Gelatin-based carbon nanofibers and preparation method thereof
A carbon nanofiber, gelatin-based technology, applied in the field of gelatin-based carbon nanofibers and their preparation, can solve problems such as difficulty in maintaining fiber morphology, and achieve the effects of avoiding coagulation and sedimentation, high porosity and smooth surface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
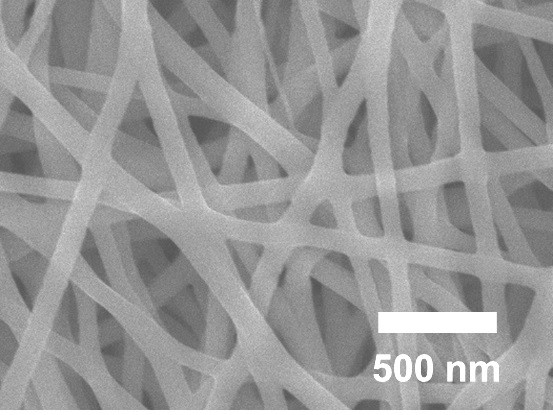
[0034] Add 1.25 g of gelatin solid particles into 7 g of deionized water, heat and stir at 70 °C for 2 h, and prepare an aqueous gelatin solution with a mass fraction of 15%. Add 62.5 mg of sodium iron edetate to the aqueous gelatin solution, the mass ratio of gelatin solid to sodium iron edetate is 20:1, and continue heating and stirring for 2 h. The gelatin / sodium iron ethylenediamine tetraacetate mixed spinning solution obtained above was sucked into a syringe, and then loaded into an electrospinning machine. Under specific spinning parameters (spinning temperature was 70 °C, and the syringe advance rate was 0.53 mL h -1 , the spinning voltage was controlled at 15.0 kV) to obtain gelatin-based fibers by electrospinning. The spun gelatin-based fibers were placed in a muffle furnace under specific pre-oxidation conditions (in an air atmosphere, from room temperature to 5 °C min -1 The heating rate was increased to 150 °C, kept for 2 h, and then at 1 °C min -1 The heating r...
Embodiment 2
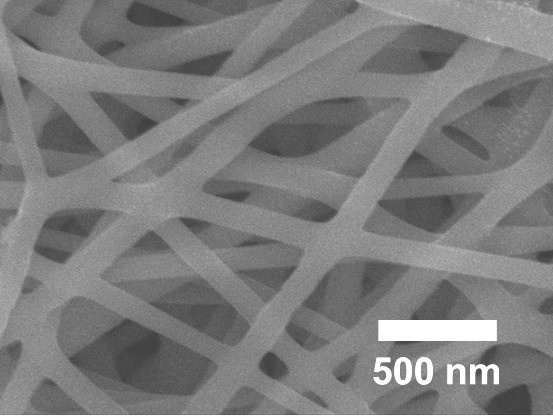
[0036] Change the mass of sodium ferric edetate powder to 125 mg, that is, the mass ratio of gelatin solid to sodium ferric edetate powder is 10:1, and change the propulsion rate of the syringe during spinning to 0.7 mL h -1 , the spinning voltage was controlled to be 18.5kV, and other experimental conditions and processes were the same as in Example 1. The gelatin-based carbon nanofiber that embodiment 2 obtains sees figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
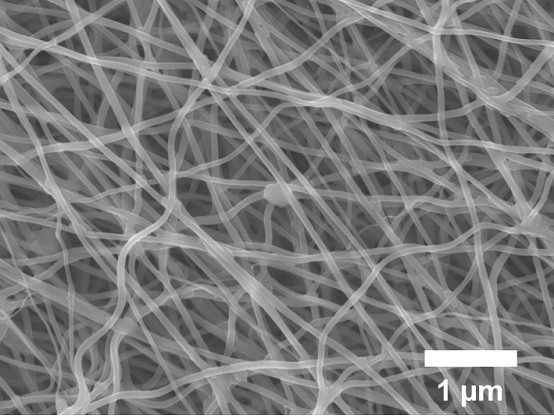
[0038] Add 1.25 g of gelatin solid particles into 7 g of deionized water, heat and stir at 70 °C for 2 h, and prepare an aqueous gelatin solution with a mass fraction of 15%. Add 110 mg of potassium ferricyanide to the aqueous gelatin solution, the mass ratio of gelatin solid to potassium ferricyanide is 125:11, and continue heating and stirring for 2 h. The pre-oxidation conditions were changed to: in air atmosphere, from room temperature to 5 ℃ min -1 The heating rate was increased to 150 °C, kept for 2 h, and then at 1 °C min -1 The heating rate was increased to 310 °C, and the holding time was 1 h. Other experimental conditions and process are identical with embodiment 1. The gelatin-based carbon nanofiber that embodiment 3 obtains sees image 3 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com