QRT-PCR (quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) method for identifying novel coronavirus Lambda variant
A technology of coronavirus and mutant strains, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems affecting the detection timeliness, throughput and cost of virus mutant strains, high cost of testing materials and labor, and many uncontrollable influencing factors, so as to achieve easy high-throughput operation , Reduce the probability of operational contamination, and improve the effect of detection throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A qRT-PCR method for identifying novel coronavirus Lambda mutant strains, comprising the following steps:
[0054] Step 1, use the Trizol method to extract the RNA of the new coronavirus;
[0055] Step 2, ARMS-based qRT-PCR primer probe design:
[0056] Step 2.1, primer design: According to the general principles of primer design, combined with the nucleotide sequence near the mutation site of the new coronavirus Indian variant, two pairs of primers were designed for each mutation site, in which the 3' ends of the upstream primers matched the mutation and non-coronavirus respectively. Variation point, that is, a variation upstream primer and a non-variation upstream primer, two pairs of upstream primers share a downstream primer;
[0057] When the variable site to be identified is G75V, the nucleotide sequence of the mutated upstream primer is shown in SEQ ID NO.1: 5'-CATGTCTCTGGGACCAACGT-3', and the nucleotide sequence of the non-variant upstream primer is shown in SE...
Embodiment 2
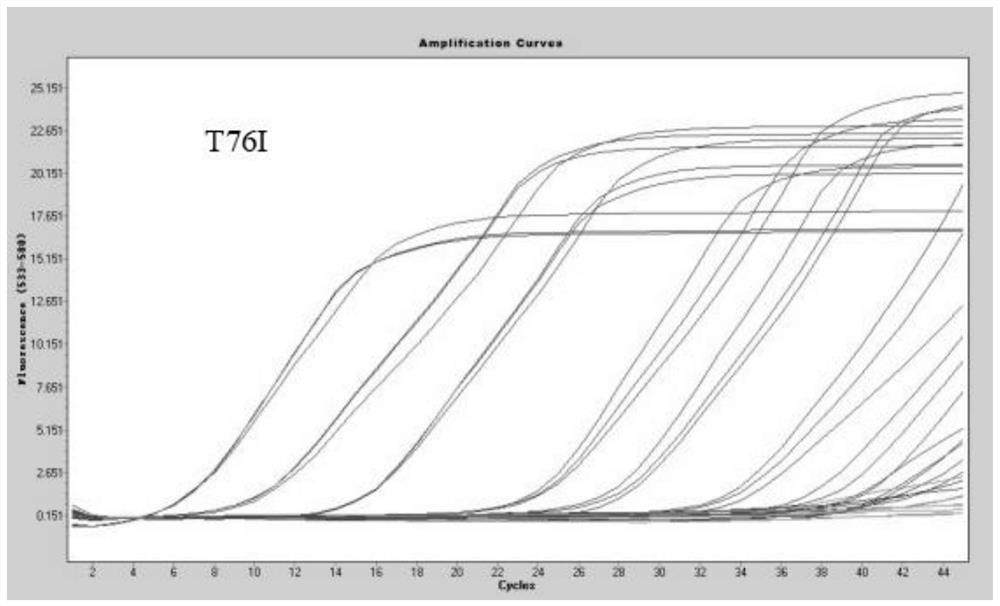
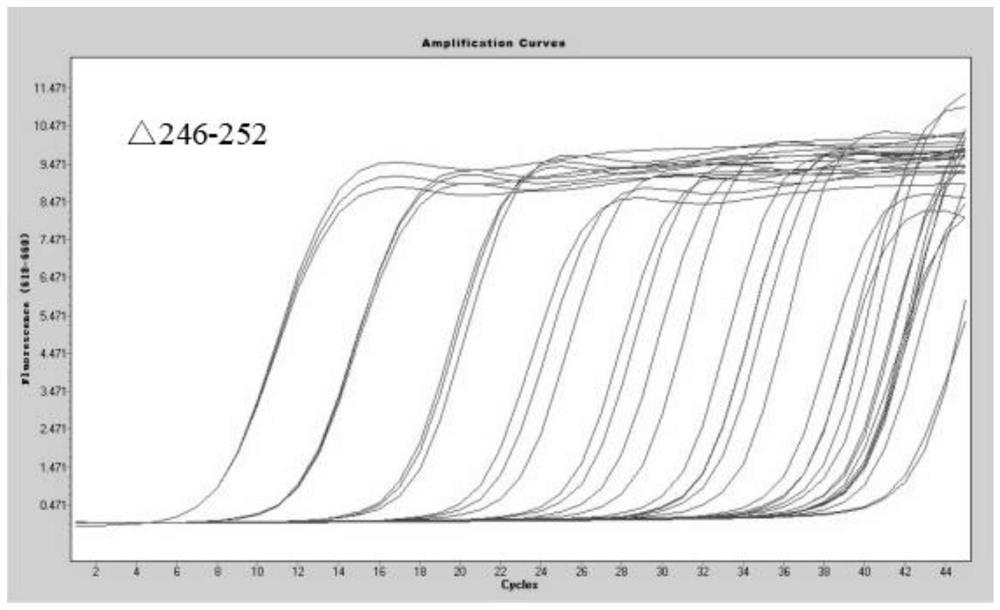
[0079] Method of the present invention is done sensitivity experiment (template dilution 10 7 -10 0 copy / microliter), the experimental results are as follows Figure 1-7 As shown, when the variable site to be identified is G75V, the detection sensitivity is 5.63 copies / microliter; when the variable site to be identified is T76I, the detection sensitivity is 9.10 copies / microliter; when the variable site to be identified is When it is △246-252, the detection sensitivity is 3.85 copies / microliter; when the mutation site to be identified is L452Q, the detection sensitivity is 4.02 copies / microliter; when the mutation site to be identified is F490S, the detection sensitivity is 6.39 copies / microliter; when the mutation site to be identified is D614G, the detection sensitivity is 2.47 copies / microliter; when the mutation site to be identified is T859N, the detection sensitivity is 4.16 copies / microliter.
Embodiment 3
[0081] The precision of the repeatability test evaluation method refers to the closeness between a series of single measurement values obtained by repeated measurements of the same specimen under certain conditions, and is an index reflecting the size of random errors. It is divided into intra-batch repeatability experiments, Inter-batch repeatability experiments (intra-day, day-to-day repeatability experiments), operator / instrument repeatability experiments, etc.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com