Planting process and manufacturing process for semiconductor device thereby, and plating apparatus
a manufacturing process and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of electrical equipment, semiconductor devices, electrolysis components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult stable film formation, achieve the effects of preventing fluctuation in current density, improving the yield of plated films, and improving stability in the formation of metal films
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
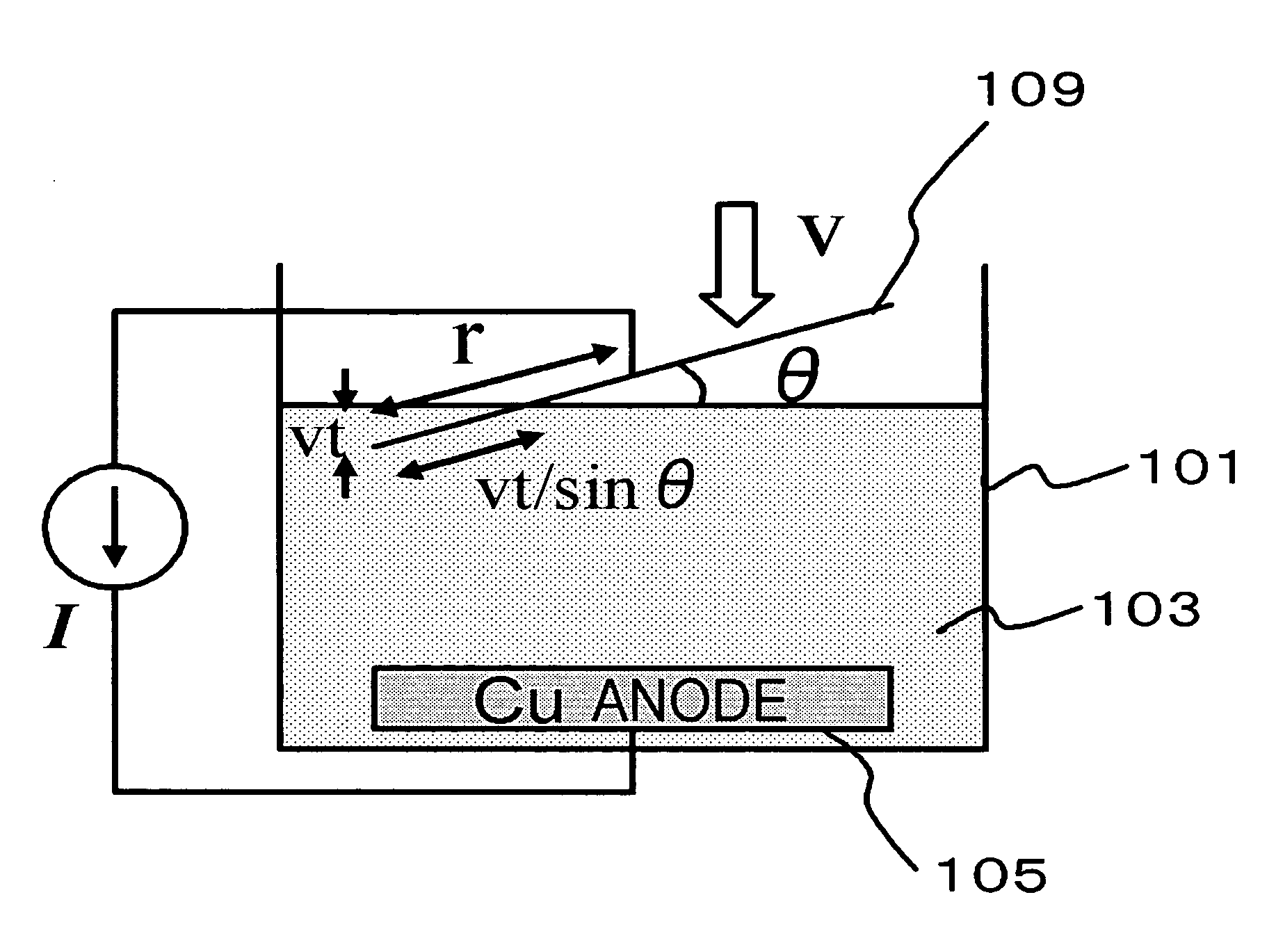
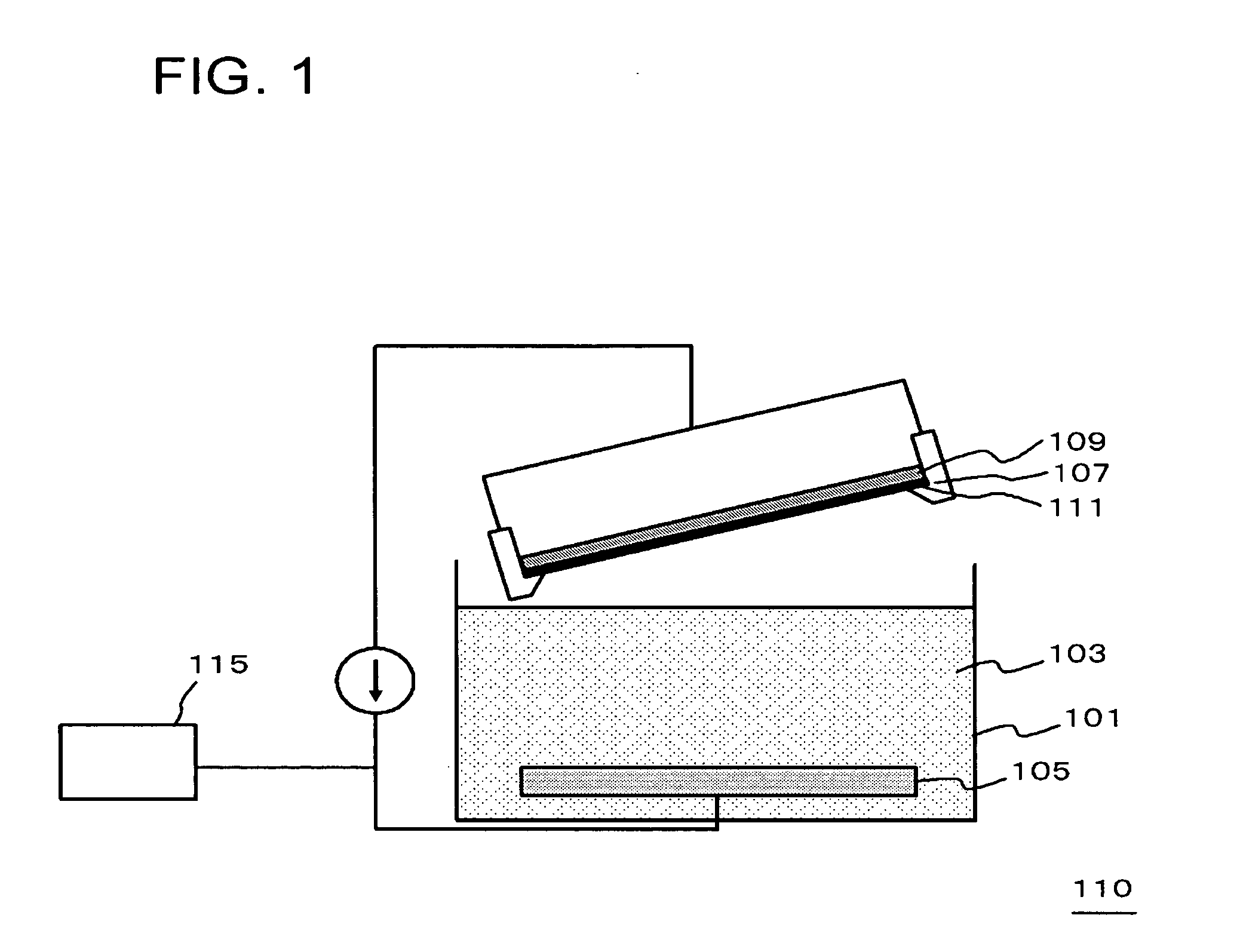
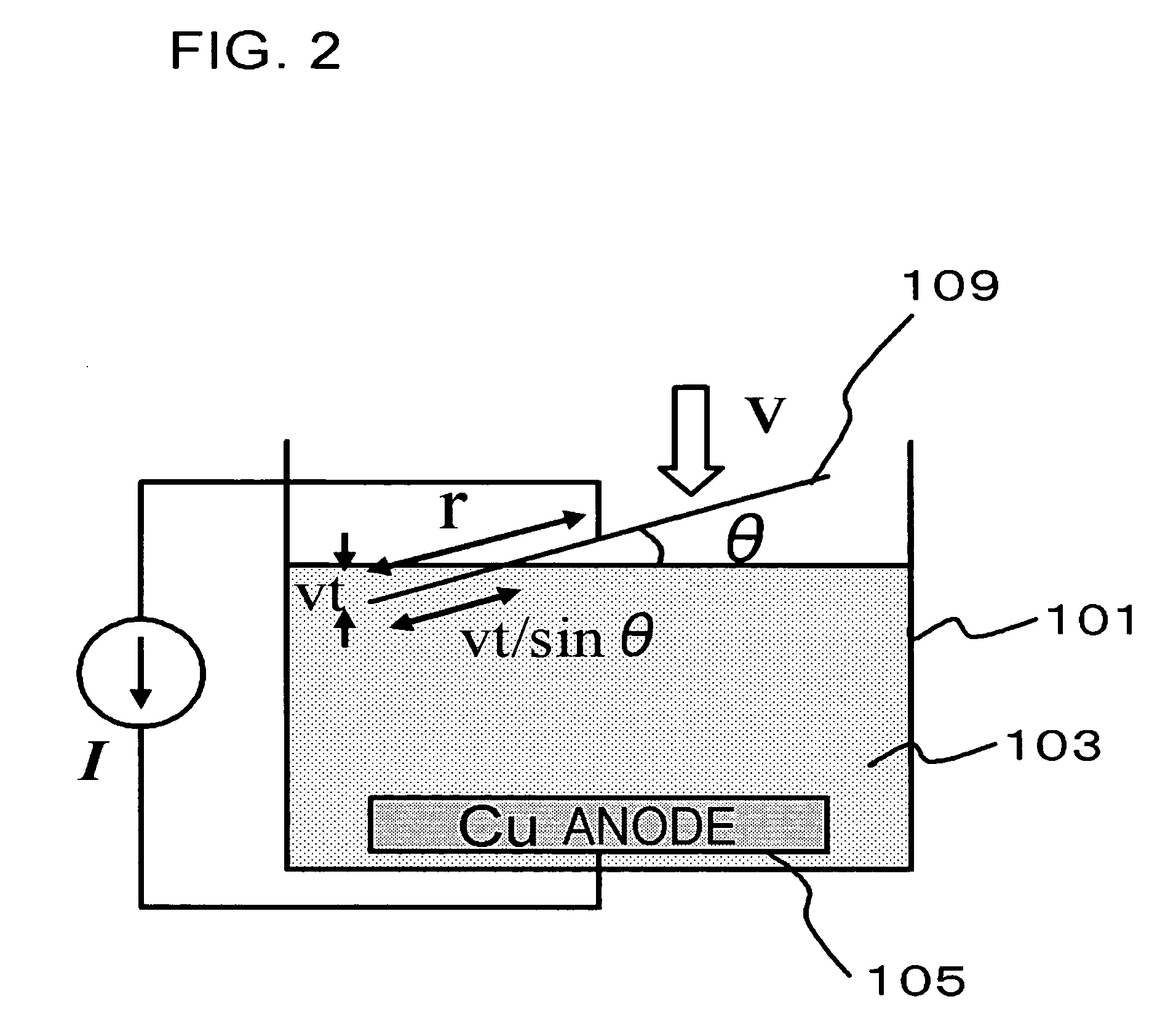
[0068]FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a configuration of a plating apparatus in this embodiment. The plating apparatus 110 shown in FIG. 1 has
[0069] a plating bath 101 to be filled with a plating solution 103,
[0070] a wafer moving unit (a driving unit, not shown) whereby a wafer 109 held by a cathode electrode 107 is immersed into the plating solution 103,
[0071] the cathode electrode 107 feeding a current to the wafer 109 when it comes into contact with the wafer 109,
[0072] an anode electrode (Cu anode electrode 105) disposed in the plating bath 101 such that it faces the cathode electrode 107,
[0073] a power source 115 for applying a current between the Cu anode electrode 105 and the cathode electrode 107, and
[0074] a controller 117 controlling a current intensity applied between the Cu anode electrode 105 and the cathode electrode 107 on the basis of an inclination angle of the film-formation surface from the liquid surface (FIG. 5). The cathode electrode 107 ac...
embodiment 2
[0109] This embodiment relates to another process for controlling a current applied between a cathode electrode and an anode electrode in electrolytic plating using the plating apparatus 110. In embodiment 1, a current intensity applied between a cathode electrode and an anode electrode is controlled in accordance with the above equation (1) in step 101 in forming a plating film. In this embodiment, the wafer 109 is immersed into the plating solution at a substantially constant speed while a current intensity applied between the electrodes is varied in proportion to an elapsed time t after the wafer 109 contacts with the plating solution 103 in step 101.
[0110] Specifically, in step 101 described above in embodiment 1, a current intensity I represented by the following equation (2) instead of equation (1) is applied.
I=I0t / t0 (2)
[0111] wherein I0 is an intensity of the second current and t0 is a time of completion of the first step.
[0112] More specifically, in this embodiment, θ ...
embodiment 3
[0116] This embodiment relates to another process for controlling a current applied between a cathode electrode and an anode electrode in electrolytic plating using the plating apparatus 110. Although there has been described immersion with a constant inclination angle θ of the wafer 109 from the plating solution 103 in embodiments 1 and 2 as examples, an inclination angle θ may be a time-dependent variable.
[0117]FIGS. 9, 10A, 10B, 11A, 11B and 12 illustrate a plating process using the plating apparatus 110. FIG. 9 is a plane view illustrating immersion of the wafer 109 into the plating solution 103. FIGS. 10A, 10B, 11A, 11B and 12 are cross-sectional views illustrating immersion of the wafer 109 into the plating solution 103. FIG. 13 shows relationship between an elapsed time after the wafer 109 contacts with the plating solution 103 and a current intensity I applied between the Cu anode electrode 105 and the cathode electrode 107 in the plating apparatus 110.
[0118] As shown in F...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| constant voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com