Modulation of excitable tissue function by peripherally administered erythropoietin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
6. EXAMPLE 1
Peripherally Administered EPO Enhances Cognitive Function
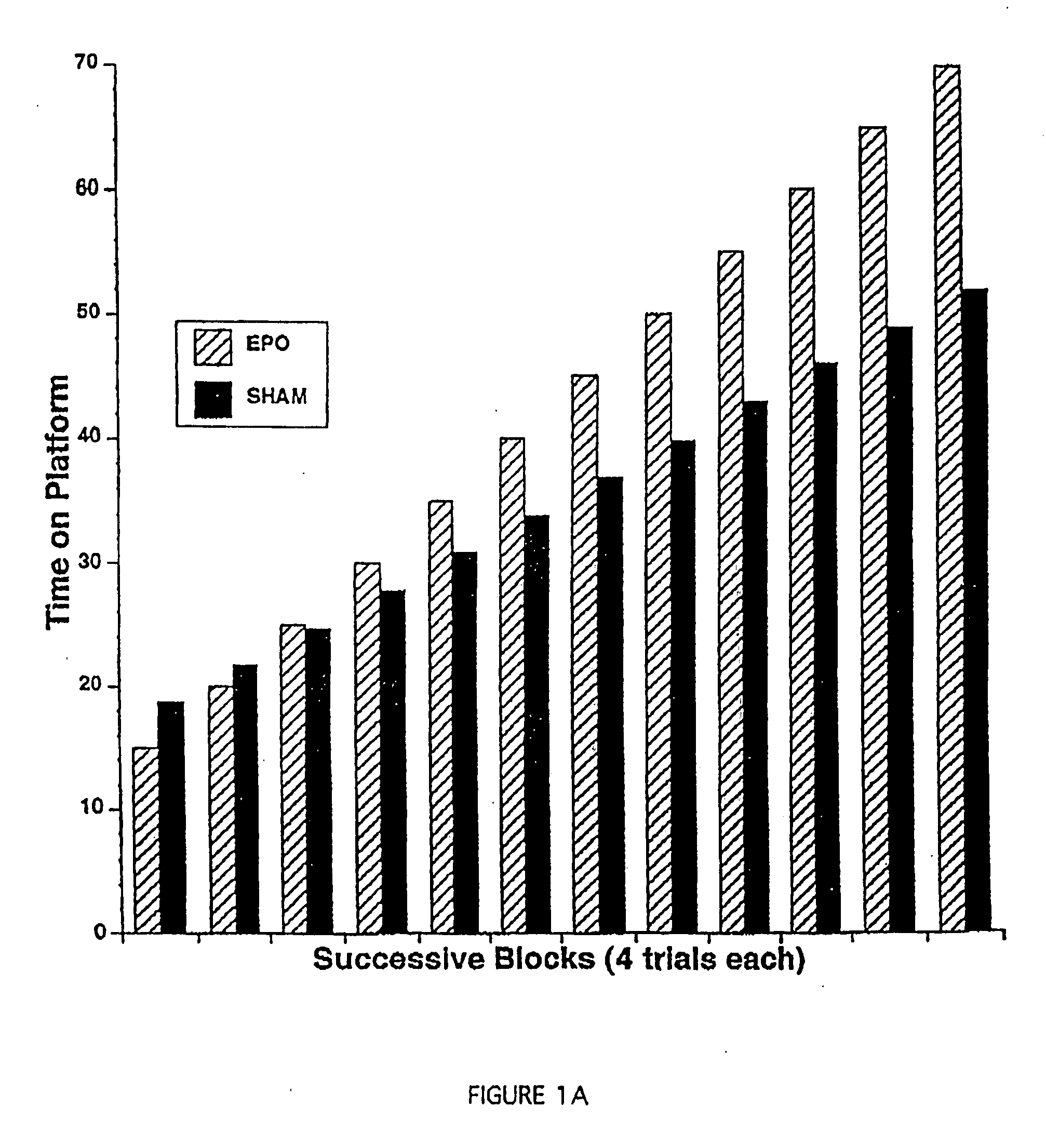
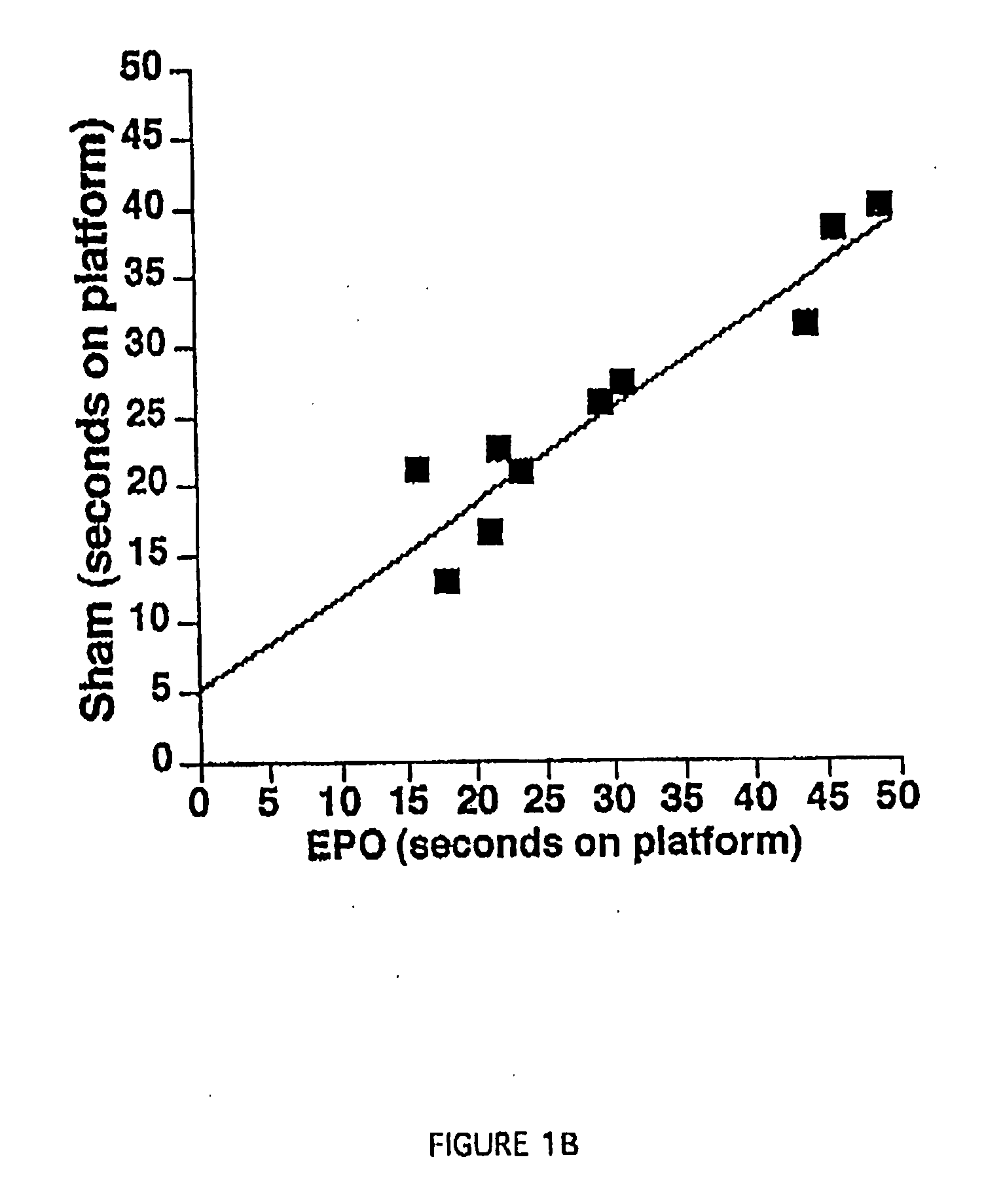
[0108] In this Example, a spatial navigation experiment, known as the Morris Water Maze test, demonstrates EPO-induced enhancement of cognitive function in mice. In this test, a small transparent platform is placed in one quadrant of a swimming pool with opaque water. Mice placed into this swimming pool must swim until they reach the resting platform below the surface, which is invisible to the swimming mice. The test consists of measuring the time the animals take to get to the platform (i.e., the length of time they spend swimming). On successive trials, the time each mouse takes to reach the platform will decrease as a function of them learning its location. This type of learning experiment involves the hippocampus, as hippocampal lesions prevent learning in this test.
[0109] Experiments were carried out in a circular black pool, 150 cm in diameter. Four points were arbitrarily assigned: north, south, east and ...
example 2
7. EXAMPLE 2
Peripherally Administered EPO Strengthens a Learned Conditioned Taste Aversion
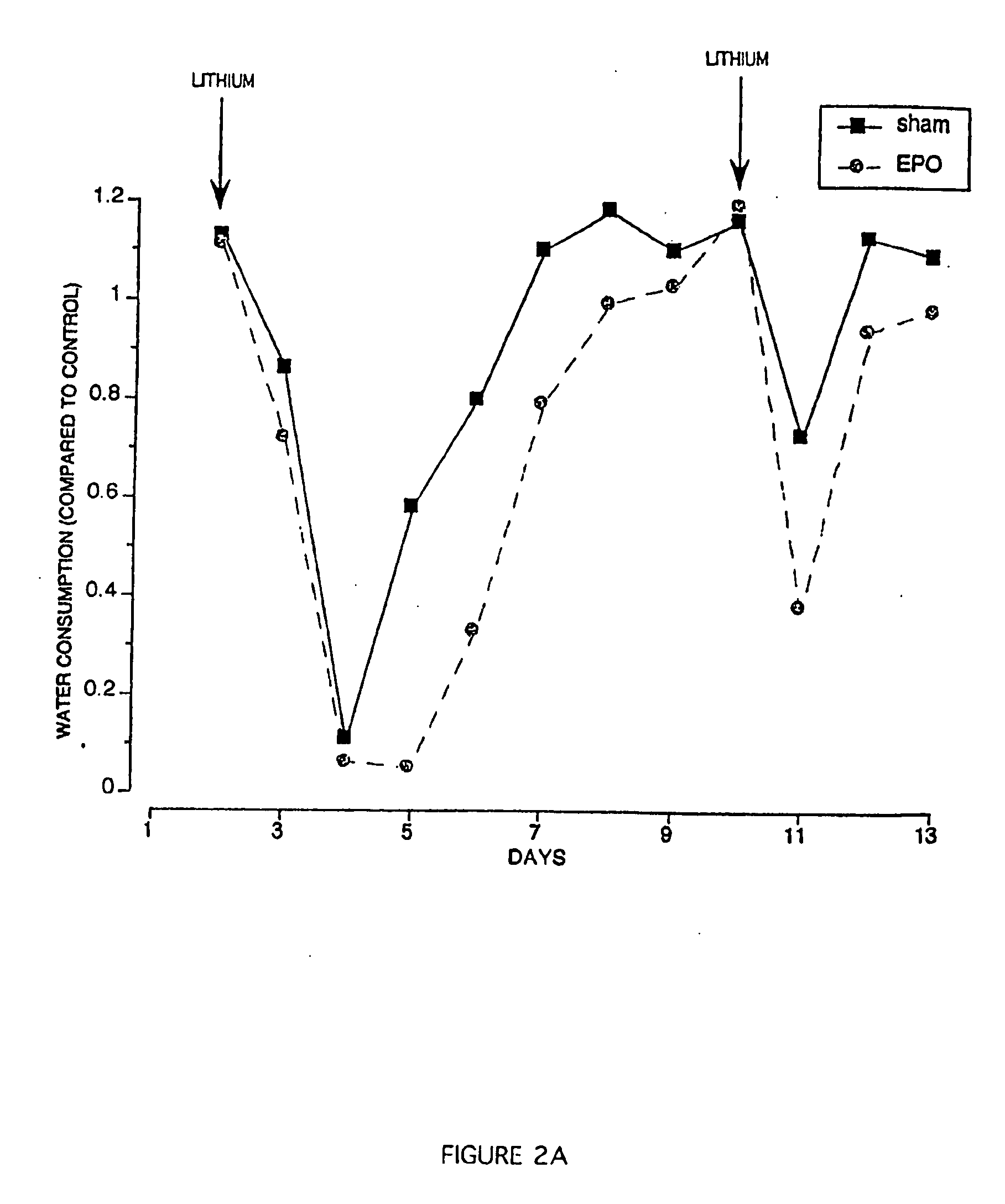
[0112] The Conditioned Taste Aversion (CTA) test performed in this Example demonstrates that EPO dramatically affects the ability of mice to remember, and learn to avoid, an unpleasant taste sensation, in this case an illness-provoking substance. In this example, lithium chloride is used to produce CTA, because lithium chloride reliably produces malaise and anorexia in a dose-dependent manner. Like a naturally occurring illness, lithium produces a CTA by stimulating the pathways described above, including cytokine release.
[0113] Female Balb / c mice were trained to limit their total daily water intake to a single minute drinking period per day, and learned to drink enough water during this period to remain at equilibrium. Animals were divided into groups and administered either a sham control (saline) or EPO (5000 U / kg), injected intraperitoneally (IP), 4 hours before presentation of a novel sa...
example 3
8. EXAMPLE 3
Peripherally Adminstered EPO Protects Brain from an Excitotoxin
[0116] This Example demonstrates that EPO crosses the blood brain barrier and has a neuroprotective effect in mice treated with the neurotoxin kainate. Many compounds exist in nature which exhibit toxicity specifically for neurons. These molecules typically interact with endogenous receptors for the amino acid transmitter glutamate, subsequently causing excessive stimulation and neuronal injury. One of these, kainate, a substance widely used to study neuronal injury due to excitotoxicity, is an analogue of glutamate. Kainate is a potent neurotoxin which specifically destroys neurons, particularly those located in regions with a high density of kainate receptors, such as the hippocampus, and induces seizures, brain injury, and death.
[0117] The following neurotoxicity studies were performed with mice using kainate. This model is used to assess the protective benefit of treatments for conditions such as tempor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com