Optical system with laser beam uniform irradiation
An optical system, a technology for uniform illumination, applied in the field of optical systems, can solve the problems of reduced degrees of freedom of the optical system, complex and complicated configuration of multiple mirrors, etc., and achieve the effect of uniform illumination intensity distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
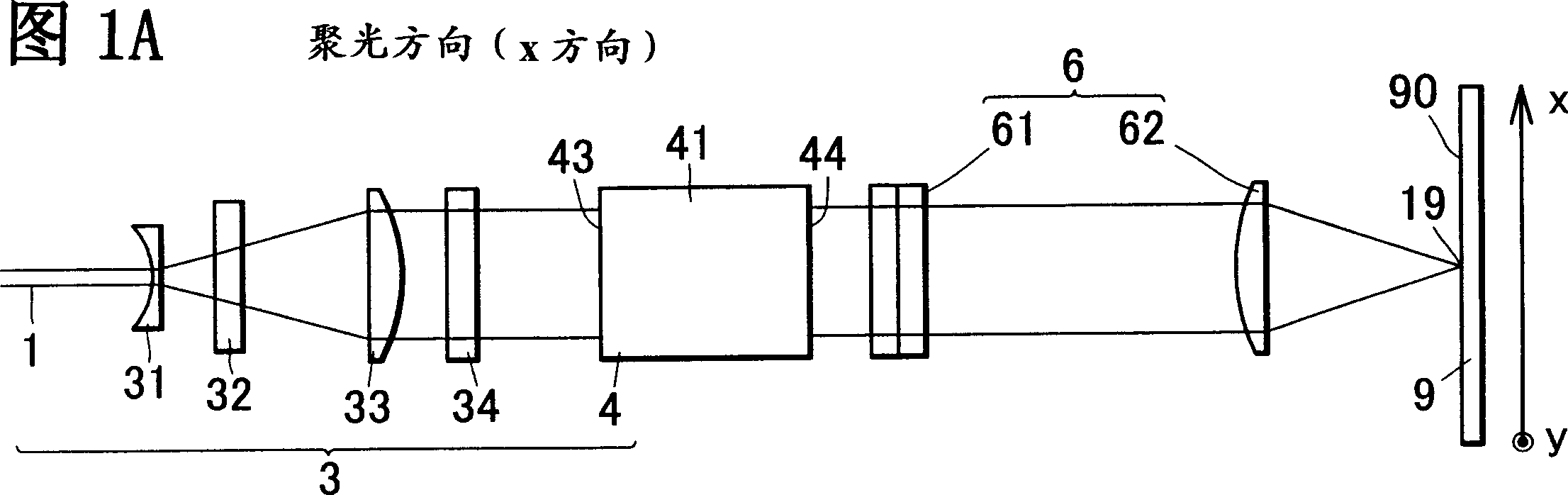
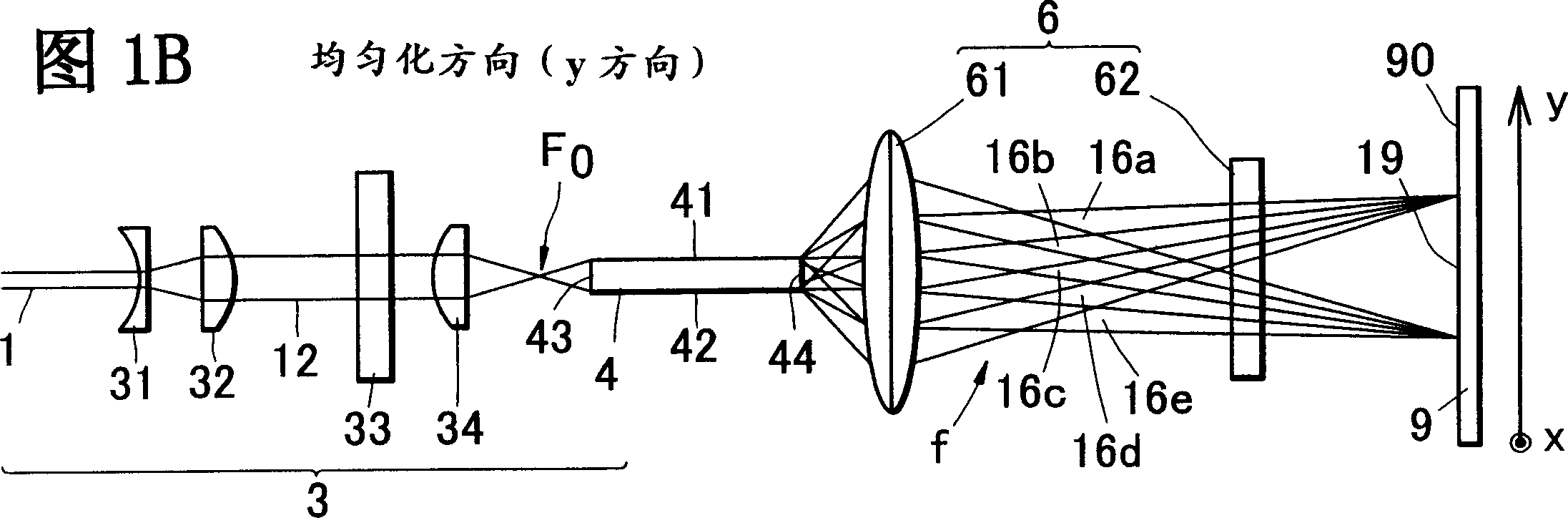
[0088] In Embodiment 1 of the present invention, Fig. 1A and Fig. 1B represent the optical system uniformly irradiated by the laser beam, but represent that the optical system is formed on the irradiated surface, spreads with a uniform distribution in the y direction, and converges into a line in the x direction An example of a straight-line irradiation profile.
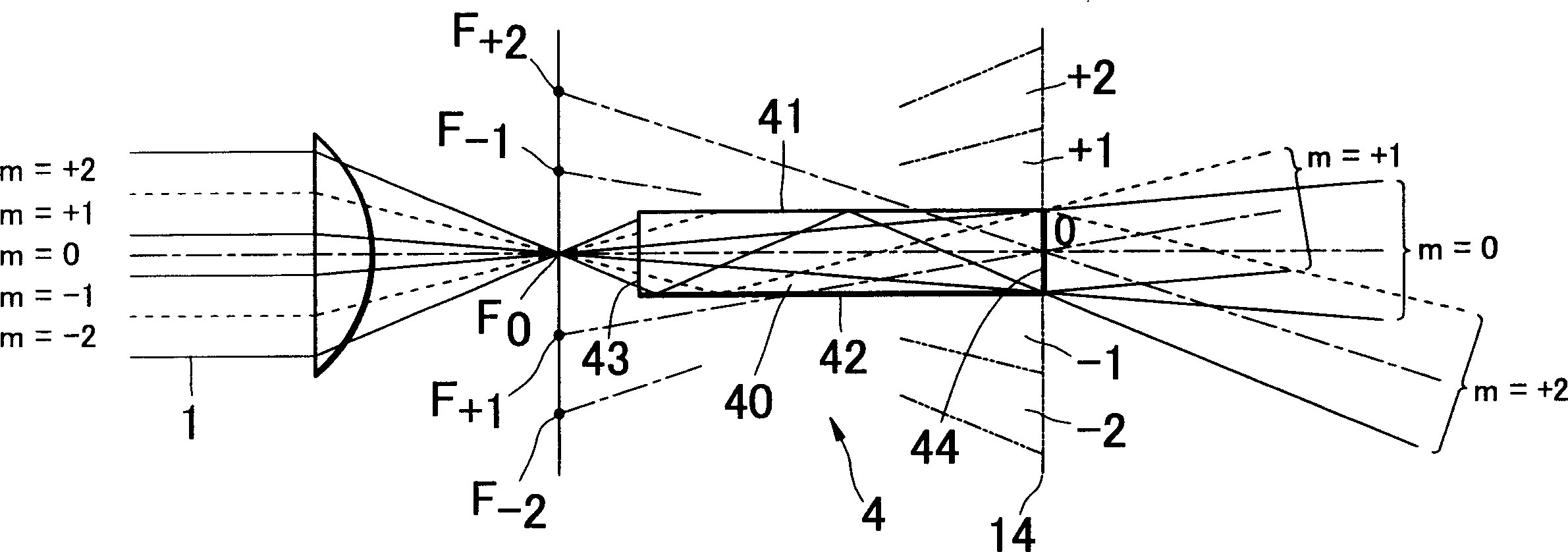
[0089] The optical system includes laser beam splitting means 3 and coincident irradiation means 6 (61, 62). In this example, the waveguide 4 is used in the laser beam splitting part 3 to split the laser beam 1 into a required number of split beams 16a-16e, and these split beams are imaged in a linear shape on the irradiation surface 90 by overlapping the irradiation part 6. Contoured illumination beam 19 .
[0090] In this embodiment, the laser beam splitting unit 3 includes an optical system for making the laser beam 1 from the laser oscillator incident into the waveguide 4, and includes a beam expander lens 31 an...
Embodiment 2
[0105] In this embodiment, a cylindrical lens array is used as another beam splitting component. As shown in FIGS. 8A and 8B in this example, the optical system for uniform irradiation of the laser beam includes an optical system for making the laser beam 1 from the laser oscillator incident to the cylindrical lens array 5, including a beam expander lens 31 for generating parallel beams. , a y-direction collimator lens 32 and an x-direction collimator lens 33 , the parallel beams from the collimator lens 33 are incident on the cylindrical lens array 5 .
[0106] In the cylindrical lens array 5, the cylindrical lens refers to a lens that is cylindrical in the x direction in the figure, and the cross-sectional convex lens is stacked in the y direction toward the optical axis, but the illustration includes five tiny cylindrical lenses 5a to 5e. Constituting, accordingly, five segmented bundles are formed.
[0107] Split beams 15 a to 15 e in the y direction from the cylindrical ...
Embodiment 3
[0112] In the optical system according to the embodiment of the present invention, the homogenizing means includes: one of the adjacent split beams formed by the waveguide is delayed by a time-interference distance of the laser beams with respect to the other. Long optical delay components. In order to prevent interference between the two split beams emitted from adjacent areas of the laser beam, the optical delay member provides an optical path difference equal to or greater than the time interference distance between the two split beams in the adjacent areas.
[0113] This example shows an optical system using a light-transmitting retardation plate as an optical retardation member. As shown in Fig. 12A and Fig. 12B, the optical system uses: the laser beam splitting part 3 utilizing the waveguide 4, the orthogonal two cylindrical lenses (61, 62) as the coincident irradiation part 6, the retardation part as the optical delay part plate 7. In this example, the waveguide 4 div...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com