Method for regulating and controlling two-dimensional magnetic material through small molecule chemisorption
A magnetic material and chemical adsorption technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of poor controllability of magnetic adjustment, low Curie temperature of two-dimensional materials, and complex Curie Problems such as high temperature to achieve the effect of improving magnetic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] A method for regulating two-dimensional magnetic material by chemical adsorption of small molecules, comprising the following steps;
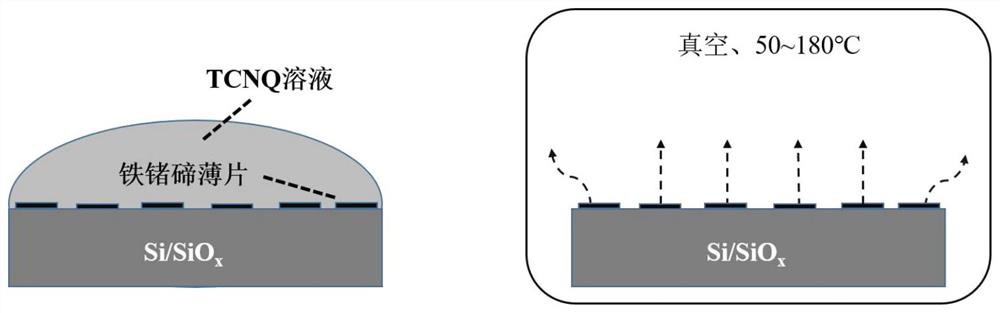
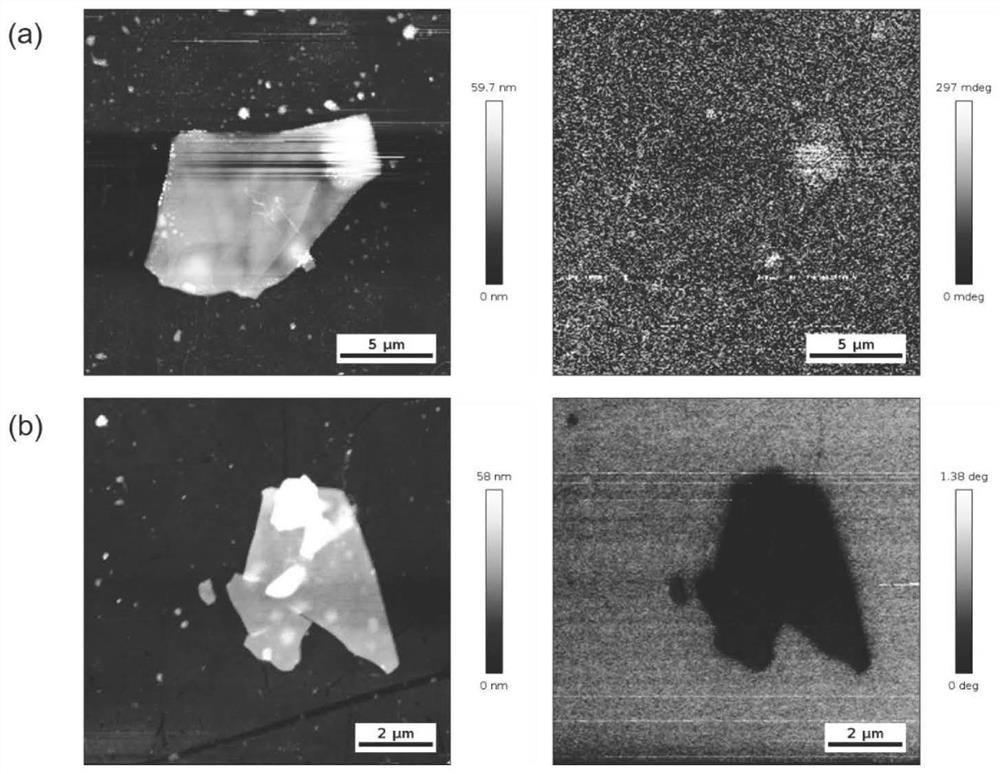
[0030] Step 1, exfoliation and transfer of the two-dimensional magnetic material: the single crystal of the two-dimensional magnetic material is fully washed to remove impurities, the single crystal is thinned by mechanical exfoliation or liquid phase exfoliation, and the obtained nanosheet is transferred to silicon with an oxide layer. On the substrate, the thickness of the nanosheets was measured by atomic force microscopy (AFM);
[0031] Step 2, preparation of TCNQ solution: dissolve TCNQ powder into N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) or tetrahydrofuran (THF) solvent, and the preparation concentration is 10 -6 ~10 -3 The mol / L TCNQ solution is ready for use, suck the TCNQ solution through a pipette, and slowly drop it on the silicon oxide wafer substrate with the nanosheets transferred to ensure that the nanosheets on the substrate are full...
Embodiment 2
[0036]A method for regulating two-dimensional magnetic material by chemical adsorption of small molecules, comprising the following steps;
[0037] Step 1, exfoliation and transfer of two-dimensional magnetic materials: fully wash the iron-germanium-tellurium single crystal to remove impurities, and then exfoliate by mechanical exfoliation or liquid phase exfoliation. Transfer to the silicon oxide wafer substrate cleaned in advance; in the step 1, the thickness of the silicon oxide wafer substrate is 200 nm. The thickness of the nanosheets exfoliated in the first step is all below 200 nanometers, and the average lateral size is 25 micrometers.
[0038] Step 2, TCNQ solution preparation: Dissolve TCNQ powder into DMF solvent, the preparation concentration is 1×10 -6 The mol / L TCNQ solution is ready for use, suck the TCNQ solution through a pipette, and slowly drop it on the silicon oxide wafer substrate with the nanosheets transferred to ensure that the nanosheets on the subst...
Embodiment 3
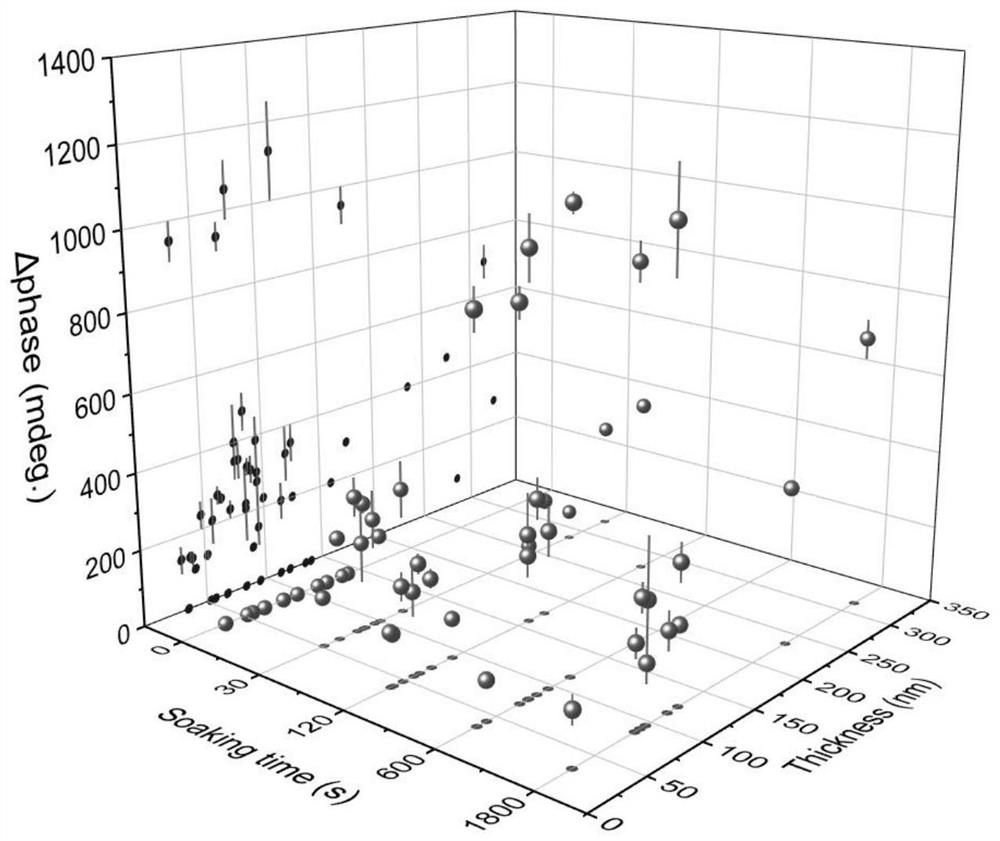
[0041] The difference from Example 2 is that in step 3, the mechanically exfoliated two-dimensional FeGeTe flake solution was immersed for 5 minutes, the drying temperature was 55 degrees Celsius, and the drying time was 5 hours.
[0042] In step 2, the preparation concentration is 5 × 10 -5 mol / L TCNQ solution was used.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Horizontal size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com