Methods and compositions to prevent microbial infection
A technology of microorganisms and target microorganisms, applied in the direction of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, drug delivery, etc., can solve the problems of variable recurrence of pathogenic microorganisms, inability to induce β-lactamase, low toxicity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0672] Example 1. Field study - Exclusive niche using benign microbes:
[0673] Clinical Research - Inhibition and Replacement
[0674] A clinical study was designed to identify MRSA positive subjects, suppress MRSA strains, replace MRSA by administering Bioplx-01 (ie, MSSA 502a) and periodically retest subjects for recurrence of MRSA. The study population was mainly medical staff and medical students from the Meerut region. Subjects without symptoms were included in the study.
[0675] This was a 'proof-of-principle' study using largely unrefined materials and methods - any result greater than a 55% relapse-free rate would be considered an indicator of the potential efficacy of these methods. Any result of a recurrence-free rate of 80% or higher would be considered a strong indicator of the current technical strength of the method.
[0676] Study objectives and primary endpoints:
[0677] 1) To determine the prevalence of asymptomatic S. aureus and MRSA in the general pop...
example 2
[0727] Example 2. Selection of one or more inducible promoters
[0728] In this example, promoter candidates were evaluated. Fold induction and basal expression of six promoter candidates in MSSA strain BioPlx-01 were assessed by incubation with human whole blood and serum. Expression was normalized to a housekeeping gene (gyrB) and compared to that in cells grown logarithmically in liquid tryptic soy broth (TSB) medium.
[0729] BioPlx-01 was grown to mid-log phase (2OD / mL), then washed extensively and transferred to freshly collected serum and heparinized blood from donor TK.
[0730] Samples were incubated at 125 rpm in slowly stirred vented flasks; and samples were removed for RNA isolation at 15 min, 45 min or 75 min at 37°C. Collected bacteria were washed and RNA was extracted using Qiagen Allprep kit, eluted and frozen. Coding DNA (cDNA) was prepared from RNA and expression of target genes was assessed by real-time PCR (Taqman) in an ABI 7500 Fast instrument.
[073...
example 3
[0748] Example 3. Selection of one or more death genes
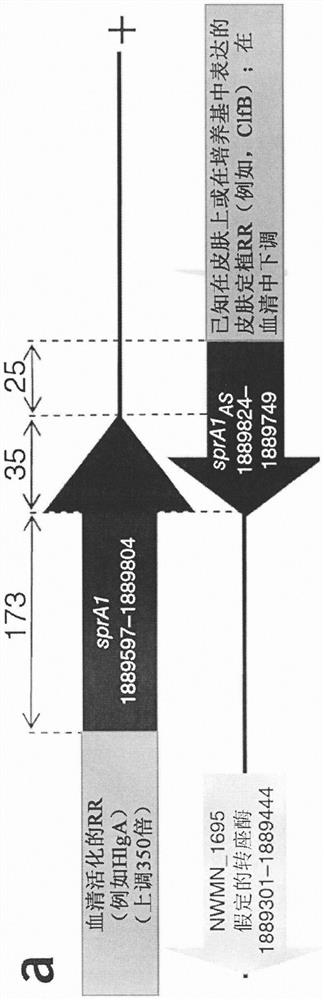
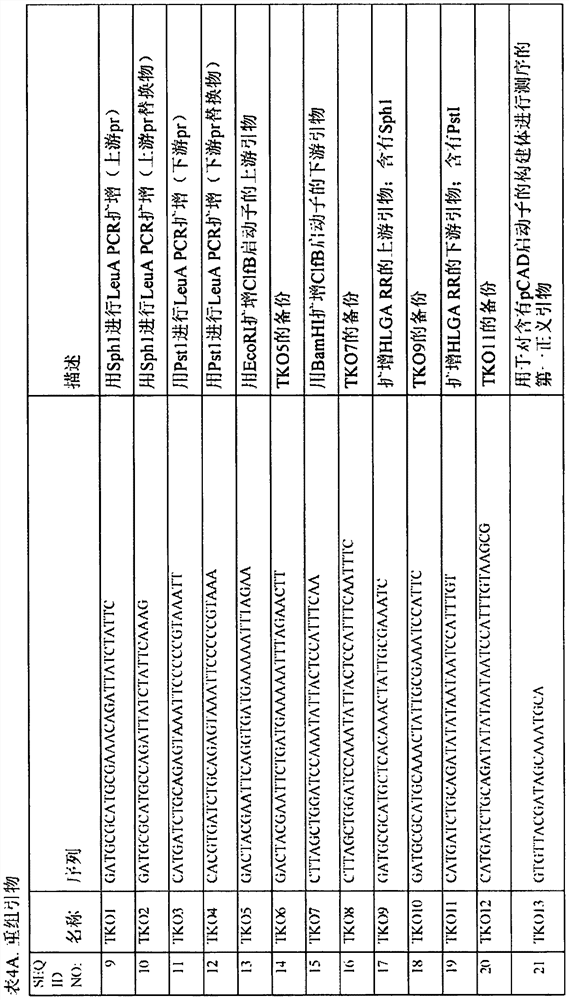
[0749] In this example, cell death gene candidates are evaluated to produce synthetic microorganisms having at least one molecular modification comprising a first cell death operably linked to a first regulatory region comprising a first inducible promoter Gene. The relative potency of death genes is unknown. Because of leaky expression, the best-looking death gene is not necessarily the most efficient gene. The diversity of mechanisms of action may result in the synergistic killing effect of combinations of two or more death genes. Candidate death genes include: SprA1: membrane rupture; smal: genome disruption; and rsaE: block central metabolism. Various combinations of death genes are shown in Table 14. These plasmids were created and sequenced to test the P leuA and P hlgA Driven KS variants.
[0750] Table 14. Death gene KS constructs
[0751]
[0752] The death gene is commercially available (Atum), as is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com