Analog of haemophilus Hin47 with reduced protease activity
a protease activity and haemophilus technology, applied in the field of haemophilus influenza, can solve the problems of ineffective children under 24 months, reimmunisation fails to elicit either a booster response or an increase in memory cells, and haemophilus conjugate vaccines do not protect against other diseases, so as to enhance the effectiveness of vaccination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
This Example illustrates the cloning of the hin47 gene from non-typable H. influenzae strain SB33.
Chromosomal DNA was prepared from H. influenzae strain SB33, and an EMBL3 library was prepared and screened with a labelled oligonucleotide probe specific for the 5'-end of hin47. Non-typable H. influenzae strain SB33 was grown on Mueller-Hinton agar or in brain heart infusion broth as described by Harkness et al, 1992. Chromosomal DNA was prepared as follows: cells from 50 ml of culture were pelleted by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 15 to 20 min, at 4.degree. C., in a Sorvall RC-3B centrifuge. The cell pellet was resuspended in 10 ml of TE (10 mM Tris / HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 7.5), pronase was added to 500 .mu.g ml.sup.-1 and SDS to 1%. The sample was incubated at 37.degree. C. until a clear lysate was obtained. The lysate was gently extracted once with Tris-saturated phenol (pH 7.4), once with Tris-saturated phenol / chloroform (1:1) and once with chloroform. The final aqueous phase was dial...
example 2
This Example illustrates the characterization and sequence analysis of the hin47 gene and deduced amino acid sequence of the Hin47 protein from NTHi strain SB33.
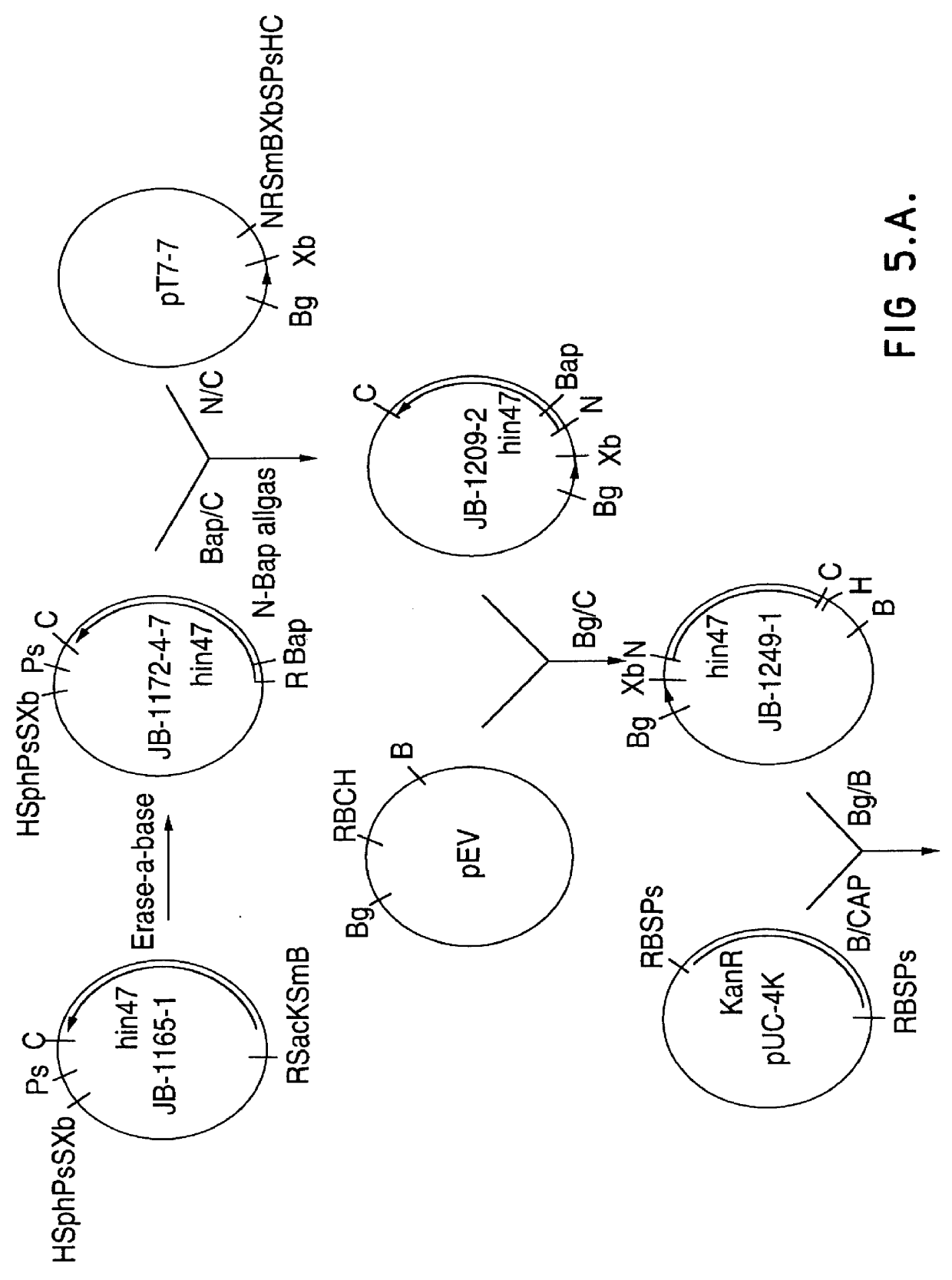
Restriction mapping and Southern blot analysis of clones JB-1031-1-14 and JB-1068-2-2 localized the hin47 gene on a 4.7 kb BamH I / BamH I or a 2.7 kb BamH I / Pst I DNA fragment. The 4.7 kb BamH I / BamH I fragment from JB-1068-2-2 was subcloned into pUC8 / BgXb generating plasmid DS-755-1. The 3.1 kb BamH I to Xba I fragment of DS-755-1 was subcloned into pUCl8 generating plasmid JB-1165-1 which has restriction sites suitable for the Erase-a-base (Promega) procedure (FIG. 1). This technique generates successive clones with increasing truncations of insert DNA, with the deletions occurring from the same end. The resultant nested set of clones can be sequenced rapidly using a universal primer.
DNA from plasmid JB-1165-1 was digested with BamH I and Sac I and subjected to exoIII digestion using an Erase-a-base kit. The resultant set o...
example 3
This Example describes the discovery of serine protease activity of Hin47 protein.
The deduced amino acid sequence of Hin47 protein determined in Example 2 above was compared with all other known proteins in the Genbank data base. As described above, Hin47 protein is described in published PCT applications WO 94 / 00149, WO 92 / 11367 and WO 92 / 10936 to be an adhesin molecule of Haemophilus. It was, therefore, a surprising and unexpected discovery of the present invention that Hin47 protein has significant amino acid homology (55%) with the serine proteases E. coli htrA and S. typhimurium htrA and other proteases. These amino acid sequence homologies are shown in FIGS. 3 and 4. Furthermore, Hin47 protein was found to autodigest unless it was stored in the presence of a serine protease inhibitor, such as PEFABLOCK.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com