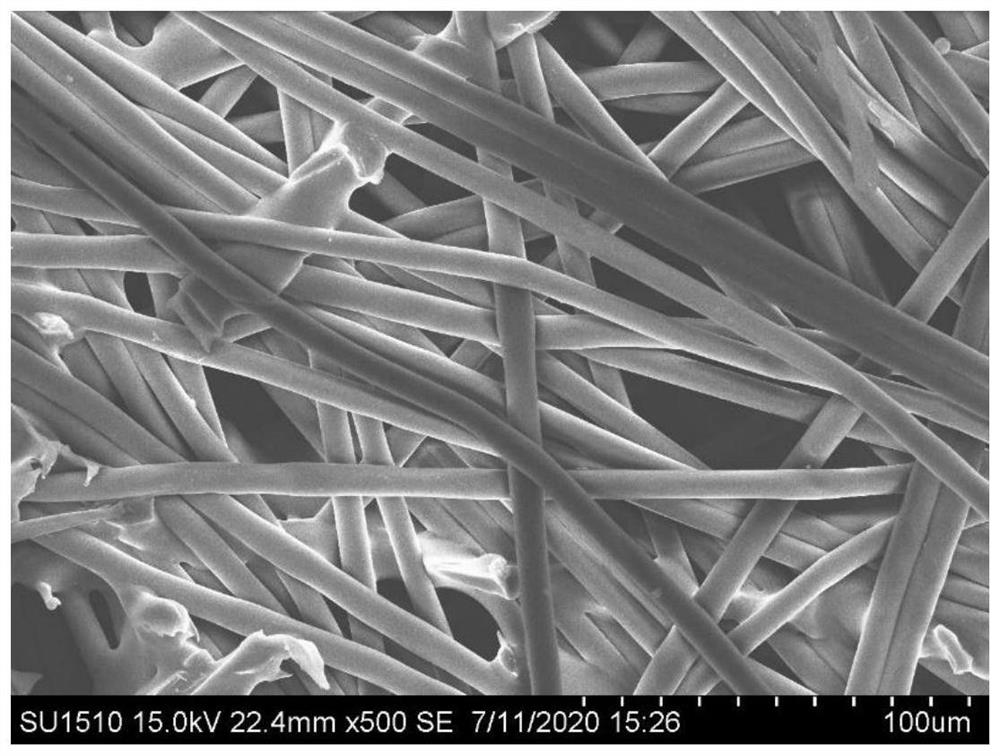
Wet-process non-woven fabric for water treatment reverse osmosis membrane support body base material and preparation method of wet-process non-woven fabric
A reverse osmosis membrane and wet-laid non-woven technology, which is applied in the field of wet-laid non-woven fabrics for water treatment reverse osmosis membrane support substrates and its preparation, can solve the problems of complex preparation process, difficult control, and cost reduction. To achieve the effect of simple and reasonable preparation process, improved retention rate and good uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0056] The present invention also provides a method for preparing the above-mentioned wet-laid non-woven fabric used for water treatment reverse osmosis membrane support base material, comprising the following steps:
[0057] a) Dispersion pretreatment of raw fiber: Put the raw fiber into the fiber disperser equipped with water, continue to add water to the specified liquid level, and disperse the slurry to the fiber dispersion state; pump the fiber slurry prepared in the fiber disperser to In the slurry storage tank, turn on the agitator of the slurry storage tank, and add a dispersant, dilute and disperse the fiber slurry to a state where the fiber is single and suspended in water, and the fiber slurry is obtained;
[0058] The main fibers and hot-melt bonding fibers that make up this non-woven fabric, due to their hydrophobic properties, are not easy to maintain in the dispersed state in water, and are prone to flocculation, and the fibers are easy to intertwine and entangle...
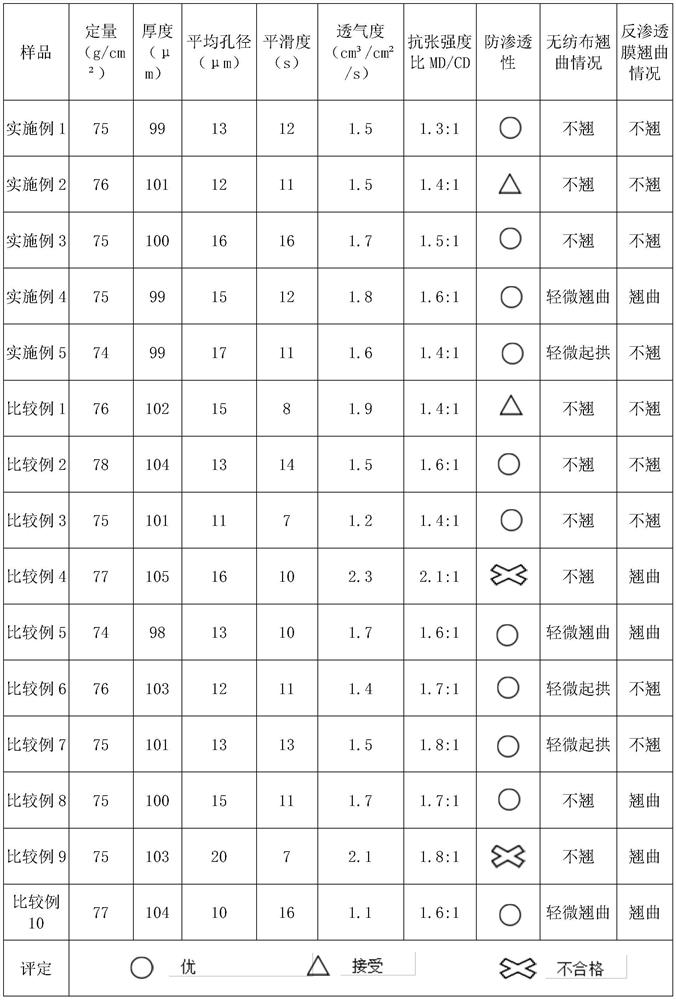
Embodiment 1
[0076] A wet-laid non-woven fabric used for water treatment reverse osmosis membrane support base materials, the raw material fibers include main fibers and hot-melt bonding fibers; the material of the main fibers is PET; the hot-melt bonding fibers include a surface layer and an inner core The material of the surface layer is modified COPET, and the material of the inner core is PET; the weight ratio of the main fiber is 60% of the total weight, and the weight ratio of the hot-melt bonding fiber is 40% of the total weight;
[0077] The diameter of the main fiber is 1.0dtex, and the fiber length is 6mm; the diameter of the hot-melt bonding fiber is 1.1dtex, and the fiber length is 6mm; the ratio of the surface layer of COPET fibers with a melting point of 110°C to 180°C is 3:7, The melting point temperature of the inner core is 250°C; the melting point temperature of the main fiber is 250°C; the moisture absorption rate of the raw material fiber is 0.4%, and the heat shrinkage ...
Embodiment 2
[0088] The difference from Example 1 is that based on Example 1, the difference is that the surface layer COPET fiber with a melting point of 110°C and a fiber with a melting point of 180°C is 2:8, and the final surface density is 76g / cm 2 base non-woven fabric.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fiber length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com