Method for simultaneously improving coercive force and corrosion resistance of sintered NdFeB
A technology of coercive force and corrosion resistance, which is applied in the field of surface engineering of sintered NdFeB magnetic materials, can solve the problem that the coercive force and corrosion resistance of sintered NdFeB cannot be improved at the same time, so as to improve corrosion resistance, avoid failure, Effect of improving coercive force and corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] A method for simultaneously improving the coercivity and corrosion resistance of sintered NdFeB, comprising the following steps:
[0048] (1) pre-coating treatment;
[0049] (2) Glow plasma cleaning;
[0050] (3) grain boundary diffusion layer - heavy rare earth coating deposition;
[0051] (4) Barrier layer - high entropy alloy nitride coating deposition;
[0052] (5) Corrosion-resistant layer - high-entropy alloy coating deposition;
[0053] (6) Vacuum heat treatment;
[0054] (7) Wait for the sample to cool down to room temperature.
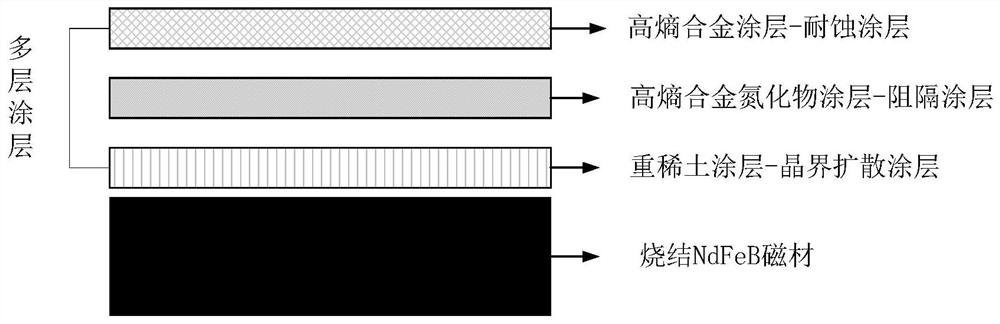
[0055] The method uses magnetron sputtering to prepare a new type of multilayer coating on the surface of sintered NdFeB magnetic materials, such as figure 1 As shown, the overall structure of the prepared multilayer coating is as follows figure 1 As shown, the bottom layer: use heavy rare earth coating (Dy or Tb or its alloy) as grain boundary diffusion coating; outermost layer: use high entropy alloy coating (AlCrTiVZr) as corro...
Embodiment 2
[0057] In this embodiment, a sintered NdFeB magnet with a size of 25mm*25mm*3mm and a grade of 52N is selected. Dy coating, (AlCrTiVZr)N coating and AlCrTiVZr coating were deposited on the surface sequentially by magnetron sputtering technology, followed by vacuum heat treatment. The specific process is as follows:
[0058] (1) Pre-coating treatment. The sintered NdFeB magnetic material is derusted, polished and ultrasonically cleaned in sequence, and then dried;
[0059] (2) Glow plasma cleaning. Fix the NdFeB magnetic material on the workpiece frame of the vacuum chamber and vacuumize the cavity to 5×10 -3 Pa; Introduce Ar into the vacuum cavity and adjust the flow rate so that the vacuum chamber pressure is 1.5Pa; load the negative bias voltage on the workpiece holder, and set the predetermined voltage value, frequency and duty cycle. The specific parameters are: voltage value -600V, frequency 40Khz, duty cycle 90%, glow cleaning time 10min;
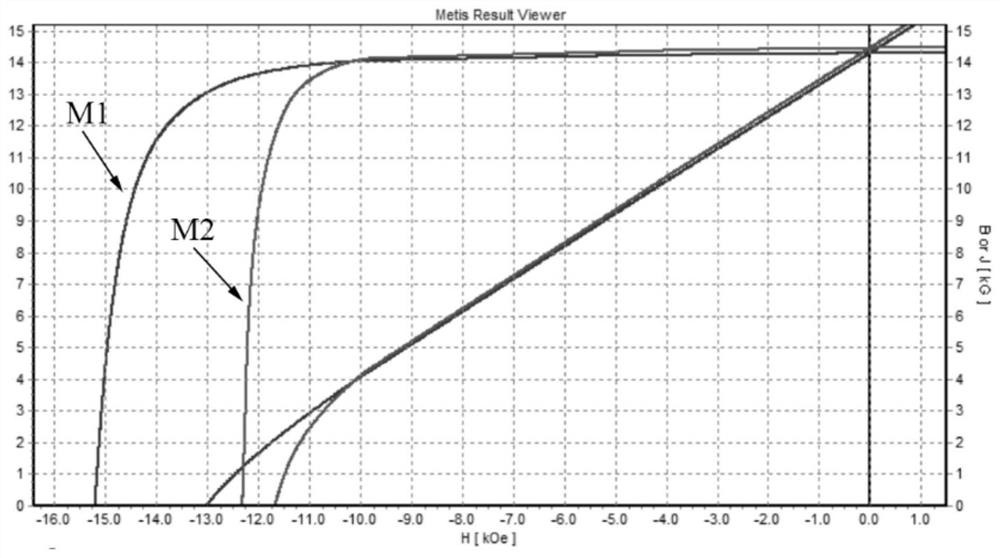
[0060] (3) Heavy rare ear...
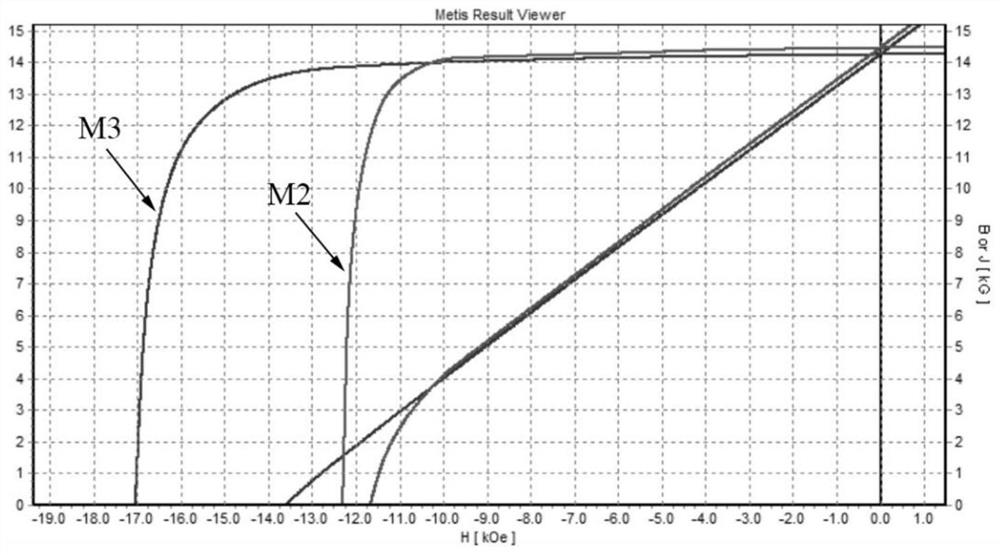
Embodiment 3
[0071] In this embodiment, the substrate is exactly the same as that in Embodiment 2, and the Dy coating, (AlCrTiVZr)N coating, and AlCrTiVZr coating are sequentially deposited on its surface by magnetron sputtering technology, followed by vacuum heat treatment. The specific process is as follows:
[0072] (1) complete the same as step 1 in embodiment 2;
[0073] (2) exactly the same as step 2 in embodiment 2;
[0074] (3) Heavy rare earth coating deposition. After glow plasma cleaning, adjust the Ar flow rate so that the vacuum chamber pressure is 0.5 Pa, and turn the workpiece until the magnetic material faces the Dy target. Turn on the magnetron sputtering power supply, and sputter the heavy rare earth Dy target. The setting parameters of the magnetron sputtering power supply are: sputtering current 1A, frequency 40Khz, duty cycle 50%. The specific parameters of its negative bias voltage: voltage value -700V, frequency 40Khz, duty cycle 90%. The temperature parameter o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com