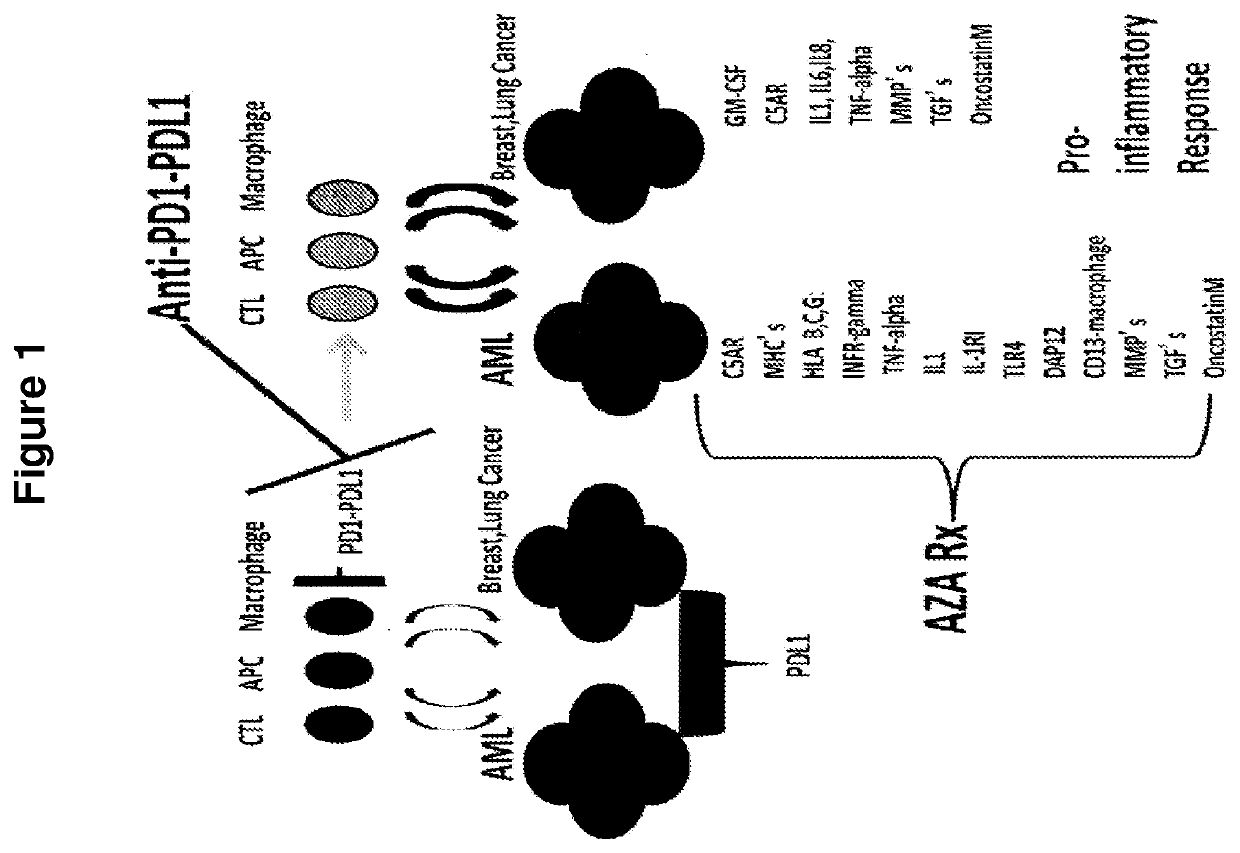
Cancer therapy via a combination of epigenetic modulation and immune modulation
a technology of epigenetic modulation and cancer therapy, applied in the direction of antibody medical ingredients, drug compositions, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of few effective chemotherapeutic options, and achieve dramatic tumor shrinkage, unexpected anti-neoplasia synergistic effects, and de novo expression.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Observation of Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Combined Epigenetic and Anti-PD-1 Therapies
[0148]Five patients who received treatment on a clinical trial of epigenetic therapy (specifically, here. AZA treatments) for advanced treatment-refractory NSCLC were placed on trials for immunotherapy targeting the PD-1 / PDL1 immune tolerance checkpoint. Of these five patients, three experienced durable partial responses to immunotherapy now ongoing for 14 to 26 months, and the other two had stable disease that lasted 8.25 and 8.5 months, respectively. (see FIGS. 23 and 25) For comparison, 41-46% of NSCLC patients on these two trials of immunotherapy alone, one for anti-PD1 and the other for anti-PD-L1 therapy, passed 24 weeks without progression and 16-17% had durable partial response rates.(6-8)
example 2
mmatory Changes in Gene Expression Revealed to Increase with AZA Treatment
[0149]The clinical effect observed in Example 1 was believed to relate to the modes of action of both epigenetic treatments such as AZA and to anti-PD-1 immune tolerance checkpoint immunotherapies, such as anti-PD1 and / or anti-PDL1 antibodies (FIG. 1). The impact of AZA administration upon tumor-derived cell lines was then assessed for a number of genes, and revealed pro-inflammatory changes in expression of a wide number of genes to increase with AZA treatment. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 2, such effects were observed across genes CSAR; GM-CSF; MHCs; TNF-alpha; IL1 alpha / beta; IL6; IL8; IL-15; IL-15R; IL15RA; MMPs-TIMP1; COX2; OncostatinM; ICAM1; VCAM1; and TGF-betas and their receptors in epithelial cell lines, while effects were also observed for genes IFN-gammaR; TNF-alpha; MHCs; HLA B, C, G; TLR4; DAP12; CD13-macrophage maturation; IL-1RI; IL1 alpha / beta; MMPs-TTMP1; OncostatinM; and TGF-betas and thei...
example 3
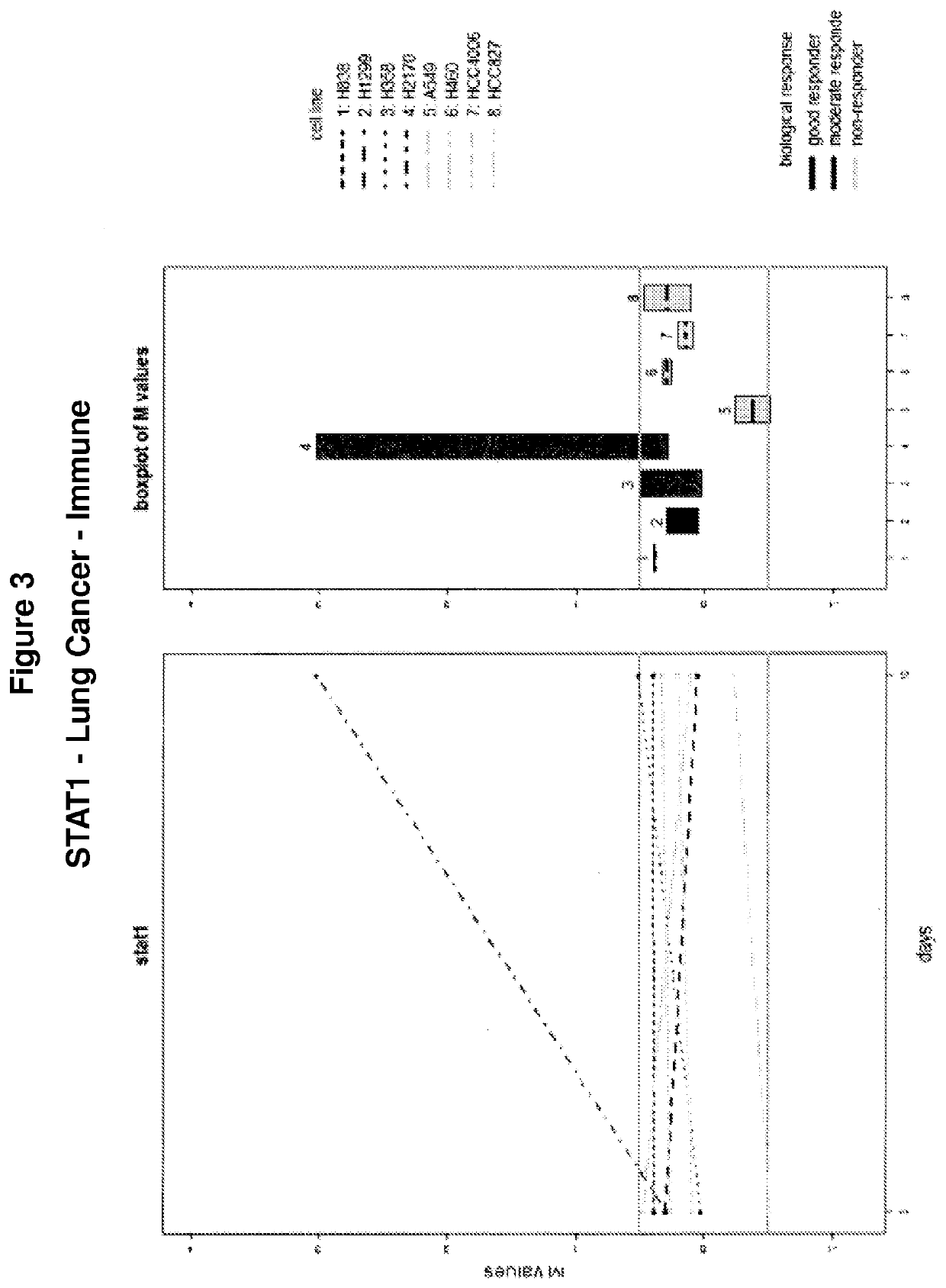
g of STAT1, IFI27, OAS1, IFI16, HLA-A, IL18, and IL11 in Lung Cancer Cell Lines During Treatment Revealed Varying Levels of Molecular Response
[0150]Lung cancer-derived cell lines (including human NSCLC cell lines H838, H1299, H358, H1270 and H460; human adenocarcinoma / lung cell lines A549 and HCC827, and hepatocellular carcinoma / lung cell line HCC4006) were assayed for levels of STAT1 (FIG. 3), IFI27 (FIG. 4), OAS1 (FIG. 5), IFI16 (FIG. 6), HLA-A (FIG. 7), IL18 (FIG. 8), and IL11 (FIG. 9) during a treatment regimen including AZA administration over the course of 10 days. As shown in each of FIGS. 3-8, levels of these genes were also assessed in each of eight clinical subjects as shown (including two “good responders”, two “moderate responders” and four “non-responders”).
[0151]The above observations suggested that an adaptive resistance model of tumor-T cell interaction could be relevant to the PD-L1 upregulation-related response effects that were observed (FIG. 10). Indeed, while a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com