High-strength difficult-to-deform nickel-based superalloy and preparation method thereof
A nickel-based superalloy, hard-to-deform technology, applied in the field of preparation of nickel-based superalloys, can solve the problems of high Co content, high alloy manufacturing costs, etc., to achieve the effect of improving bonding force, excellent durability, and improving temperature bearing capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0047] The above-mentioned high-strength and difficult-to-deform nickel-based superalloy adopts the following preparation method, including the following steps:
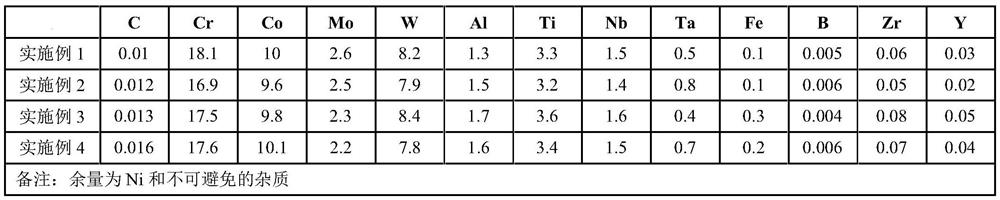
[0048] S1, Vacuum induction smelting, batching according to the above element ratio, adding Ni, Cr, Co, W, Mo, C into the induction furnace, under the conditions of vacuum degree ≤ 2.7Pa, power 300 ~ 600KW, complete melting Afterwards, refine for 30-60 minutes under the conditions of power 600-800KW and refining temperature 1520-1580°C; then reduce the power to 200-600KW and lower the temperature of molten steel to 1470-1520°C, then add Ti, Al, Nb, Ta , Zr, and B are alloyed and smelted to obtain molten steel. The measured elements in molten steel satisfy C: 0.005-0.02%, Cr: 15.0-19.0%, Co: 8.0-11.0%, Al: 1.0-2.0%, Ti: 3.0- 4.0%, Nb: 1.0~2.0%, Ta: 0.3~1.0%, Mo: 1.0~3.0%, W: 7.0~9.0%, B: 0.004~0.01%, Zr: 0.05~0.11%, after charging 10000Pa Ar Gas, after adding Y, continue to smelt for 5-10 minutes under the power of 2...
Embodiment 1
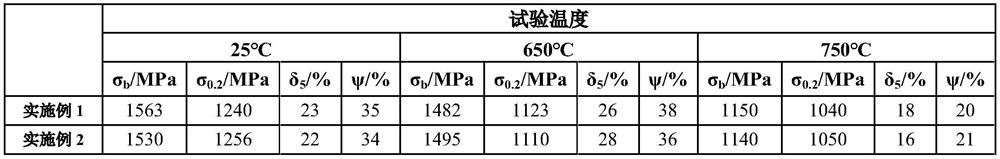
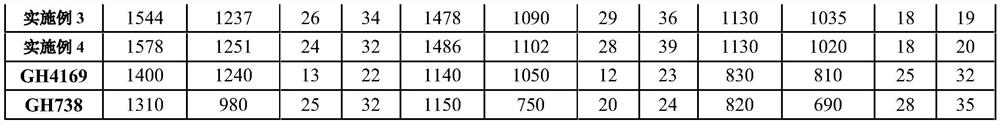
[0059]S1, vacuum induction smelting, using selected high-purity raw materials as alloy raw materials and mixing them according to the ratio of the above elements. It is necessary to ensure that the surface of the alloy raw materials is derusted, clean and free of oil, etc., and special attention should be paid to Si, Mn, Cu Substituting C into the upper limit; put Ni, Cr, Co, W, Mo, C into the induction furnace, and carry out the material under the conditions of vacuum degree ≤ 2.7Pa and power of 300 ~ 600KW. After complete melting, the power is 600 ~800KW, refining temperature is 1520℃ for 30min; then reduce the power to 200~600KW, reduce the molten steel temperature to 1480℃, add Ti, Al, Nb, Ta, Zr, B for alloying and smelting to obtain molten steel, It is measured that molten steel satisfies C: 0.010%, Cr: 18.1%, Co: 10.0%, Mo: 2.60%, W: 8.2%, Al: 1.3%, Ti: 3.3%, Nb: 1.5%, Ta: 0.5%, B: 0.005%, Zr: 0.06%, the content of each element in the molten steel is within the index ra...
Embodiment 2
[0069] S1, vacuum induction smelting, using selected high-purity raw materials as alloy raw materials and mixing them according to the ratio of the above elements. It is necessary to ensure that the surface of the alloy raw materials is derusted, clean and free of oil, etc., and special attention should be paid to Si, Mn, Cu Substituting C into the upper limit; put Ni, Cr, Co, W, Mo, C into the induction furnace, and carry out the material under the conditions of vacuum degree ≤ 2.7Pa and power of 300 ~ 600KW. After complete melting, the power is 600 ~800KW, refining temperature 1540℃ for 45min; then reduce the power to 200~600KW, lower the molten steel temperature to 1500℃, add Ti, Al, Nb, Ta, Zr, B for alloying and smelting to obtain molten steel, The measured element content in molten steel satisfies C: 0.012%, Cr: 16.9%, Co: 9.6%, Mo: 2.50%, W: 7.9%, Al: 1.5%, Ti: 3.2%, Nb: 1.4%, Ta: 0.8 %, B: 0.006%, Zr: 0.05%, the content of each element in the molten steel is within the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com