Power MOS transistor having capability for setting substrate potential independently of source potential
a power mos transistor and source potential technology, applied in the field of power mos transistors, can solve the problems of significant stray capacitance between the gate electrode and the substrate, the overall chip area occupied by the ldmos transistor becomes large,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
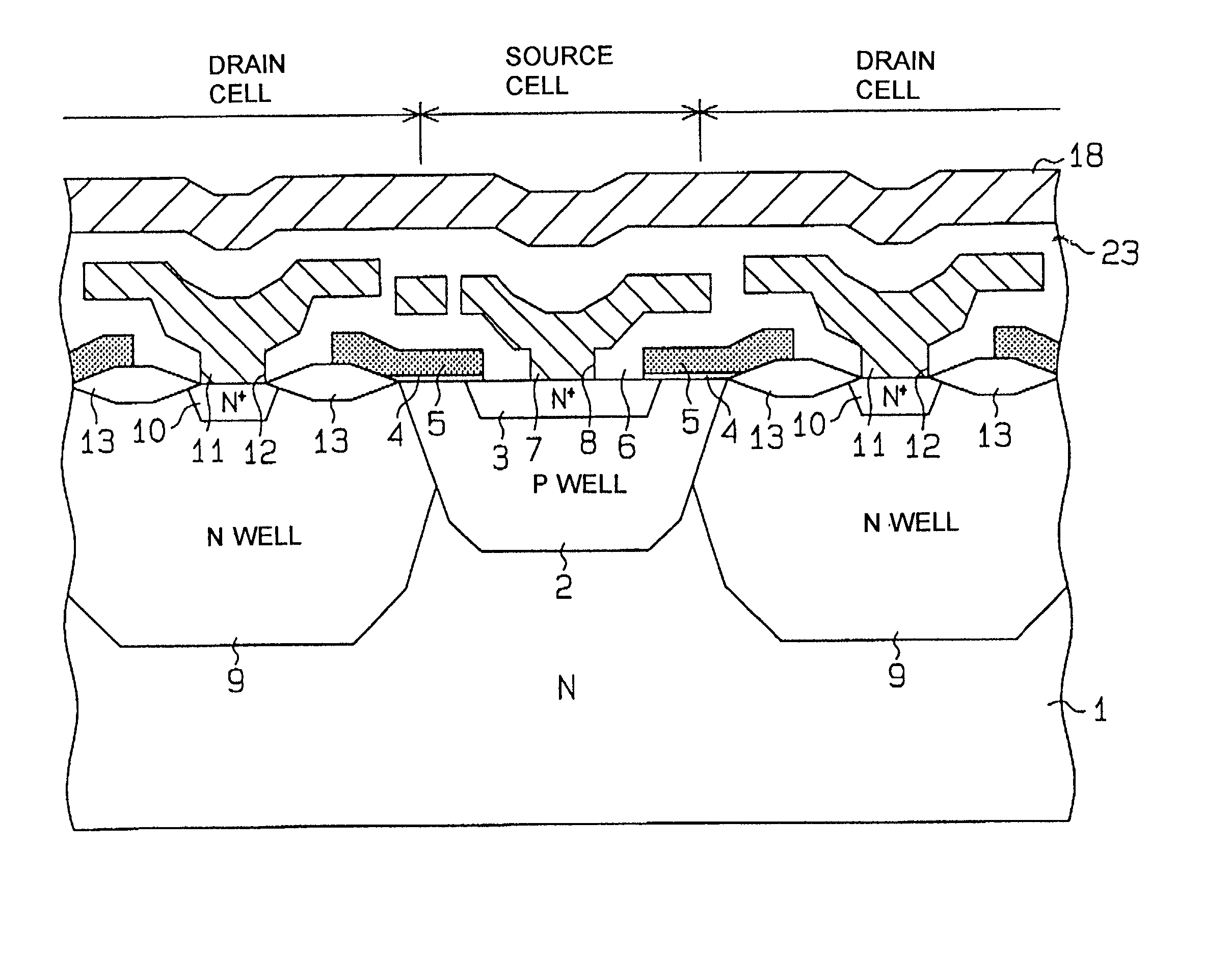
[0067] FIG. 9 shows an embodiment which constitutes an IC chip 45 on which a power MOS (LDMOS) transistor having the configuration of the first embodiment described above, designated as Tr1, is formed in conjunction with a gate drive circuit 30 and a substrate bias circuit 40. The drain side (specifically, the second-layer drain connecting lead 19 of the power MOS transistor Tr1 is connected to a load 44 which is external to the chip 45, while the source side of the power MOS transistor Tr1 (i.e., the second-layer source connecting lead 18) is connected to ground potential. That is to say, the load 44 is connected through the power MOS transistor Tr1 between the high potential of a power source and ground potential of that power source. The gate drive circuit 30 includes a buffer amplifier 31 and a transistor drive command signal (i.e., transistor ON / OFF switching signal) .phi..sub.0 inputted to the gate electrode of the power MOS transistor Tr1 through the buffer amplifier 31. The ...
third embodiment
[0073] A third embodiment is illustrated in the circuit diagram of FIG. 10, in which a power MOS transistor Tr1 configured in accordance with the present invention and a substrate bias circuit 50 are formed on an IC chip 46, with the power MOS transistor Tr1 driving an external load 44. This embodiment differs from that of FIG. 9 in that the substrate bias circuit 50 utilizes the fact that, when a reverse bias is applied to the substrate, the threshold voltage Vt of the power MOS transistor Tr1 is increased due to the substrate effect. Hence, the substrate bias circuit 50 can be used to control the value of Vt. Specifically, when the power MOS transistor Tr1 is in the OFF state (i.e., with 0 V applied as the gate voltage), a reverse bias is applied to the substrate (e.g., having a value of several pad volts, which is of positive polarity in the case of the N-MOS structure) causing the threshold voltage Vt of transistor Tr1 to become high. When transistor Tr1 is set in the ON state (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com