A hydrogen shaft furnace ironmaking system and method using electric energy heating
A hydrogen and shaft furnace technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of insufficient hydrogen shaft furnace, insufficient physical energy, power consumption and heat loss, etc., and achieve the effects of saving equipment operating costs, improving energy utilization, and reducing process energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
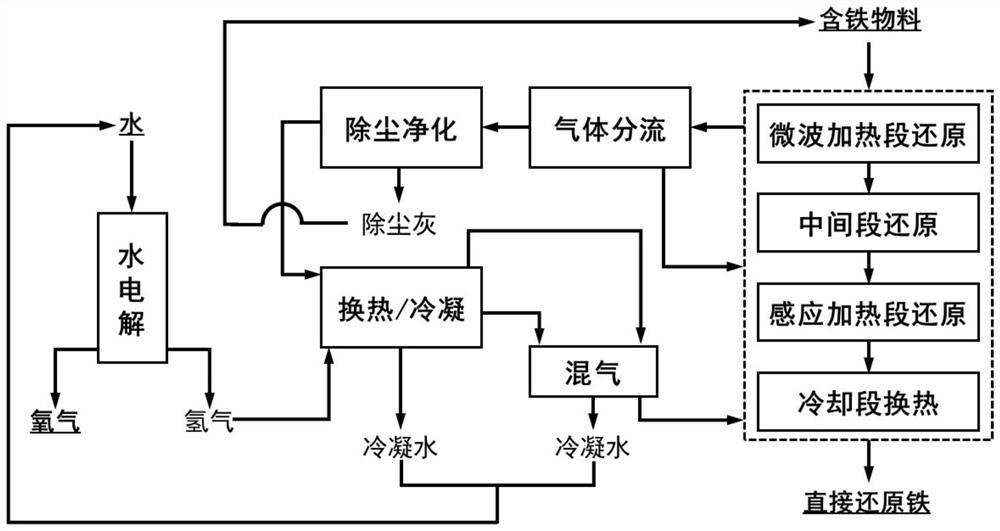
[0066] The structure of the hydrogen shaft furnace ironmaking system heated by electric energy is as follows: figure 1 As shown, it includes water electrolyzer 1, hydrogen storage tank 3, electric energy heating hydrogen shaft furnace 4, heat exchanger 7, gas mixing tank 8;
[0067]The cover of the furnace body of the electric energy heating hydrogen shaft furnace 4 is provided with a feed port to communicate with the feeder 401, and the feed port of the feeder 401 is communicated with the discharge port of the feed bin; the bottom of the cover of the furnace body is successively Microwave heating section I, middle section II, induction heating section III, cooling section IV and screw discharger 407, tail gas outlet 402 is provided on the head, microwave radiation source 403 is installed on the side wall of microwave heating section I, middle section The side wall of II is provided with an air inlet pipe 404, and the side wall of the furnace body inside the air inlet pipe 404...
Embodiment 2
[0091] The structure of the hydrogen shaft furnace ironmaking system using electric energy heating is the same as in Example 1;
[0092] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0093] (1) The iron-containing material A is a pellet material with a particle size of 9 mm;
[0094] (2) Control the temperature in microwave heating section I to 700°C, and the temperature in induction heating section III to 880°C;
[0095] (3) control split tail gas to account for 20% of the total volume of tail gas;
[0096] (4) The metallization ratio of direct reduced iron F is 98.4%.
Embodiment 3
[0098] The structure of the hydrogen shaft furnace ironmaking system using electric energy heating is the same as in Example 1;
[0099] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0100] (1) The iron-containing material A is a pellet material with a particle size of 10mm;
[0101] (2) Control the temperature in microwave heating section I to 800°C, and the temperature in induction heating section III to 920°C;
[0102] (3) control split tail gas to account for 30% of the total volume of tail gas;
[0103] (4) The metallization ratio of direct reduced iron F is 98.5%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com