Processing method for improving luminous efficiency and moisture resistance of stannate red-light-emitting material
A technology of luminous efficiency and processing method, applied in the field of optimization of the properties of inorganic solid luminescent materials, can solve the problems of high air-sensitive metal nitrides, lack of synthesis requirements, low light color purity, etc., to reduce radiation-free cross-relaxation, The effect of improving moisture resistance and increasing luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
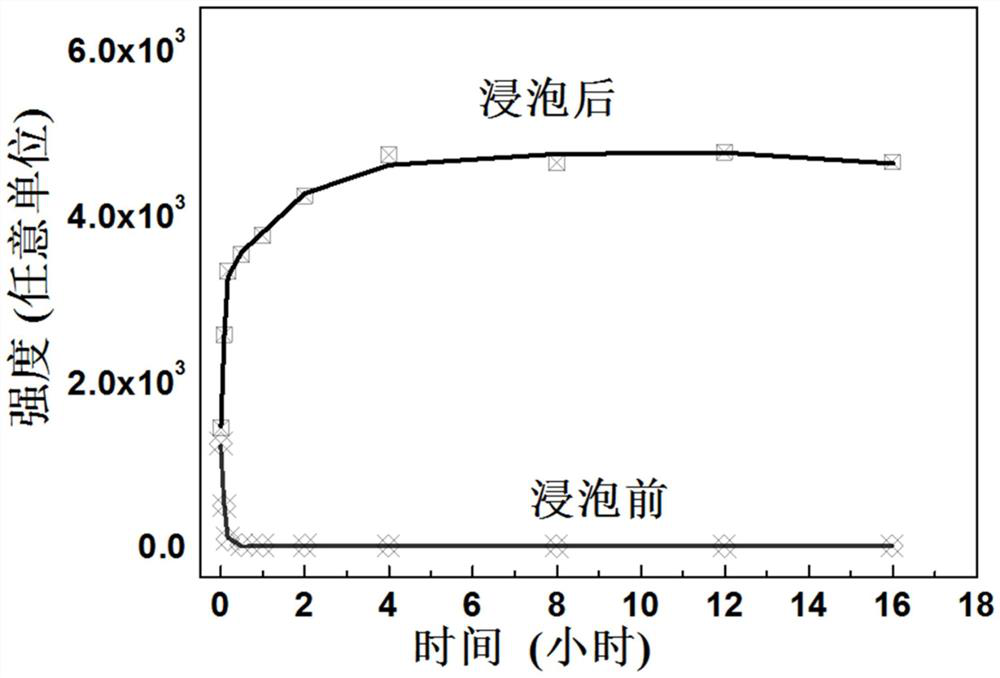
[0022] In 100 mL of water, add stannous oxide SnO to form a salt solution with a mass of 5%. Put the red light material NaRbSnF6:Mn4+ into the solution, accounting for 50% of the mass. In order to fully soak, use a stirring speed of 1500 rpm Stir separately, soak after 20 minutes, then suction filter, dry in the air, obtain the product after optimization. The product processed by this embodiment emits deep red fluorescence under near ultraviolet irradiation. Such as figure 1 As shown in the present embodiment, the emission peak table does not change, but the intensity is greatly enhanced; as attached figure 2 Shown XRD characterizes that the product that the technology of the present invention is processed is the NaRbSnF of pure phase; As attached image 3 As shown, the luminous intensity of the NaRbSnF6:Mn4+ product obtained in this embodiment is increased, and the moisture resistance is greatly enhanced. The XRD and fluorescence spectra of other examples are basically si...
Embodiment 2
[0024] In 100 mL of water, add stannous oxide SnO to form a salt solution with a mass of 1%. Put the red light material NaRbSnF6:Mn4+ into the solution, accounting for 30% by mass. For sufficient immersion, use a stirring speed of 2000 rpm Stir separately, soak for 10 minutes, then suction filter and dry to obtain the optimized product. The product treated with this embodiment emits deep red fluorescence under near-ultraviolet irradiation. Compared with the untreated sample, the luminous intensity and moisture resistance of the product of this embodiment are greatly enhanced.
Embodiment 3
[0026] In 100 mL of water, add stannous oxide SnO to form a salt solution with a mass of 10%. Put the red light material NaRbSnF6:Mn4+ into the solution, accounting for 70% of the mass. For sufficient soaking, use a stirring speed of 2000 rpm Stir in minutes, soak for 30 minutes, then suction filter and dry to obtain the optimized product. The product treated with this embodiment emits deep red fluorescence under near-ultraviolet irradiation. Compared with the untreated sample, the luminous intensity and moisture resistance of the product of this embodiment are greatly enhanced.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com