Method for producing heterologous cannabichromenol using Saccharomyces cerevisiae
A technology of cannabinoid phenolic acid and recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in the fields of biotechnology and medicine, can solve the problems of high cost, complicated preparation methods of cannabinol and cannabinoid phenolic acid, low yield and the like, and achieves low cost , The method is accurate and efficient, and the genetic performance is stable.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
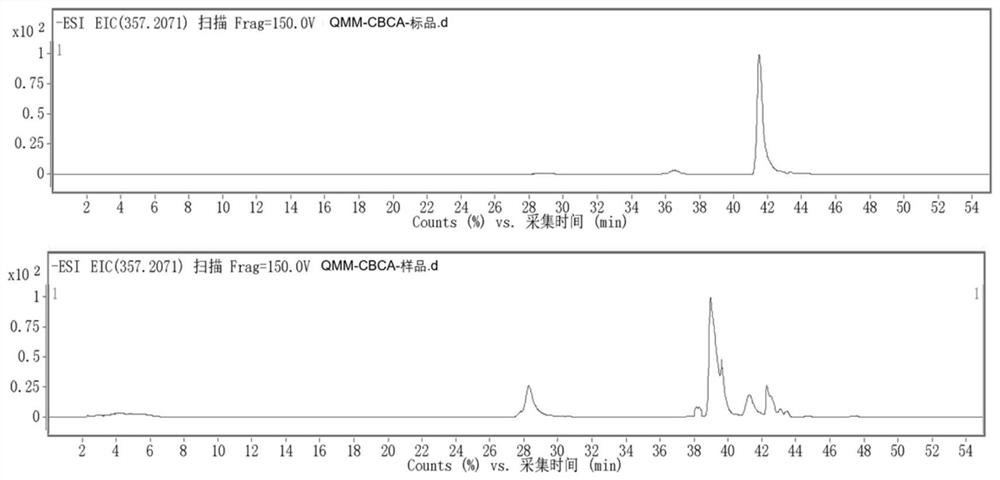
[0054] Construction of recombinant yeast strains capable of expressing cannabigeroid acid synthase and cannabichromene phenolic acid synthase
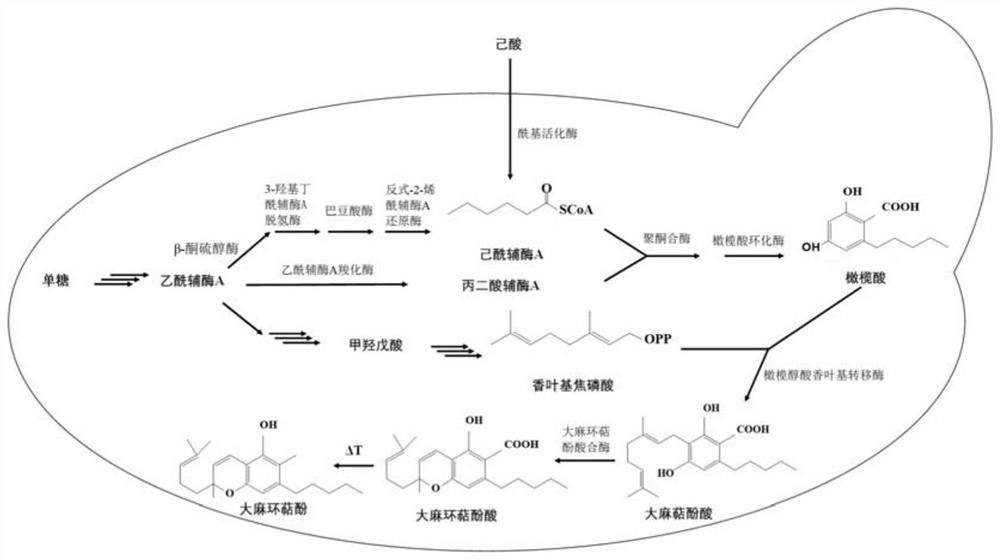
[0055] The host bacterium of the present invention is Saccharomyces cerevisiae INVSc1, and the diploid INVSc1 has high robustness, and its complex gene regulation network is beneficial to the expression and catalysis of enzymes under unfavorable environmental conditions. The present invention is based on the discovery that geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) and olivolic acid (OA) generate cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) under the action of cannabinoid acid synthase (CsPT4), and cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is passed through cannabinoid Terpene phenol synthase (CBCAS) catalyzes the formation of cannabichromene phenolic acid (CBCA), and constructs two gene expression cassettes: the codon-optimized CsPT4 gene expression cassette and the codon-optimized CBCAS gene expression cassette, and the CsPT4 gene expression cassette uses GAL10 promoter and CYC1 t...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Construction of Recombinant Yeast Strain Capable of Utilizing Sugars to Produce Cannabichromenic Acids
[0058] In order to enable the biosynthesis of olivolic acid in the recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae of Example 1, a biosynthetic pathway for olivetolic acid generation by using sugars through hexanoyl-CoA was constructed in the above-mentioned recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Six codon-optimized gene expression cassettes were constructed: RebktB gene expression cassette, CnpaaH1 gene expression cassette, Cacrt gene expression cassette, Tdter gene expression cassette, CsTKS gene expression cassette and CsOAC gene expression cassette. RebktB gene expression cassette uses TEF1 promoter and TEF1 terminator, CnpaaH1 gene expression cassette uses GAL10 promoter and CYC1 terminator, Cacrt gene expression cassette uses GAL1 promoter and ADH1 terminator, Tdter gene expression cassette uses PGK1 promoter and HXT7 terminator CsTKS gene expression cassette uses GAL10 pr...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Construction of biosynthetic pathway from hexanoic acid to olivolic acid in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0061] In order to increase the flux of hexanoyl-CoA in the recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae of Example 2, construct the biosynthetic pathway from hexanoic acid to olivolic acid in the recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and construct two gene expression cassettes: the codon-optimized CsAAE1 gene expression cassette and ACC1 gene expression cassette, both CsAAE1 and ACC1 gene expression cassettes use the GPD promoter and CYC1 terminator, and through gene editing technology, the ACC1 gene expression cassette is integrated into the Saccharomyces cerevisiae X3 genomic locus, and one copy of the above gene is overexpressed; CsAAE1 The gene expression cassettes were integrated into Saccharomyces cerevisiae 208a, 911b and 106a genome sites to express 3 copies of the above-mentioned genes, and by supplying hexanoic acid, hexanoic acid was converted into hexan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com