Method for preparing hafnium boride powder
A technology of hafnium boride and powder, which is applied in the field of polyethylene glycol-assisted preparation of hafnium boride powder, which can solve the problem of many steps, high requirements for preparation conditions, and unsatisfactory particle size, purity, and output of hafnium boride powder scientific research and production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
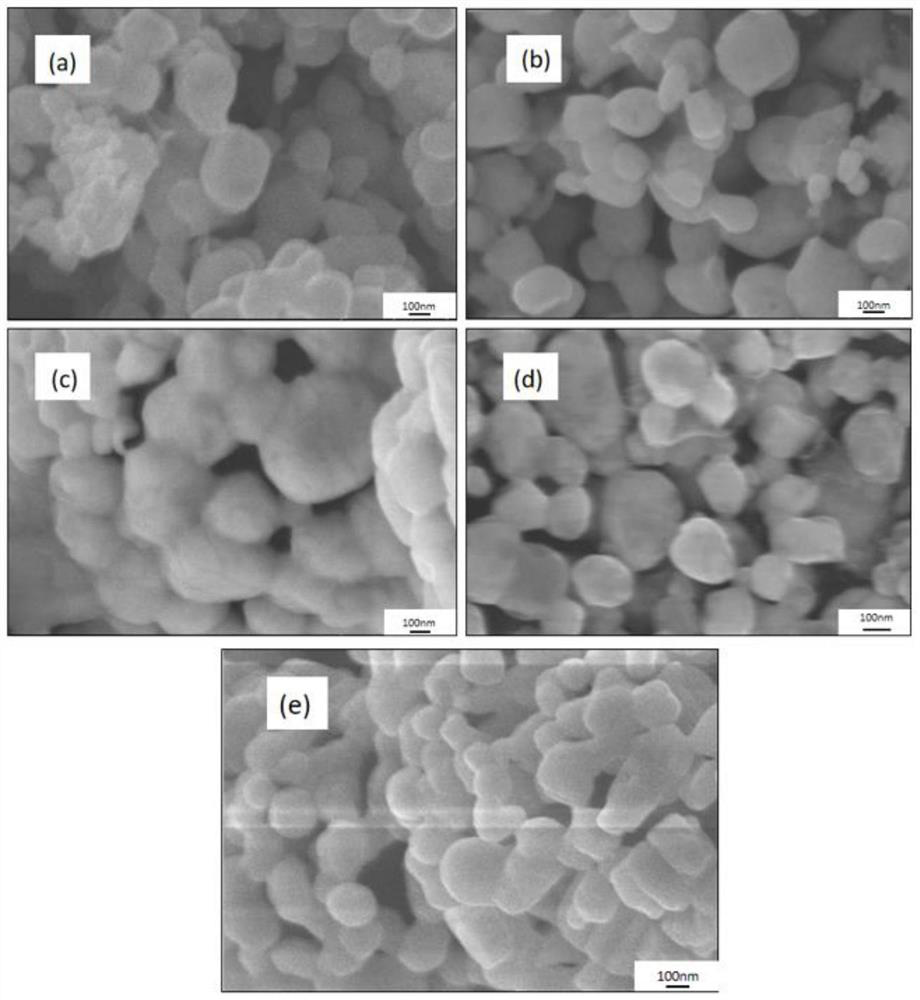
Embodiment 1
[0073] Weigh 2g (32mmol) of boric acid and 3g (16mmol) of sorbitol, mix them in the same beaker, then pour 20mL of acetic acid (analytical grade, 21g) into it, and use an oil bath magnetic stirrer to gradually raise the temperature to 60°C , stirring at constant temperature, until boric acid and sorbitol are completely dissolved in acetic acid, and the solution is completely clear, thereby obtaining clear solution 1. Add 0.4 g of polyethylene glycol (molecular weight: 2000) to the clear solution 1, stop heating, keep stirring until cooled to room temperature, and then keep stirring.
[0074] Weigh 3.2g (10mmol) hafnium tetrachloride and put it into a beaker, pour 10ml of acetic acid (analytical grade, 10.5g) into it, and use a magnetic stirrer to stir at normal temperature until the hafnium tetrachloride is completely dissolved in acetic acid to obtain a solution 2. The solution is light yellow. Slowly drop the light yellow solution into solution 1 at a rate of 10 mL / min (1 m...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Weigh 2g (32mmol) of boric acid and 3g (16mmol) of sorbitol, mix them in the same beaker, then pour 20mL of acetic acid (analytical grade, 21g) into it, and use an oil bath magnetic stirrer to gradually raise the temperature to 60°C , stirring at constant temperature, until boric acid and sorbitol are completely dissolved in acetic acid, and the solution is completely clear, thereby obtaining clear solution 1. Add 0.8 g of polyethylene glycol (molecular weight: 2000) to the clear solution, stop heating, keep stirring until cooled to room temperature, and then continue to keep stirring.
[0078] Weigh 3.2g (10mmol) hafnium tetrachloride and put it into a beaker, pour 10ml of acetic acid (analytical grade, 10.5g) into it, and use a magnetic stirrer to stir at normal temperature until the hafnium tetrachloride is completely dissolved in acetic acid to obtain a solution 2. The solution is light yellow. Slowly drop the light yellow solution into solution 1 at a rate of 10 m...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Weigh 2g of boric acid (32mmol) and 3g of sorbitol (16mmol), mix them in the same beaker, then pour 20mL of acetic acid (analytical grade, 21g) into it, and use an oil bath magnetic stirrer to make it gradually warm up to 60°C , stirring at constant temperature, until boric acid and sorbitol are completely dissolved in acetic acid, and the solution is completely clear, thereby obtaining clear solution 1. Add 2 g of polyethylene glycol (molecular weight: 2000) to the clear solution, stop heating, keep stirring until cooled to room temperature, and then continue to keep stirring.
[0082] Weigh 3.2g (10mmol) hafnium tetrachloride and put it into a beaker, pour 10ml of acetic acid (analytical grade, 10.5g) into it, and use a magnetic stirrer to stir at normal temperature until the hafnium tetrachloride is completely dissolved in acetic acid to obtain a solution 2. The solution is light yellow. Slowly drop the light yellow solution into solution 1 at a rate of 10 mL / min (1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com