Axial turbomachine blade with platforms having an angular profile
a technology of axial turbomachine blades and platforms, which is applied in the direction of machines/engines, efficient propulsion technologies, liquid fuel engines, etc., can solve the problems of reducing performance, rotor and stator blade damage, and the block can become particularly heavy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
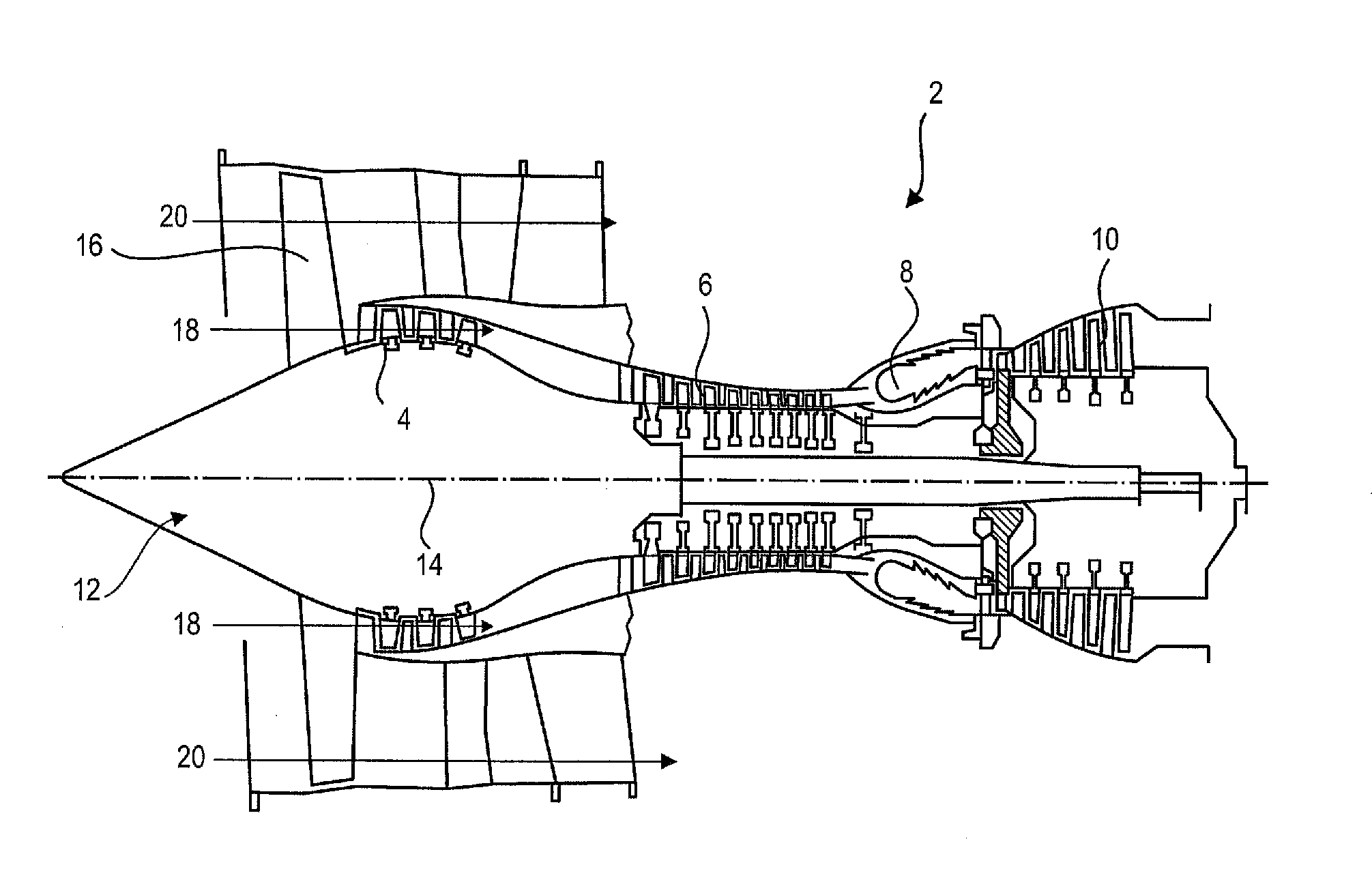
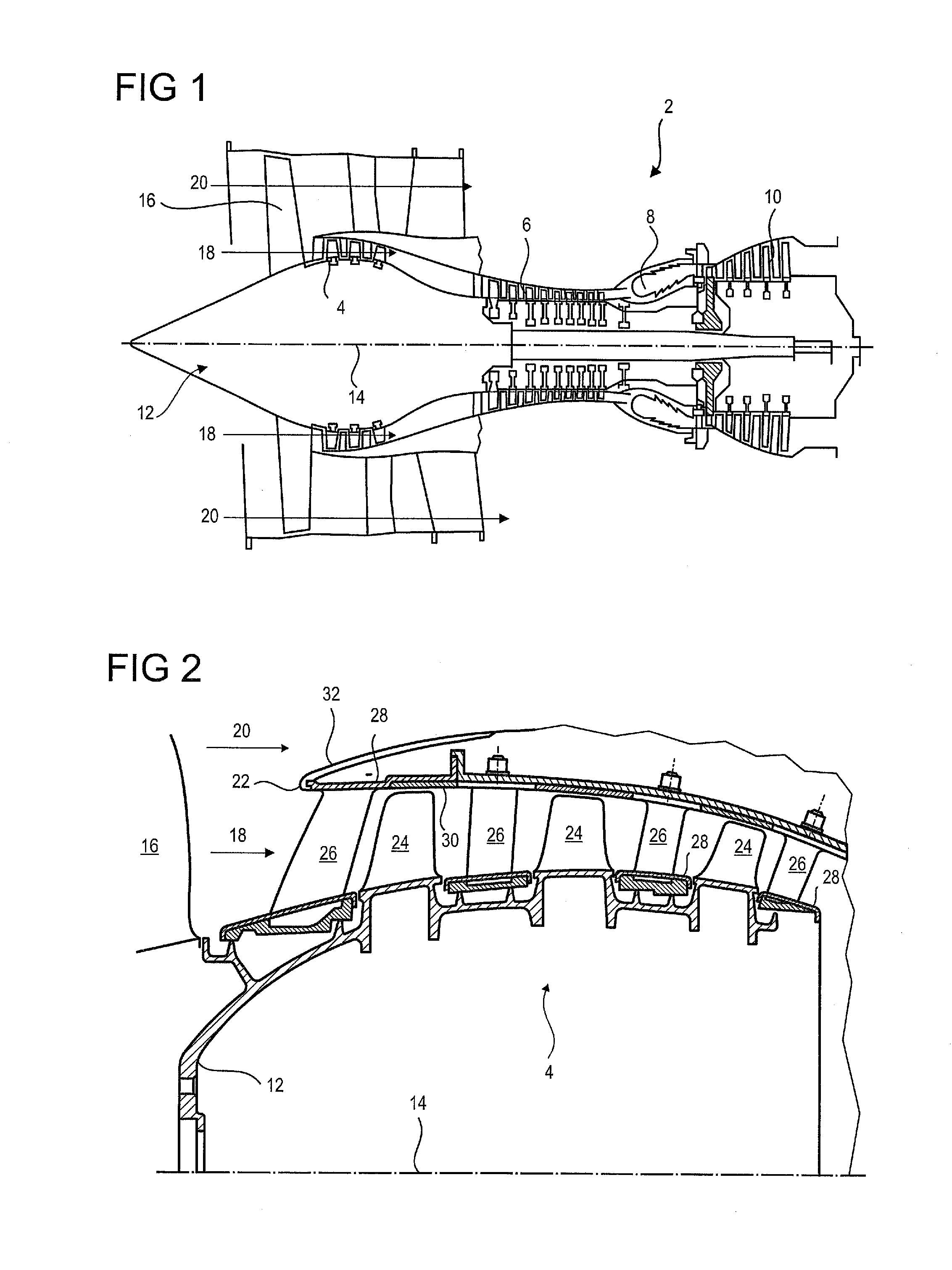
[0059]FIG. 3 illustrates a splitter nose 22 of an axial turbomachine according to the present application.
[0060]The splitter nose 22 is circular in shape. It has a body 32. The latter has a shape of revolution. It comprises an outer wall 34, also of revolution, which is in contact with the secondary flow 20. It is connected to the outer shell 28 of the stator via means of fastening located on its upstream section. Its means of attachment 36 may comprise an annular groove with an axial opening facing downstream. The outer shell 28 may comprise additional means for fixing 38, for example a cylindrical surface designed to mate with the groove 36. The outer shell 28 may also be connected to the outer wall 34 further downstream.
[0061]In order to prevent the formation of ice or to make it melt in a discontinuous manner, the splitter nose 22 has a de-icing device. The latter comprises a channel 40 through which a heat transfer fluid, preferably hot air, circulates. This hot gas can come fr...
second embodiment
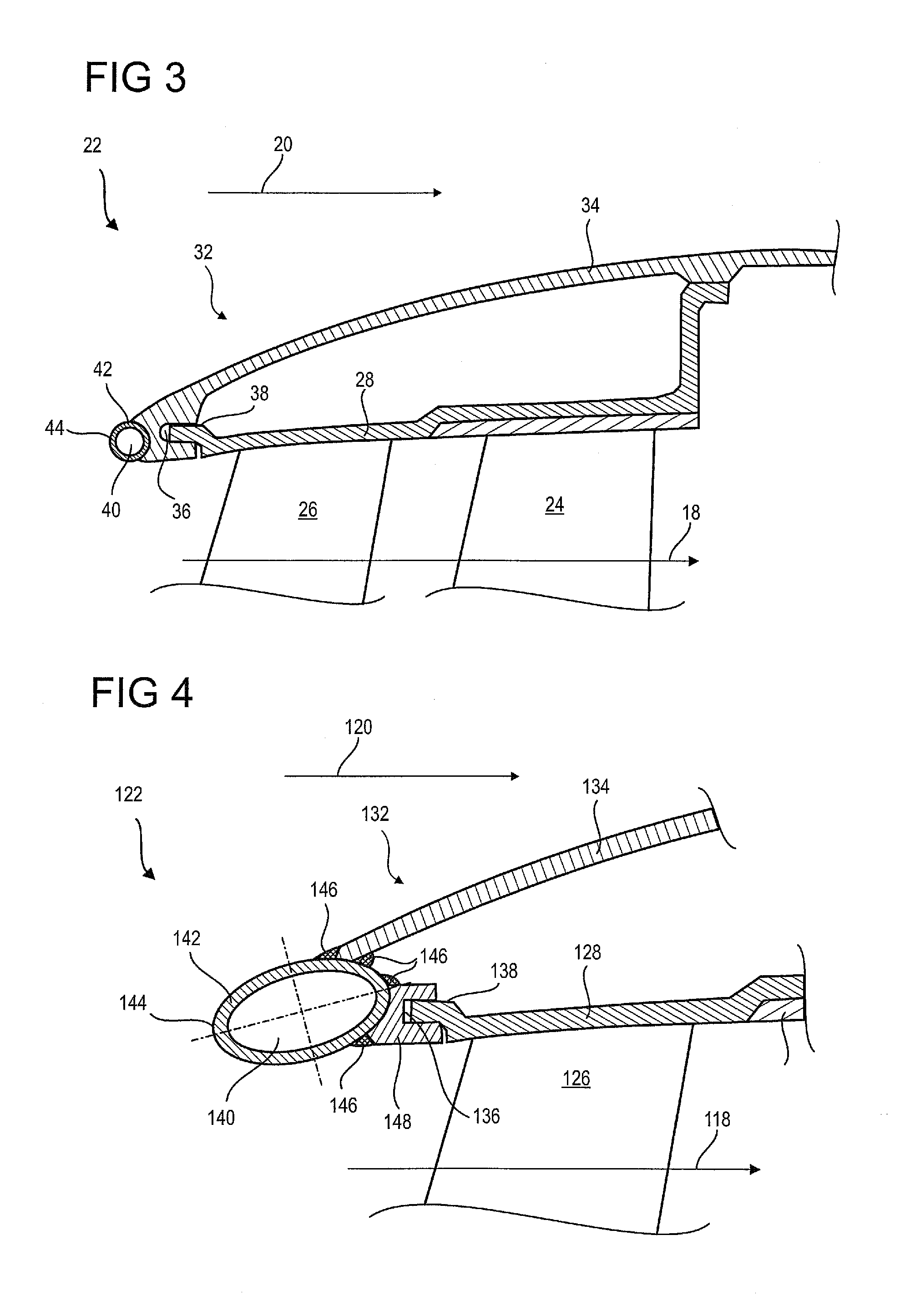
[0067]FIG. 4 illustrates a splitter nose according to the present application. FIG. 4 has the same numbering scheme as in previous figures for the same or similar elements, but the numbering is incremented by 100. Specific numbers are used for items specific to this embodiment.
[0068]The splitter nose 122 comprises a body of revolution 132 with an outer wall 134. It has a de-icing device with a channel 140 defined by a wall 142. The channel 140 travels around the splitter nose 122. The cross section of the wall is profiled. The cross section of the wall 142 and the channel 140 are circular. It may have a flattened portion so as to form a cam shape or an ellipse. The upstream end of major axis of the ellipse or of the cam is inclined inwards. This feature allows the flow to be separated more accurately.
[0069]The wall may have a variable thickness, it can be thinner where it is in contact with the flow, and thicker when in contact with the remainder of the nose This design enables the ...
third embodiment
[0072]FIG. 5 illustrates a splitter nose according to the present application. FIG. 5 has the same numbering scheme as in previous figures for the same or similar elements, but the numbering is incremented by 200. Specific numbers are used for items specific to this embodiment.
[0073]The splitter nose 222 comprises a body of revolution 232 with an outer wall 234. It has a de-icing device with a channel 240 defined by a contoured wall 242. The wall 242 may be welded using weld beads 246 sealing the channel 240. The profile of the wall can comprise curved and straight parts, which facilitates constructing any desired geometry. These straight sections improve the overall strength and the curved parts can concentrate the absorption of impact energy by deforming.
[0074]The profile of the wall can be closed or advantageously open. The body 232 has a front surface 250 extending generally radially. It contributes to delimiting the channel 240 in combination with the wall 242. This feature sav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com