Chemisorption of ethyl acetate during hydrogenation of acetic acid to ethanol
a technology of ethyl acetate and hydrogenation acetic acid, which is applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal-oxide/metal-hydroxide catalysts, etc., can solve the problem of affecting the commercial viability of catalysts, requiring excessive operating temperatures and pressures, and potentially prohibitively expensive and/or non-selective catalysts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
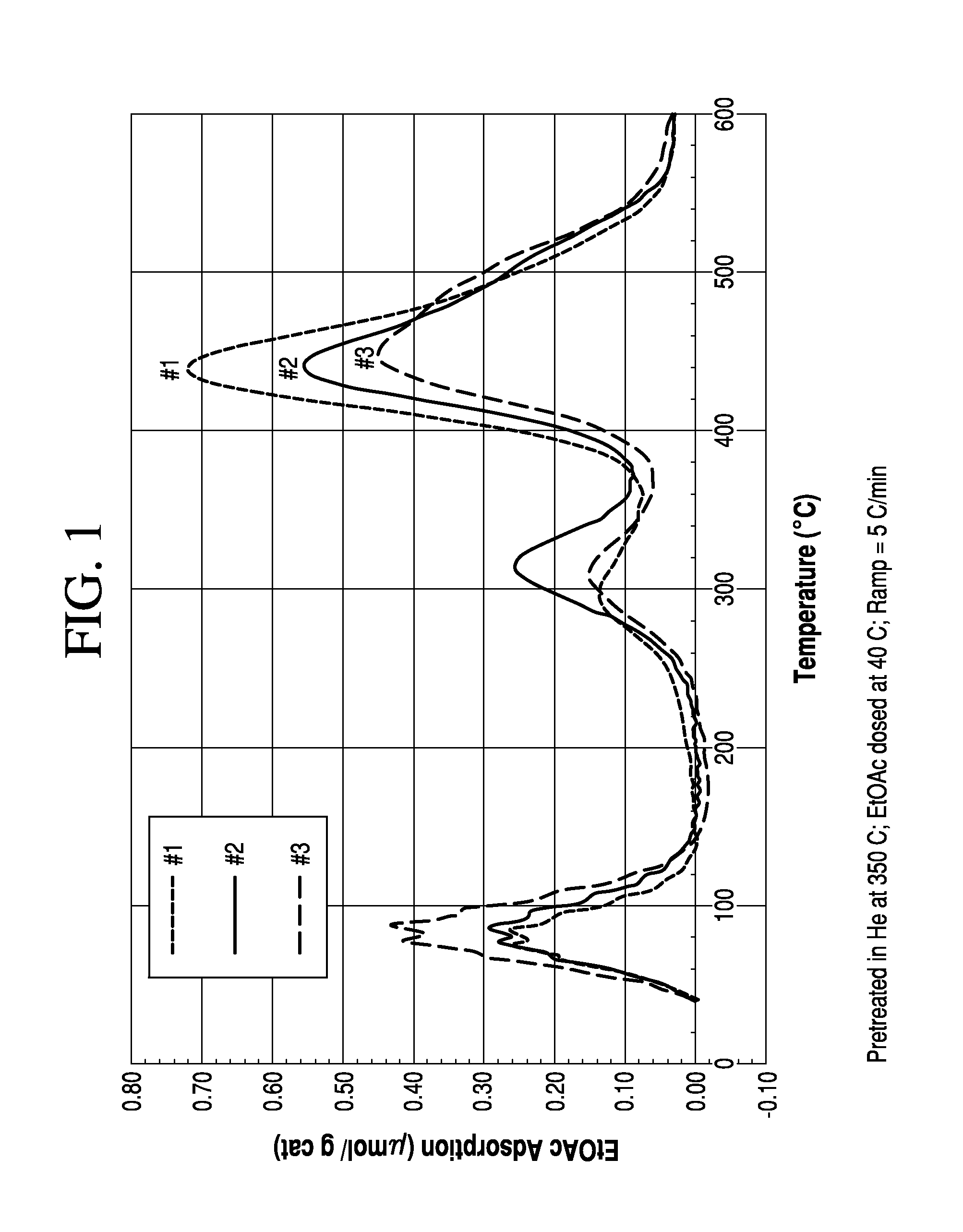
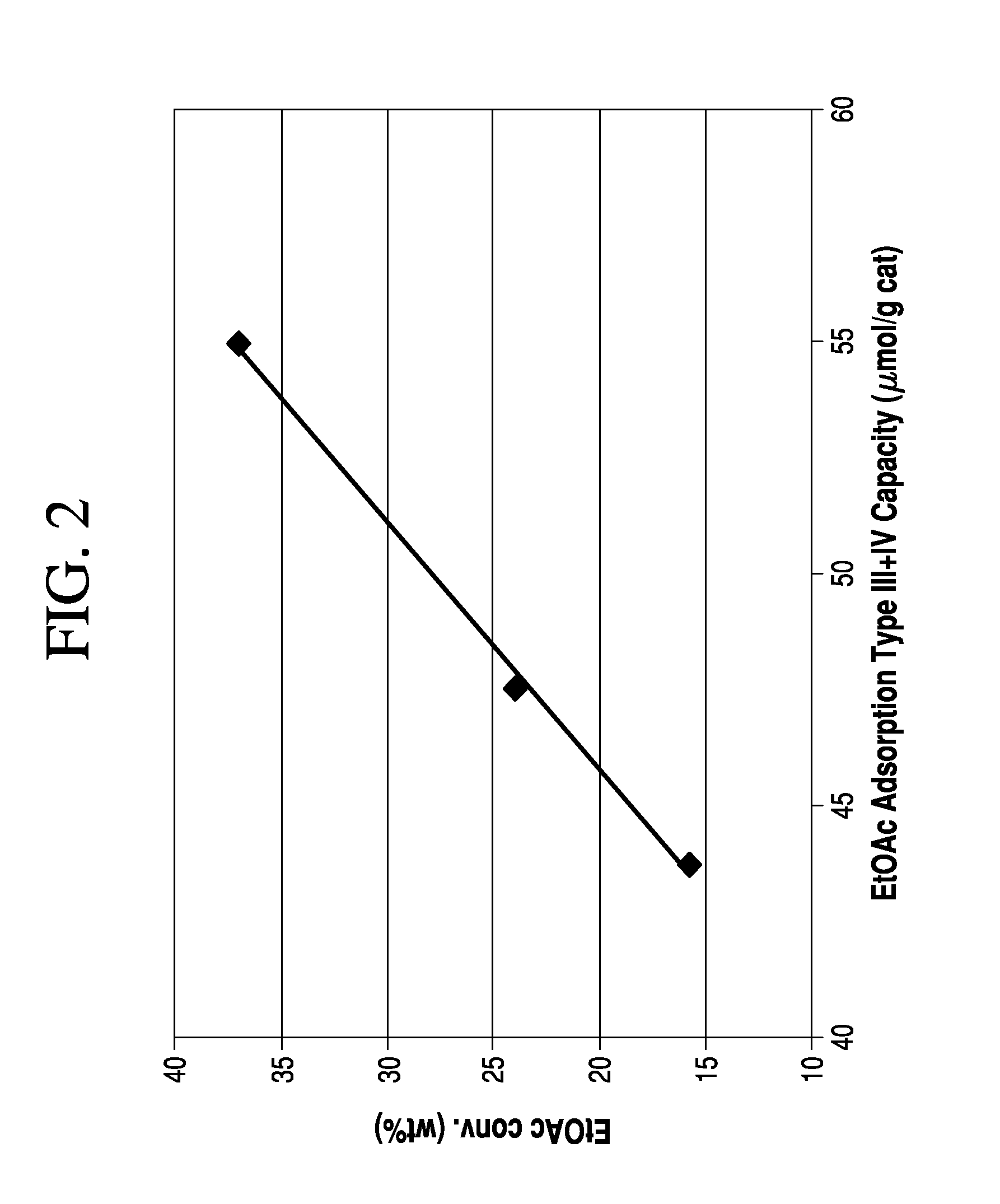
[0083]Surface reactions and molecular adsorption on surfaces can be studied very effectively using Temperature Programmed Desorption (TPD). The TPD technique involves the adsorption of a species on the surface of the catalyst at low temperature, e.g., close to room temperature, and heating the sample at a linear ramp rate while monitoring the species that evolve from the surface of the catalyst. Desorption of the gas from the surface produces a signal in the detector. This signal is plotted against temperature to obtain the TPD profile as shown in FIG. 1. Generally, the area under the peak of the desorbed signal will be proportional to the amount of adsorbed gas. In other words, the area under the curve may be indicative of the surface coverage. The position of peak temperature may be indicative of the strength of adsorption. If there are multiple binding sites on the surface, multiple peak temperatures are observed in the TPD graph.
[0084]In some embodiments, TPD experiments may be ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt. % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com