Method and application of green solvent for preparing airgel-like environmental functional materials
A technology of functional materials and green solvents, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable application of powder particles, low production efficiency, and inability to degrade, so as to promote Application and upgrade, low crystallinity, easy to scale up effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method for preparing an airgel-like environmental functional material by a green solvent, comprising the following preparation steps:
[0038] Step 1. Recycle the discarded corn stalks in the crops, and after natural air drying, remove the leaves, outer skin and stem nodes of the corn stalks to obtain corn pith, and cut the corn pith to a length of 1 cm for later use;
[0039] Step 2: Weigh 56g of choline chloride and 36g of organic carboxylic acid and put them in the same beaker, the organic carboxylic acid is oxalic acid, put it in an oven at 120°C, melt the reagent in the beaker completely, and then take out the beaker Cool the molten reagent to obtain a deep eutectic solvent, add 270 g of distilled water to the beaker, stir with a glass rod, and make it fully mixed to obtain a mixed solution;
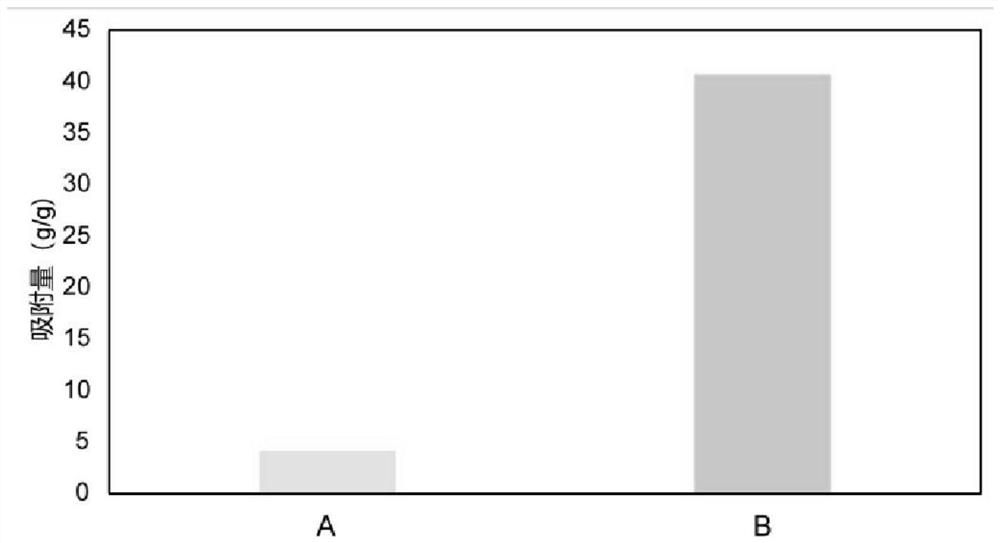
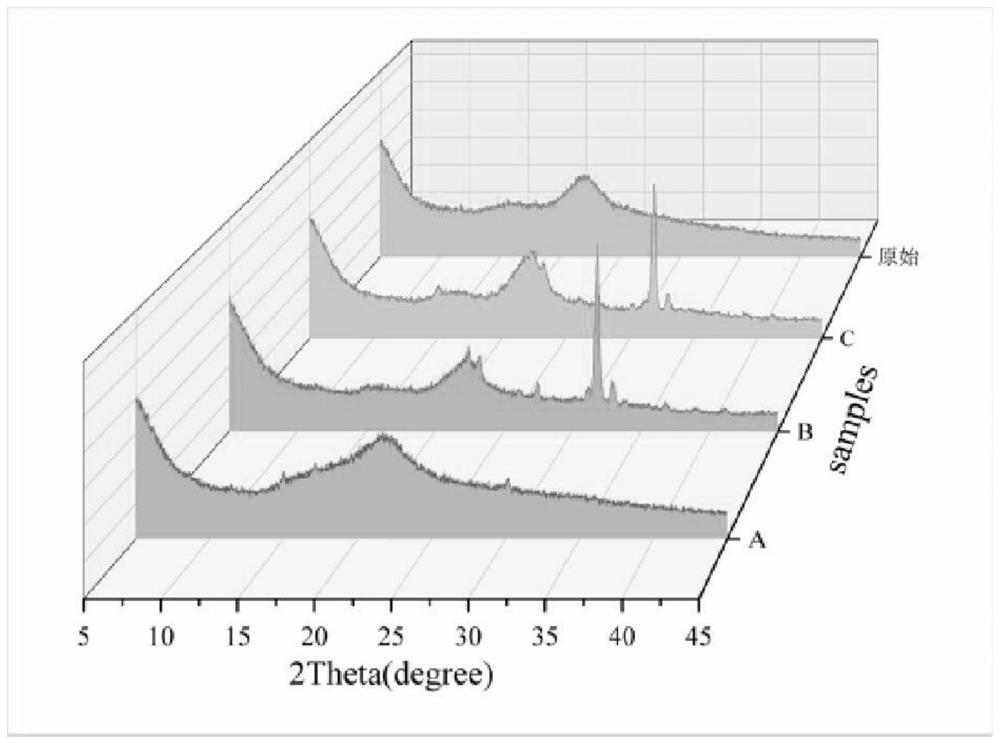
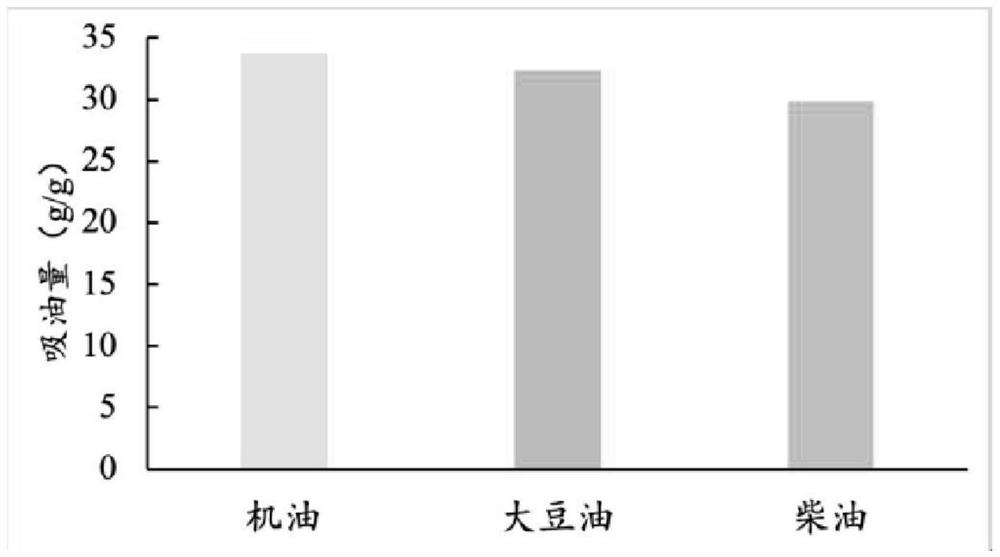
[0040] Step 3. Take 100mL of the mixed solution, add three pieces of corn pith treated in step 1, and react in a water bath at 100°C for 2 hours, then take out the corn pit...
Embodiment 2
[0047]A method for preparing an airgel-like environmental functional material with a green solvent. The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is that in step 3, corn pith is reacted in a water bath at 60°C. Other preparations of the preparation method of Example 2 Step is identical with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0049] A method for preparing an airgel-like environmental functional material with a green solvent. The difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is that in step 3, the corn pith is reacted in a water bath at 70°C. Other preparations of the preparation method of Example 3 Step is identical with embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com