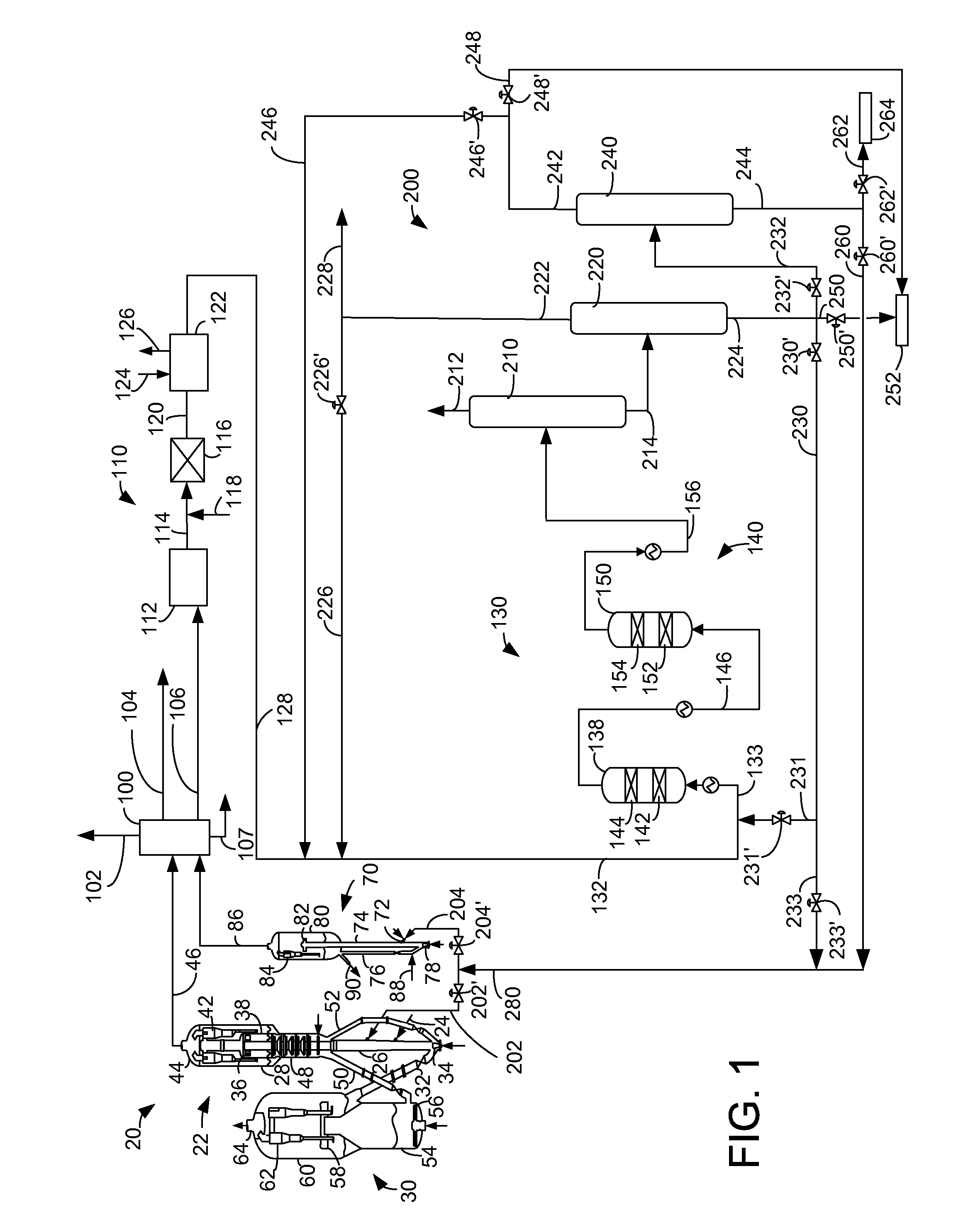
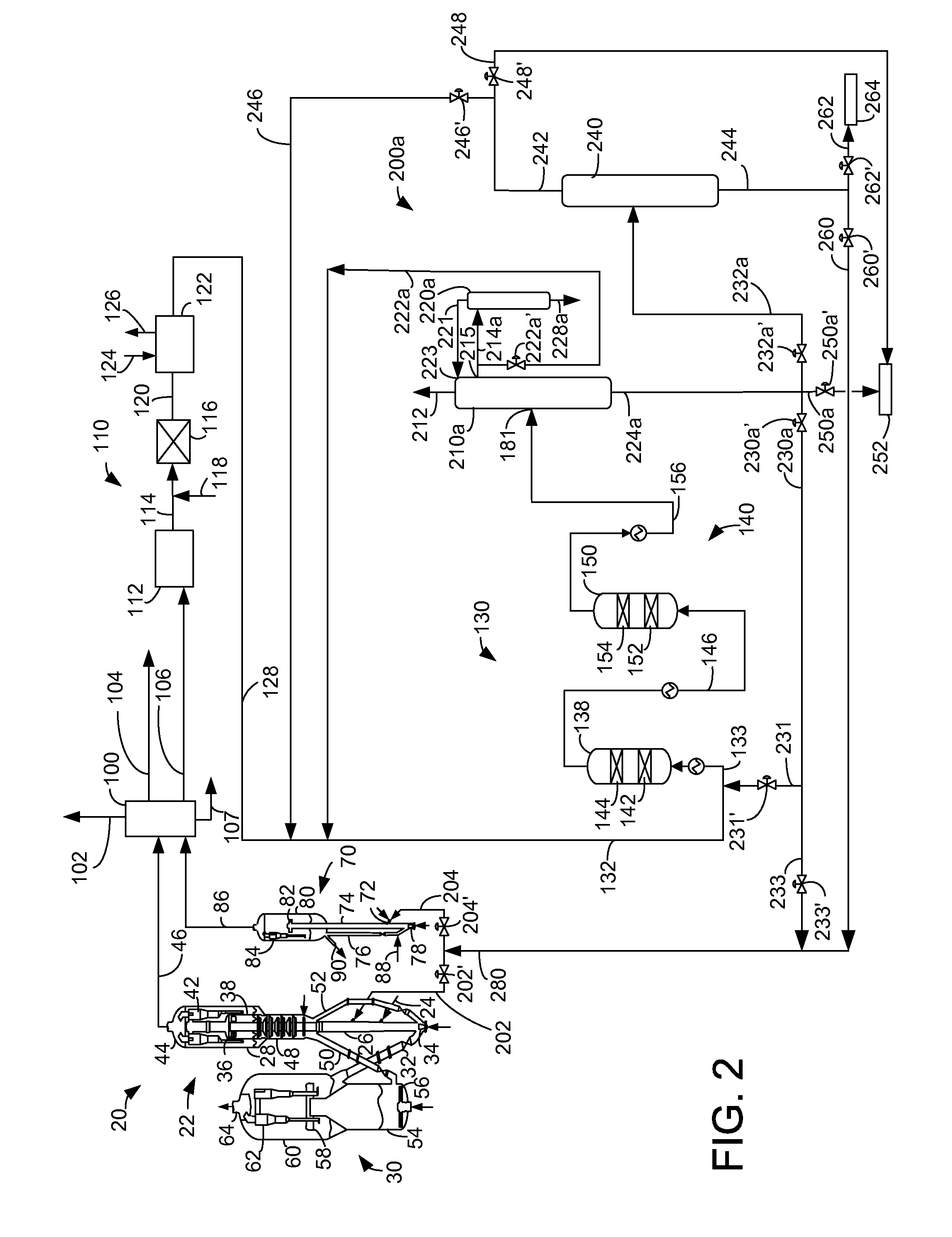
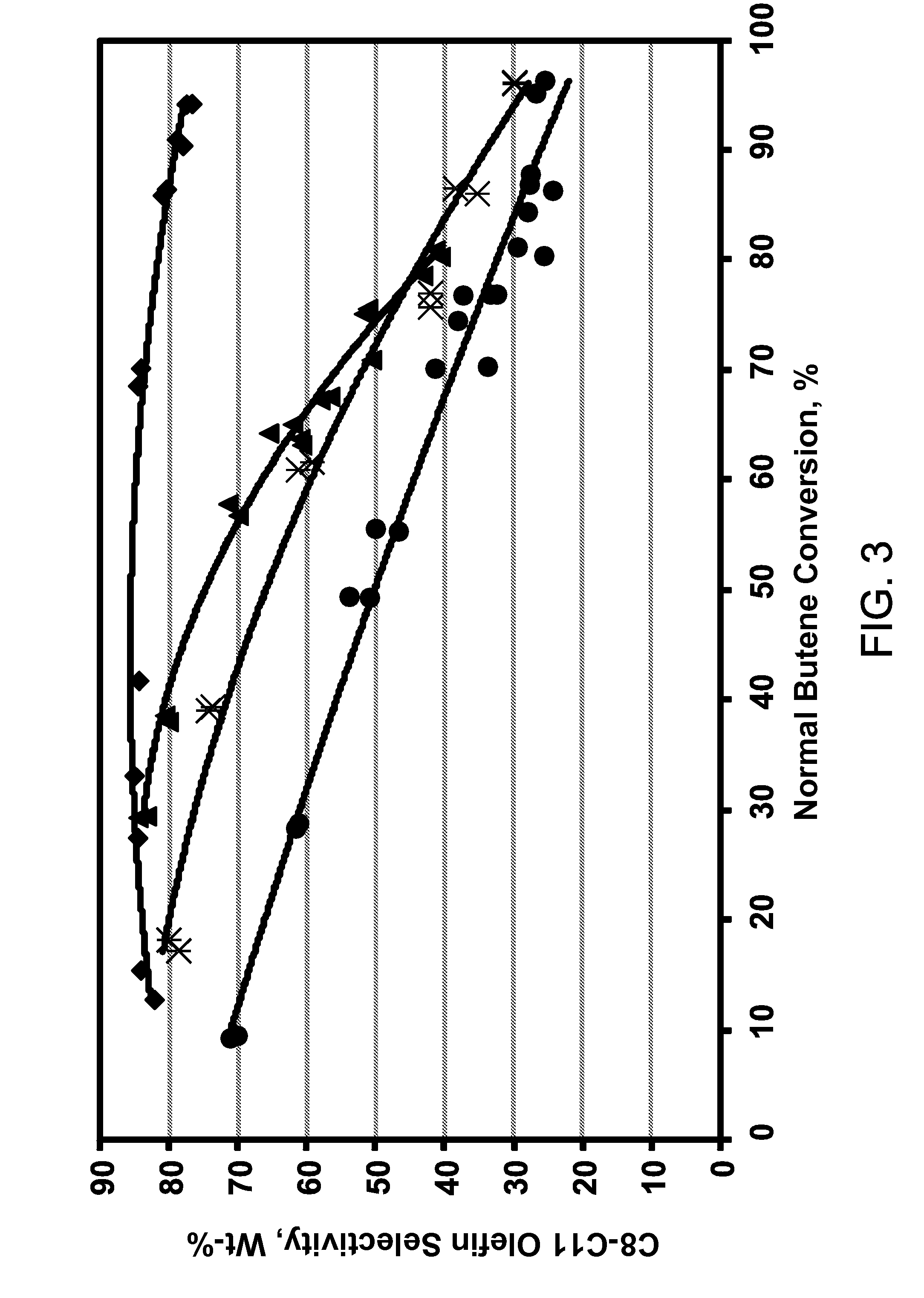
Process for making propylene from oligomerization and cracking
a technology of oligomerization and cracking, which is applied in the direction of hydrocarbon preparation catalysts, hydrocarbon oil treatment products, alkylation treatment, etc., can solve the problems of less and poorer quality gasoline, less and poorer diesel products, and limit as to what can be achieved by oligomerizing butenes, etc., to achieve the effect of easy cracking of propylene molecules and rapid cracking of fluid catalytically to propylen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0118]Feed 1 in Table 2 was contacted with four catalysts to determine their effectiveness in oligomerizing butenes.
TABLE 2ComponentFraction, wt %propylene0.1Iso-C4's70.04isobutylene7.71-butene5.72-butene (cis and trans)16.283-methyl-1-butene0.16acetone0.02Total100
[0119]Catalyst A is an MTT catalyst purchased from Zeolyst having a product code Z2K019E and extruded with alumina to be 25 wt % zeolite. Of MTT zeolite powder, 53.7 grams was combined with 2.0 grams Methocel and 208.3 grams Catapal B boehmite. These powders were mixed in a muller before a mixture of 18.2 g HNO3 and 133 grams distilled water was added to the powders. The composition was blended thoroughly in the muller to effect an extrudable dough of about 52% LOI. The dough then was extruded through a die plate to form cylindrical extrudates having a diameter of about 3.18 mm. The extrudates then were air dried, and calcined at a temperature of about 550° C. The MTT catalyst was not selectivated to neutralize surface aci...
example 2
[0129]A comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with flame ionization detection (GC×GC−FID) method was developed and utilized to analyze the composition of light olefin oligomerization product streams. To develop the peak identifications, a GC×GC instrument equipped with a time of flight mass spectrometer (TOFMS) was used. Peak identifications were checked against a table of C8 olefin boiling points for consistency and by performing GC-FID of the olefinic sample with and without hydrogenation catalyst in the GC inlet to ensure that peaks assigned to a particular C8 mono-olefin moved to their respective saturated C8 isoparaffins. The identification of C8 paraffin isomers can be achieved using the UOP690 method. Careful matching of chromatographic conditions between GC×GC−FID and GC×GC−TOFMS allows one to translate identifications made from the TOFMS analysis to the GC×GC−FID for quantitative analysis. The following 48 compounds in the C8 region were identified and quantified...
example 3
[0135]Two types of feed were oligomerized over oligomerization catalyst A of Example 1, MTT zeolite. Feeds 1 and 2 contacted with catalyst A are shown in Table 7. Feed 1 is from Example 1.
TABLE 7Feed 1Feed 2ComponentFraction, wt %Fraction, wt %propylene0.10.1isobutane70.049.73isobutylene7.76.31-butene5.74.92-methyl-2-butene09.02-butene (cis & trans)16.289.83-met-1-butene0.160.16n-hexane060acetone0.020.01Total100100
[0136]In Feed 2, C5 olefin is made up of 2-methyl-2-butene and 3-methyl-1-butene which comprises 9.16 wt % of the reaction mixture representing about a third of the olefins in the feed. 3-methyl-1-butene is present in both feeds in small amounts. Propylene was present at less than 0.1 wt % in both feeds.
[0137]The reaction conditions were 6.2 MPa and a 1.5 WHSV. The maximum catalyst bed temperature was 220° C. Oligomerization achievements are shown in Table 8.
TABLE 8Feed 1Feed 2Inlet Temperature, ° C.192198C4 olefin conversion, %9899nC4 olefin conversion, %9799C5 olefin con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pore structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pore | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com