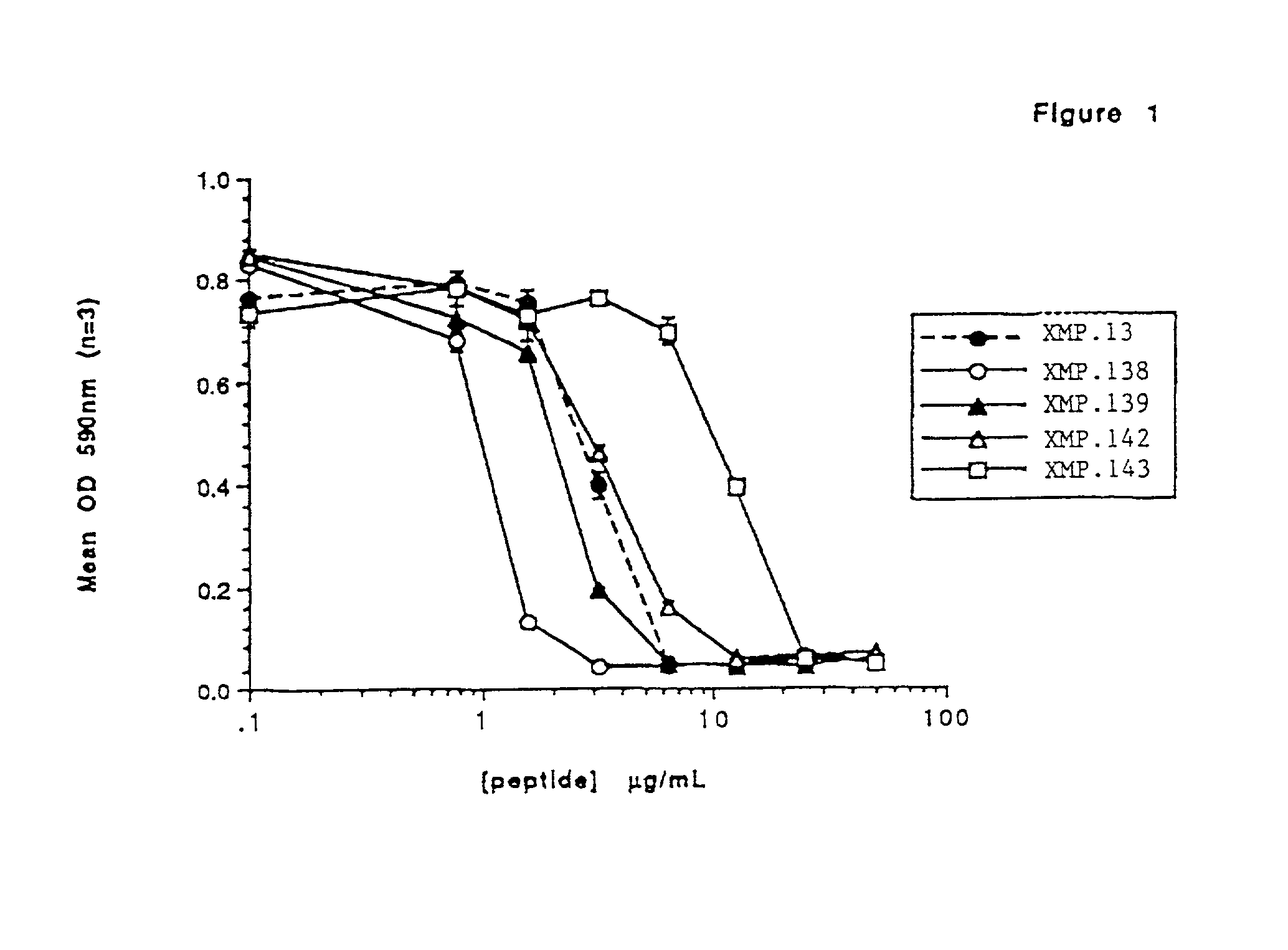
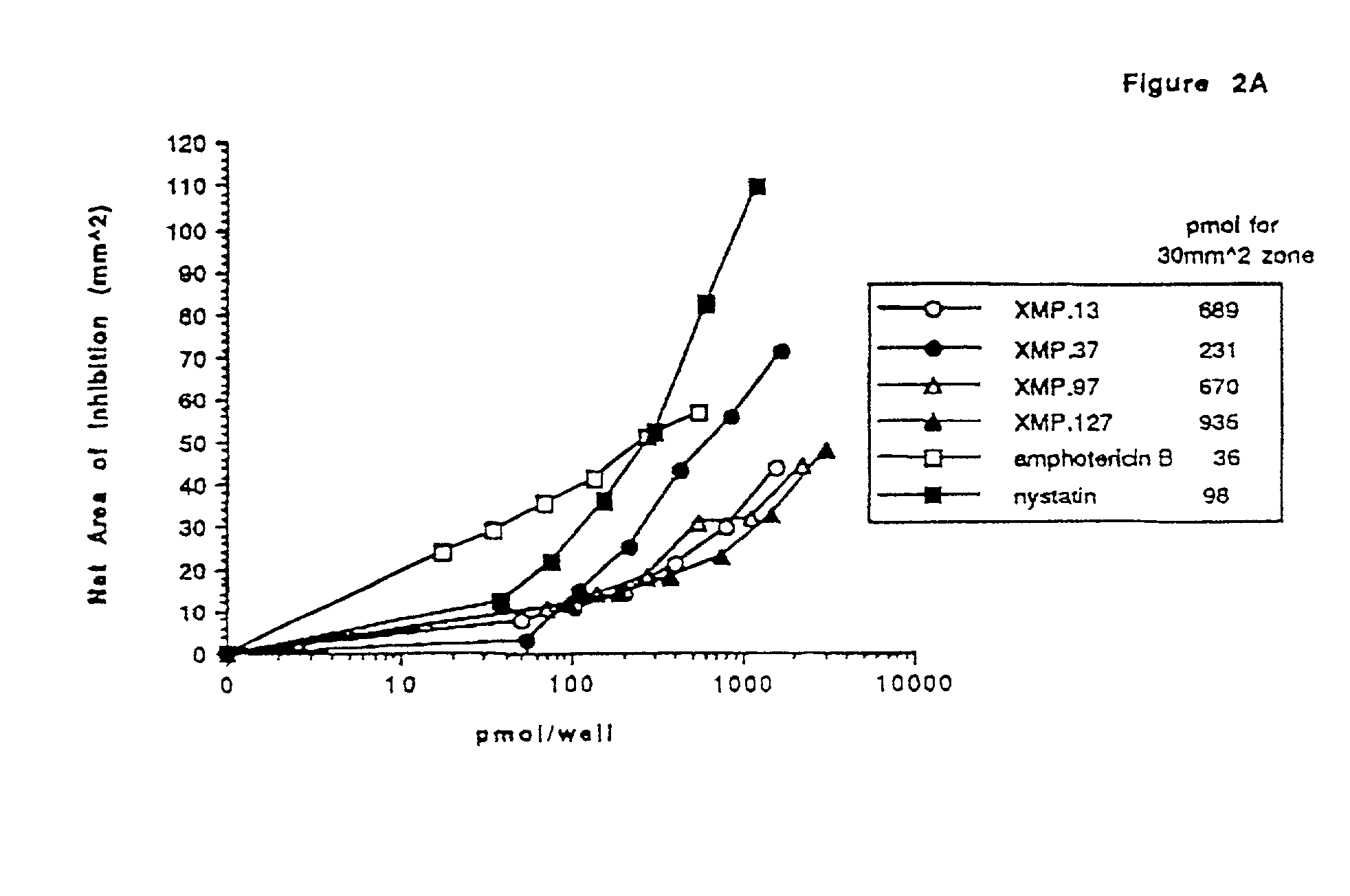
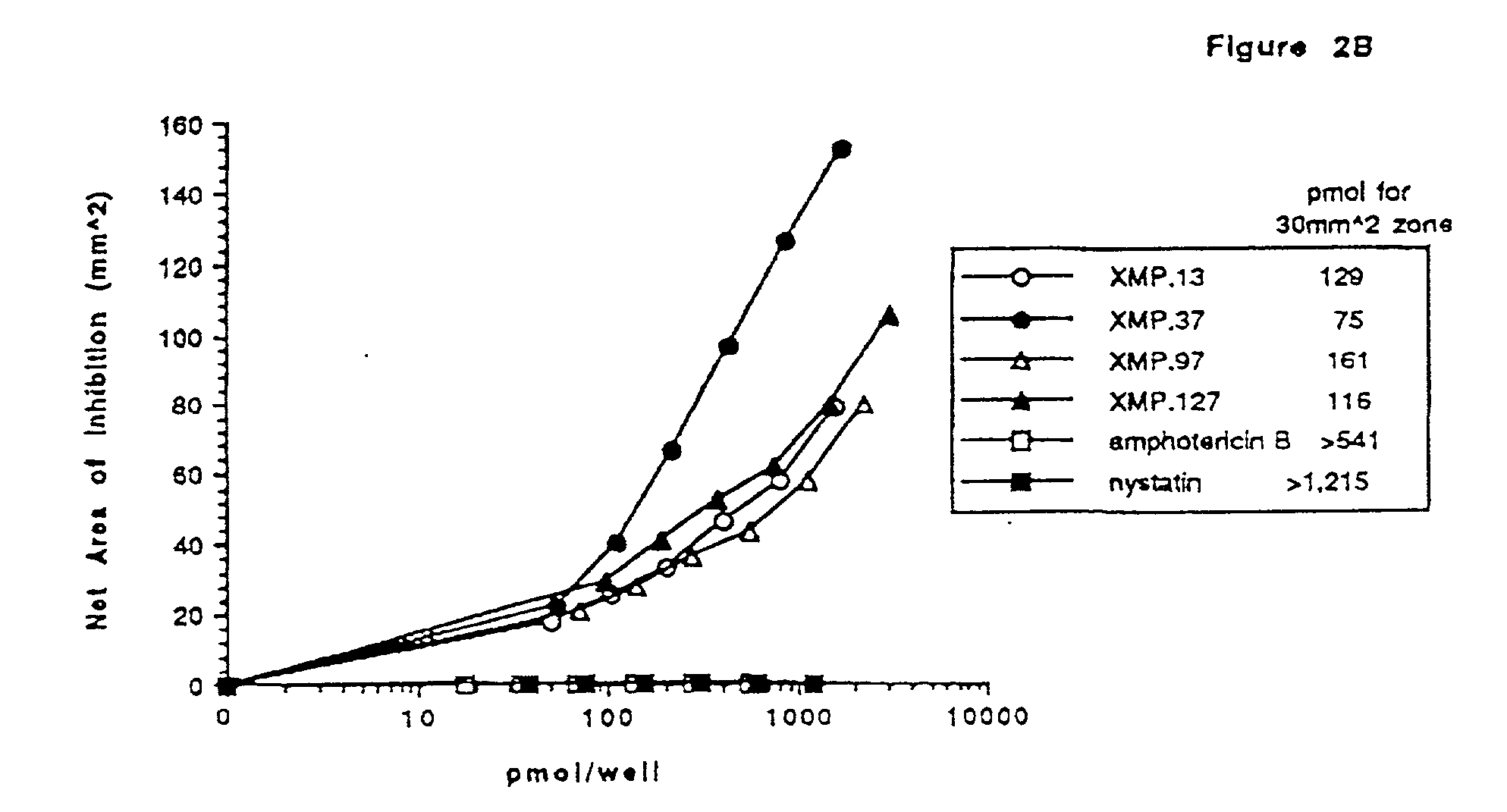
Anti-fungal peptides
a technology of antifungal peptides and peptides, which is applied in the field of antifungal peptides, can solve the problems of cell death, limited administration, and altering the permeability of the cell's outer membran
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Peptide Preparation and Purification
[0064] This example addresses the preparation and purification of Domain III derived peptides.
[0065] Peptides may be prepared according to a variety of synthetic procedures. Some peptides (e.g., XMP.5) were prepared by solid phase peptide synthesis as described in parent U.S. patent application Ser. Nos. 08 / 209,762 and 08 / 183,222 according to the methods of Merrifield, J. Am Chem. Soc. 85: 2149 (1963) and Merrifield et al. Anal. Chem., 38: 1905-1914 (1966) using an Applied Biosystems, Inc. Model 432 peptide synthesizer.
[0066] Alternatively, peptides were synthesized on a larger scale using solid phase peptide synthesis on an Advanced Chemtech (ACT-Model 357 MPS) synthesizer utilizing a 1 -Fluorenylmethyl-oxycarbonyl (Fmoc) protection strategy with a double coupling procedure employing N,N-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC) / 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt) and 2-(1-H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3,-tetramethyluronium hexa-fluorophosphate (HBTU) / HOBt / diisopropy...
example 2
In Vitro Anti-Fungal Effects
[0072] This example addresses in vitro screening of Domain III derived peptides for anti-fungal activity in a broth assay and / or in a radial diffusion assay.
[0073] Table 1 below sets out peptides derived from or based on Domain III BPI sequences. Such peptides may be identified by peptide number with a prefix XMP or BPI (e.g., XMP.1 or BPI.1, XMP.2 or BPI.2, etc.). Table 1 also sets out the SEQ ID NO: of each peptide, the amino acid sequence based on reference to position within BPI and the designation of amino acid substitutions and additions. Also set out in Table 1 are HPLC estimates of purity of the peptides. The HPLC purity analysis was performed as described in Example 1.
[0074] In each broth assay screening procedure, a colony of C. albicans designated CA-1, Strain SLU- 1 that was received from the laboratories of G. Matuschak and A. Lechner, St. Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, Mo., where the strain was maintained, was inoculated into a tube c...
example 3
In Vitro and In Vivo Effect of Anti-fungal Peptides on a Variety of Fungal Species
[0079] This example addresses in vitro and in vivo screening of various Domain III derived peptides for anti-fungal activity against a number of fungal species, including Candida species and strains resistant to various anti-fungal agents, in a radial diffusion assay. The example also addresses the effects of combinations of peptide and amphotericin B against Candida strain SLU-1.
[0080] Domain III derived peptides were tested for their fungicidal activity on amphotericin resistant Candida. Resistant colonies of Candida were isolated using a gradient plate technique. A slanted Sabouraud dextrose agar plate was poured and allowed to harden. The plate was made level and additional agar supplemented with nystatin (Sigma, St. Louis, Mo., cat. no. N-3503) at a concentration of 10 .mu.g / mL was poured. Cells from the the CA-1 colony of Candida albicans SLU-1 strain described in Example 2 (10.sup.7 cells in a v...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com