Stapled intracellular-targeting antimicrobial peptides to treat infection
a technology of antimicrobial peptides and intracellular targeting, which is applied in the direction of antibacterial agents, peptide sources, peptide/protein ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of increasing antibiotic discovery burden, falling antibiotic discovery burden on academic research centers and hospitals, and increasing antibiotic resistance, so as to enhance antimicrobial activity and import the effect of little to no off-target toxicity and little to no toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
of Stapled I-TAMP Analogues
[0432]We synthesized a complete i, i+4, and 1, i+7 staple scanning panel of stapled buforin II peptides to identify which staple insertion position(s) yield I-TAMP analogues with optimal biological and pharmacologic properties (FIG. 1). In some compositions, replacement of the central proline residue was avoided given the potential role of prolines as breakpoints in secondary structure. Also, in some panels, the phenylalanine adjacent to the proline was replaced with tryptophan for facile determination of peptide concentration by UV spectroscopy. The production of these exemplary panels allowed us to interrogate the effects of structural stabilization of various segments of the parent I-TAMP on its antimicrobial and hemolytic activity.
example 2
ical Characterization of Stapled I-TAMP Analogues
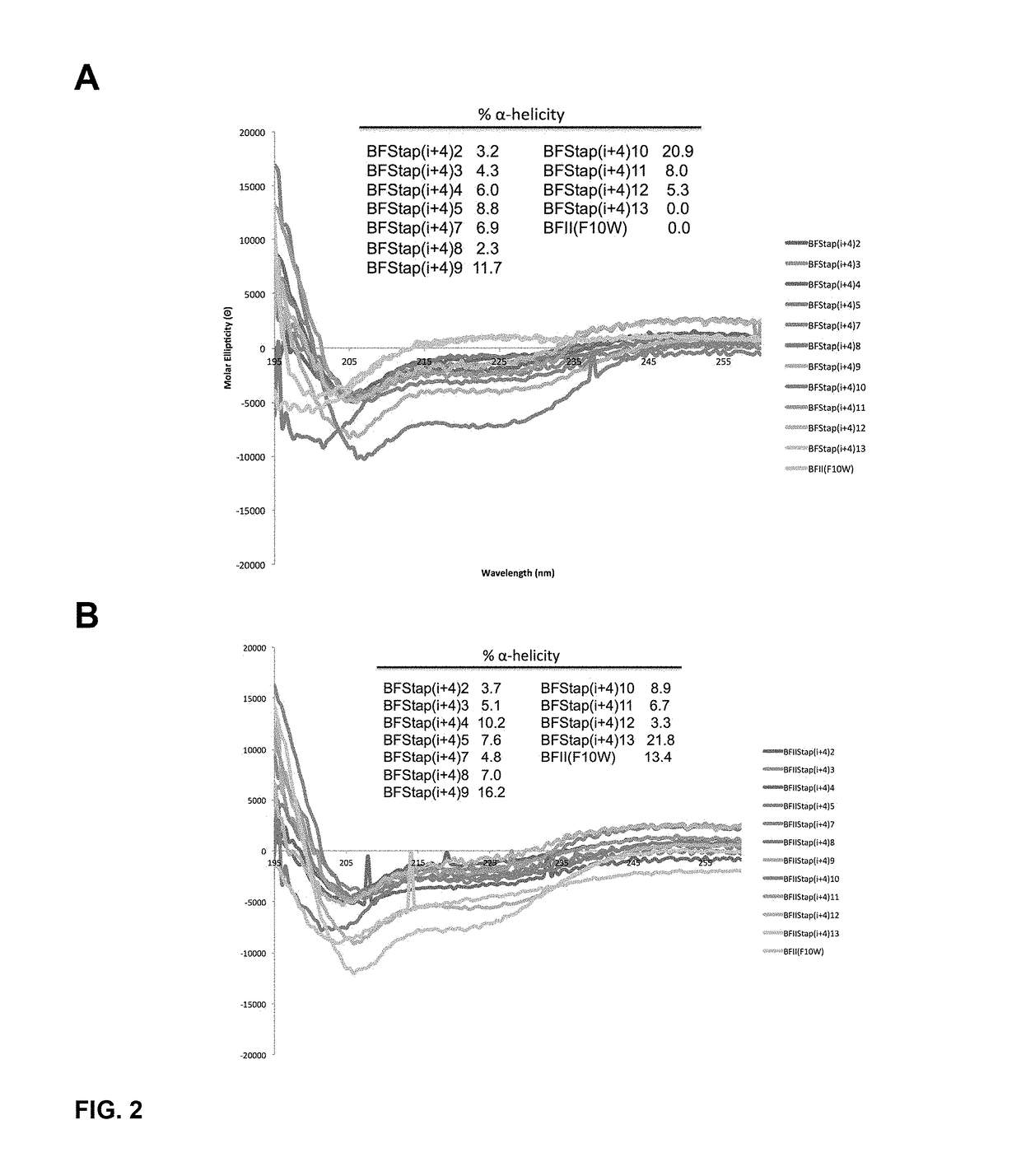
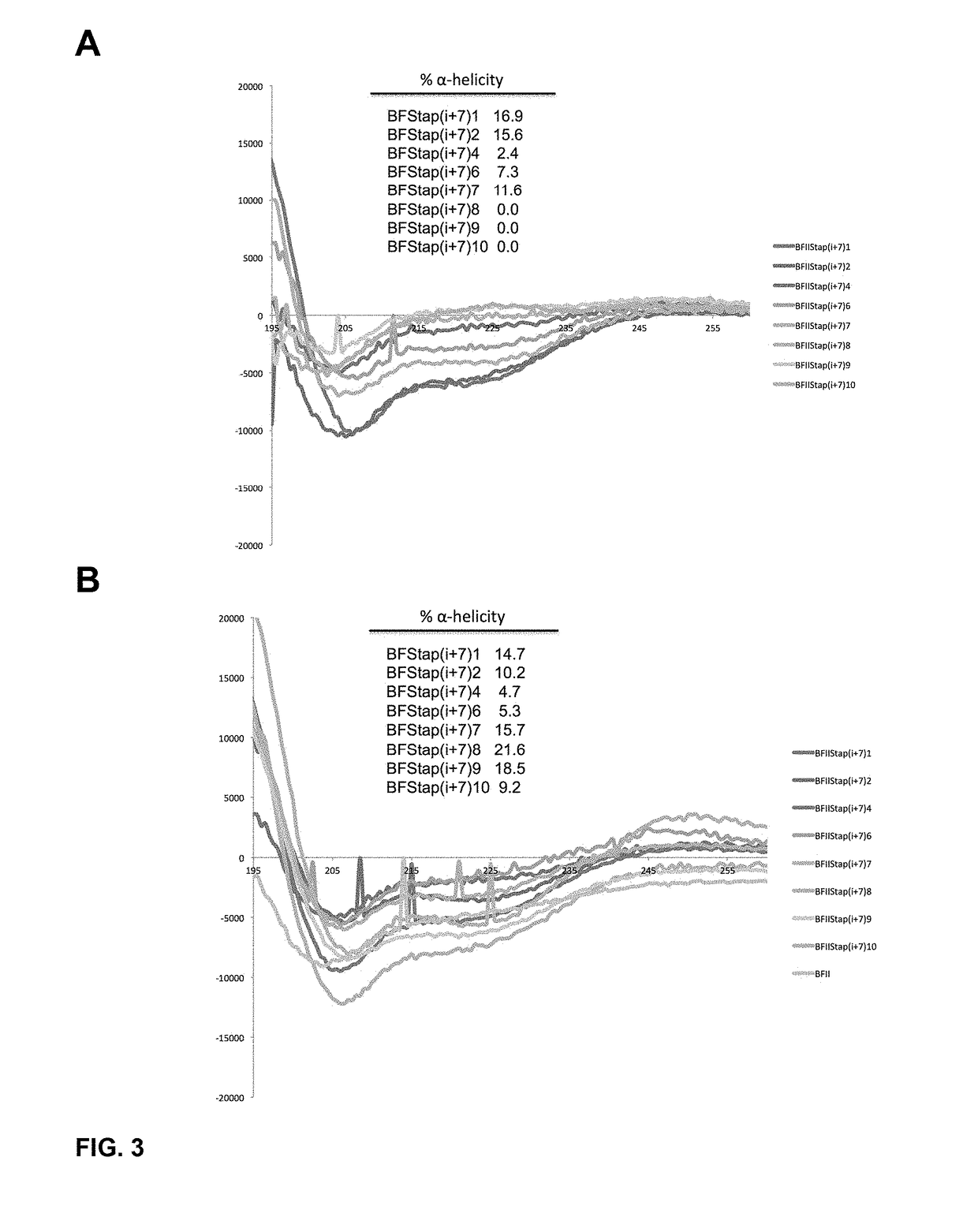
[0433]To determine the α-helical content for each peptide within our panel of stapled I-TAMP analogues, we studied the peptides dissolved in 10 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) using CD spectroscopy in the presence and absence of trifluoroethanol (TFE; 50% v / v), an α-helix promoting solvent. In the absence of TFE, the i, i+4 stapled analogues displayed modestly improved α-helical structure compared to the unstapled parent I-TAMP, buforin II (F10W), which was otherwise completely disordered (FIG. 2 Panel A). Upon the addition of TFE, the α-helical content increased for some of the stapled analogues and the parent I-TAMP (F10W), but not as dramatically as we previously observed for α-helical AMPs (FIG. 2 Panel B), consistent with the incorporation of a helix-breaking proline within the buforin II sequence. The i, i+7 stapled analogues displayed higher levels of α-helicity when compared to their i, i+4 counterparts, both in the presence and ...
example 3
Activity of Stapled I-TAMP Peptides
[0434]One of the key obstacles that have long impeded the use of AMPs in systemic infections such as sepsis is their tendency to lyse human cells, such as red blood cells (RBCs). Thus, it is critical to minimize hemolytic activity as much as possible to achieve a therapeutic window. When we tested stapled analogues of the I-TAMP buforin II in a 1% RBC suspension in phosphate buffer, most i, i+4 analogues displayed low hemolytic activity, although in some cases there was a 5-fold increase in hemolysis (TABLE 1). Generally, the i, i+7 analogues had higher hemolytic activity, likely due to the greater hydrophobicity of the longer hydrocarbon staple (Table 1). Of note, in those circumstances where hydrocarbon staples increase hemolytic activity due to increasing hydrophobicity, the alkene moiety can be modified, e.g., by dihydroxylation, to install hydrophilic residues and potentially mitigate hemolysis.
[0435]Balancing antimicrobial potency and suppres...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com