Method for manufacturing wood fiber insulating boards
a technology of wood fiber insulation and manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of making wood fiber insulation boards, can solve the problems that did not influence the manufacture of wood fiber insulation boards with multi-component plastic fibers, and achieve the effect of high quality and sufficient flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
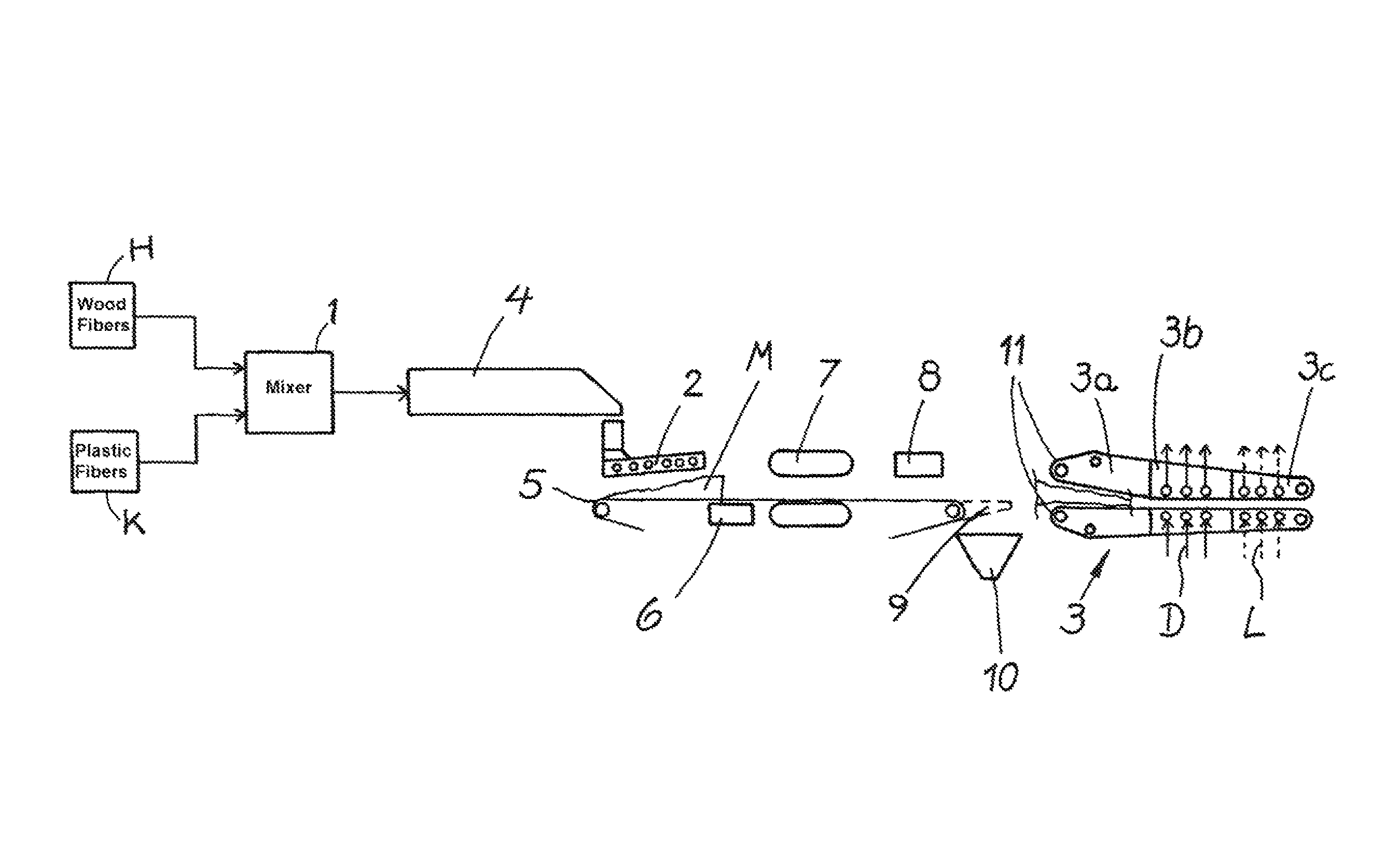
[0018]Essential components of such a facility are a mixer 1 for mixing the wood fibers H and the thermoplastic plastic fibers K, a spreader 2 for the production of a fiber mat and a compacting and calibrating unit 3. In detail, the following steps are conceivable:
[0019]The starting components for the production of the wood-fiber insulating boards are, on the one hand, wood fibers from a supply H and, on the other hand, multicomponent plastic fibers from a supply K that are produced in ways known in the art and added to a mixer 1. From the mixer 1 the fiber mixture reaches a storage bin 4. From the bin 4 the fiber mix is mechanically dispersed by a spreader 2 to form a fiber mat on a conveyor belt 5. The spreader 2 can be configured in ways known in the art, such as with a strewing head, for example a roller head. Below the belt it is possible to provide a scale 6, for example a belt scale for continuously detecting the weight of the mat. To prevent dust from escaping it is possible ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com