Solidification stabilizing material for water-based drilling cutting landfill and solidification method of water-based drilling cutting
A technology for stabilizing materials and drilling cuttings, applied in the field of environmentally friendly curing and stable materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] Its concrete preparation steps are as follows:
[0031] Step S1: Thoroughly mix p-hydroxyphenylglycine (or hydroxyphenylglycine), ammonium sulfate and sodium hydroxide solution to obtain a mixture.
[0032] Step S2: Then heat the mixture obtained in step S1 to 80-90° C. and evaporate ammonia under vacuum until the content of ammonium sulfate is less than 1%.
[0033] Step S3: On the basis of step S2, cool down to 30°C, then add carbon disulfide (CS 2 ) and warming up to 50-60 degrees Celsius to react for 6-8 hours to obtain sodium p-hydroxyphenylglycine dithiocarbamate or sodium hydroxyphenylglycine dithiocarbamate.
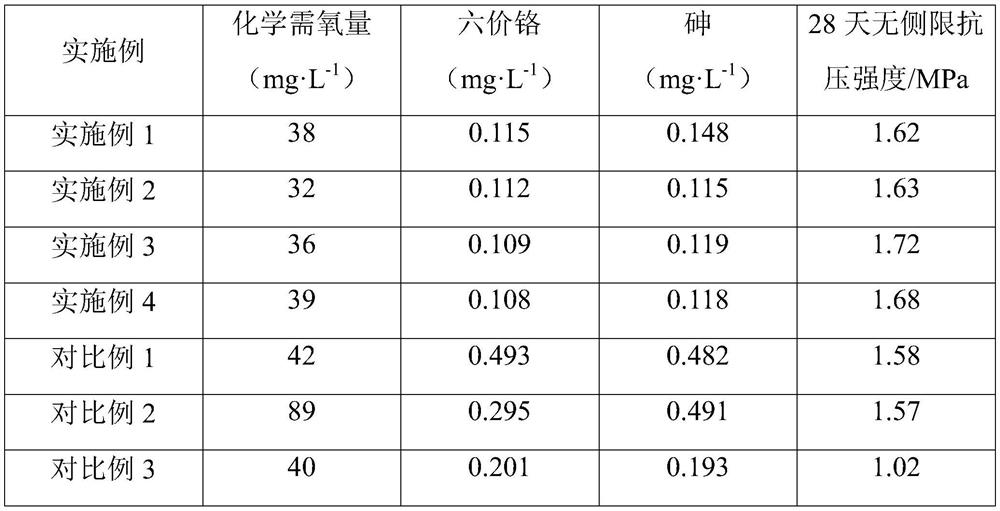
Embodiment 1
[0037] A solidification and stabilization material for water-based drilling cuttings landfill, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 30 parts of cinder, 18 parts of cement, 12 parts of carbide slag, 10 parts of citrate gypsum, and 3 parts of metal ion curing agent , 3 parts of sodium hydroxyphenylglycine dithiocarbamate, 15 parts of oxidation unit.
[0038]Specifically, the metal ion curing agent includes microsilica, diatomaceous earth and sodium silicate; and the mass ratio of microsilica, diatomaceous earth and sodium silicate is 10:30:4. The oxidation unit includes citric acid, H 2 o 2 and FeSO 4 , where citric acid adjusted the pH of water-based cuttings to 6-7, H 2 o 2 and Fe 2+ The molar ratio is 2:83.
[0039] Further, when the above-mentioned solidified and stable material for water-based drill cuttings landfill is used for water-based drill cuttings solidification, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0040] Step 1: first the oxida...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A solidification and stabilization material for water-based drilling cuttings landfill, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 50 parts of cinder, 25 parts of cement, 18 parts of carbide slag, 16 parts of citrate gypsum, and 6 parts of metal ion curing agent , 4 parts of hydroxyphenylglycine dithiocarbamate sodium salt, 23 parts of oxidation unit.
[0045] Specifically, the metal ion curing agent includes microsilica, diatomaceous earth and sodium silicate; and the mass ratio of microsilica, diatomaceous earth and sodium silicate is 18:55:9. The oxidation unit includes citric acid, H 2 o 2 and FeSO 4 , specifically, citric acid adjusted the pH of water-based cuttings to 6-7, H 2 o 2 and Fe 2+ The molar ratio is 2:91.
[0046] Further, the solidification method of the above-mentioned water-based drilling cuttings embedding solidification and stabilization material in water-based drilling cuttings in this implementation is the same as the steps desc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com