Mixed fiber filament superfine fiber non-woven material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A non-woven material, microfiber technology, used in non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
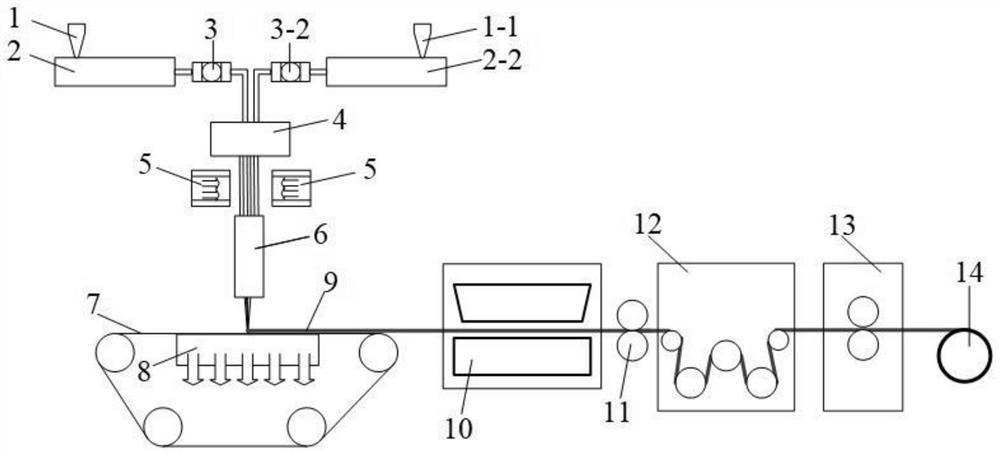
[0029] The invention provides a kind of preparation method of mixed filament superfine fiber nonwoven material, comprises the following steps:
[0030] (1) Polymer A is melted to obtain the first melt;
[0031] (2) Polymer B and polymer C are mixed and melted to obtain a second melt; the polymer B is different from polymer A and polymer C; the viscosity of the polymer B is lower than that of polymer C viscosity;
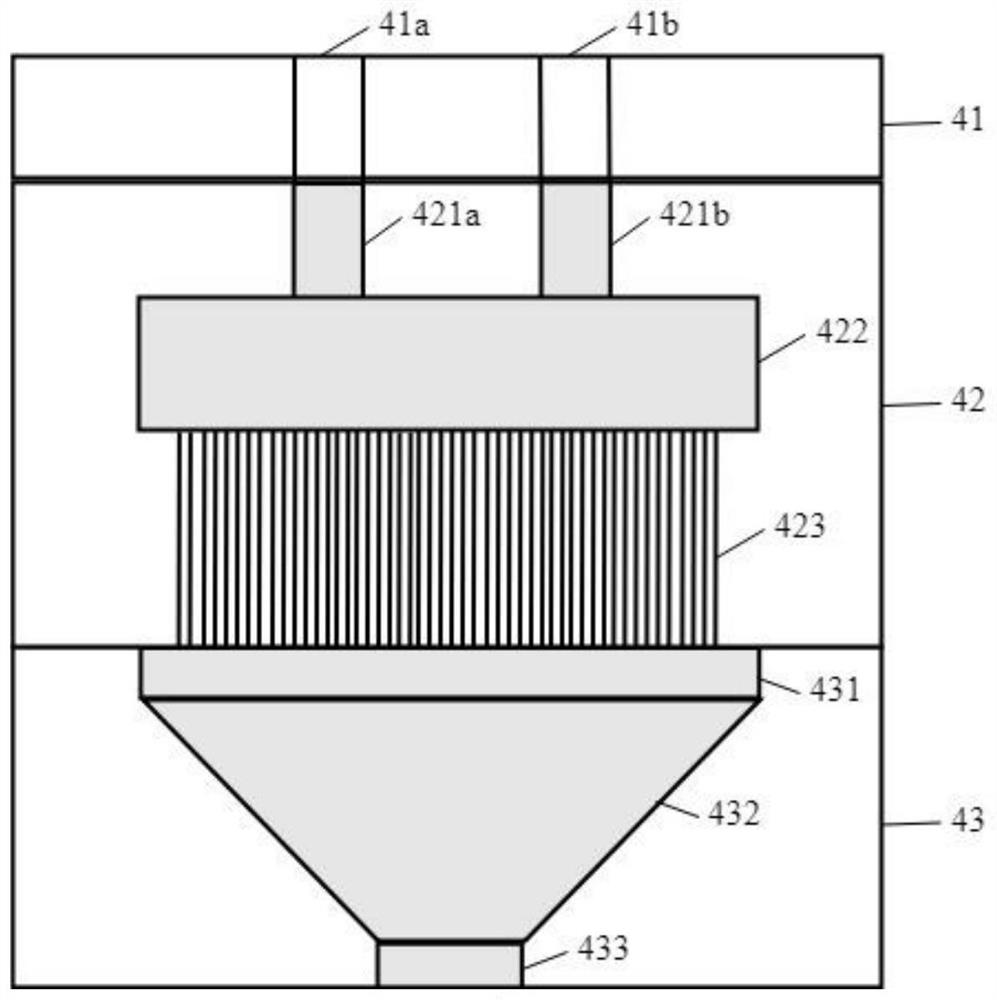
[0032] (3) the first melt obtained in the step (1) and the second melt obtained in the step (2) are respectively passed through the spinneret and composited into matrix fibril type composite filaments, and then formed into a web, Obtain matrix fibril type composite filament fiber network;
[0033] (4) The matrix fibril-type composite filament fiber web obtained in the step (3) is sequentially opened and consolidated to obtain a split-off composite fiber nonwoven material;
[0034] (5) The split-type composite fiber nonwoven material obtained in the step (4) is seq...
Embodiment 1
[0075] Mixed fiber filament superfine fiber nonwoven material, composed of polyethylene terephthalate fiber with orange segment shape and diameter of 3000-5000nm and polyethylene terephthalate fiber with round shape of cross-section and diameter of 100-1500nm Composed of polyamide 6 fibers.
[0076] Preparation Process:
[0077] (1) Add polyethylene terephthalate to a single-screw extruder through a hopper for segmental melting to obtain a first melt; wherein, the temperature of segmental melting is 295° C.;
[0078] (2) After mixing low-density polyethylene and polyamide 6 in a mass ratio of 7:3, they are added to a twin-screw extruder through another hopper for segmental melting to obtain a second melt; wherein, the segmental melting The temperature is 270 ° C; the viscosity difference between low-density polyethylene and polyamide 6 is 2.05 Pa s; the apparent viscosity ratio of polyethylene terephthalate and low-density polyethylene is 1.0;
[0079] (3) The first melt tha...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Mixed fiber filament superfine fiber nonwoven material, composed of polyethylene terephthalate fiber with orange segment shape and diameter of 3000-5000nm and polyethylene terephthalate fiber with round shape of cross-section and diameter of 100-1500nm Polyamide 6 fiber composition;
[0085] The difference from Example 1 is that the low-density polyethylene is replaced by cellulose acetate butyrate.
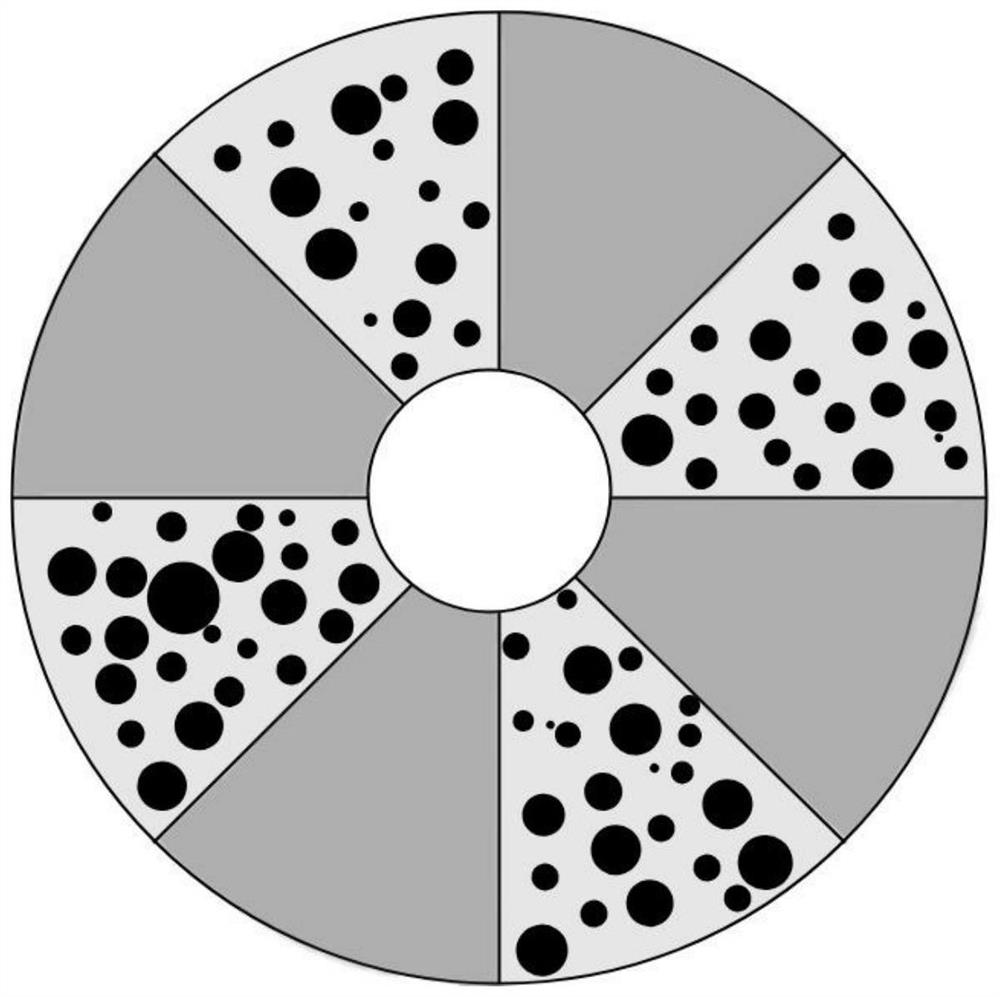
[0086] Figure 4 SEM image of the cross-section of the mixed filament superfine fiber nonwoven material prepared for this example. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the pie-shaped fibers are uniformly mixed with the round fibers to form a mixed filament ultrafine fiber nonwoven material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com