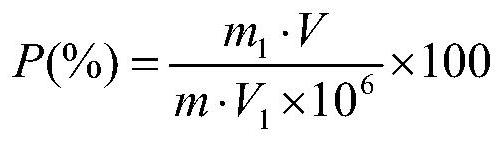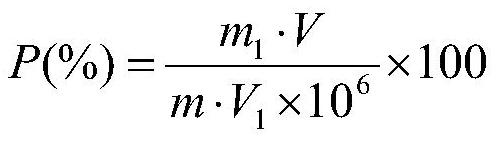Method for determining phosphorus content in iron ore by bismuth-phosphorus-molybdenum blue
A technology for iron ore and phosphorus content, applied in the field of chemical detection, can solve the problems of high cost, long heating time, large power consumption, etc., to ensure detection accuracy and precision, good repeatability, and reduce costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
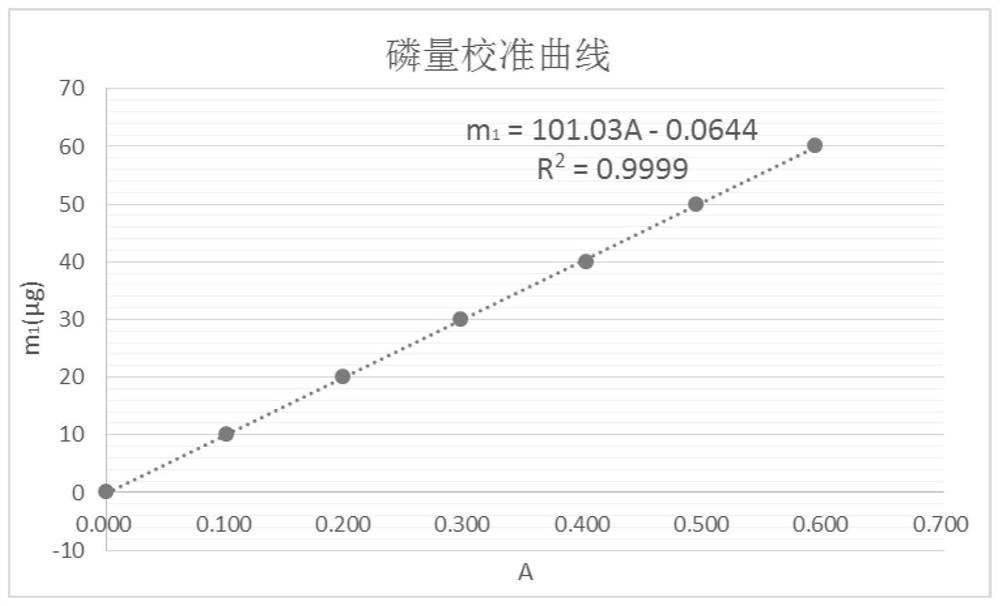
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Determination of Phosphorus Content in Standard Samples of Zhaocheng Iron Mine Ore
[0082] ——(Zhaocheng Iron Mine YSBC 15707-2003, P(%)=0.032)
[0083] 1) Preparation of relevant detection reagents:
[0084] sulfuric acid:
[0085] Slowly inject 100mL of concentrated sulfuric acid into 200mL of water while stirring with a glass rod to dissipate heat;
[0086] Nitric acid: commercially available, the concentration is 70%;
[0087] Hydrochloric acid: commercially available, the concentration is 38%;
[0088] Sodium hydroxide solution: prepared by dissolving 40g of sodium hydroxide in 100mL of water.
[0089] Potassium Sodium Tartrate Solution: Prepared by dissolving 5g of Potassium Sodium Tartrate in 100mL of water.
[0090] Bismuth nitrate solution: weigh 9.309 bismuth nitrate [Bi(NO 3 ) 3 ·5H 2 O], add 25ml of nitric acid, heat to dissolve, add about 100ml of water, boil to drive off nitrogen oxides, add 100ml of sulfuric acid, cool to room temperature, transfe...
Embodiment 2
[0131] Determination of phosphorus content in iron ore standard samples
[0132] ——(iron ore GSB03-2583-2010, P(%)=0.099)
[0133] 1) Preparation of relevant detection reagents:
[0134] The preparation of related detection reagents is the same as the preparation of related detection reagents in Example 1.
[0135] 2) Detection and calculation of phosphorus content in the sample:
[0136] S2, sample dissolution:
[0137] Sample dissolving is identical with the S2 step in embodiment 1;
[0138] S3, filter:
[0139] Filter the S2 solution while it is hot, and use a 100mL volumetric flask to take over, and control the volume of the solution in the volumetric flask to not exceed 50mL.
[0140] S4. Acidity adjustment:
[0141] Acidity regulation is identical with step S4 among the embodiment 1;
[0142] S5, color rendering:
[0143] Color development is the same as step S5 in Example 1;
[0144] S6. Measurement:
[0145] Measurement is identical with step S6 in embodiment...
Embodiment 3
[0154] Determination of phosphorus content in iron ore standard samples
[0155] ——(Hematite 7011, P(%)=0.323)
[0156] 1) Preparation of relevant detection reagents:
[0157] The preparation of related detection reagents is the same as the preparation of related detection reagents in Example 1.
[0158] 2) Detection and calculation of phosphorus content in the sample:
[0159] S2, sample dissolution:
[0160] Sample dissolution is the same as step S2 in Example 1;
[0161] S3, filter:
[0162] Filter the S2 solution while it is hot, take it up with a 100mL volumetric flask, and dilute to volume after filtering to obtain the mother liquor. Pipette 10mL of mother liquor to a 100mL volumetric flask;
[0163] S4. Acidity adjustment:
[0164] Acidity regulation is identical with step S4 among the embodiment 1;
[0165] S5, color rendering:
[0166] Color development is the same as step S5 in Example 1;
[0167] S6. Measurement:
[0168] Measurement is identical with ste...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com