Nitride compound semiconductor device and process for producing the same
一种化合物系、制造方法的技术,应用在半导体/固态器件制造、半导体激光器、光波导半导体的结构等方向,能够解决难以实现激光振荡、结晶表面刮伤等问题,达到提高可靠性及制造成品率、降低电阻的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
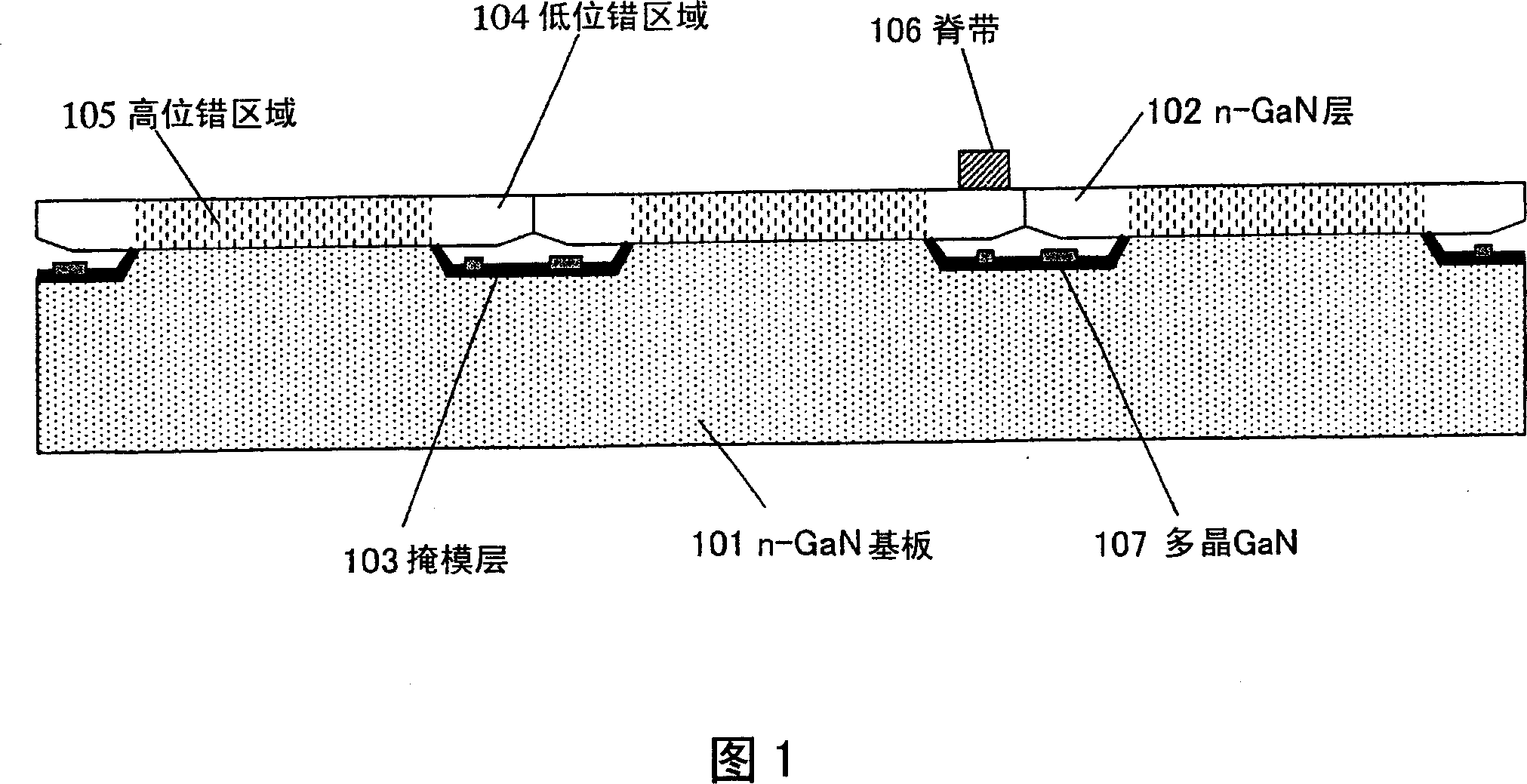
[0062] First, refer to FIG. 1 . FIG. 1 schematically shows a cross section of a nitride-based semiconductor device according to this embodiment.
[0063] The semiconductor device shown in FIG. 1 has a GaN substrate 101 with a plurality of band-shaped ridges formed on its main surface, and an n-GaN layer 102 grown on the GaN substrate 101 . In an actual semiconductor device, generally, a nitride-based semiconductor layer is also stacked on the n-GaN layer 102 . However, when the n-GaN layer 102 in FIG. 1 is used as a channel layer of a transistor or the like, a gate insulating film or a wiring structure is formed on the n-GaN layer 102 .
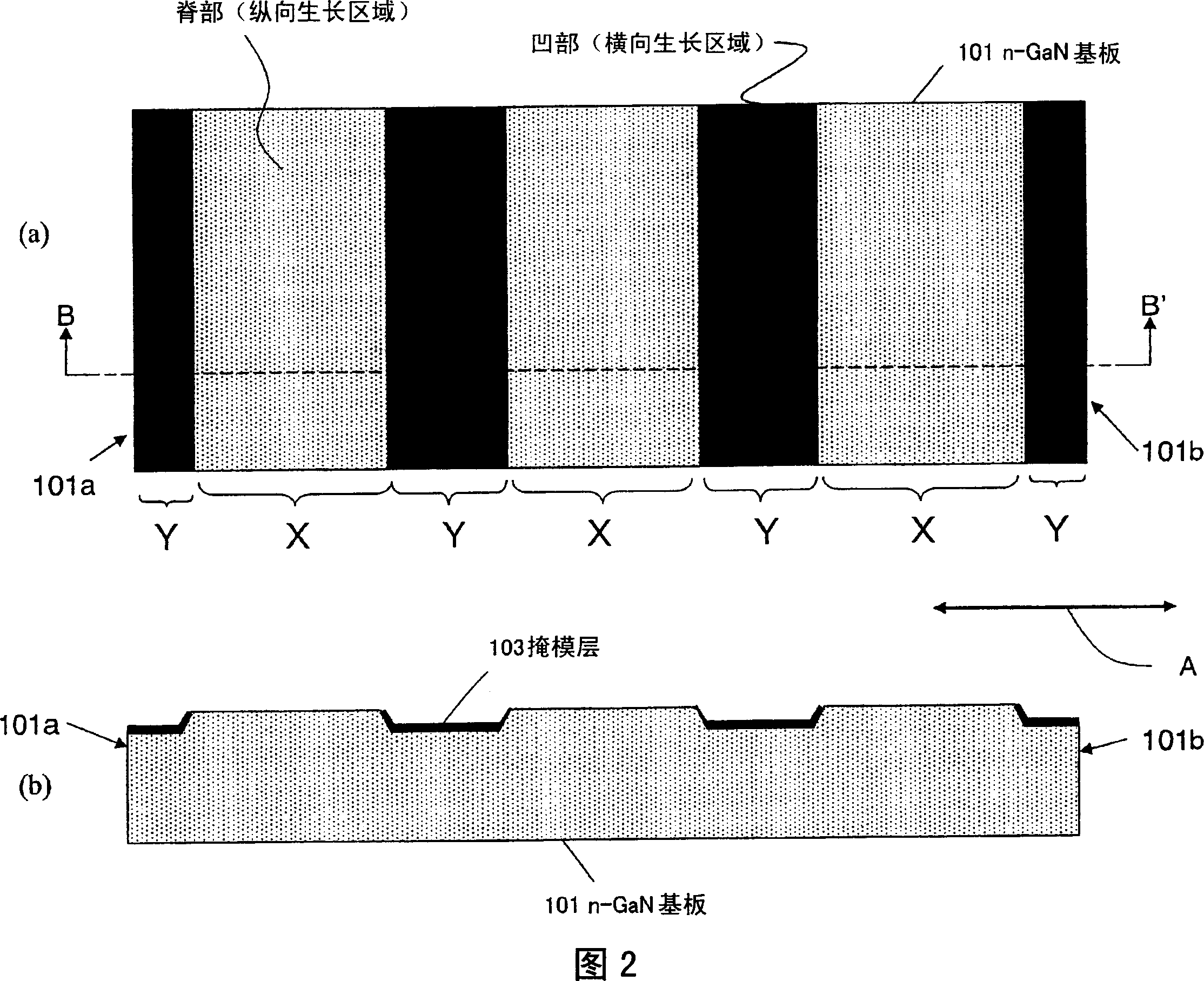
[0064] Referring to FIG. 2 , the structure of the GaN substrate 101 will be described in more detail. Fig. 2(a) is a plan view showing the principal surface of a GaN substrate 101 of a nitride-based semiconductor device, and Fig. 2(b) is a cross-sectional view along line B-B' thereof. As shown in FIG. 2 , the upper surface of the ridge por...
Embodiment approach 2
[0095] Next, a second embodiment of the nitride-based semiconductor device of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 6 . FIG. 6 schematically shows the cross-sectional structure of the nitrogen compound semiconductor laser of this embodiment.
[0096] The illustrated semiconductor laser includes an n-GaN substrate 101 in which a strip-shaped concave portion is formed on a main surface, and a semiconductor stacked structure grown on the GaN substrate 101 . The lowest layer of the semiconductor stack structure is the n-GaN layer 102 grown on the n-GaN substrate 10-. The n-GaN substrate 101 and n-GaN layer 102 of this embodiment are produced in the same manner as the n-GaN substrate 101 and n-GaN layer 102 of Embodiment 1 described above.
[0097] The above-mentioned semiconductor laminate structure is formed on the n-GaN layer 102 by forming an n-AlGaN type GaN superlattice contact layer 201, an n-AlGaN type GaN superlattice cladding layer 202, an n-GaN ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0106] Next, a third embodiment of the nitride-based semiconductor device of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 8 .
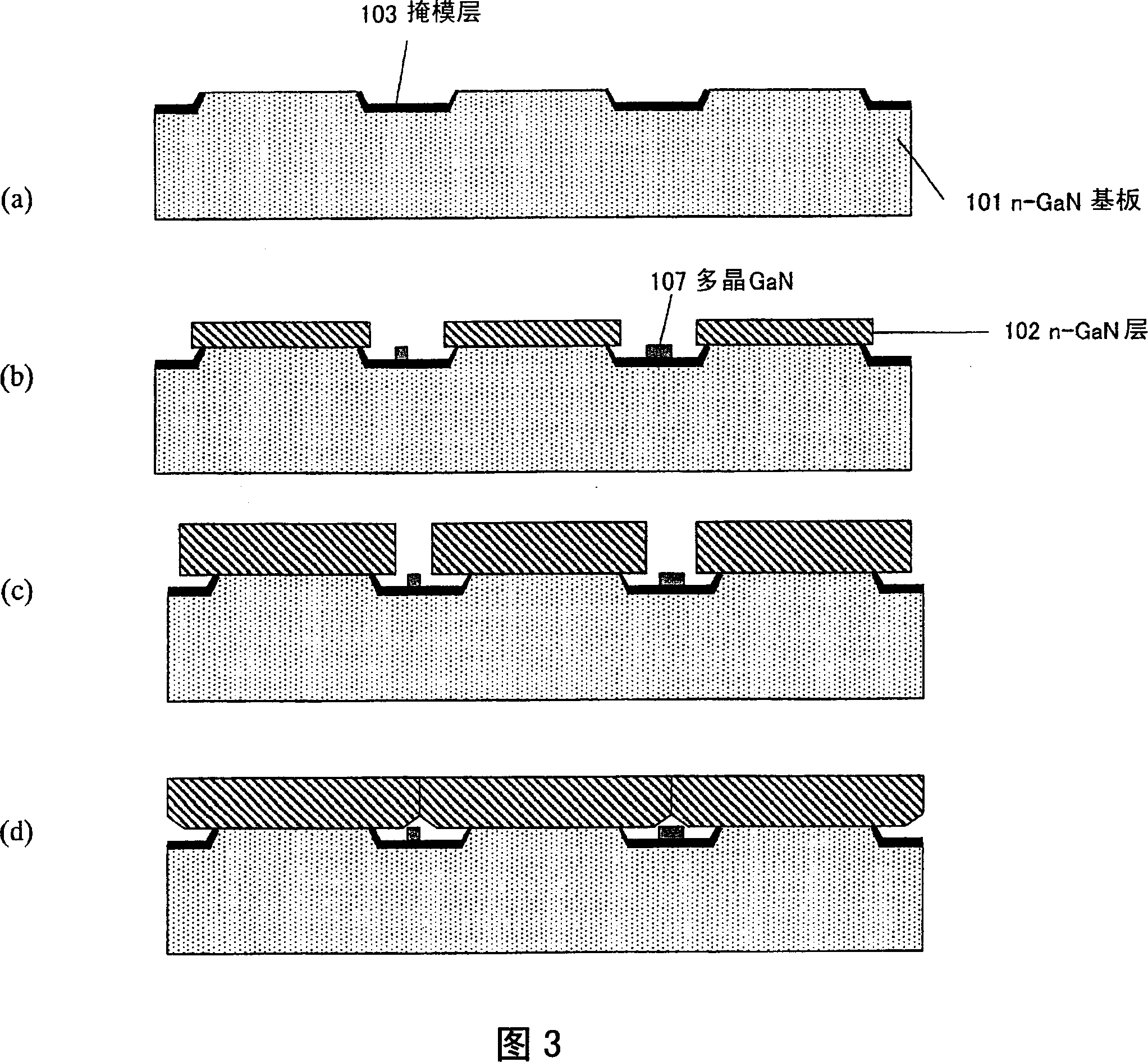
[0107] The structure of this embodiment differs from the structure shown in FIG. 1 in that a GaN layer 801 (thickness: 1 μm) is provided on the surface of the n-GaN substrate 101 of this embodiment. Specifically, after the GaN layer 801 is grown on the main surface of the n-GaN substrate 101, band-shaped ridges are formed on the main surface of the substrate by the method described in Embodiment Mode 1. FIG.
[0108] In this embodiment, the width X of the ridge (protrusion with resist) is set to about 20 μm, and the width Y of the concave portion is set to about 5 μm. The bottom and side surfaces of the recess are covered with a mask layer 103 made of SiO deposited by ECR sputtering or thermal CVD. 2 constitute.
[0109] The selective lateral growth of the n-GaN layer 102 is performed in the same manner as the method described in t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com