Method for generating target product from glycollic acid under action of enzyme
A technology of glycolic acid and acetate kinase, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, botanical equipment and methods, and the use of vectors to introduce foreign genetic materials, etc., to achieve the effect of high light efficiency mechanism, improved utilization efficiency, and less accumulation of intermediate by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1: Preparation of glycolaldehyde with glycolic acid as raw material
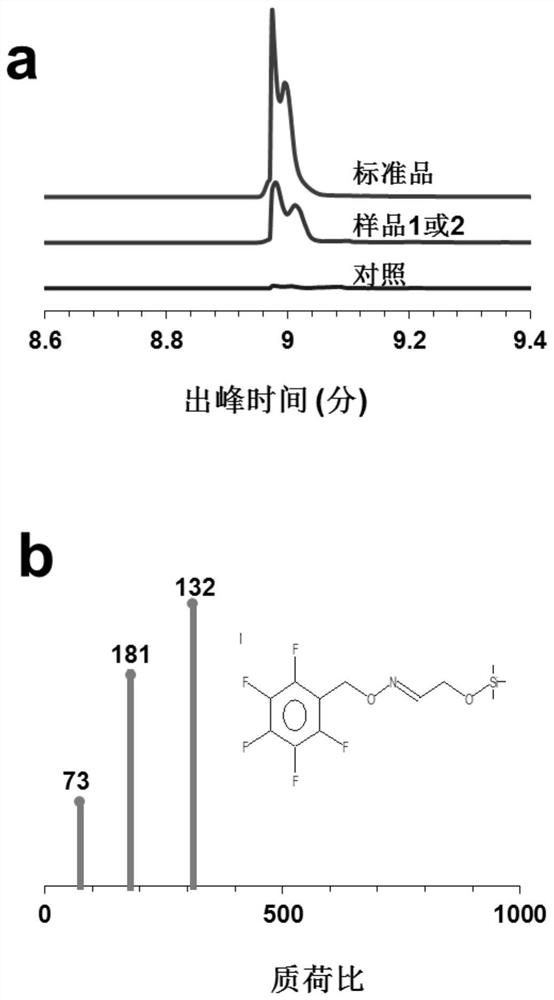
[0063] Sample 1: Add 20 mM glycolic acid, 1 mM NAD(P)H, 1 mM ATP, 1 mM CoA, ACS, GCR at 2 mg / mL each to a 200 μL system. Sample 2: Add 20 mM glycolic acid, 1 mM NAD(P)H, 1 mM ATP, 1 mM CoA, AckA, PTA, GCR at 2 mg / mL each to a 200 μL system. Control: 20 mM glycolic acid, 1 mM NAD(P)H, 1 mM ATP, 1 mM CoA, no enzyme was added to a 200 [mu]L system. After reacting at 30°C for 1 h, after the reaction was completed, the reaction system was lyophilized. 60 μL of pentafluorobenzene hydroxylamine hydrochloride (PFBOA, 200 mM) was then added, vortexed, and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature. 300 μL of hexane was added and allowed to stand at room temperature for 5 min. A 100 μL sample of the organic layer was taken, and 30 μL of trimethylsilyl trifluoroacetamide containing 1% trimethylchlorosilane and 20 μL of pyridine were added to silylate the PFBOA derivative. The derivatized glycolaldehyde...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2: Preparation of Acetyl-CoA with Glycolic Acid as Raw Material
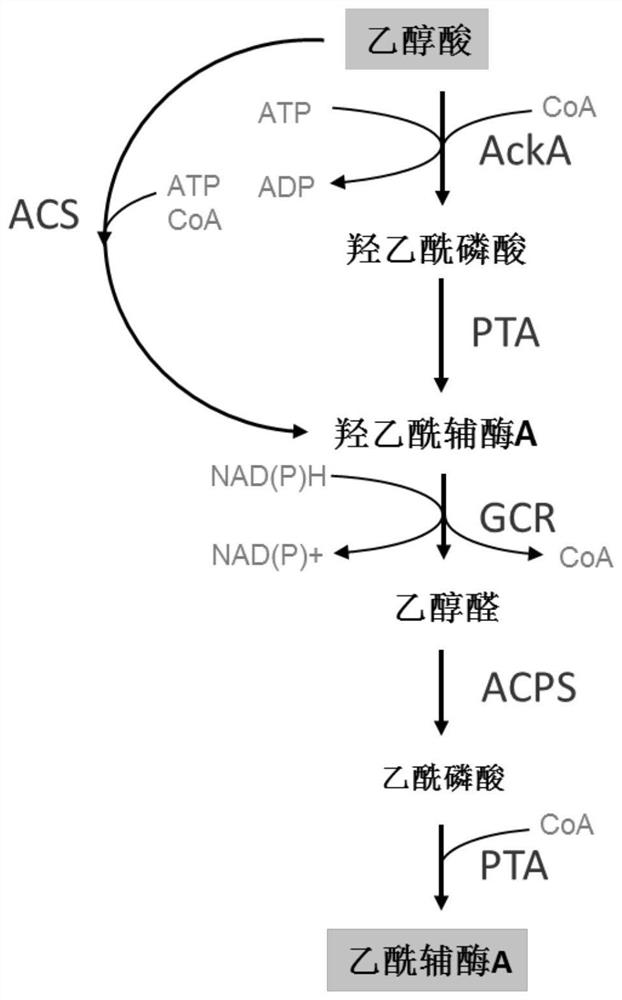
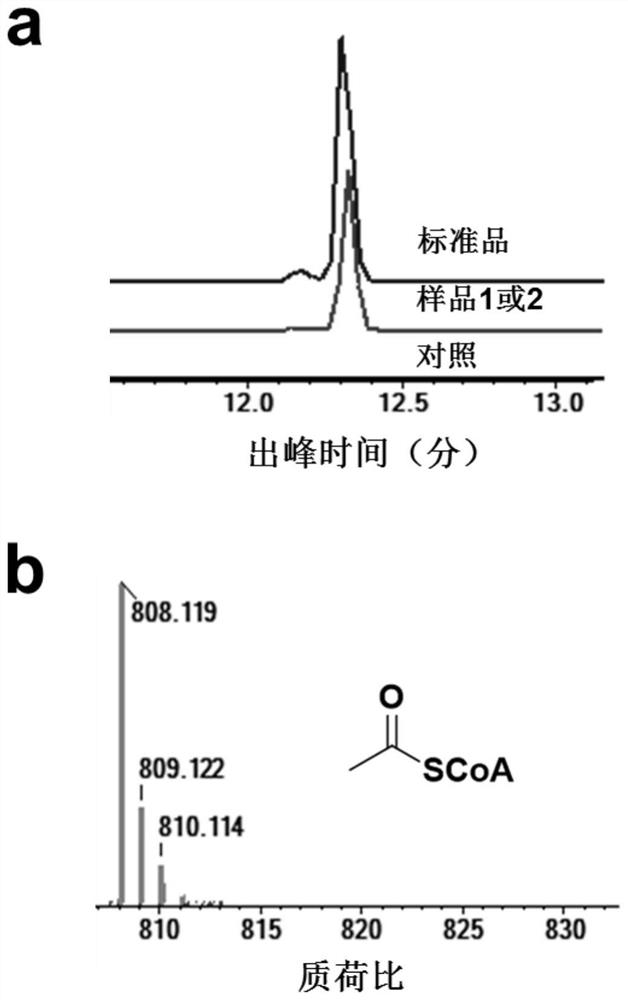
[0067]Sample 1: 20 mM glycolic acid, 1 mM NAD(P)H, 1 mM ATP, 1 mM CoA, 2 mg / mL each of ACS, PTA, GCR, ACPS were added to a 200 μL system. Sample 2: Add 20 mM glycolic acid, 1 mM NAD(P)H, 1 mM ATP, 1 mM CoA, AckA, PTA, GCR, ACPS at 2 mg / mL each to a 200 μL system. Control: 20 mM glycolic acid, 1 mM NAD(P)H, 1 mM ATP, 1 mM CoA, no enzyme was added to a 200 [mu]L system. After 1 h of reaction at 30 °C, acetyl-CoA was detected by liquid-phase mass spectrometry, and the results were as follows image 3 shown. Depend on image 3 know, use figure 1 Middle cofactors and enzymes can realize the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from glycolic acid, and build a complete glycolic acid utilization pathway.
[0068] Liquid mass spectrometry detection conditions: LC conditions: Instrument: Shimadzu LC-30A; chromatographic column: Merck zic-HILIC (100 mm×2.1 mm, 3.5 μm); mobile phase A is 10 mM ammonium acetate, B is ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3: Application of Glycolic Acid Synthesis Acetyl-CoA Pathway in Plants
[0071] The genes related to the acetyl-CoA pathway of glycolic acid synthesis were transferred into rice by Agrobacterium transfection, so that AckA, PTA, GCR and ACPS or ACS, PTA, GCR and ACPS proteins were localized and expressed in rice chloroplasts. The transgenic plants were passed for another generation, and the seeds were collected and cultured to obtain T1 homozygous plants. 1 g of leaves of wild-type plants (6 plants) and transgenic plants (6 plants) were taken respectively, extracted by Beijing Nuohezhiyuan Technology Co., Ltd. and analyzed for metabolomics in leaves. The result is as Figure 4 shown.
[0072] The results showed that, compared with wild-type plants, transgenic plants contained higher concentrations of amino acids. The results of significant difference analysis showed that the P values were all lower than 0.01, indicating that the difference in amino acid cont...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com