Genetically modified microorganism and method for producing target substance using same
A microorganism and transgenic technology, applied in the field of modified phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity, can solve the problems such as no aspartate conversion efficiency or reaction speed, no record of aspartate dehydrogenase, etc., Achieving the effect of increasing productivity, cutting costs, and improving conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
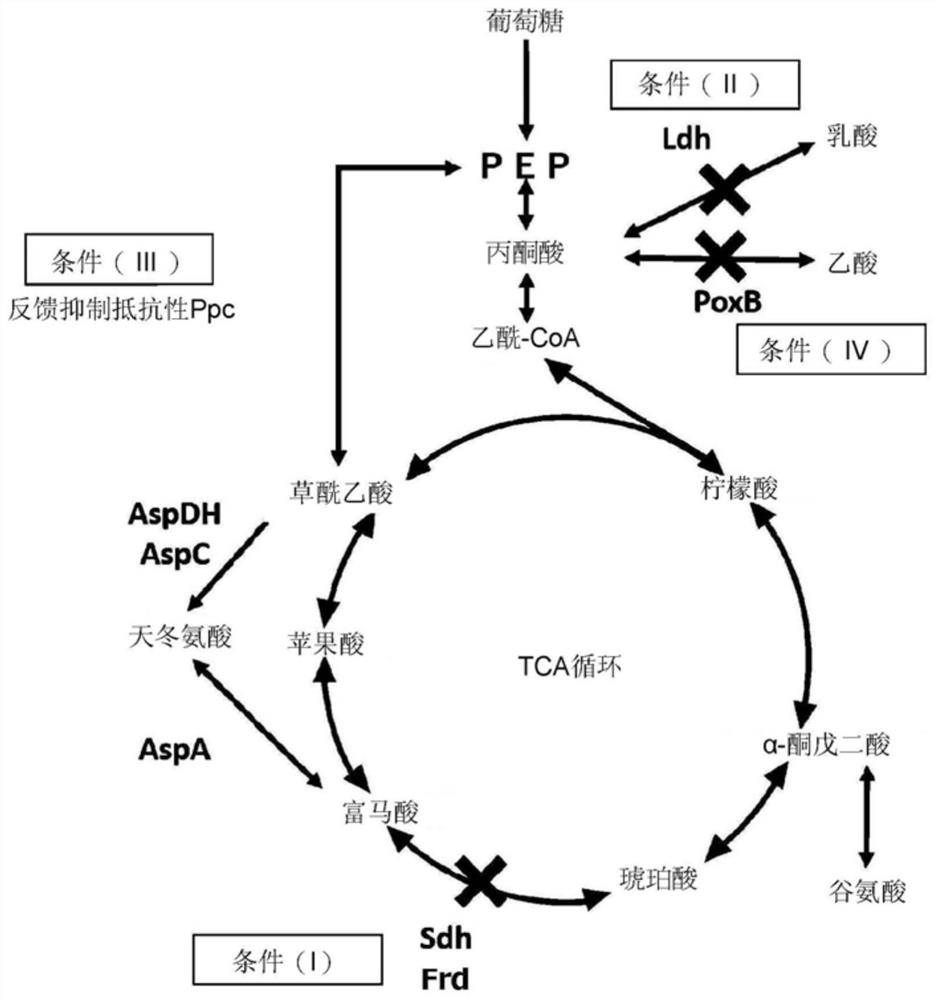
[0141] According to the first embodiment of the present invention, the following transgenic microorganisms are provided.
[0142] A genetically modified microorganism that satisfies at least one of the following conditions (I), condition (II) and condition (IV), and meets the following condition (III):
[0143] Condition (I) Compared with the corresponding wild-type microorganism of the transgenic microorganism, succinate dehydrogenase activity or fumarate reductase activity is reduced or inactivated;
[0144] Condition (II) Compared with the wild-type microorganism, the lactate dehydrogenase activity is reduced or inactivated;
[0145] Condition (III) has modified phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity or exogenous phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity, and the modified phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity is relative to wild-type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity Resistance to feedback inhibition by aspartic acid in pyruvate carboxylase activity that exhibit...
Embodiment approach
[0147] Furthermore, according to the second embodiment of the present invention, the following genetically modified microorganisms are also provided.
[0148] A genetically modified microorganism that satisfies all of the following conditions (I) to (III):
[0149] Condition (I) Compared with the corresponding wild-type microorganism of the transgenic microorganism, succinate dehydrogenase activity or fumarate reductase activity is reduced or inactivated;
[0150] Condition (II) Compared with the wild-type microorganism, the lactate dehydrogenase activity is reduced or inactivated;
[0151] Condition (III) has modified phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity or exogenous phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity, and the modified phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity is relative to wild-type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity Resistance to feedback inhibition by aspartic acid in pyruvate carboxylase activity that exhibits resistance to exogenous phosphoenolpyruvate c...
Embodiment
[0431]
[0432] Using the Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 strain as the starting material, a recombinant phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene was produced in which the specified enzyme activity was inactivated by gene disruption and a mutated phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene with specified amino acid substitutions was introduced. Coryneform bacteria. The flow thereof is shown below.
[0433] (1) Preparation of gene deletion strain (Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032ΔldhΔsdhΔpoxB strain)
[0434] First, the SacB gene fragment was amplified by PCR using the plasmid pNIC-Bsa4 (Source BioScience) as a template and using the primer pairs shown in Table 12 below.
[0435] [Table 12]
[0436]
[0437] Use BamHI and HindIII to treat the amplified DNA fragment and plasmid pHSG299 (TakaraBio Co., Ltd.) with restriction enzymes, and then use the second edition (Ver.2) of the DNA Ligation Kit (DNA Ligation Kit) (Takara Bio Co., Ltd.) to obtain plasmid pGE015.
[043...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com