RPA primer, probe, kit and method for detecting enterocytozoon hepatopenaei
A technology of Enteroplasma hepatica and kit, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of high false positive of LAMP, inability to quantify Enteroplasma hepatica, difficulty in primer design, etc. Achieve the effects of good detection repeatability, suitable for popularization and use, and improve specificity and sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
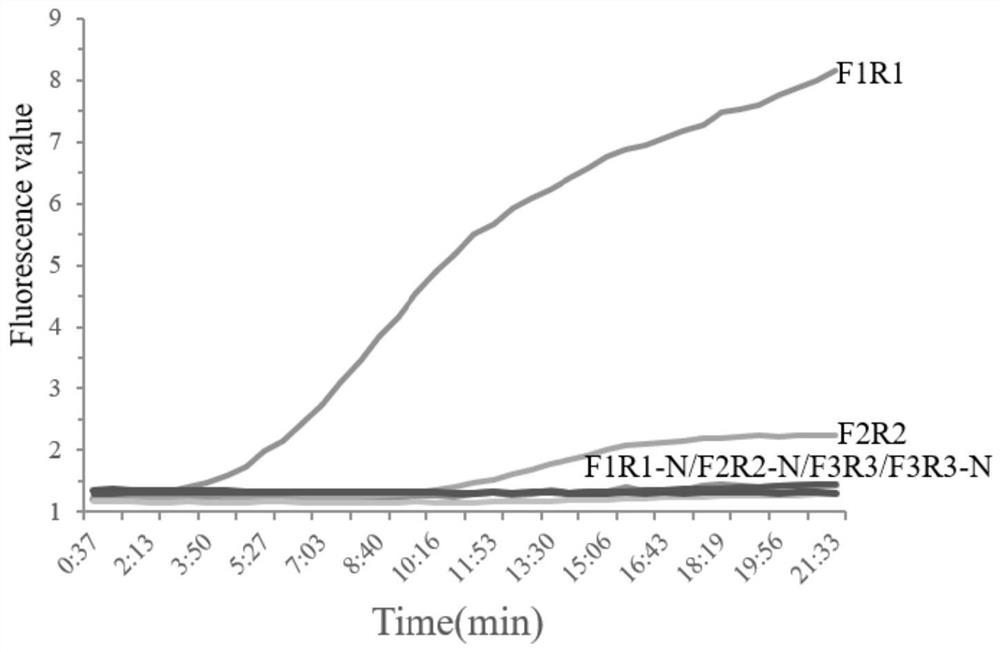
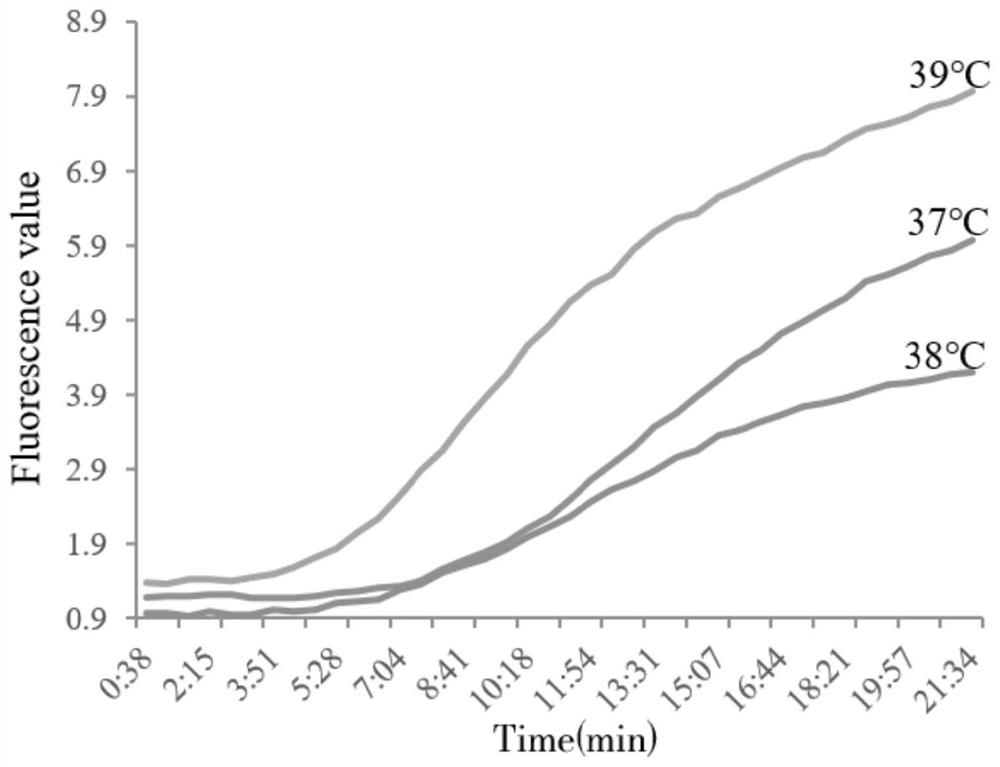
[0037] Example 1 Construction and optimization of Real-time RPA reaction system
[0038] The present invention takes enteroplasma hepatica (EHP) cell wall protein SWP gene (spore wall protein gene) as the target gene, and the accession number of the target gene is KX258197.1.
[0039]1. Firstly, according to the gene sequence of the Enterocystis hepatopenaei (EHP) in Environmental Samples in Shrimp published in GeneBank, references (JaroenlakP, Sanguanrut P, Williams B, et al. 2 pairs of PCR amplification primers in Farms[J].Plos One,2016,11(11):e0166320.) were used to amplify and sequence the gene of SWP by PCR. The primers were synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd.
[0040] The sequences of the 2 pairs of PCR amplification primers are as follows:
[0041] swp-514-F: TTGCAGAGTGTTGTTAAGGGTTT
[0042] swp-514-R: CACGATGTGTCTTTGCAATTTTC
[0043] swp-148-F: TTGGCGGCACAATTCTCAAACA
[0044] swp-148-R: GCTGTTTGTCTCCAACTGTATTTGA
[0045] 2. Genomic DNA extraction
...
Embodiment 2
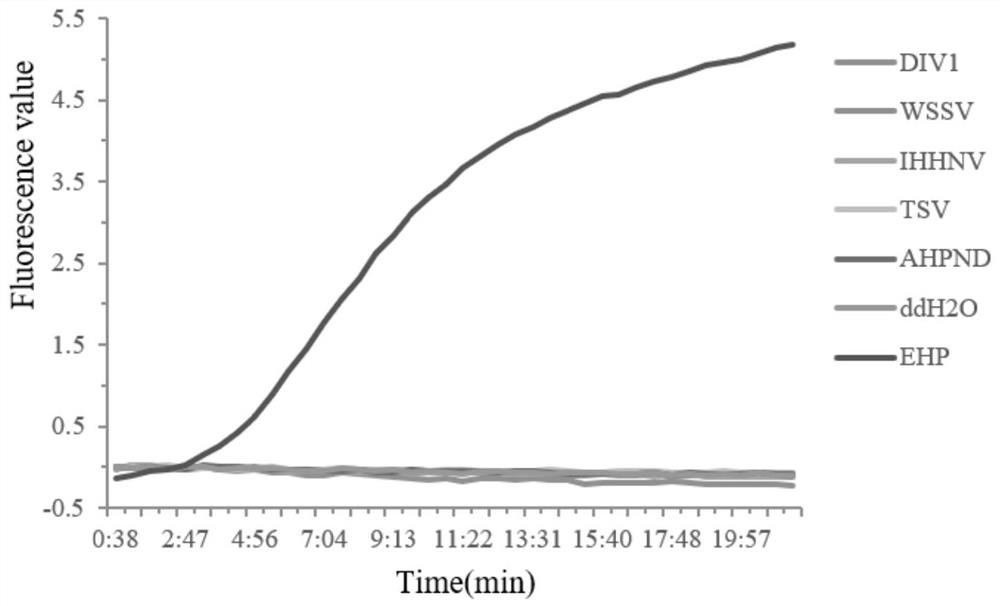
[0069] Embodiment 2 specificity test
[0070] In order to detect the specificity of the Real-time RPA detection method, the present invention selects several common shrimp pathogenic genomic DNAs, including white spot syndrome virus (White Spot Syndrome Virus, WSSV), taura disease virus (TauraSyndrome Virus, TSV), infection Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV), Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) and Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND).
[0071] The DNA of various genomes was diluted to 10 ng / μL, and the reaction system and temperature were the same as in Example 1 to verify the specificity of the optimized Real-time RPA detection method. Specific test results such as image 3 As shown, the results showed that except for the positive amplification curve of EHP, no amplification curve appeared for other pathogens, and no amplification curve appeared for the water-added control group, indicating that the constructed Real-time RPA detection me...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Embodiment 3 sensitivity test
[0073] The positive control plasmid constructed in Example 1 was used ddH 2 O was diluted sequentially, and the dilution concentration was 10 8 copies / μL, 10 7 copies / μL, 10 6 copies / μL, 10 5 copies / μL, 10 4 copies / μL, 10 3 copies / μL, 10 2 copies / μL, 10 1 copies / μL, 10 0 copies / μL total of 9 concentration gradients. Take 0.8 μL template DNA of different concentrations for Real-time RPA and Nested PCR detection respectively, test the sensitivity difference by different methods, and use ddH 2 O is the control. The reaction system and reaction conditions of Real-time RPA are the same as in Example 1.
[0074] The present invention quotes the primer sequences reported in the literature as the control of the constructed Real-time RPA method. The amplification primers of Nest PCR are respectively swp-514-F / R and swp-148-F / R, and the specific sequences are referred to in Example 1, wherein swp-514-F / R is an amplification primer, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com