Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130 results about "Ablative surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ablative surgery. A generic term for an operative procedure in which tissue is ablated (destroyed) by diathermy, cryotherapy, abrasion or other means.
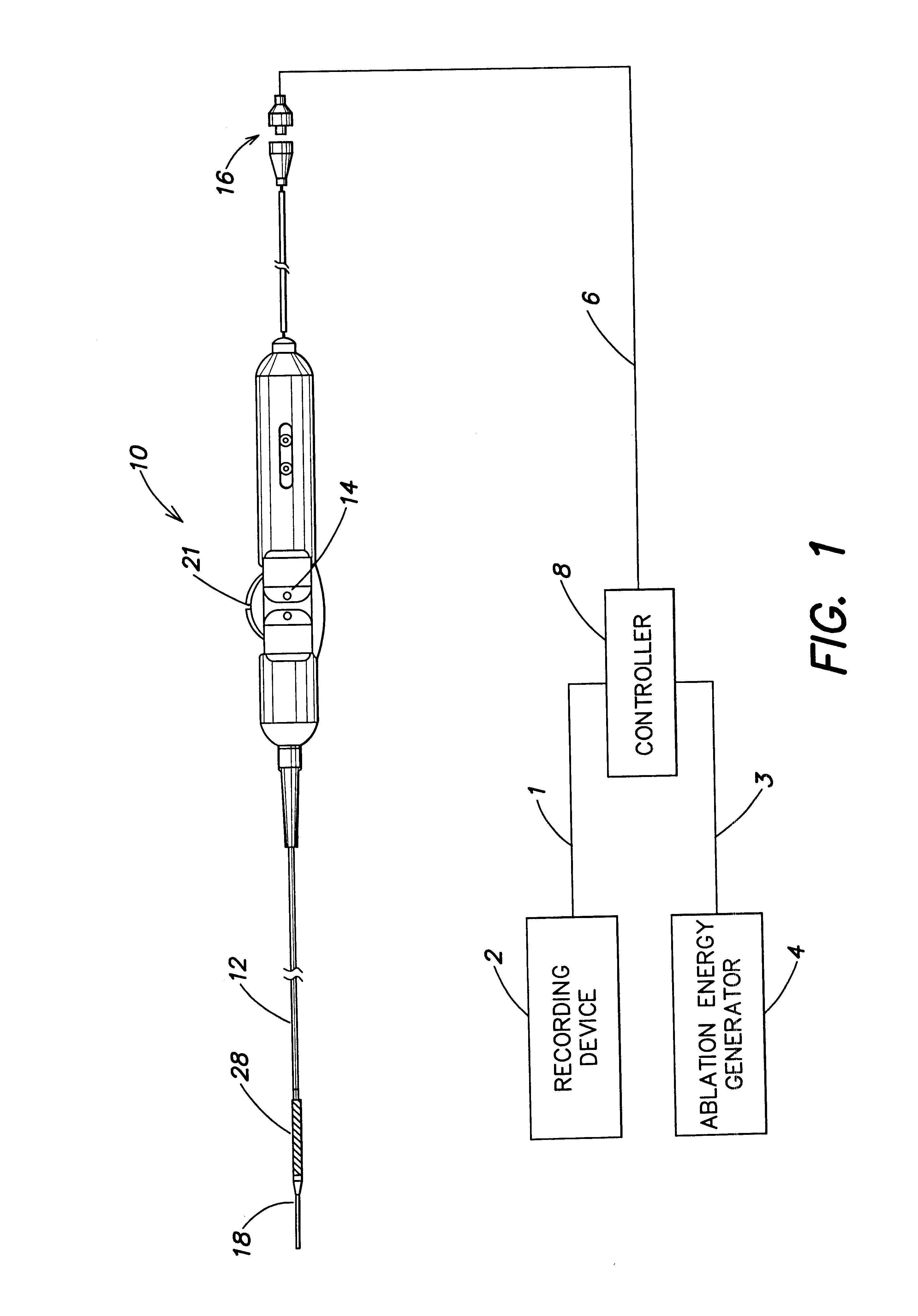
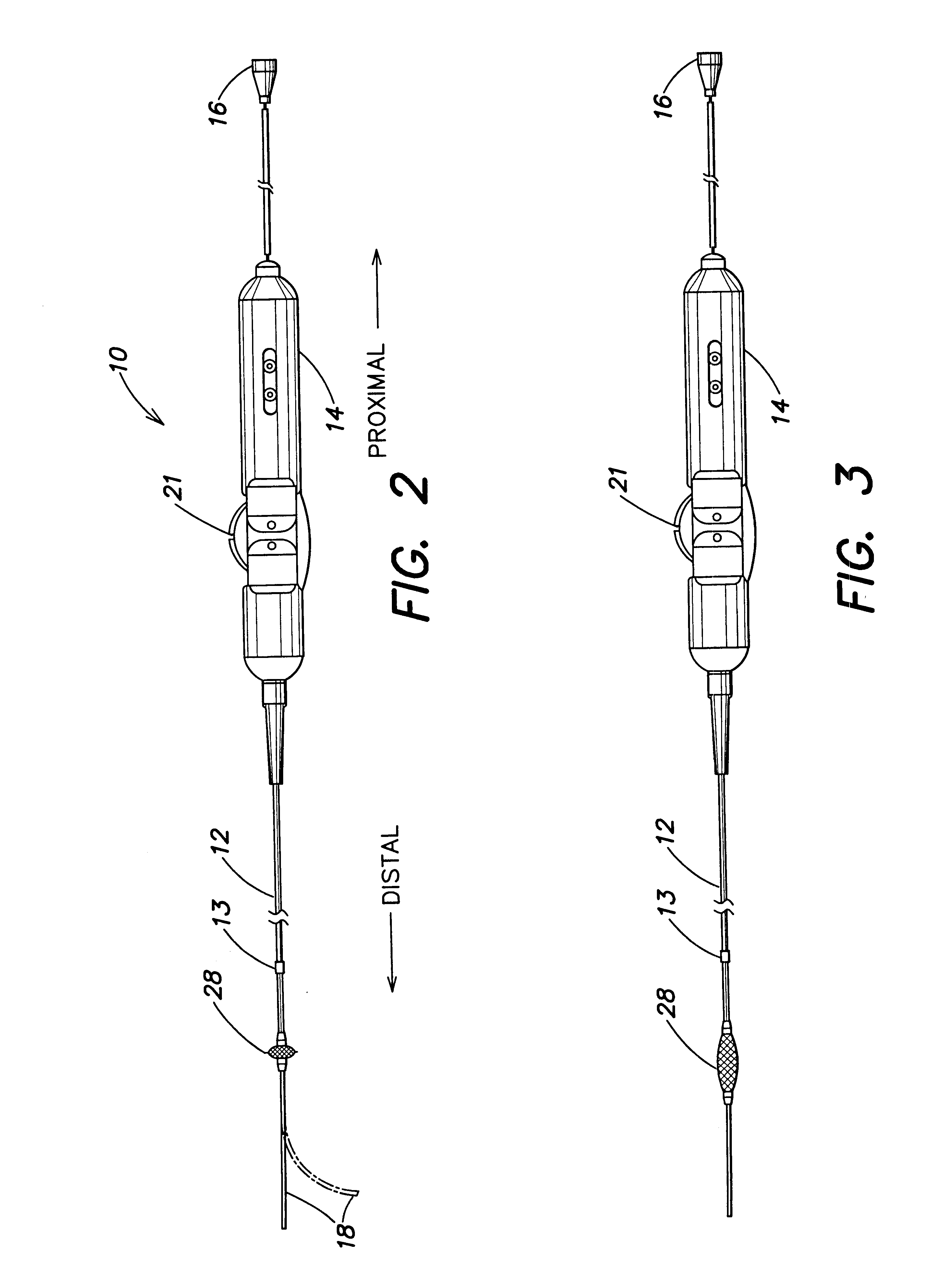
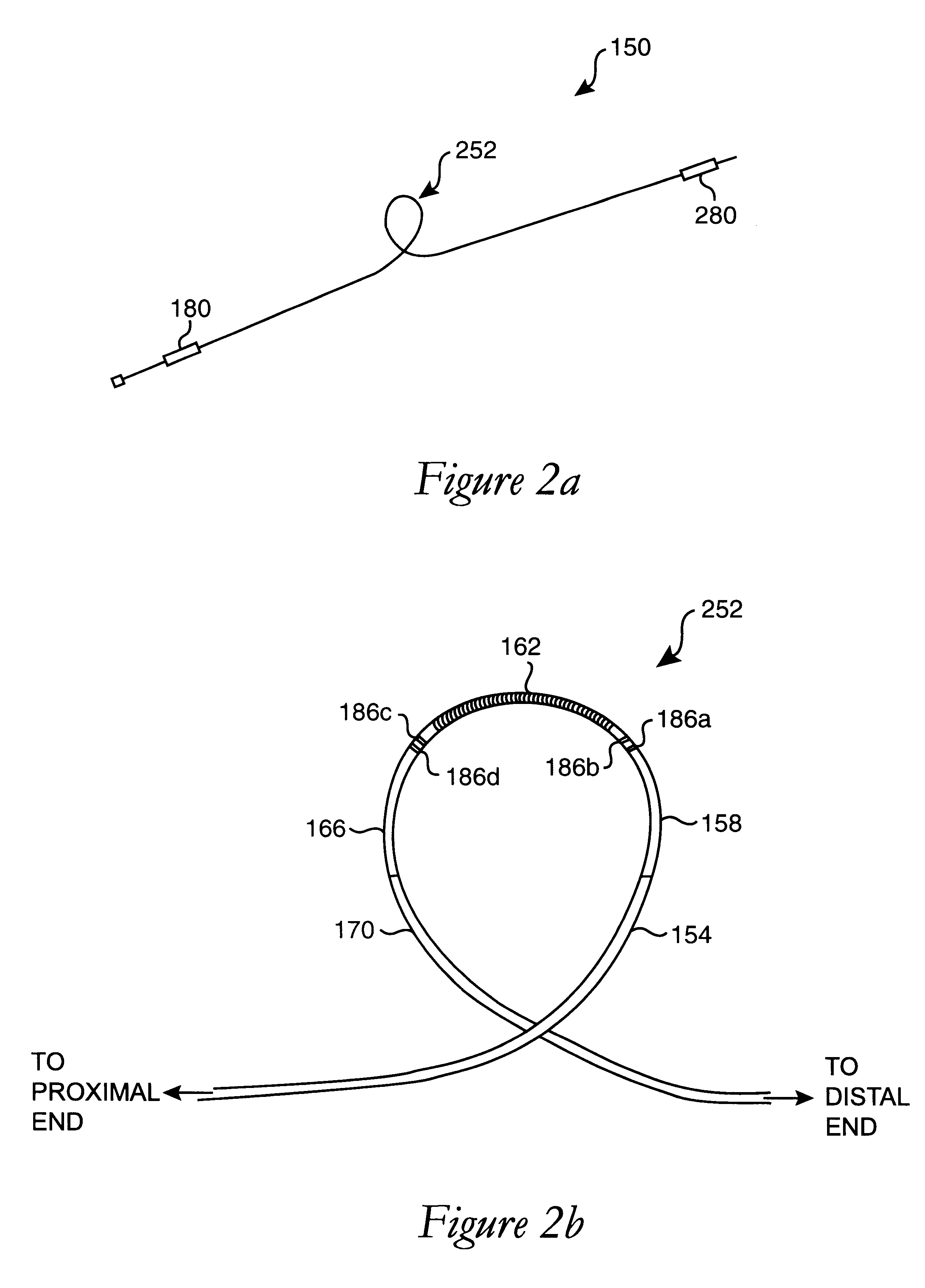
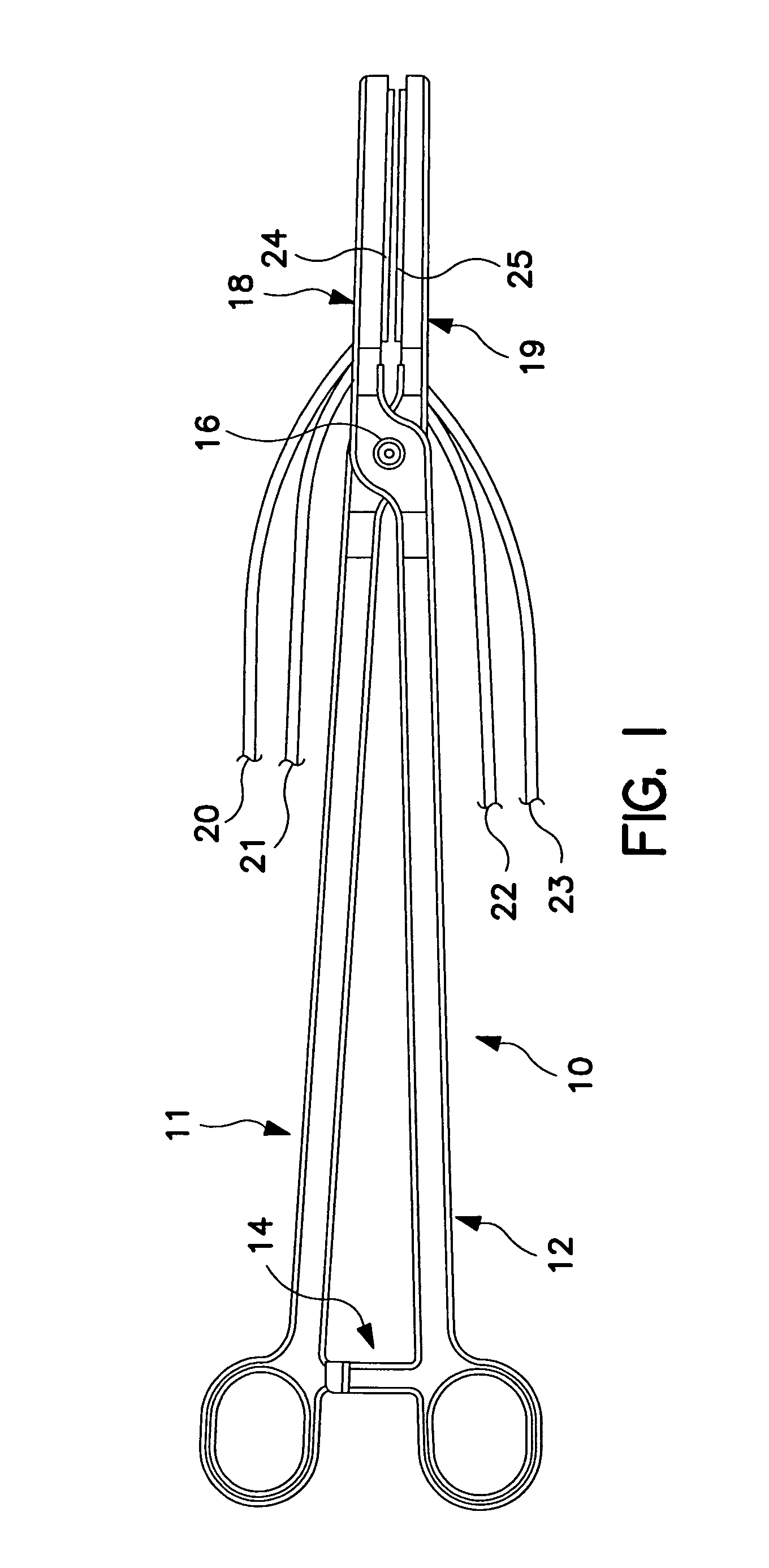
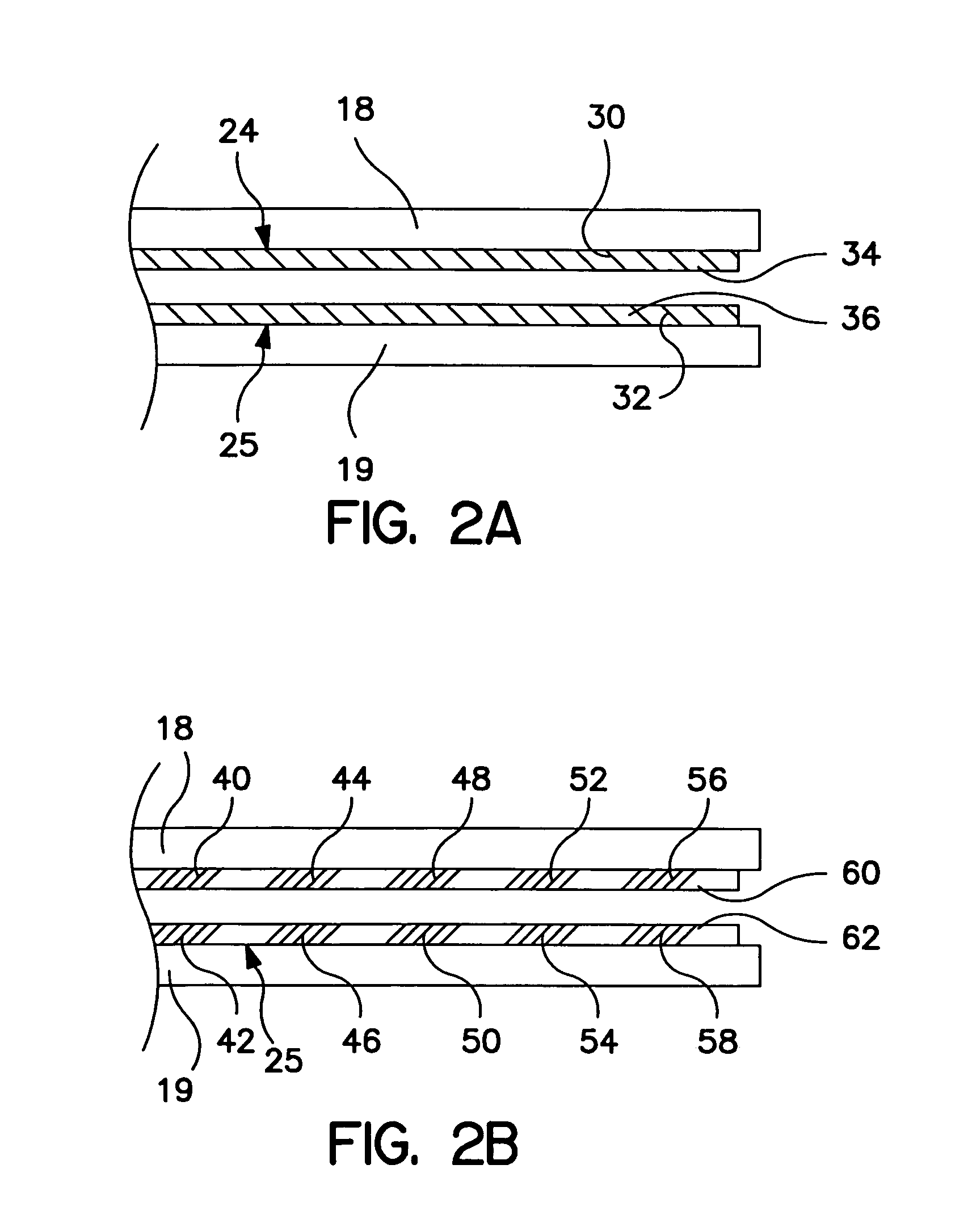
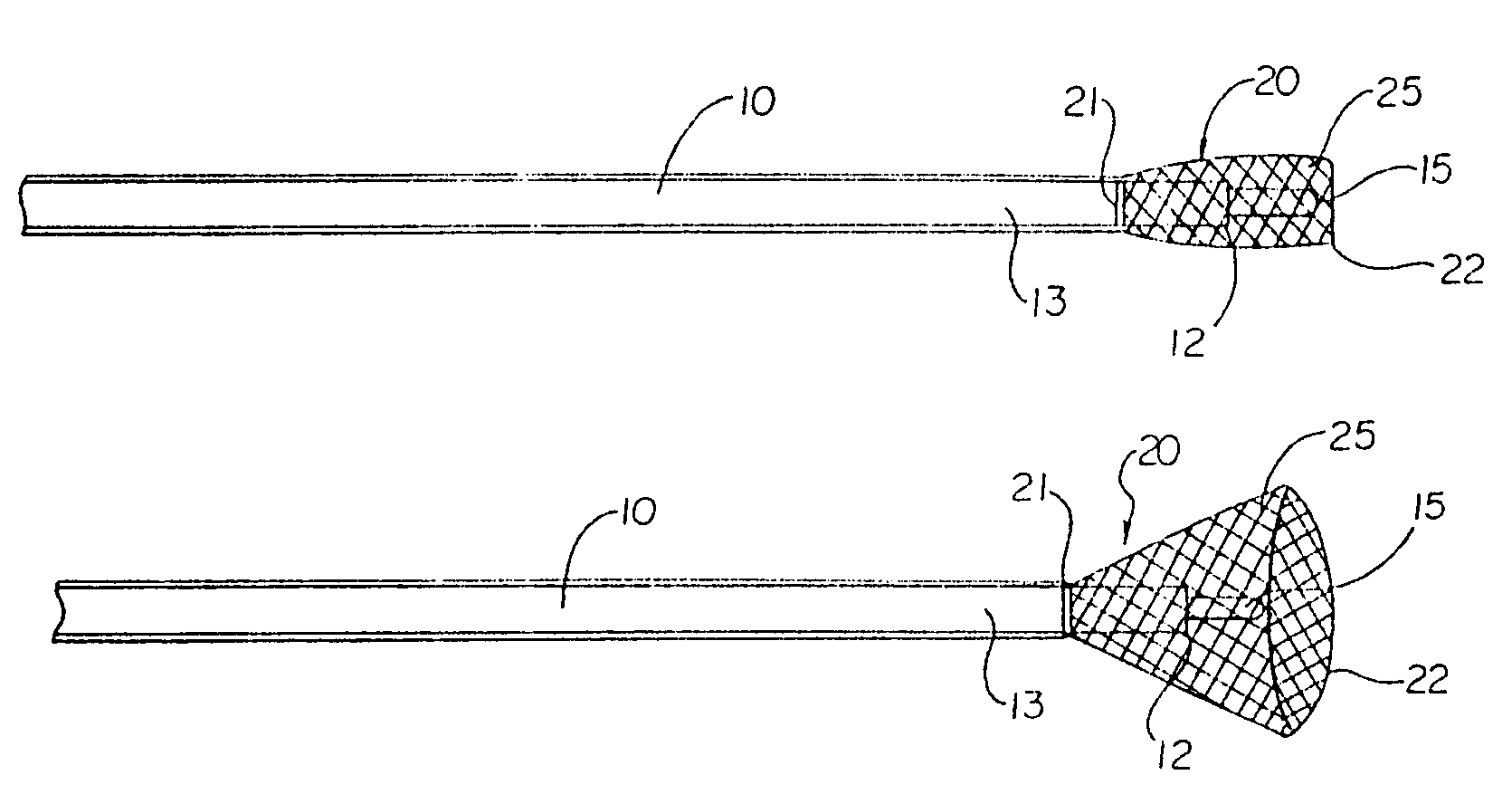
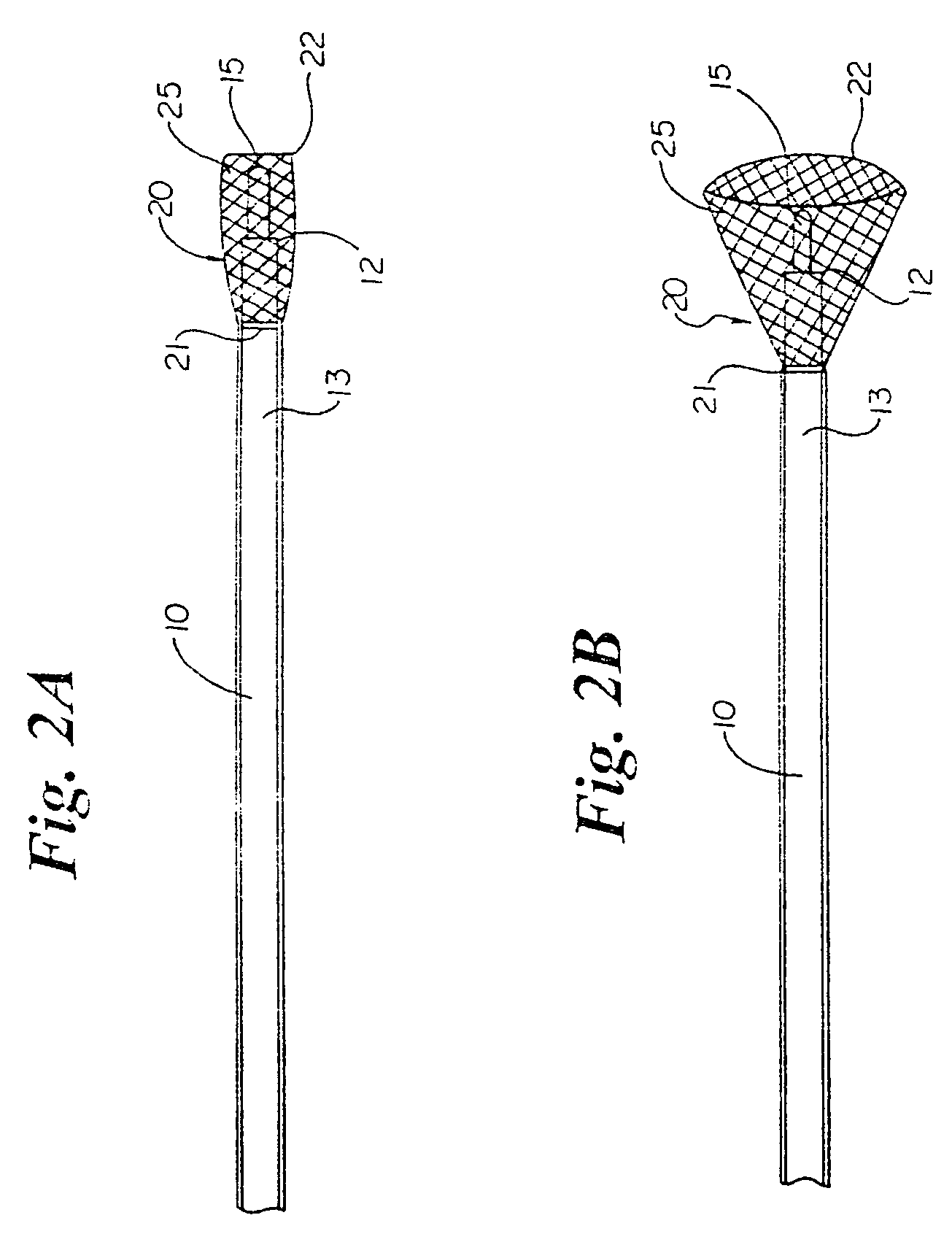
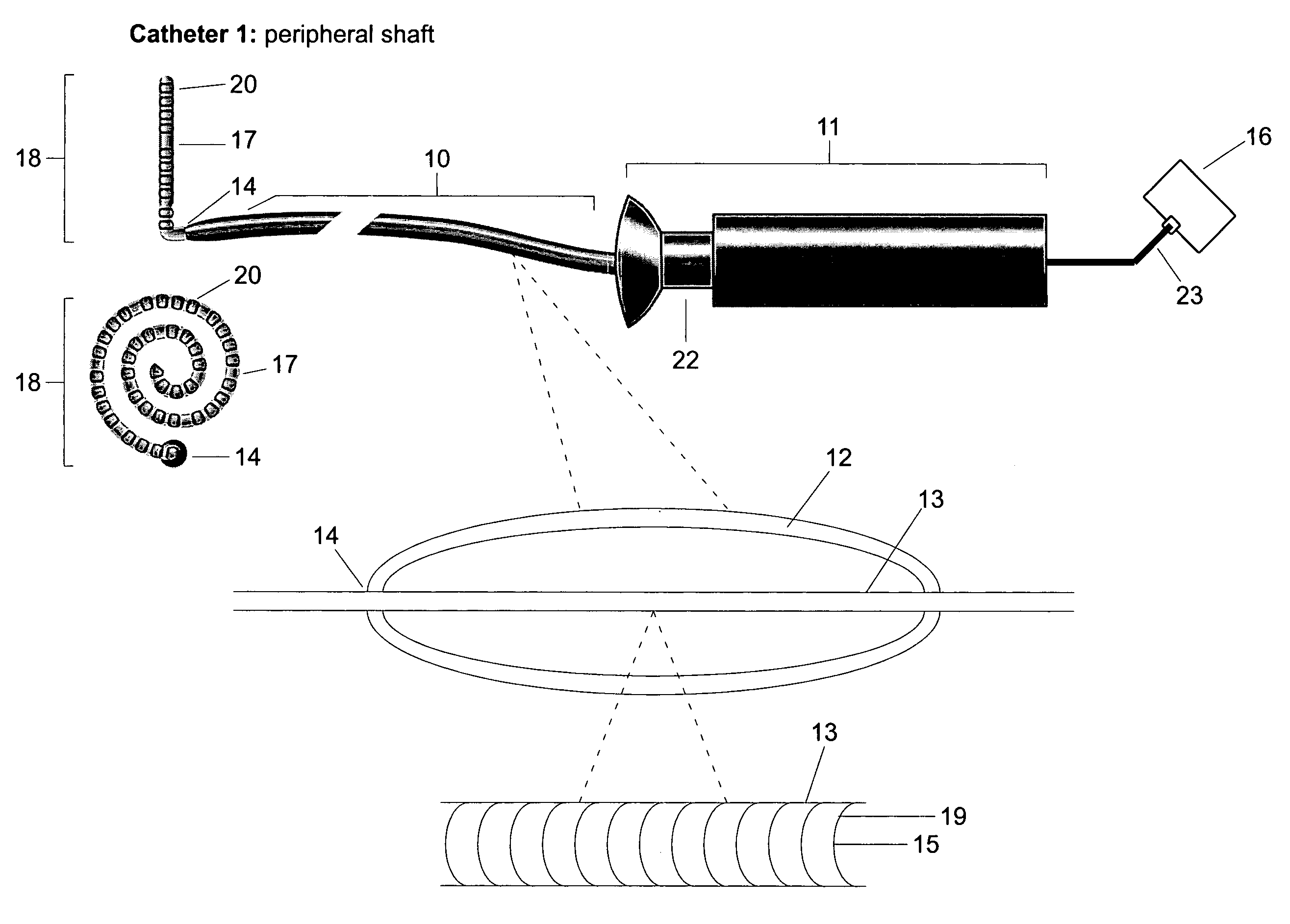
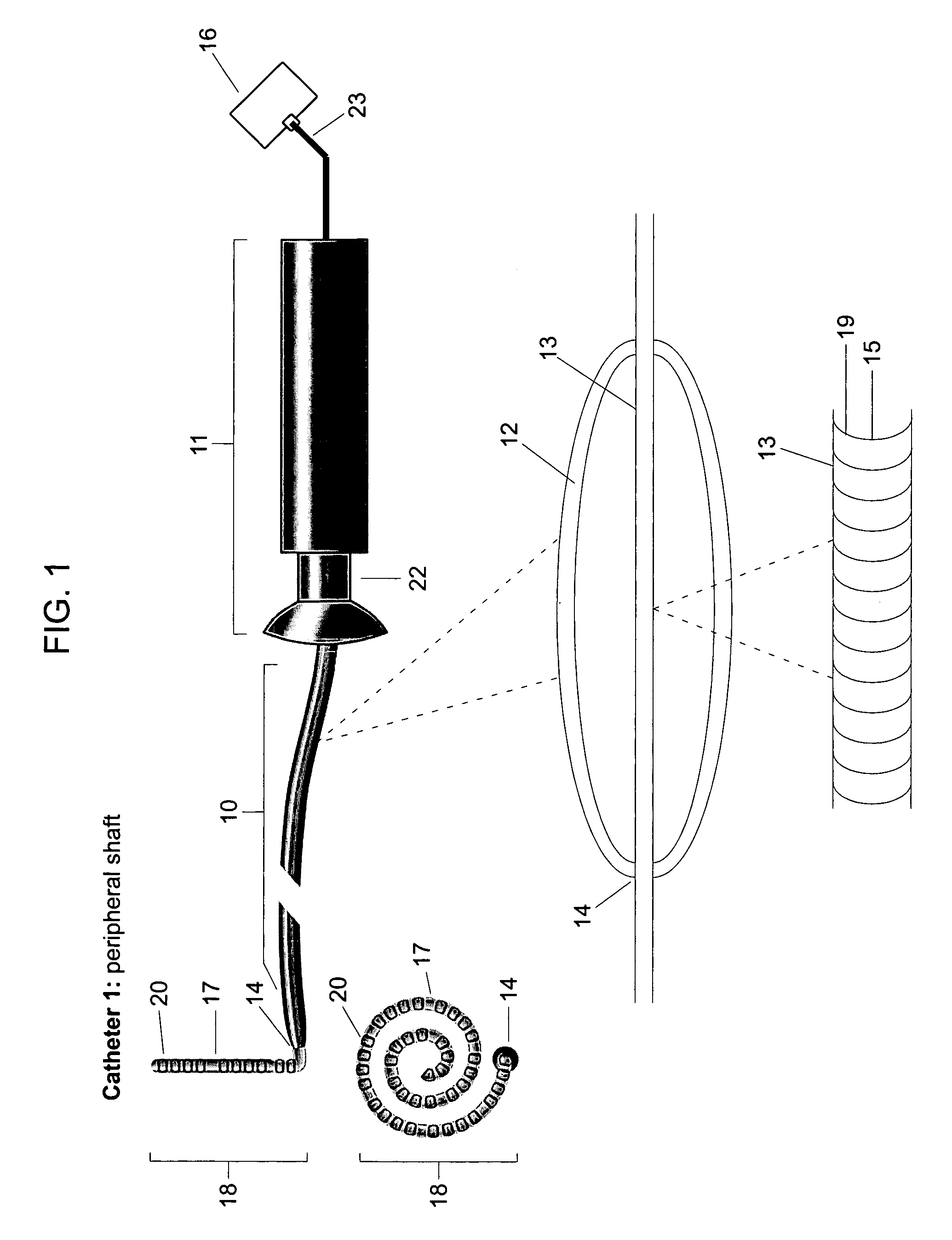
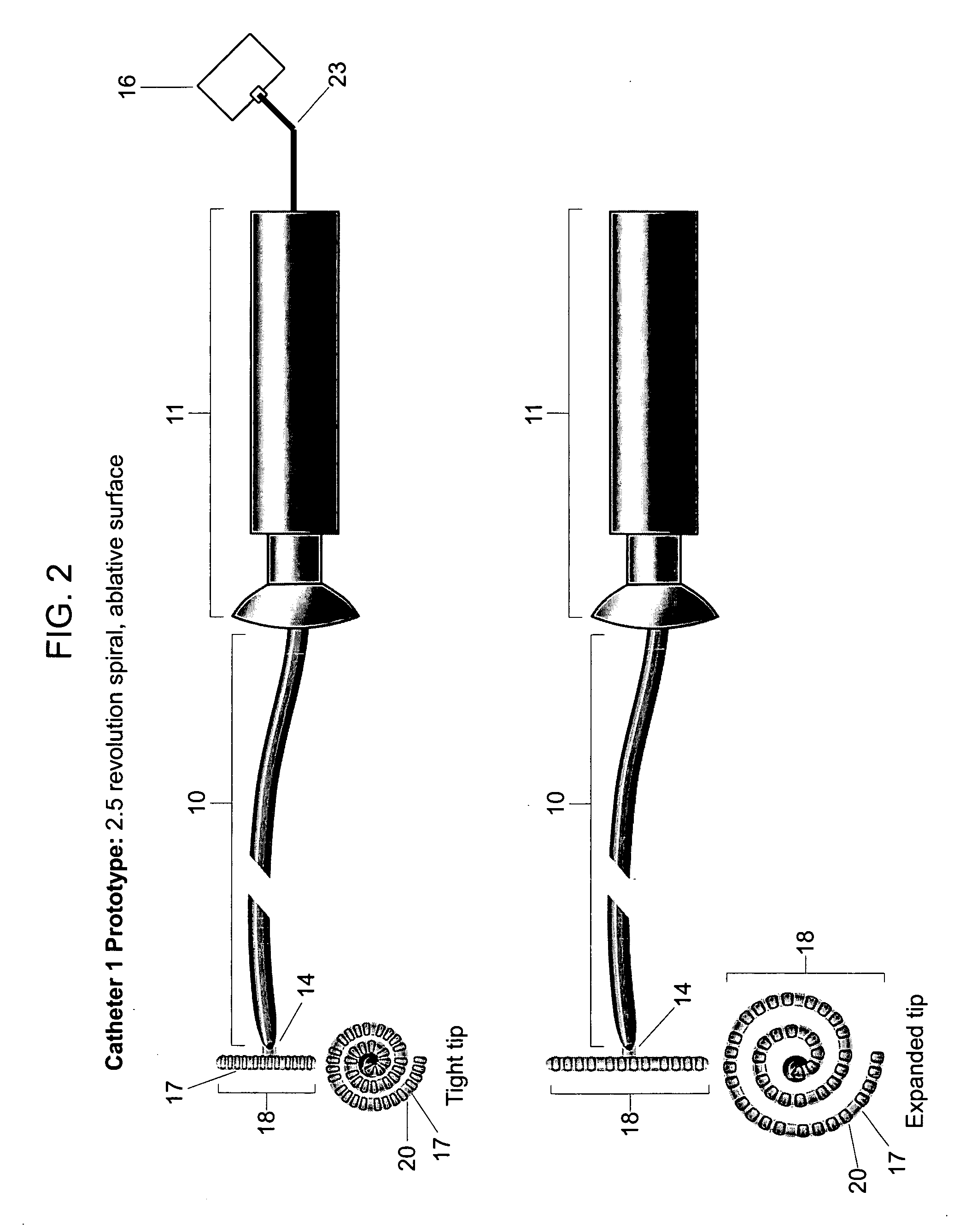
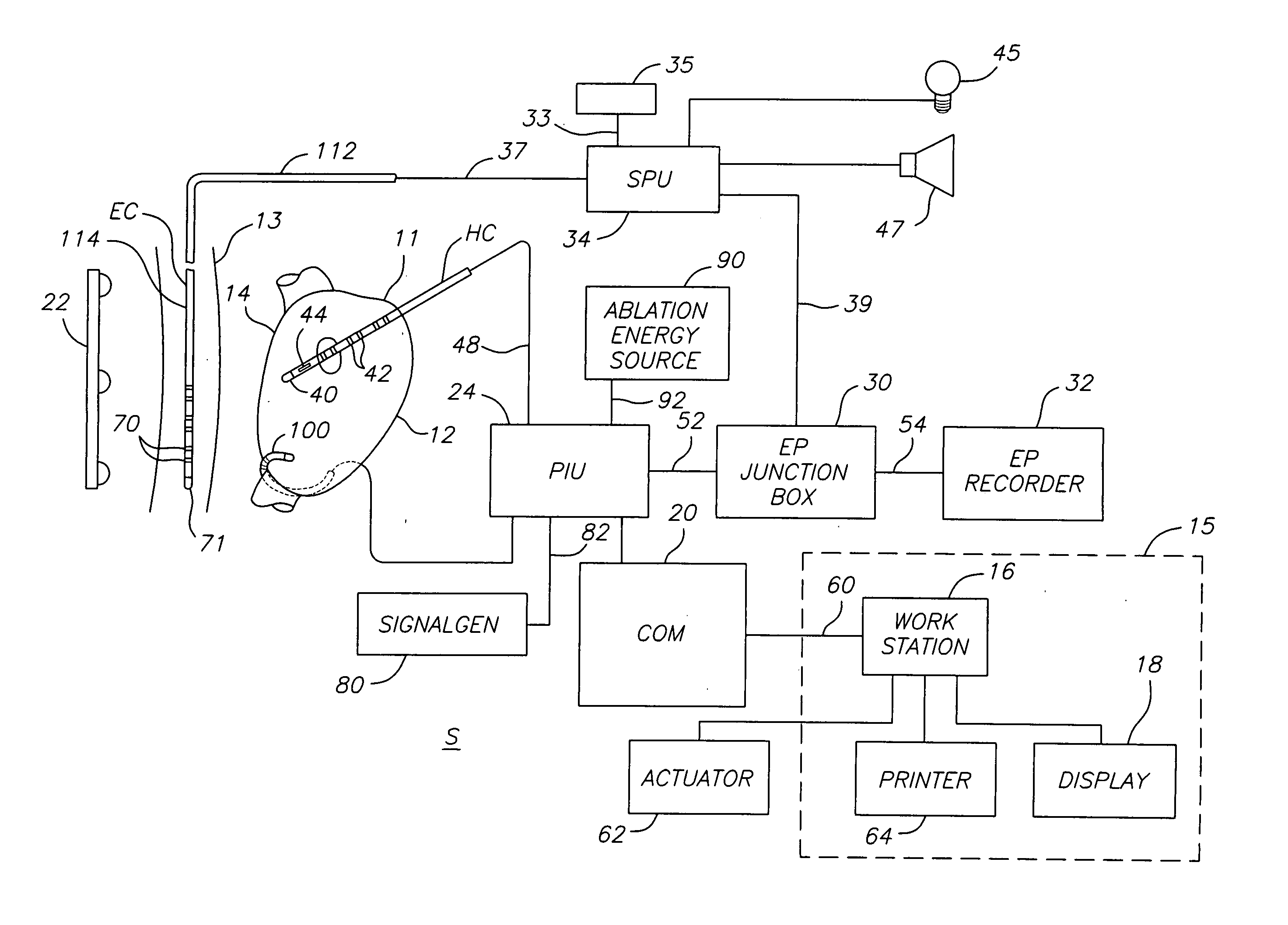
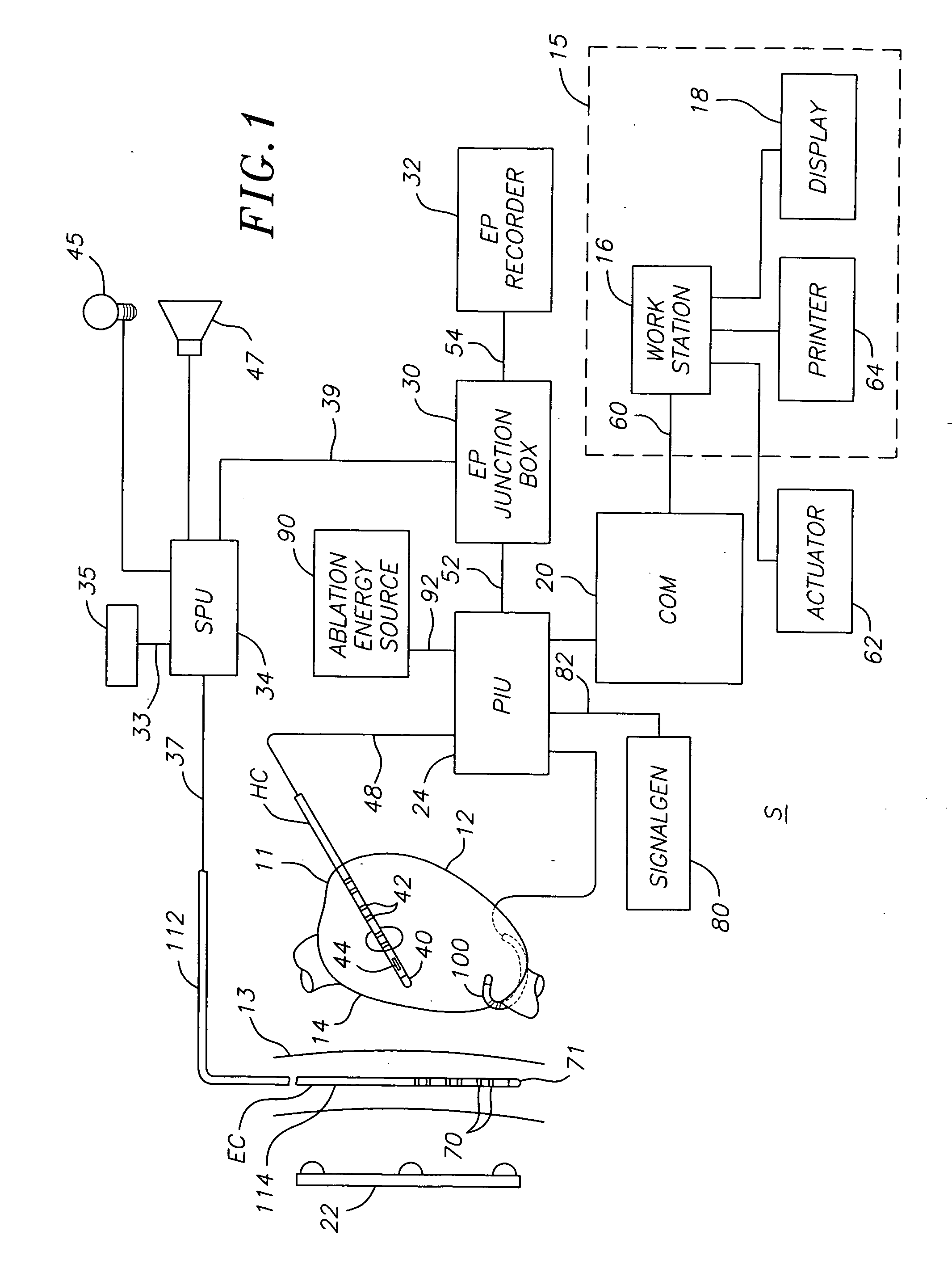
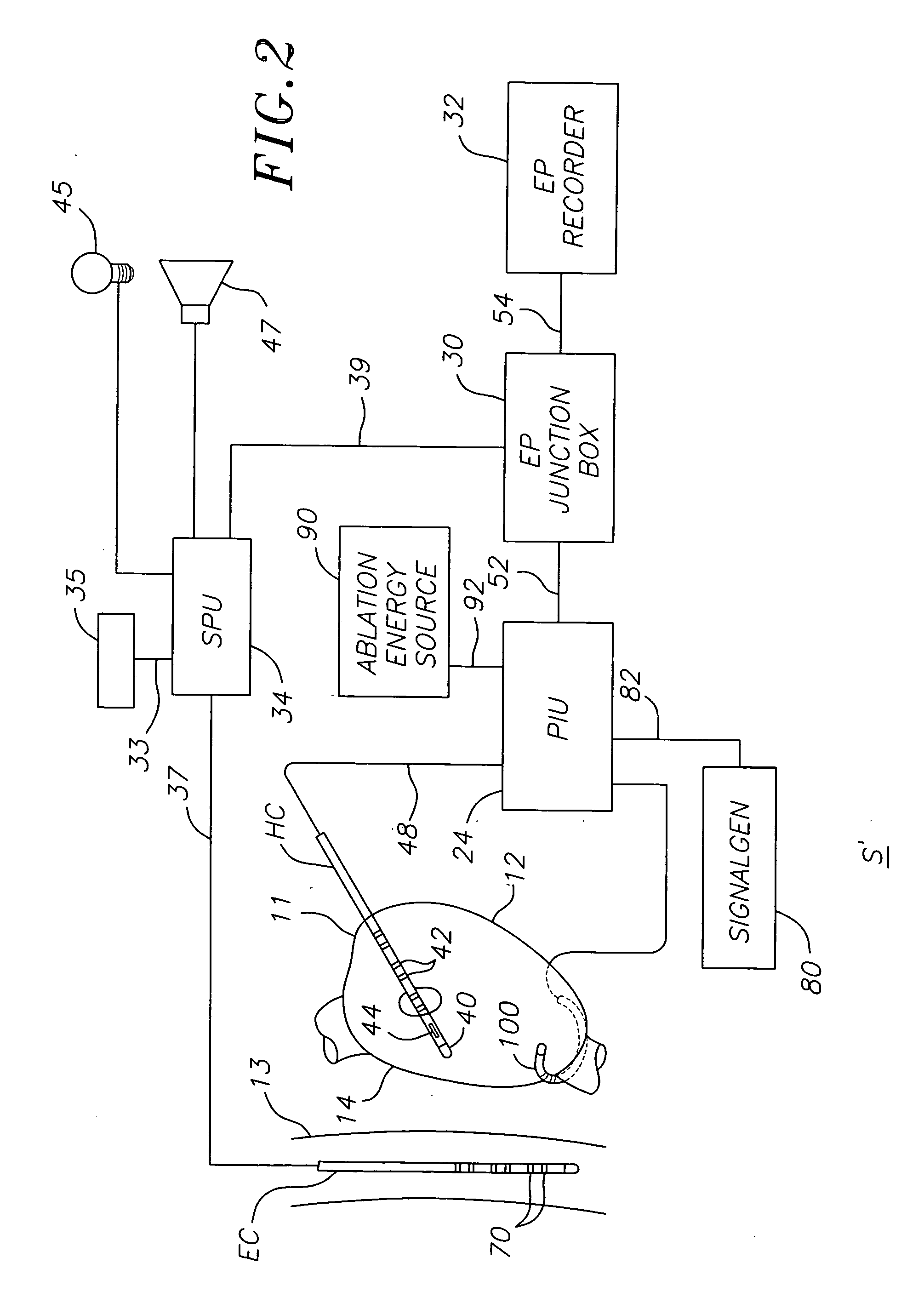
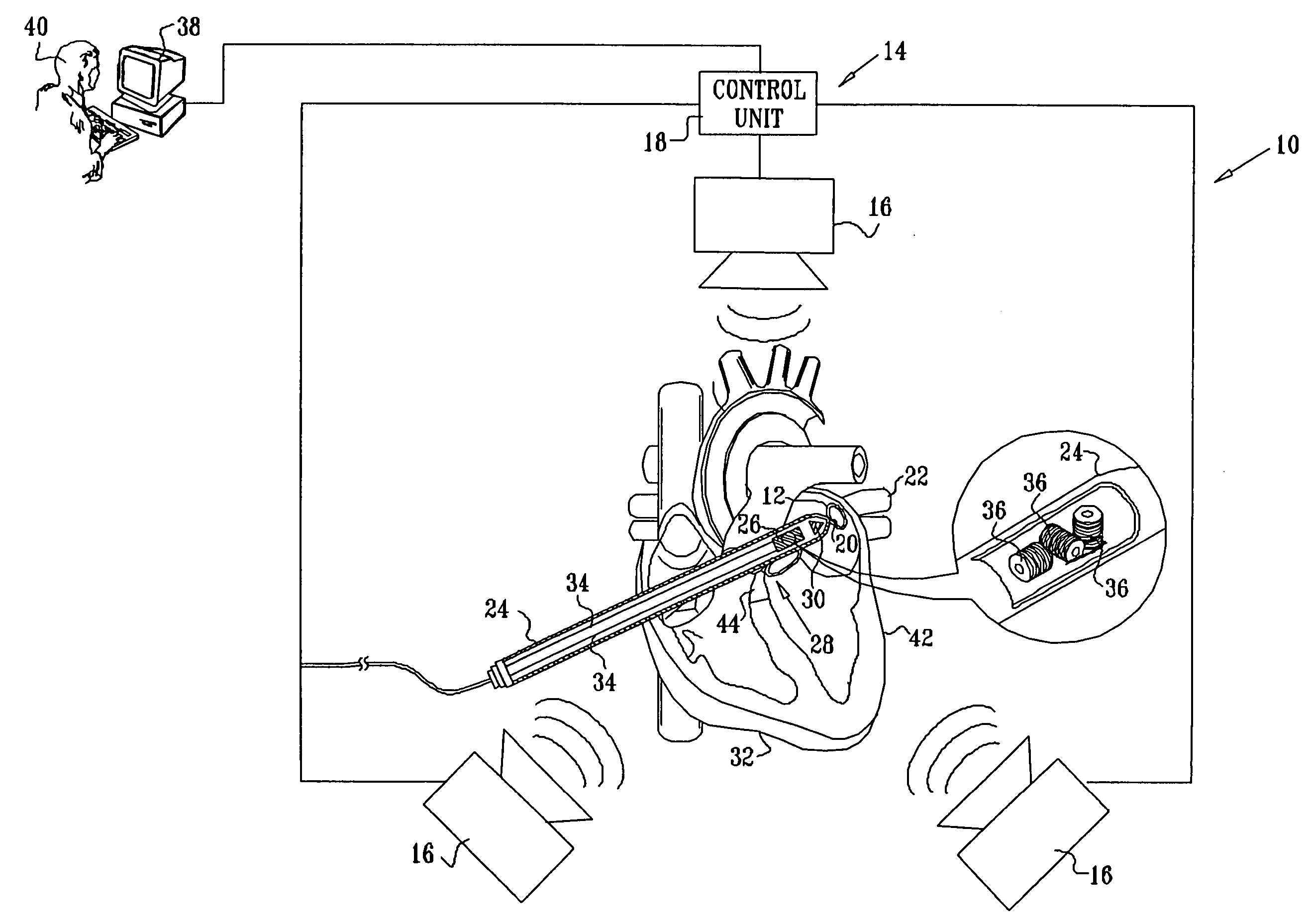
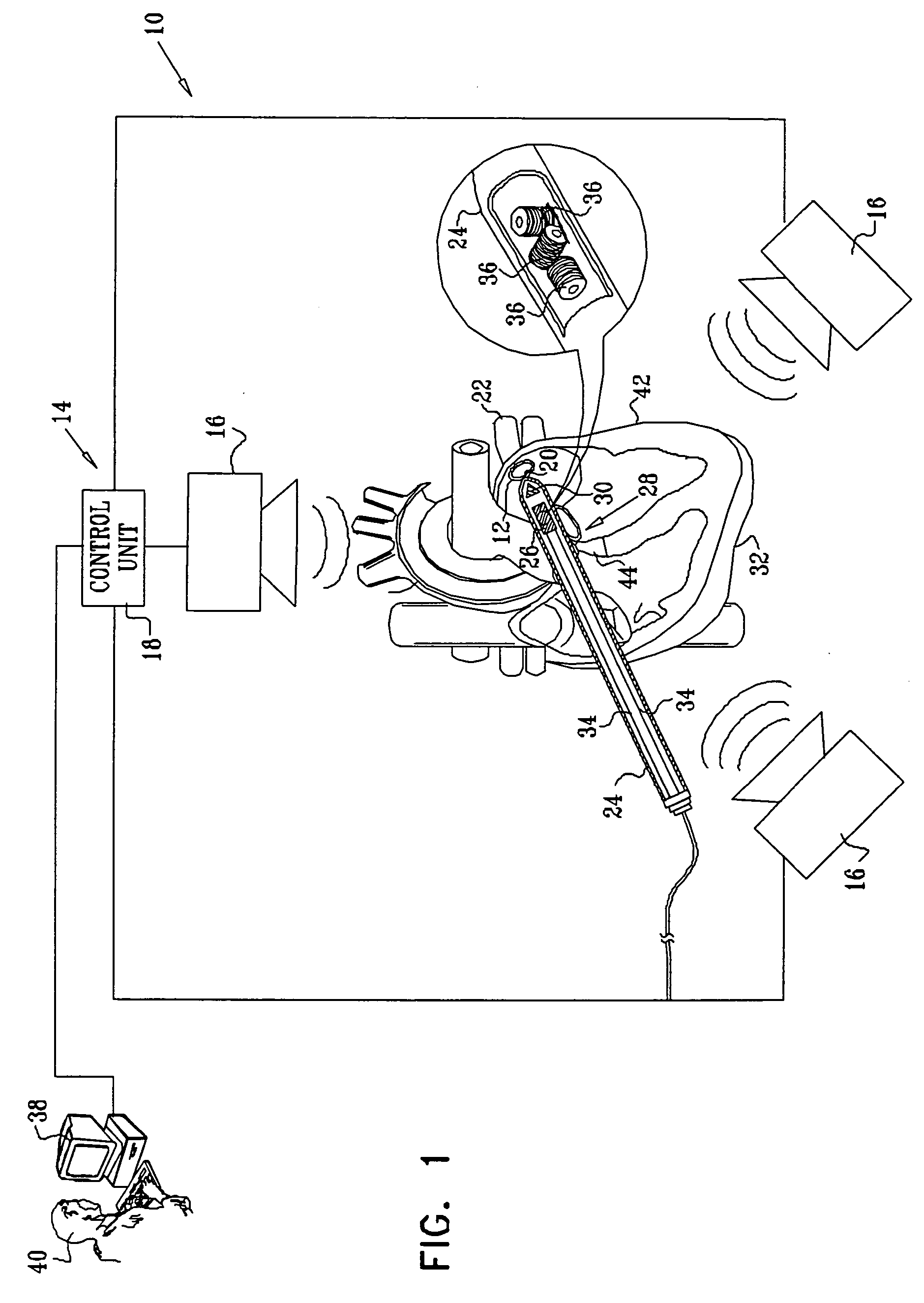
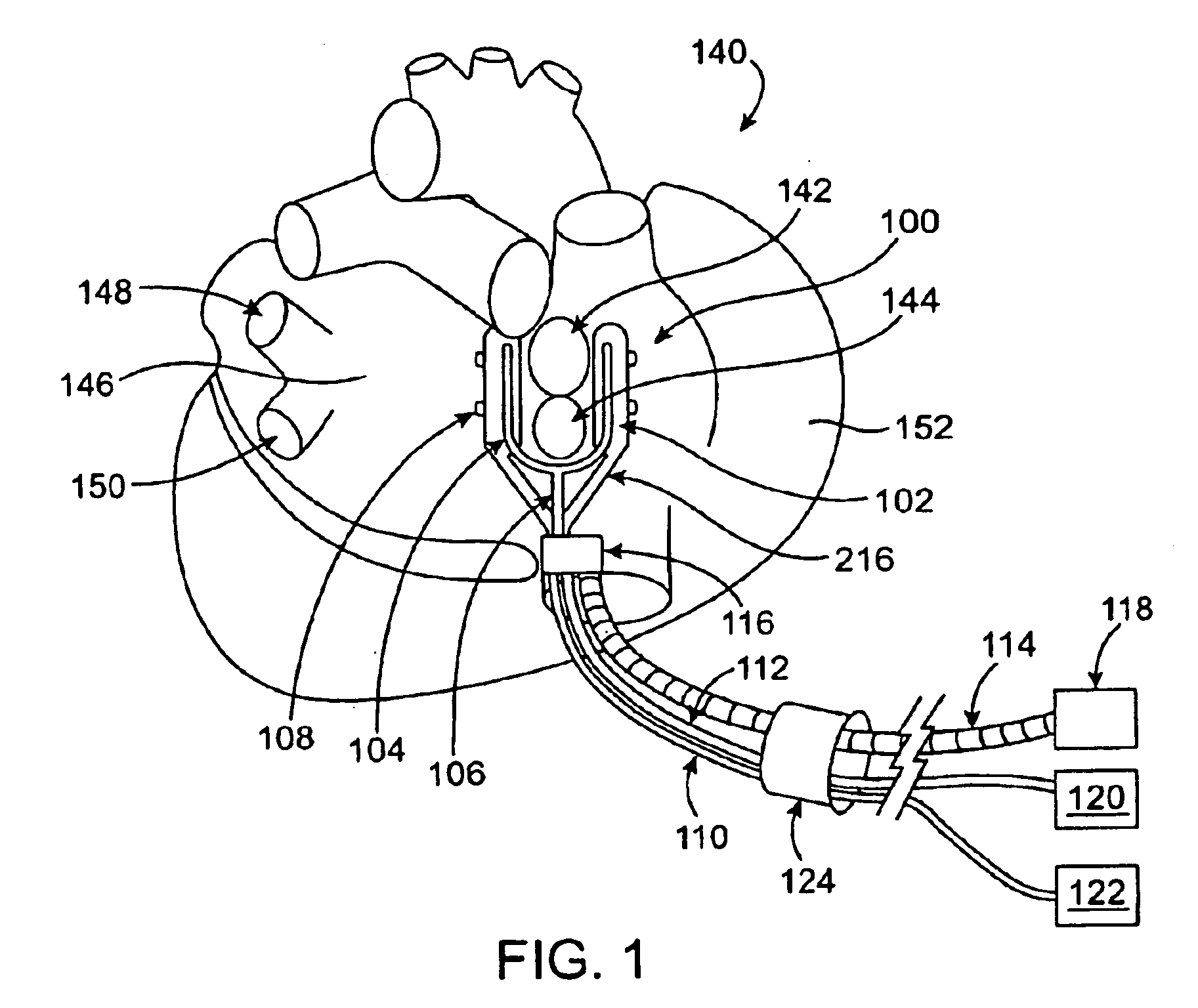
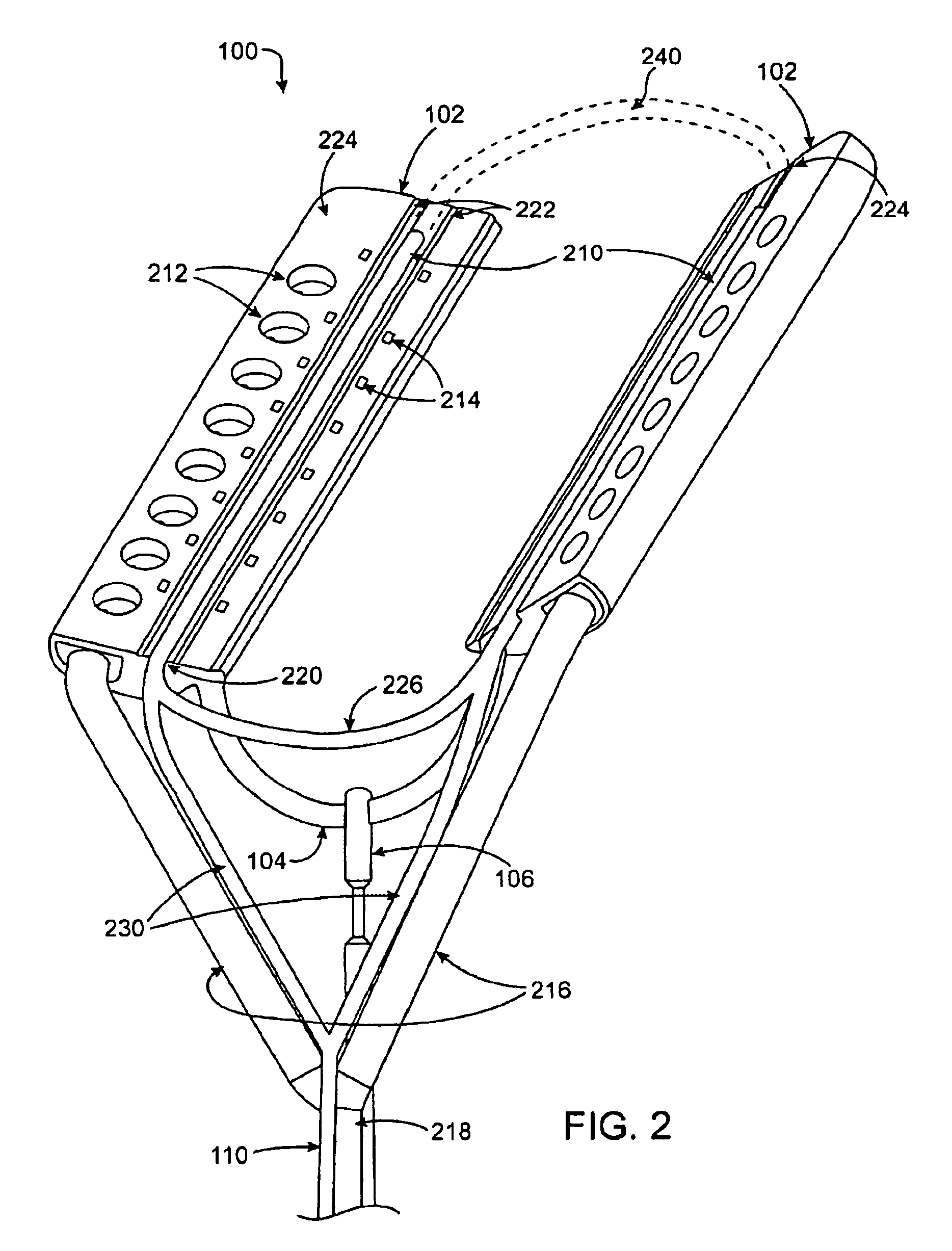
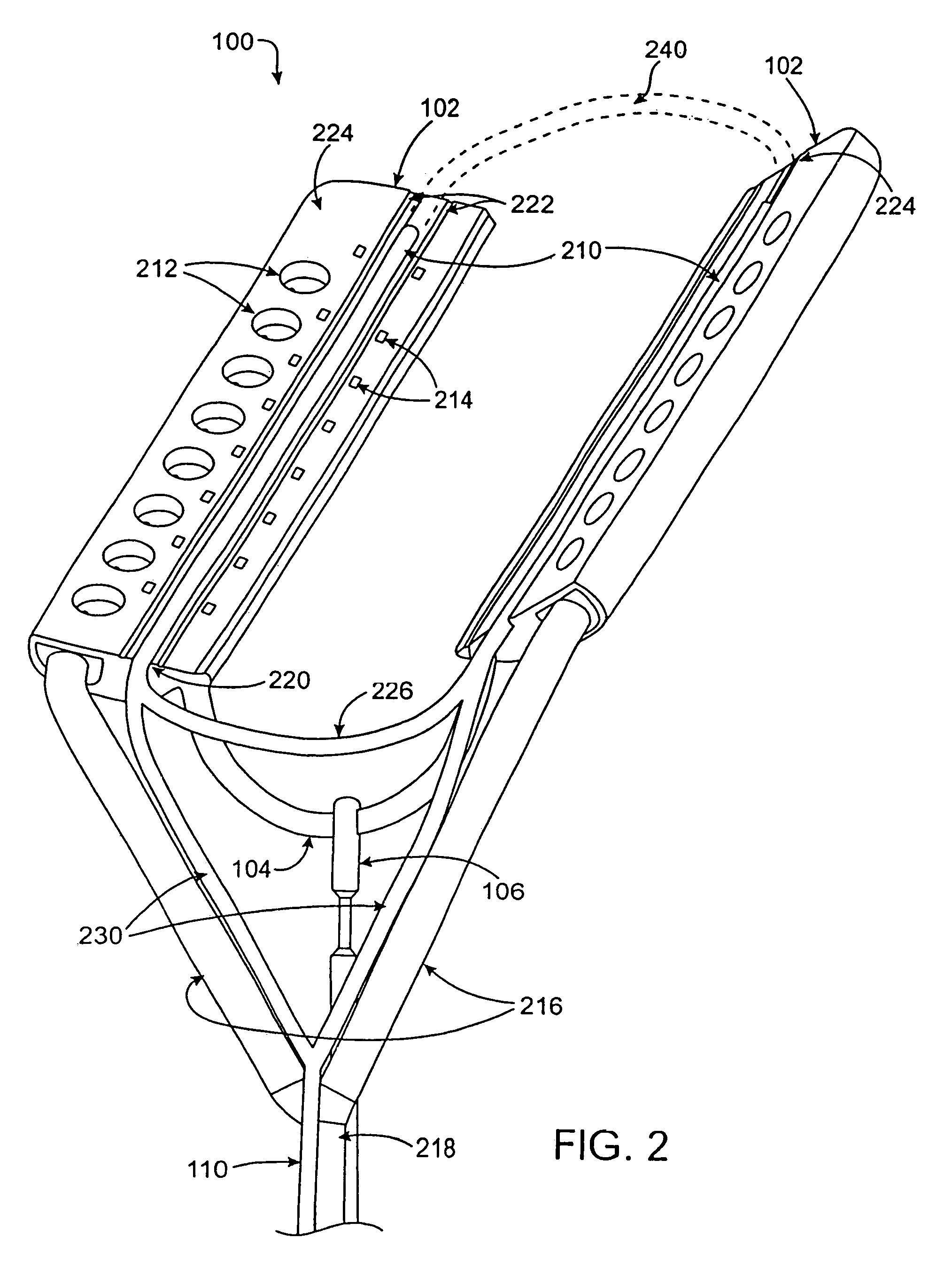
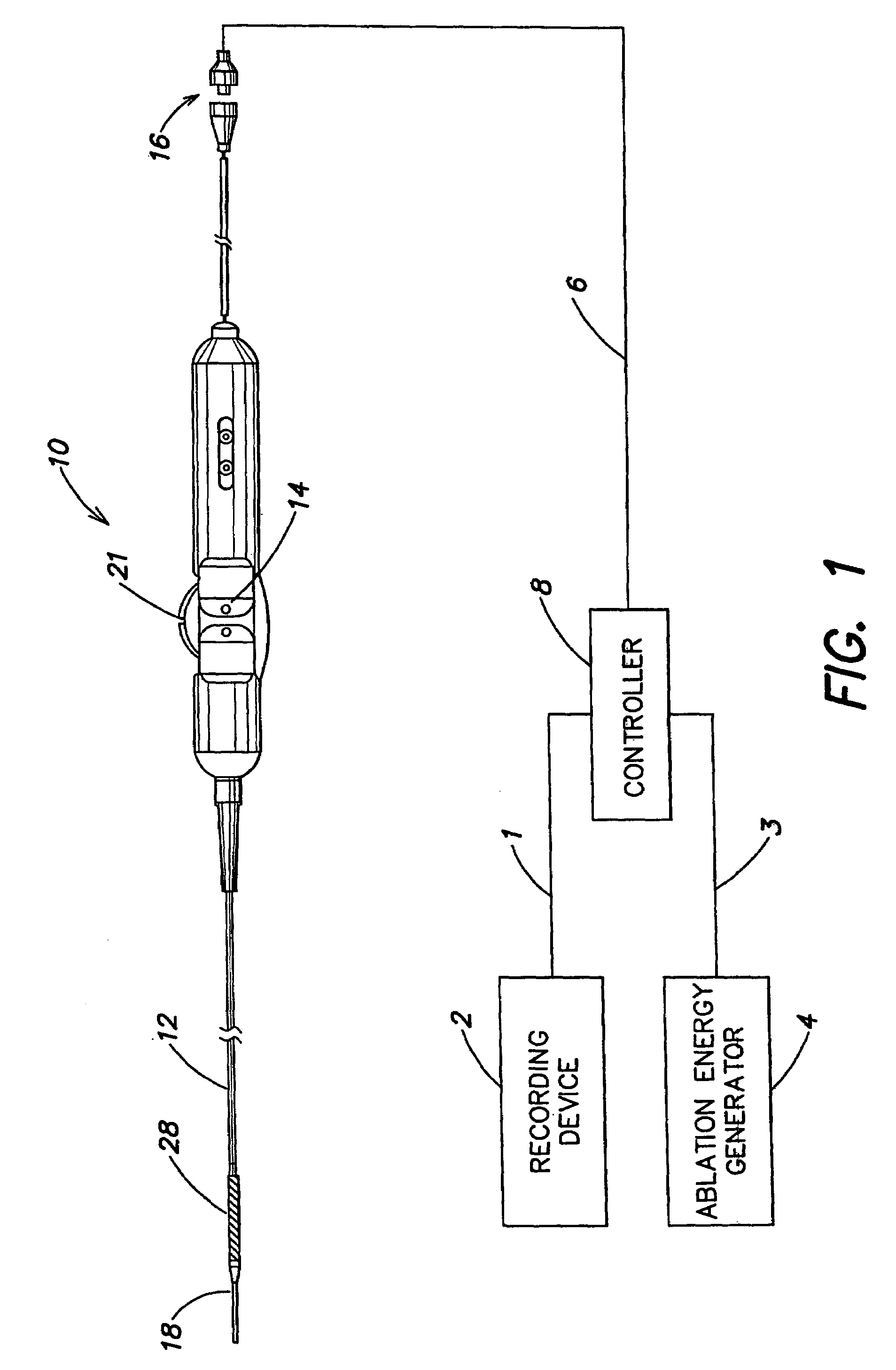
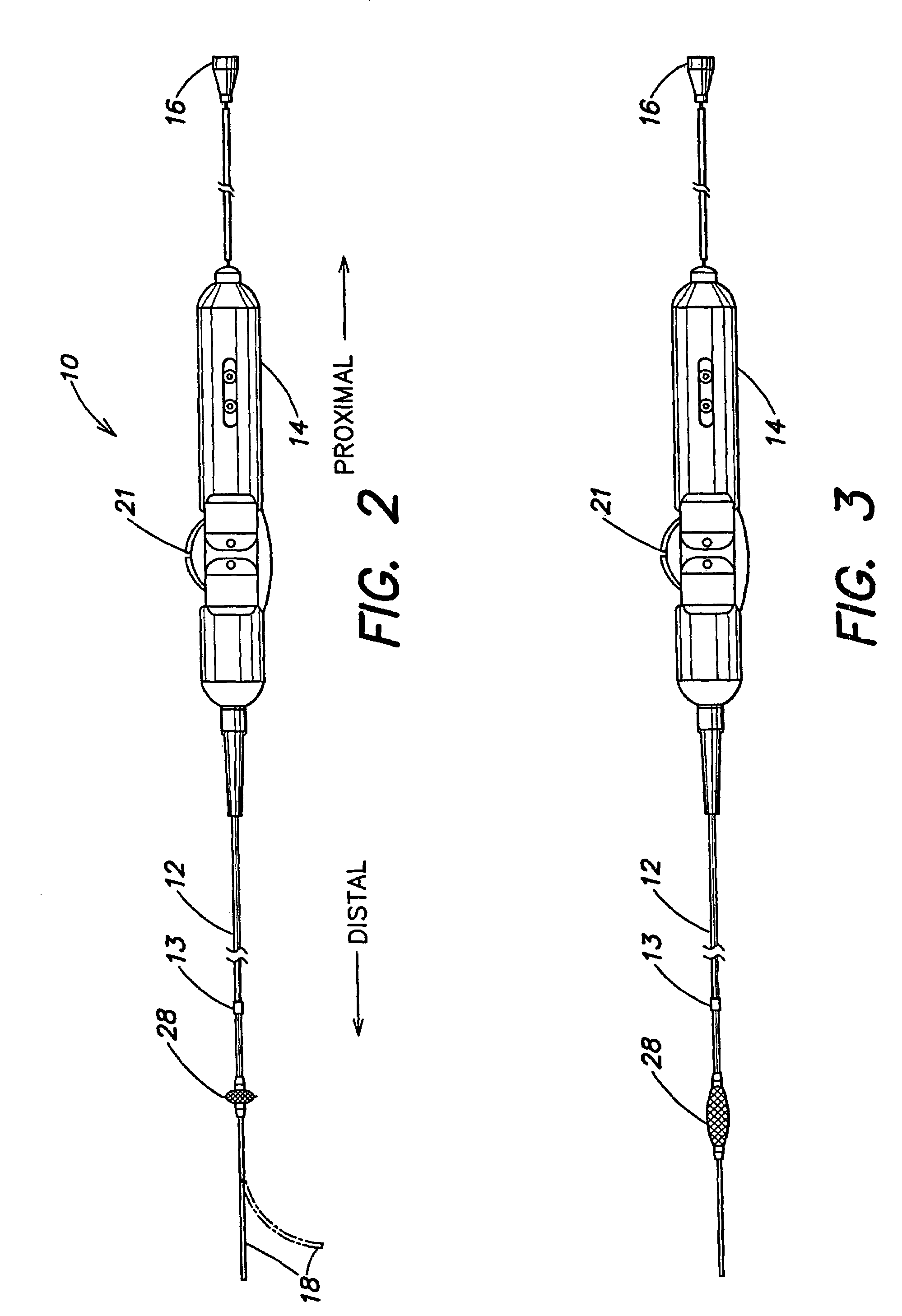
Multi-purpose catheter apparatus and method of use
InactiveUS20050010095A1Easy to adaptEfficiently and accurately deliverElectrocardiographySurgical needlesDistal portionSaline solutions
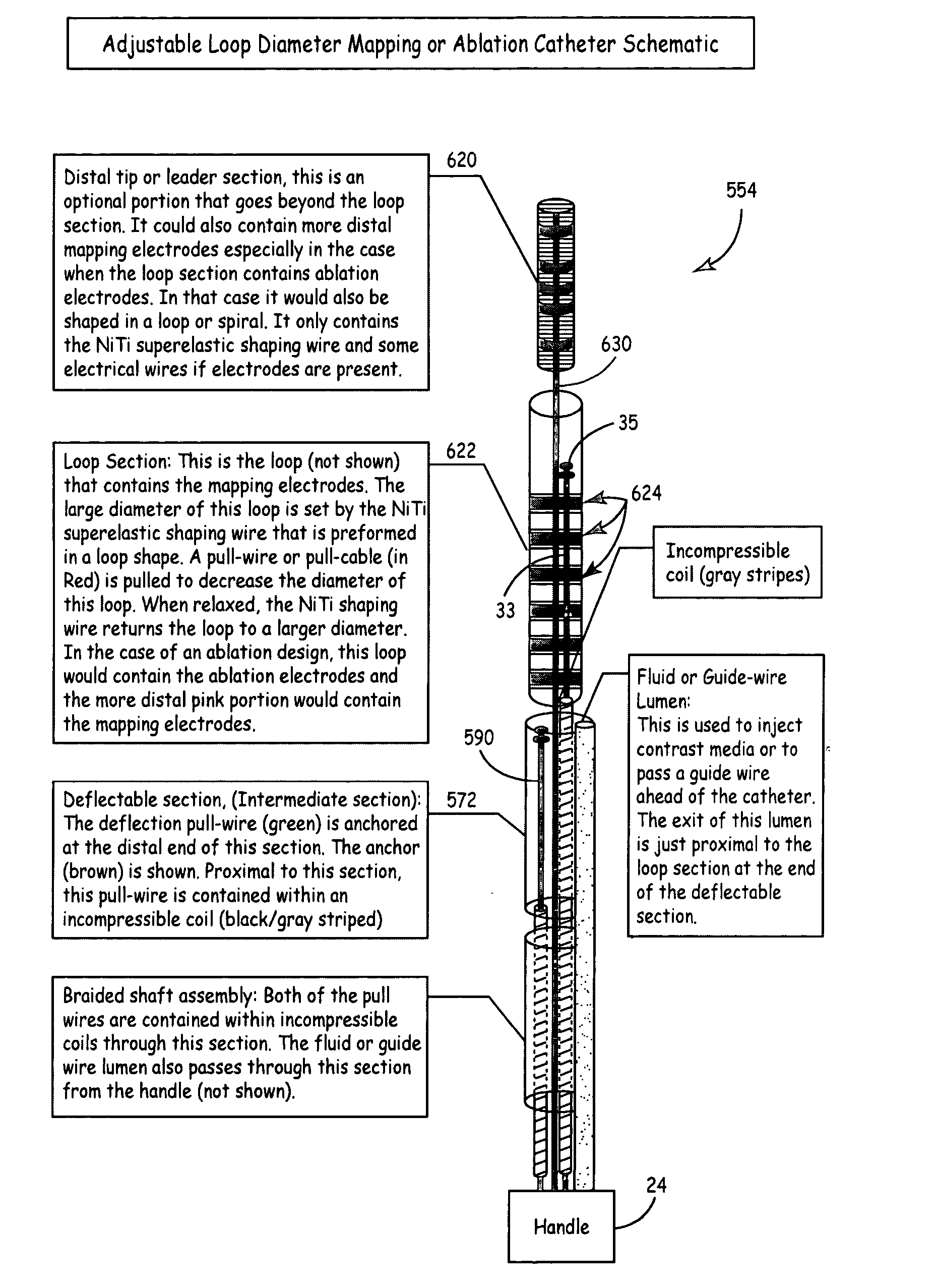
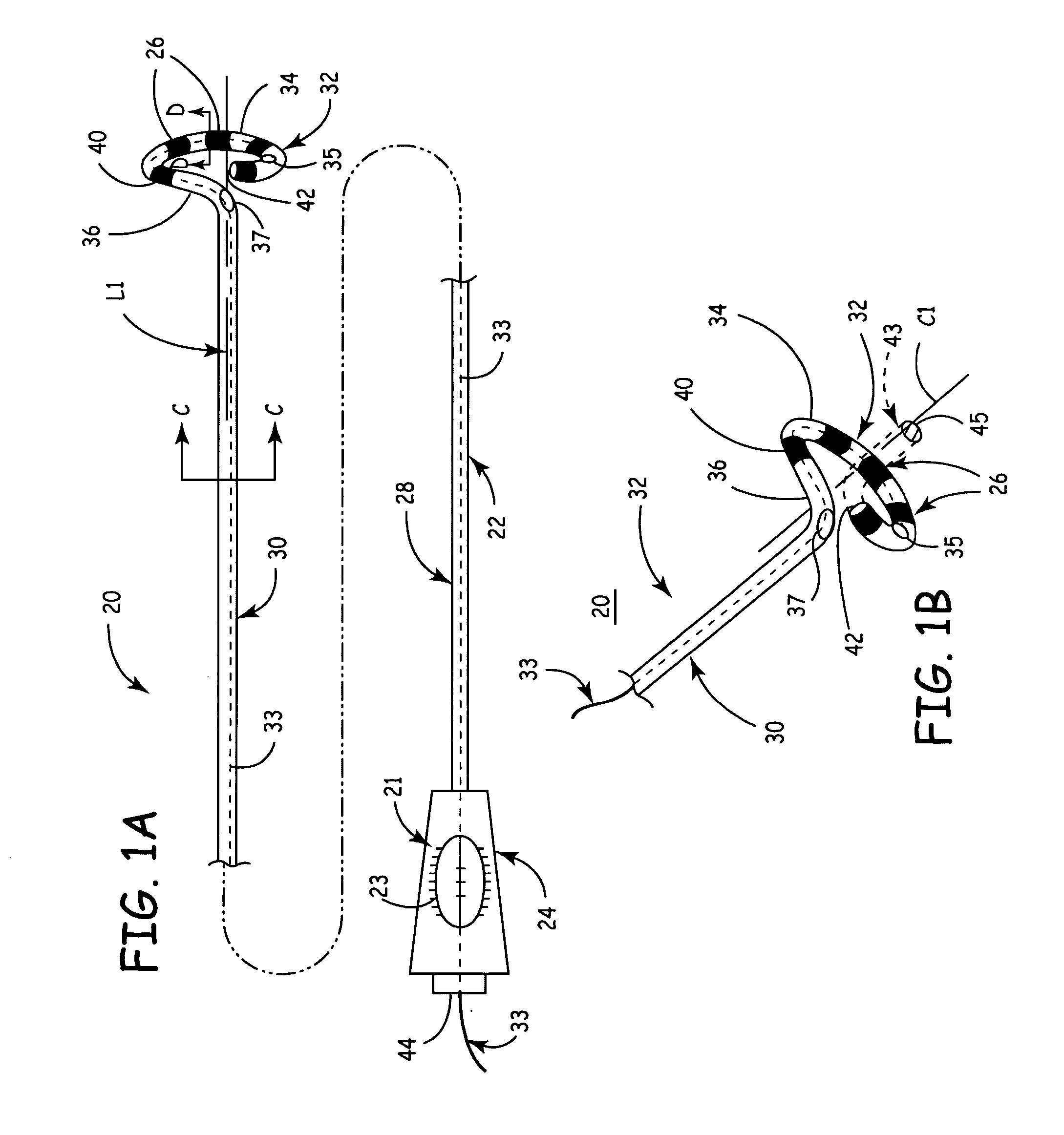
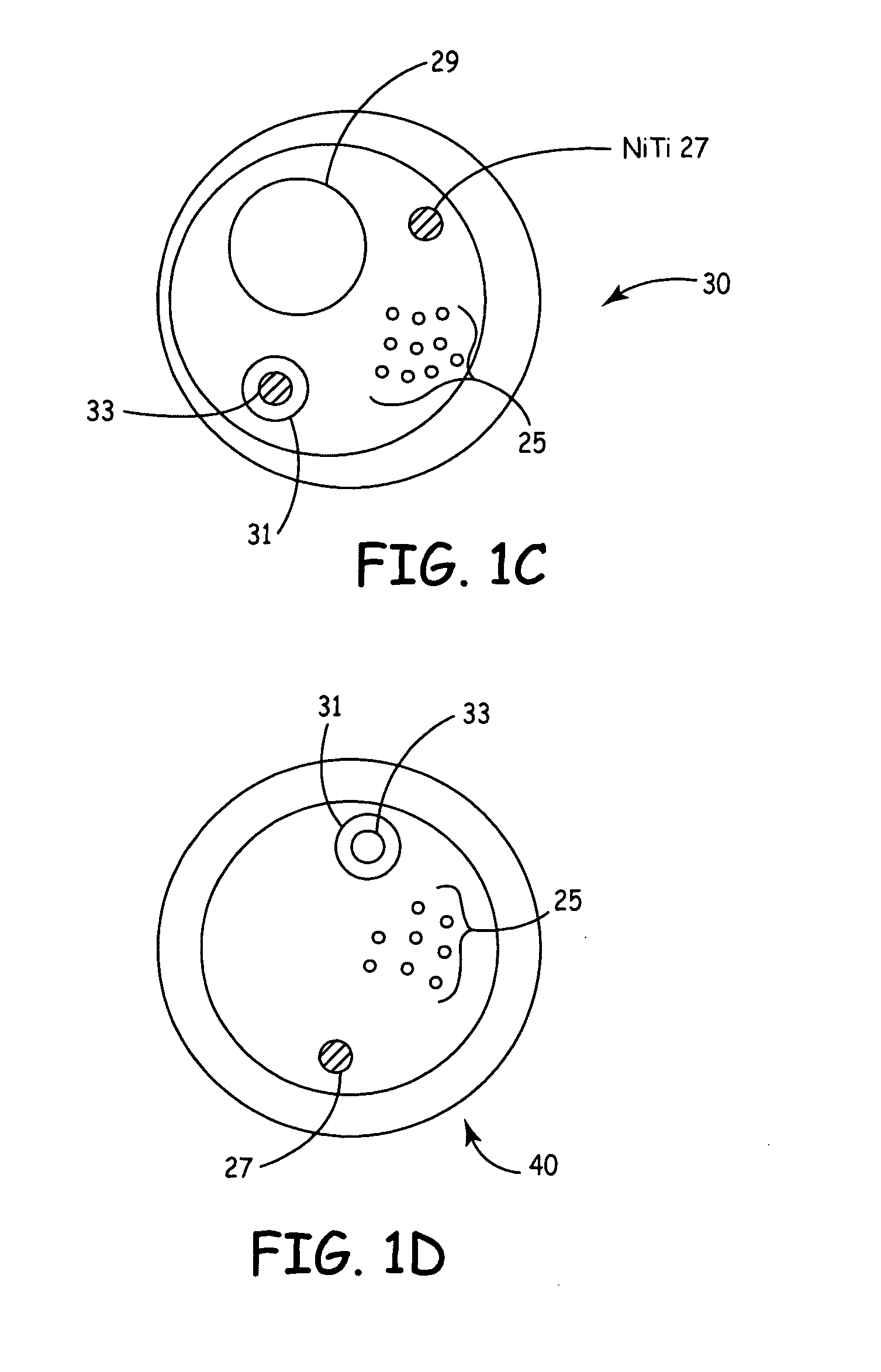
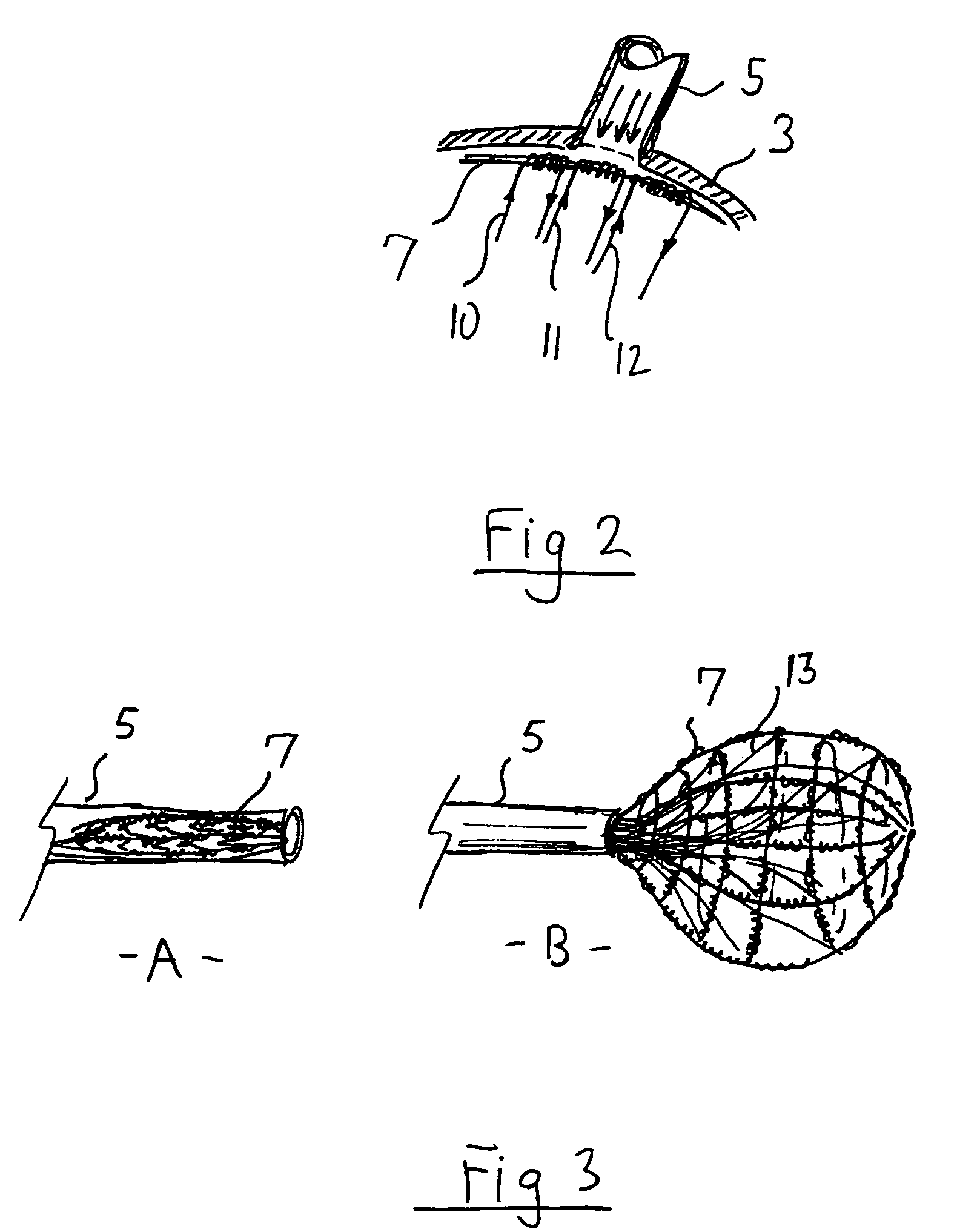
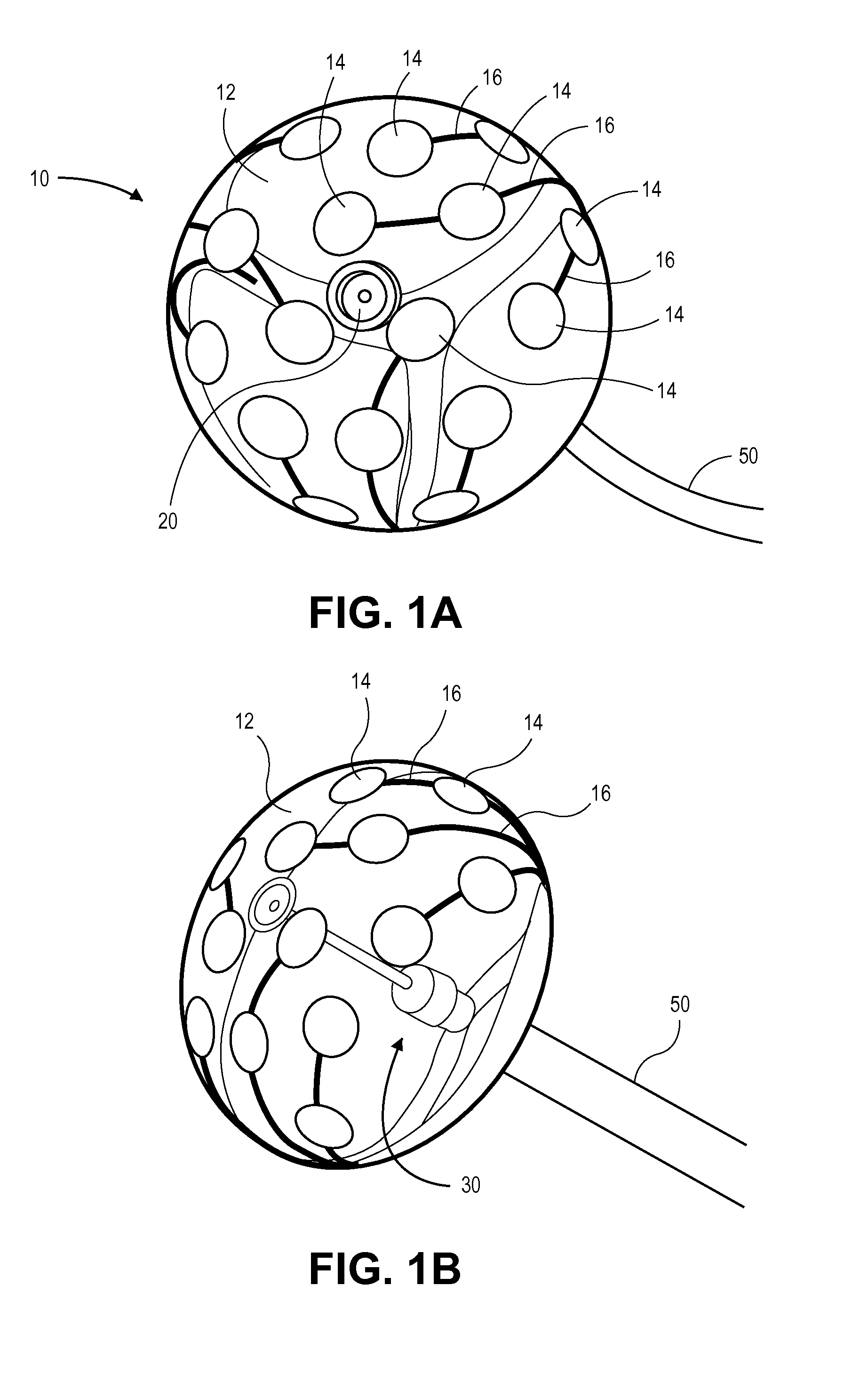
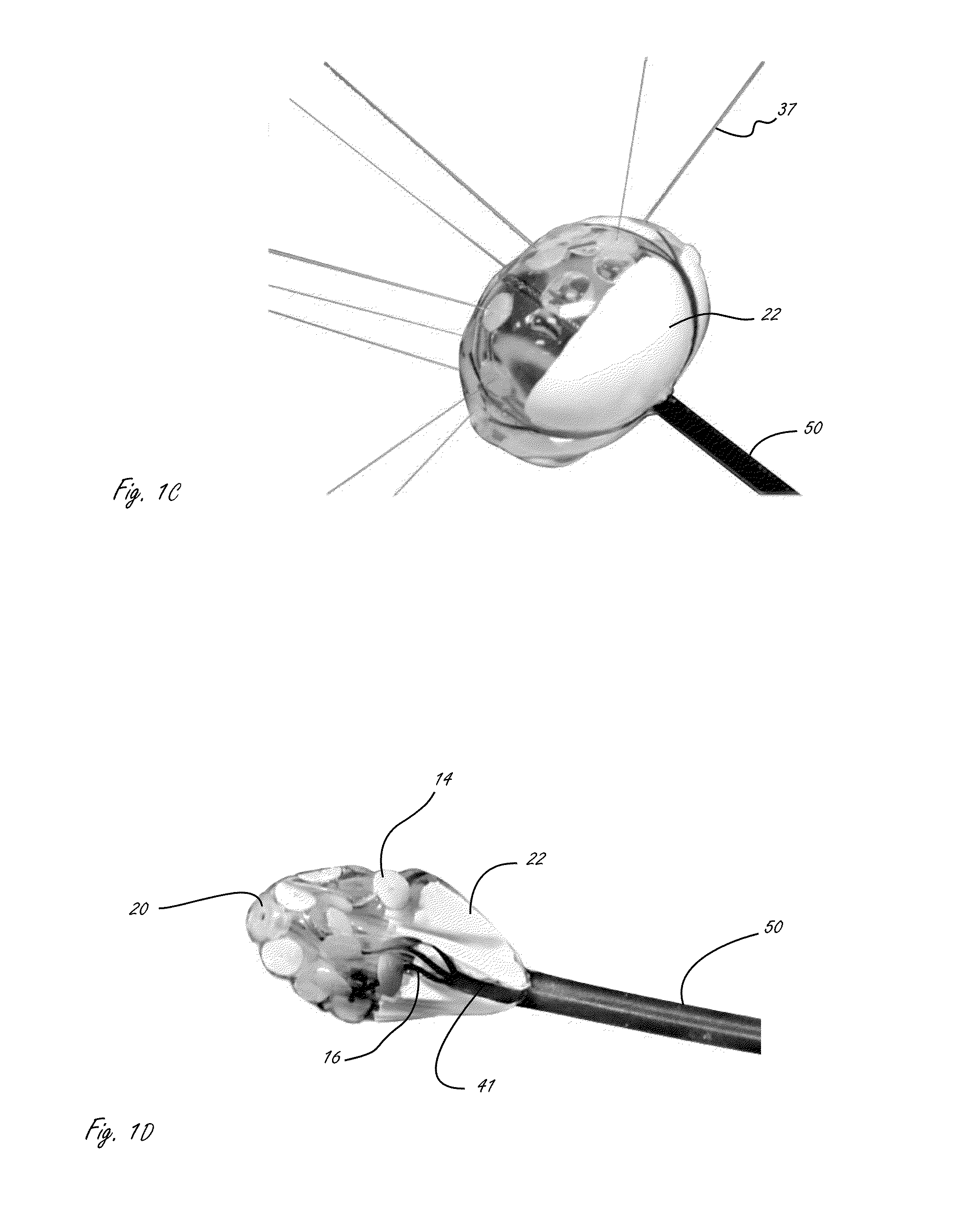
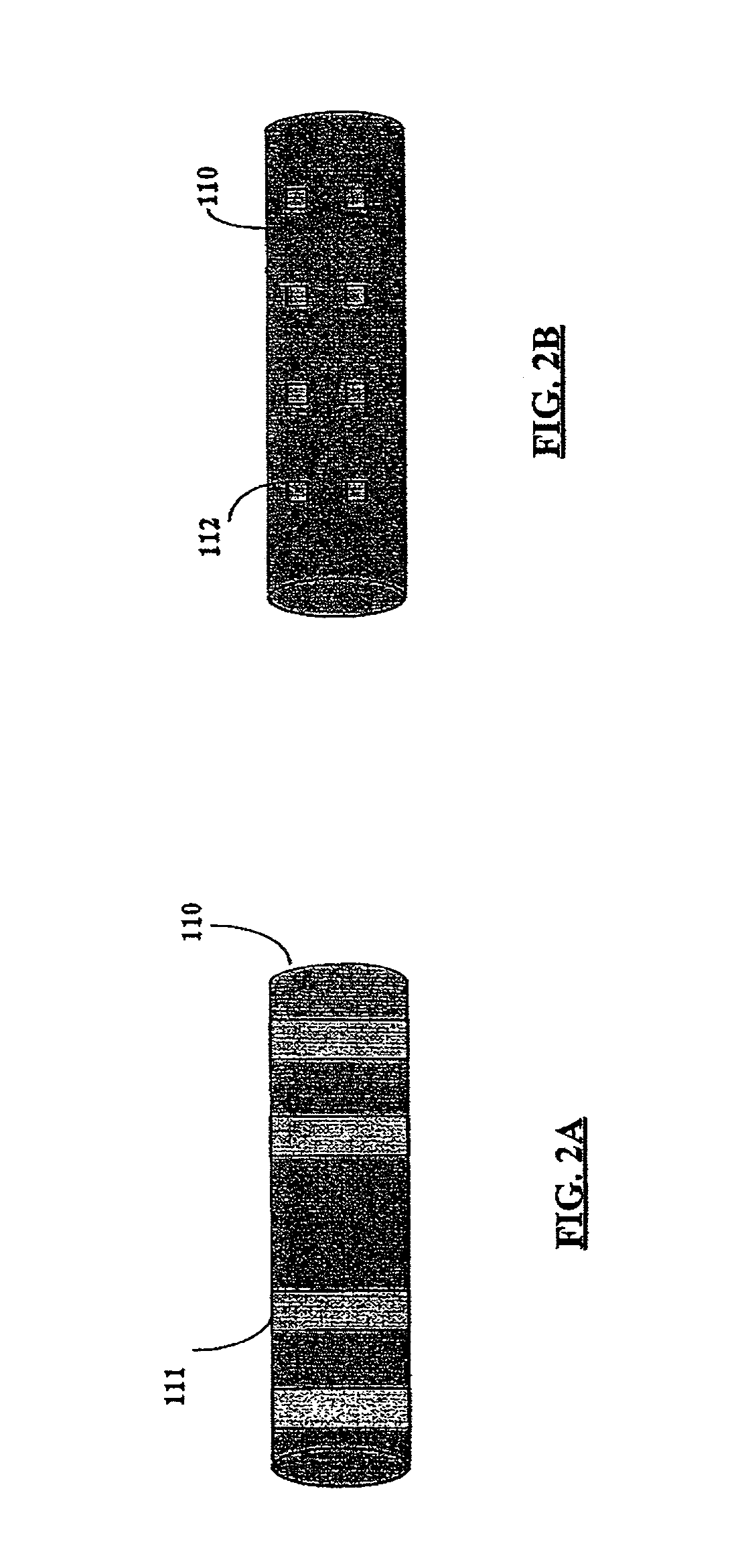
According to the present invention, a catheter having at least one multi-purpose lumen formed through the catheter terminates proximal a relatively complex-shaped distal portion thereof. In one form of this embodiment, the relatively complex-shaped distal portion comprises a looped portion having diagnostic- and / or ablation-type electrodes coupled thereto and an elongated diameter-adjusting member coupled proximal the distal end of the looped portion. The multi-purpose lumen may be used to alternately accommodate a variety of dedicated materials; such as, (i) a guide wire for initial deployment or later repositioning of the catheter, (ii) a volume or flow of a contrast media and the like, (iii) a deployable hollow needle or tube and the like used to biopsy adjacent tissue or dispense a therapeutic agent into a volume of tissue, and (iv) a cooling fluid, such as saline solution and the like dispensed at least during therapeutic tissue ablation procedures.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
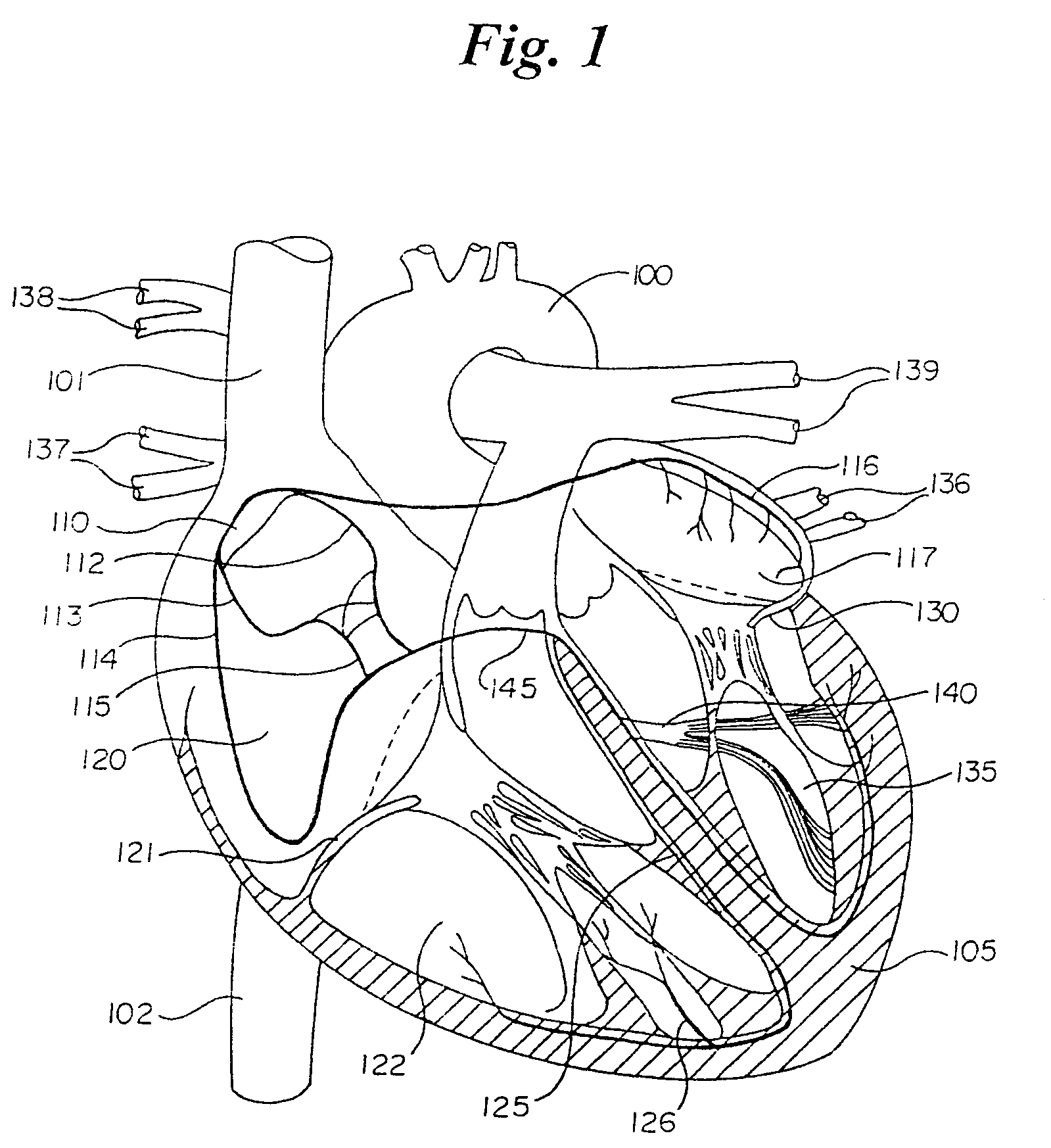
Apparatus and methods for mapping and ablation in electrophysiology procedures
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
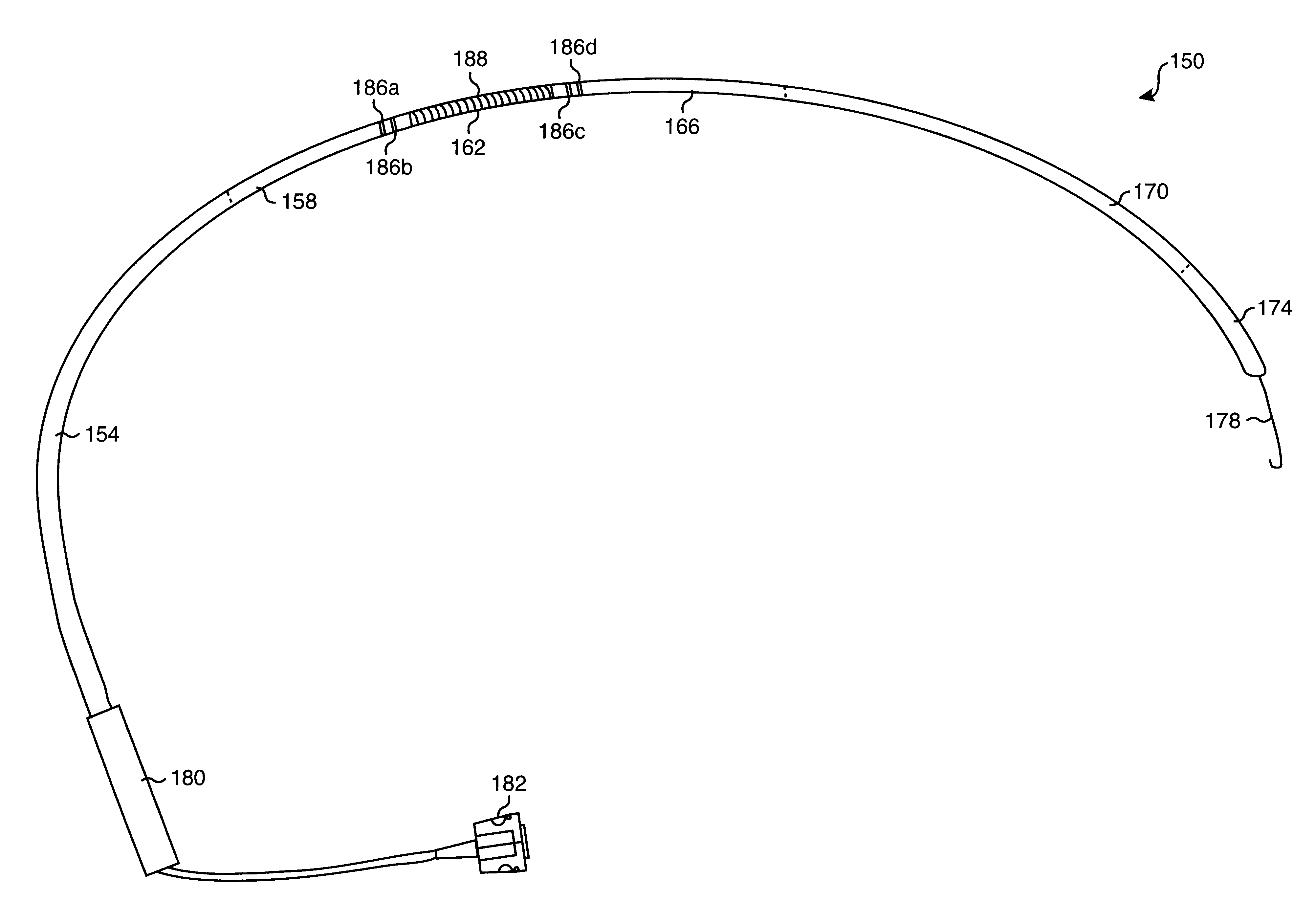
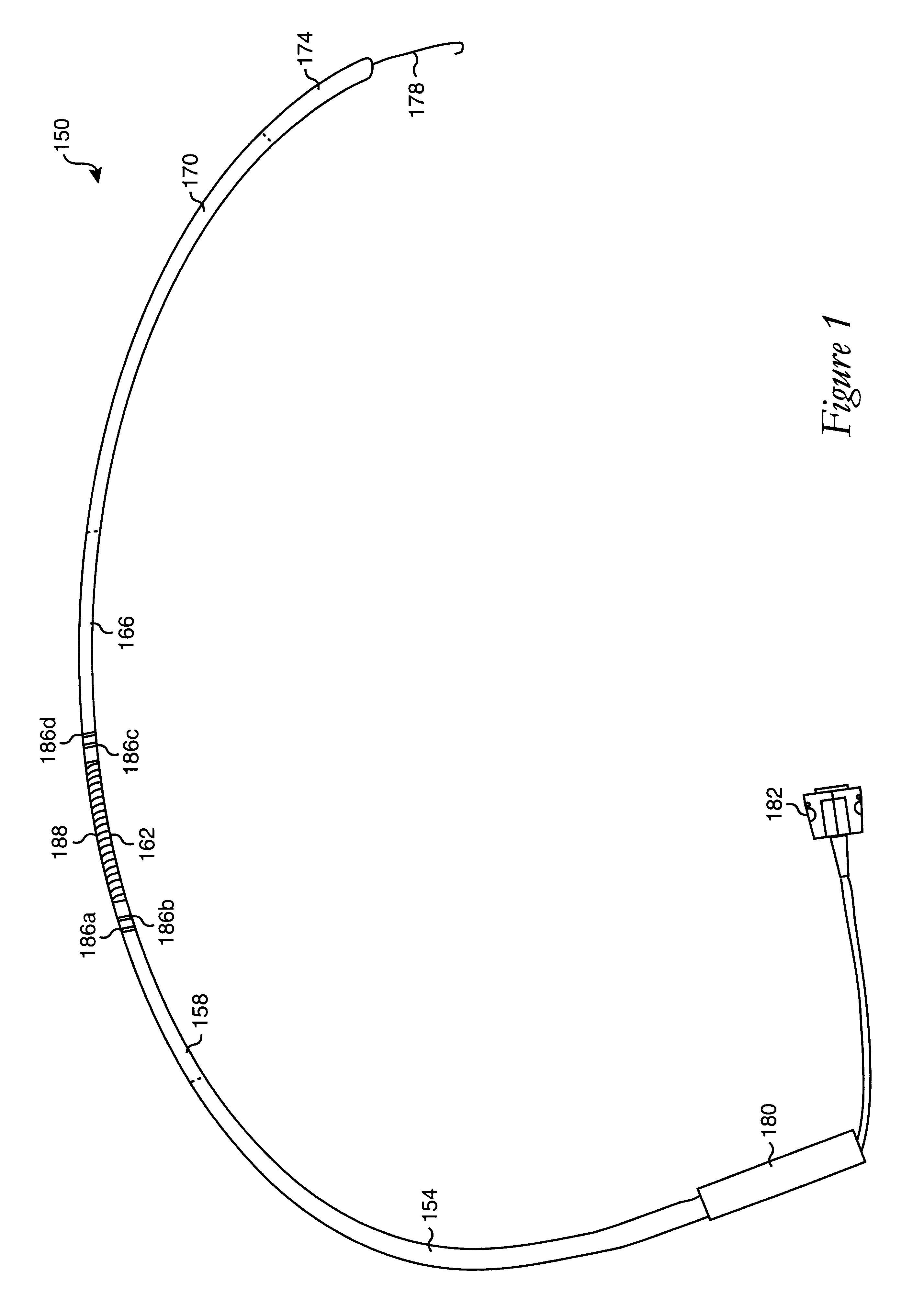
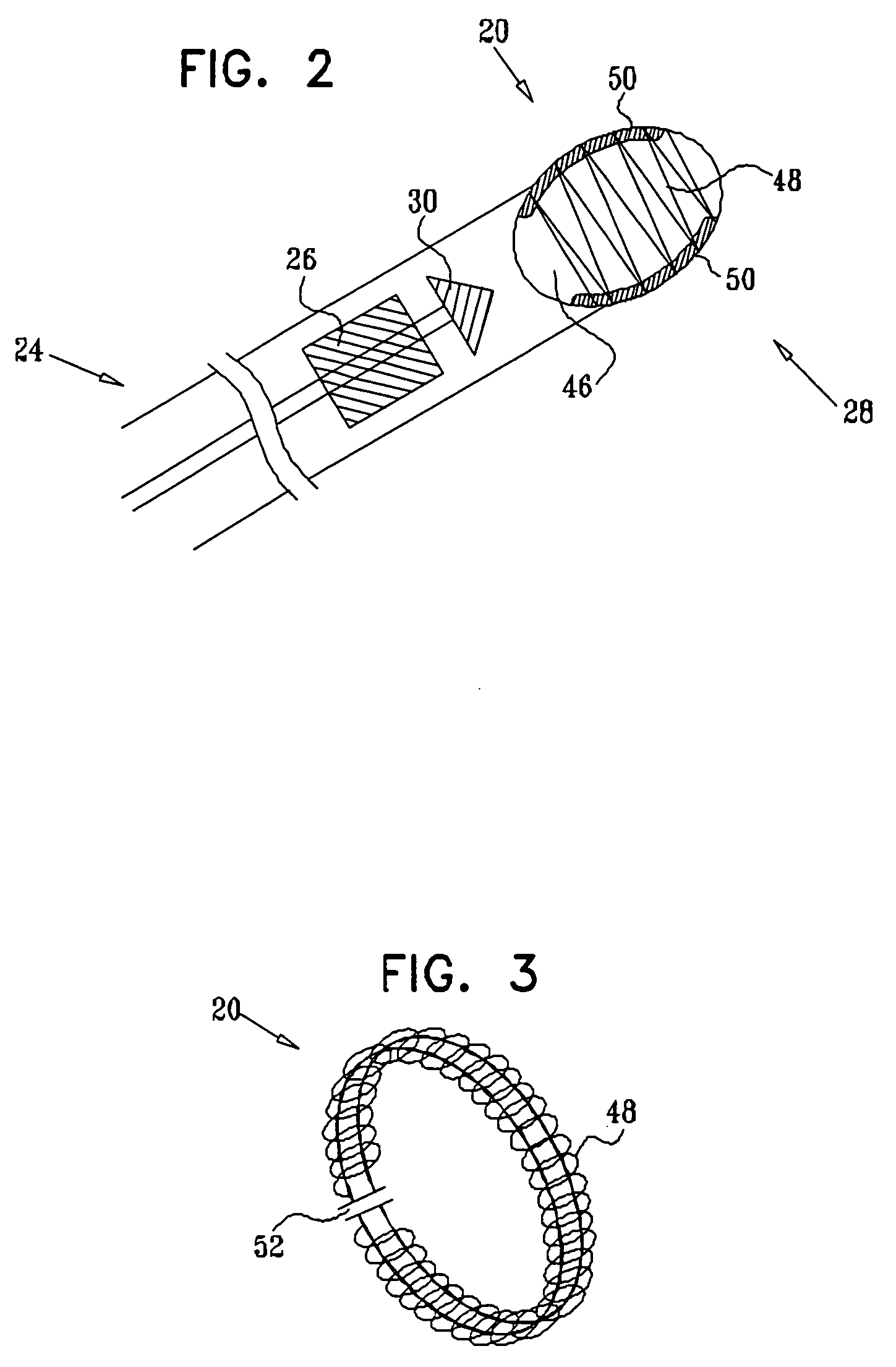
Microwave ablation catheter with loop configuration
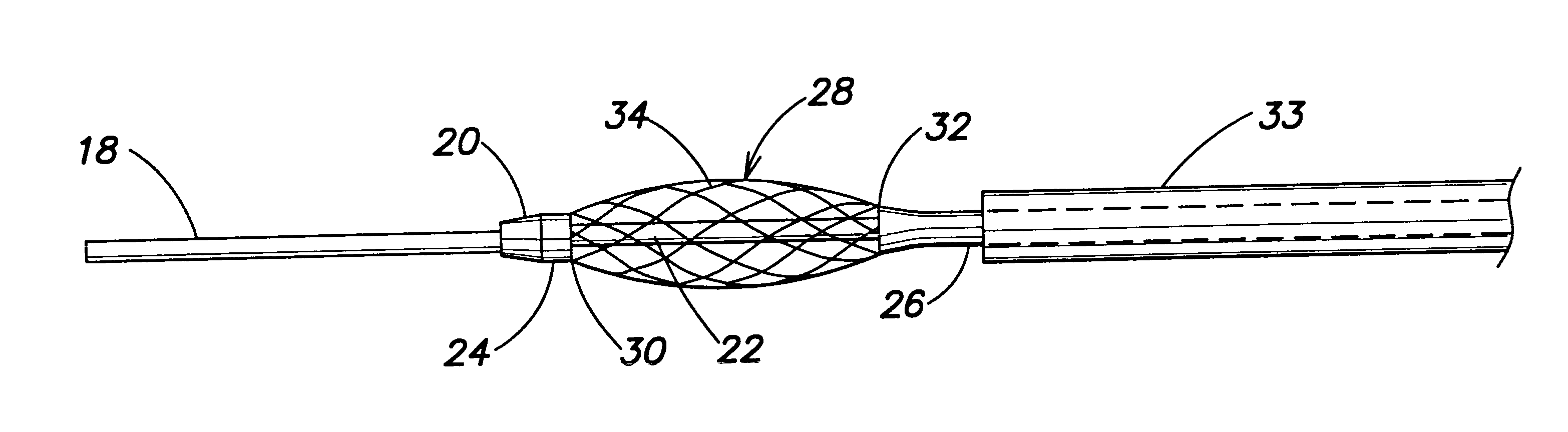
A catheter which may be configured as a loop during an ablation procedure, and a method of use for such a catheter, are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, an ablation catheter includes a flexible distal member arranged to inserted into a first vessel in the body of a patient, and an elongated flexible tubular member with a distal portion which is coupled to a proximal portion of the flexible distal member. The elongated flexible tubular member has a flexibility that is greater than or equal to the flexibility of the flexible distal member. The catheter also includes a transmission line which is at least partially disposed within the elongated flexible tubular member. A proximal end of the transmission line is suitable for connection to an electromagnetic energy source. The catheter further includes a transducer that is coupled to the transmission line, and is arranged to generate an electric field sufficiently strong to cause tissue ablation. In one embodiment, a distal portion of the flexible distal member is arranged to protrude from a second vessel of the body of the patient while at least part of the elongated flexible tubular member is located in a cardiac chamber of the heart of the patient.
Owner:AFX
Ablation instrument having a flexible distal portion
InactiveUS6893436B2Increased mechanical advantageAccurate placementDiagnosticsCatheterProximateDistal portion
An ablation instrument having a flexible portion at or near the distal portion of the instrument, is provided. The instrument includes an elongated tubular member having a steerable distal end configured to deflect, or otherwise direct, and properly position at least a portion of the distal portion, comprising an ablation device, during an ablation procedure. The instrument further includes a deflectable member which cooperates with the steering system allowing for the proper placement of the ablation device adjacent or proximate to the target tissue surface. The steering system may alternatively be incorporated into a separate guiding catheter as part of the catheter system.
Owner:AFX +1
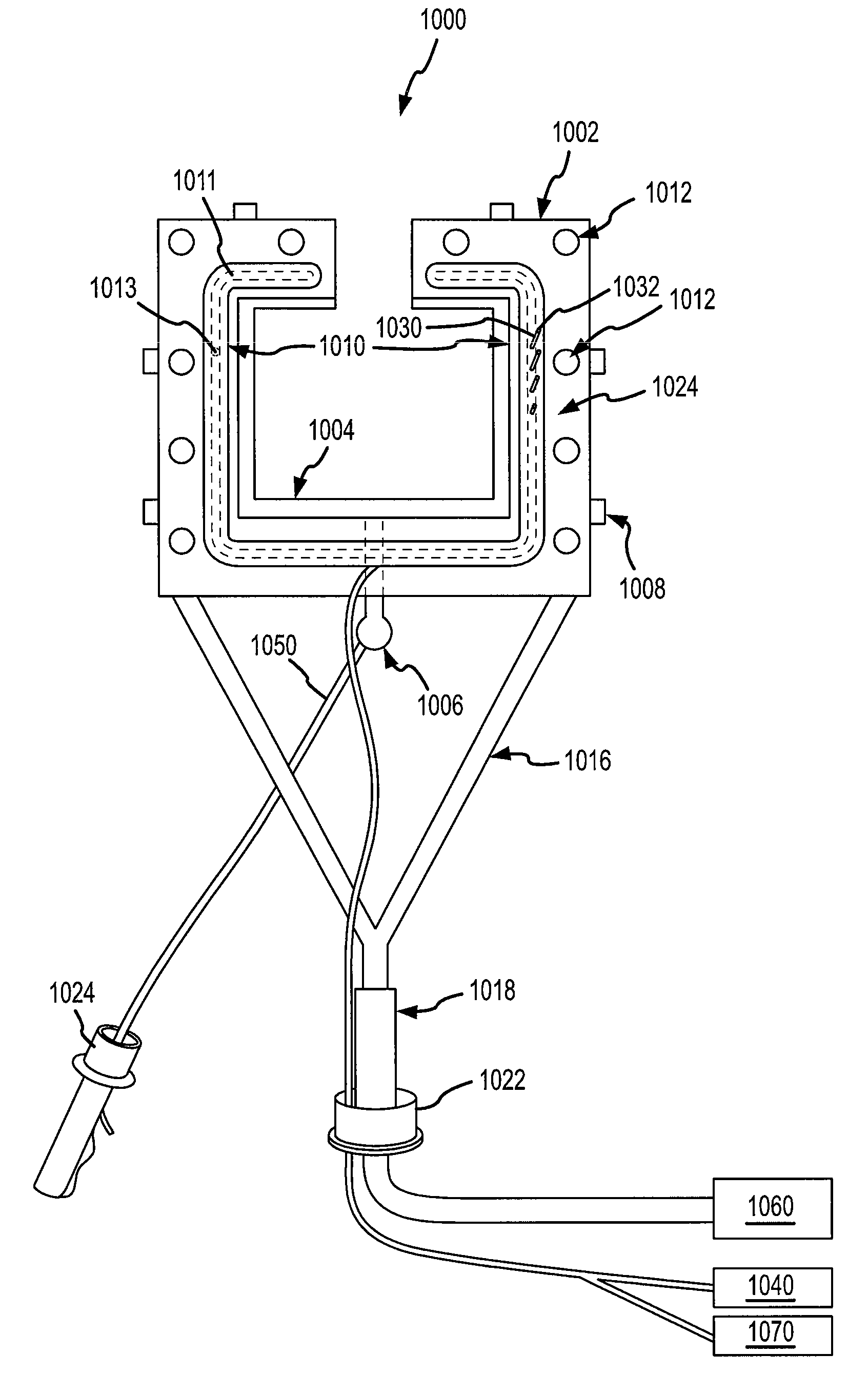
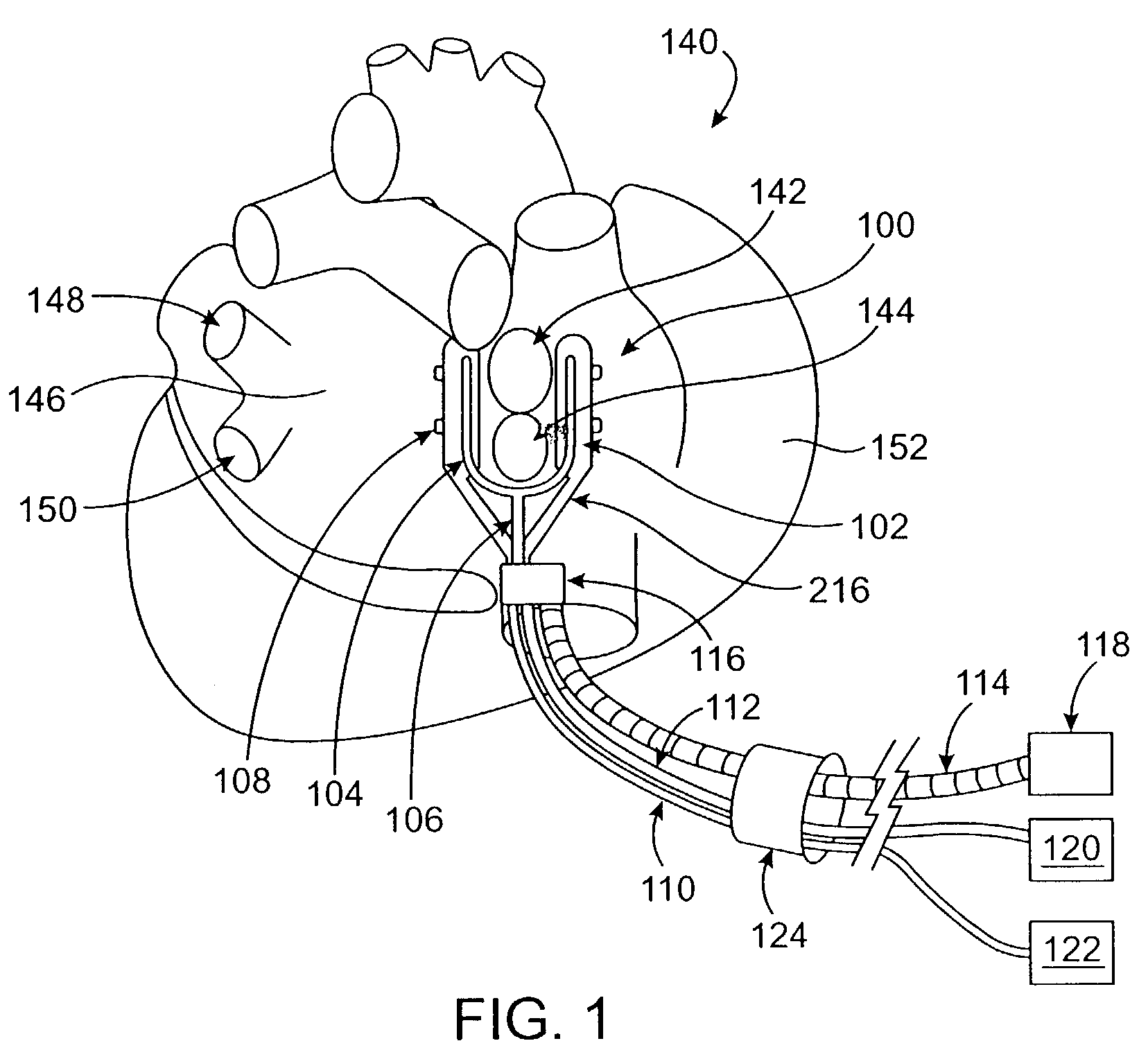
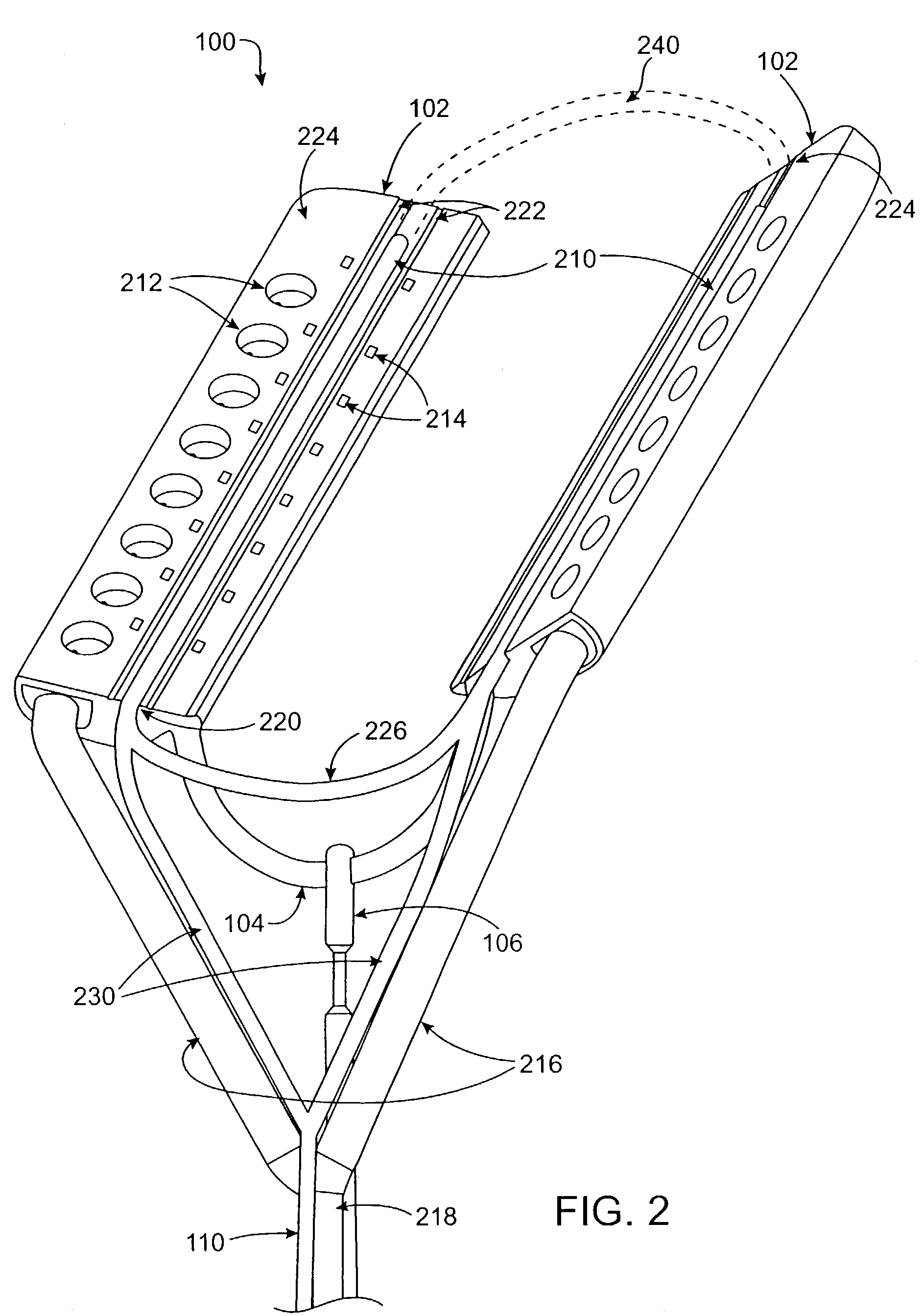
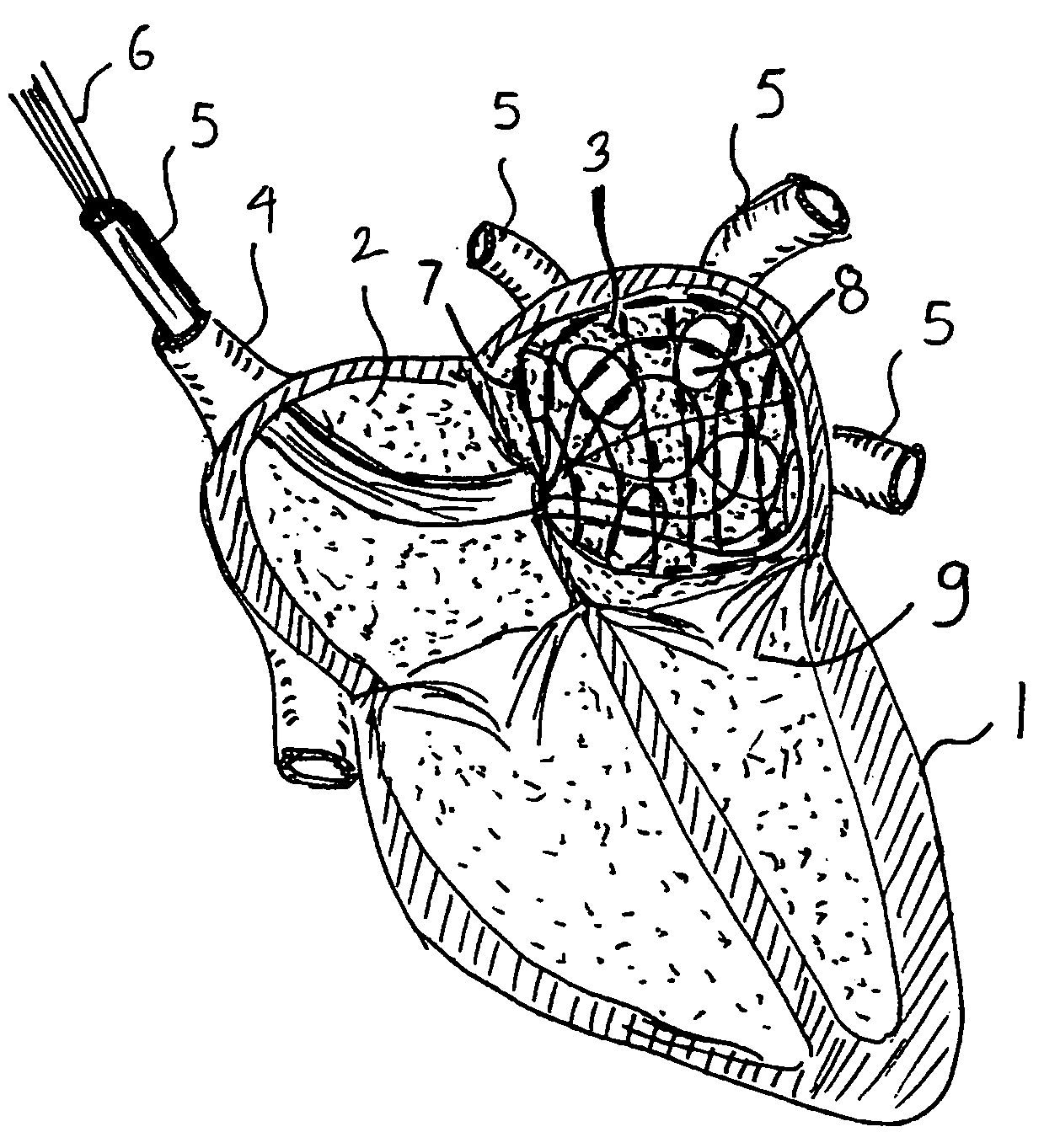
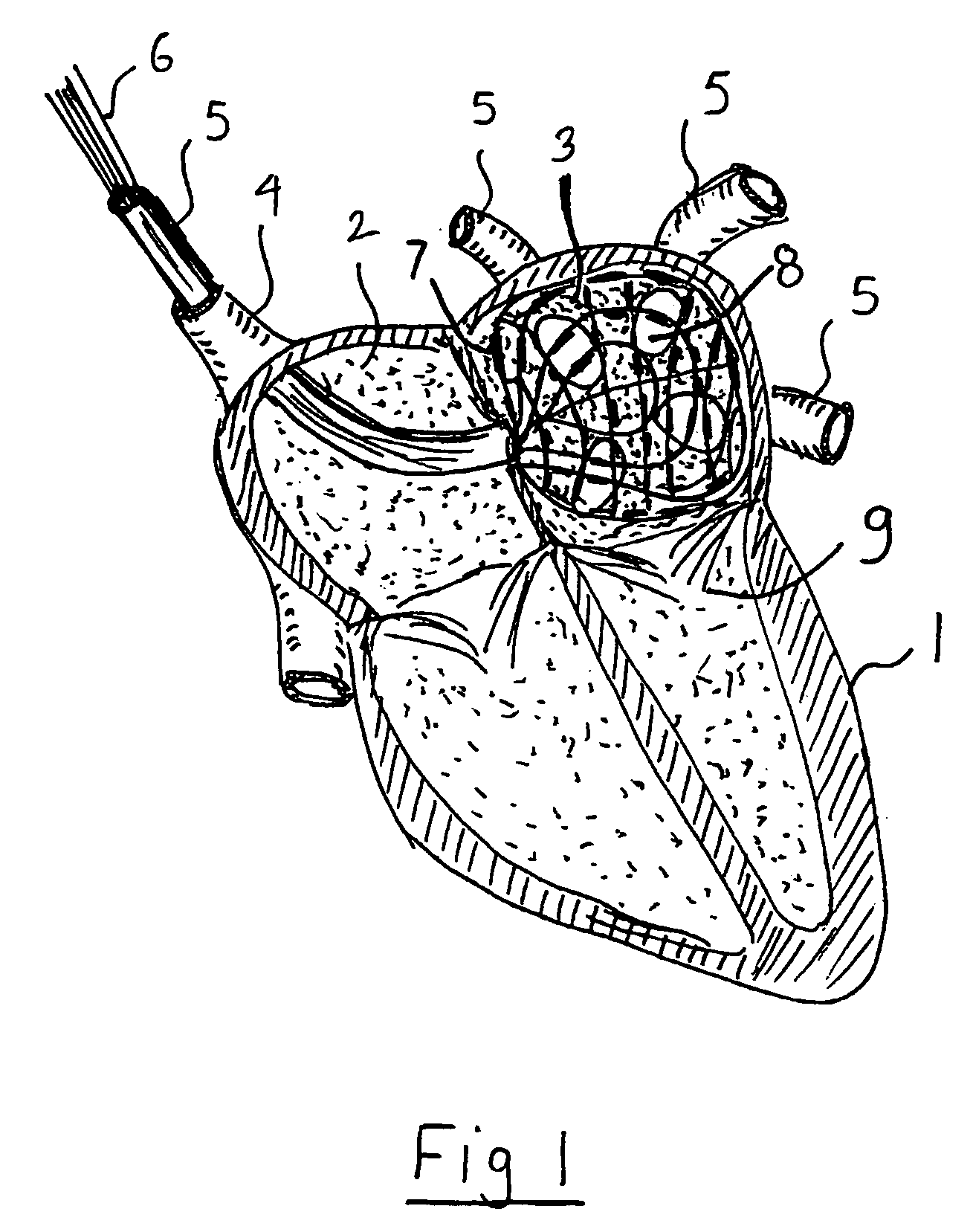
Cardiac treatment devices and methods
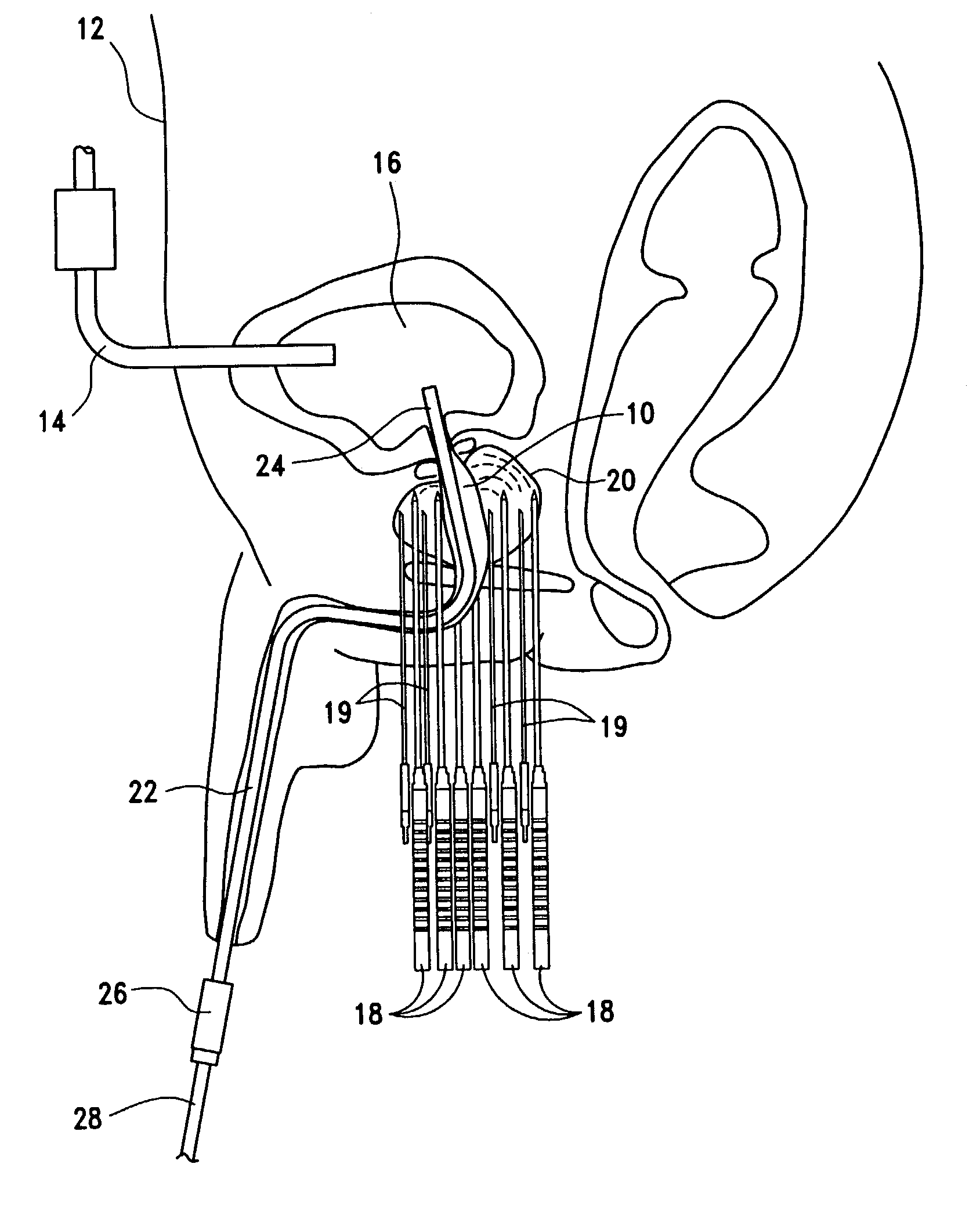
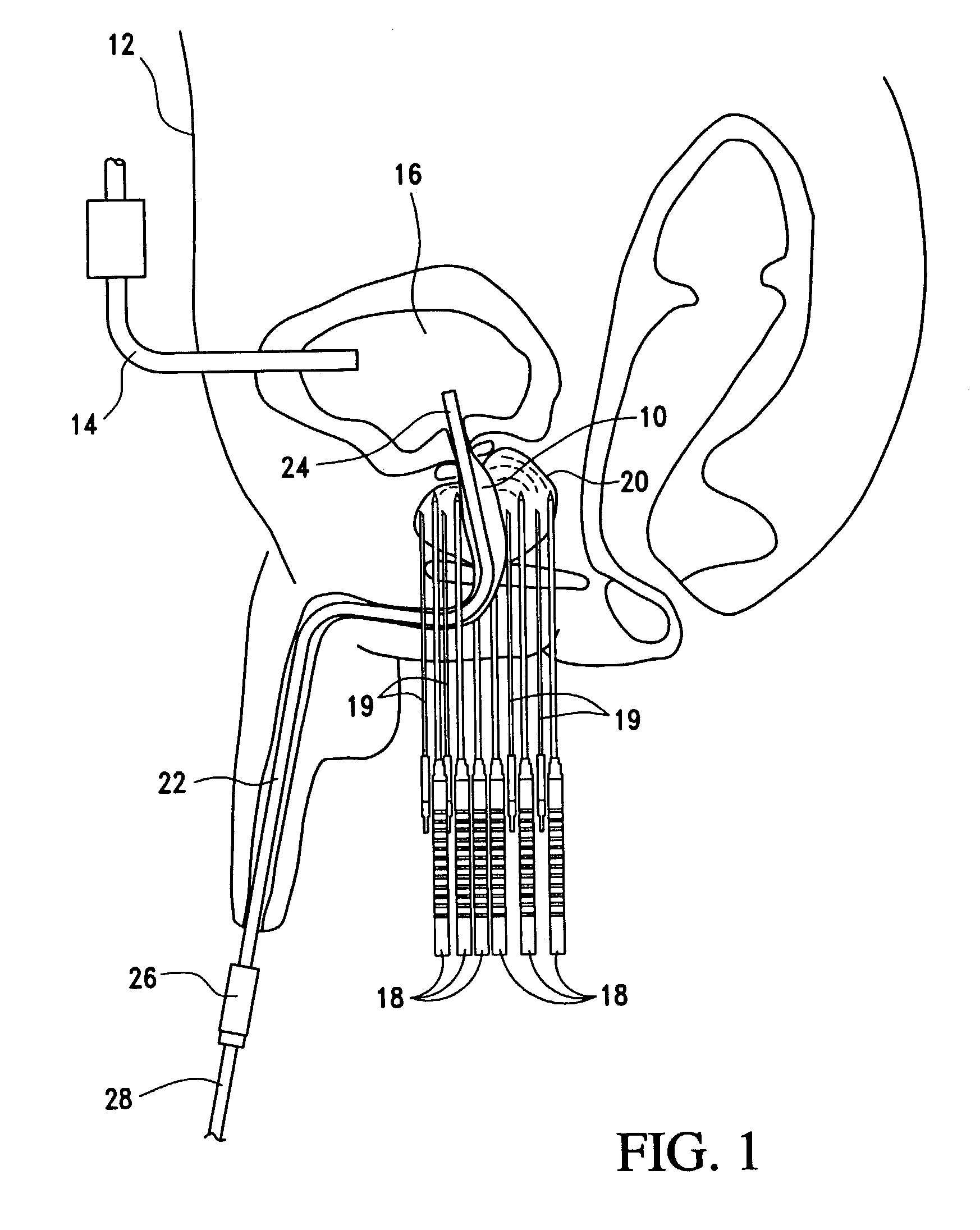
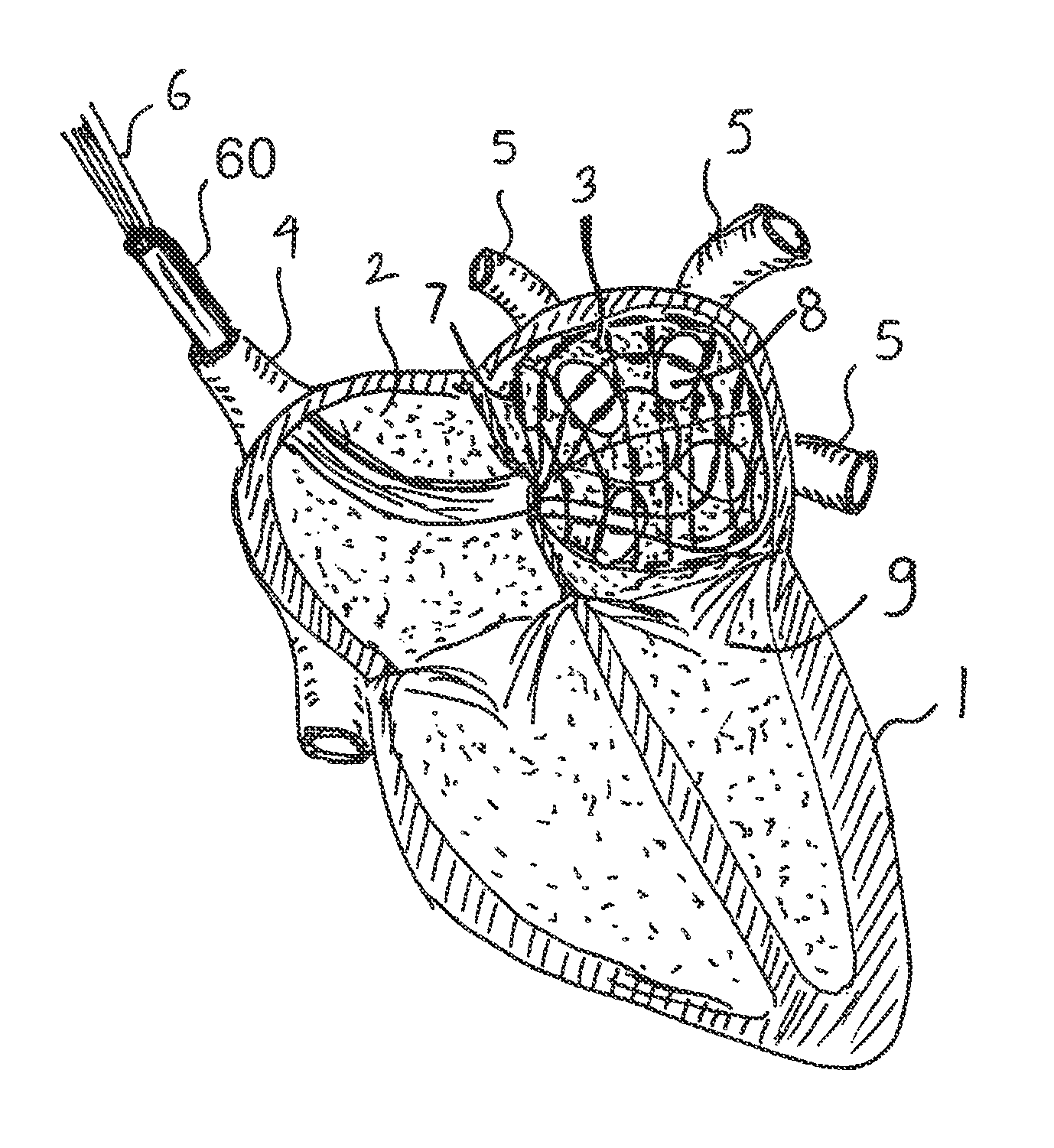
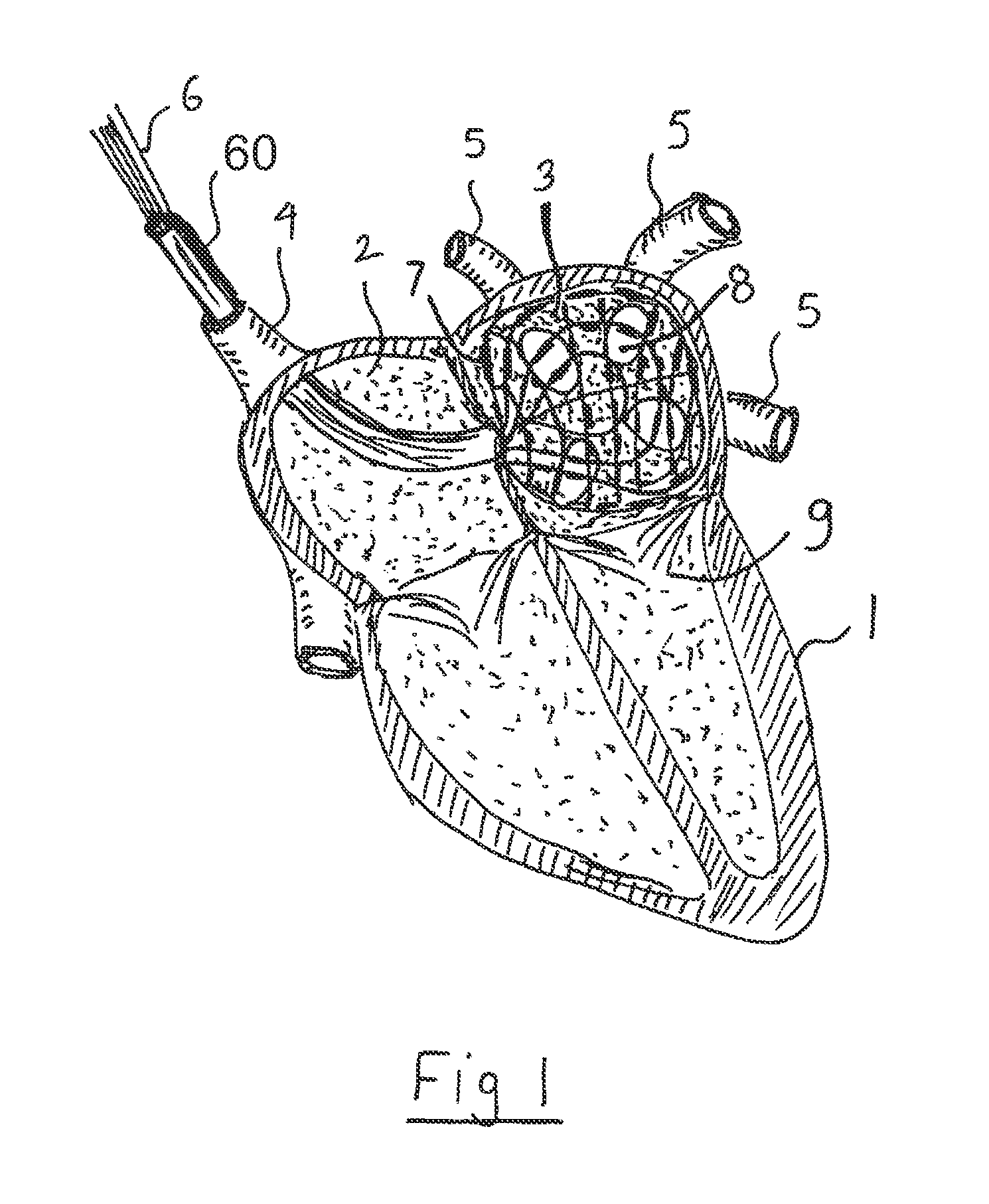
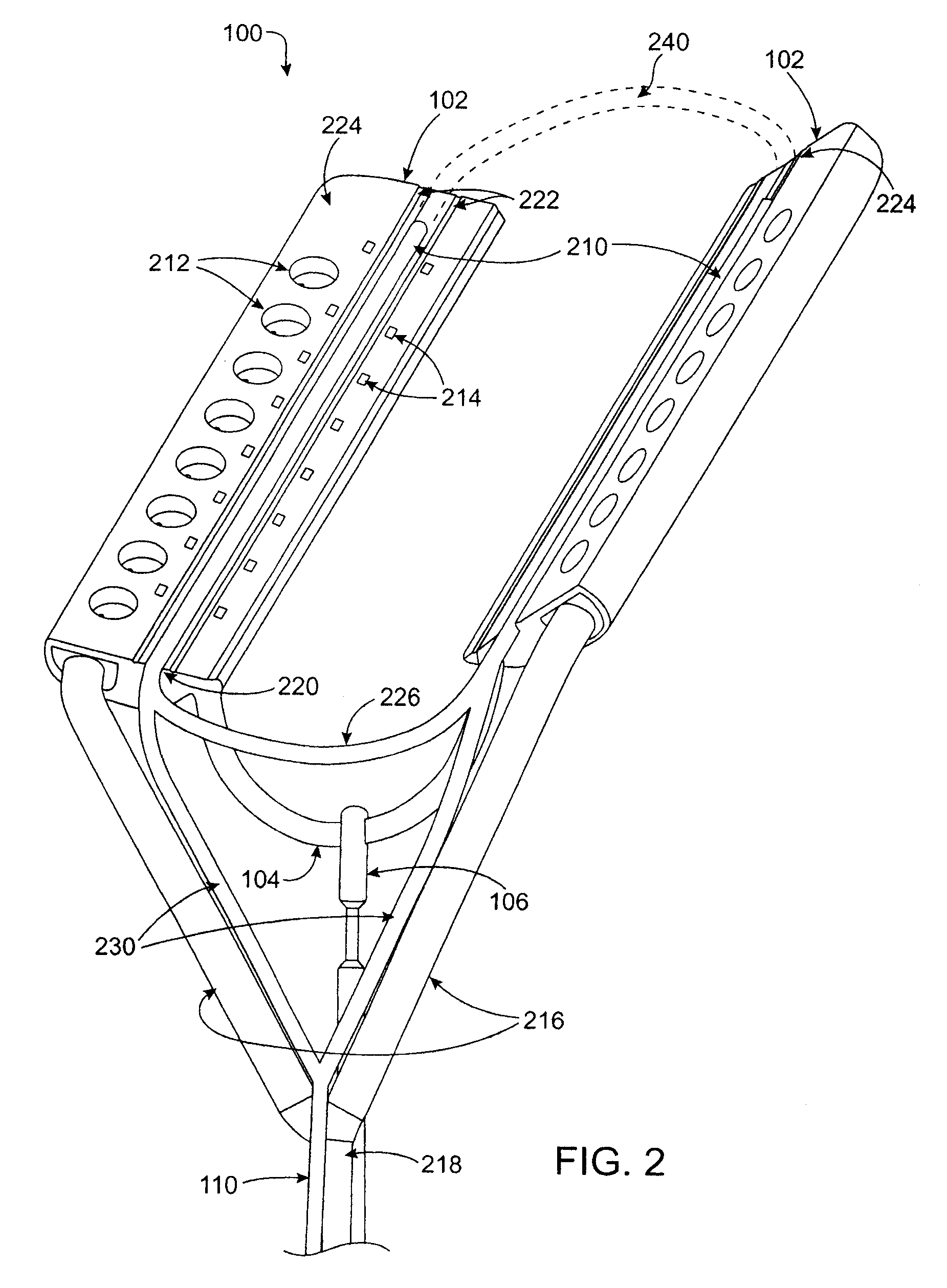
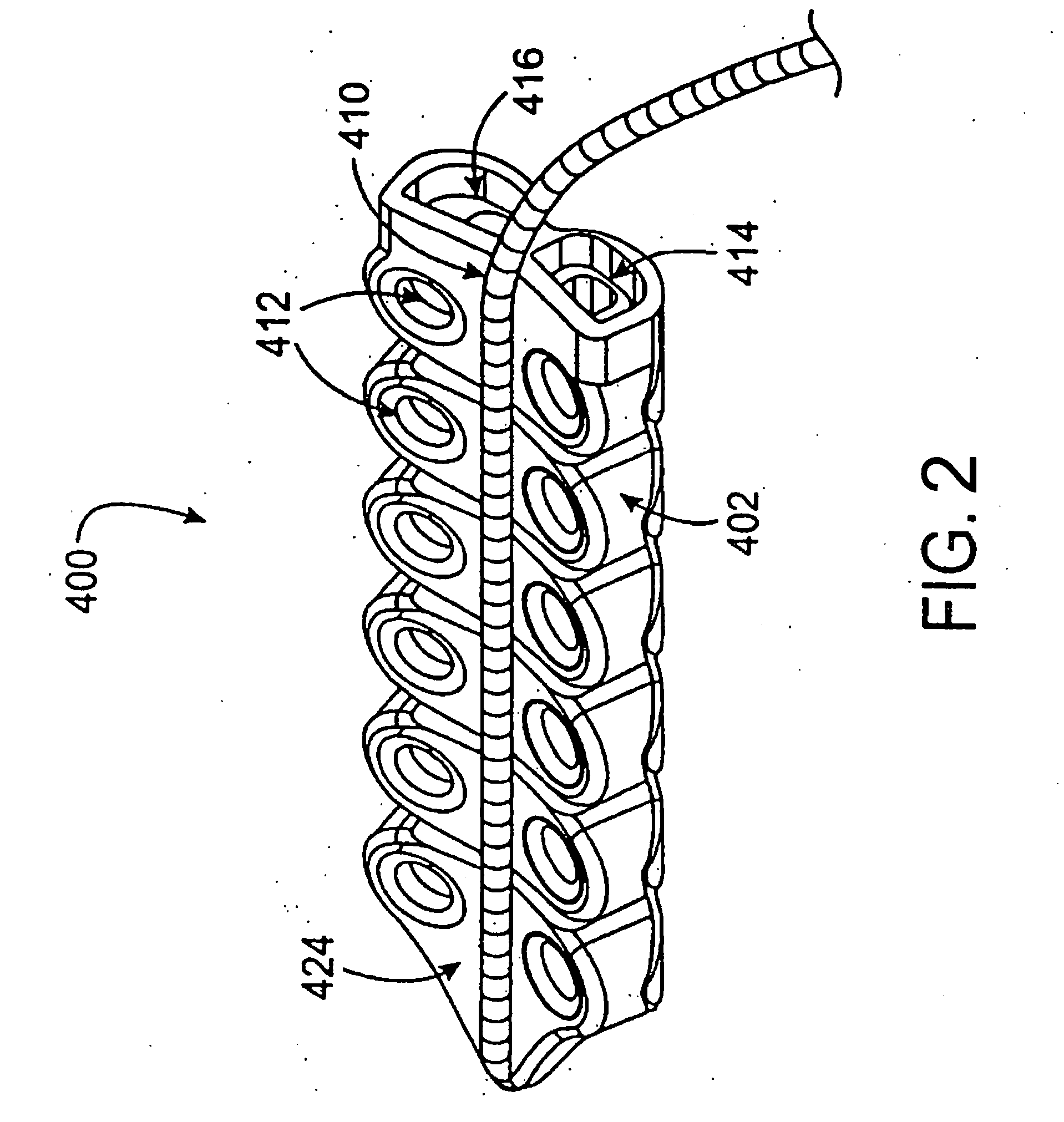
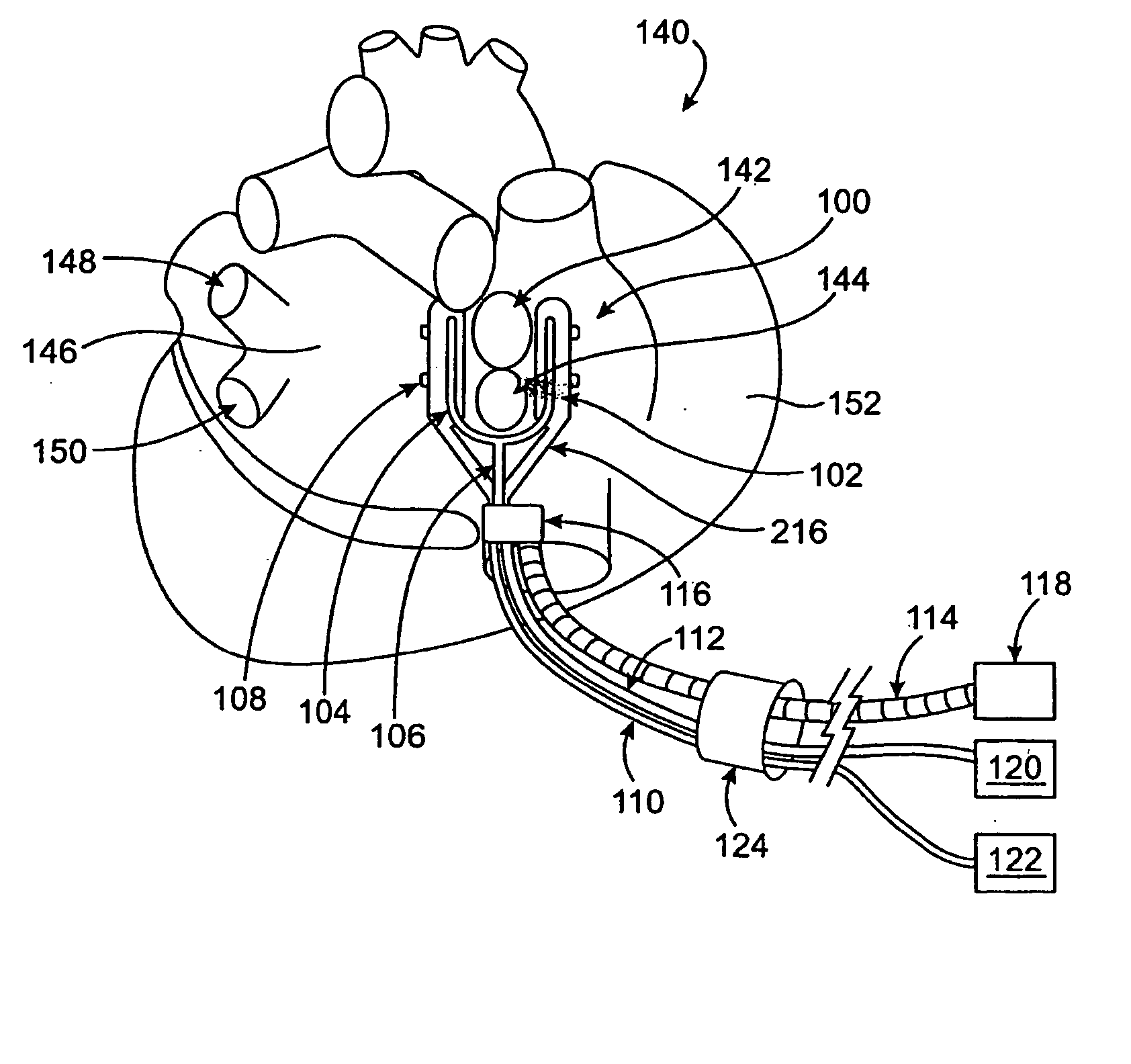
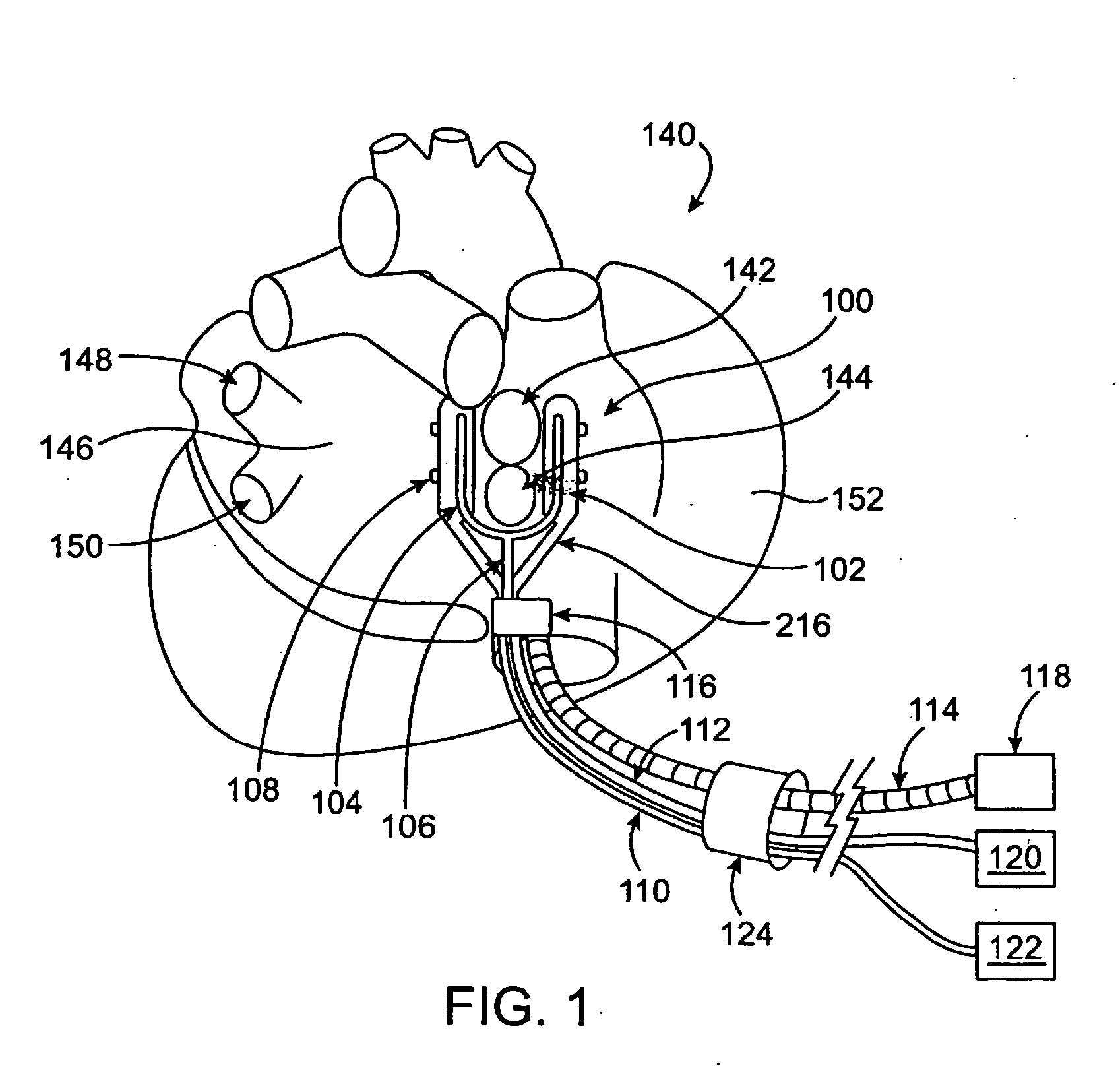
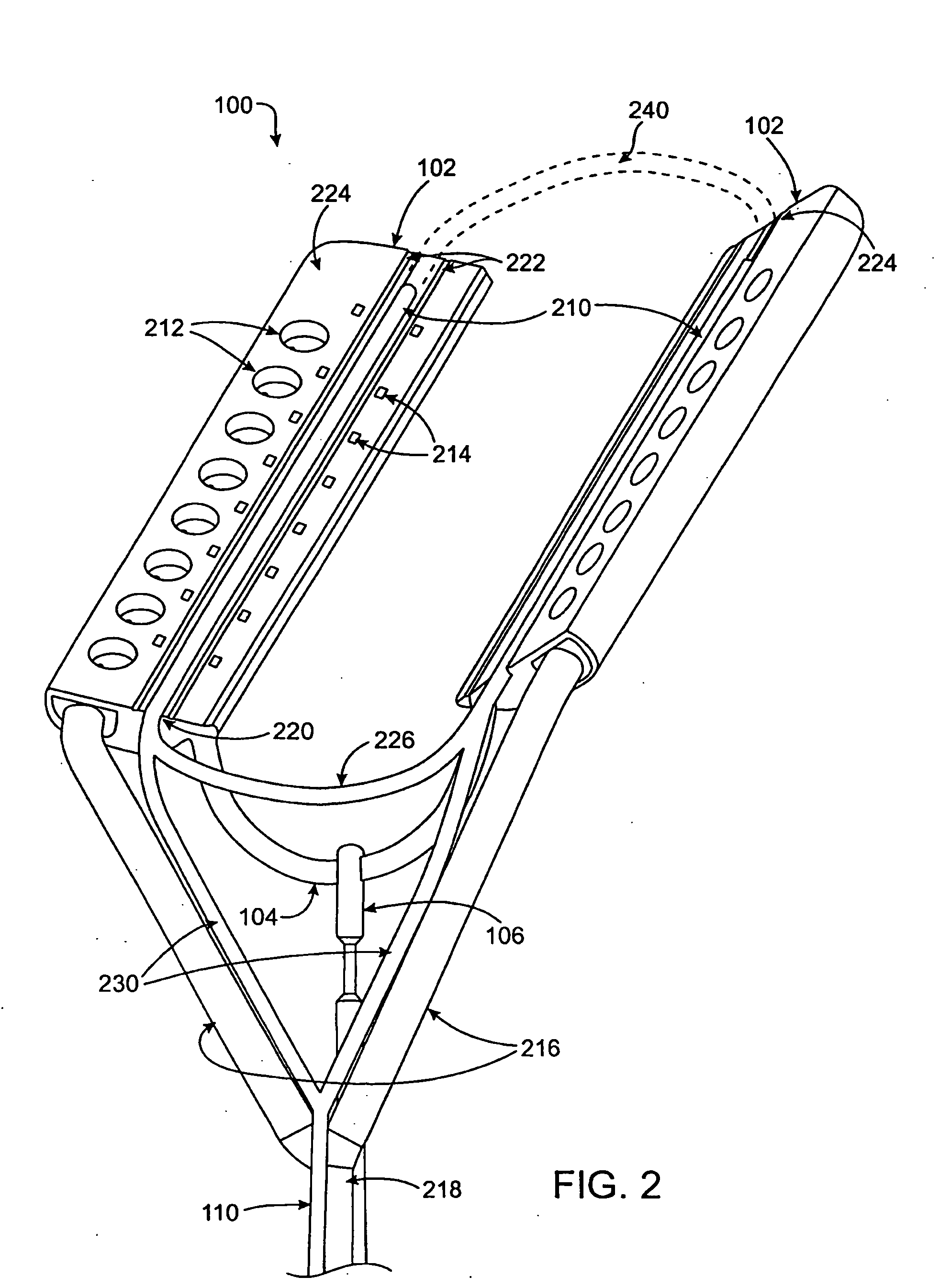
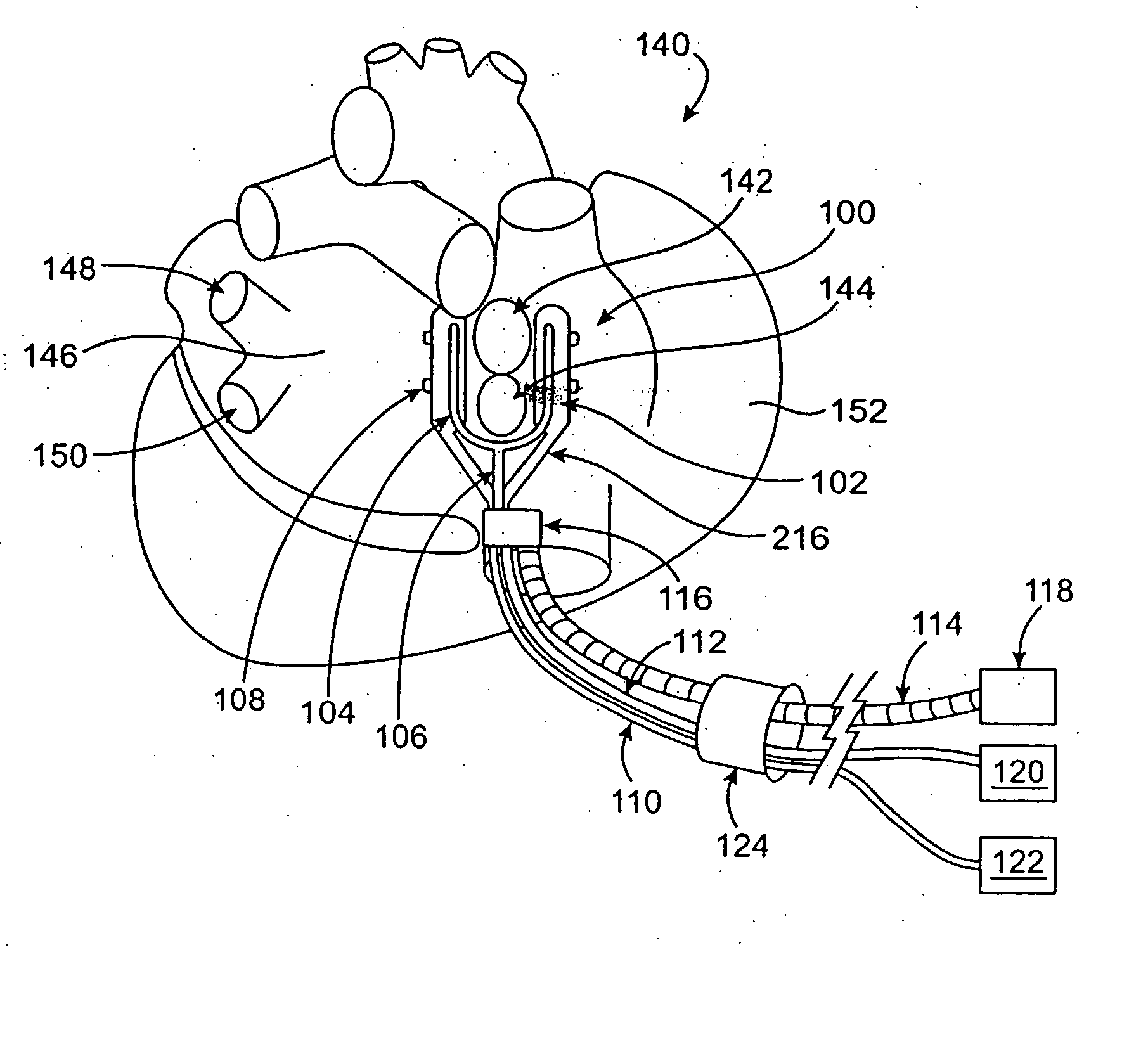
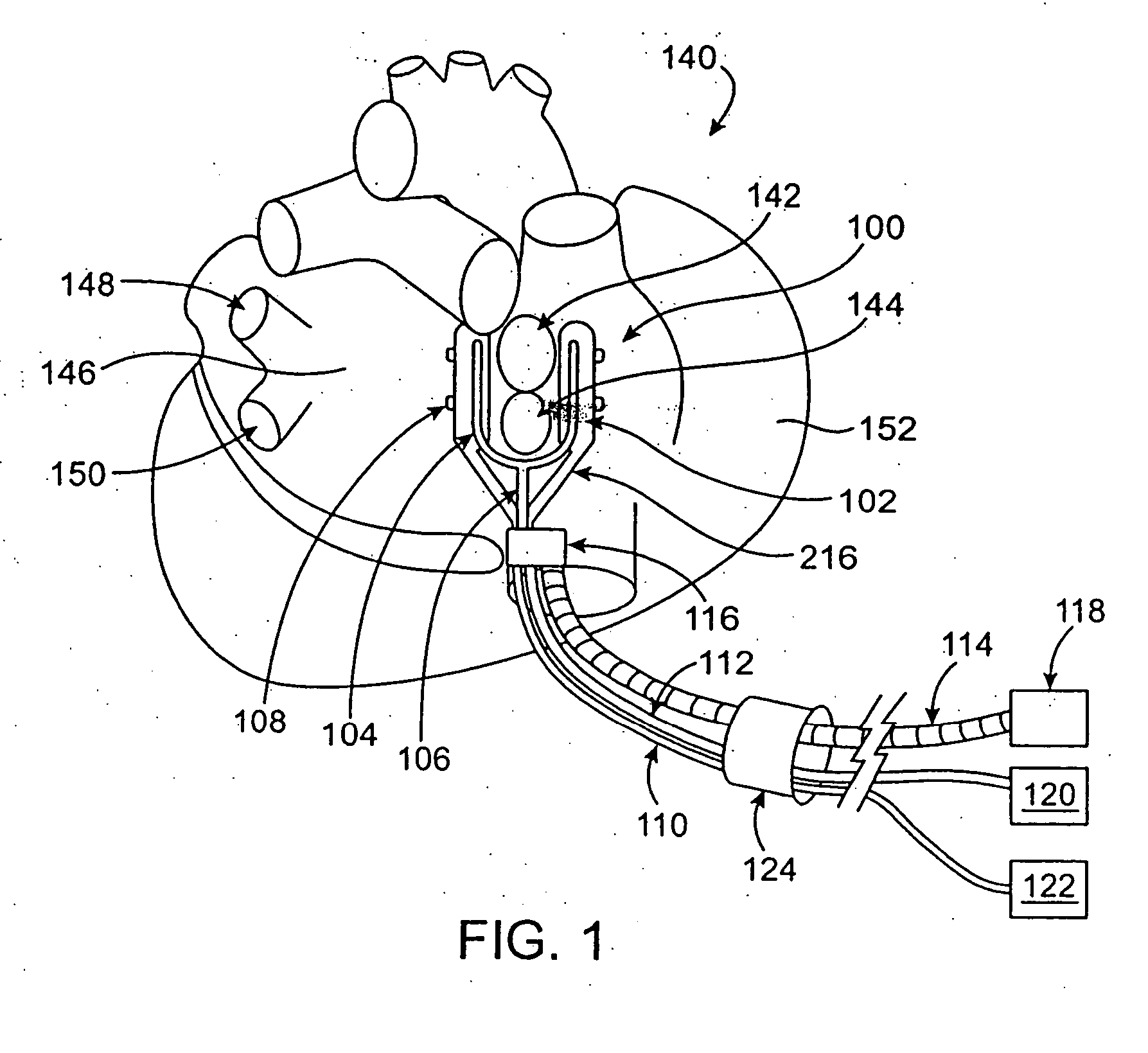
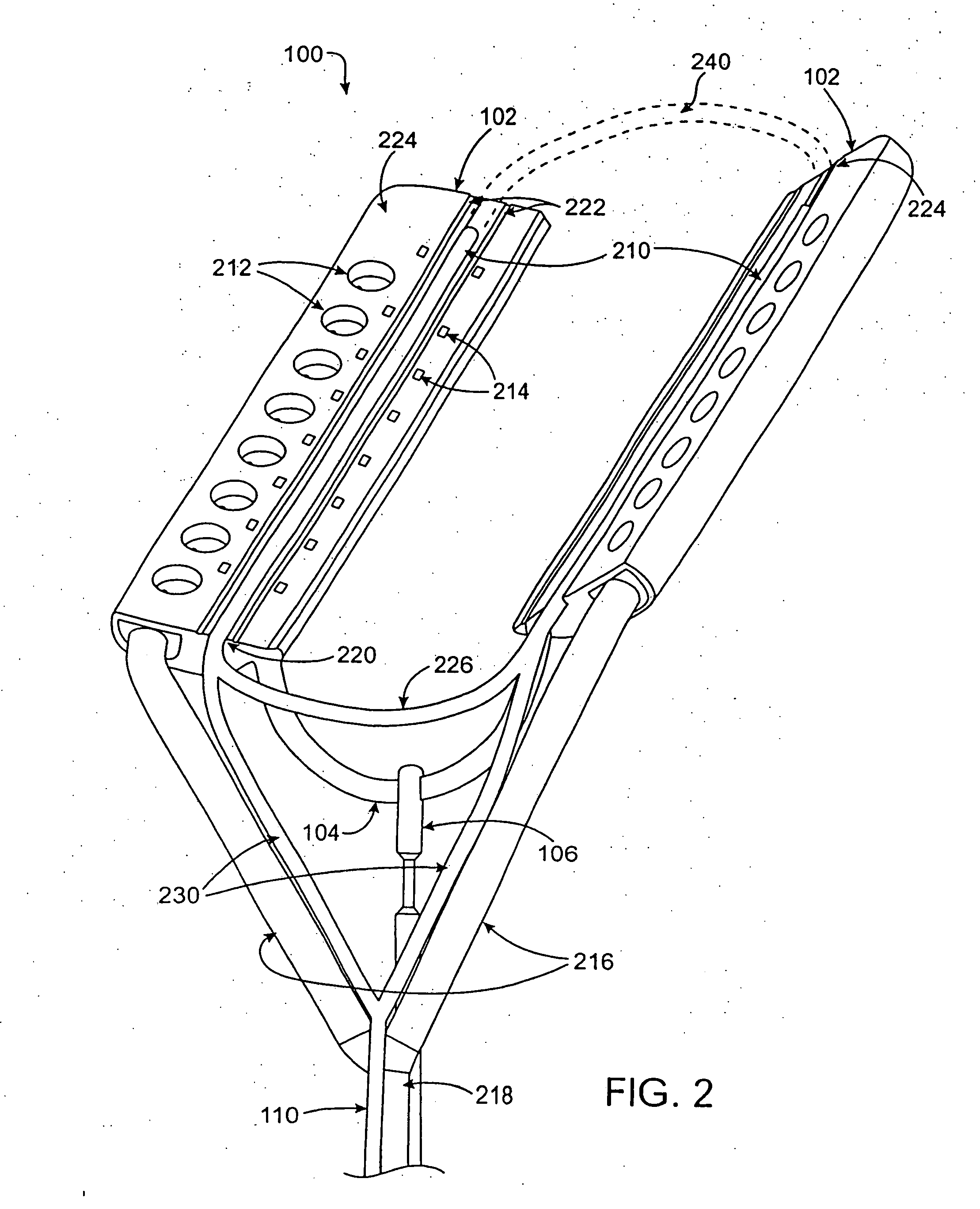
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ESTECH ENDOSCOPIC TECH +1
Ablation system and method of use
A system and method for creating lesions and assessing their completeness or transmurality. Assessment of transmurality of a lesion is accomplished by monitoring the impedance of the tissue to be ablated. Rather than attempting to detect a desired drop or a desired increase impedance, completeness of a lesion is detected in response to the measured impedance remaining at a stable level for a desired period of time, referred to as an impedance plateau. The mechanism for determining transmurality of lesions adjacent individual electrodes or pairs may be used to deactivate individual electrodes or electrode pairs, when the lesions in tissue adjacent these individual electrodes or electrode pairs are complete, to create an essentially uniform lesion along the line of electrodes or electrode pairs, regardless of differences in tissue thickness adjacent the individual electrodes or electrode pairs. Complete or partial submersion in a fluid of the ablating portion of the ablation device may be detected prior to, during or following an ablation procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for magnetic-resonance-guided electrophysiologic and ablation procedures
InactiveUS7155271B2Increased resolution and reliabilityImprove accuracySurgical instrument detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringMr guidanceMr contrast agent
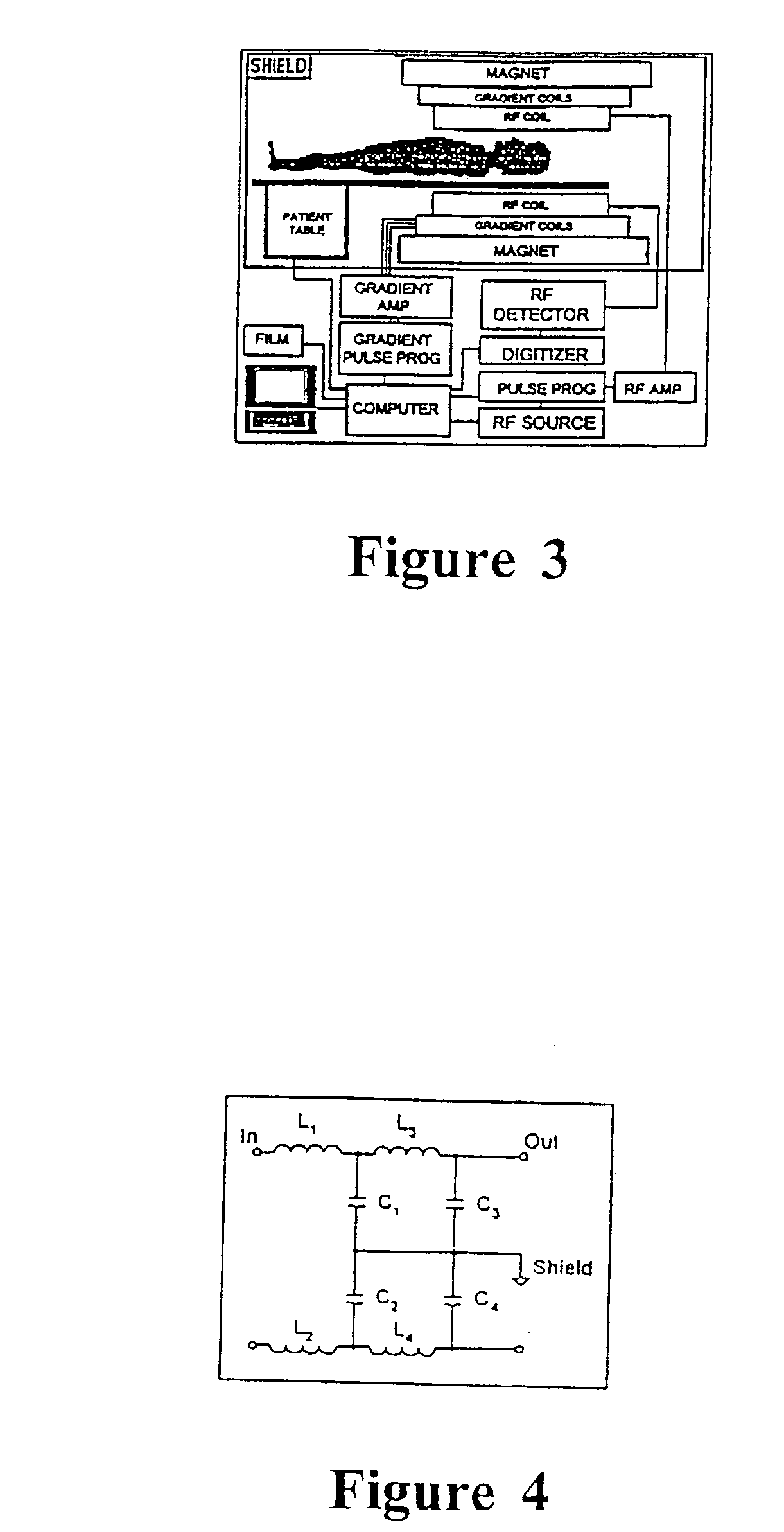
A system and method for using magnetic resonance imaging to increase the accuracy of electrophysiologic procedures is disclosed. The system in its preferred embodiment provides an invasive combined electrophysiology and imaging antenna catheter which includes an RF antenna for receiving magnetic resonance signals and diagnostic electrodes for receiving electrical potentials. The combined electrophysiology and imaging antenna catheter is used in combination with a magnetic resonance imaging scanner to guide and provide visualization during electrophysiologic diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. The invention is particularly applicable to catheter ablation, e.g., ablation of atrial fibrillation. In embodiments which are useful for catheter ablation, the combined electrophysiology and imaging antenna catheter may further include an ablation tip, and such embodiment may be used as an intracardiac device to both deliver energy to selected areas of tissue and visualize the resulting ablation lesions, thereby greatly simplifying production of continuous linear lesions. The invention further includes embodiments useful for guiding electrophysiologic diagnostic and therapeutic procedures other than ablation. Imaging of ablation lesions may be further enhanced by use of MR contrast agents. The antenna utilized in the combined electrophysiology and imaging catheter for receiving MR signals is preferably of the coaxial or “loopless” type. High-resolution images from the antenna may be combined with low-resolution images from surface coils of the MR scanner to produce a composite image. The invention further provides a system for eliminating the pickup of RF energy in which intracardiac wires are detuned by filtering so that they become very inefficient antennas. An RF filtering system is provided for suppressing the MR imaging signal while not attenuating the RF ablative current. Steering means may be provided for steering the invasive catheter under MR guidance. Other ablative methods can be used such as laser, ultrasound, and low temperatures.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
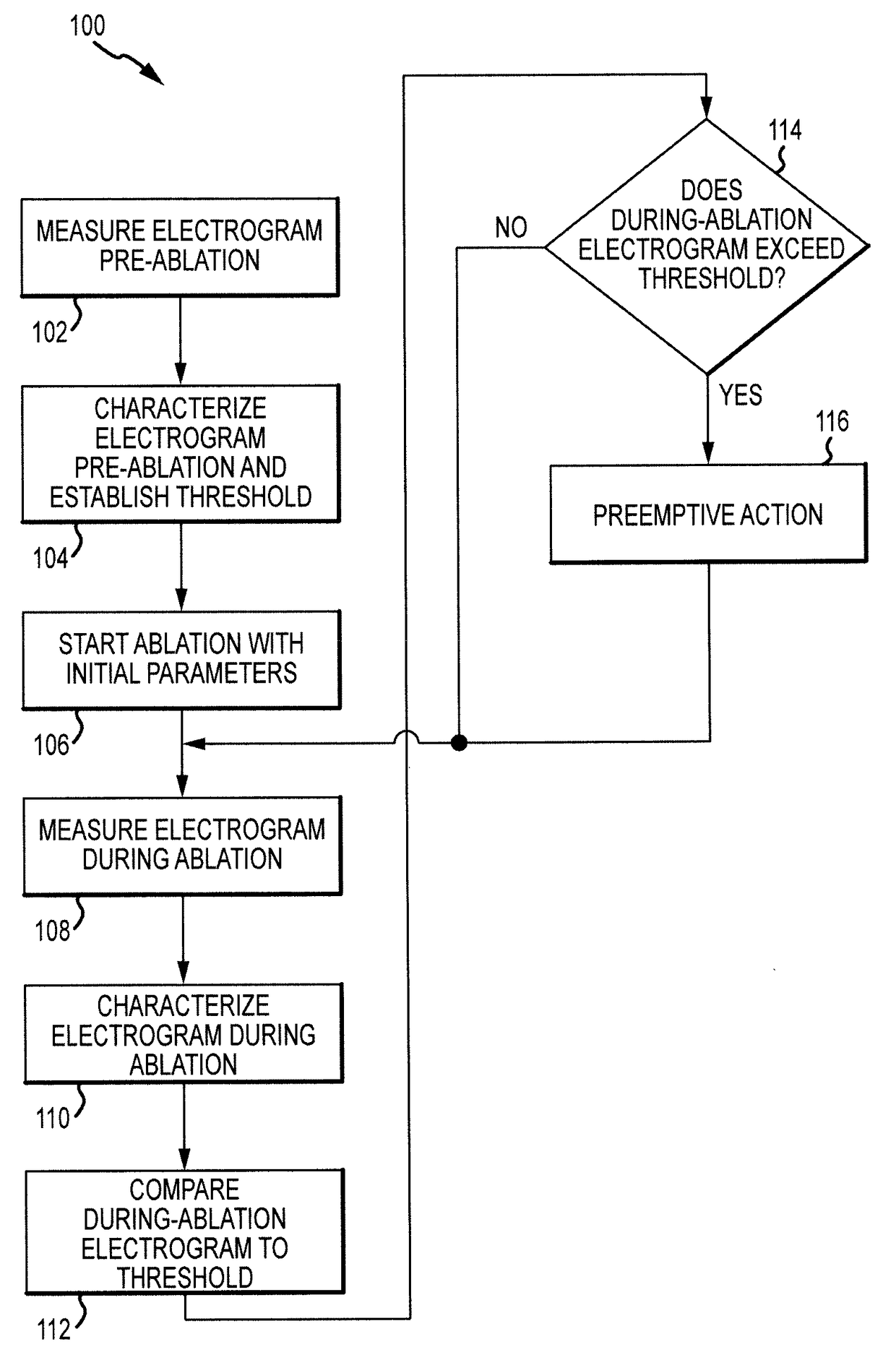
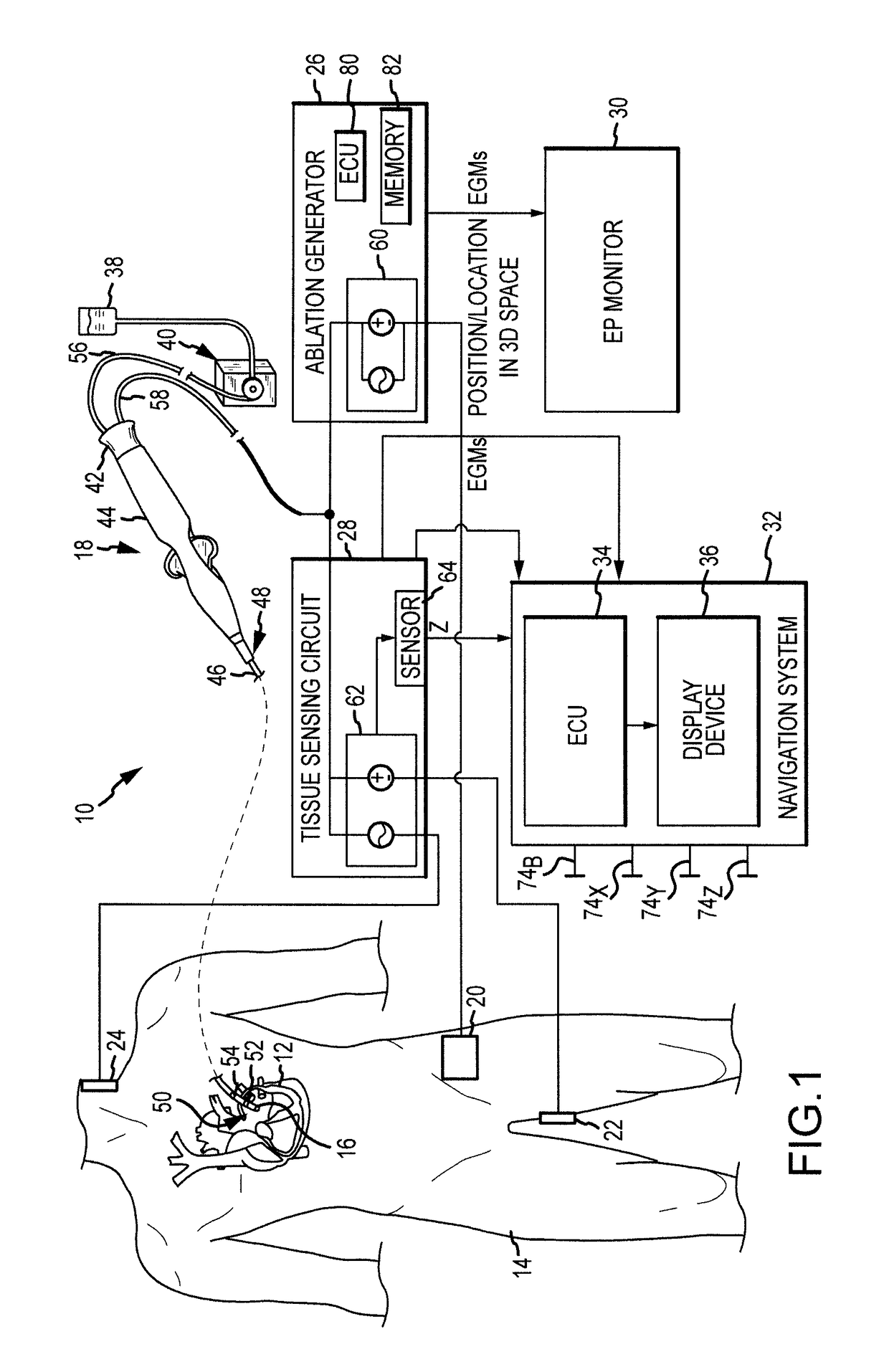
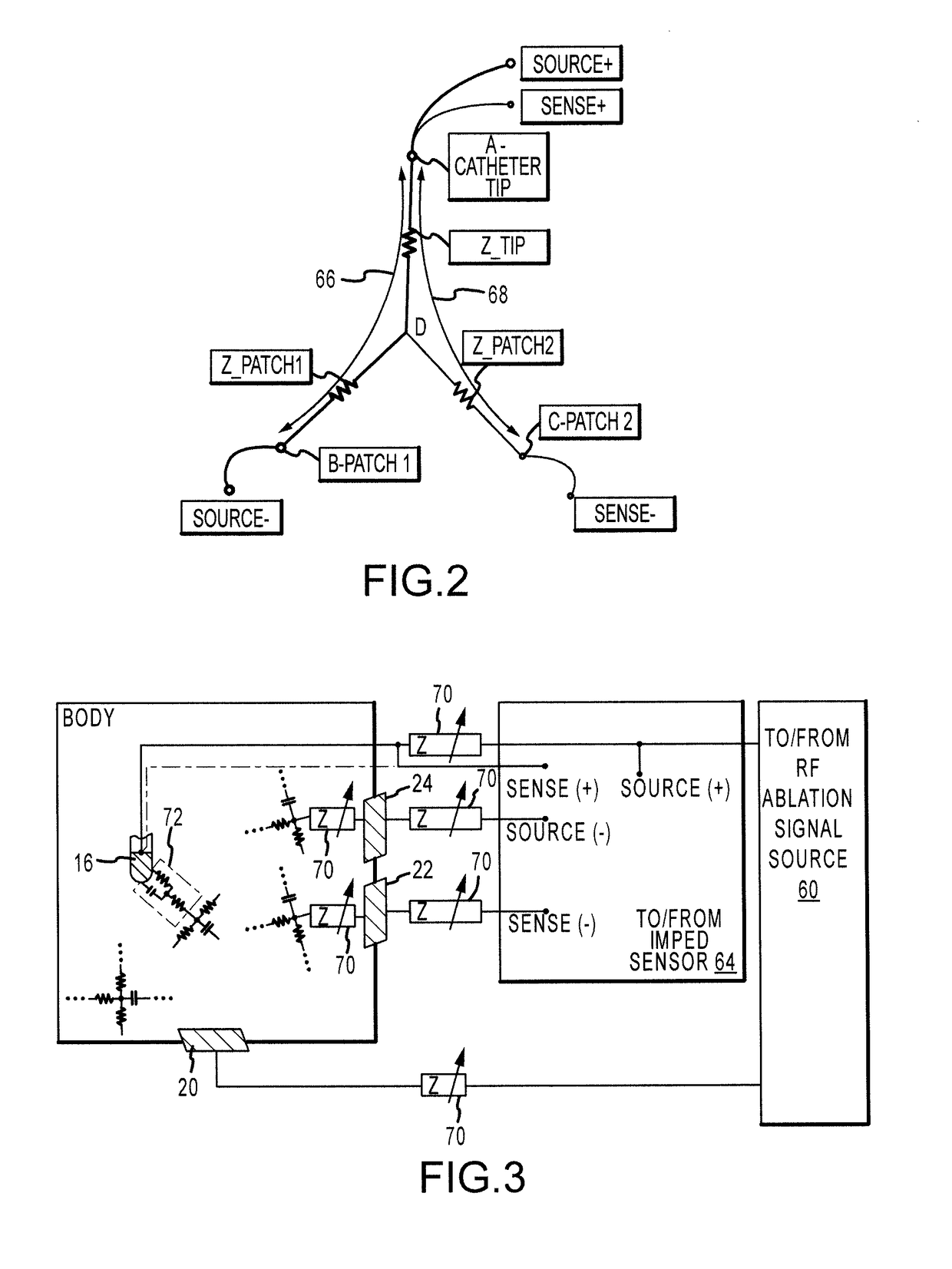
Electrogram-based ablation control
ActiveUS9918788B2Surgical navigation systemsSurgical instruments for heatingData setDrug biological activity
Methods, devices, and systems for predicting, diagnosing, and preventing adverse events during an ablation procedure are described. A method for providing ablation energy includes receiving a first signal based on biological activity of a tissue of a patient. The method further includes analyzing the first signal to yield a first data set, establishing a threshold parameter according to the first data set, and providing ablation energy for the ablation of a biological site.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Percutaneous catheter and guidewire for filtering during ablation of myocardial or vascular tissue
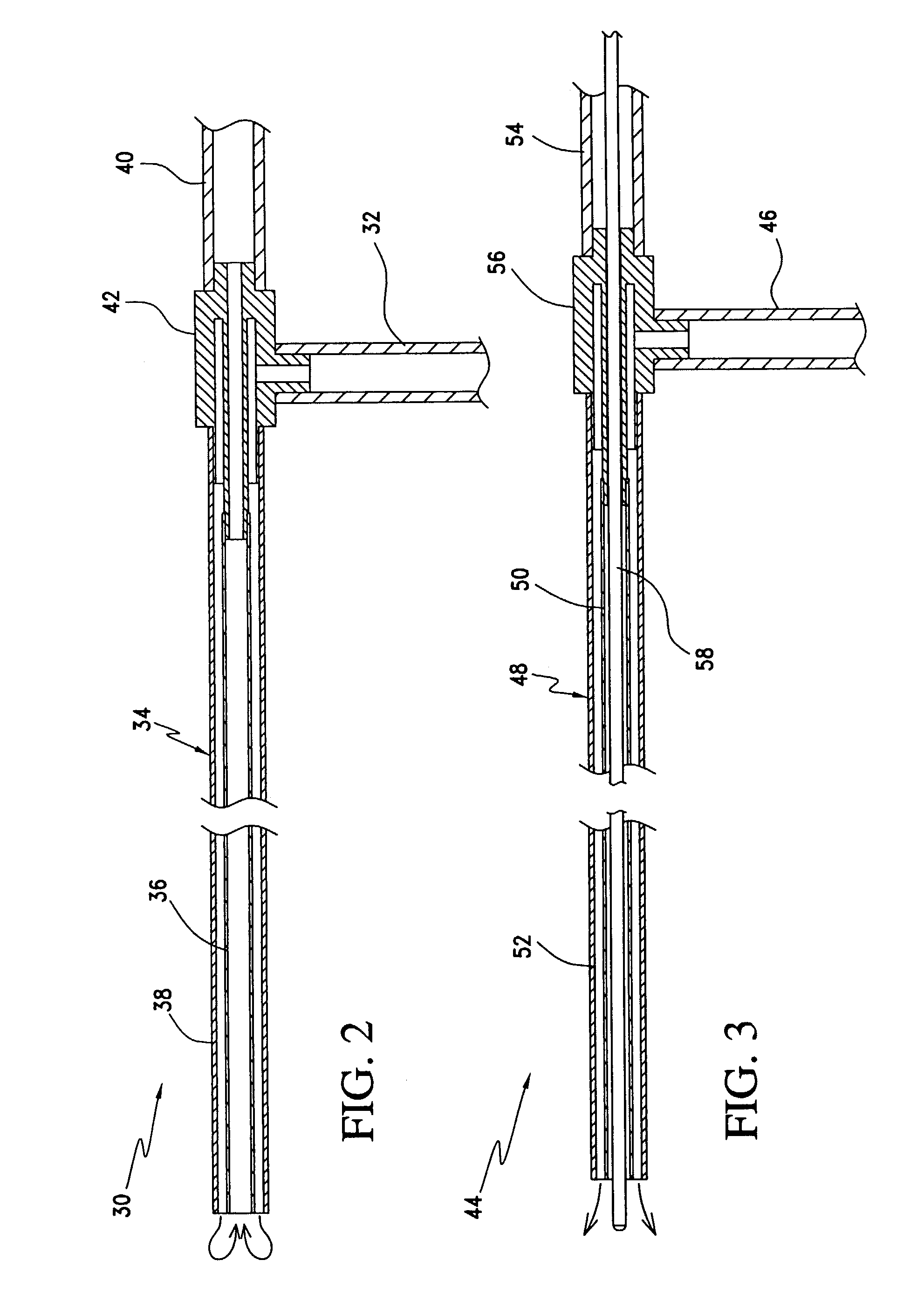
An ablation catheter system for capturing and removing necrotic tissue and thrombi generated during an ablative procedure is disclosed. The catheter typically includes an elongate member, a filtration assembly disposed within the distal region, and an ablation instrument at the distal end. Alternatively, the ablation instrument is carried on the distal end of an ablation catheter, which is disposed within a lumen of the catheter system. The catheter may further include an aspiration port and lumen. Methods of using the devices in preventing distal embolization during ablative procedures are disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ablation catheters and methods for their use
InactiveUS20050033137A1Reduce riskGood electrical contactDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseCardiac disorders
The present invention relates generally to multifunctional catheters for performing ablation procedures, and more particularly to ablation catheters utilized in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and other cardiac disorders. The present invention eliminates many of the problems associated with previous ablation catheters by providing an ablation treatment not dependent upon continuous lesions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
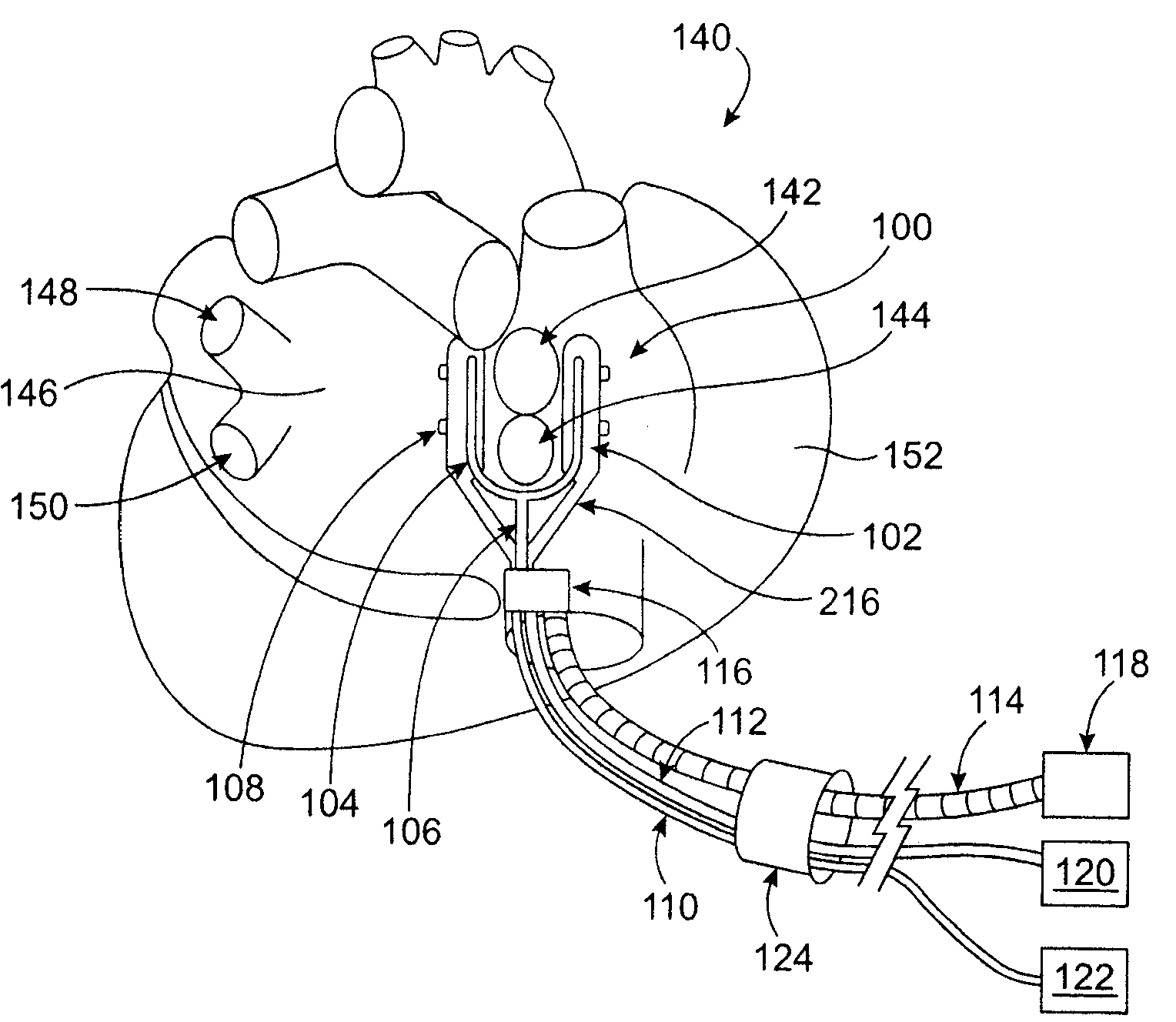
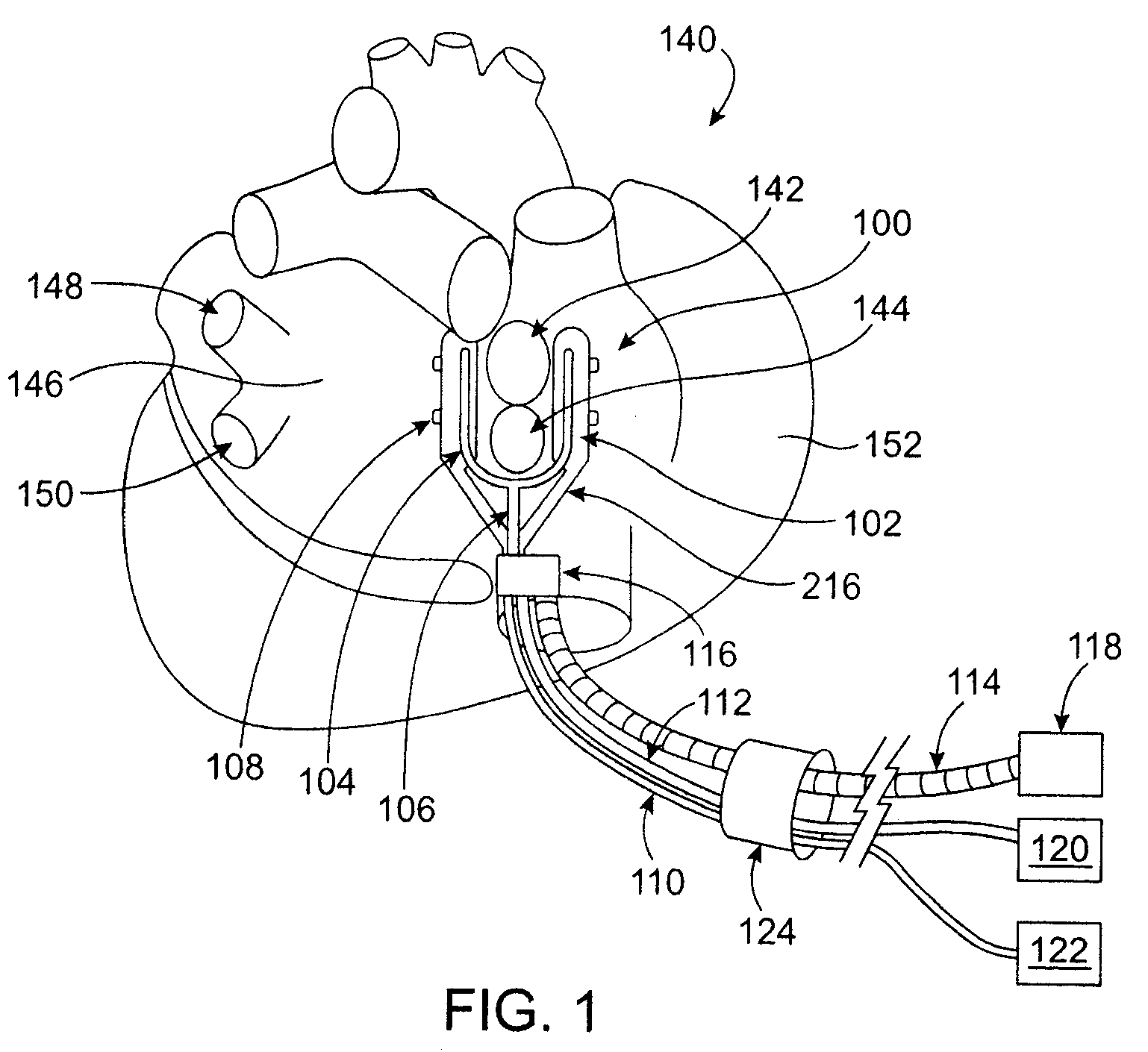
Intra-cardiac mapping and ablation method
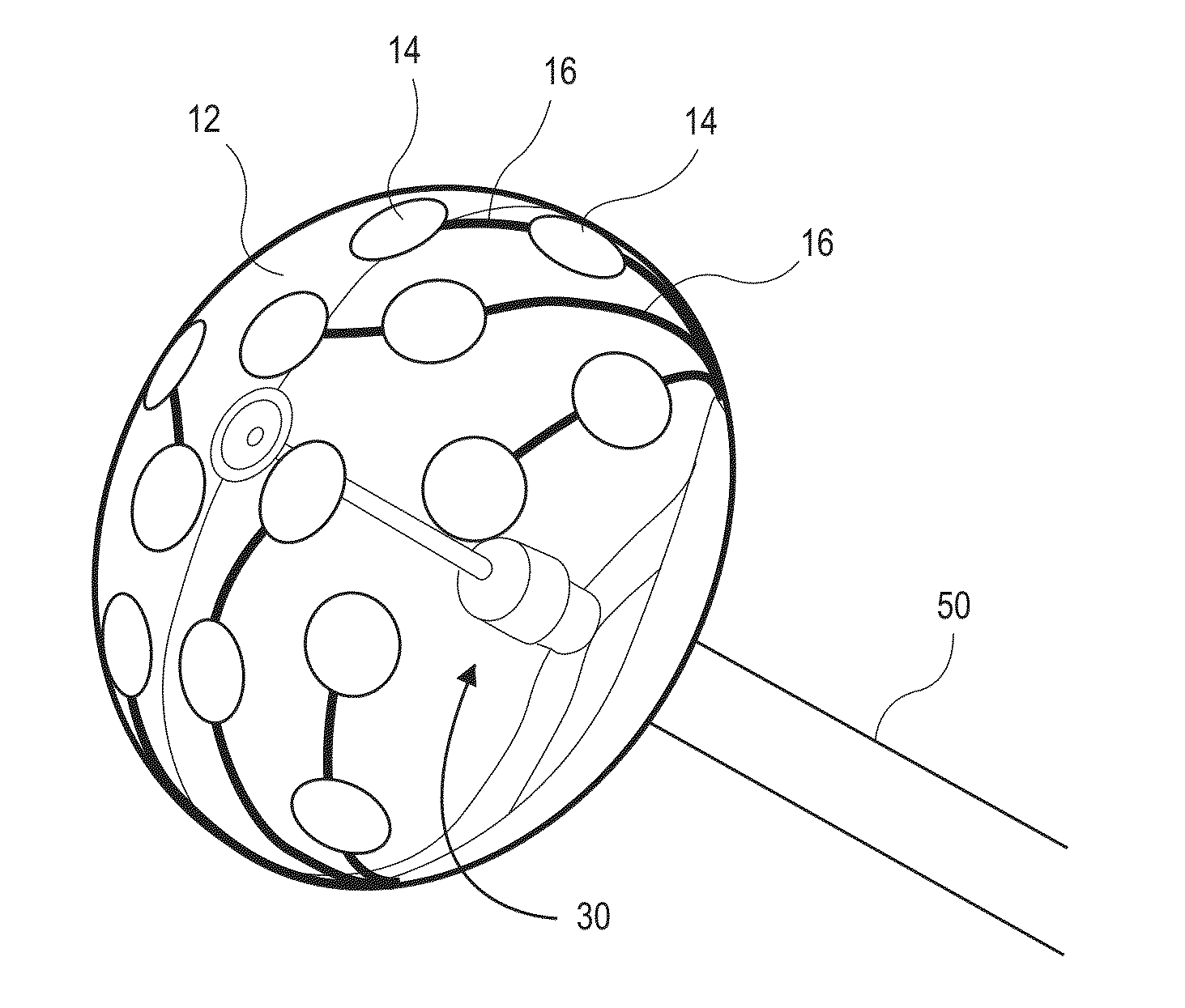
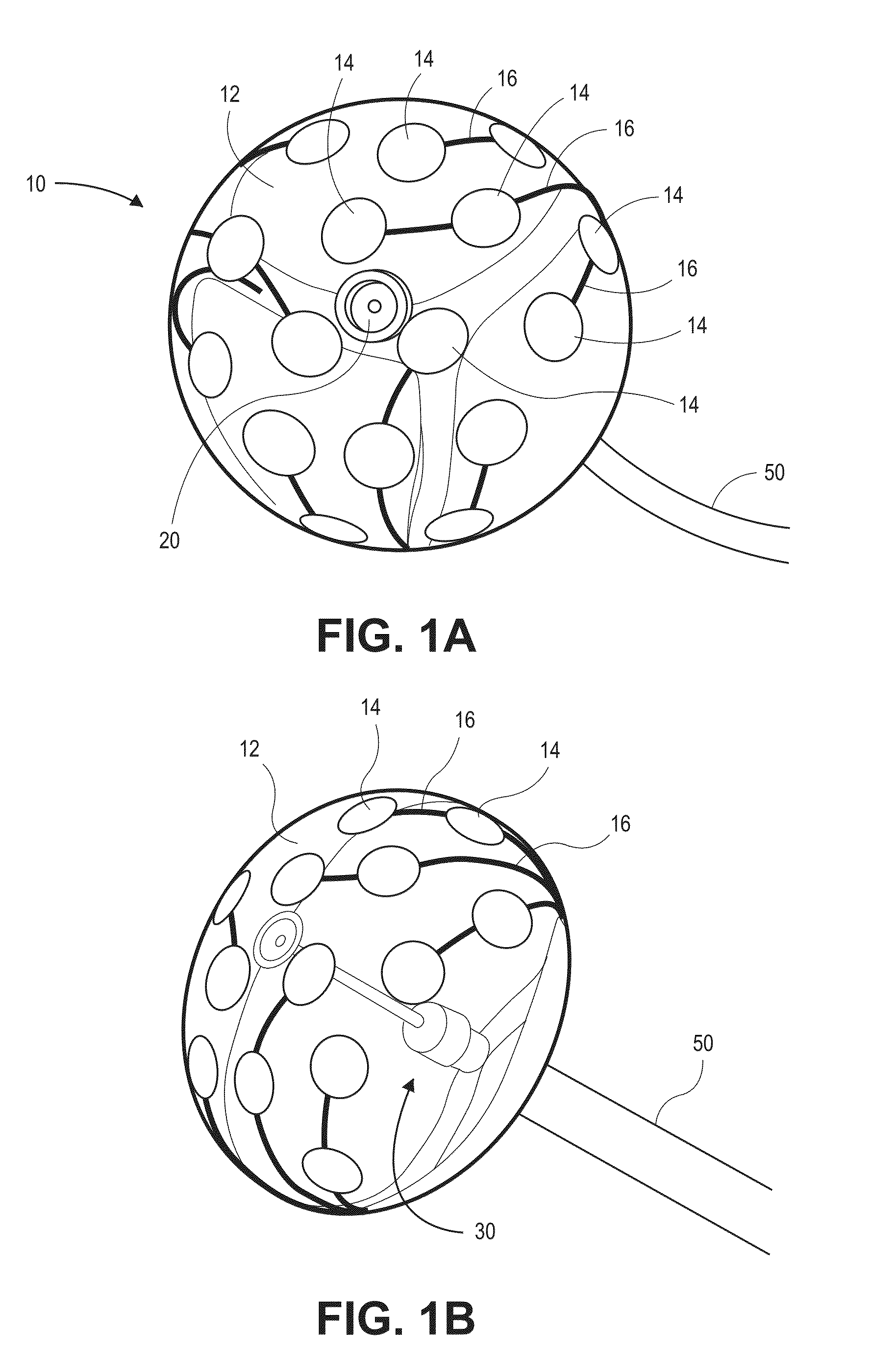
ActiveUS20080004534A1Accurate locationMinimize the numberElectrotherapySurgical systems user interfaceHeart chamberCooling effect
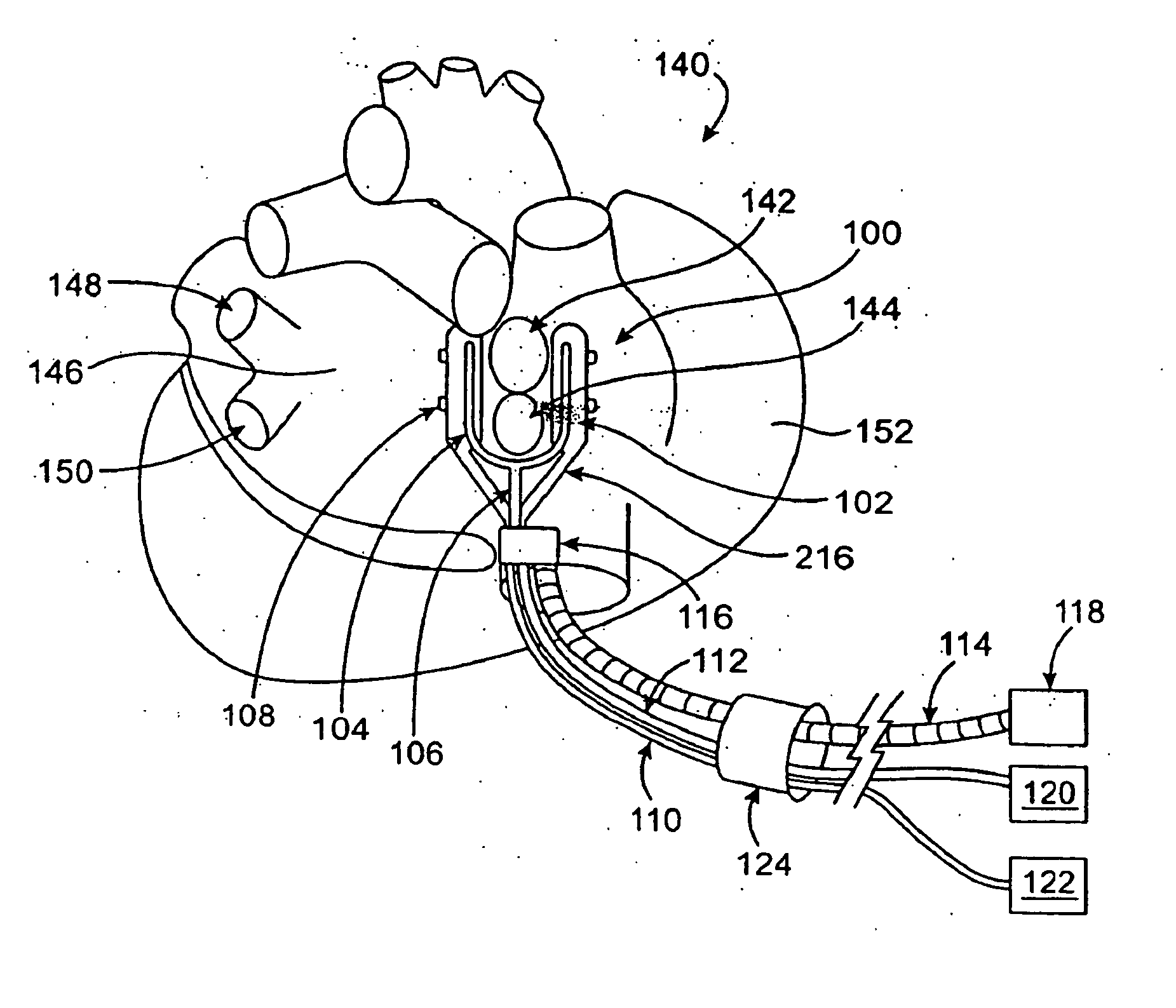
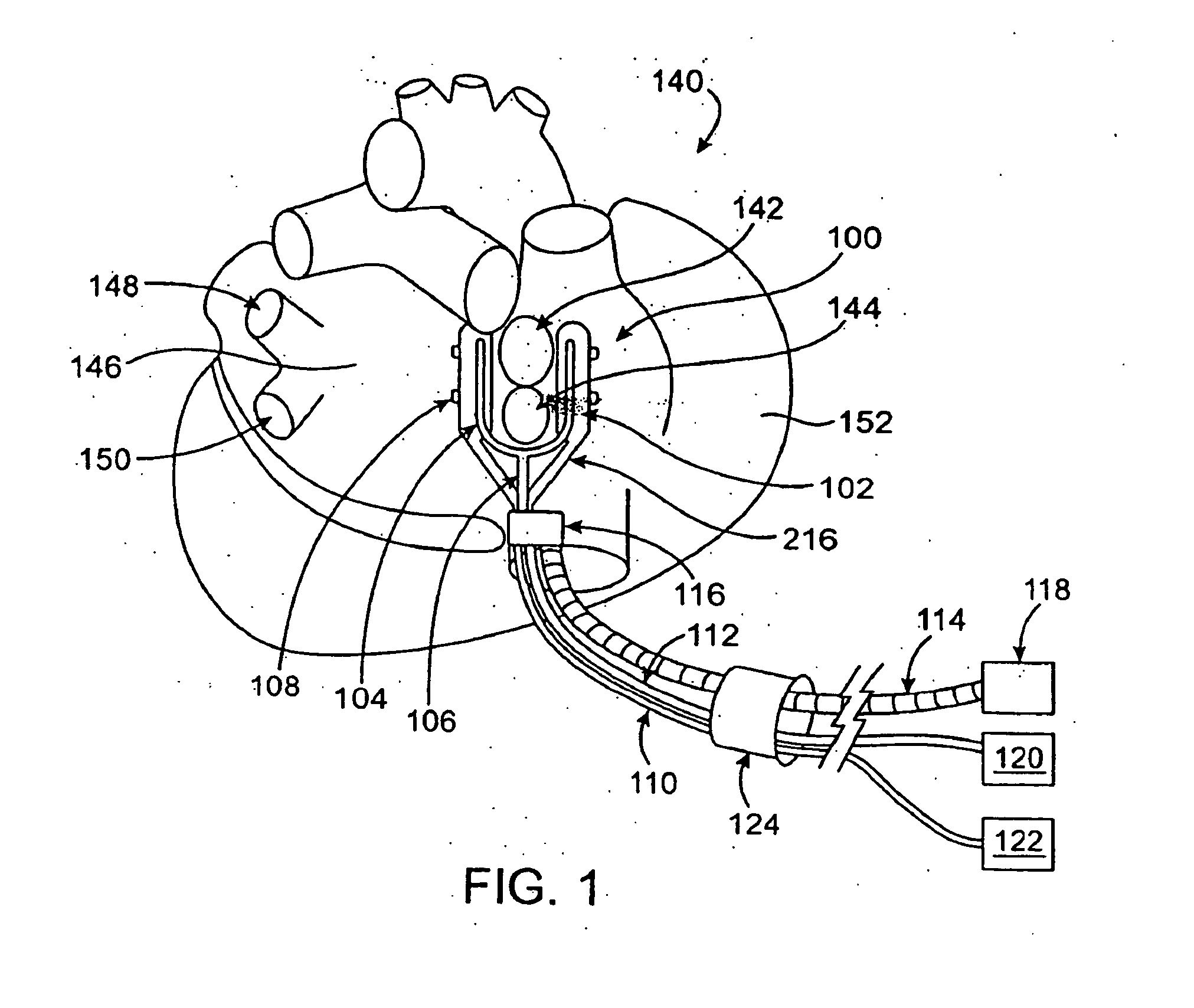
An intra-cardiac mapping system is based on locating the ports through which blood flows in or out the heart chambers. For many procedures, such as ablation to cure atrial fibrillation, locating the pulmonary veins and the mitral valve accurately allows to perform a Maze procedure. The location of the ports and valves is based on using the convective cooling effect of the blood flow. The mapping can be performed by a catheter-deployed expandable net or a scanning catheter. The same net or catheter can also perform the ablation procedure.
Owner:KARDIUM
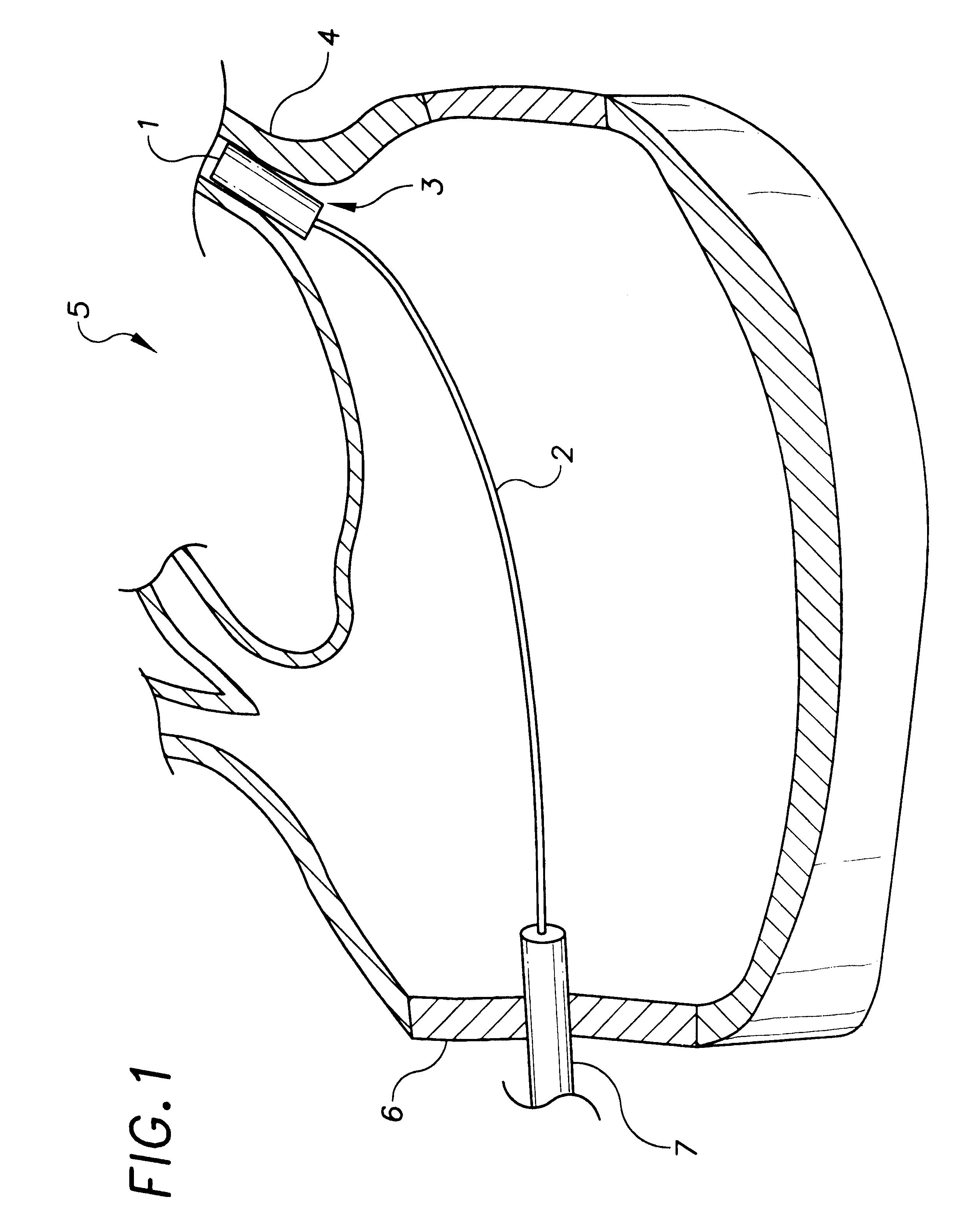
Open system heat exchange catheters and methods of use
InactiveUS6972014B2Eliminate needDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingUrethraSuprapubic aspirate
Various embodiments of open system heat exchange catheters and methods of use are disclosed. The various catheters can be used with various ablative surgical devices. One specific exemplary use is in conjunction with cryosurgical probes involving ablation of the prostate, in which the integrity of the urethra is desired to be maintained. Other uses involve various heating ablative devices. In one embodiment an injection tube assembly is used to provide heat exchange fluid through the urethra to the bladder where it is then expelled via a suprapubic suction tube. In other embodiments a coaxial tube assembly is utilized which defines a passageway for either expelling the bladder fluid or for providing access to an endoscope. In other embodiments a double lumen assembly is utilized that defines a passageway for expelling bladder fluid.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
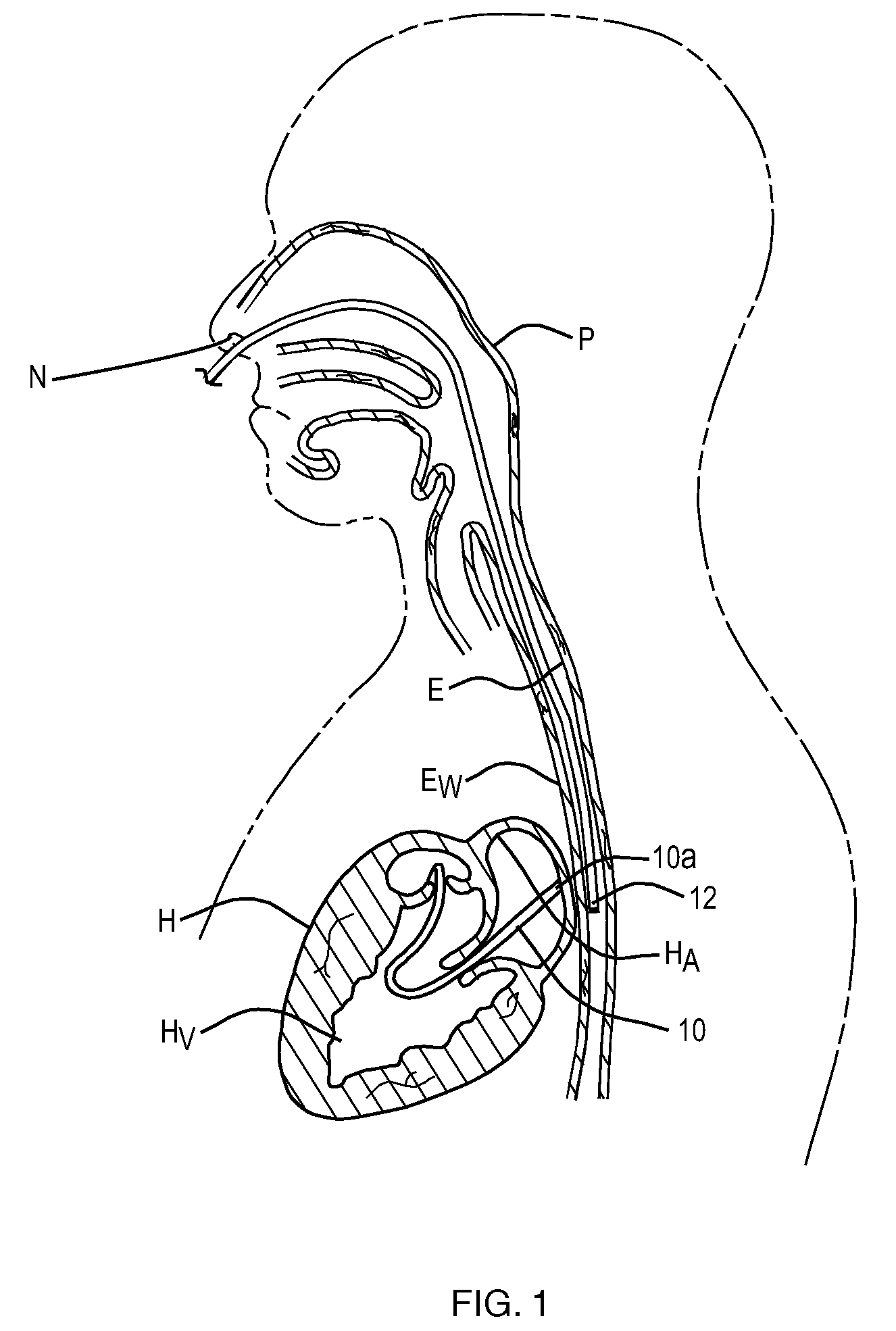
System and method for monitoring esophagus proximity
ActiveUS20070106289A1Reduce riskRisk minimizationSurgical navigation systemsSurgical instrument detailsAnesthesiaSignal processing
A system for determining the proximity of the esophagus to the ablation electrode of an ablation catheter during an ablation procedure is disclosed. The system comprises an ablation catheter having at least one ablation electrode, an esophageal probe catheter having at least one electrode, and a signal processing unit. Both the ablation electrode and the esophageal probe catheter are electrically connected to the signal processing unit. The signal processing unit receives electrical signals from the ablation electrode on the ablation catheter and the electrode on the esophageal probe catheter and compares the signals to determine the proximity of the esophagus to the ablation electrode.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Cardiac ablation catheters and methods of use thereof
Cardiac ablation catheters and methods of use. In some embodiments the catheter includes at least one camera inside an expandable membrane for visualizing an ablation procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Apparatus and method for intra-cardiac mapping and ablation
ActiveUS8920411B2Accurate locationMinimize the numberSurgical systems user interfaceCatheterHeart chamberCooling effect
An intra-cardiac mapping system is based on locating the ports through which blood flows in or out the heart chambers. For many procedures, such as ablation to cure atrial fibrillation, locating the pulmonary veins and the mitral valve accurately allows to perform a Maze procedure. The location of the ports and valves is based on using the convective cooling effect of the blood flow. The mapping can be performed by a catheter-deployed expandable net or a scanning catheter. The same net or catheter can also perform the ablation procedure.
Owner:KARDIUM
Apparatus and methods for mapping and ablation in electrophysiology procedures
InactiveUS20050065420A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingEpicardial mappingTunica intima
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Externally applied RF for pulmonary vein isolation
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
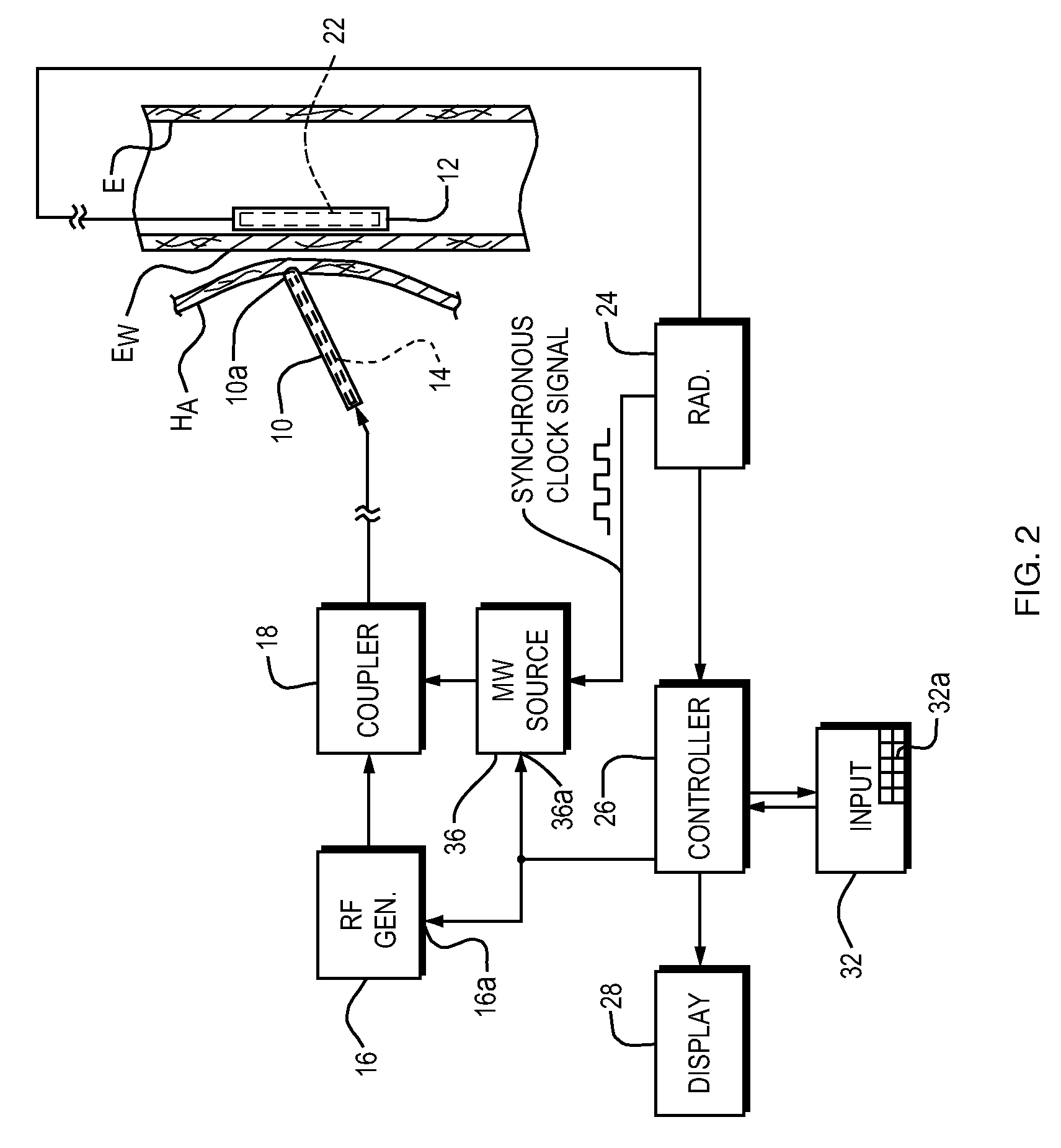
Method and apparatus for aligning an ablation catheter and a temperature probe during an ablation procedure
ActiveUS20100185191A1Precise alignmentAvoid overall overheatingBody temperature measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesRadiometerMicrowave signals
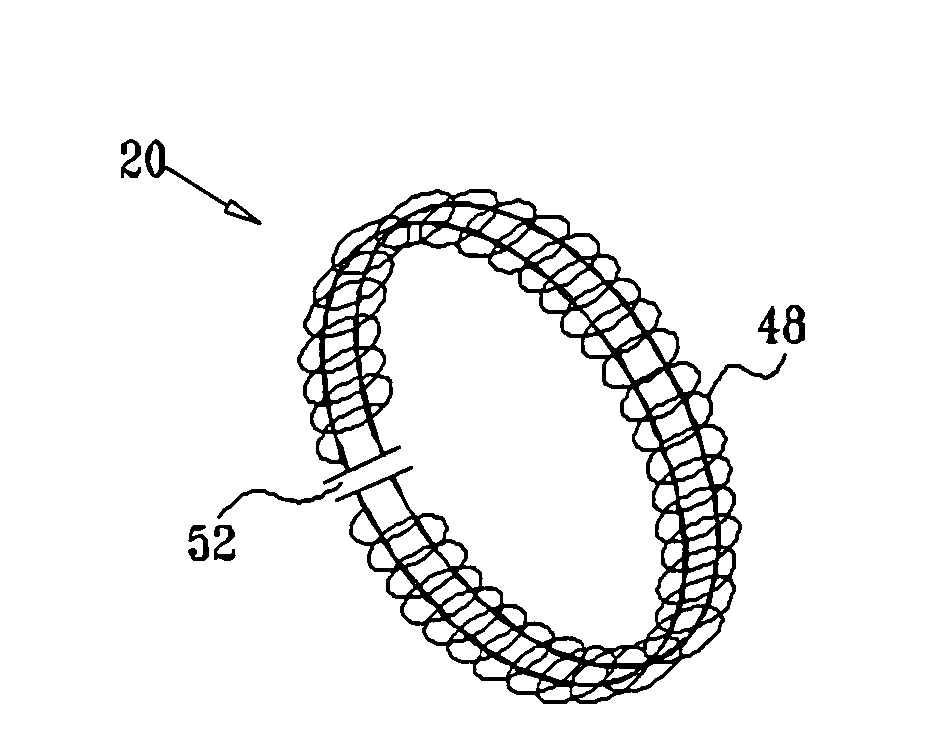
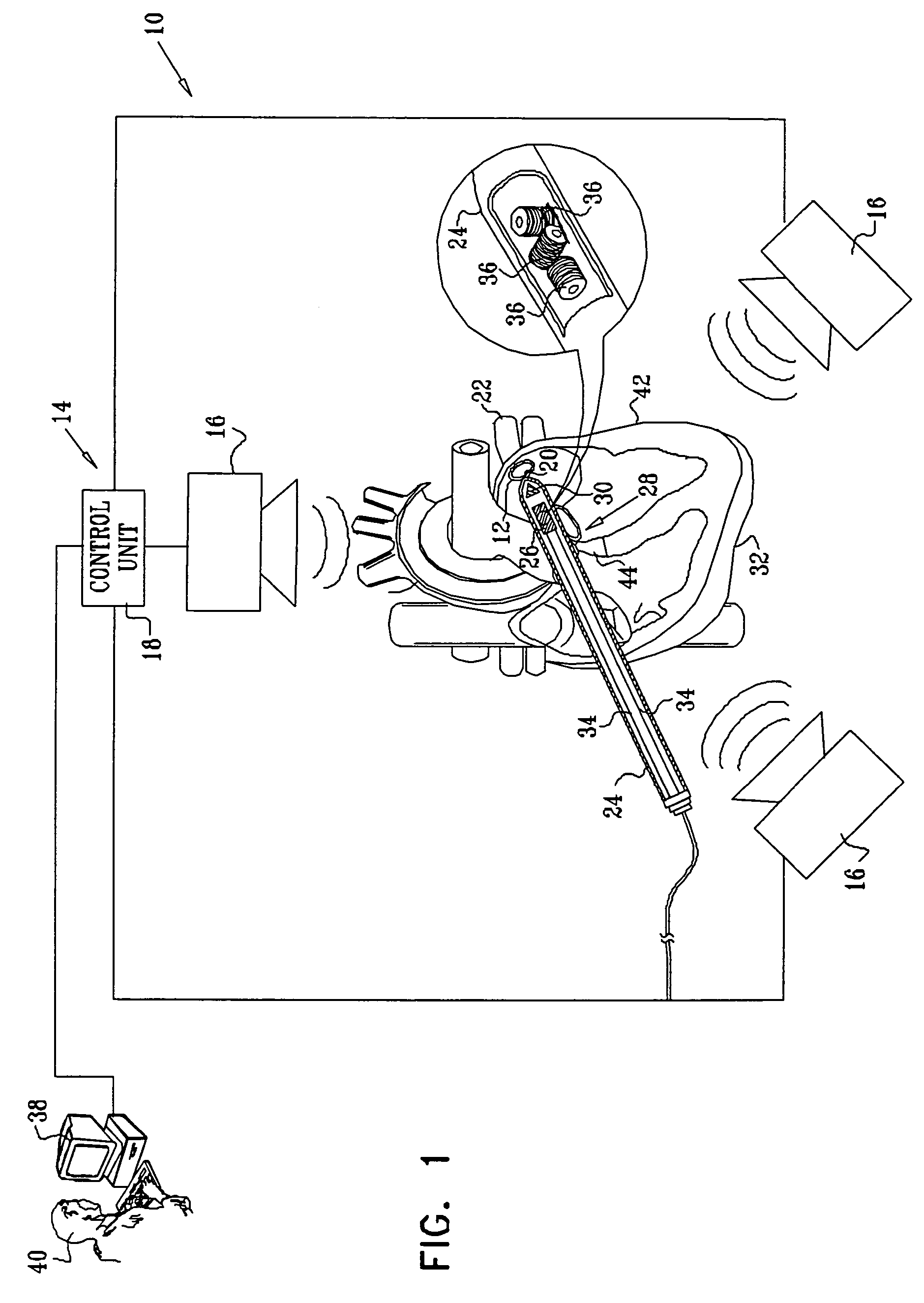
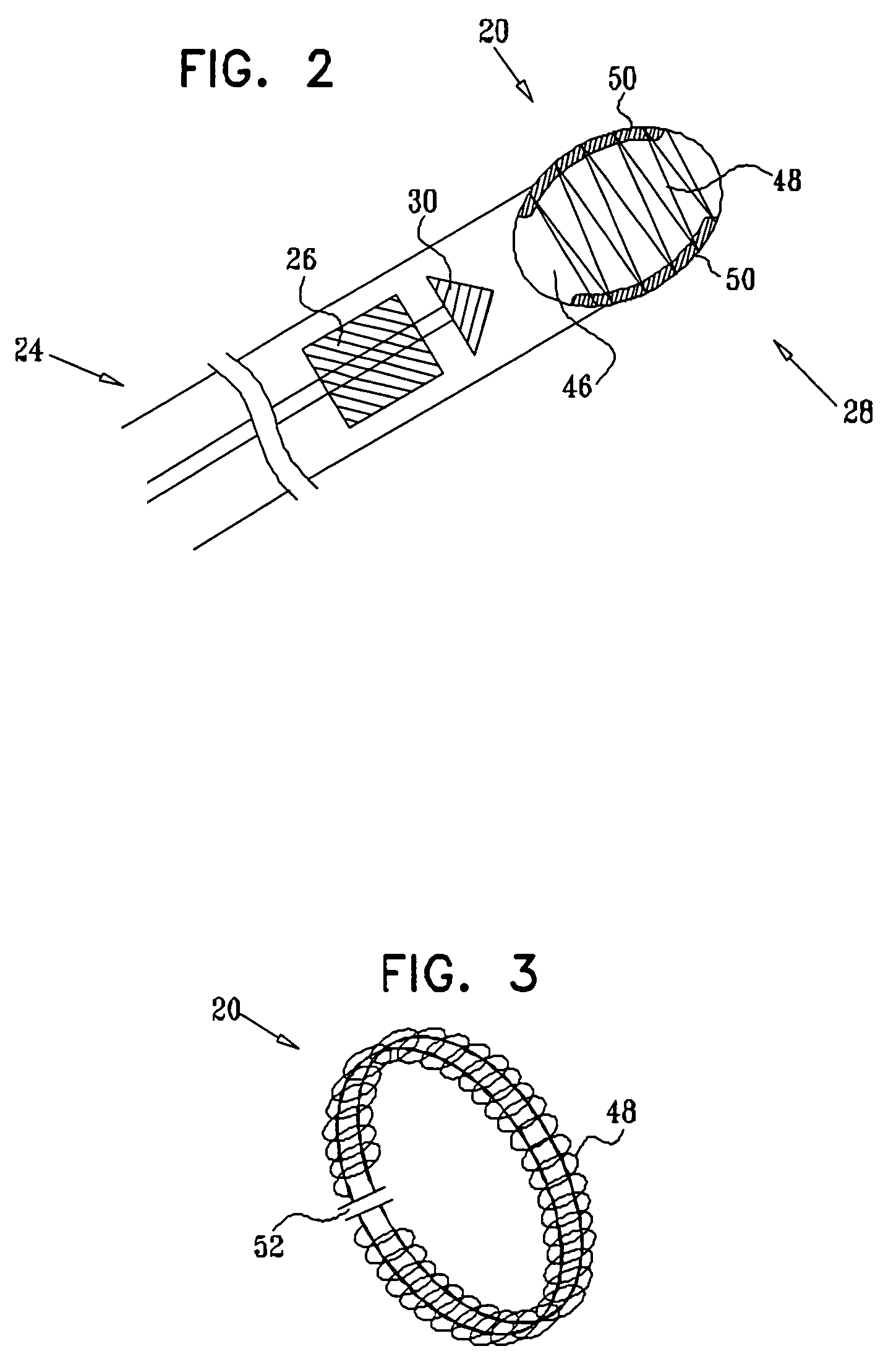
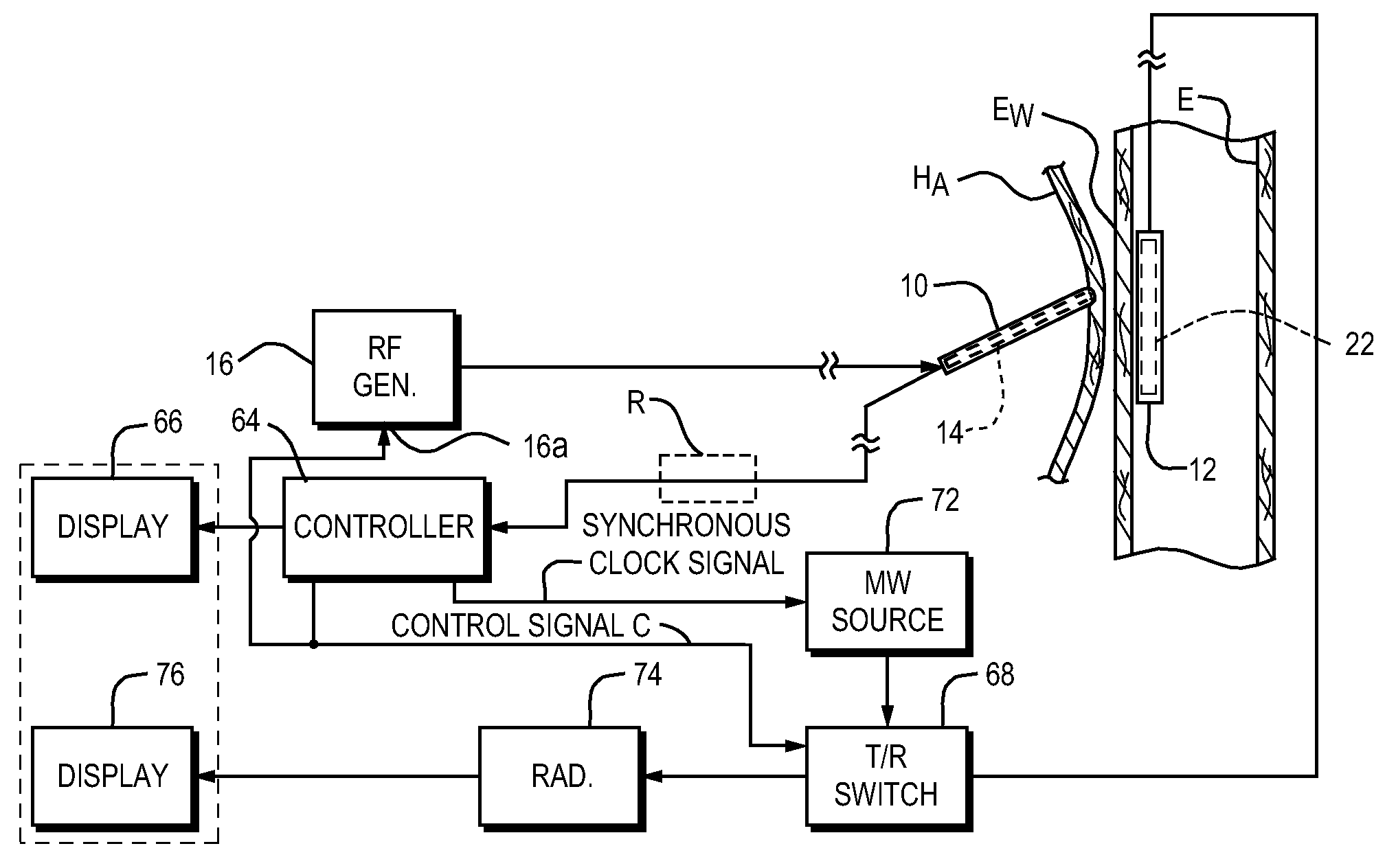
Apparatus for aligning an ablation catheter and a temperature probe relatively for an ablation procedure includes an ablation catheter with a first antenna for ablating tissue at an ablation site in a patient's body and a temperature probe for placement in a body passage having a wall portion adjacent to the ablation site so that a second antenna in the probe is positioned opposite the first antenna. A microwave source provides a pulse modulated microwave signal to one of the antennas and a radiometer is in circuit with the other antenna. A synchronizing device in circuit with the microwave source and the radiometer enables the radiometer to synchronously detect the microwave signal so that the radiometer provides an alignment signal whose strength reflects the degree of alignment of the first and second antennas which signal may be used to control an alignment display. An alignment method using the apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:CORAL SAND BEACH LLC
Cardiac ablation devices and methods
ActiveUS20090012510A1Easy to operateReduce relative motionSurgical needlesEndoscopesVeinCardiac Ablation
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ATRICURE
Ablative treatment of the heart to improve patient outcomes following surgery
ActiveUS20070156185A1Easy to operateReduce relative motionEpicardial electrodesSurgical needlesVeinAtrial cavity
Owner:ATRICURE
Externally applied RF for pulmonary vein isolation
InactiveUS20050101946A1Eliminate needInternal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringVeinInsertion stent
A resonant circuit is incorporated in a stent, which implantable in a pulmonary vein using known cardiac catheterization techniques. When an external RF field is generated at the resonant frequency of the stent, RF energy is re-radiated by the stent toward electroconductive tissue in the wall of the pulmonary vein, and produces a circumferential conduction block. The stent can be made of biodegradable materials, so that it eventually is resorbed. Following an ablation procedure, the stent may be left in situ. Repeated ablation can be performed using the inserted stent until it has been determined that the desired lesions have been formed. Furthermore, the same stent can potentially be used even years after being inserted should the treated arrhythmia reoccur or a new arrhythmia develop, thereby possibly obviating the need for an invasive procedure at that future time.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Cardiac ablation devices and methods
ActiveUS20050288666A1Lower impedanceImprove conductivityEpicardial electrodesSurgical needlesAtrial cavityCardiac arrhythmia
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ATRICURE
Ablation stent for treating atrial fibrillation
An apparatus and method for treating atrial fibrillation with ablation therapy in which a stent is deployed within a pulmonary vein and tissue surrounding the stent is ablated with radiofrequency energy to stop discharges from ectopic foci in the vein from reaching the left atrium. The deployed stent can then be left in place to prevent stenosis of the vein as well as allowing repeat ablation procedures as needed.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Cardiac treatment devices and methods
ActiveUS20050240175A1Easy to operateReduce relative motionEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingVeinHeart disease
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ATRICURE
Method and system for monitoring atrial fibrillation ablations with an ablation interface device
A computer based ablation interface system provides useful information for monitoring catheter ablations, especially left sided ablations for atrial fibrillation. Such a system provides added safety, by providing useful information during the ablation procedure. The system comprises a computer, specialized software, analog and digital input / output board, transducer, and display. The information displayed includes both electrical parameters and physiological parameters. In one aspect of the invention alarms and indicators are displayed on the screen for highlighting certain events to the physicians, for guiding them through the ablation procedure. In another aspect of the invention, the system comprises circuitry for automatically switching the ablation circuit off, based on pre-determined events.
Owner:ABL TECH
Cardiac ablation devices and methods
ActiveUS7399300B2Easy to operateReduce relative motionEpicardial electrodesSurgical needlesAtrial cavityCardiac arrhythmia
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ATRICURE
Pulmonary vein stent and method for use
Ablation of the pulmonary veins causes damage to the tissue which may affect the viability of the tissue. By placing a stent, a vascular endoprosthesis, within a target pulmonary vein it is possible to protect the functionality of the veins after the ablation procedure. Placement of a stent, endoprosthesis or mere circuit interrupting structure into a target pulmonary vein, without ablation, prevents aberrant electrical activity in the pulmonary veins from interfering with the electrical activity of the left atrium. The stent, endoprosthesis or circuit interrupting structure may also be coated or comprised of a drug-eluting compound, loaded with a drug which inhibits arrhythmia.
Owner:BIOCARDIA
Cardiac ablation devices and methods
ActiveUS20050149152A1Lower impedanceImprove conductivityEpicardial electrodesSurgical needlesAtrial cavityCardiac arrhythmia
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ATRICURE
Apparatus and methods for mapping and ablation in electrophysiology procedures
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com