Methods of decreasing dysbiosis and restoring a microbiome
A technology for dysbacteriosis and microorganisms, which can be used in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, antibacterial drugs, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1A
[0494] Example 1A: Phase 1 Dose Escalation Study of Composition VE303 in Healthy Volunteers
[0495] Clostridium difficile infection is associated with alterations in the gastrointestinal microbiota. A commonly used therapy for C. difficile infection, such as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), can prevent recurrent C. difficile infection (rCDI), but has limitations to routine use and unforeseen risks.
[0496] Composition VE303 is a rationally defined bacterial composition comprising the bacterial strains shown in Table 1, which have been found to inhibit the growth of C. difficile in vitro and to improve survival in models of C. difficile infection (CDI).
[0497] method
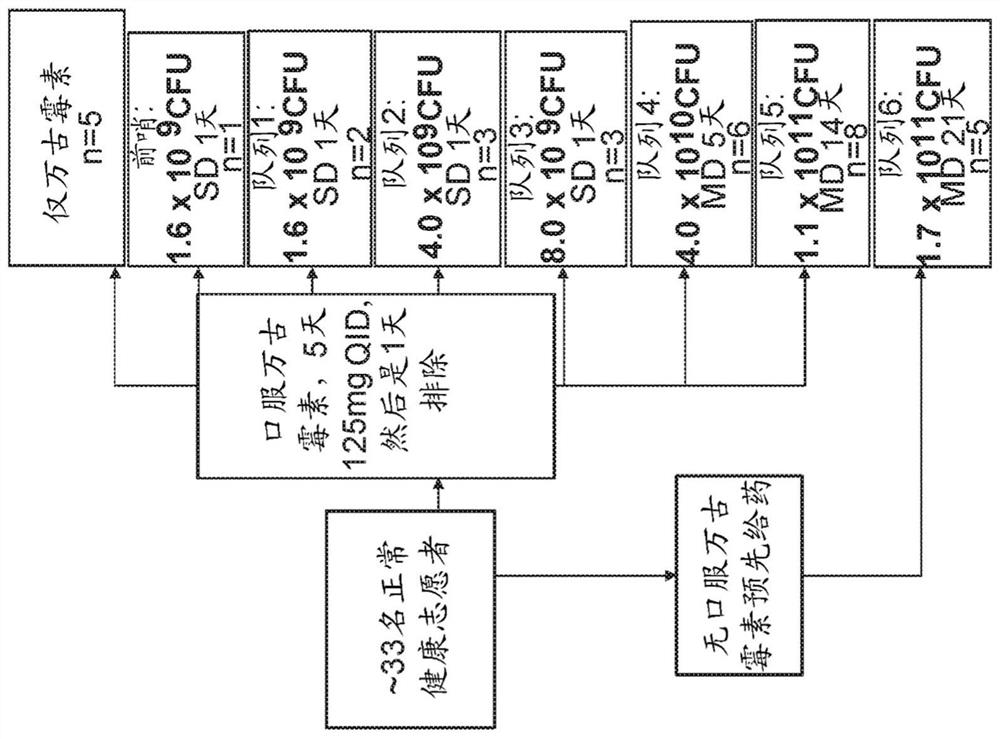
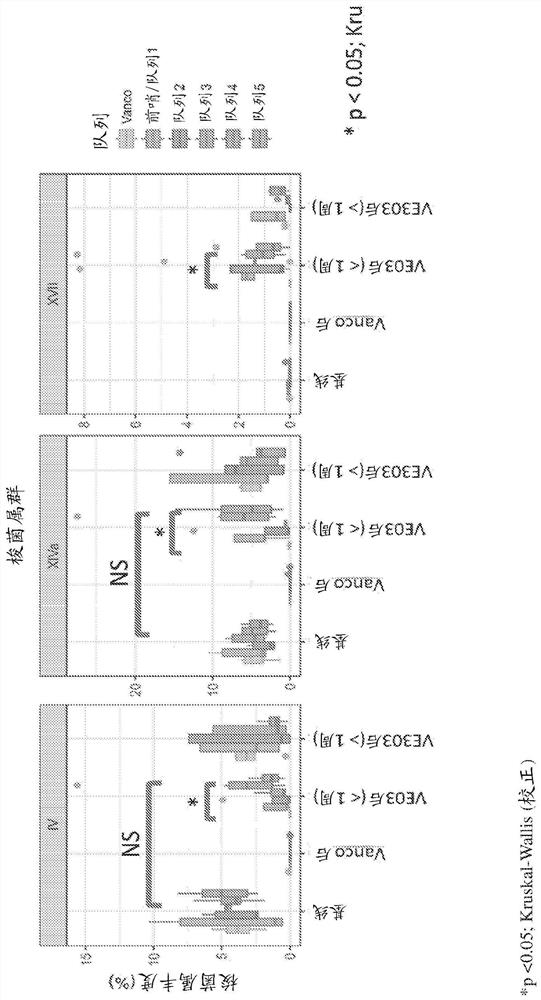
[0498] A Phase 1 dose escalation study was conducted to evaluate the safety and tolerability of Composition VE303 in healthy volunteers (HV) following vancomycin-induced dysbiosis. like figure 1 and Figure 20 As shown in , HVs were divided into seven cohorts and a vancomycin control group. Pharma...
Embodiment 1B
[0513] Example IB: Phase 1 Study of Composition VE303 in Healthy Volunteers: Cohorts 7-9
[0514] Another Phase 1 study was conducted to evaluate the safety and tolerability of the composition VE303 in healthy volunteers (HV) following vancomycin-induced dysbiosis. As shown in Table 1B, HVs were divided into three cohorts that received different doses of vancomycin before receiving the same dose of VE303. Pharmacokinetics (including colonization and persistence of strains) and pharmacodynamics (eg, recovery of resident microbiota) were assessed by metagenomic sequencing of longitudinally collected fecal bacteria.
[0515] Table 1B: Dosing Regimen for Phase 1 Cohorts 7-9
[0516]
Embodiment 1C
[0517] Example 1C: Rationally defined consortia of human bacterial strains for rCDI
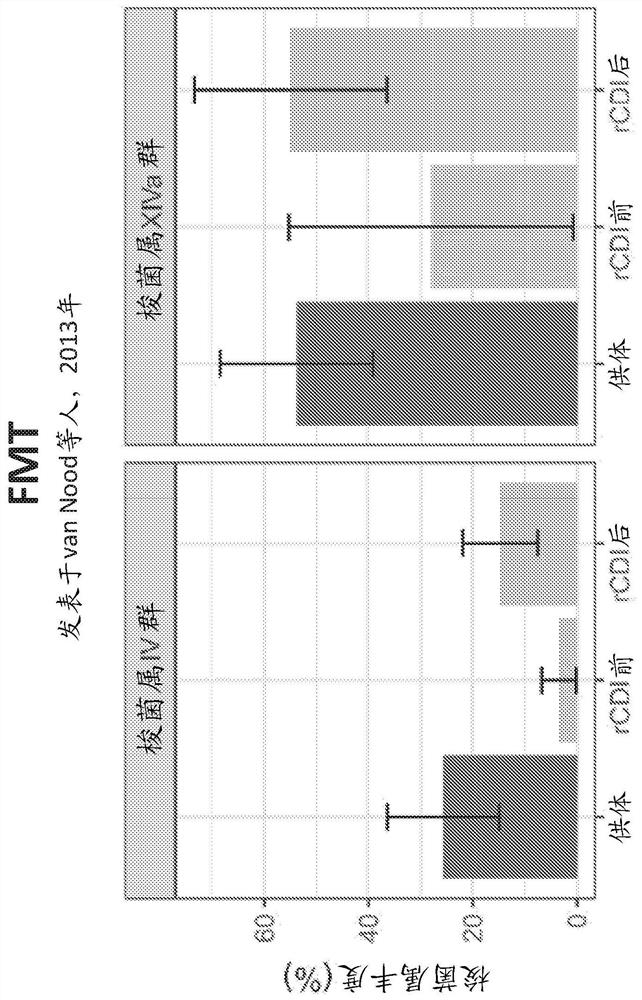
[0518] In collaboration with Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC) and the Netherlands Donor Stool Bank (NDFB), stool samples were collected from healthy donor volunteers and patients with recurrent Clostridium difficile infection (rCDI). Abundance in fecal samples of major bacterial genera associated with recovery from rCDI was analyzed before and after fecal microbiota transplantation (pre-FMT, post-FMT) ( Figure 13A ). Response to fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) in rCDI patients is associated with transfer of Clostridium IV and XIVa bacteria.
[0519] Mice were infected with Clostridium difficile (CDI) and administered VE303 or human FMT. About 85% of mice treated with VE303 and about 80% of mice treated with human FMT survived for at least 7 days after CDI. In contrast, approximately 30% of mice treated with PBS and approximately 20% of mice treated with a negative live bioth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com