Methods of detecting cancer cells and use of same for diagnosing and monitoring treatment of the disease
a cancer cell and detection method technology, applied in the field of detecting cancer, can solve the problems of abnormally fast growth of cancer cells, toxic side effects of the current generation of chemotherapeutic drugs utilized in cancer treatment, and the cultulation of healthy cells/tissues within the patien
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Manufacture of the Nano-Bio-Chip
[0131]A nano-bio-chip was designed and fabricated using standard micro-system-technology (MST) methods. Its architecture included an array of miniaturized electrochemical cells. The cells were placed in the nano-volume chambers (i.e. the electrochemical-cells). The cylindrical chambers held 100 nL volume each. All arrays included positive and negative controls chambers.
[0132]The device was manufactured in two parts: a) a disposable chip—with the nano-chambers where the cells were placed, and b) a reusable chip, with an interface to electronic circuitry which included a multiplexer, potentiostat, temperature control and a pocket PC for sensing and data analysis. This setting allowed continuous reusing for multiple measurements.
[0133]The chip was produced from silicon, and contained an array of eight miniaturized electrochemical cells. Each electrochemical-cell consisted of three circular-shaped electrodes, surrounded by an insulating silicon nitride la...
example 2
Effect of Drugs on Colon Cancer Cells as Assayed by the Biochip of the Present Invention
[0140]In order to individualize cancer therapy, the influence of various single-source drugs on human colon cancer cells (HT-29), was examined.
[0141]Results
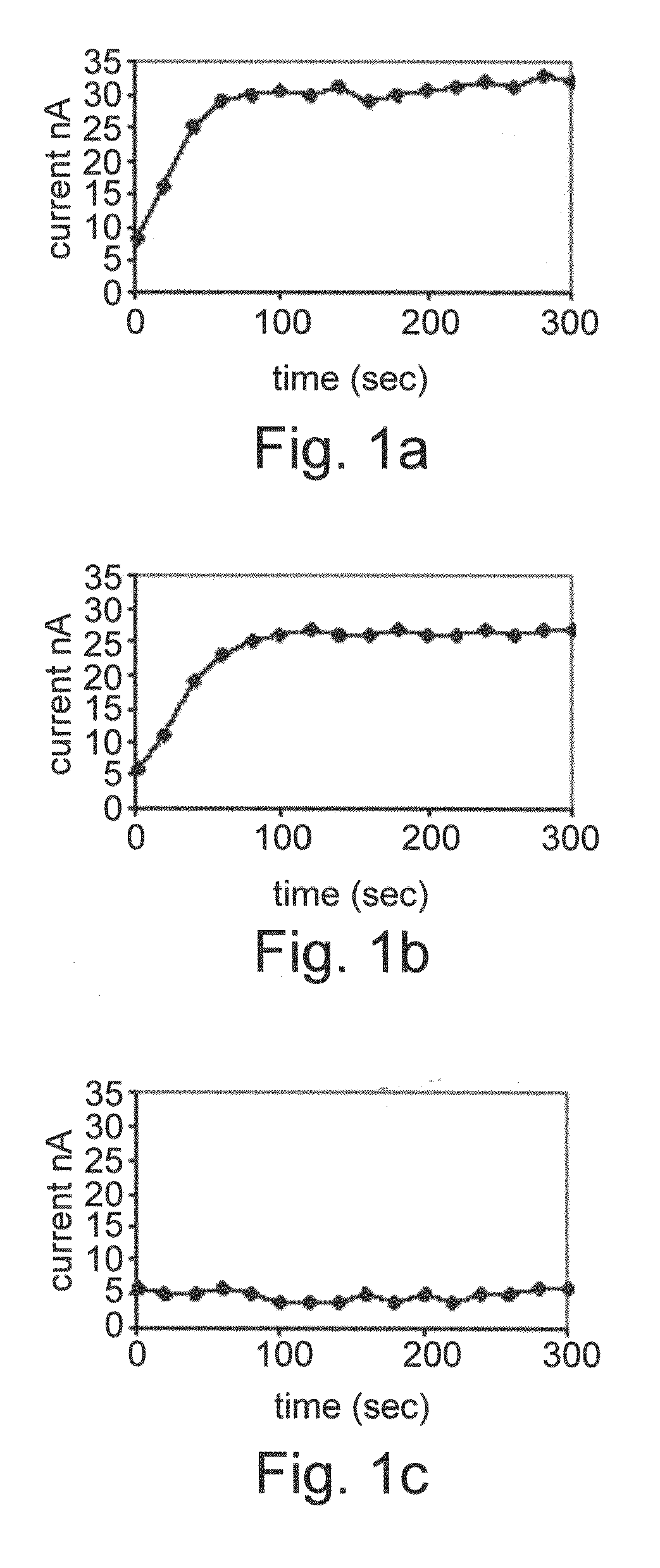
[0142]HT-29 colon cancer cells were exposed for 96 hours to various differentiation therapy agents and the induced alkaline phosphatase activity was measured. Each electrochemical chamber on the array was loaded with cells exposed to a different agent—namely Butyric acid, butyroylmethyl-diethyl phosphate and pivaloyloxymethyl butyrate. The results are shown in FIG. 1A-C. Normal enzymatic activity denotes that the cells differentiate properly as a consequence of the particular drug treatment. As shown in FIGS. 1A-C, BA and butyroylmethyl-diethyl phosphate induced enzymatic activity of alkaline phosphatase, whilst pivaloyloxymethyl butyrate did not induce any enzyme activity at 50 μM concentration exposure, which may be related to its reduced po...
example 3
Quantification of Cancer Cells by the Biochip
[0143]Results
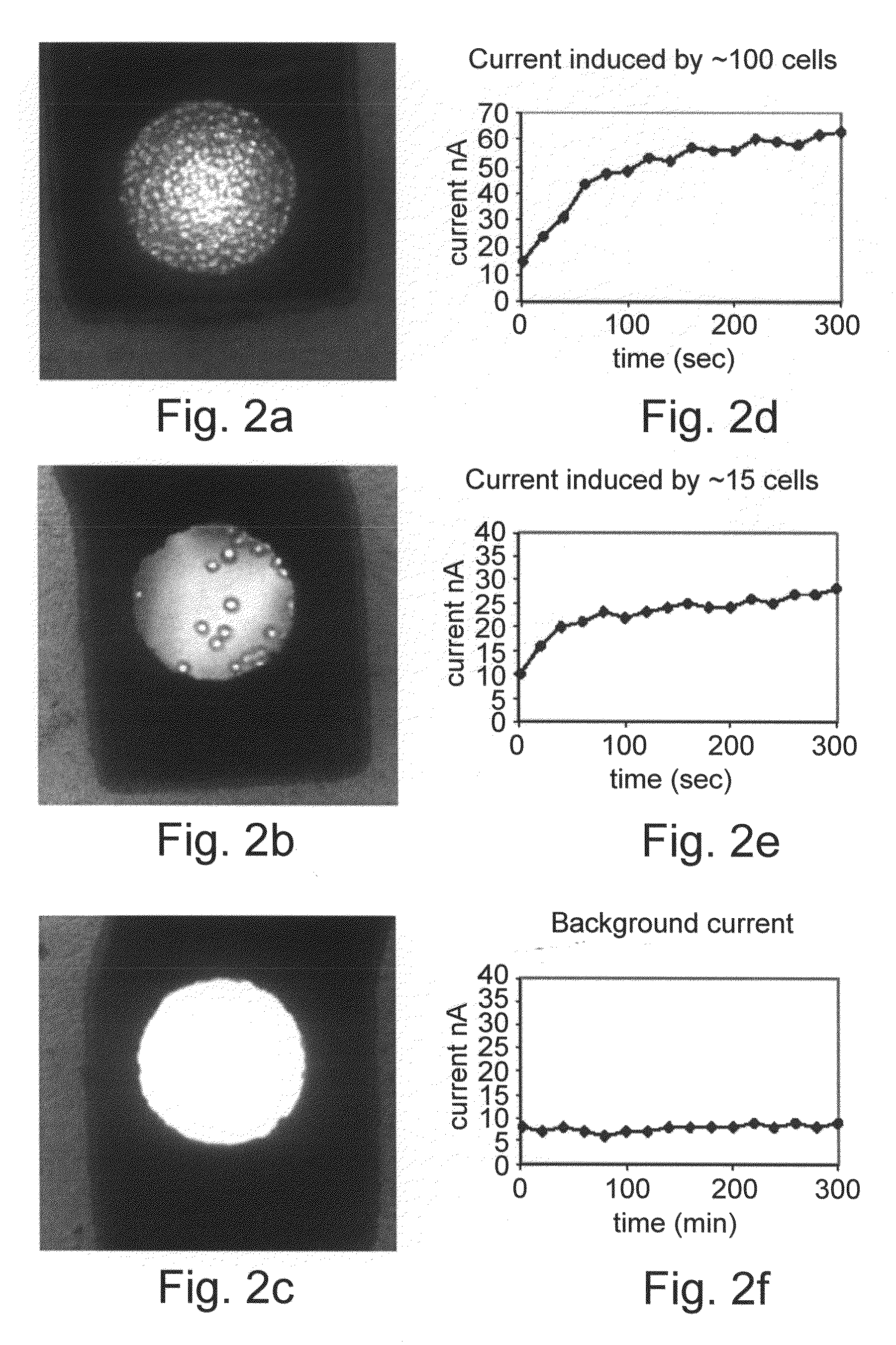
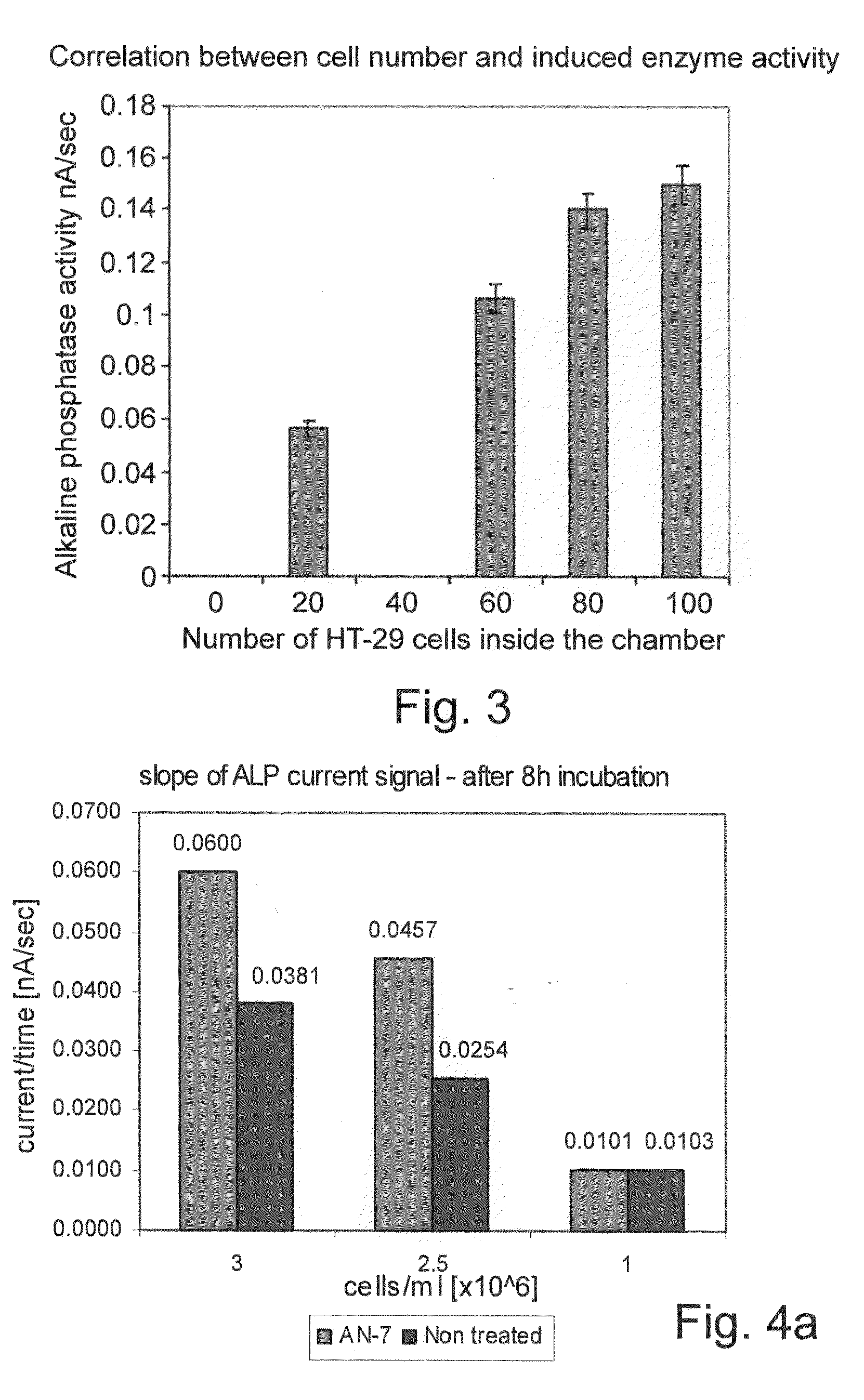
[0144]A remarkable quantitative correlation between the induced current signals and the number of cancer cells counted inside the nano-volume chamber was detected. Numeration of the cancer cells and the relative enzymatic activity are shown in FIGS. 2A-F. Amperometric response curves for monitoring of alkaline phosphatase activity were generated using the electrochemical array chip. The HT-29 colon cancer cells were exposed to Butyric acid (2.5 mM). The HT-29 cells with the substrate PAPP were placed into the 100 mL volume electrochemical chambers on the chip. Current was measured using the amperometric technique at 220 mV. Upper middle and lower curves represent the current response of about 100 cells, 15 and 0 cells counted inside the chamber, respectively. Multiple measurements demonstrated high correlation between cell number counted inside the chamber and alkaline phosphatase activity. The results are shown in FIG. 3. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com