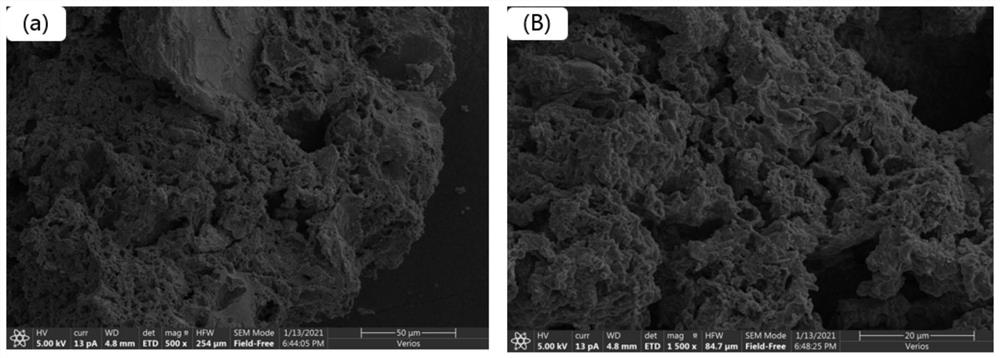
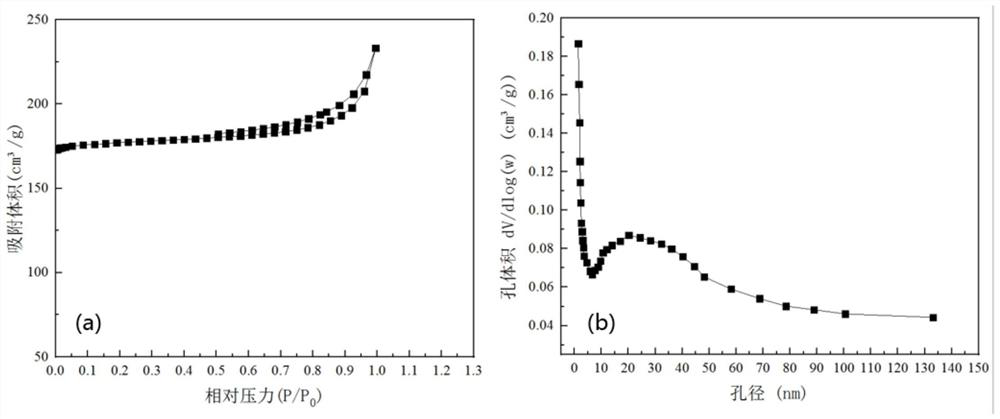
Method for preparing activated carbon by using betel nuts and sludge as materials
A technology for preparing activated carbon and sludge, applied in the field of activated carbon, can solve the problems of poor performance, low yield and insufficient adsorption capacity, and achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption, high yield and strong iodine adsorption capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1 betel nut sludge activated carbon preparation
[0038] 1.1 Experimental equipment and chemicals
[0039] ZnCl 2 、H 3 PO 4 , sodium thiosulfate, iodine, potassium iodide, hydrochloric acid and other reagents are all chemically pure; activated sludge, betel nut (local direct sampling).
[0040] Electric blast drying oven, tube furnace, crucible, electronic precision balance, nitrogen cylinder, glass instrument, etc.
[0041] 1.2 Preparation of activated carbon
[0042] S1. Raw material preparation: wash the whole betel nut fruit with water to remove surface dirt, mix and dry the betel nut and sludge according to the mass ratio of 1:1 until the moisture content is 10%-20%, and the drying temperature is 105°C ±5°C; crush the dried product and pass through a 100-200 mesh sieve to obtain mixed particles of betel nut and sludge;
[0043]S2. High-temperature carbonization process: place the mixed particles of betel nut and sludge obtained in step S1 in a tube...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2-activation temperature research
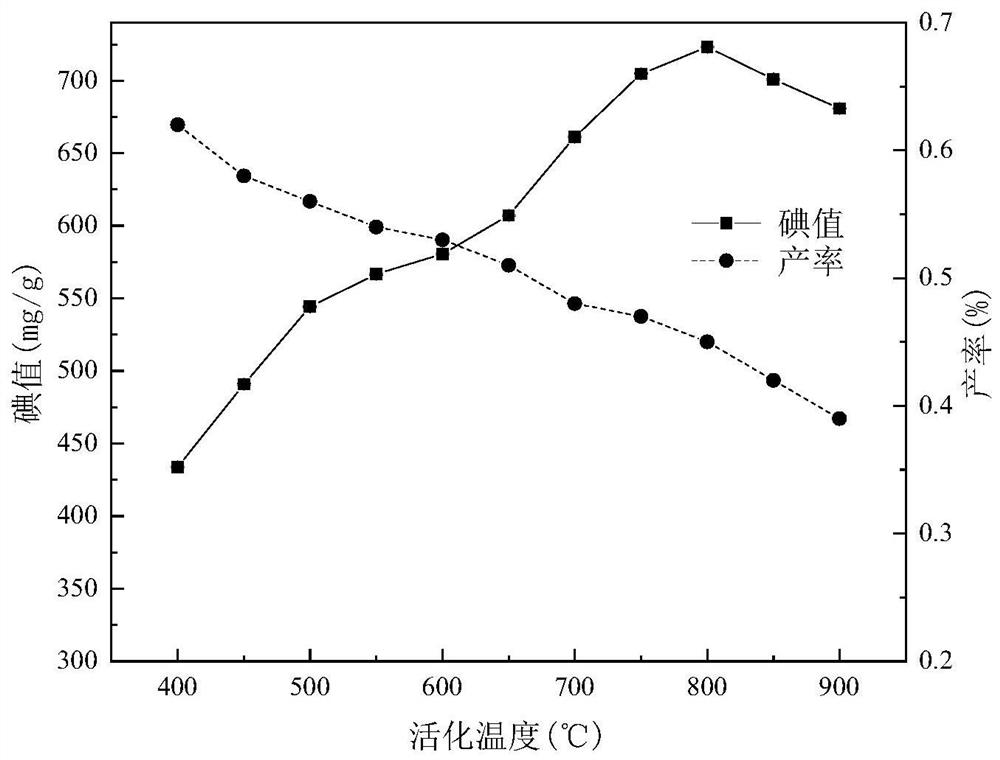
[0060] The activation process mainly includes the contact between the activator and the carbonized product and the change process of the pore structure after carbonization. Activation temperature is a key factor in the preparation of high-performance activated carbon. On the basis of Example 1, the activation temperature is adjusted to be 400°C, 500°C, 600°C, 700°C, 800°C, and 900°C respectively, and the iodine value and productive rate under different activation temperatures are as follows: image 3 shown.
[0061] Such as image 3 As shown, the iodine value increases rapidly with the activation temperature from 400 °C to 800 °C, but when the temperature exceeds 800 °C, the iodine value decreases. This may be due to the increased diffusion of activated molecules into the interior of the carbonized product at higher temperatures; thus, more carbons undergo activation reactions with phosphoric acid and hydrogen chloride, ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 - Activation Time Study
[0063] On the basis of Example 1, the activation time was adjusted to be 30-120 minutes respectively.
[0064] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the iodine value of AC increased sharply from 545.69 mg / g to 634.72 mg / g before 60 minutes, and then decreased from 634.72 mg / g to 493.99 mg / g. A better iodine value of 634.72 mg / g was exhibited with a yield of 51% as the carbonized precursor was obtained at 600°C for 60 minutes. The reason may be that the shorter the activation time, the incomplete activation, and the lower the adsorption capacity; the highly developed pore structure needs enough time to stimulate micropore corrosion to meet the adsorption demand; and the prolonged activation time has a negative impact on the formation of pores, It even causes adjacent micropores to expand into pores. With the activation time ranging from 30 min to 120 min, a continuous decrease in yield could be observed, which may be due to further decomposit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com