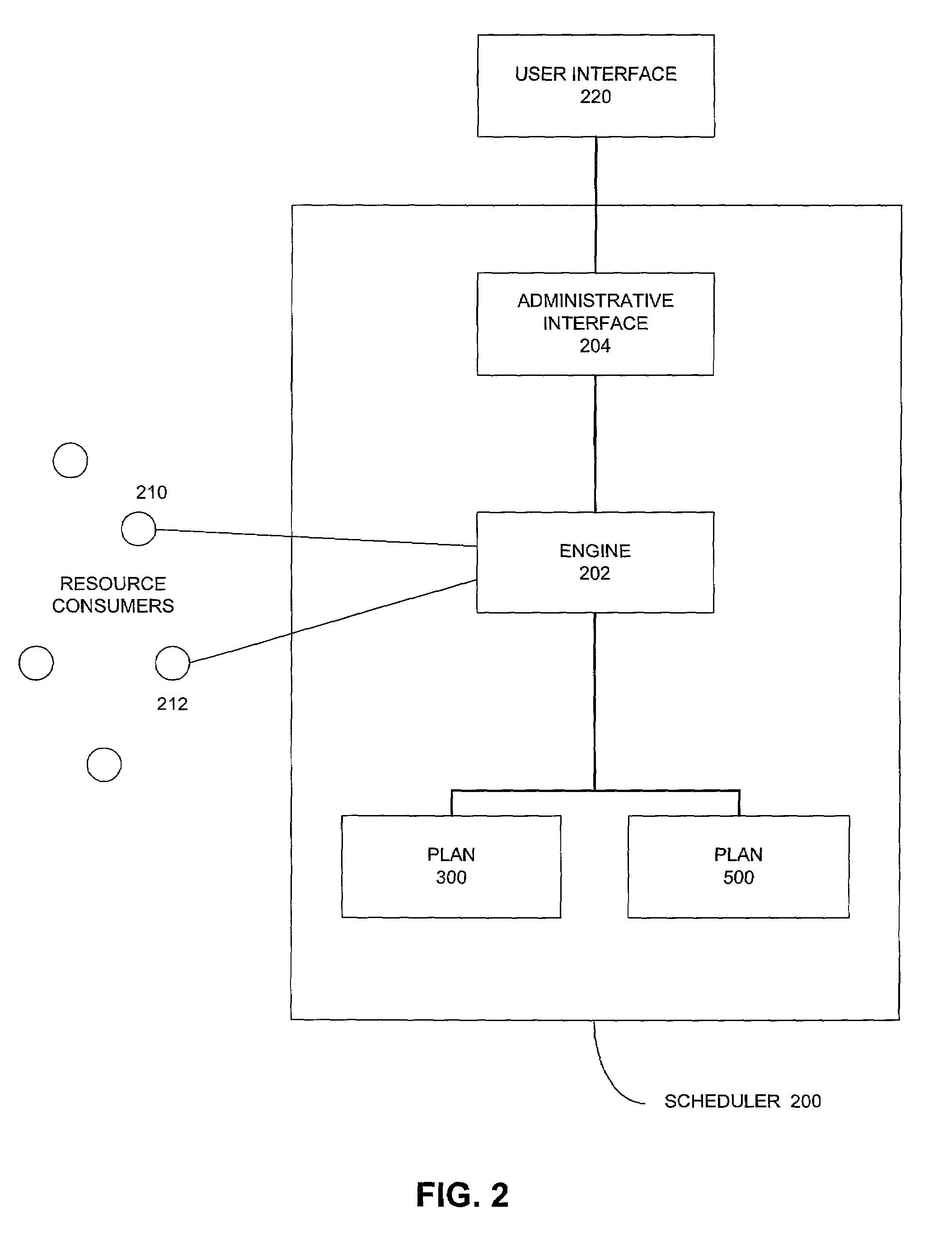
System for allocating resource using the weight that represents a limitation on number of allowance active sessions associated with each resource consumer group
InactiveUS7020878B1Increase and decrease system resourceMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsMass storageActivity scheduling
One embodiment of the present invention provides a resource scheduler for allocating a computer system resource, such as memory or mass storage, within a processor, to database management system (DBMS) processes. The resource scheduler operates according to resource plans and resource allocation methods. One or more plans may be configured and loaded with the DBMS. Each plan allocates the resource according to an associated resource allocation method. During operation of the DBMS, any or all of the active plans and resource allocation methods may be exchanged for alternate plans or resource allocation methods. In one embodiment of the invention the resource scheduler enforces a maximum active sessions resource allocation method in which system resources are allocated by limiting the number of active sessions allowed in groups of database processes grouped according to common execution requirements. A selected plan includes multiple process groups and / or sub-plans. The resource scheduler allocates system resources among the sub-plans and groups of database processes according to their associated limits on active session numbers, with sub-plans and groups having higher active session limits getting access to more system resources than sub-plans and groups having lower active session limits.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
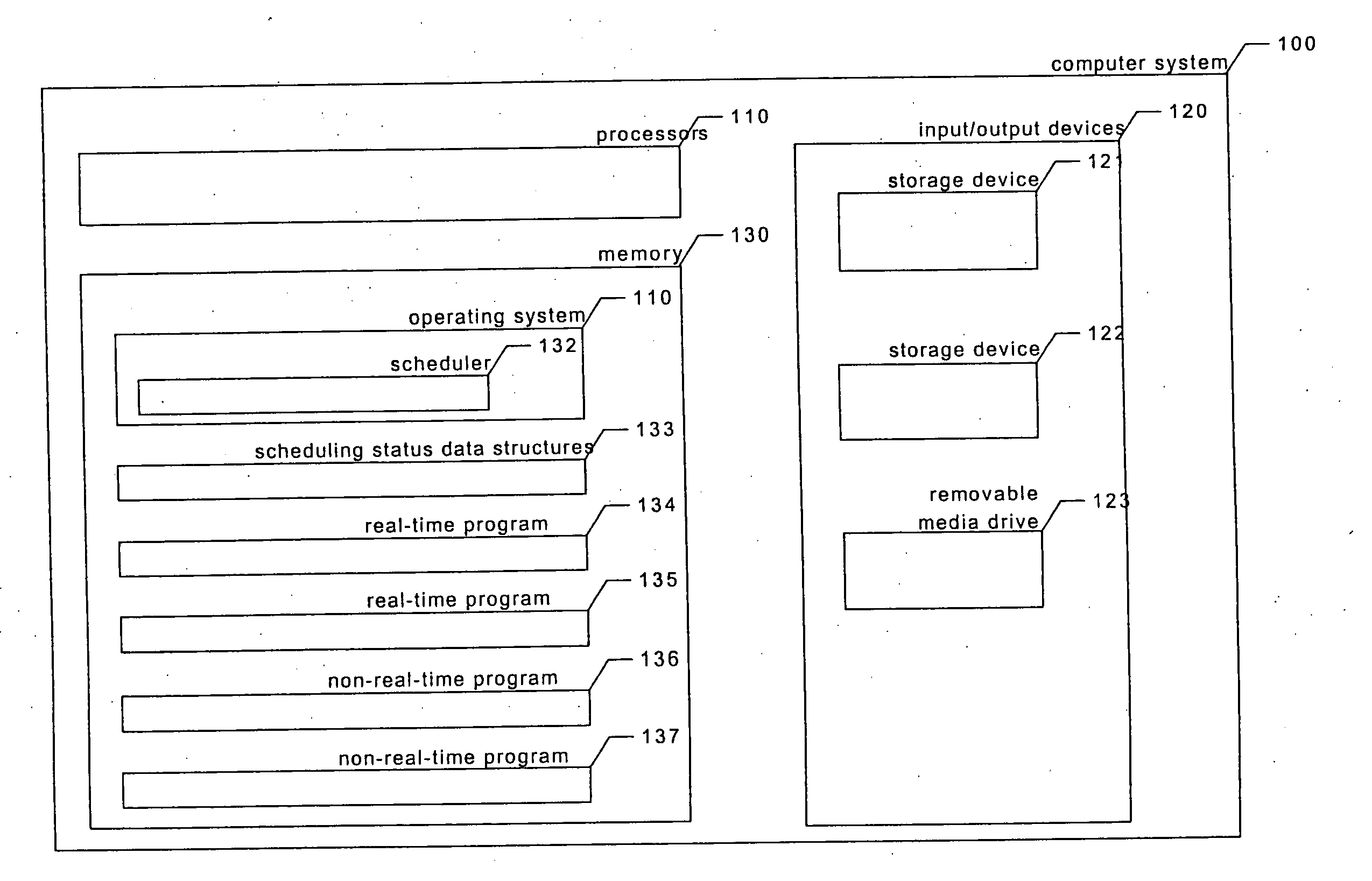
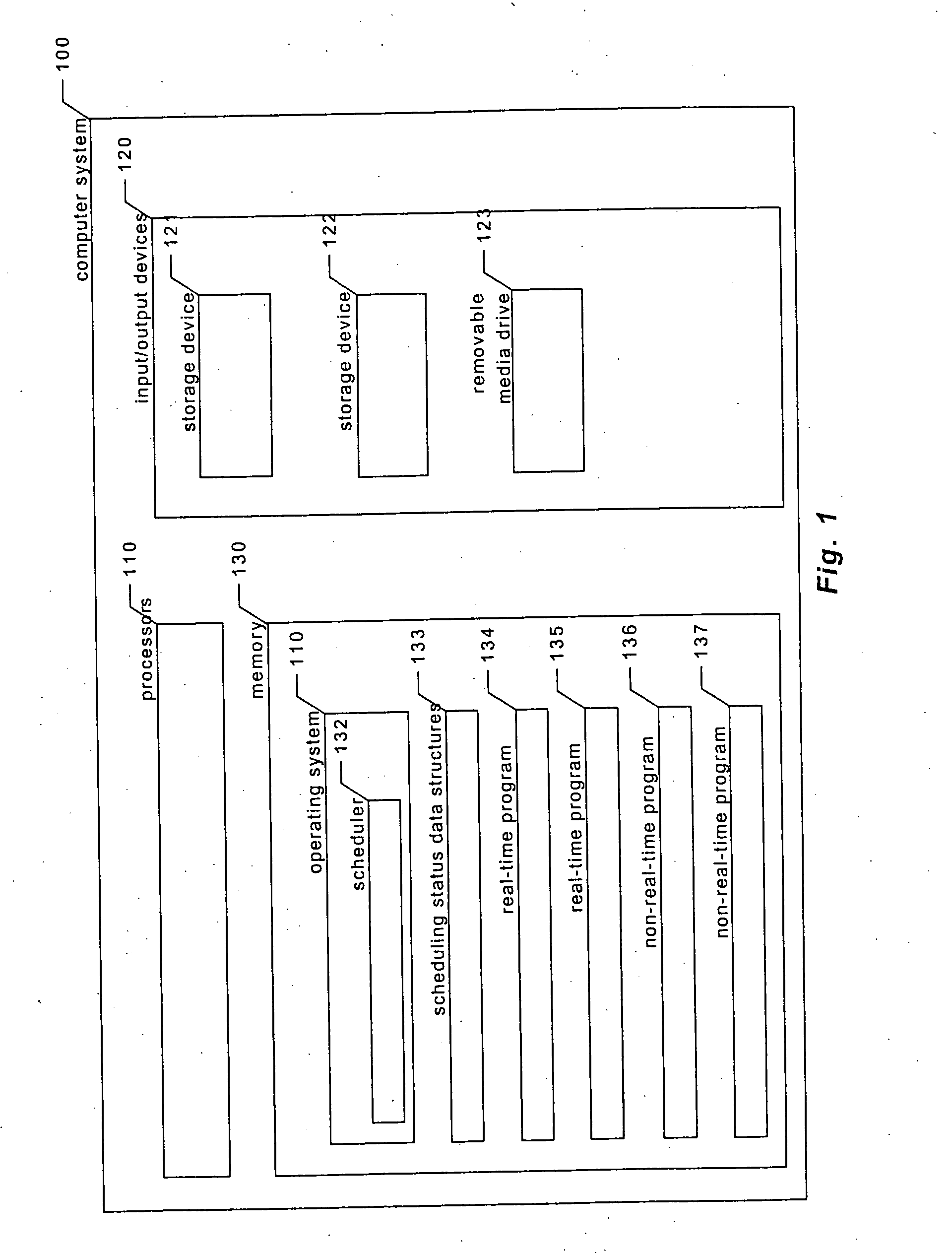
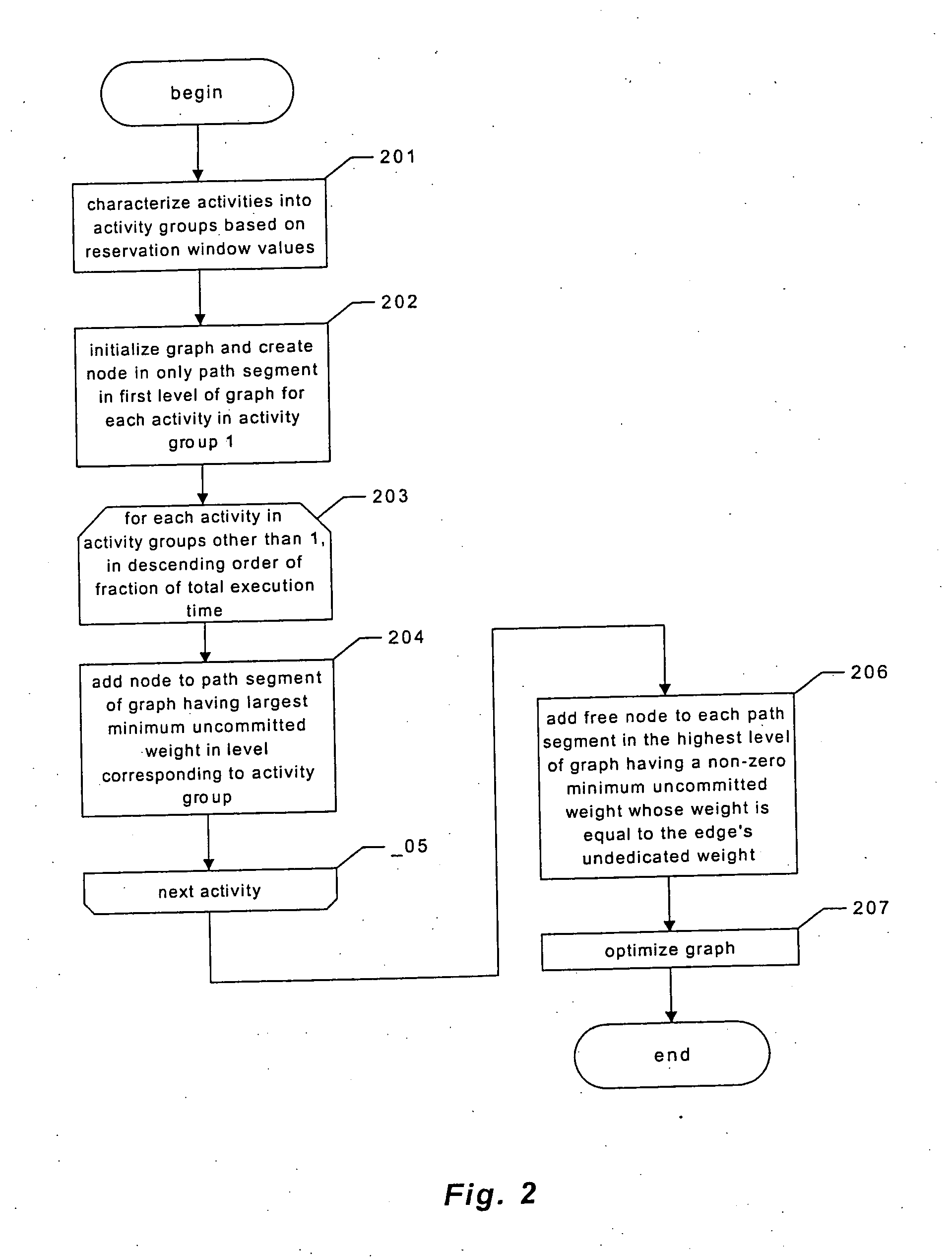
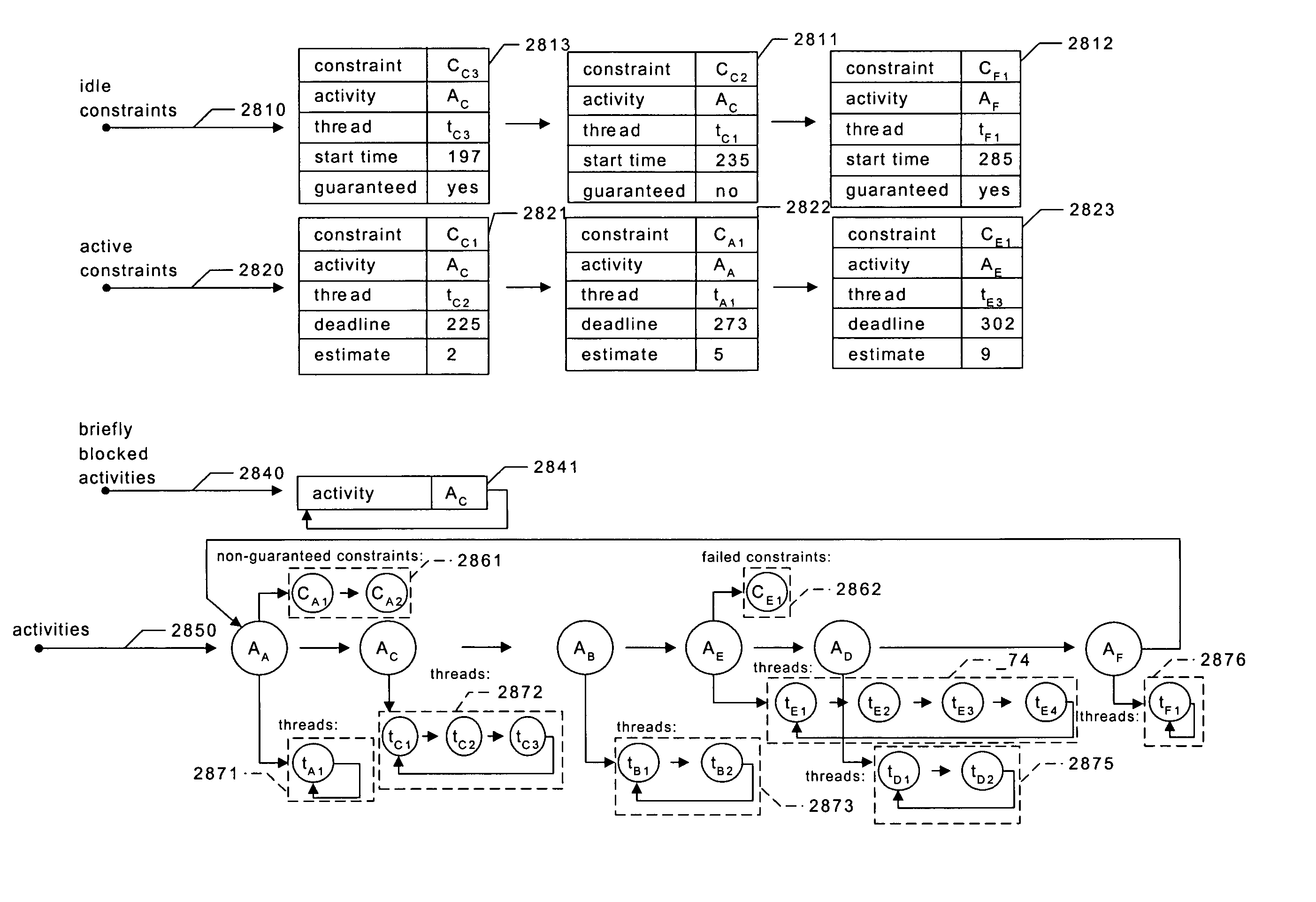
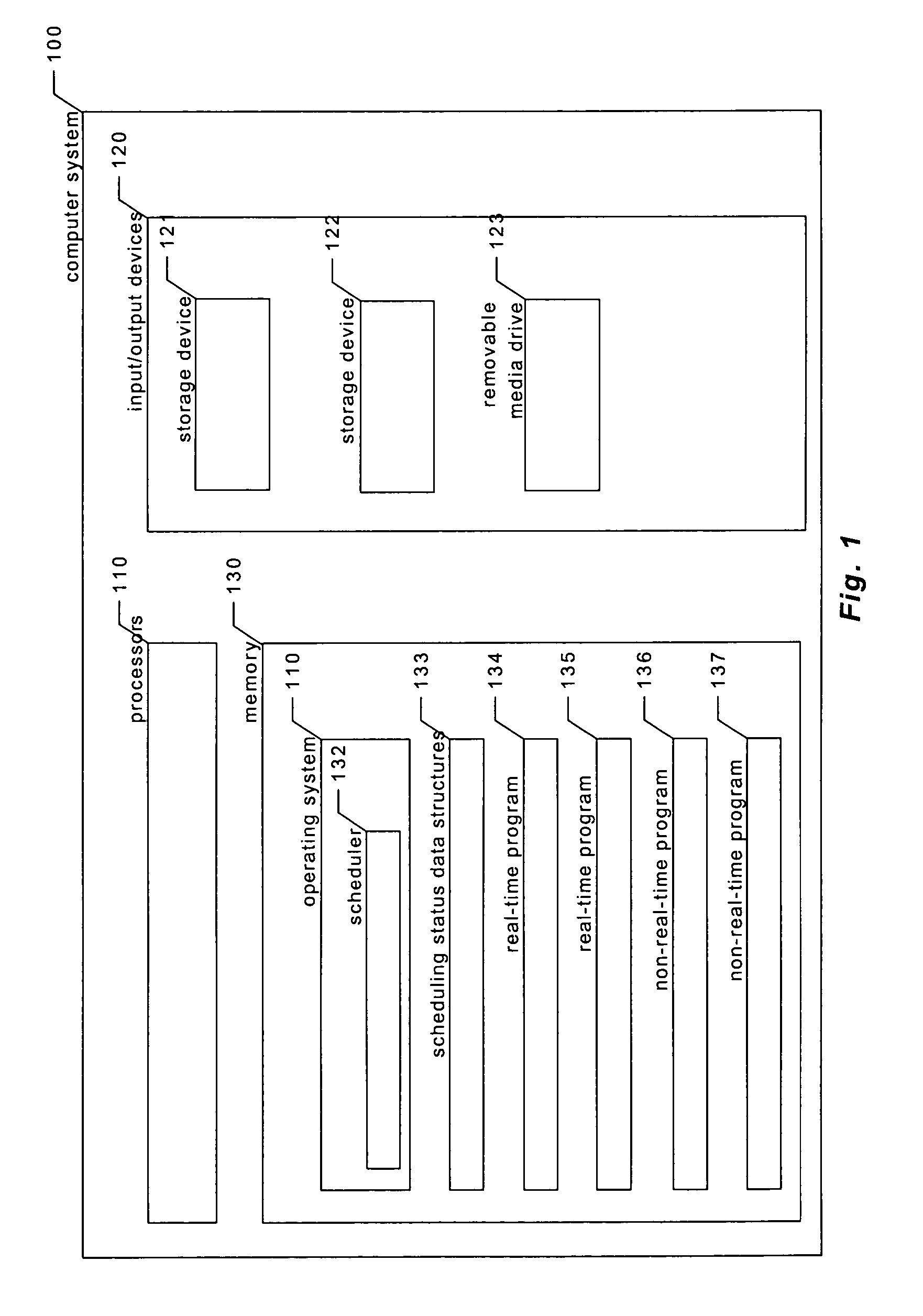
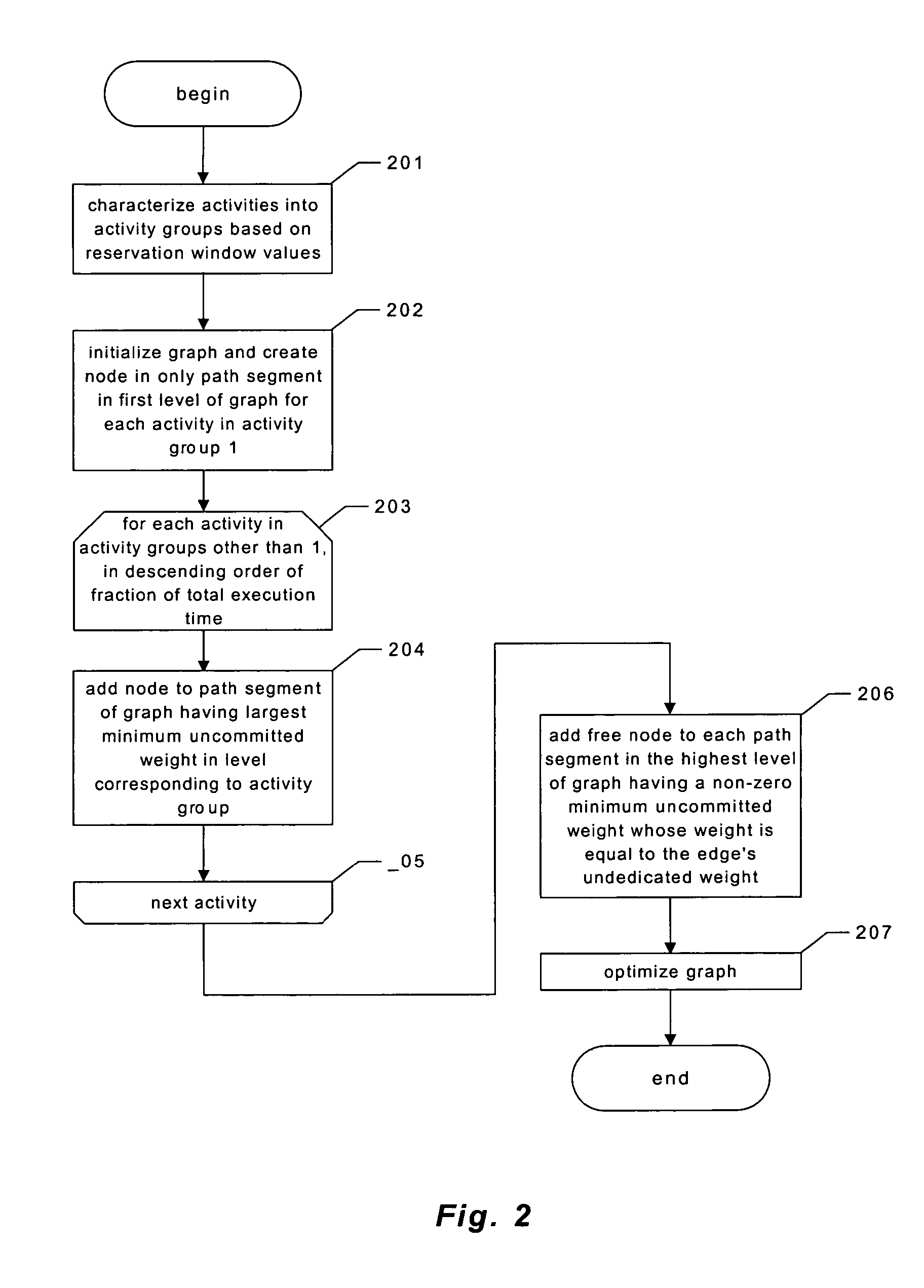
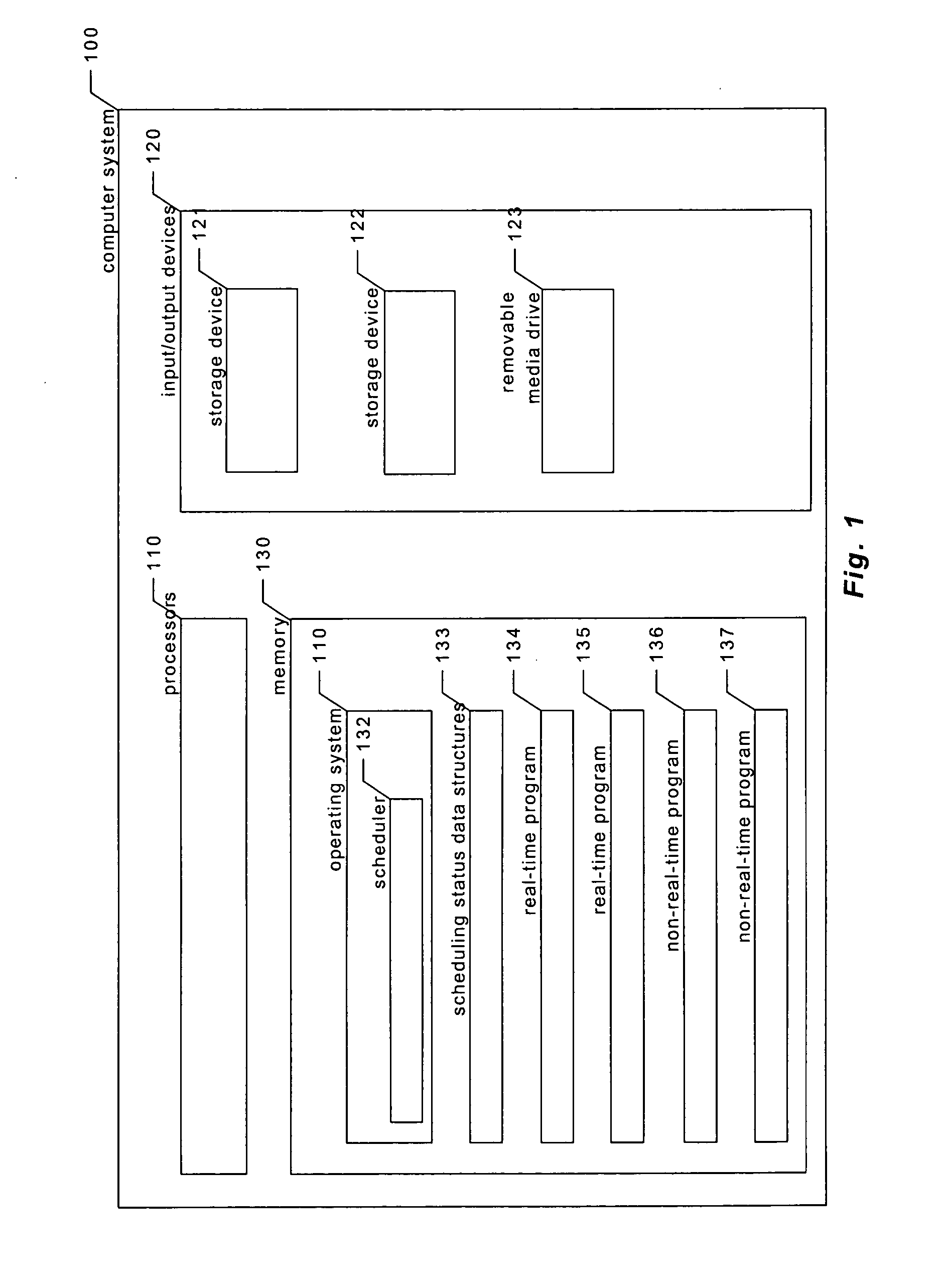
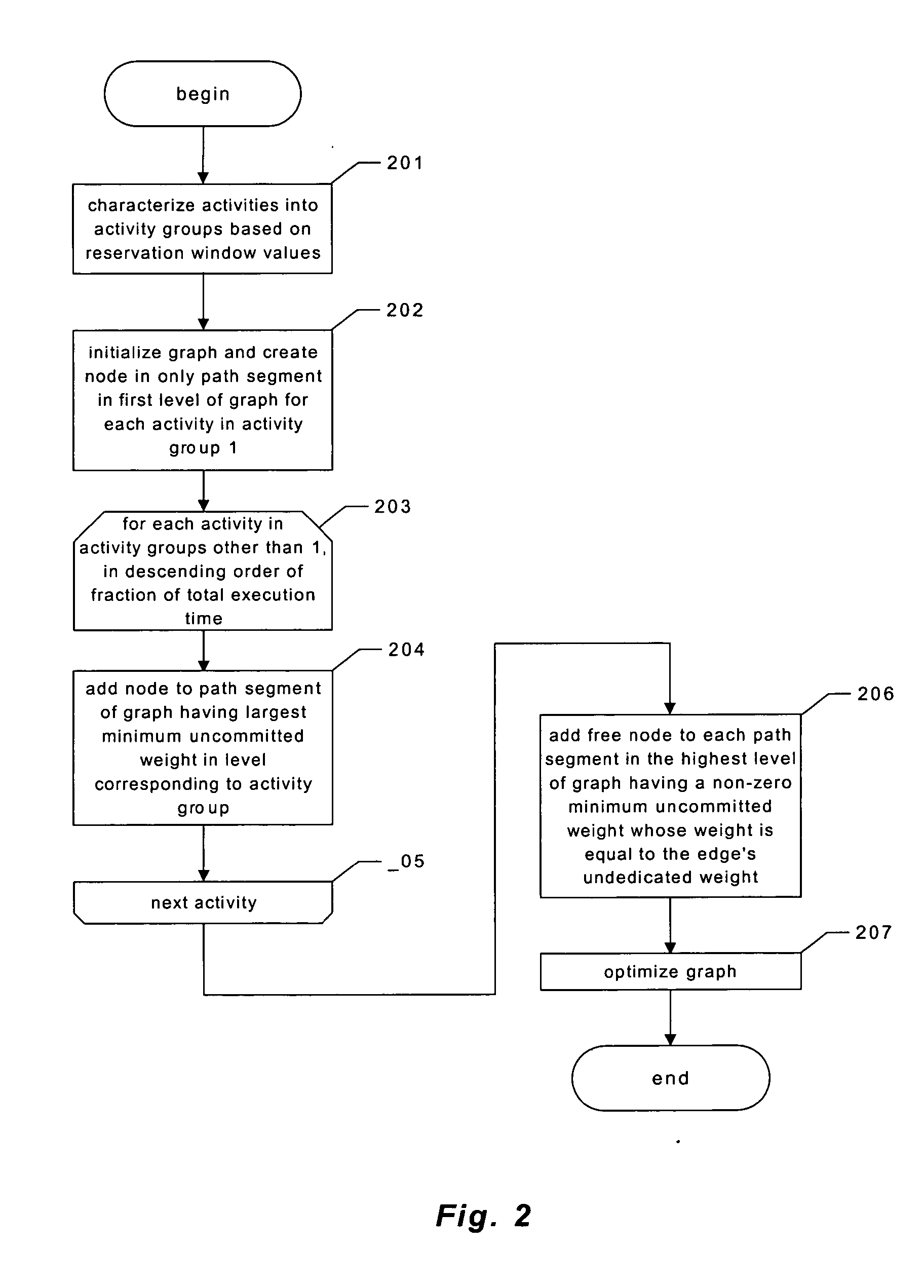
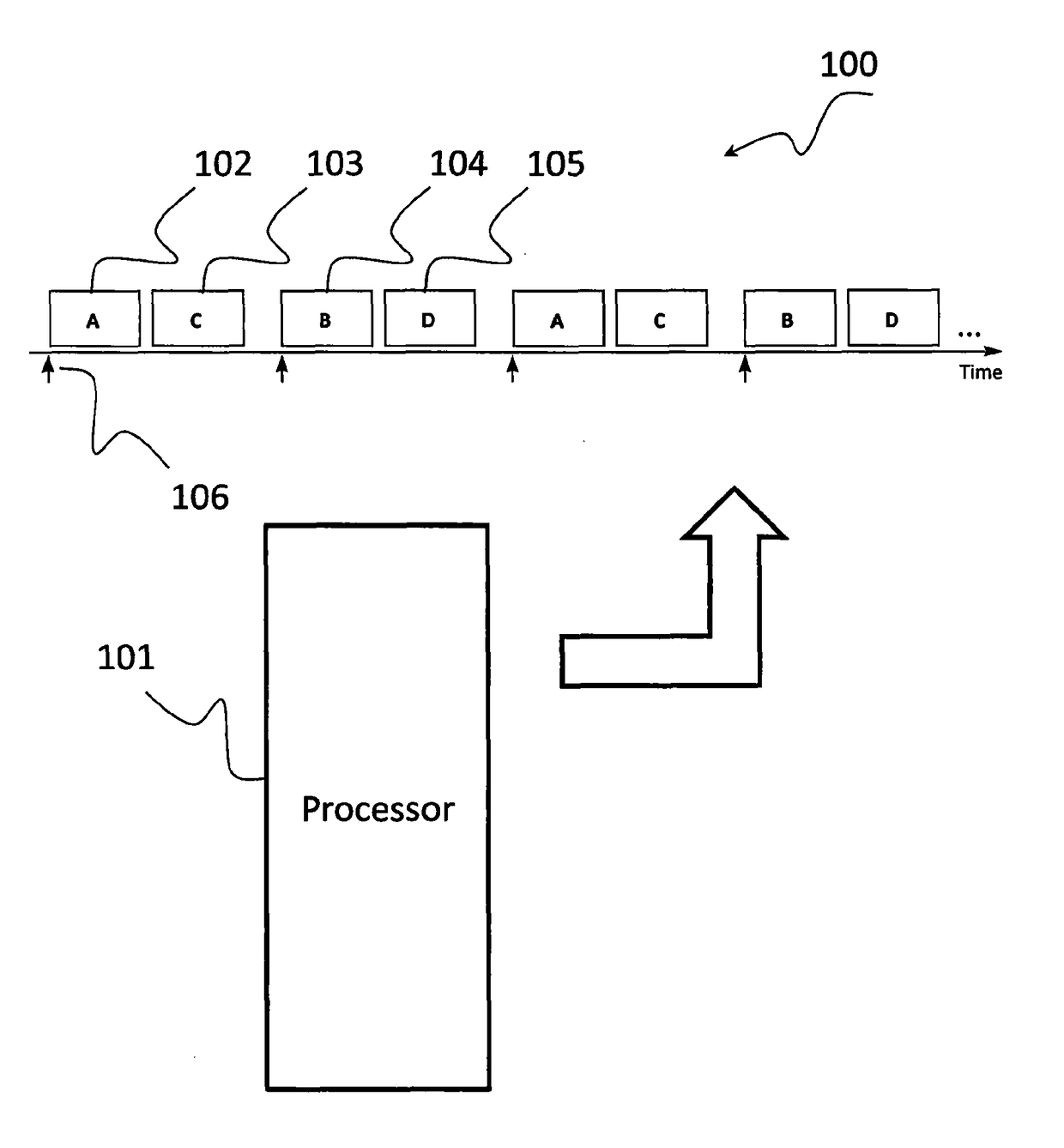
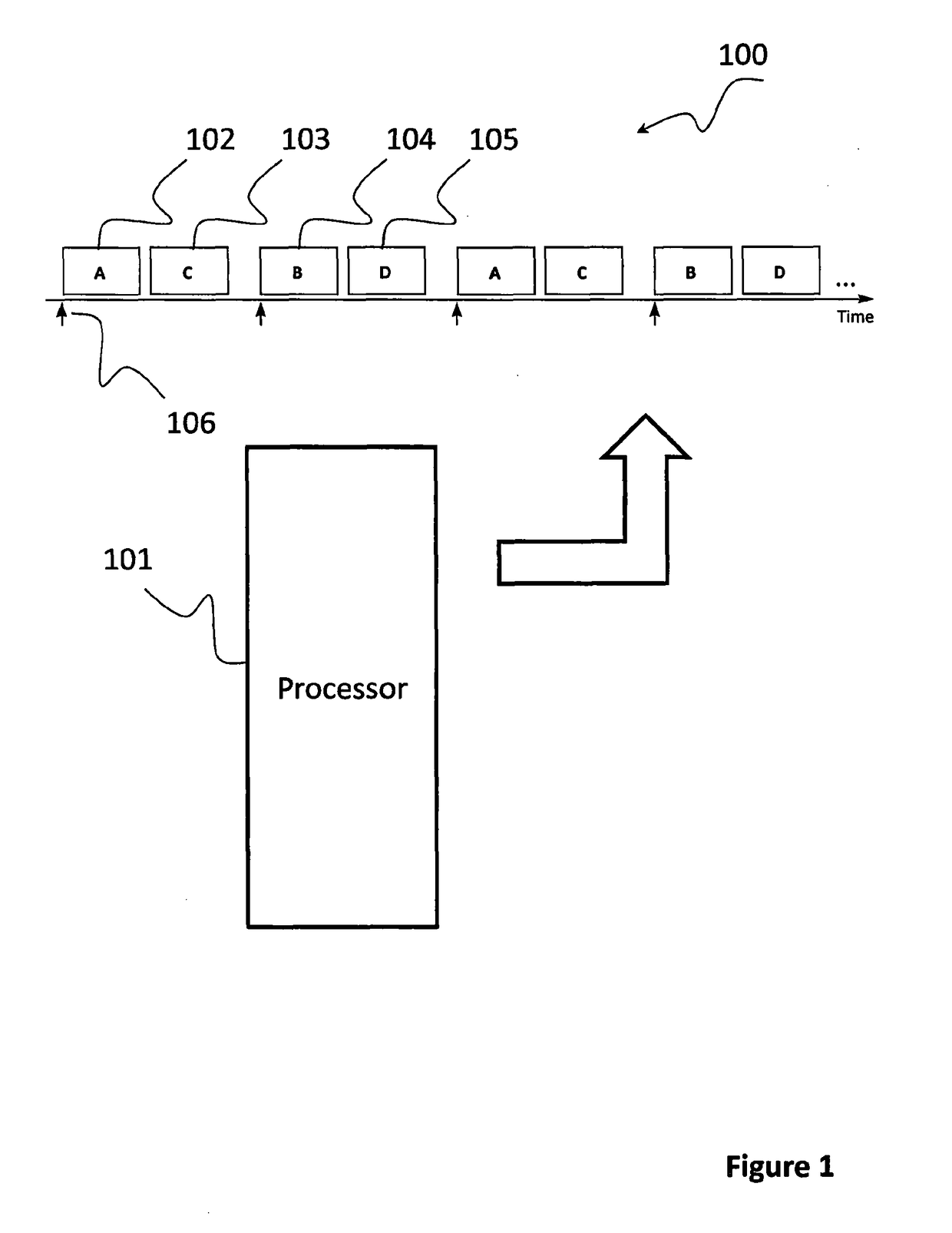
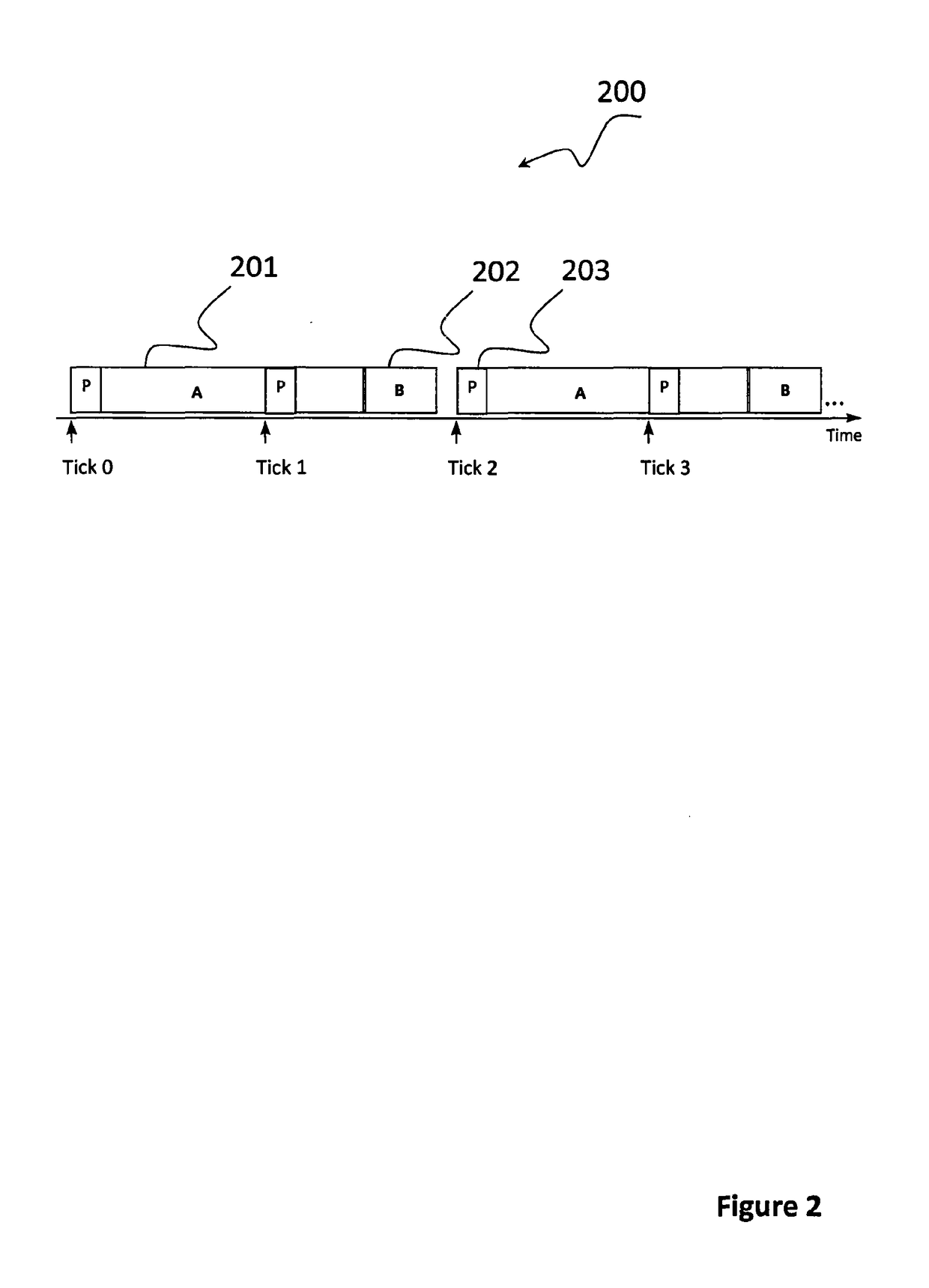
Providing predictable scheduling of programs using repeating precomputed schedules on discretely scheduled and/or multiprocessor operating systems
InactiveUS20060053423A1Maximize lengthEasy to useProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationGraphicsOperational system
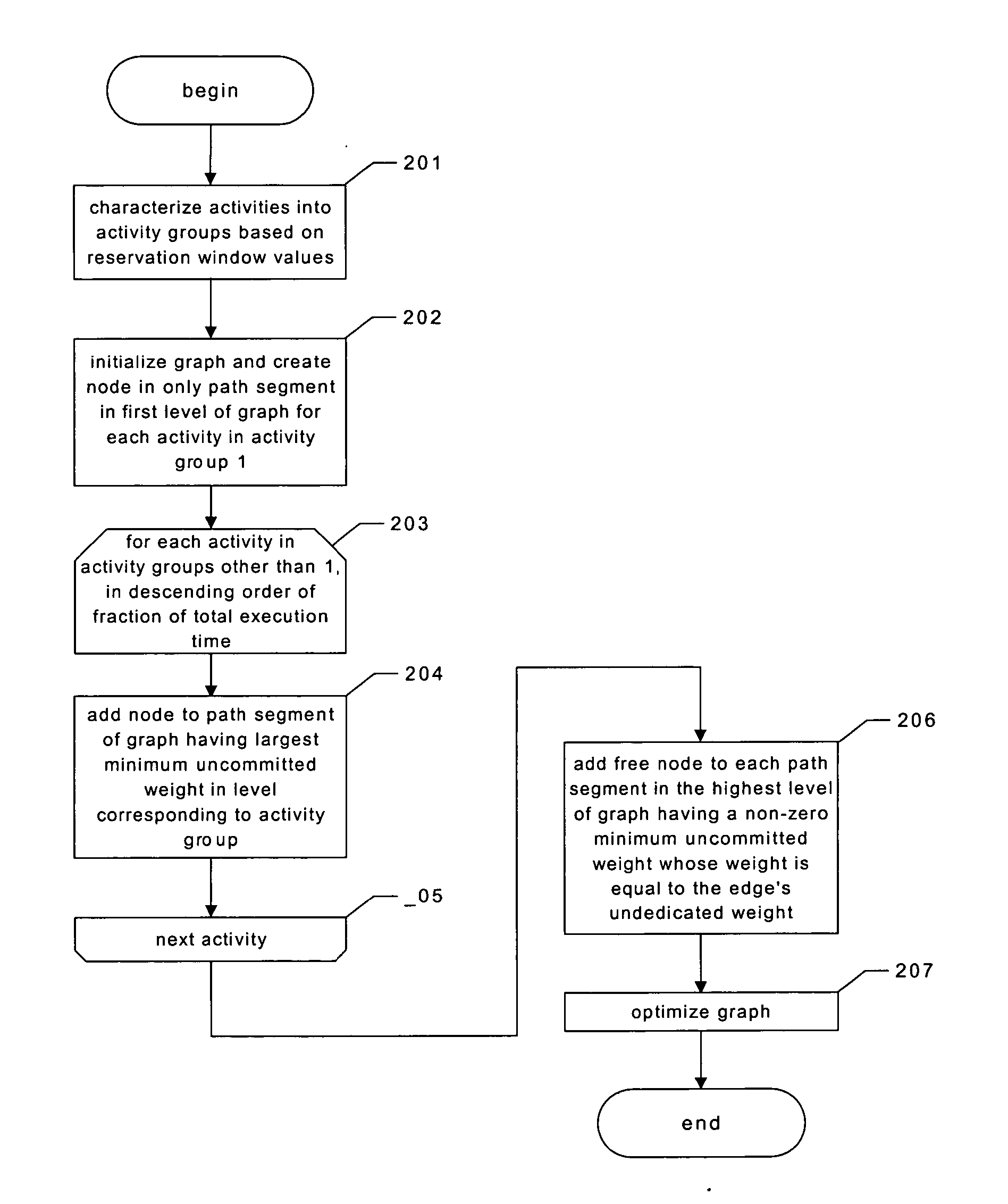
The present invention provides providing predictable scheduling of programs using repeating precomputed schedules on discretely scheduled and / or multiprocessor operating systems. In one embodiment, a scheduler accesses an activity scheduling graph. The activity scheduling graph is comprised of nodes each representing a recurring execution interval, and has one root, one or more leaves, and at least one path from the root to each leaf. Each node is on at least one path from the root to a leaf, and the number of times the execution interval represented by each node occurs during the traversal of the graph is equal to the number of paths from the root to a leaf that the node is on. Each node has associated with it an execution interval length, and is adapted to being dedicated to executing the threads of a single activity. There may be one scheduling graph for each processor, or a scheduling graph may traverse multiple processors. Start and end times for reservations and constraints are adjusted to compensate for the granularity of the clock of the system. Furthermore, the scheduler may use an existing priority-based scheduler in order to cause scheduling decisions it has made to be acted upon.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems and methods of enabling integrated activity scheduling, sharing and real-time social connectivity through an event-sharing platform
InactiveUS20160055215A1New levelFacilitate adding activityDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesWeb siteActivity scheduling
Embodiments herein provide for an interactive event-scheduling platform (ESP), wherein locating activities via location data, notifying and alerting of them via real-time feeds and encouraging interaction through a full-service social media suite (SMS), enhanced with live streaming and “always-on” connectivity, could provide a fresh experience for users and hosts. A real-time data procuring system and method may solve problems with stale or incomplete activity data within a geographic area, bridge gaps between users and hosts by shortening time periods—from activity announcement, to discovery, to launch, to action—create buzz, maximize venue attendance, boost sales and ensure promotional success. Software crawlers may mine public Web sites for thorough activity data coverage. Stored activities, profiles and collected user interaction data may produce behavioral reports to increase ROMI. Security packages, installations and access controls may incite users to safely register themselves in the SMS to engage, interact and transact.
Owner:KAUWE JOSEPH GREGORY
Providing predictable scheduling of programs using repeating precomputed schedules on discretely scheduled and/or multiprocessor operating systems
InactiveUS7000232B2Maximize lengthEasy to useProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationOperational systemActivity scheduling
The present invention provides providing predictable scheduling of programs using repeating precomputed schedules on discretely scheduled and / or multiprocessor operating systems. In one embodiment, a scheduler accesses an activity scheduling graph. The activity scheduling graph is comprised of nodes each representing a recurring execution interval, and has one root, one or more leaves, and at least one path from the root to each leaf. Each node is on at least one path from the root to a leaf, and the number of times the execution interval represented by each node occurs during the traversal of the graph is equal to the number of paths from the root to a leaf that the node is on. Each node has associated with it an execution interval length, and is adapted to being dedicated to executing the threads of a single activity. There may be one scheduling graph for each processor, or a scheduling graph may traverse multiple processors. Start and end times for reservations and constraints are adjusted to compensate for the granularity of the clock of the system. Furthermore, the scheduler may use an existing priority-based scheduler in order to cause scheduling decisions it has made to be acted upon.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
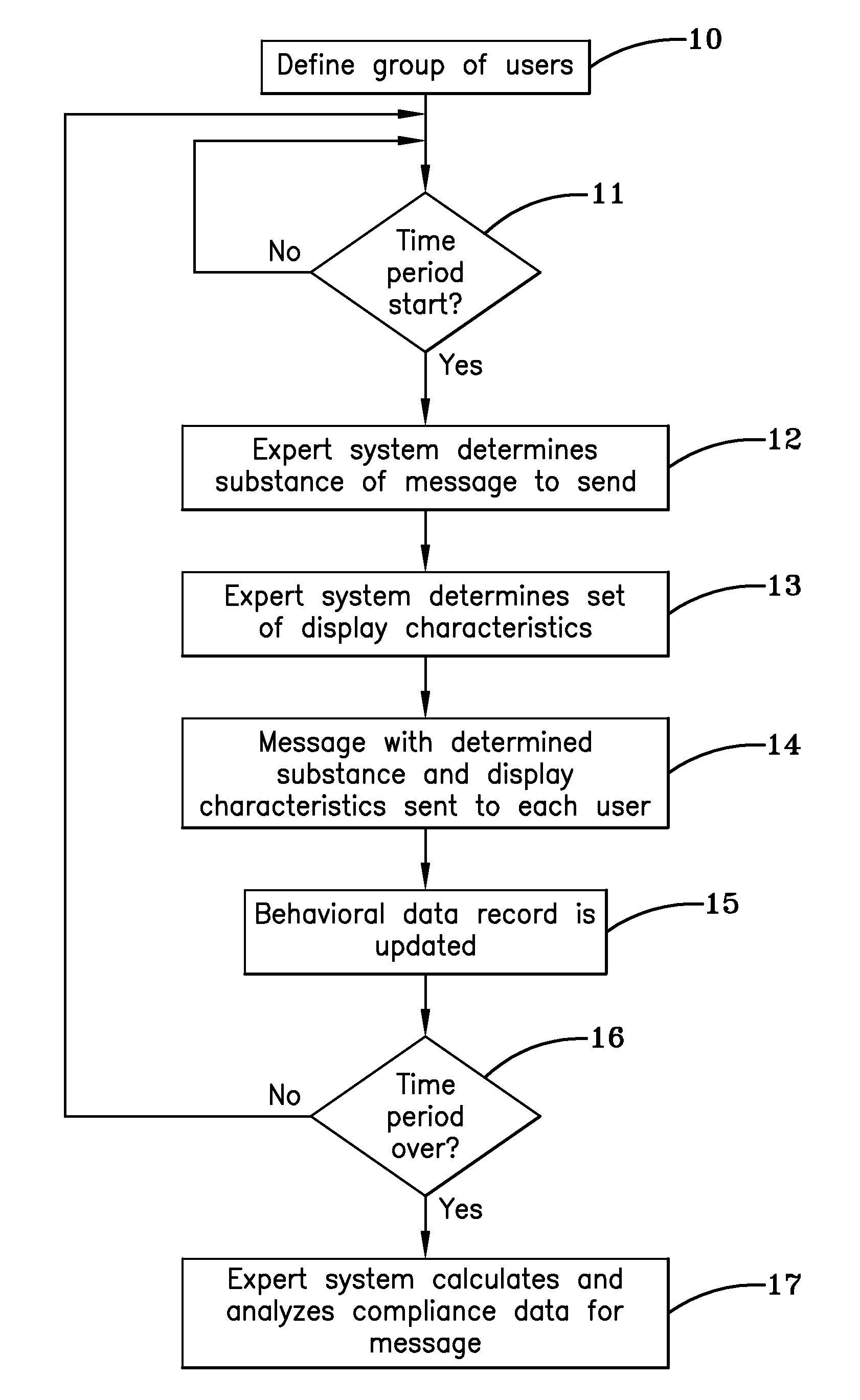
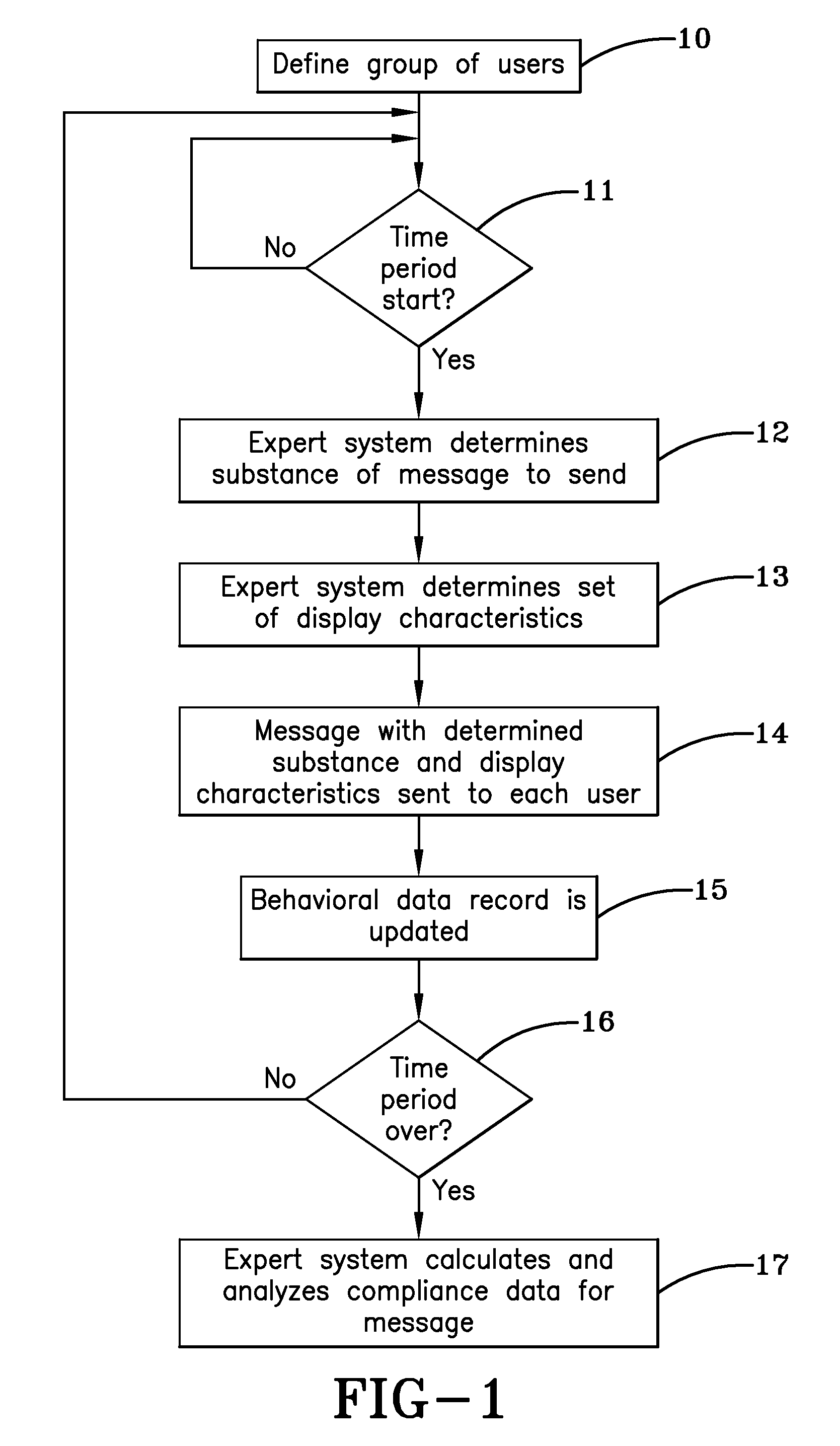
System and method for increasing compliance with a health plan
ActiveUS8560336B2Improve complianceConstant accessPhysical therapies and activitiesData processing applicationsPersonalizationHealth planning
System and method to determine user compliance with personalized diet and exercise plans by analyzing responses to messages about the plans. An expert system has a number of stored messages and display characteristics from which it chooses. The expert system generates message relating to the user's diet or physical activity that are sent to a user's mobile device and analyzes responses. Display characteristics change periodically and compliance data relating to the user's adherence to the plan when certain display characteristics are used is stored (e.g., meal plan adherence, acceptance of specific food selections, and adherence to instructions and advice in messages). The expert system then determines which messages and display characteristics achieve the greatest compliance to the dietary and physical activity schedule and goals.
Owner:HUMANA INNOVATIONS ENTERPRISES
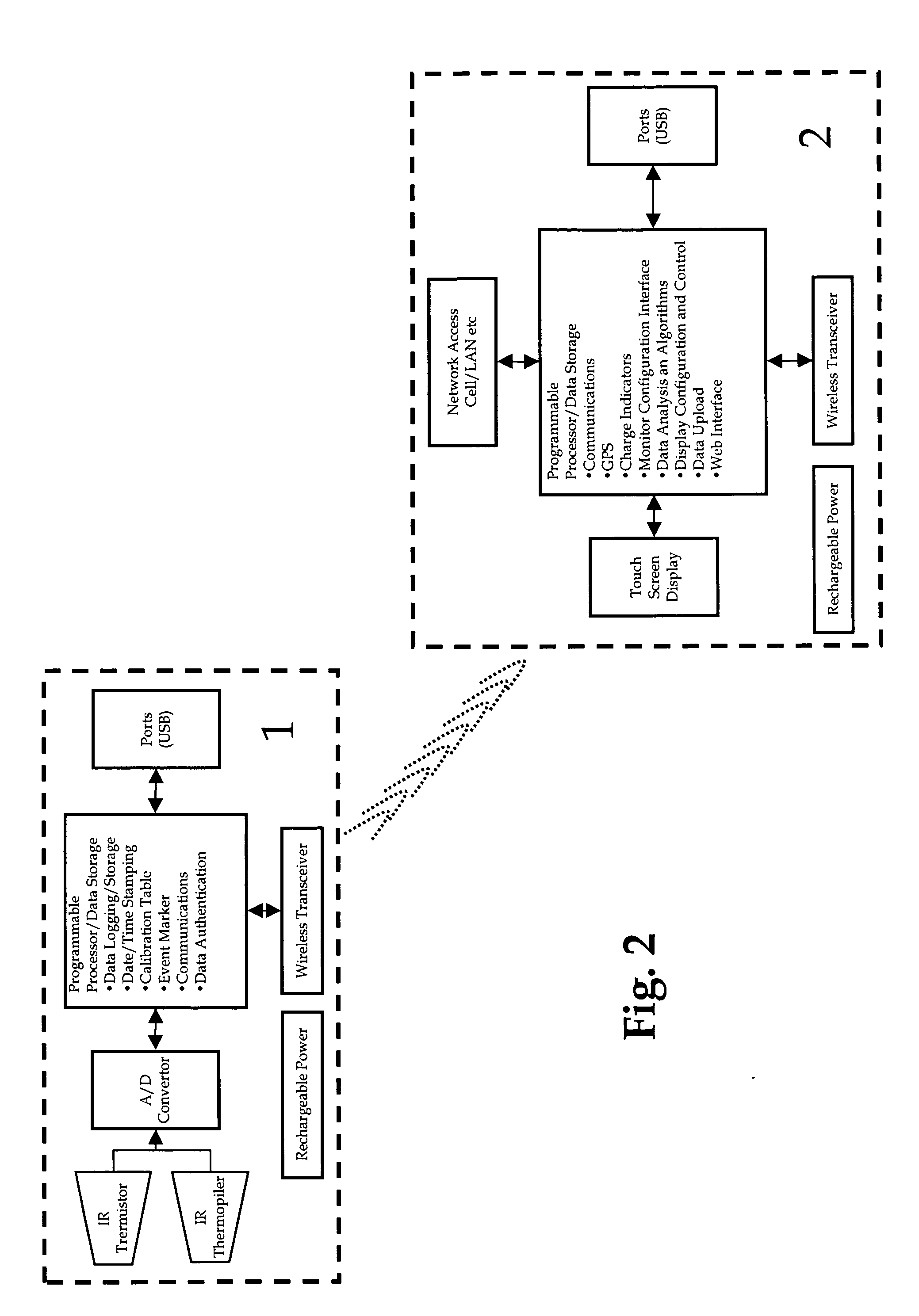
System for circadian rhythm monitor with synchrony and activity planning
InactiveUS20110144528A1Reduce desynchronyTelemedicineDiagnostic recording/measuringActivity schedulingCircadian rhythm
A personal health system which includes a suitable Core Body Temperature (CBT) monitor that can be worn for all or part of a 24 hour day and collect continuous CBT data. The CBT data is collected and compared to determine circadian desynchrony. A conveniently carried or worn processor / display unit, in communication with the CBT monitor, algorithmically determines activity types and activity timing based on the collected CBT data to improve synchrony. The activities and when to perform them are displayed to the user.
Owner:GURLEY VIRGINIA F
Automated activity processing
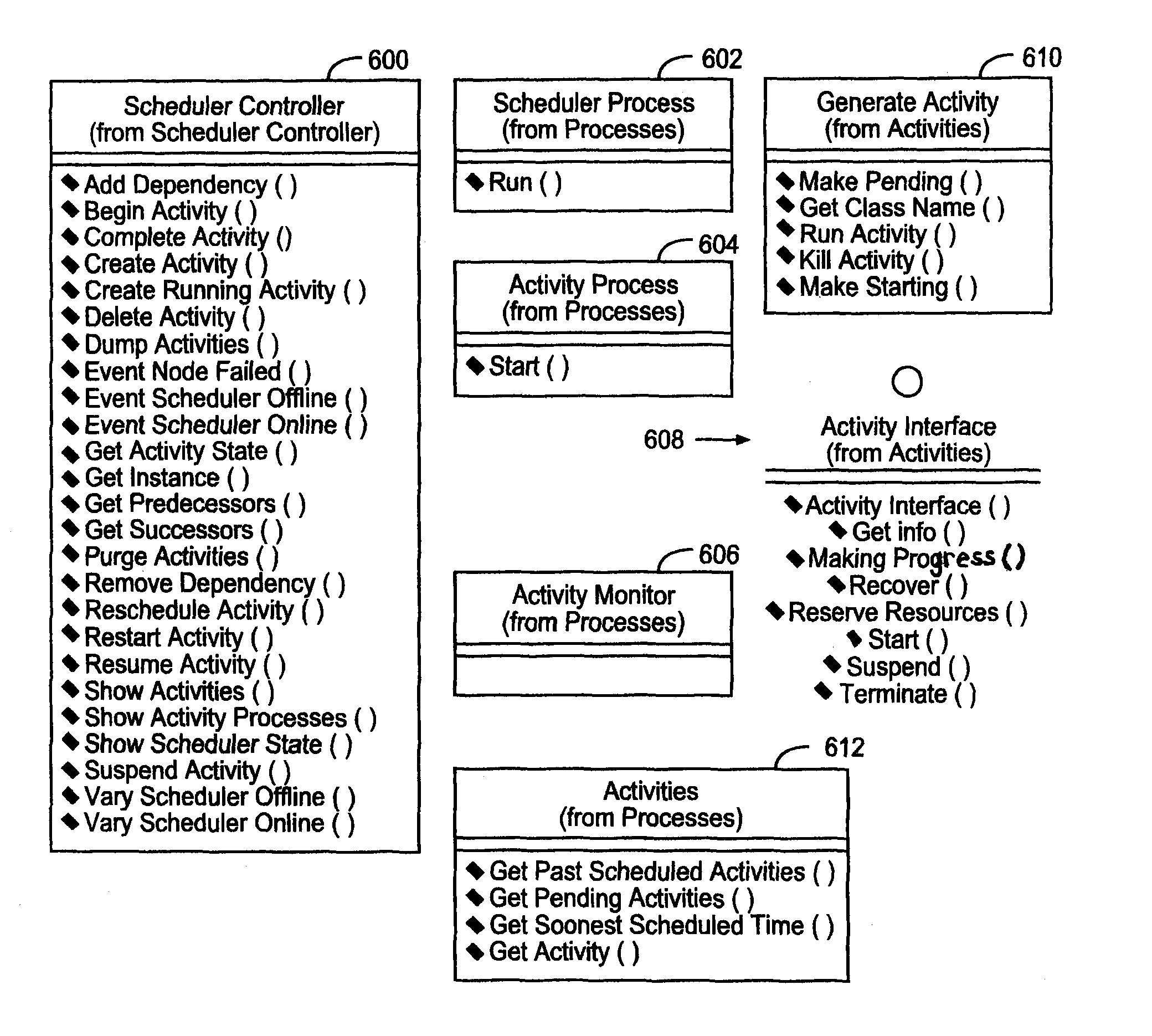
ActiveUS8087021B1Multiprogramming arrangementsComputer security arrangementsActivity schedulingData store
A virtual data storage system includes a device emulator and a storage system. The virtual data storage system requires the performance of activities on a scheduled basis. An activity scheduler manages a set of pending, running, and completed activities. The activity scheduler provides scheduler services for use by external processes. A scheduler process examines a list of to-be-run activities. For each activity that has reached its scheduled time, that activity is considered for starting. An activity monitor process monitors started activities. Upon determining a problem with an activity, a recovery process is performed. The recovery process includes returning the problem activity to the list of to-be-run activities.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Urban traffic planning simulation method and system based on multi-agent activity model
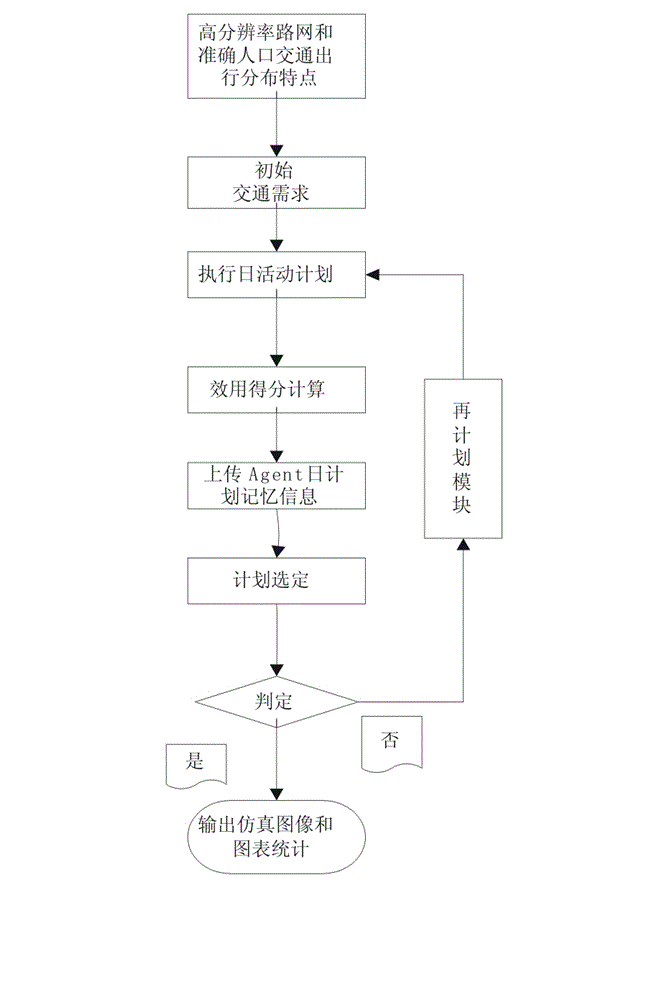
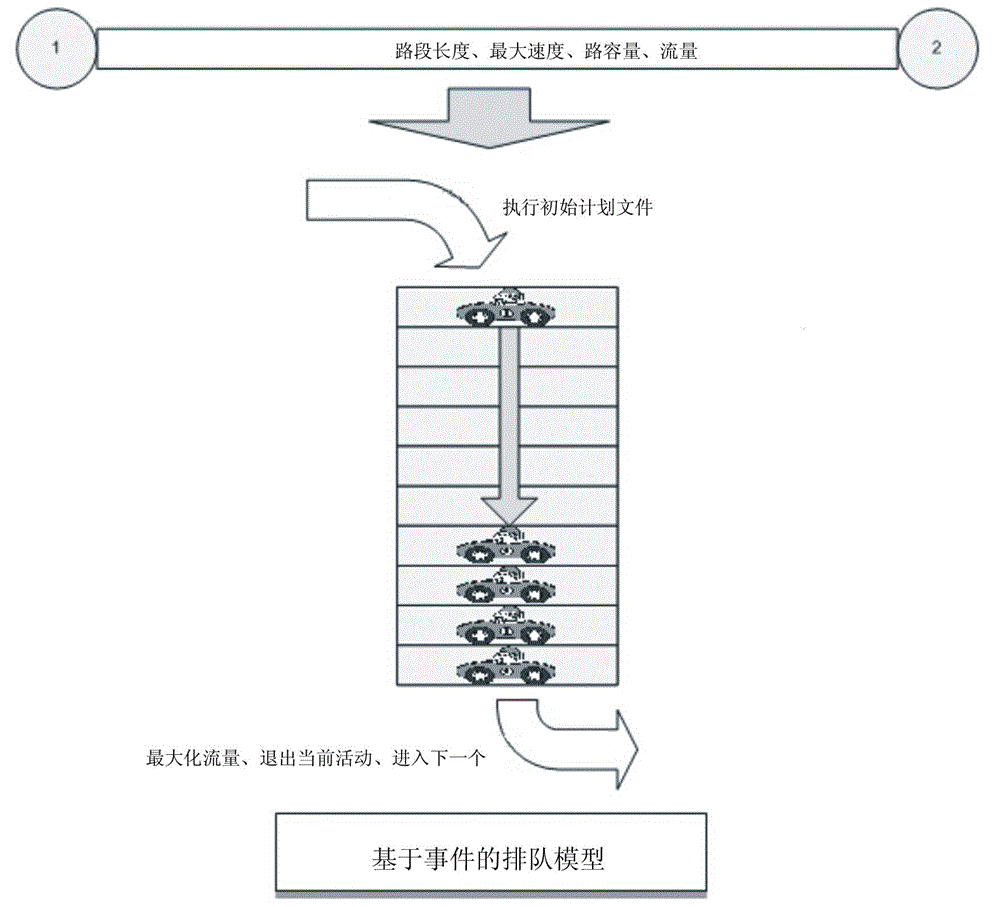
InactiveCN102750427AStrong real-timeImprove accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlSpecial data processing applicationsActivity schedulingSimulation
The invention relates to an urban traffic planning simulation method and system based on a multi-agent activity model. The method comprises the following steps: firstly acquiring urban road information to generate a road network information file; secondly, generating initial traffic requirements and an initial daily activity plan according to the acquired survey data; thirdly, loading the daily activity plan to the road network information file; fourthly, calculating a utility value and planned selective probability for each surveyed object; and finally, performing an iterative process to output the simulation result. The system comprises a client end and a server client which communicate in an http communication manner. According to the invention, a four-stage traffic simulation method is discarded; a traffic requirement generating and distributing method based on the activity model is completely adopted; a multi-agent technology and a genetic evolution algorithm are integrated for use; utility optimal limitation is used to generate and select an optimal path, so that maximum utilization efficiency of a vehicle and a road network is achieved, and traffic accidents and traffic jams are reduced.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
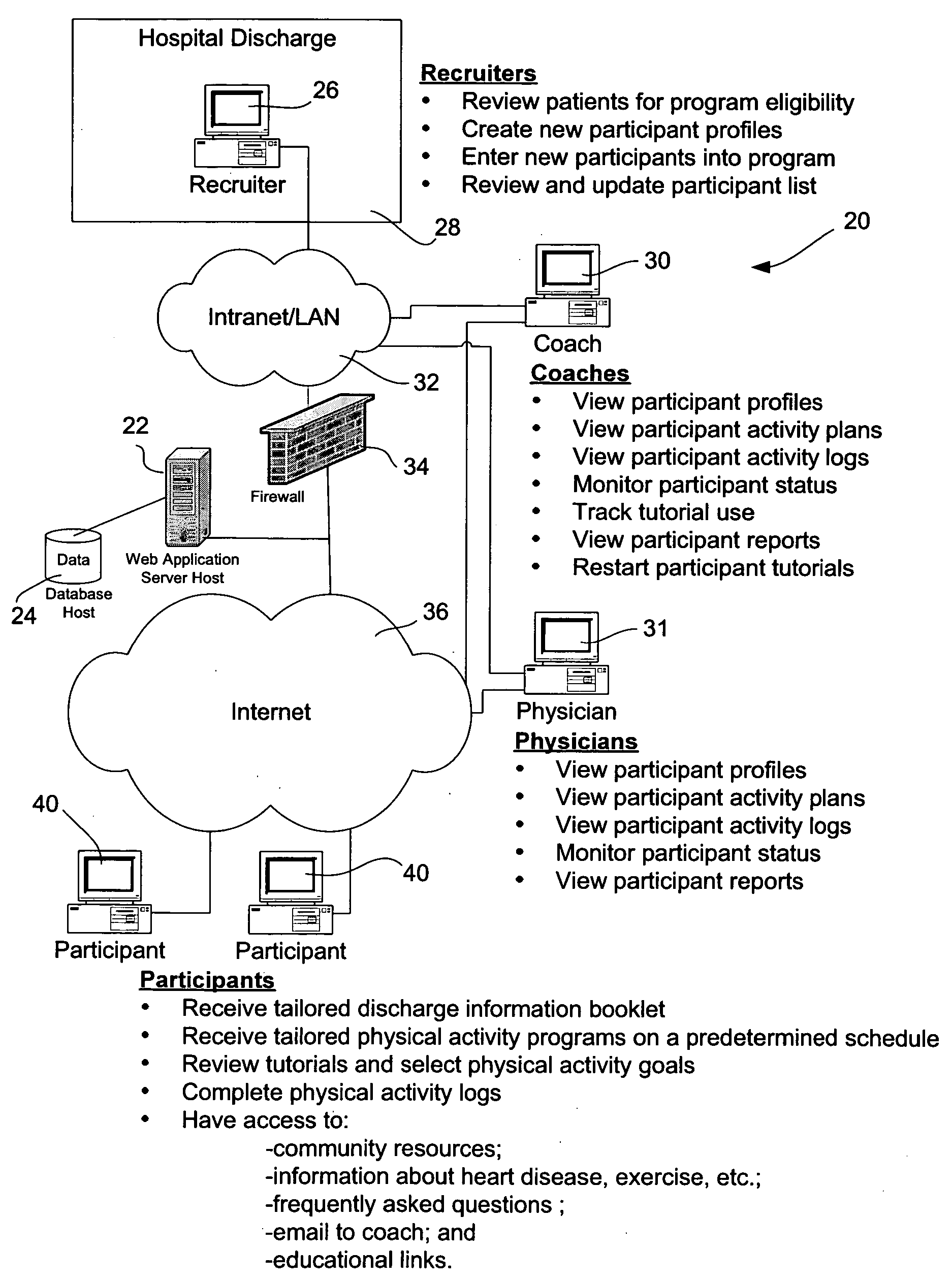
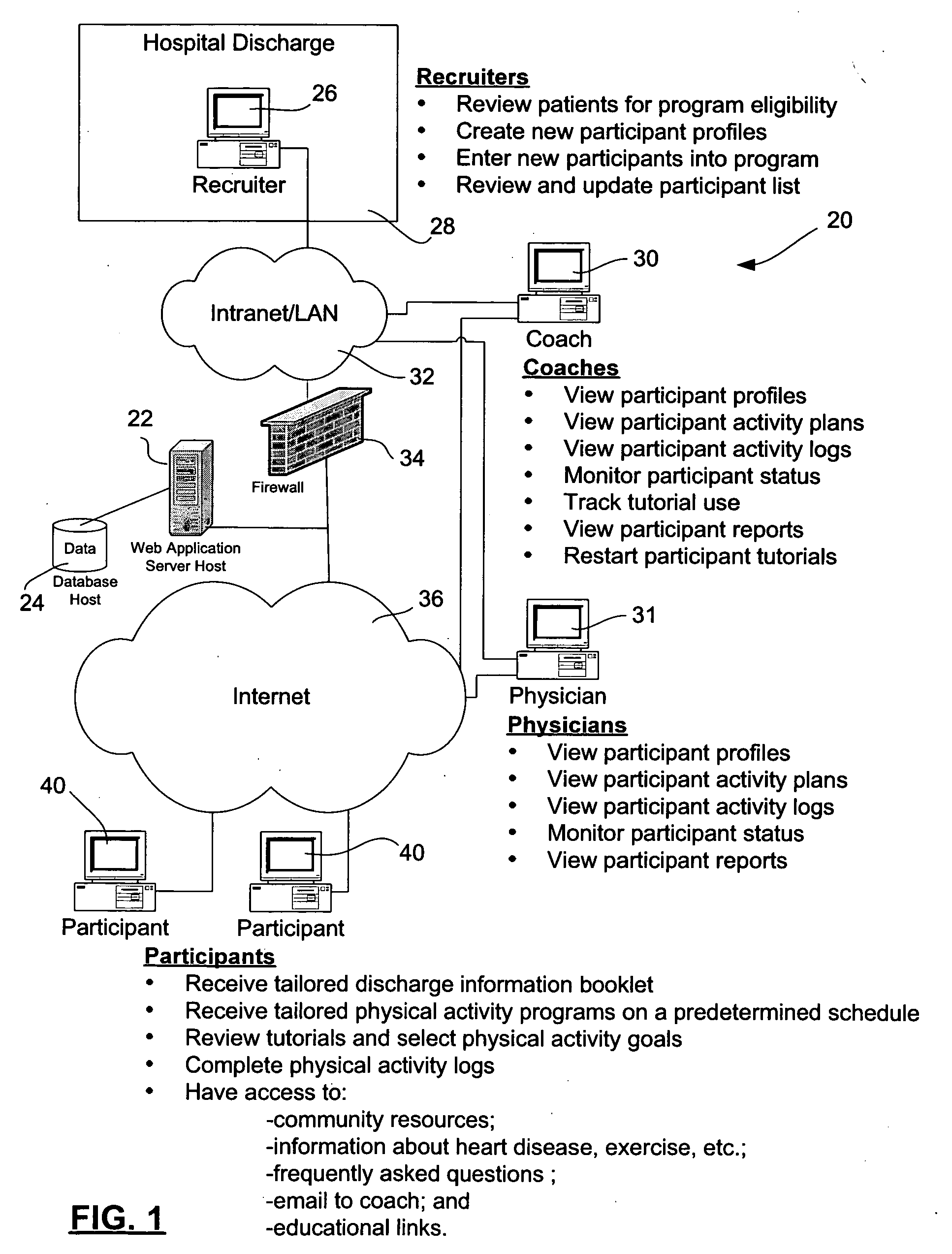
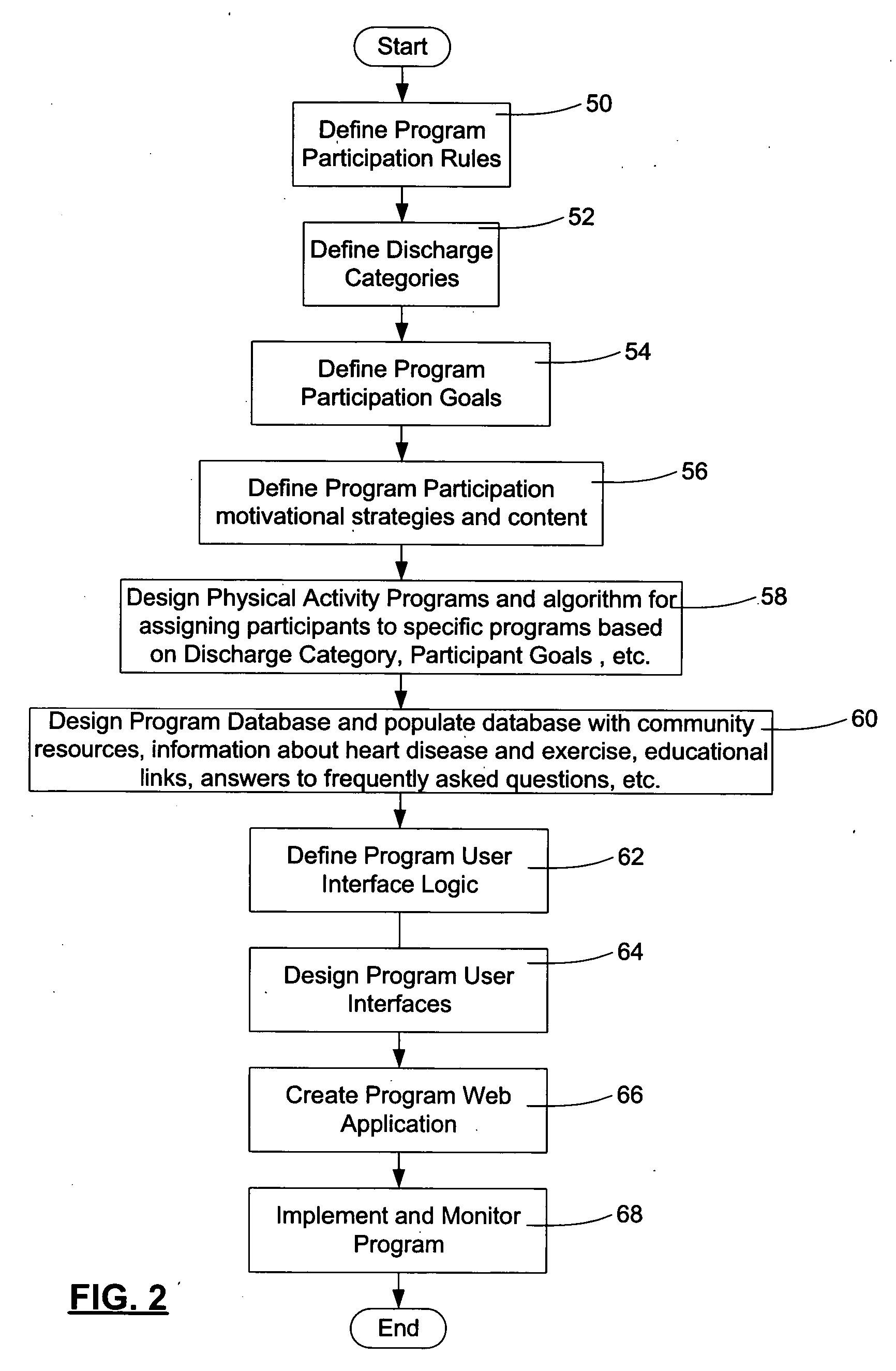
Expert system for prescribing and tracking physical activity programs for patients with coronary artery disease and method of creating same
InactiveUS20070179925A1Physical therapies and activitiesMedical automated diagnosisCoronary artery diseaseActivity scheduling
An expert system for assigning and tracking physical activity programs for patients with coronary artery disease provides user interfaces for recruiters who screen and enroll the patients as program participants in the physical activity programs; for coaches who monitor program participants and guide them through the physical activity program; and for program participants who create their own physical activity schedules,and log their physical activities. Expert system algorithms assign predefined physical activity programs to the program participants at predefined program milestones based on predefined criteria.
Owner:UNIV OF OTTAWA HEART INST
Method and system for creating and maintaining activity plans
InactiveUS20130055086A1ResourcesInput/output processes for data processingActivity schedulingMobile device
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for activity management. During operation, the system provides a user interface that allows a user to access previously authored activity plans on a mobile device. An activity plan includes one or more activity items, in which each activity item includes at least a title and description. The system then receives a user selection of an activity plan. Subsequently, the system obtains the activity plan from a database storing the previously authored activity plans and presents the activity plan to the user on the mobile device.
Owner:LABAGH JUSTIN R
Providing predictable scheduling of programs using repeating precomputed schedules on discretely scheduled and/or multiprocessor operating systems
InactiveUS20050005273A1Reduce processMaximize lengthProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationActivity schedulingOperational system
The present invention provides providing predictable scheduling of programs using repeating precomputed schedules on discretely scheduled and / or multiprocessor operating systems. In one embodiment, a scheduler accesses an activity scheduling graph. The activity scheduling graph is comprised of nodes each representing a recurring execution interval, and has one root, one or more leaves, and at least one path from the root to each leaf. Each node is on at least one path from the root to a leaf, and the number of times the execution interval represented by each node occurs during the traversal of the graph is equal to the number of paths from the root to a leaf that the node is on. Each node has associated with it an execution interval length, and is adapted to being dedicated to executing the threads of a single activity. There may be one scheduling graph for each processor, or a scheduling graph may traverse multiple processors. Start and end times for reservations and constraints are adjusted to compensate for the granularity of the clock of the system. Furthermore, the scheduler may use an existing priority-based scheduler in order to cause scheduling decisions it has made to be acted upon.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Patient check-in/scheduling kiosk
ActiveUS8165900B2Improve efficiencyData processing applicationsHealthcare resources and facilitiesTime scheduleActivity scheduling
A method and system for facilitating activity scheduling for a patient including the steps of providing an interface device for checking a patient in at the facility, receiving identifying information for the patient, identifying currently scheduled appointments for the patient where the currently scheduled appointments are associated with currently scheduled appointment activities, identifying at least one additional unscheduled activity for the patient in addition to the currently scheduled appointment activities, identifying at least one suggested appointment schedule including at least one open time slot during which the patient may complete the additional unscheduled activity and the currently scheduled appointment activities and presenting the at least one suggested appointment schedule to the patient.
Owner:EPIC SYST CORP (US)
A monitoring unit as well as method for predicting abnormal operation of time-triggered computer systems
InactiveUS20170102968A1Reduce the likelihood of failurePreventing harm to a patientProgram initiation/switchingHardware monitoringActivity schedulingTelecommunications link
The invention relates to a time-triggered computer system (800) that involves [i] a Main Processor (801) that has been designed to run one or more tasks according to one or more predetermined task schedules, only one of which, the “active task schedule”, will be active at any point in time; [ii] a Monitor Processor (802) that has been designed to determine whether the Main Processor (801) is about to execute a task that is not in accordance with the active task schedule; [iii] a Communication Link (803) for passing information about future task executions between the Main Processor (801) and the Monitor Processor (802); and [iv] a Control Mechanism (comprising a System Control output (805), and / or a Communication Link B (806), and / or a Reset Link (807)) by means of which the Monitor Processor can halt or reset the Main Processor and take other corrective actions involving devices to which the computer system is connected, if the Monitor Processor determines that the Main Processor is about to execute a task that is not in accordance with the active schedule.
Owner:SAFETTY SYST
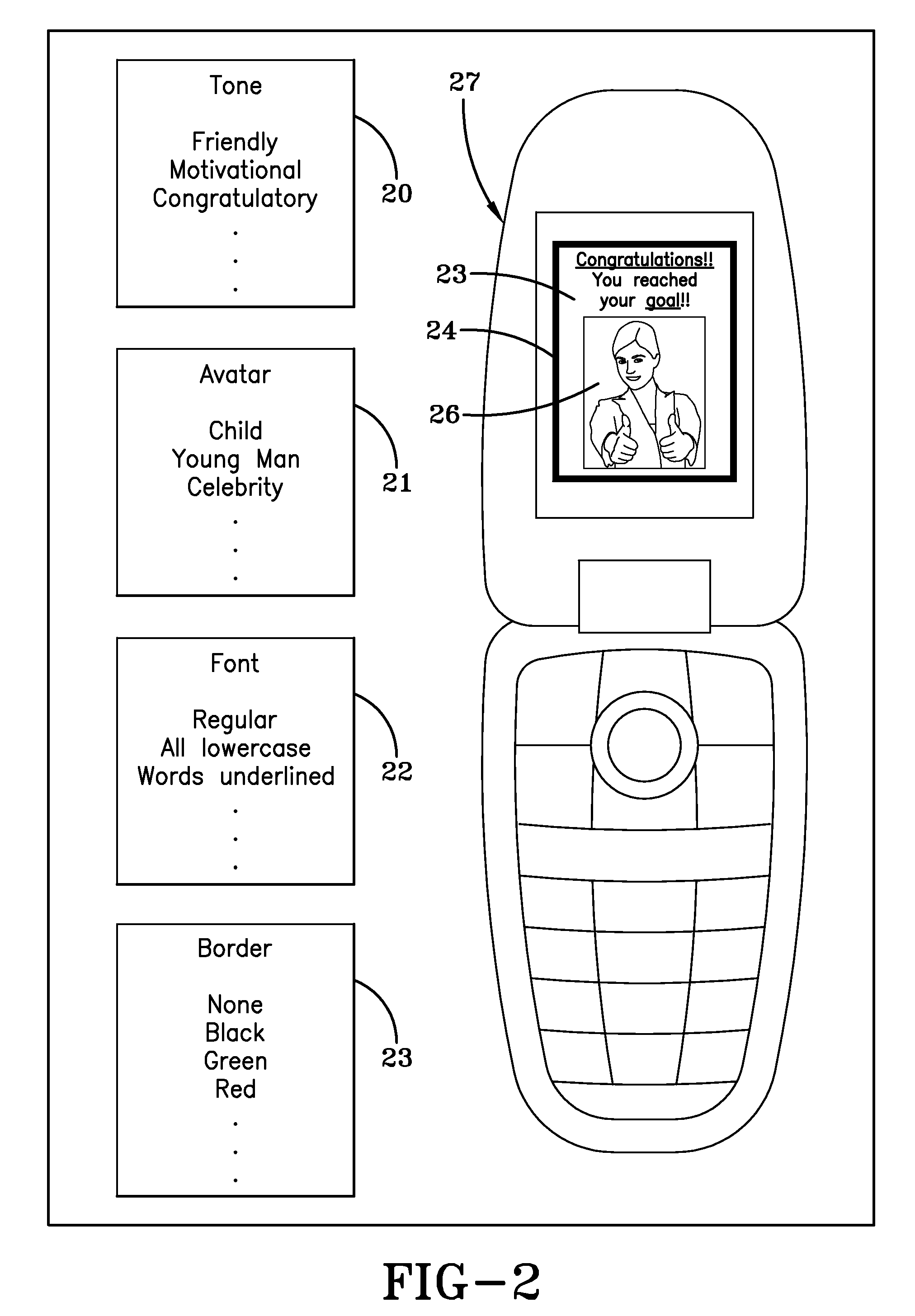
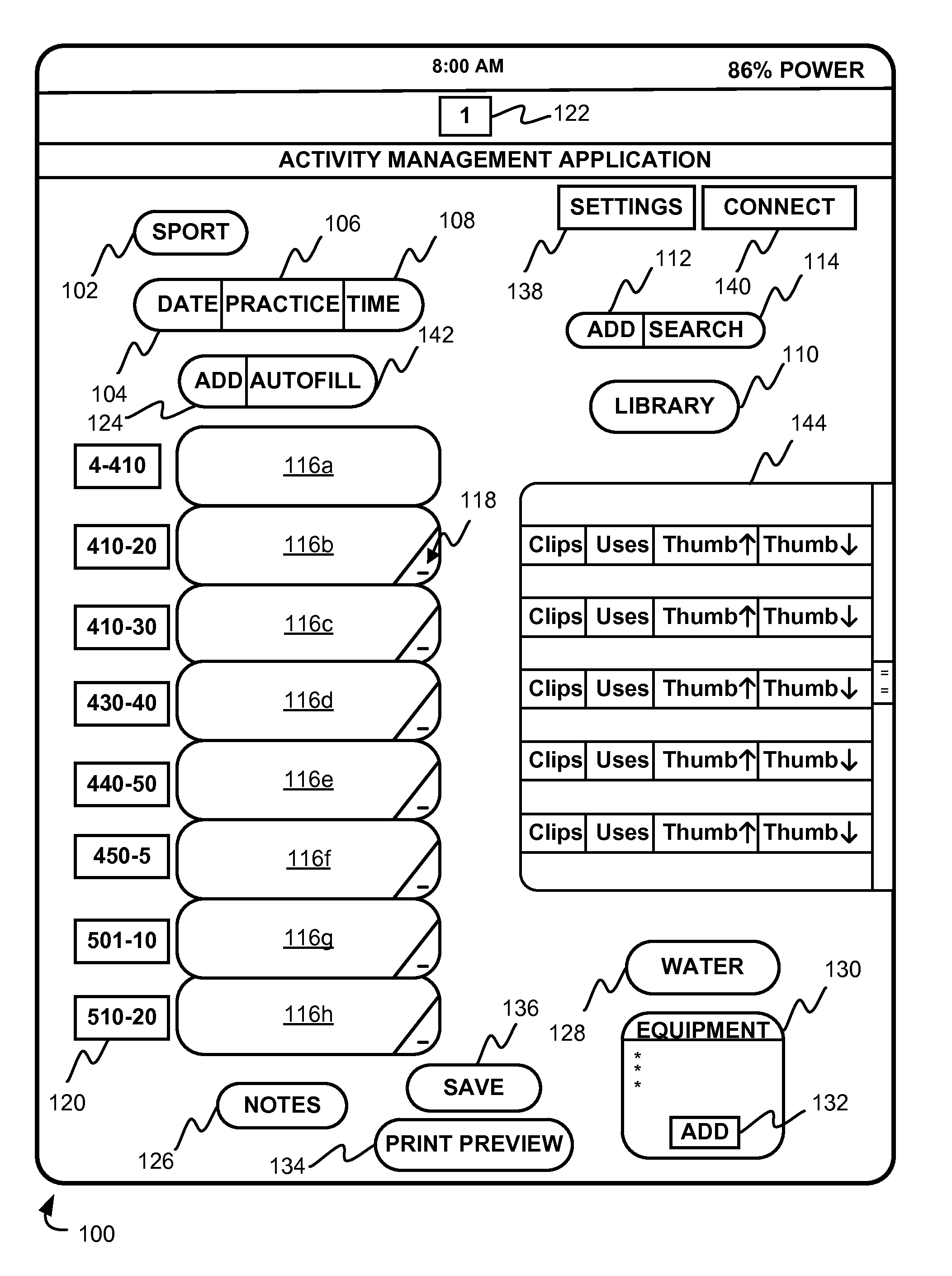
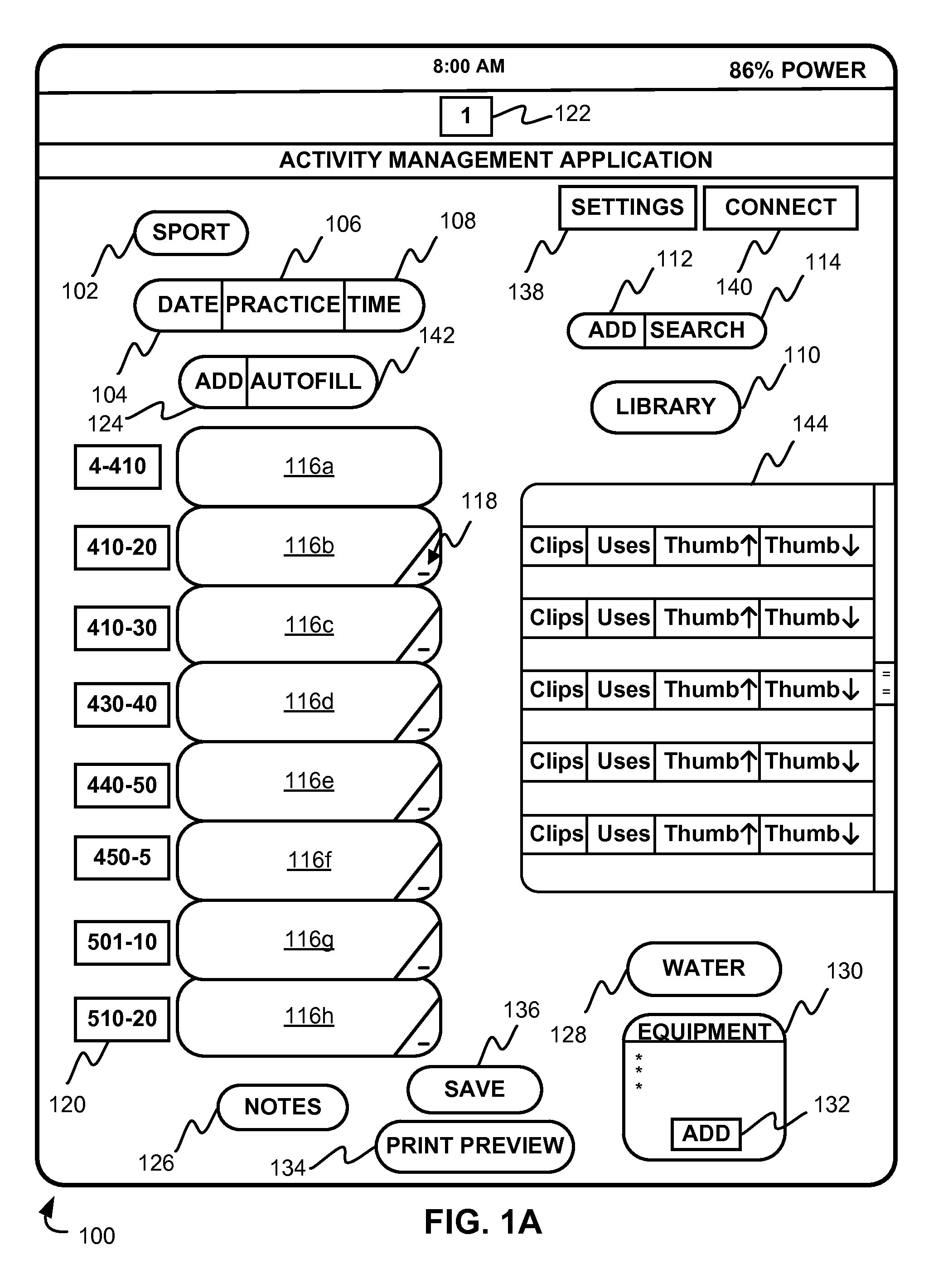
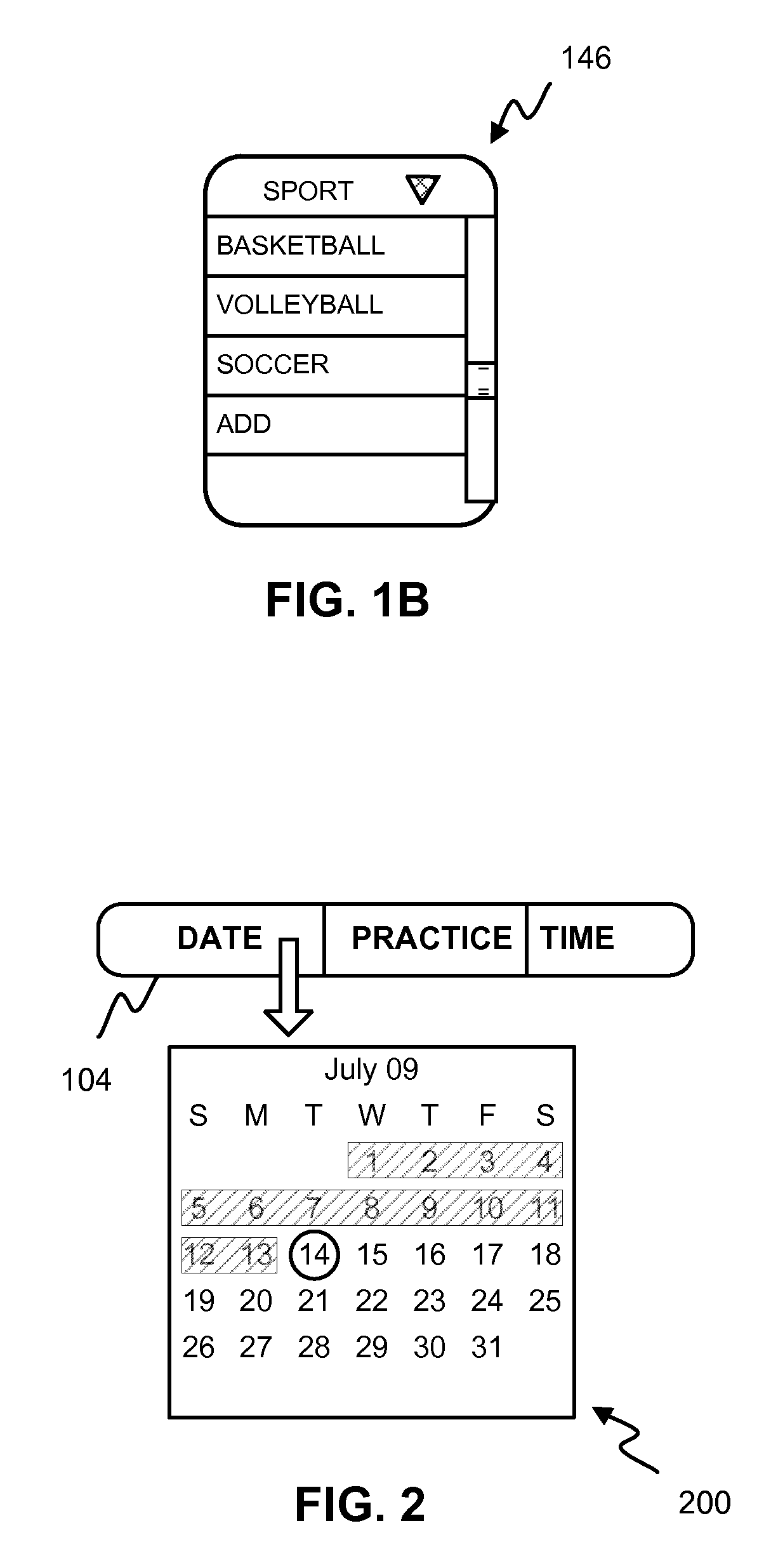
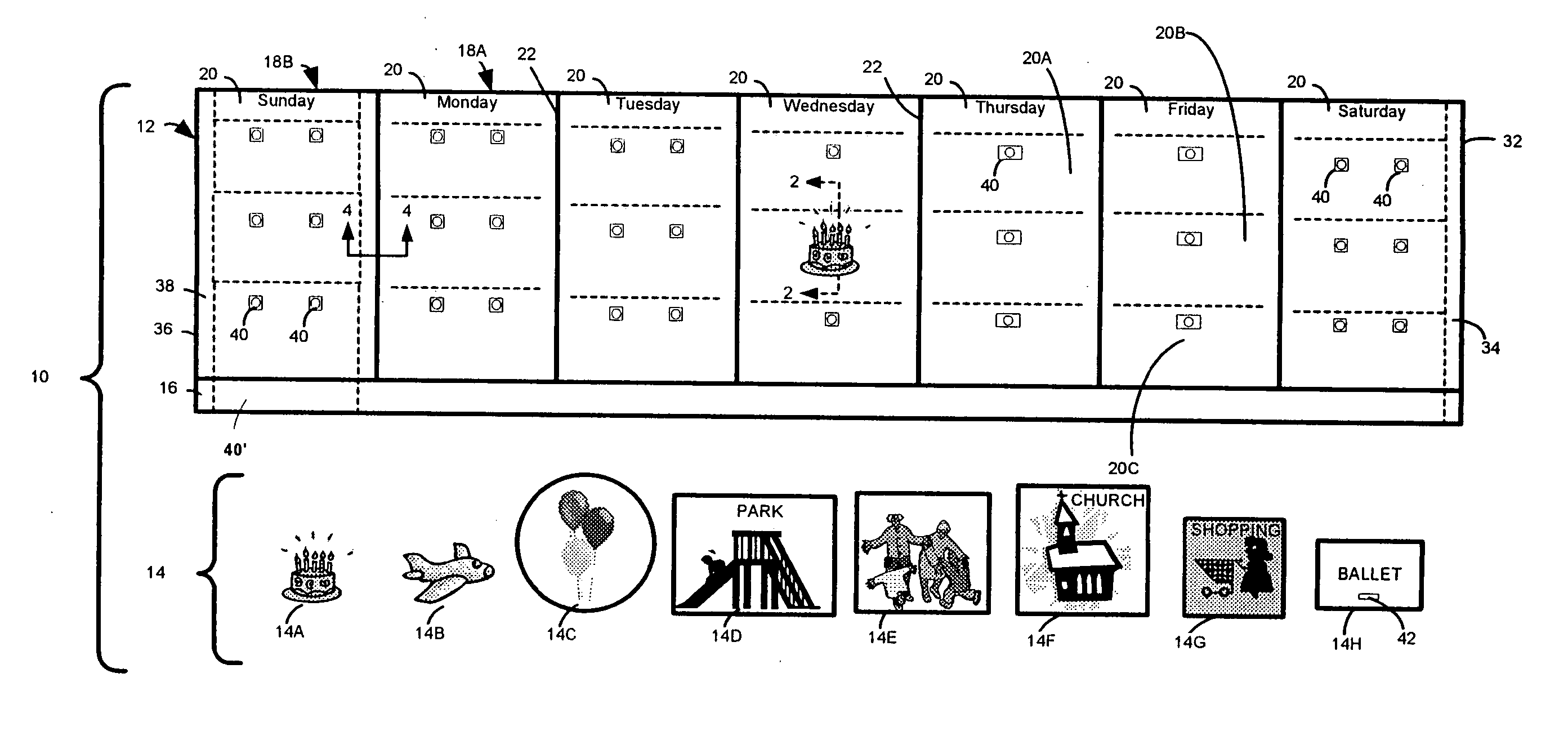
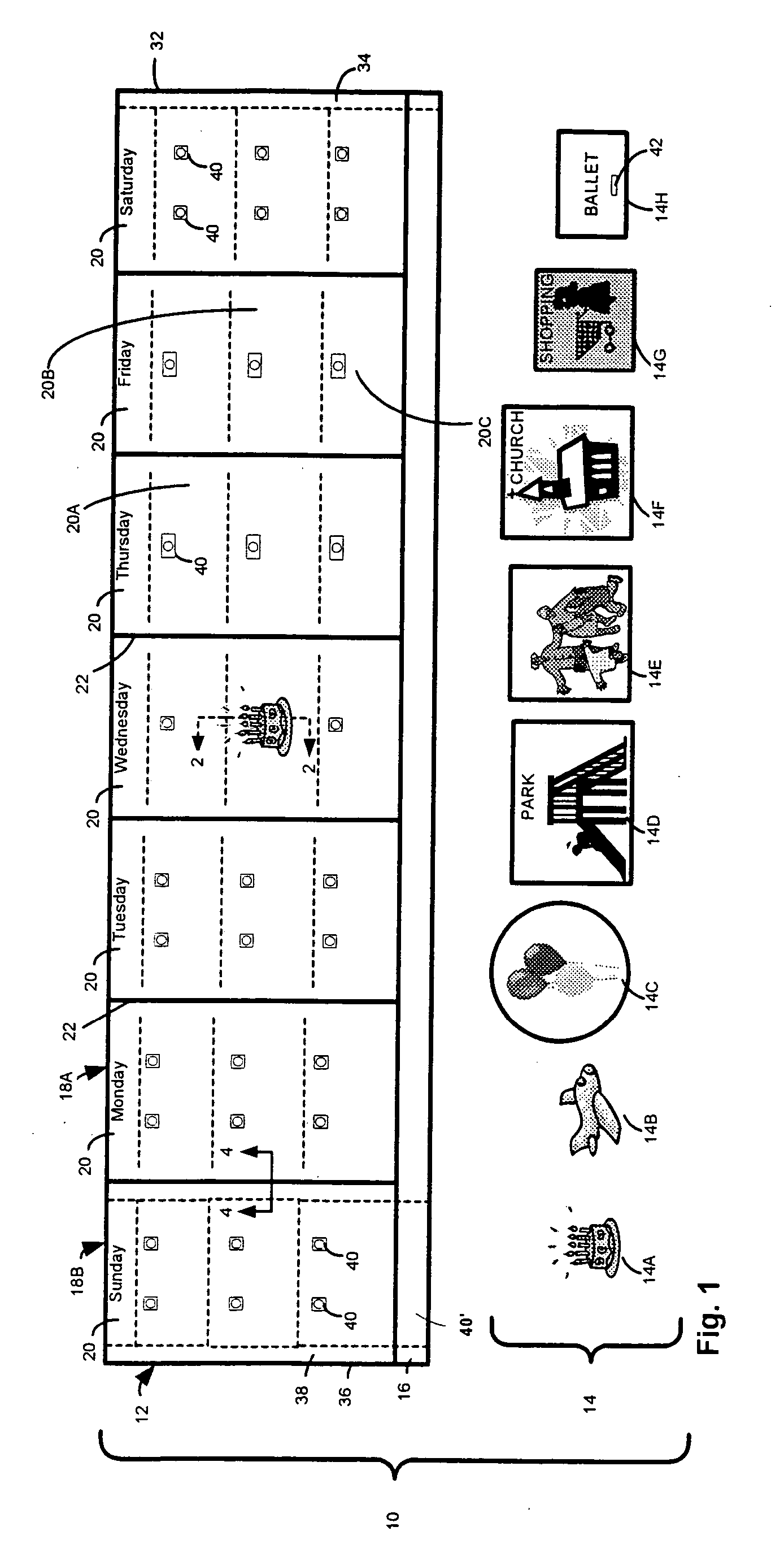
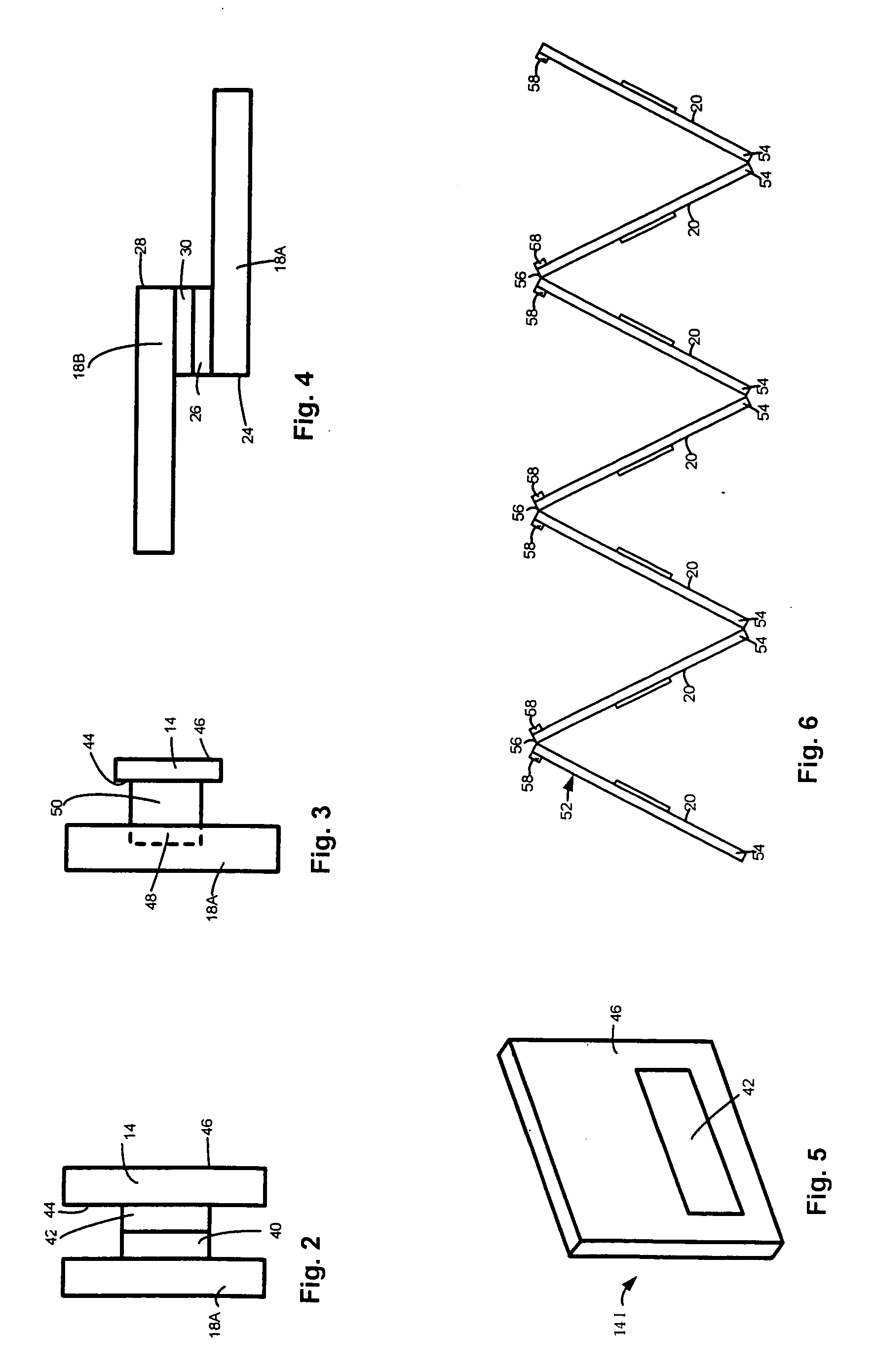
Activity scheduling device
Activity scheduling device including a display board having sections demarcated from one another. Each section represents a period of time such as a day and includes subsections, each representing a portion of the period of time, for example, hours of the day. Indicators are provided, each indicative of an activity, and an attachment mechanism is provided to attach the indicators to the display board. The activity may take the form of a picture and / or text on one or both surfaces of a substrate forming the indicator. In use, indicators indicative of a specific activity are placed on the appropriate day and at the appropriate time at which the activity is scheduled.
Owner:FEINSTEIN JANET
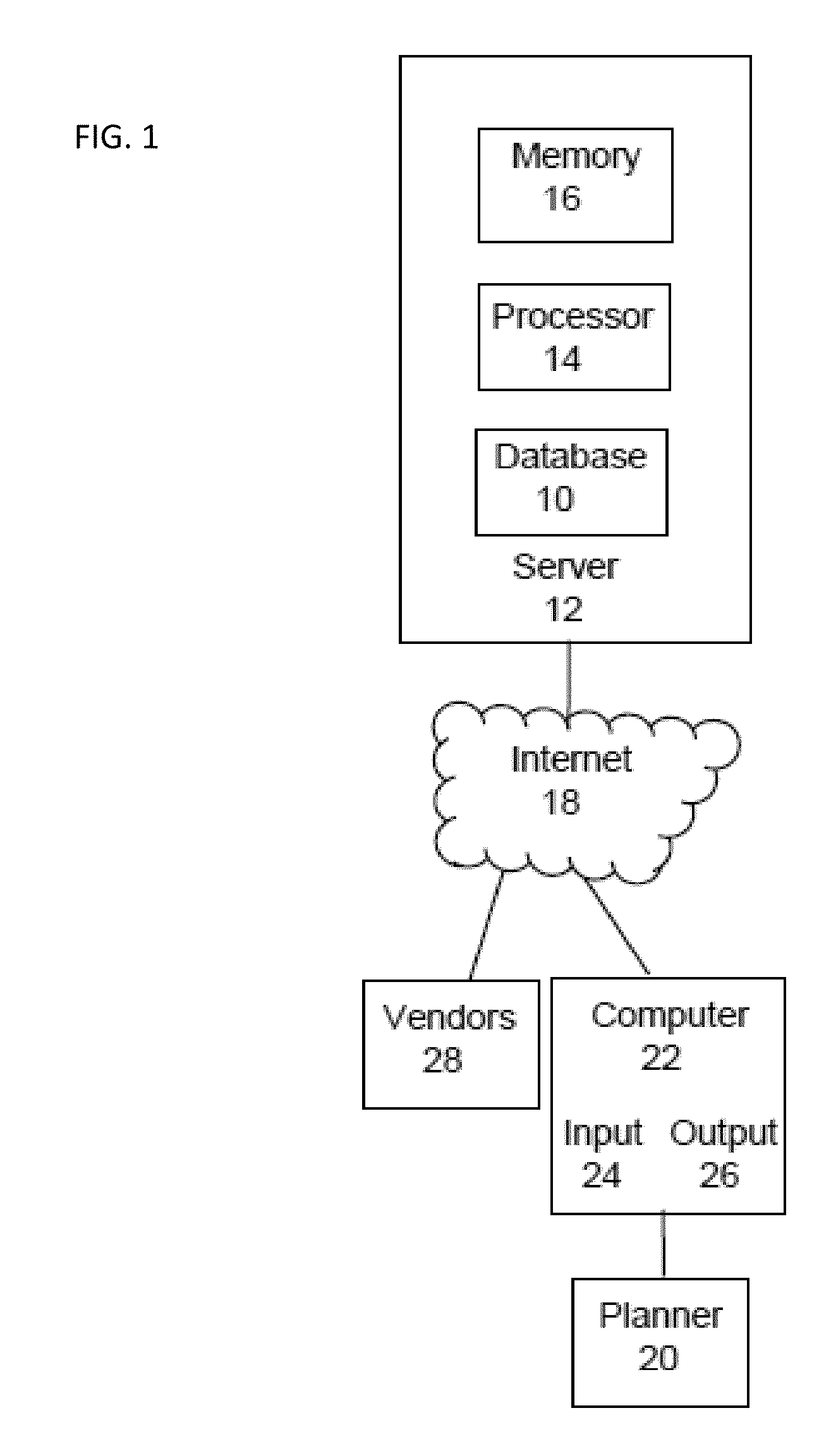
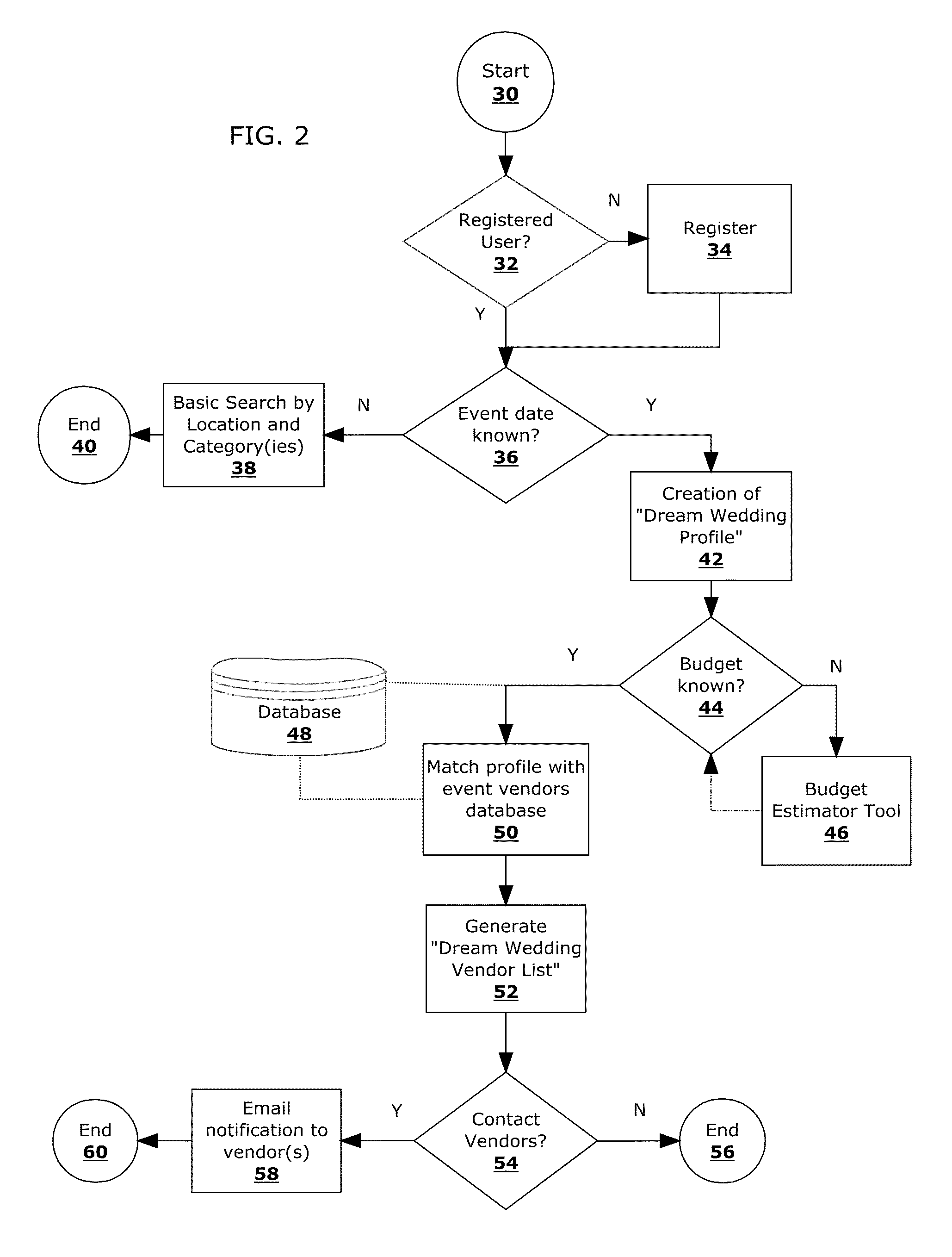
System and database for matching event vendors with event planners in real-time.
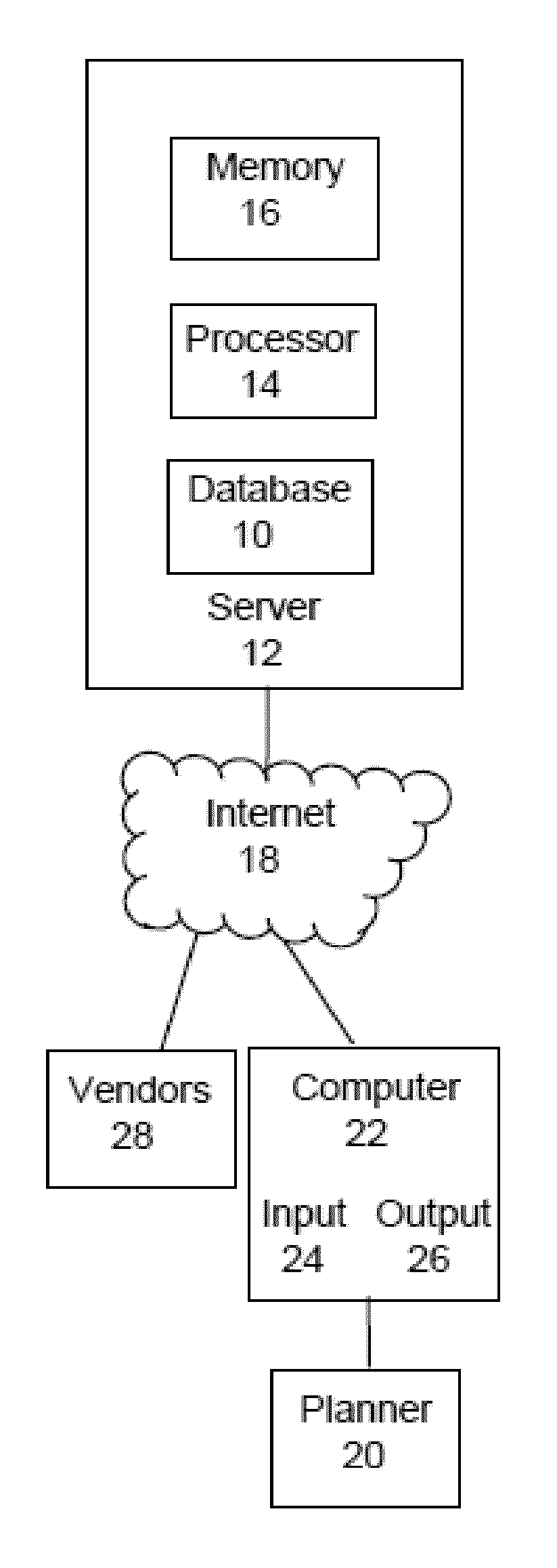
InactiveUS20130054293A1Shorten the timeOffice automationResourcesTime informationActivity scheduling
A process for matching event planners with vendors using real-time information. with the steps of: a server having a memory configured to store data and instructions, a database stored in the memory and accessed by vendors and event planners through a website and, a processor associated with the server and configured to execute instructions to: receive and store in the database profiles of a plurality of vendors, receive and store in the database criteria of planner, Method, in response to the profile of the planner, access the database and match the planner with at least one vendor having a profile that meets at least one criteria of the planner, receive an input from the planner indicating one or more vendors the event planner would like to obtain more information from, and in response to the planner accepting contact by the selected vendors, transmit an e-mail notification to the selected vendors.
Owner:SEN NAYANA +1
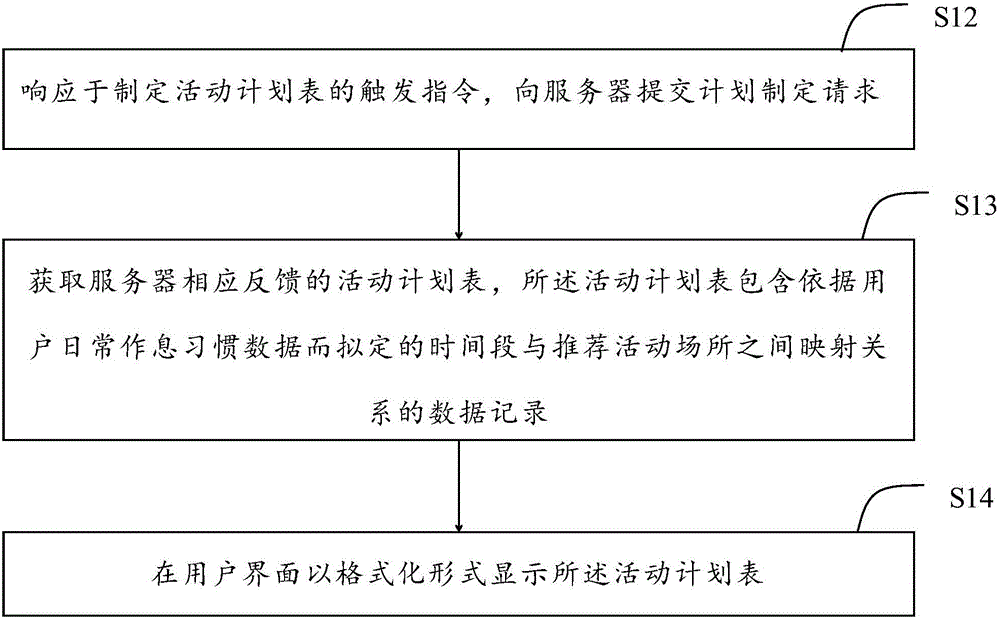
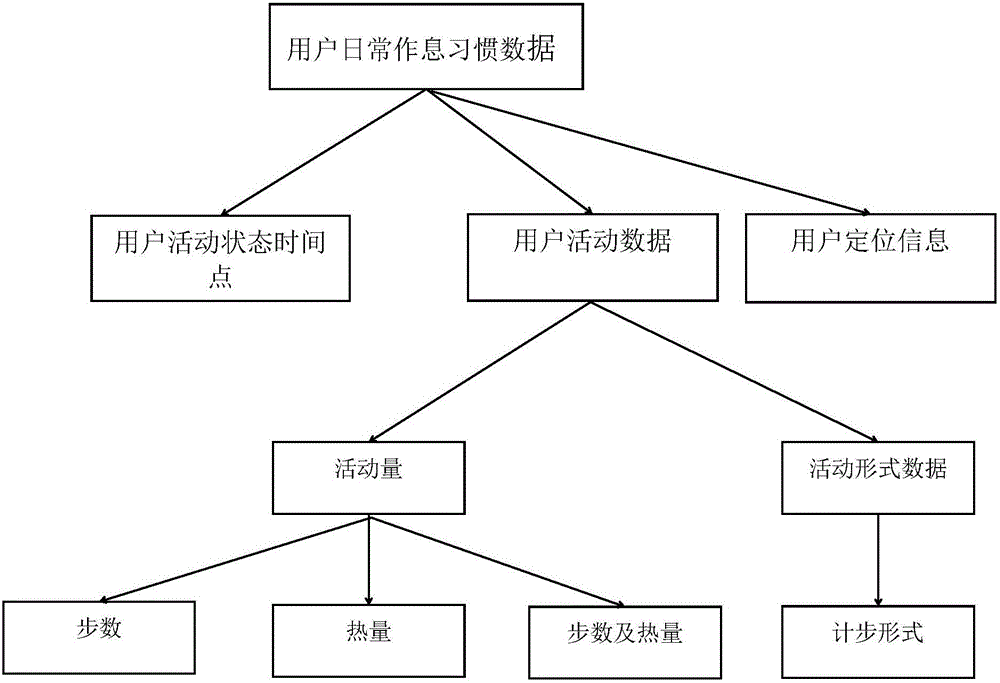
Activity plan obtaining and making method
InactiveCN106022724APlay the role of organic integrationIncrease exerciseOffice automationMental stateActivity scheduling
The invention provides an activity plan obtaining and making method. The method comprises the following steps of submitting a plan making request to a server in response to a triggering instruction of making an activity plan table; obtaining the activity plan table correspondingly fed back by the server, wherein the activity plan table contains a data record of a mapping relationship between a time period set according to daily work and rest habit data of a user and a recommended activity place; and displaying the activity plan table in a formalized form on a user interface. According to the method, the user can be assisted to make a trip at any time, the opportunity of the user in outdoor activities and body exercise is added, a positive mental state is given to the user, and the life is healthier.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD +1
Calendar generator and calendar generating method
InactiveUS20050257176A1Easy to modifySure easySpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingActivity schedulingTime lag
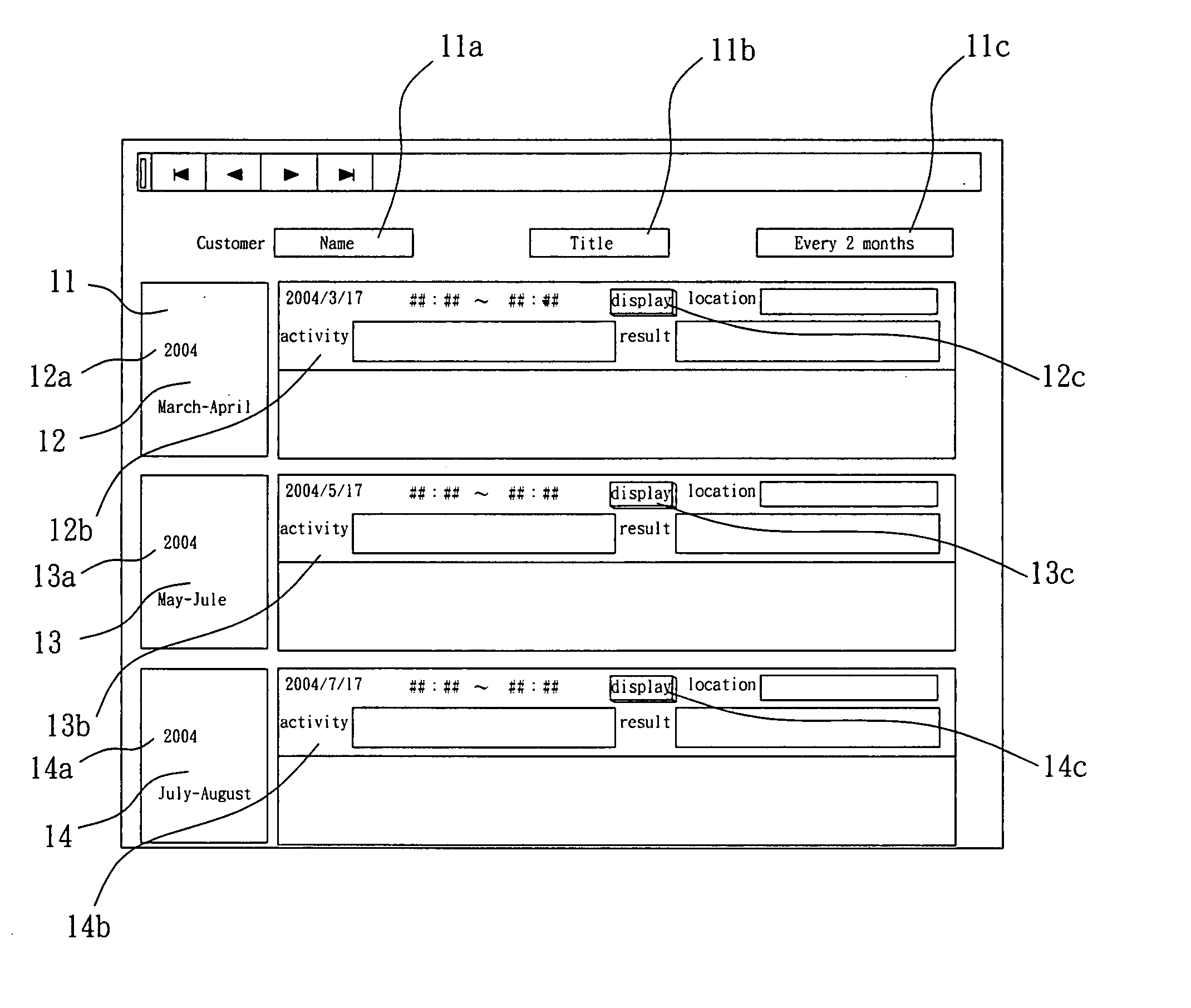
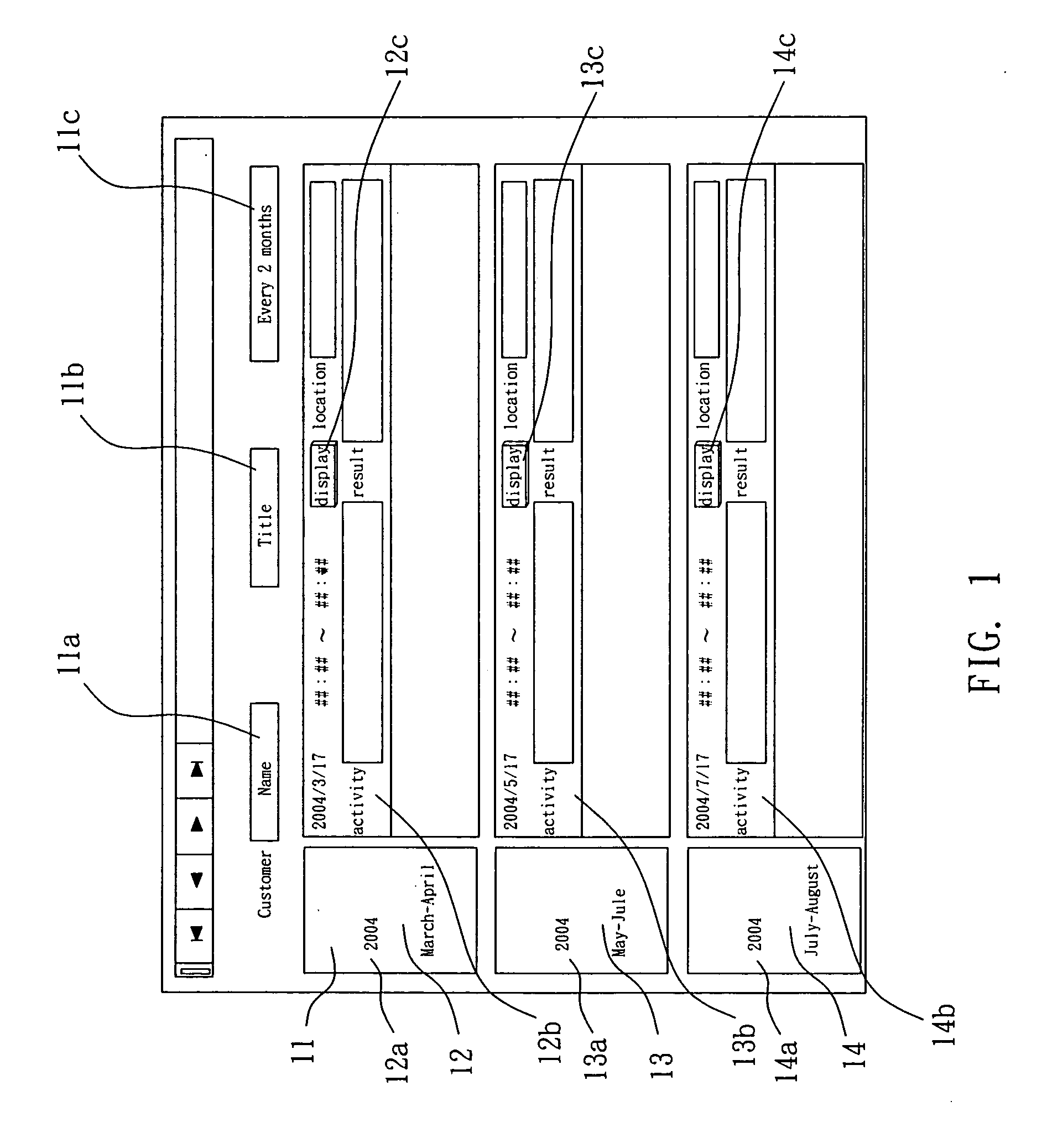
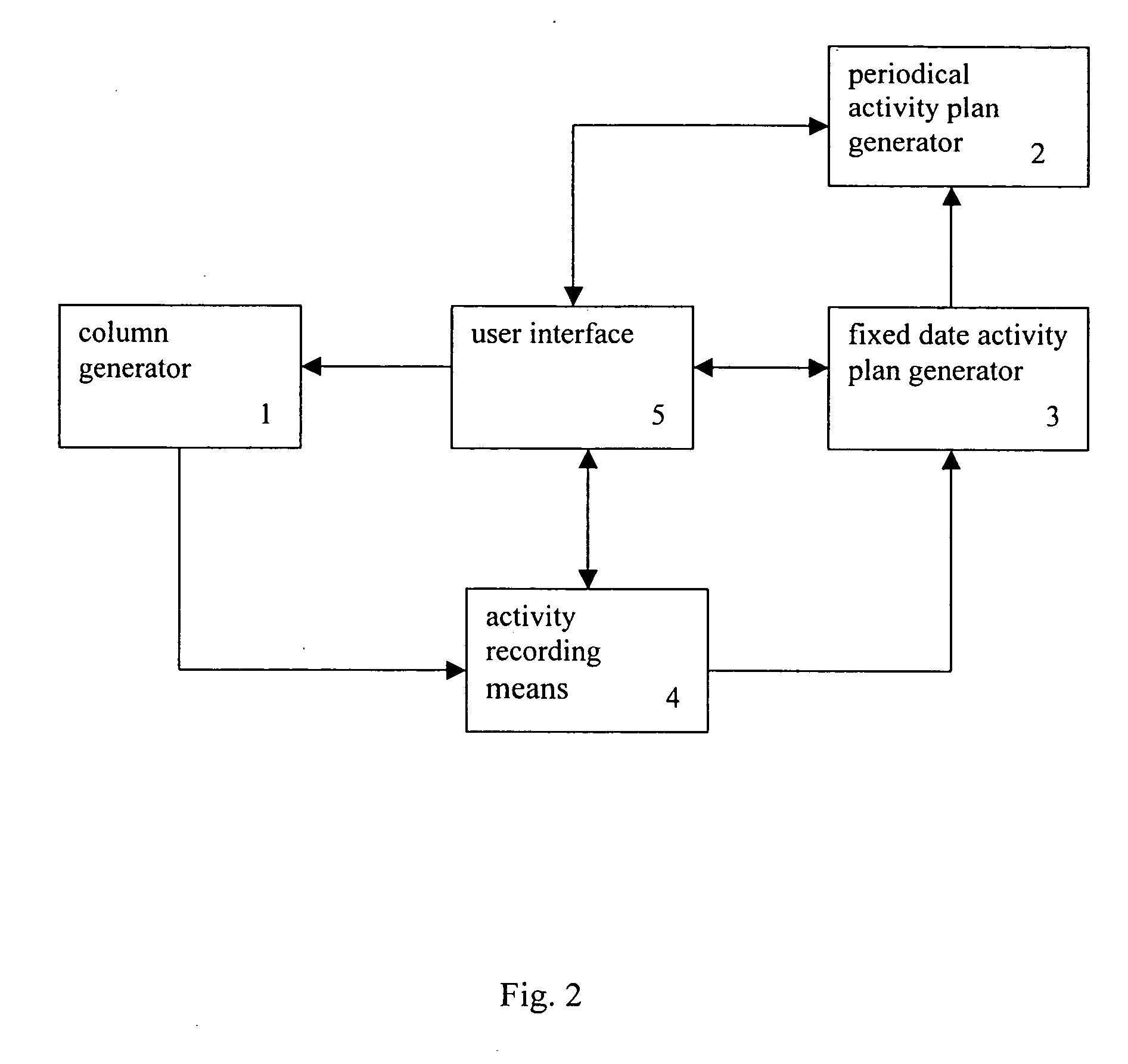
The presentation relates to a calendar generator, comprising: a column generator to generate description of columns, which columns comprise blank space units representing fixed term and are labeled with time lags as represented, wherein width of columns corresponds to length of term as represented; a periodical activity plan generator to record starting date and period for at least one periodical activity plan in order to generate description of a plurality of date and corresponding activity; a fixed date activity plan generator to record at least one date and content of activity for at least one activity plan; said fixed date activity plan generator being able to grab date and activity information of said periodical activity plan generated by said periodical activity plan generator; an activity recording means to generate records of activity, including description and dates of past activities, according to inputs of user; and a user interface to display columns and contents of said columns according to description generated by said column generator, said periodical activity plan generator, said fixed date activity generator and said activity recording means and to allow user to add, revise and / or delete a periodical activity plan, a fixed date activity plan or an activity record.
Owner:LU LI CHIN
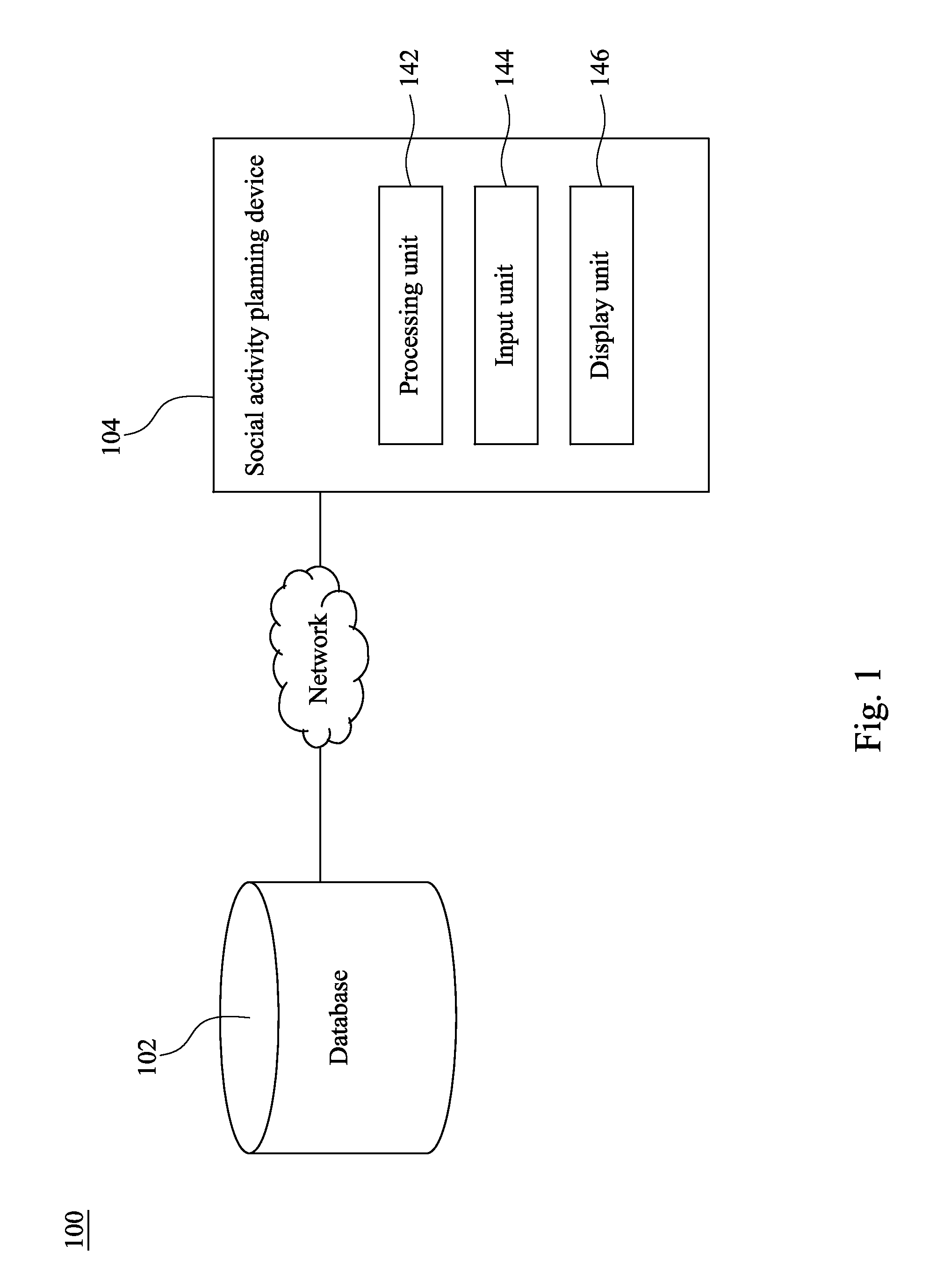
Social activity planning system and method
ActiveUS20150046473A1Simplify the tedious processImproving quality and atmosphereData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalActivity schedulingSocial graph
A social activity planning method includes the following operation. A database storing multiple candidate invitees with their geographical locations and interest scores towards a topic, and a social graph including vertices representing the candidate invitees and edges connecting two vertices representing mutual acquaintance of the associated candidate invitees is accessed. A social activity request including an invitation number, information about a social activity, and a familiarity condition for the social activity request is received. At least one feasible solution including the invitation number of the candidate invitees and meeting the familiarity condition is generated. A group of selected invitees are found based on the feasible solution and the information about the social activity.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
System for circadian rhythm monitor with synchrony and activity planning
A personal health system which includes a suitable Core Body Temperature (CBT) monitor that can be worn for all or part of a 24 hour day and collect continuous CBT data. The CBT data is collected and compared to determine circadian desynchrony. A conveniently carried or worn processor / display unit, in communication with the CBT monitor, algorithmically determines activity types and activity timing based on the collected CBT data to improve synchrony. The activities and when to perform them are displayed to the user.
Owner:GURLEY VIRGINIA F
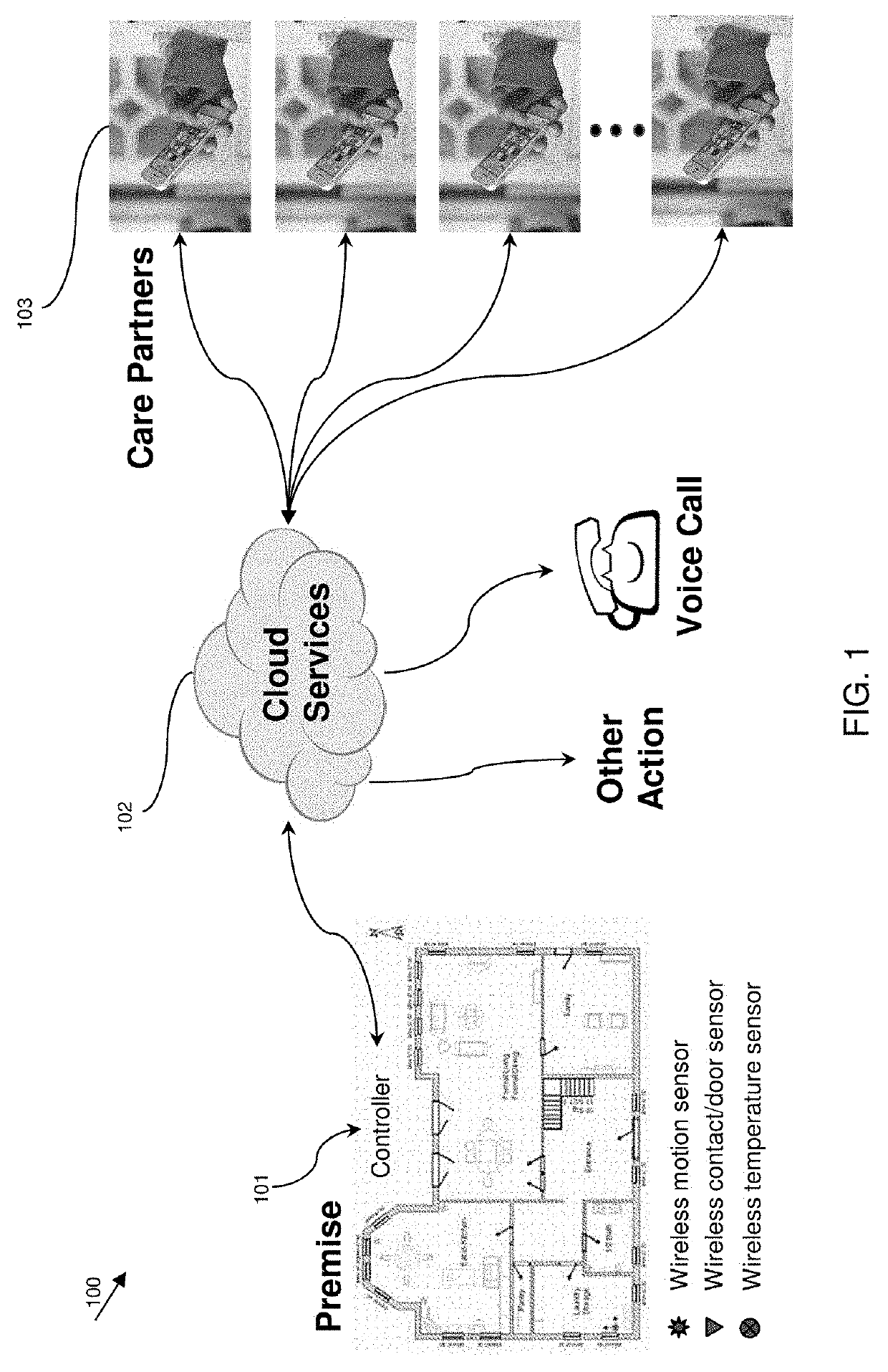
Easily customizable inhabitant behavioral routines in a location monitoring and action system
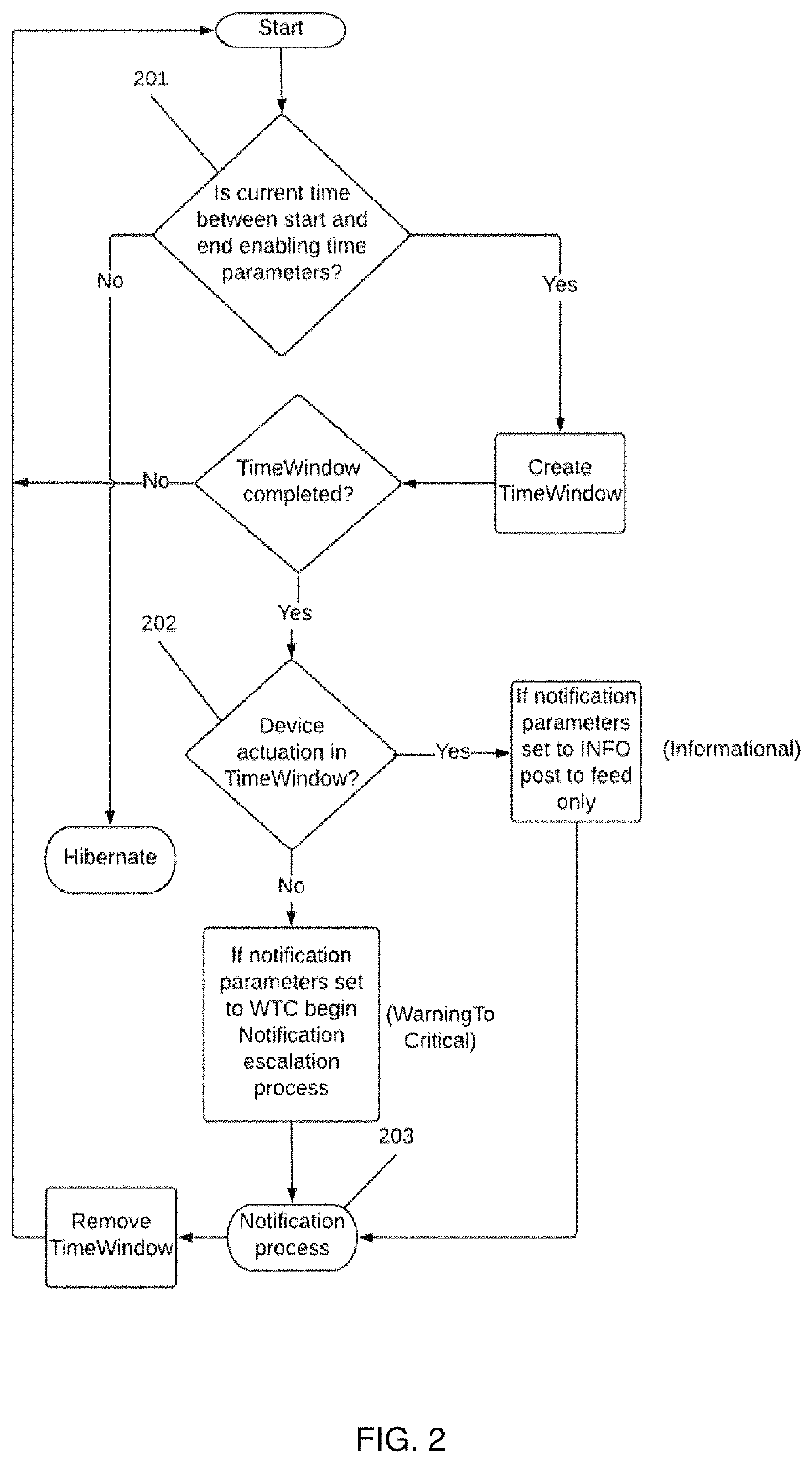
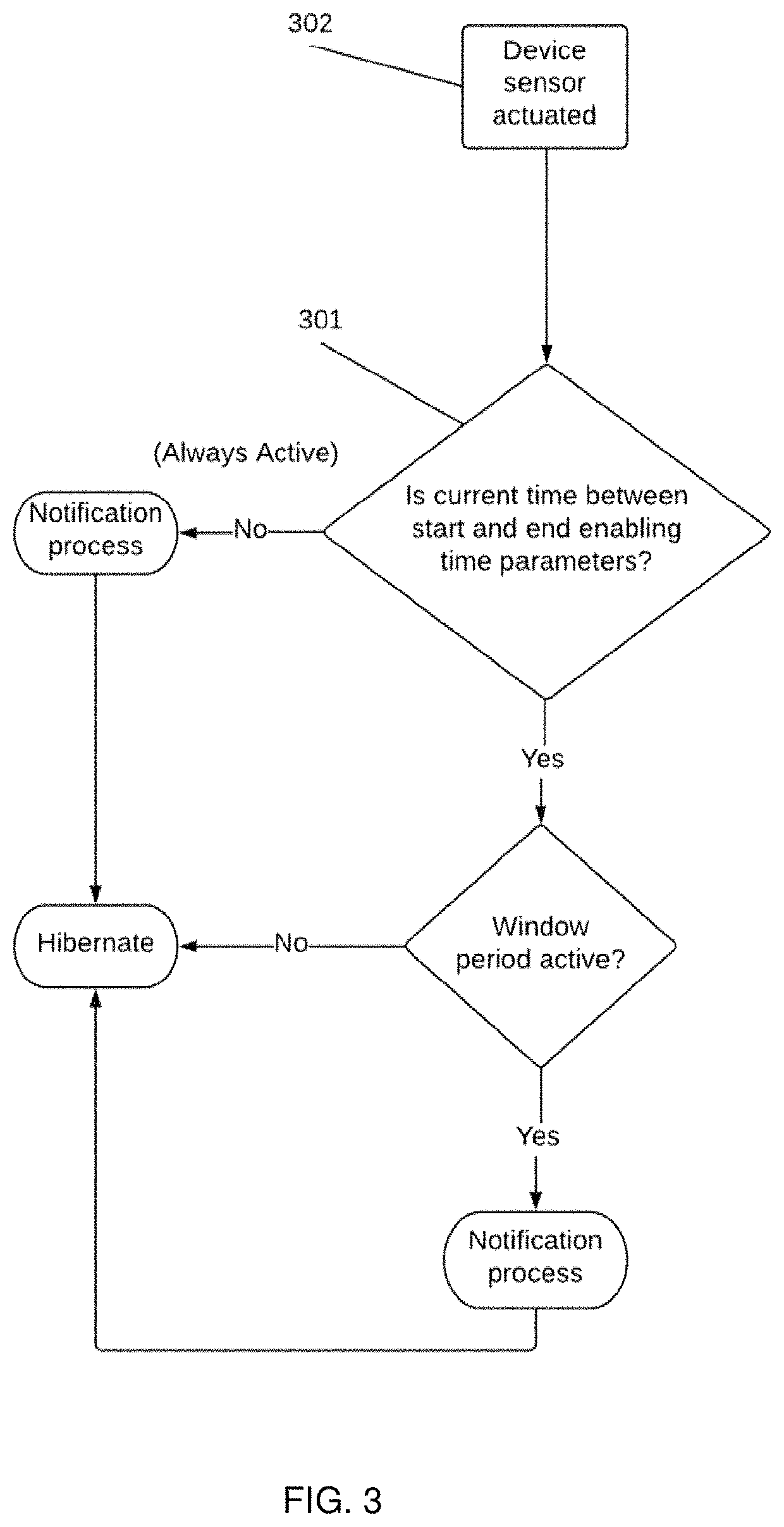
A virtual care system. The system identifies movement and status (e.g., location, time duration in a location, direction of movement, last activity) of an inhabitant of a premises, and takes actions based on the identified movement and status. The system includes an activity plan comprising a plurality of activity primitives. Each activity primitive comprises a time window, and classifies movements and / or activities of the inhabitant as, for example, expected or unexpected or abnormal patterns of behavior, based on occurrence and / or absence of output from a single sensor or paired sensors at the premises in the time window. The system is configured to notify caregivers with different levels of urgency (e.g., informational or warning to critical) based on the classifications of the detected movements and / or activities, and / or to take other actions such as turning off the lights and locking the door.
Owner:BLATT ROBERT +1
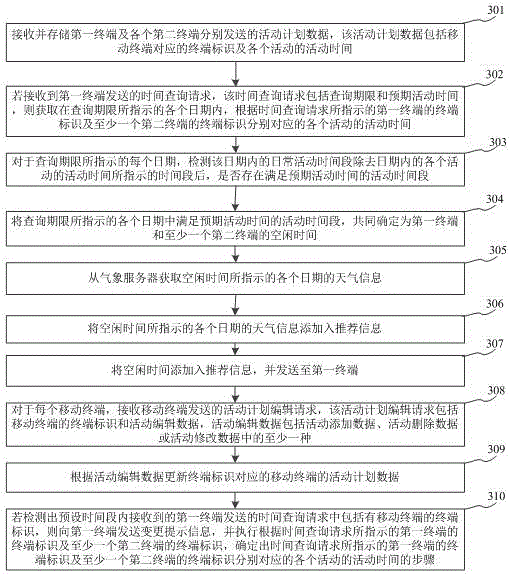
Activity time recommendation method based on activity plan of user
InactiveCN105931018ASolve the problem of low efficiency of activity time determinationOffice automationActivity schedulingActive time
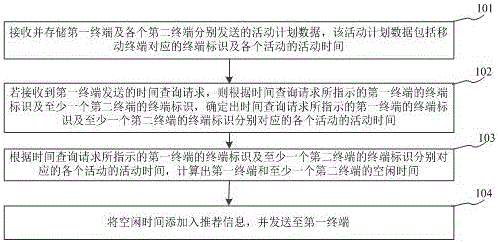
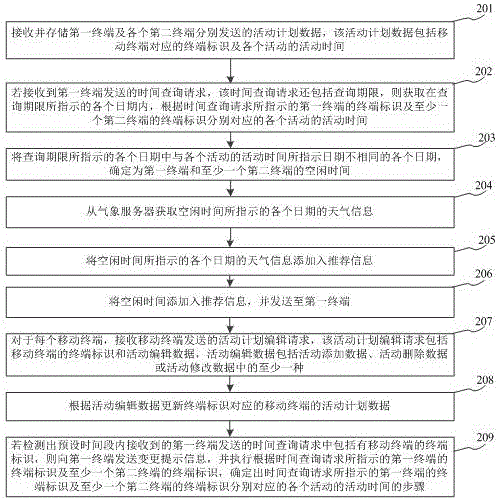
The invention relates to an activity time recommendation method based on an activity plan of a user, and belongs to the technical field of computers. The method comprises the steps: receiving and storing activity plan data transmitted by a first terminal and each second terminal; determining the time of all activities corresponding to the identifications, indicated by the time query request, of the first and second terminals according to the identifications, indicated by the time query request, of the first and second terminals if the time query request transmitted by the first terminal is received; Calculating the spare time of the first terminal and each second terminal according to the time of all activities corresponding to the identifications, indicated by the time query request, of the first and second terminals; adding the spare time to recommendation information, and transmitting the recommendation information to the first terminal. The method can solve a problem the determining efficiency of the time of a group activity is lower, and improves the determining efficiency of the time of the group activity.
Owner:张伟彬
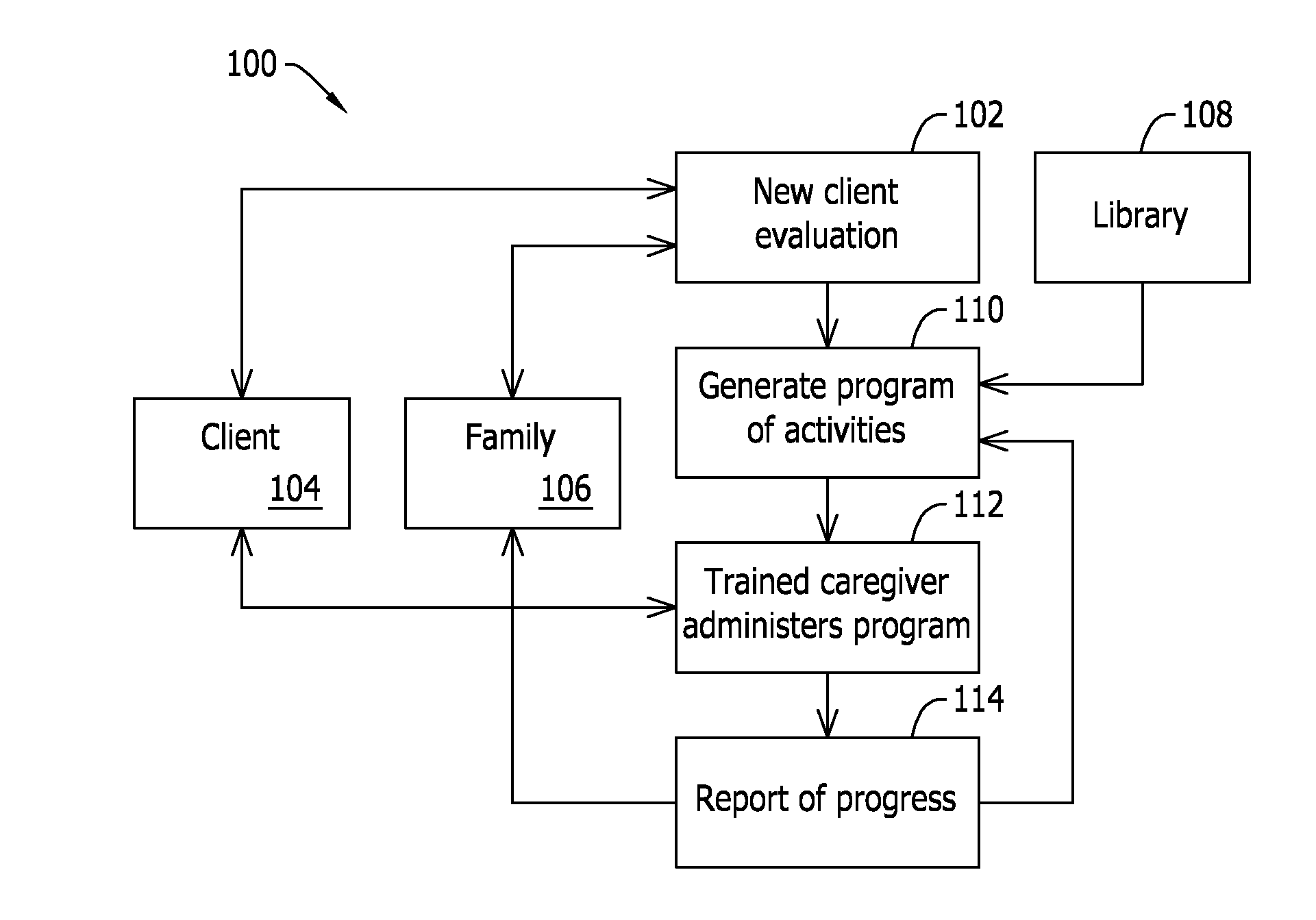
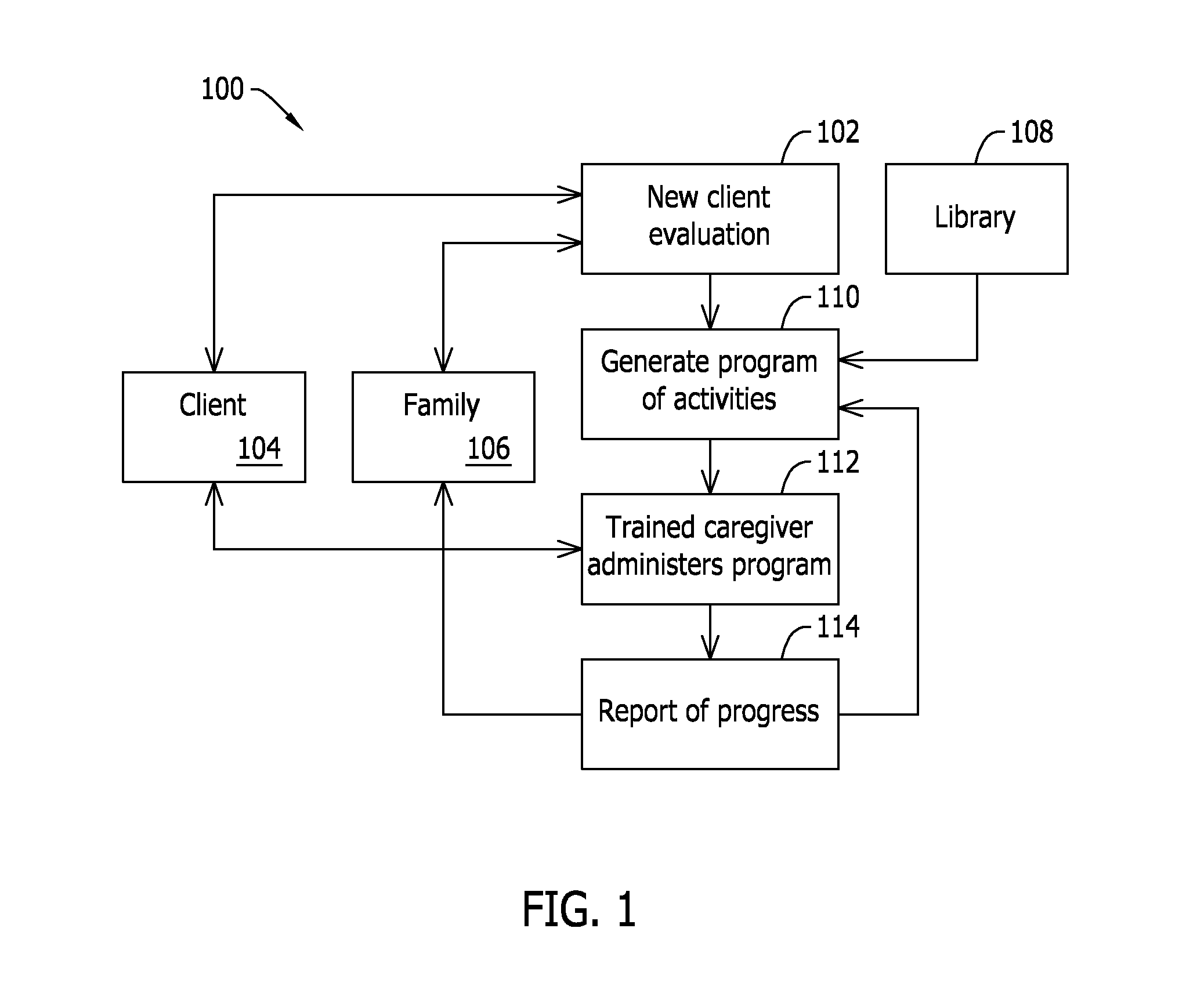
Method and system for a cognitive training program
A method for managing intervention activities for chronic progressive neurodegenerative conditions that enhance neurophysiological processes of a client includes receiving a client for evaluation and determining a first level of functioning in each of a plurality of cognitive and non-cognitive areas. The method also includes iteratively, determining a program of intervention activities associated with the cognitive and non-cognitive areas based on at least one of the first level of functioning and a generated report of a performance of the intervention activities, the program of intervention activities including one or more intervention activities selected from a plurality of intervention activities, administering the program of intervention activities to the client, and generating a report of a performance of the administered program of intervention activities. The method further includes reporting a progress of the client over time with respect to the performance of the administered program of intervention activities.
Owner:HOME CARE ASSISTANCE +1
Ticket booking prompt method based on activity plan of user
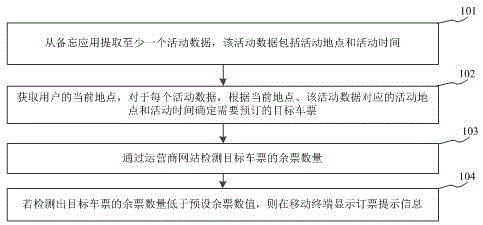
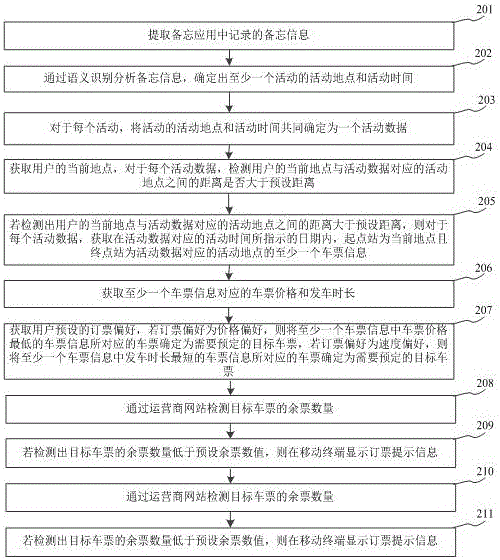
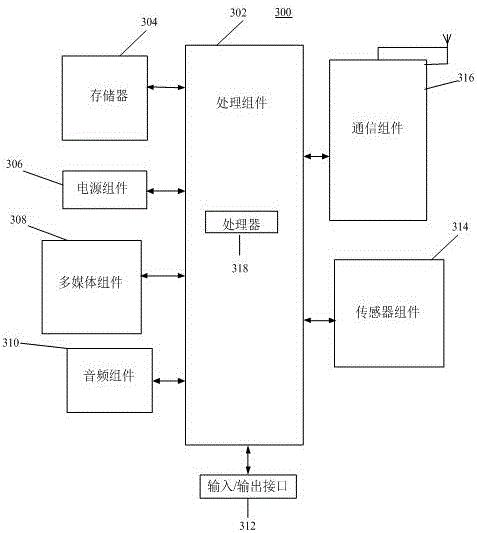
InactiveCN105931019ASolve the problem of low booking success rateIncreased booking success rateReservationsOffice automationActive timeActivity scheduling
The invention relates to a ticket booking prompt method based on an activity plan of a user, and belongs to the technical field of computers. The method comprises the steps: extracting at least one piece of activity data from a memo application, wherein the activity data comprises the activity place and activity time; obtaining a current position of the user, and determining target tickets to be booked for each piece of activity data according to the current position and the activity place and time corresponding to the activity data; determining the number of the remaining target tickets through an operator website; displaying the ticket booking prompt information at a mobile terminal if the detected number of the remaining target tickets is less than a preset number of remaining tickets. The method determines the target tickets to be booked according to the activity data of the user in the memo application, reminds the user in a mode of ticket booking prompt information when the remaining target tickets is not sufficient, can solve a problem that the ticket booking efficiency of the user is low, and improves the ticket booking success rate of the user.
Owner:张伟彬
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com