Stabilization of cells and biological specimens for analysis
A technique of biology and specimens, applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, and analytical materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
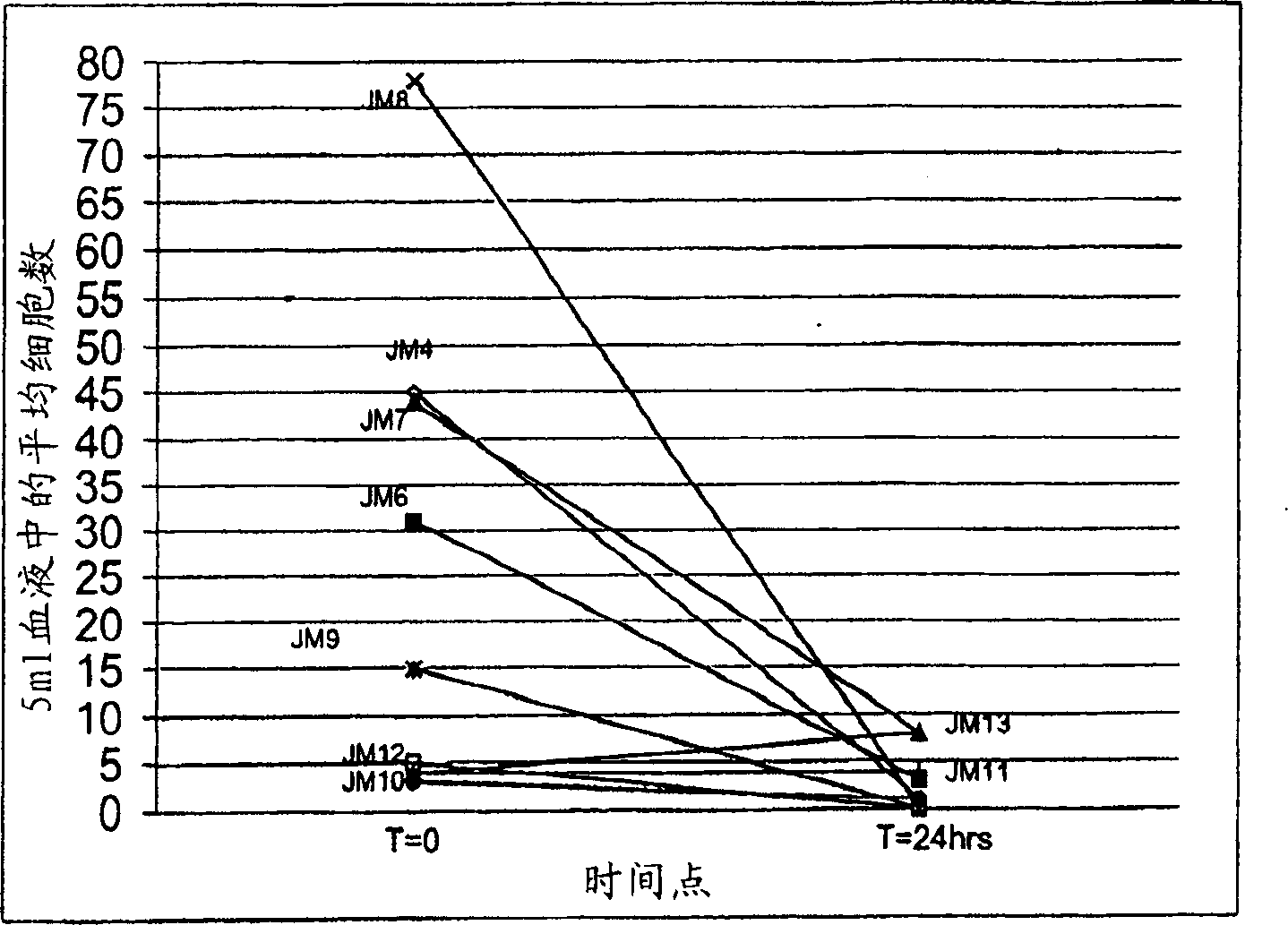
[0051] Stabilization of tumor cells circulating in the blood
[0052] Cyto-Chex TM , StabilCyte TM and TRANSfix TM is an example of three stabilizers that are commercially available and have demonstrated utility in the long-term stabilization of blood cells in blood samples. The stabilizers were optimized to preserve cell size (mainly by reducing shrinkage) and to protect antigens on the cell surface, as determined primarily by flow cytometry techniques. The intended use generally involves direct analysis and does not require extensive manipulation of the sample or enrichment of specific cell populations. In contrast, circulating tumor cells or other rare target cells that are isolated and tested in the present invention include and are determined to be pathologically abnormal or rare cells that occur at very low frequency and therefore require significant enrichment prior to detection.
[0053] CTCs can usually be detected in blood, preferably after storage at room temper...
Embodiment 2
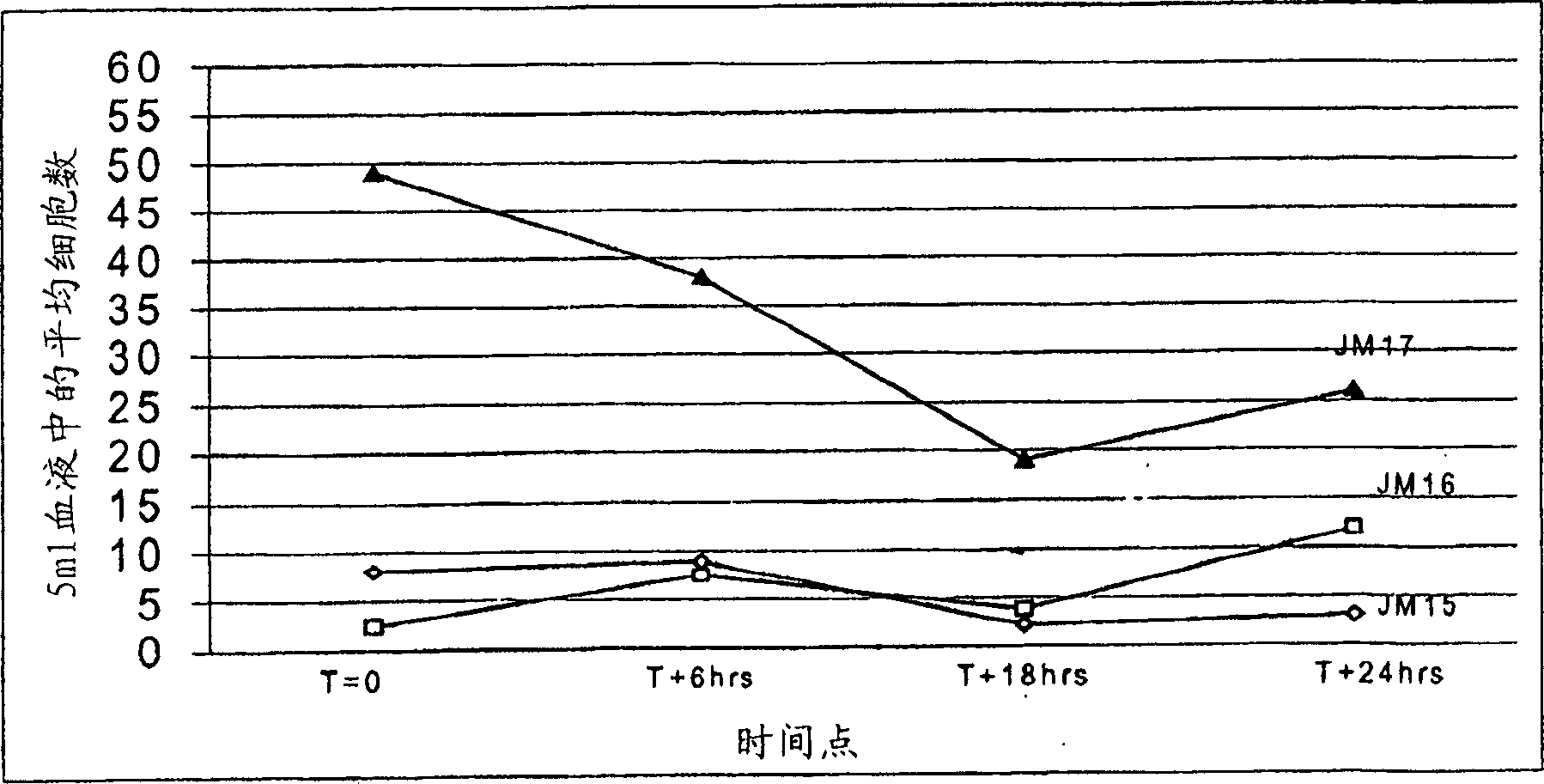
[0064] Preserve sample quality for analysis
[0065] CTCs are present in blood at low frequency and require large sample volumes and efficient enrichment methods for detection. Enrichment methods for CTCs include several washing steps, including magnetic separation methods, which can damage cells and generate debris and clumps due to leakage of DNA from cells. However, it was unexpectedly, and rather startlingly, discovered that gentle upright cylinder mixing of blood tubes on a nutator (the way most hematology laboratories typically keep blood cells in suspension) results in a large number of cells Formation of debris that may interfere with CTC detection and enumeration. In addition, it has been found that incomplete filling of blood draw or analysis tubes further exacerbates this mixed injury, however, no damage occurs in quiescent tubes. Such as image 3 As shown, any mixing of patient samples during transport or other mechanical stress has been shown to unexpectedly in...
Embodiment 3
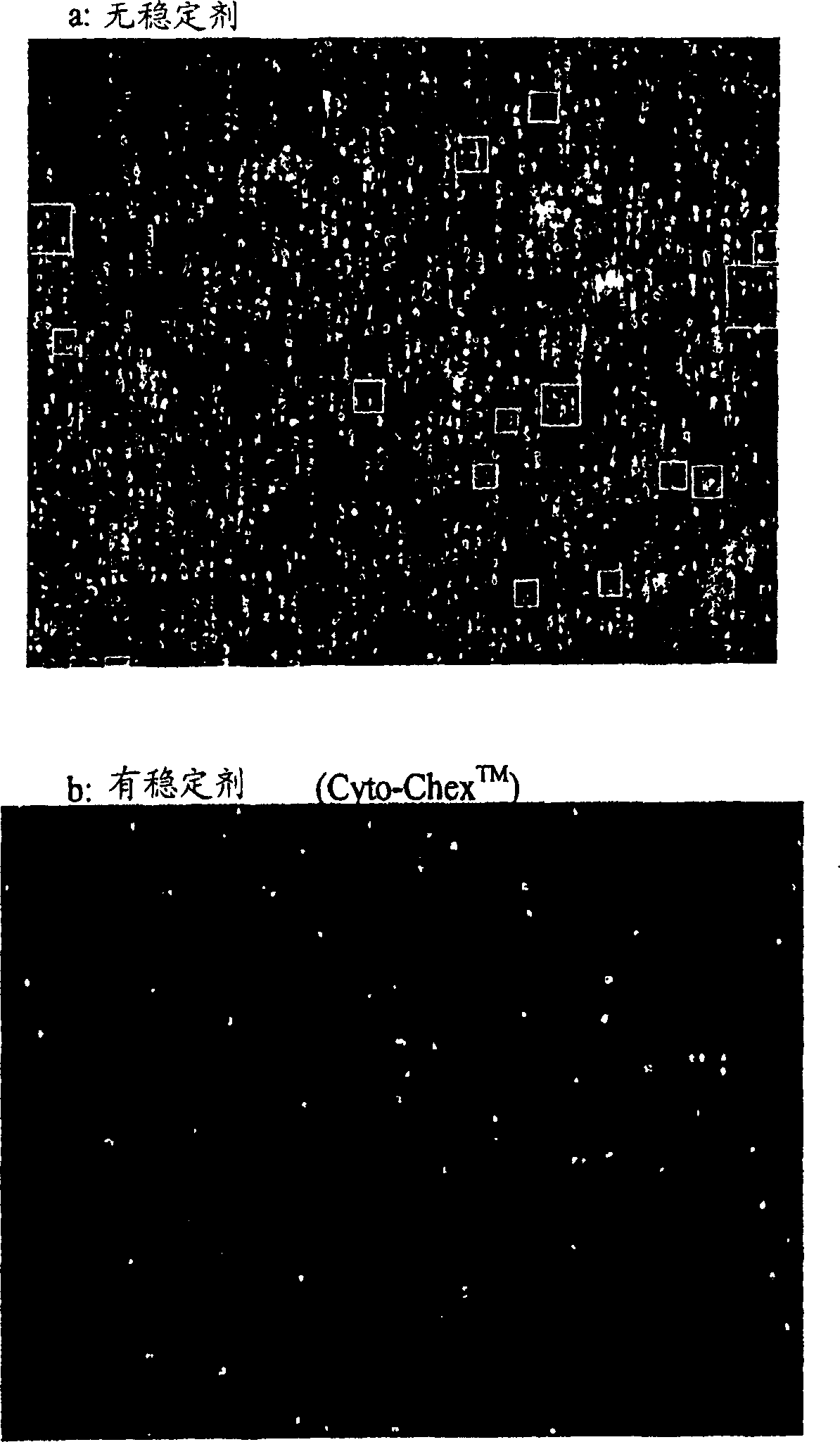
[0068] Cyto-Chex TM Effect of Stabilizers on Sample Quality of Normal Specimens Mixed for 2-3 Hours
[0069] DAPI staining of the nucleus can usually be detected in permeabilized live or dead cells if the nucleus is intact. DNA staining as stainable aggregates on the outside of the cells can also be detected in cell fragments or cell debris if the DNA leaks outside the cells. Therefore, staining with DAPI, and examining under a fluorescence microscope, can easily check the sample quality.
[0070] Pipette three tubes of blood from normal donors into 10 ml EDTA anticoagulated tubes. Without removing the cap, by using CellStabilize TM The injection device dispenses Cyto-Chex as follows TM Stabilizers are added to a blood test tube. The blood tube is placed in a graduated calibration device and the blood volume can be estimated so that the appropriate amount of stabilizer can be added to the desired final concentration. One needle (27G, 1 / 2 inch) was inserted into the cap o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com