Cores and microcapsules suitable for parenteral administration as well as process for their manufacture
a technology of microcapsules and parenteral administration, applied in the field of galenic formulations, can solve the problems of long process time, inability to meet the requirements of the patient, so as to improve stability, influence the release kinetics of the bas, and prevent or reduce aggregation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
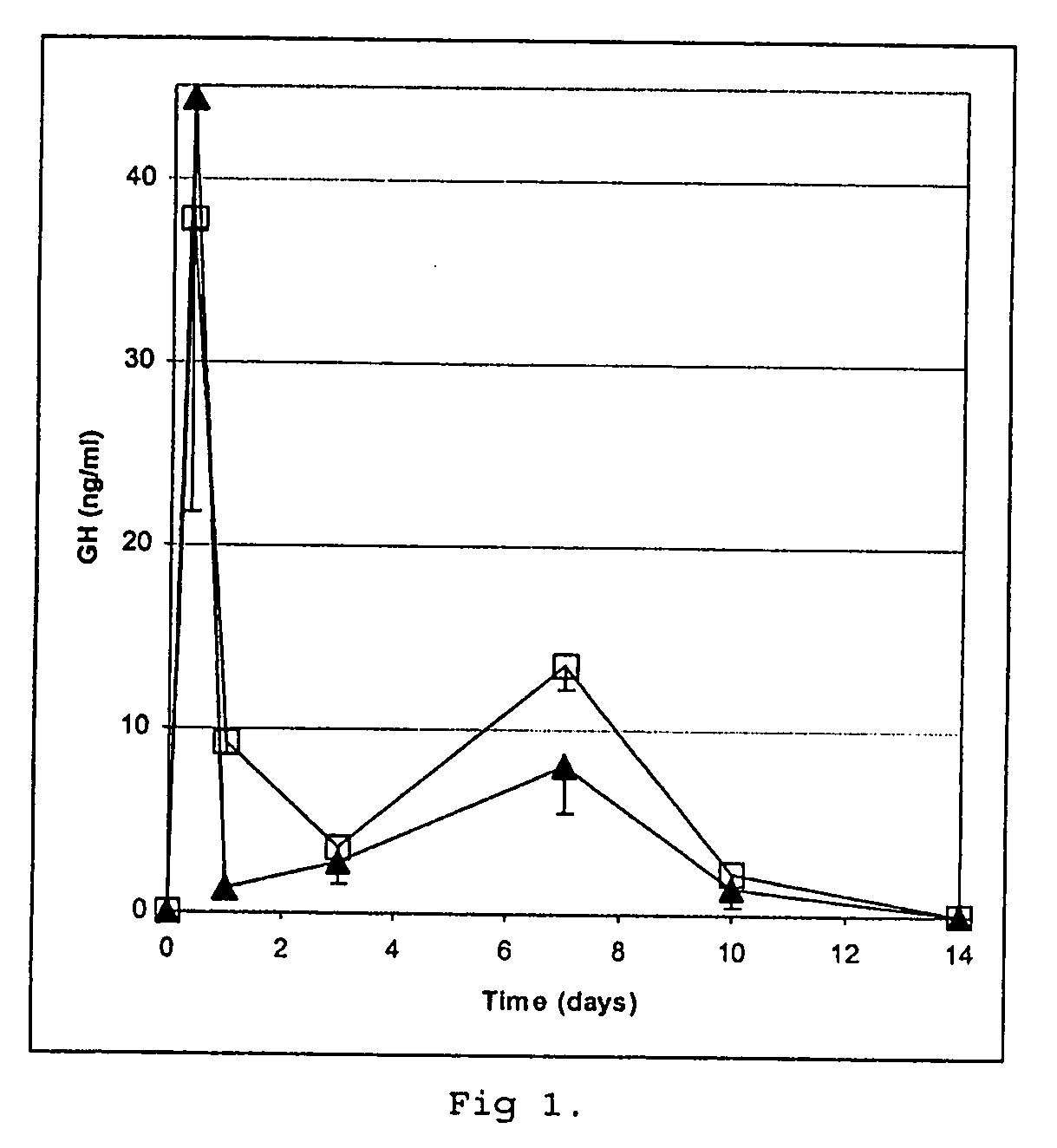
[0169] Human growth hormone (GH) was lyophilized in the presence of ammonium acetate (6.3:1 molar ratio ammonium acetate:protein), then suspended in isopropanol and allowed to air dry. Maltodextrin (Paselli MD6, Avebe, Veendam, Holland, 5 g) was dialysed against water (MilliQ, Millipore, 3 times 1500 ml) at 50° C. using a membrane (Spectra / Por) to remove substances with a molecular weight below about 3,5 kDa and then lyophilised. About 18% of low molecular weight glucose-containing material was removed.
[0170] Three batches of maltodextrin microspheres were prepared (50% W / W, 1 ml, 1 ml and 1.8 ml, respectively, in sodium acetate, 10 mM, pH 6.4, 2 mM zinc acetate) in which the GH was suspended manually. The compositions were transferred to Miglyol 829 (10, 20 and 30 ml, respectively), W / O emulsions were created by homogenization (Turrax) and left under refrigeration over night (about 16 hours), then centrifuged (Sorvall SS34, 7000 rpm, 10 min) and washed three times with cold aceton...
example 2
[0171] GH (20 mg / ml) was precipitated with high efficiency >99%) by addition of zinc acetate (10 mg / ml, 100 μl portions at a time) dissolved in Milli Q water) under magnetic stirring at room temperature to obtain a mole ratio of 3:1 zinc to protein. The stirring was continued over night at room temperature.
[0172] Cores were prepared using Zn:GH (700 mg)and sodium hyaluronate (Fermentech, lyophilized and dissolved at 2% in 10 mM sodium acetate +10 mM zinc acetate, pH 5.0 to provide a final concentration of 1% after mixing with GH and additional buffer solution). This composition was divided into 3 batches and for each a W / O emulsion was created with Miglyol 829 (20 ml) as the external phase (propeller stirring, 810 rpm, 2 min). The discontinuous phase was solidified by pouring into acetone (120 ml) under stirring.
[0173] The core loading was about 75% on the pooled batches. Protein integrity was determined after suspending the cores in a buffer (50 mM HEPES, 10 mM EDTA, pH 7.3). Aft...
example 3
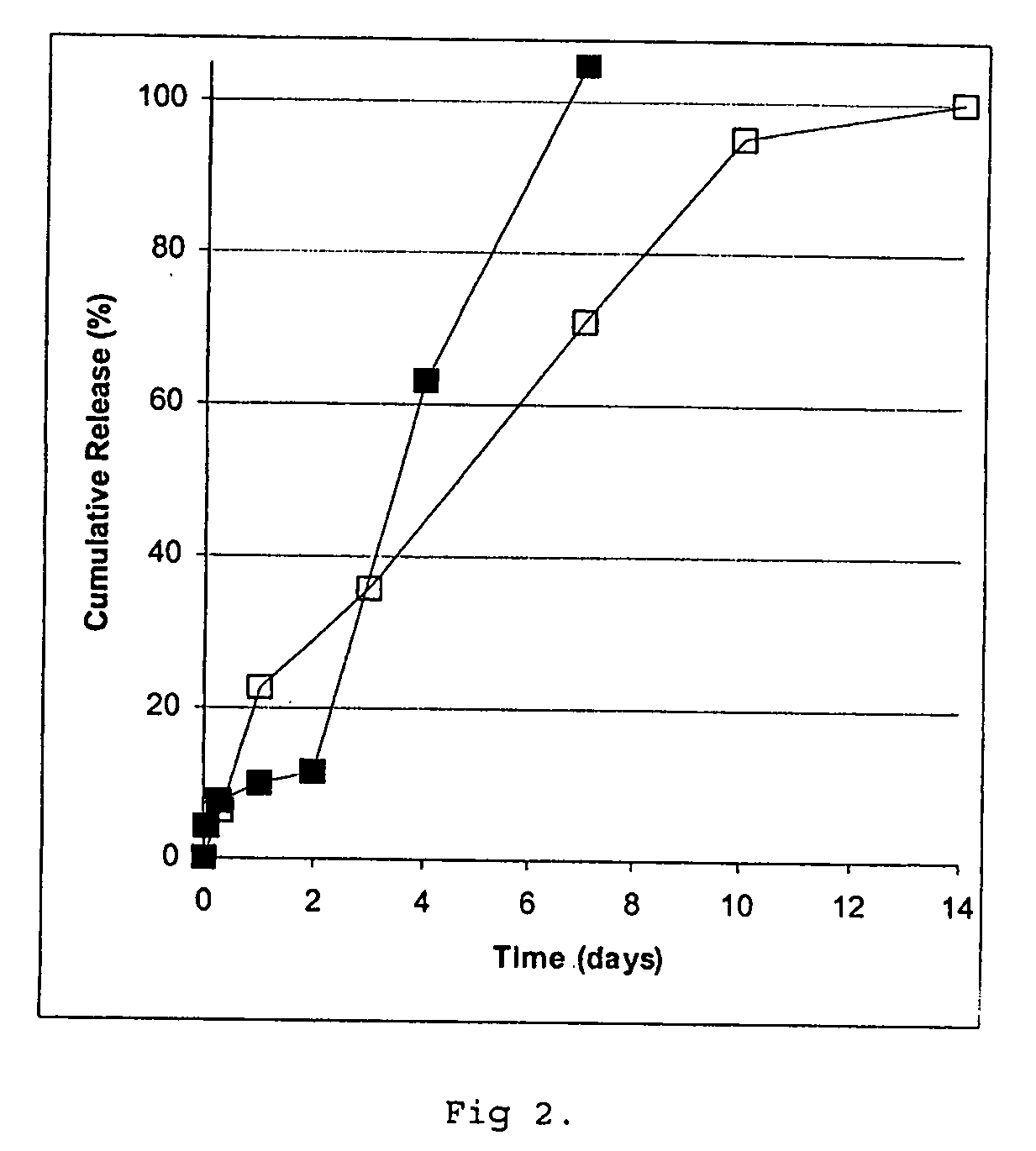
[0174] Cores prepared according to Example 1 were coated using air suspension technology essentially according to Example 6 of WO 97 / 14408, with the addition of magnetic particles to a total of 50 g, using a poly (lactic / glycolic acid) composition of 70% RG502H and 30% RG504H (Boehringer Ingelheim) to a theoretical amount of 0.6 g PLGA / g of cores to prepare a controlled release preparation containing 6.4% (w / w) of GH. Mannitol was applied onto the microcapsules by spraying, which were then dried under vacuum and stored under refrigeration.
[0175] Free flowing single core microcapsules were obtained as evaluated by light microscopy. Protein integrity was determined essentially according to Reslow et al. (supra), including removal of the PLGA coating with a mixture of methylene chloride and acetone. No polymer or aggregate forms were detected and compared to the uncoated cores no increase in dimer content was obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com