Municipal solid waste fuel steam generator with waterwall furnace platens
a technology of solid waste fuel and furnace plate, which is applied in the direction of water-tube boilers, corrosion-reducing boiler components, lighting and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of high material demands on the superheater in these extreme temperatures, inability to increase the size of the furnace adequately, and inability to meet the requirements of superheaters, etc., to reduce the furnace exit gas temperature, reduce the corrosion of the superheater, and facilitate heat transfer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
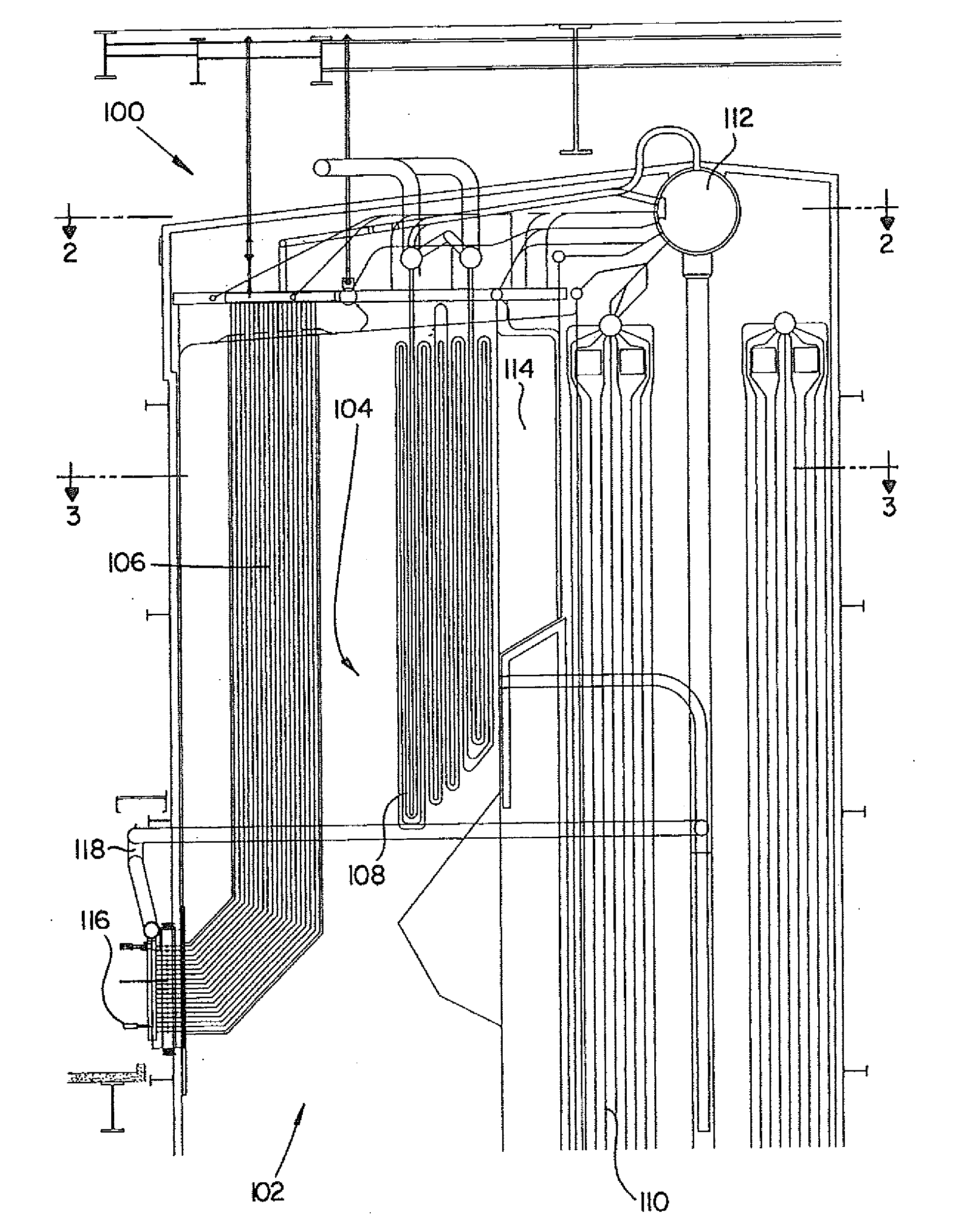
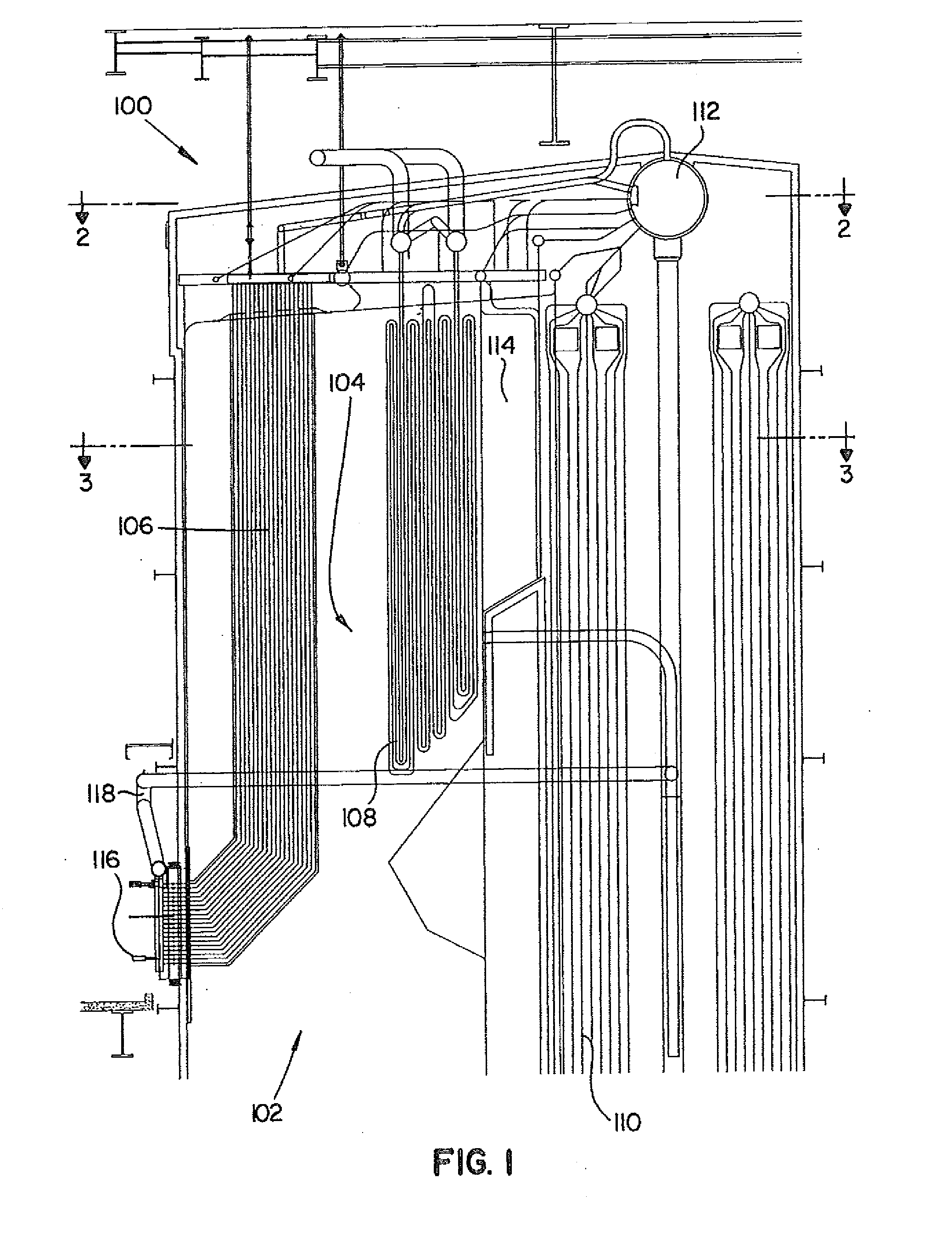
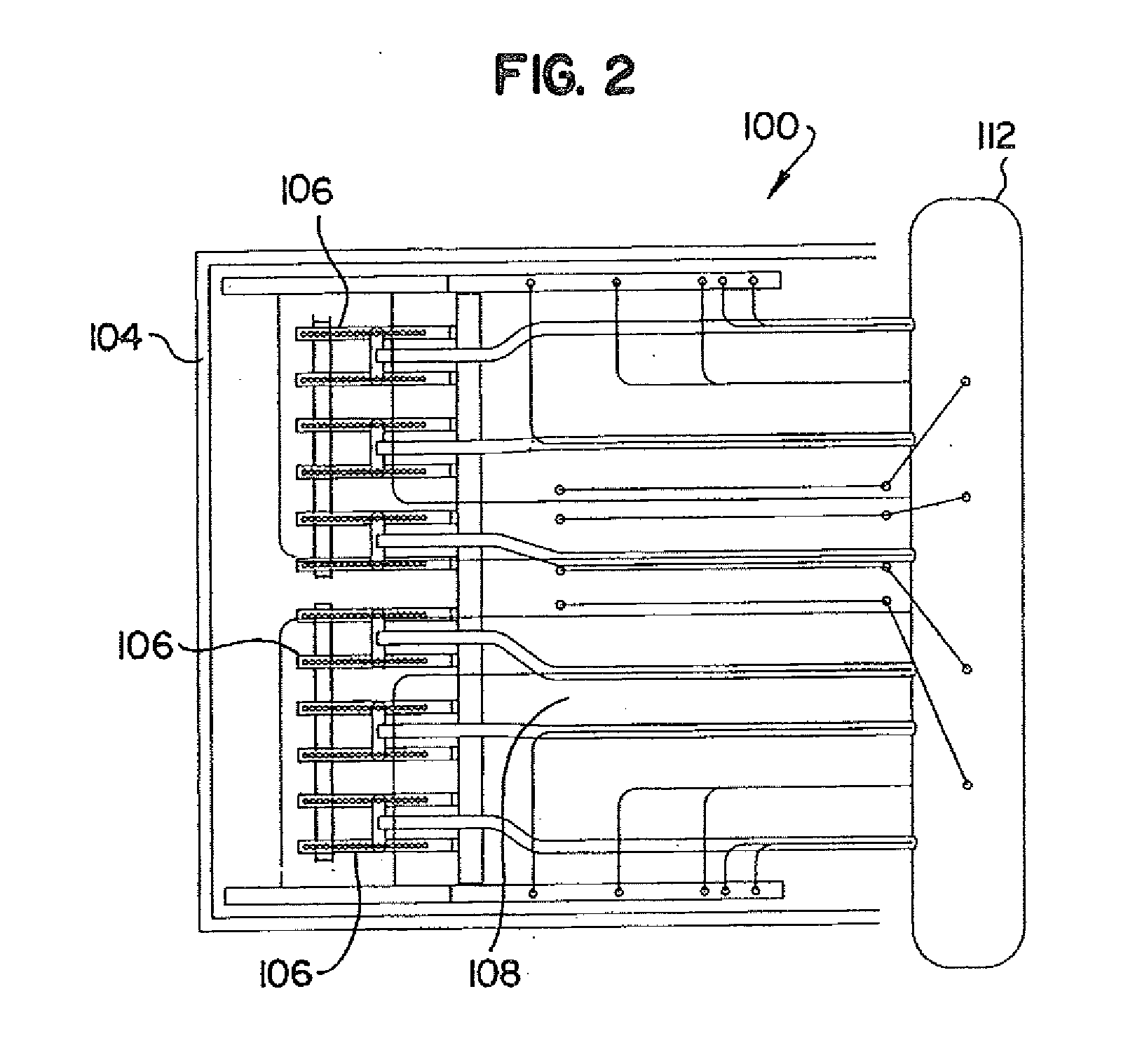
[0027]Reference will now be made in detail to the present preferred embodiments of the invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. The method and corresponding steps of the invention will be described in conjunction with the detailed description of the system. The devices and methods presented herein may be used for reducing the corrosion of superheaters in municipal solid waste fuel steam generators. The present invention is well suited to decrease furnace exit gas temperature and improve furnace gas flow distribution.
[0028]Referring to the Figures generally, wherein like numerals designate the same element throughout the several drawings, FIG. 1 shows a cross-sectional side elevation view of an exemplary embodiment of a steam generator for generating steam from combusting municipal solid waste as fuel in accordance with the invention, which is designated 100. Other embodiments of a steam generator in accordance with the invention, or aspects thereof,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com