Method for high-value utilization of PTA residue high-concentration bromine-containing wastewater
A high-value waste water technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, copper halides, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of difficult waste water treatment, high post-processing difficulty, and a large number of equipment, so as to realize high-value resource utilization Utilize, realize the process of resource utilization, and improve the effect of economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
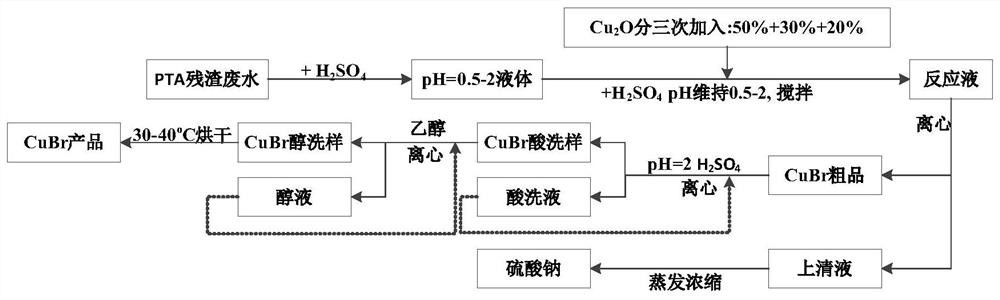
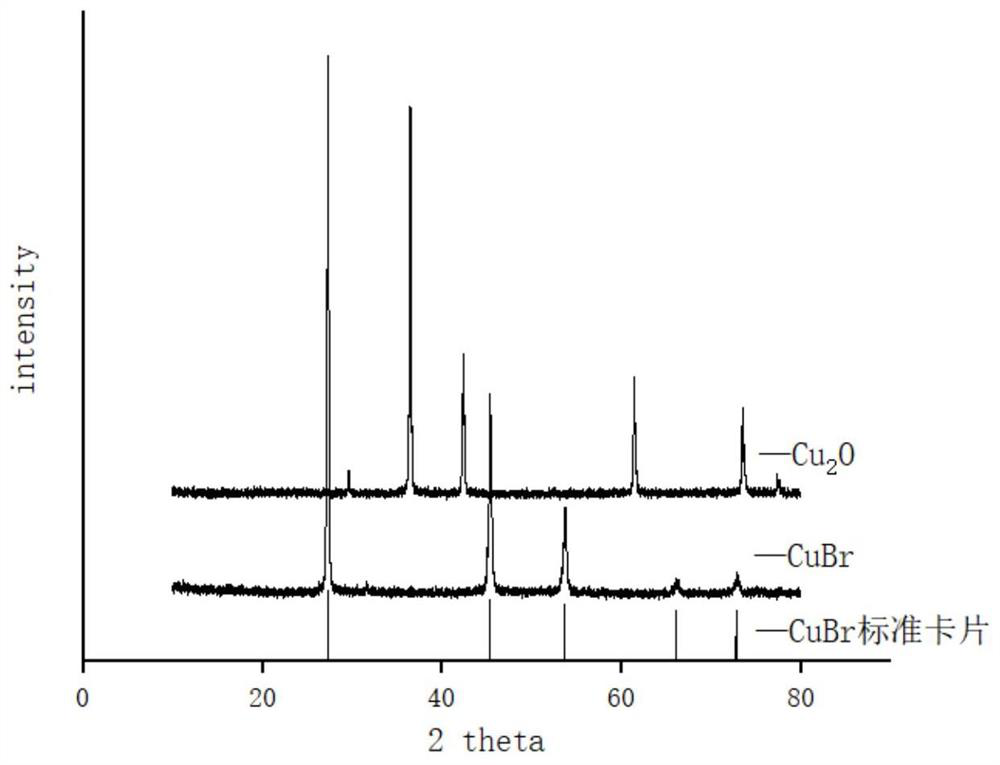
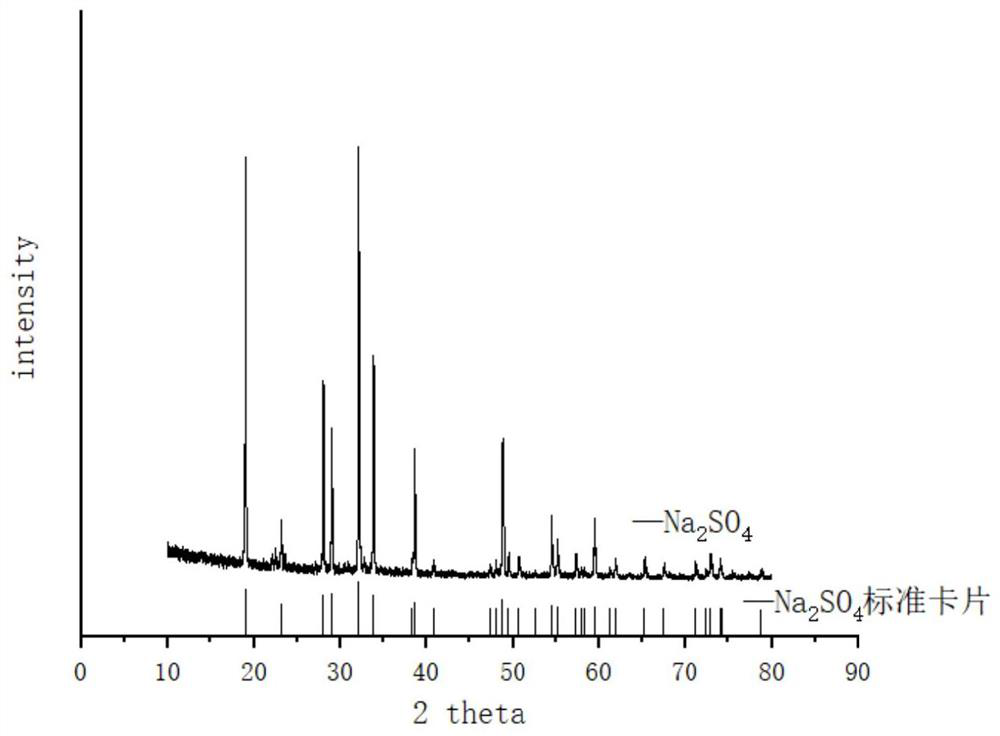
[0054] First, add a sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 2mol / L to adjust the pH of the PTA residue wastewater to 0.5, 1, 1.2, 1.5, and 2 respectively. At the same time, add an appropriate amount of distilled water to prepare the bromide ion concentration of PTA to 50g / L, and add cuprous oxide in batches. (adding in three times, 50wt% for the first time, 30wt% for the second time, 20wt% for the third time, each interval of 1min), the total copper oxide addition is based on NaBr and Cu 2 The molar ratio of O is calculated as 1:0.5. Under anaerobic conditions (nitrogen protection), 2mol / L sulfuric acid solution is continuously added to maintain its pH stability, and the stirring speed is 400r / min. Copper, centrifuged to obtain crude cuprous bromide, add a certain volume of sulfuric acid solution with pH = 2 to wash the solid phase crude product, centrifuge, repeat the operation once to obtain acid-washed cuprous bromide, then add a certain volume of absolute ethanol to ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The operating steps are the same as in Example 1, and the selected pH is 1.2 at this time, changing NaBr: Cu 2 The O molar ratios were 1:0.45 and 1:0.55, respectively, and the results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen that different additions of cuprous oxide have a certain influence on the bromine removal rate, but the influence is not significant. But when NaBr:Cu 2 When O=1:0.55, the removal rate of bromine and product yield are the best.
[0062] Table 2. Effect of molar ratio on debromine effect
[0063] NaBr:Cu 2 o
[0064] Reaction conditions: Br - (50g / L), pH=1.2, room temperature, 5min, stirring speed 400r / min.
Embodiment 3
[0066] The operating steps are the same as in Example 1, and the selected pH is 1.2 at this time, changing NaBr: Cu 2 The O molar ratio was 1:0.55, and the reaction times were 3, 10, and 20 min, respectively. The results are shown in Table 3. It can be seen that increasing the reaction time can improve the bromine removal rate, but the improvement effect is very limited, and a good bromine removal effect can be obtained within 3 to 20 minutes, but the time is too short or too long to reduce the purity of the product.
[0067] The influence of table 3 stirring time on debromine effect
[0068] T / min 3 5 10 20 Bromine removal rate 95.1% 97.1% 97.5% 98.1% CuBr yield 91.4% 92.6% 92.8% 93.5% CuBr purity 93.2% 95.8% 95.3% 90.2% Na 2 SO 4 purity
[0069] Reaction conditions: Br - (50g / L), pH value=1.2, molar ratio NaBr: Cu 2 O=1:0.55, room temperature, stirring speed 400r / min.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com