Preparation method of L-arginine-based carbon dots and application of L-arginine-based carbon dots in lemon yellow detection
An arginine-based carbon, tartrazine technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, nano-carbon, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problem of uneven particle size of carbon quantum dots, achieve high selectivity and anti-interference ability, raw materials The effect of low cost, good acid and alkali tolerance and salt tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: Preparation of L-Arg-CDs Coarse Carbon Dots
[0049] Arginine-derived CDs were prepared using a one-step hydrothermal method. First, 0.35 g of L-arginine and 0.5 g of o-phenylenediamine were weighed and dissolved in 5 mL of DMF, mixed well, and then transferred to a 20 mL polytetrafluoroethylene high-temperature reaction kettle for reaction at 210 °C for 10 h. After the product was naturally cooled, thin-layer chromatography (TLC) was used to mix the carbon dots with the concentrated solution, and the samples were drawn on a chromatographic silica gel plate. The volume ratio of methanol and dichloromethane was 1:10 as the eluent to separate the carbon dots. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain carbon dots with blue fluorescence under ultraviolet light, and then stored at 4 °C until use.
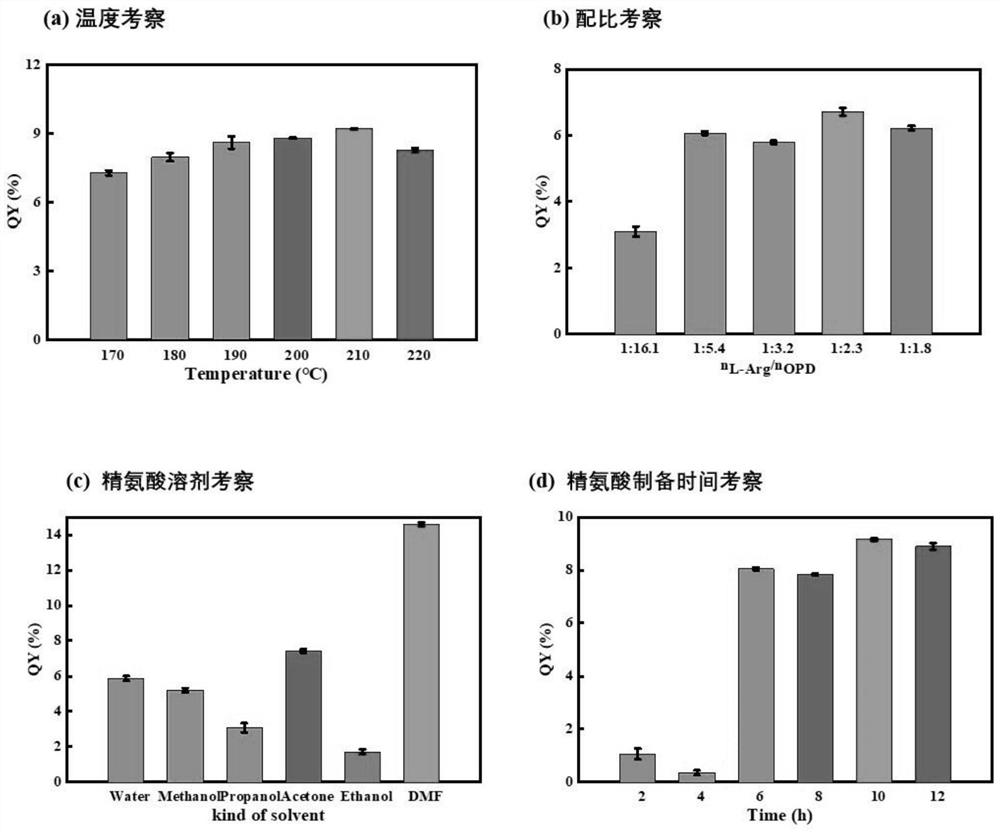
[0050] The solvent (water, DMF, n-propanol, acetone, ethanol and methanol), molar ratio (0.0621, 0.1862, 0.3104, 0.4345, 0.5587), temperature (170℃-220℃)...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Structural characterization of L-Arg-CDs coarse carbon dots
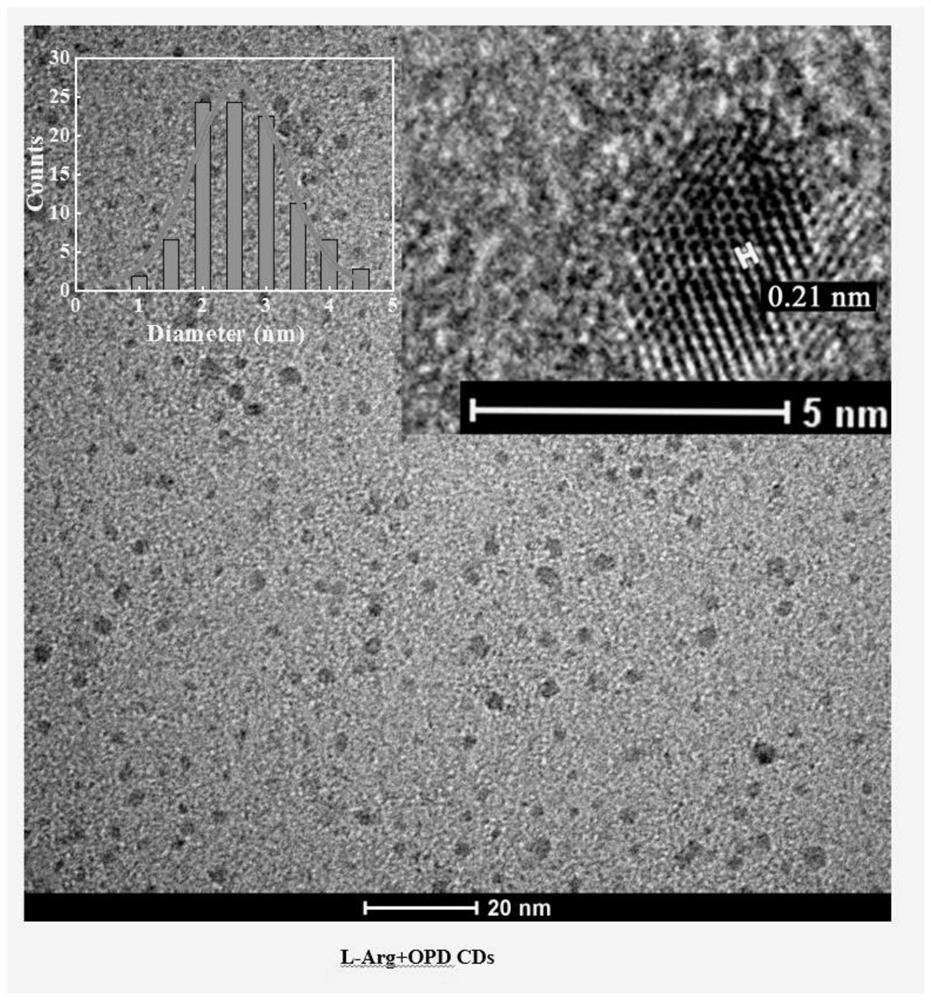
[0052] The shape characteristics and particle size distribution of L-Arg-CDs were investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), such as figure 2 As shown, the results indicated that the L-Arg-CDs had regular shapes in the form of spherical-like carbon nanoparticles with an average particle size of 2.75 nm and a lattice spacing of about 0.21 nm. It has good monodispersity and no obvious aggregation, stable structure, can be freely dispersed in water, and has good water solubility.
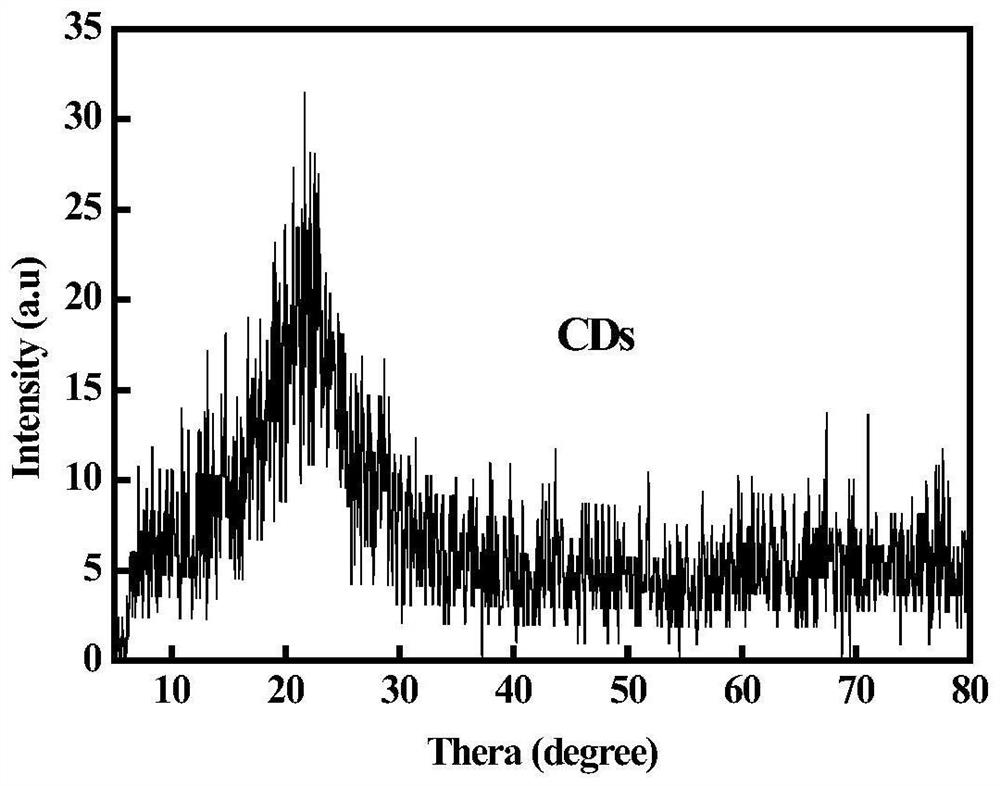
[0053] The crystal structure of carbon dots is image 3 X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) shown in . The diffraction peak of L-Arg-CDs is 2θ=22.27°, indicating that the synthesized fluorescent carbon quantum dots belong to amorphous carbon structure.
[0054] Using XPS ( Figure 4 ) to analyze the surface functional groups and components of L-Arg-CDs. The characteristic peaks of XPS full spectrum at 284.0eV,...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: Purification of L-Arg-CDs crude carbon dots
[0060] The quantum yield QY of crude carbon dots was measured after secondary purification, the QY of crude L-Arg-CDs was 14.58%; the QY of secondary purified L-Arg-CDs was 22.670%. QY increased. Measure the fluorescence absorption values of secondary purified L-Arg-CDs and crude L-Arg-CDs, such as Image 6 a It can be seen that the fluorescence performance of the secondary purified L-Arg-CDs is better than that of the crude L-Arg-CDs; 1mME102 was added to both CDs for fluorescence quenching, and the secondary purified L-Arg-CDs was also better than the crude L-Arg-CDs for the quenching of E102 L-Arg-CDs.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com