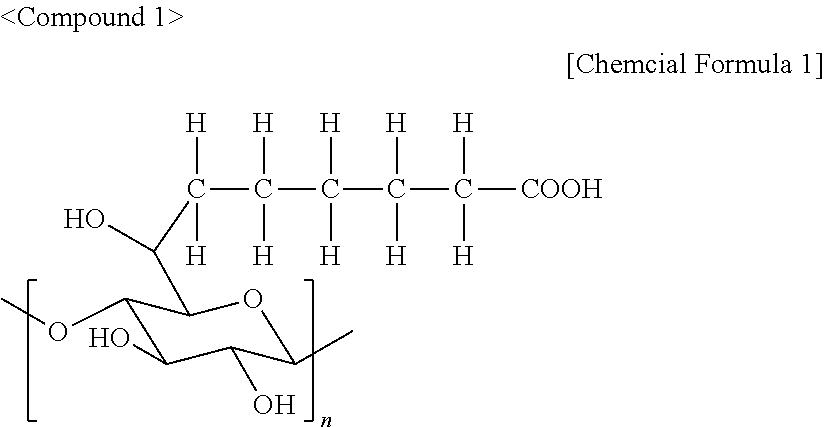
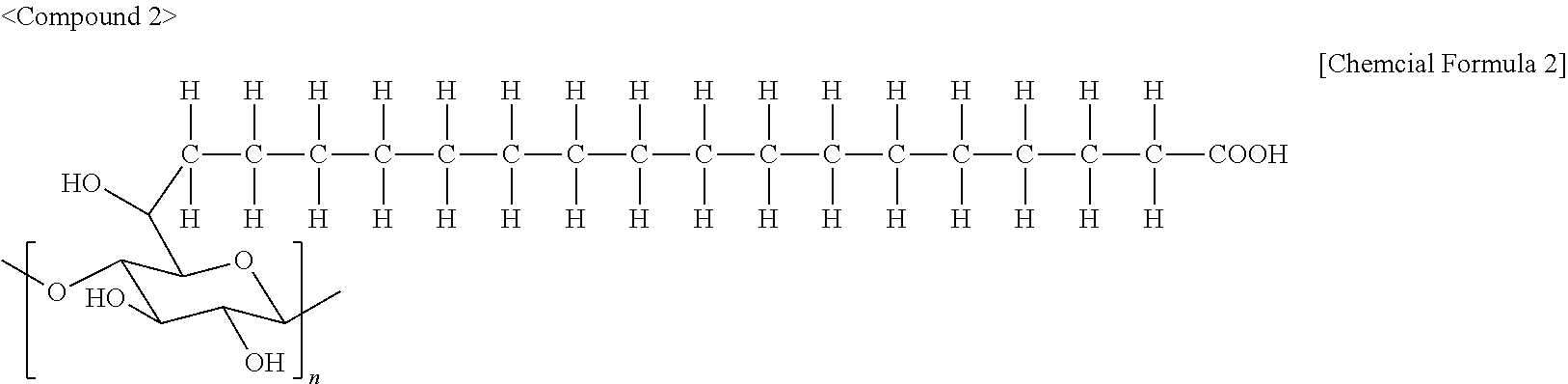
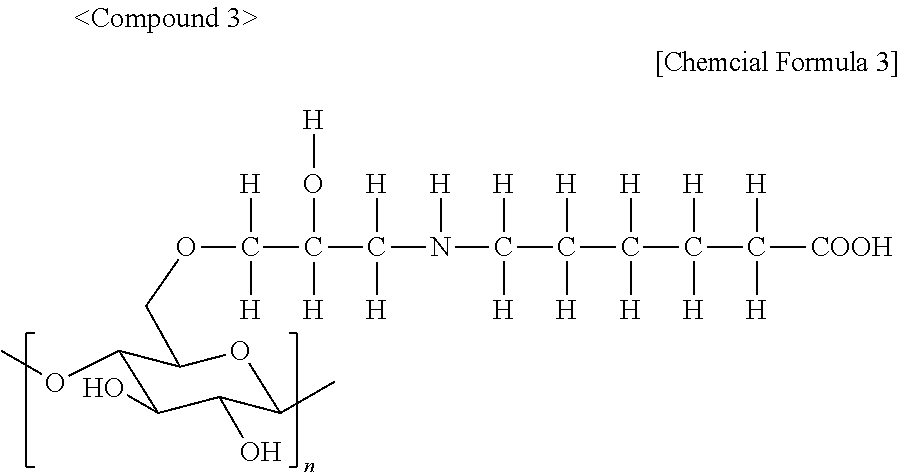
Organic colored microparticles, diagnostic reagent kit containing the same, and in vitro diagnosis method
a technology of colored microparticles and diagnostic reagents, which is applied in the field of organic colored microparticles, diagnostic reagent kits containing the same, and in vitro diagnosis methods, can solve the problems of inhibition of adsorption in the presence of surfactants, limited color to a single, and absence of fixed binding sites, etc., to achieve rapid diagnosis, improve color properties, and reduce the level of erroneous diagnosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0065]Linter cellulose was dissolved in a cuprammonium solution followed by diluting with water and ammonia to prepare a cuprammonium solution cellulose solution having a cellulose concentration of 0.37% by weight. The copper concentration of that solution was 0.13% by weight, and the ammonia concentration was 1.00% by weight. Next, a congealing liquid was prepared having a tetrahydrofuran concentration of 90% by weight and water concentration of 10% by weight. 500 g of the preliminarily prepared cuprammonium cellulose solution having a cellulose concentration of 0.37% by weight were then added while slowly stirring 5000 g of the congealing liquid using a magnetic stirrer. After continuing to stir for about 5 seconds, 1000 g of 10% by weight sulfuric acid were added to carry out neutralization and regeneration and obtain 26500 g of a slurry containing the target cellulose microparticles. The resulting slurry was then centrifuged for 10 minutes at a speed of 10000 rpm. The precipitat...
example 2
[0068]Although the unstained cellulose microparticles obtained in Example 1 were stained using the same procedure, the procedure was carried out for a total of 10 cycles to obtain stained microparticles. The results of measuring average particle size and color intensity before and after staining are shown in the following Table 1.
example 3
[0069]Cellulose microparticles and stained cellulose microparticles were obtained using the same method as Example 1 with the exception of using Levafix Rubine CA Gr. (Registered Trade Mark) manufactured by Dystar GmbH Corp. (to also be referred to as red dye B) as a reactive stain to stain the unstained cellulose microparticles obtained in Example 1. The results of measuring average grain size and color intensity before and after staining are shown in the following Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com