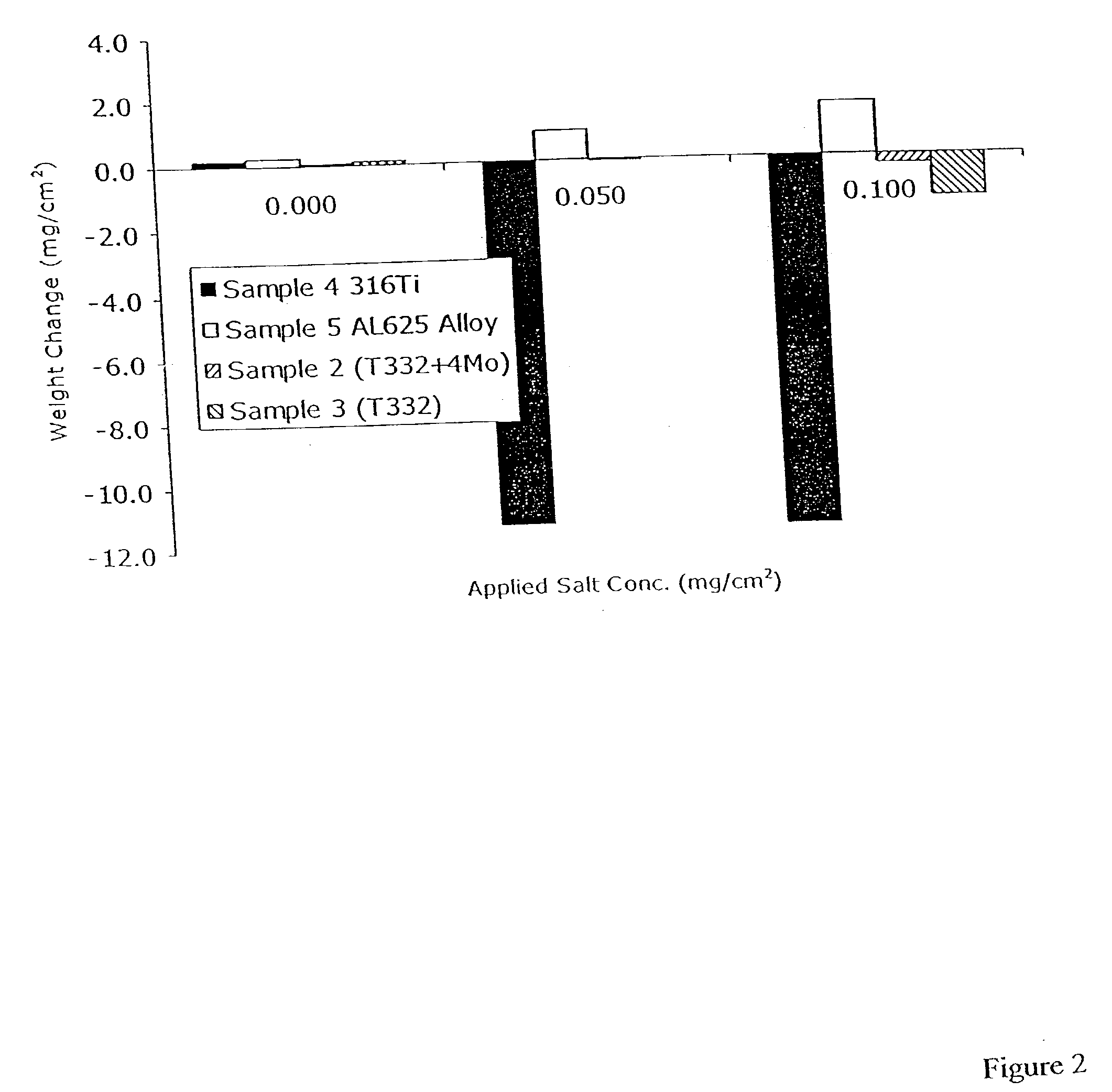Austenitic stainless steels including molybdenum
a technology of stainless steel and molybdenum, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, machines/engines, mechanical apparatuses, etc., can solve the problems of complex corrosion resistance, automotive exhaust system components and other automotive engine components are exposed to contamination, and certain automotive exhaust system applications are exposed to severe corrosion chemical environments. , to achieve the effect of less costly production and increased corrosion resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
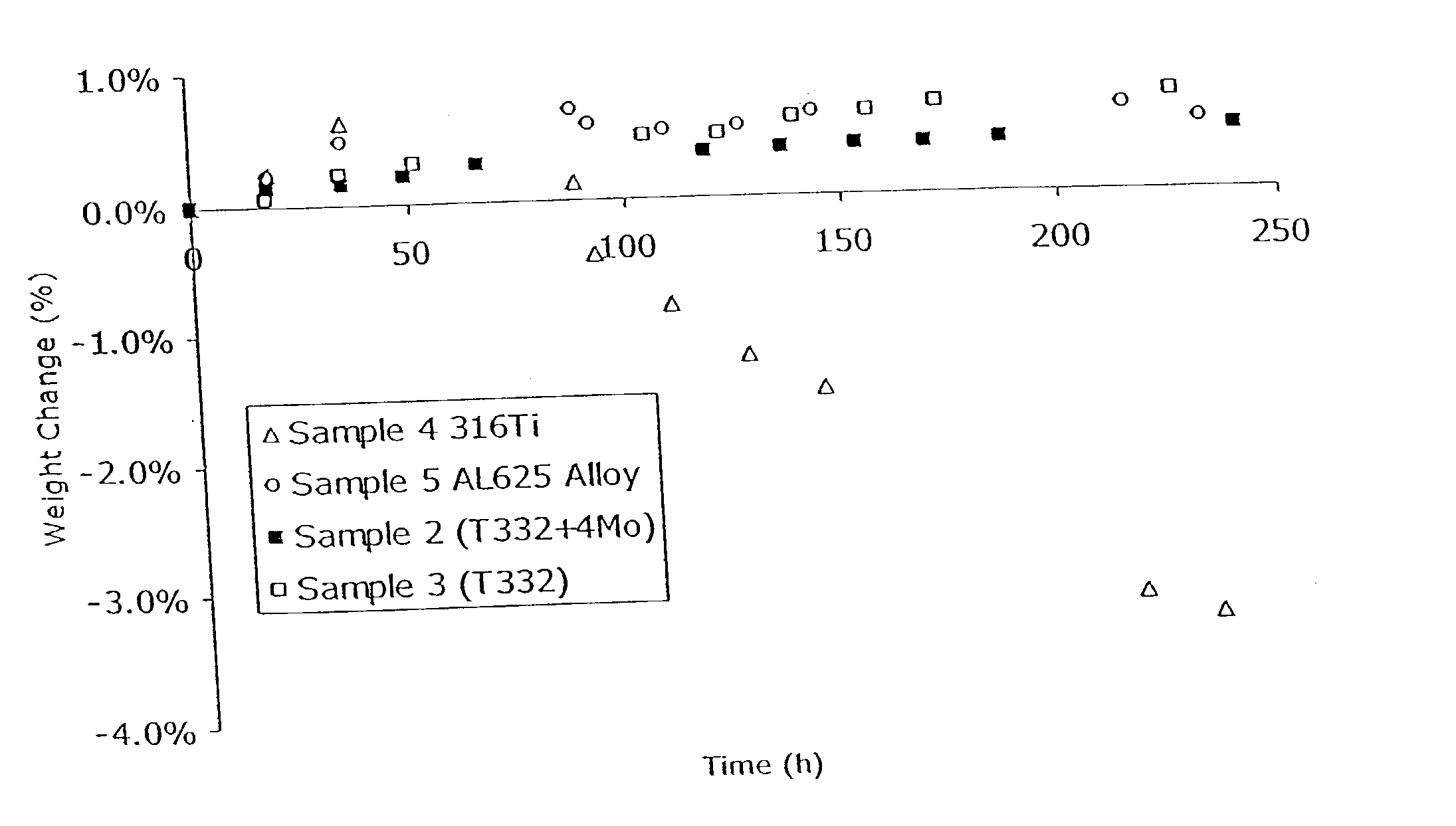
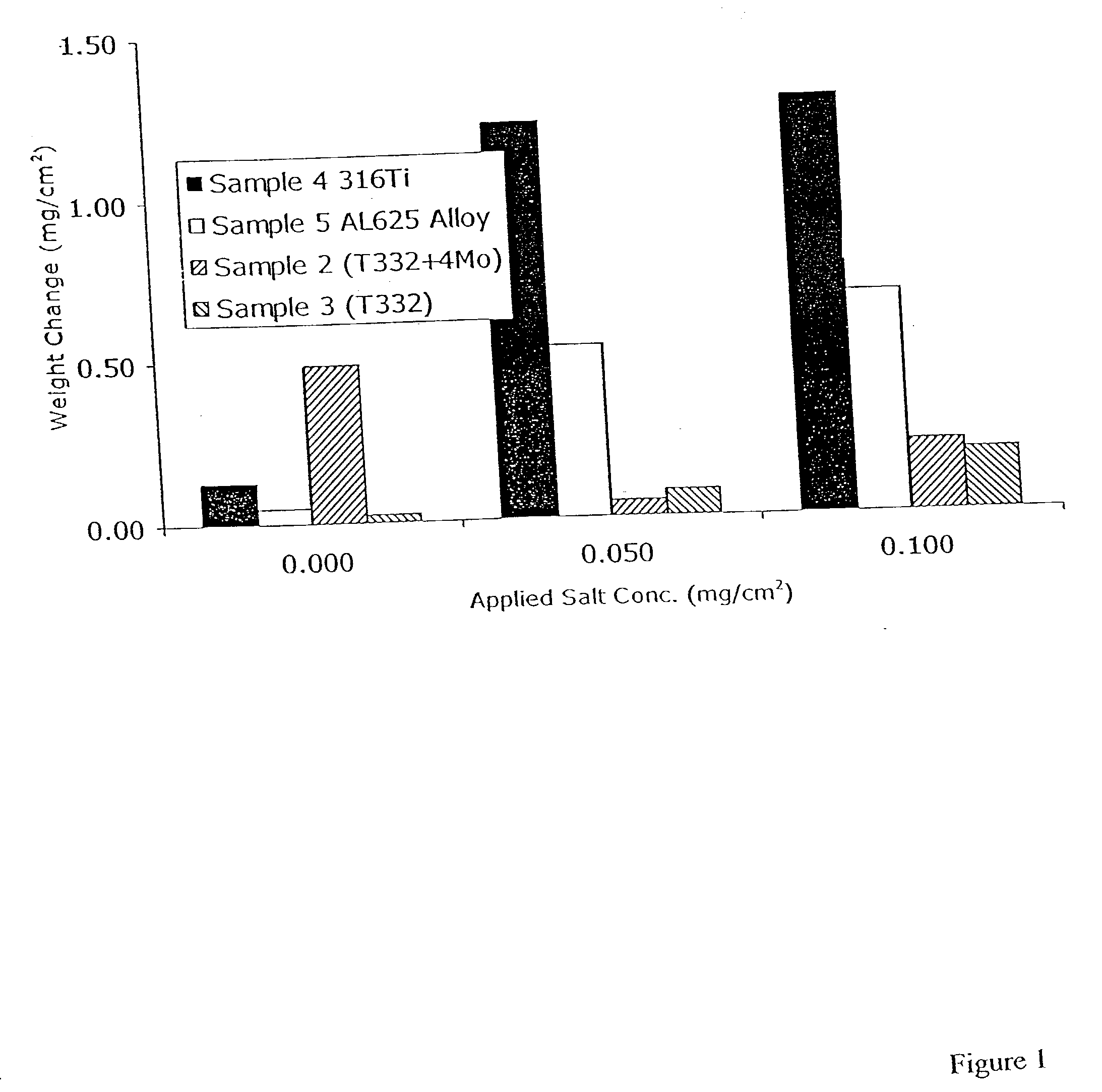
[0037] Certain embodiments of stainless steels of the present invention were prepared and evaluated for resistance to corrosion in high temperature, corrosive environments. Two heats were melted with a target composition including, by weight, 19 to 23% chromium and 30 to 35% nickel. The first alloy had a target molybdenum concentration of 2%, and the second alloy had a target molybdenum concentration of 4%. The actual compositions of the heats of the invention are shown in Table 1 as Sample 1 and Sample 2. Sample 1 contained 1.81% molybdenum and Sample 2 contained 3.54% molybdenum. The alloy Samples 1 and 2 were prepared by a conventional method, specifically, by vacuum melting the alloy components in concentrations to approximate the target specification. The formed ingots were then ground and hot rolled at approximately 2000.degree. F. (1093.degree. C.) to about 0.1 inches thick by 7 inches wide. The resulting plate was grit blasted and descaled in an acid. The plate was then cold...
example 2
[0057] Austenitic stainless steels can be subject to sensitization when exposed to high temperatures. As is known in the art, sensitization is the intergranular precipitation of chromium carbides in austenitic stainless steel when the steel is exposed to temperatures in the approximate range of 800-1500.degree. F. (427-816.degree. C.). A result of sensitization is that regions of the affected grains are depleted in chromium content, promoting susceptibility to intergranular corrosion in the presence of aqueous chlorides. In order to investigate the susceptibility to sensitization of alloys within the present invention, the present inventor prepared and tested five 50 lb. VIM heats having the chemical compositions shown in Table 3. Table 3 identifies the heats as Heats 6-10 so as to distinguish them from Samples 1-5 in above Example 1. The heats included varying additions of the carbide-forming elements titanium and niobium. Heat 6 was formulated with an aim of zero titanium and zero...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com