Semiconductor device, manufacturing method of semiconductor device and module for optical device
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, which can be used in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components, semiconductor lasers, etc., and can solve problems such as scarring
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
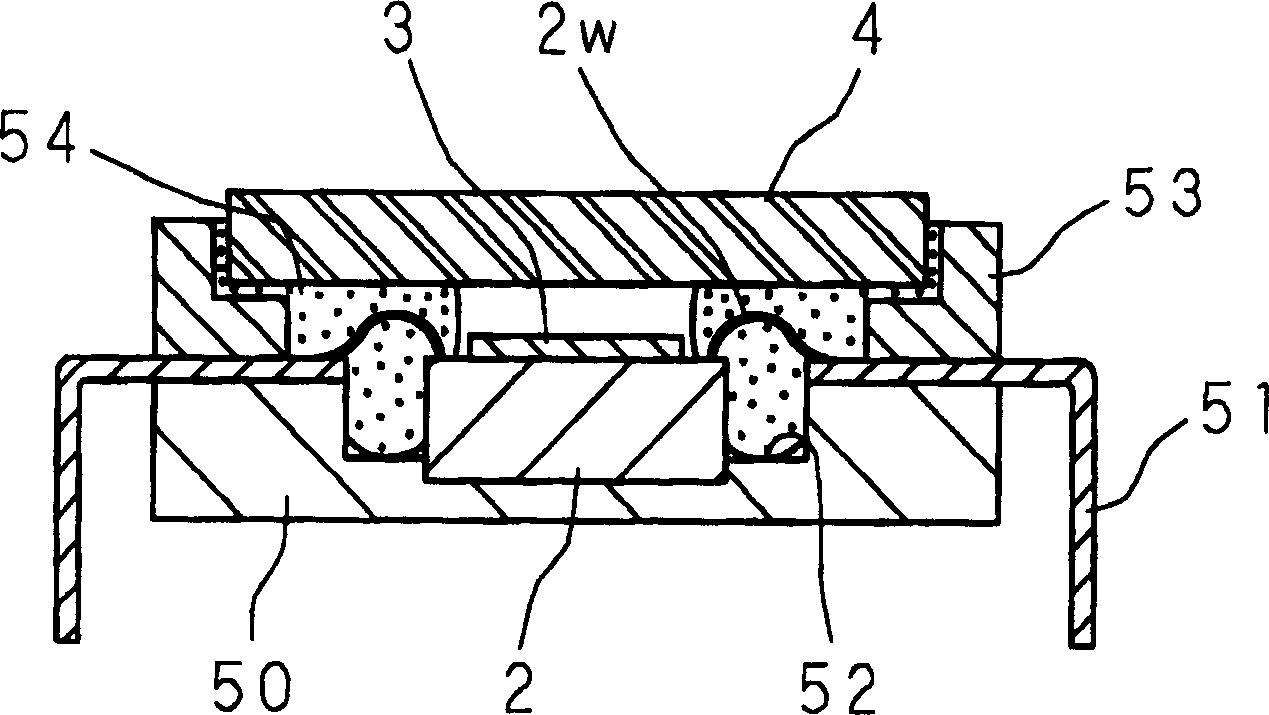
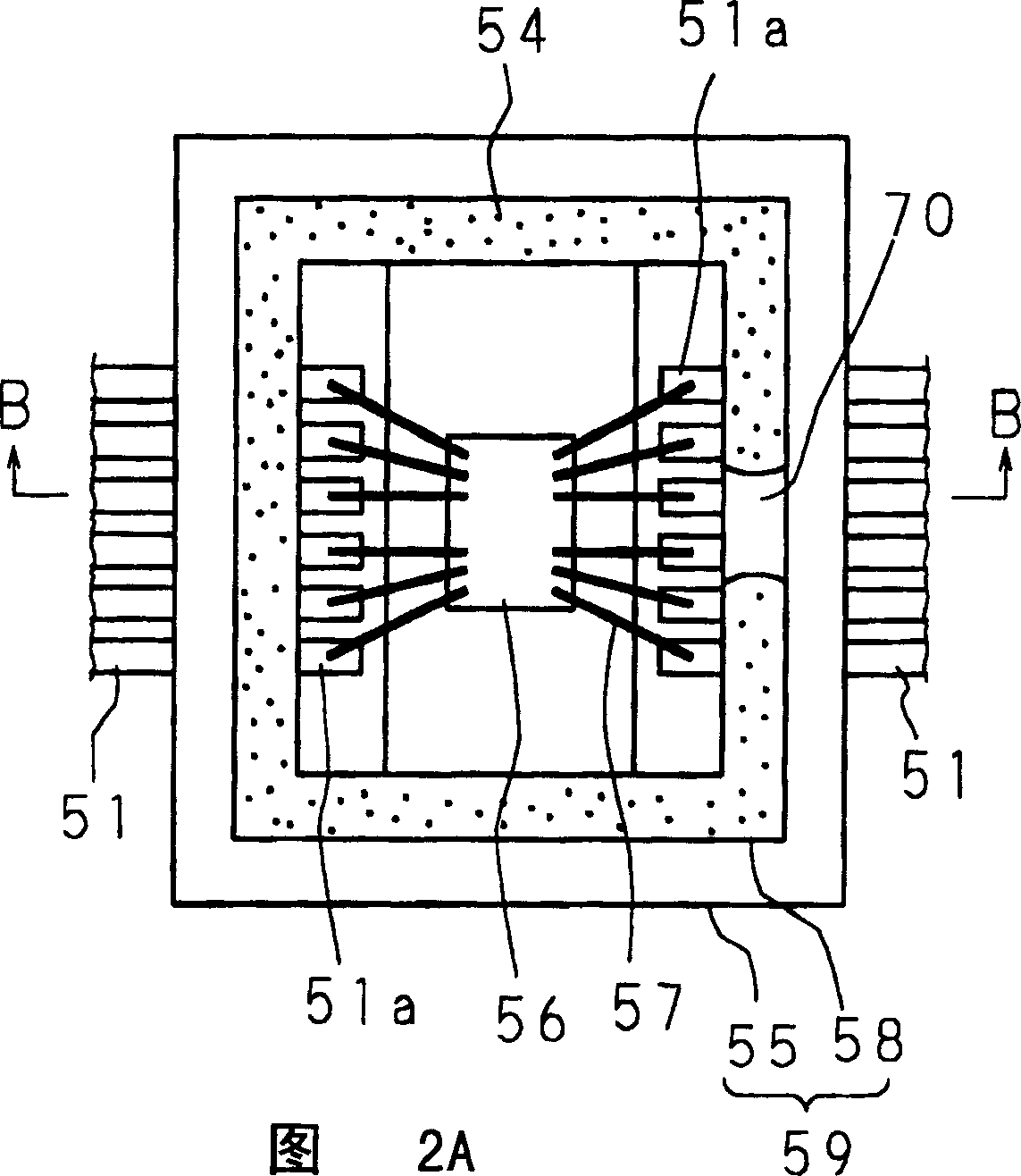
[0107] Figure 3A and 3B is a schematic diagram showing the structure of the solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, in particular, Figure 3A A plan view showing the main plane (one plane) of the solid-state imaging device shown above, Figure 3B yes Figure 3A Sectional view along line B-B in . It should be noted that the joint part 5 is equipped with an outlet path 7 with a sealing function, which is a feature of the present invention and is marked with oblique lines in the following top view for ease of understanding.
[0108] Figure 3A and 3B Among them, 1 indicates a solid-state imaging device, and the solid-state imaging device 1 includes the following main components: a solid-state imaging element 2 equipped with a semiconductor substrate (for example, a single crystal silicon substrate), which has a rectangular shape in plan, and is equipped with a semiconductor circuit; a cover portion 4 made of a transparent material (for ex...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Figure 8A to 8E, FIGS. 9A and 9B, and FIGS. 10A and 10B are schematic diagrams showing a method of manufacturing a solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, in particular, Figure 8A 8E to 8E are schematic diagrams showing the forming steps of the cover portion, FIGS. 9A and 9B are schematic diagrams showing the state of the solid-state imaging element formed on the semiconductor wafer, and FIGS. 10A and 10B are diagrams showing Figure 8A A schematic diagram of a state in which the covering portion formed in FIG. 8E is combined with the main plane (surface having an effective pixel area) of the solid-state imaging element in FIGS. 9A and 9B .
[0129] Figure 8A A transparent sheet 40 is shown having a large area, made of eg a glass sheet. The large-area sheet 40 includes a plurality of covering portions corresponding to the region 40b (with the dividing line 40a as a boundary). When splitting in subsequent steps, the area corre...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Figure 11A and 11B , FIGS. 12A to 12C are schematic diagrams showing a method of manufacturing a solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, in particular, Figure 11A and 11B 12A to 12C are schematic diagrams showing the steps of forming the covering part, and Figs. 12A to 12C are diagrams showing bonding Figure 11A and 11B A schematic diagram of the step of forming a covering portion to one plane (surface having an effective pixel area) of a solid-state imaging element formed on a semiconductor wafer.
[0145] Figure 11A A large area transparent sheet 40 is shown, formed for example from a glass sheet. The large-area sheet 40 includes a plurality of covering portions corresponding to areas 40b having a separation line 40a as a boundary. When in the subsequent division step, the area corresponding to the covered portion of the area 40b is adjusted to be the same size as the covered portion 4 in plan.
[0146] Figure 11B A ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com